Yin-Dan-Ping-Gan Capsule Mitigates CCL4-Induced Liver Fibrosis via Regulating PPAR γ/GPX4 Signaling and Suppressing Ferroptosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
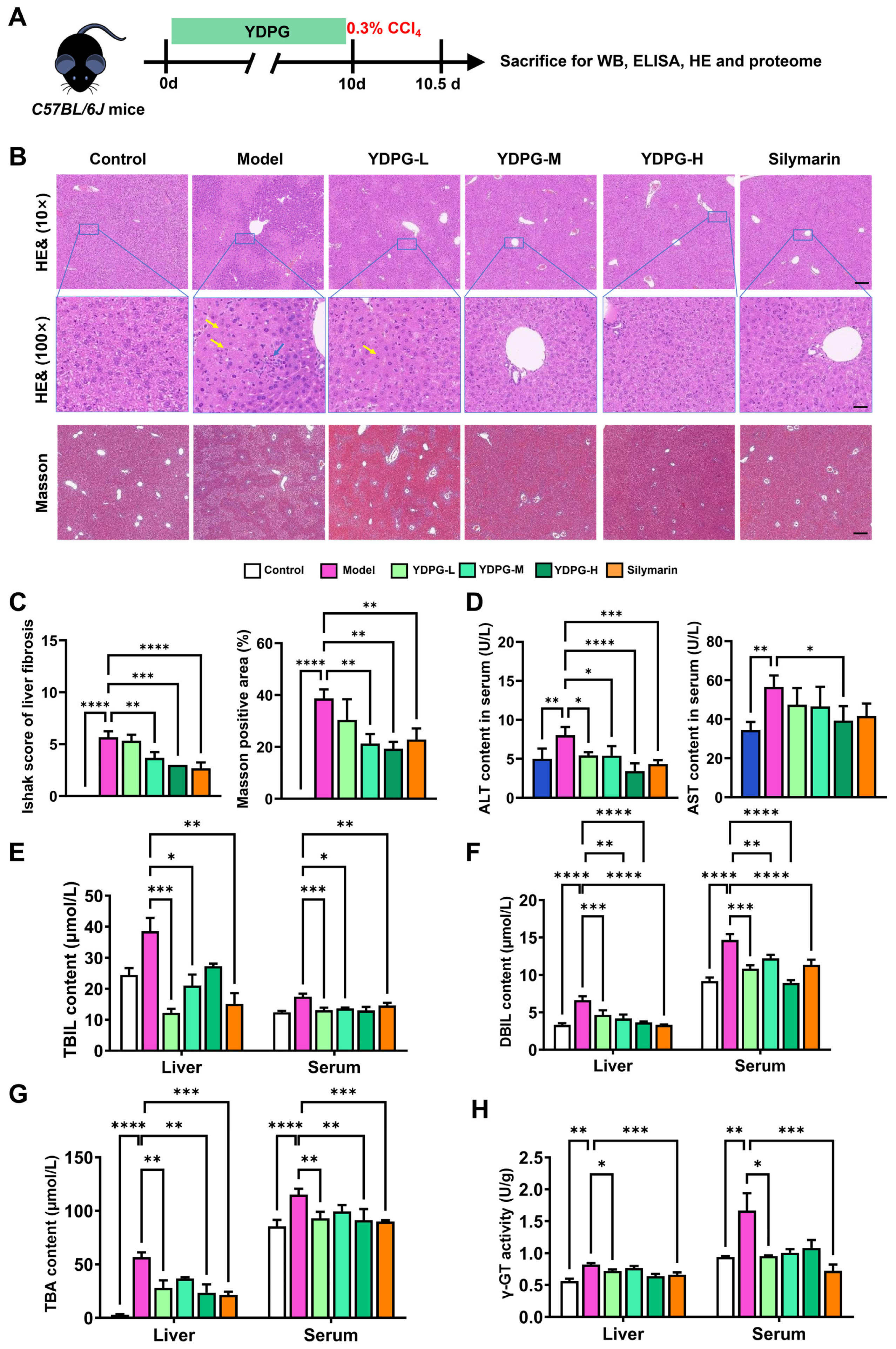
2.1. YDPG Alleviates CCL4-Induced Liver Fibrosis
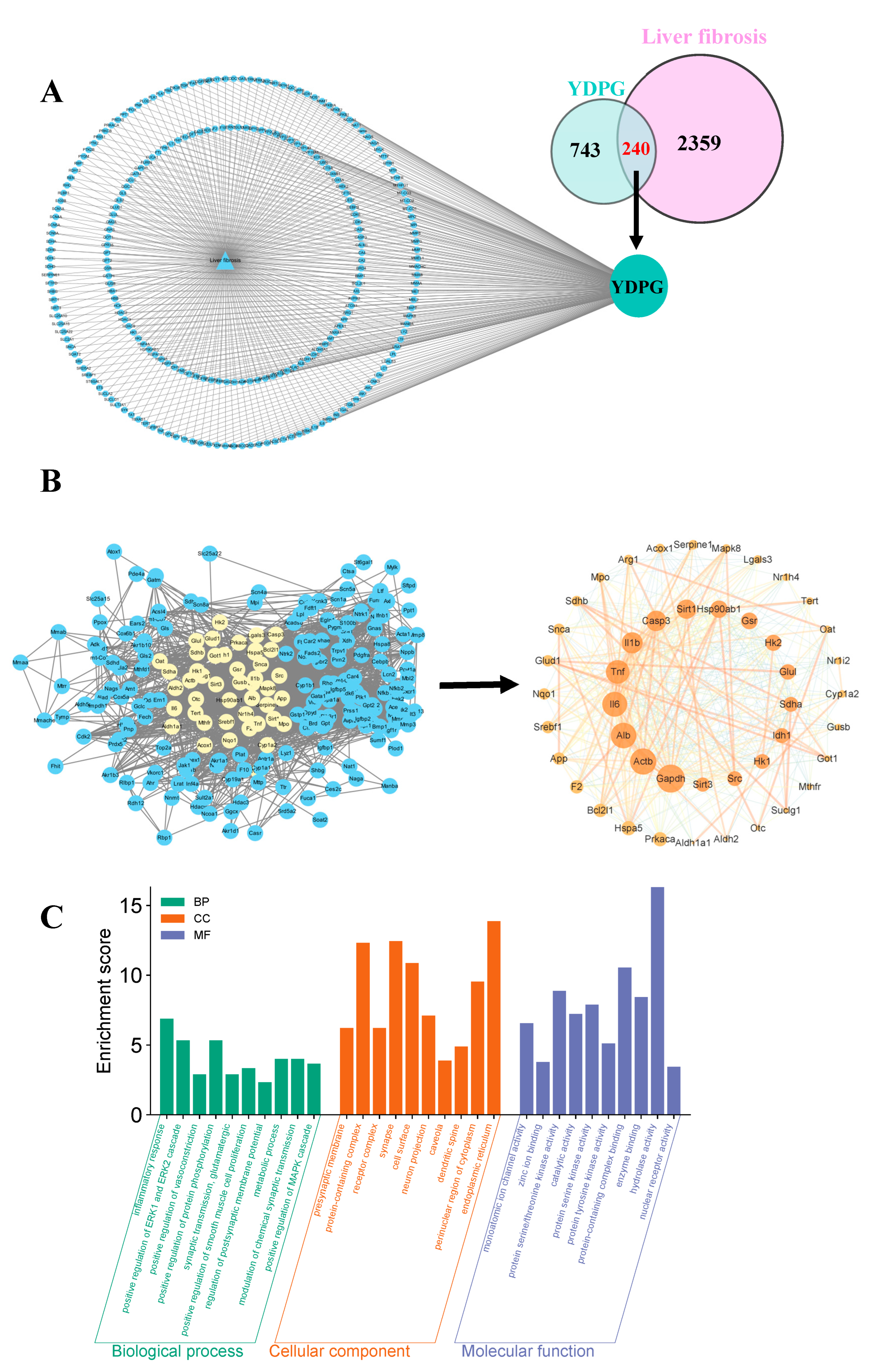
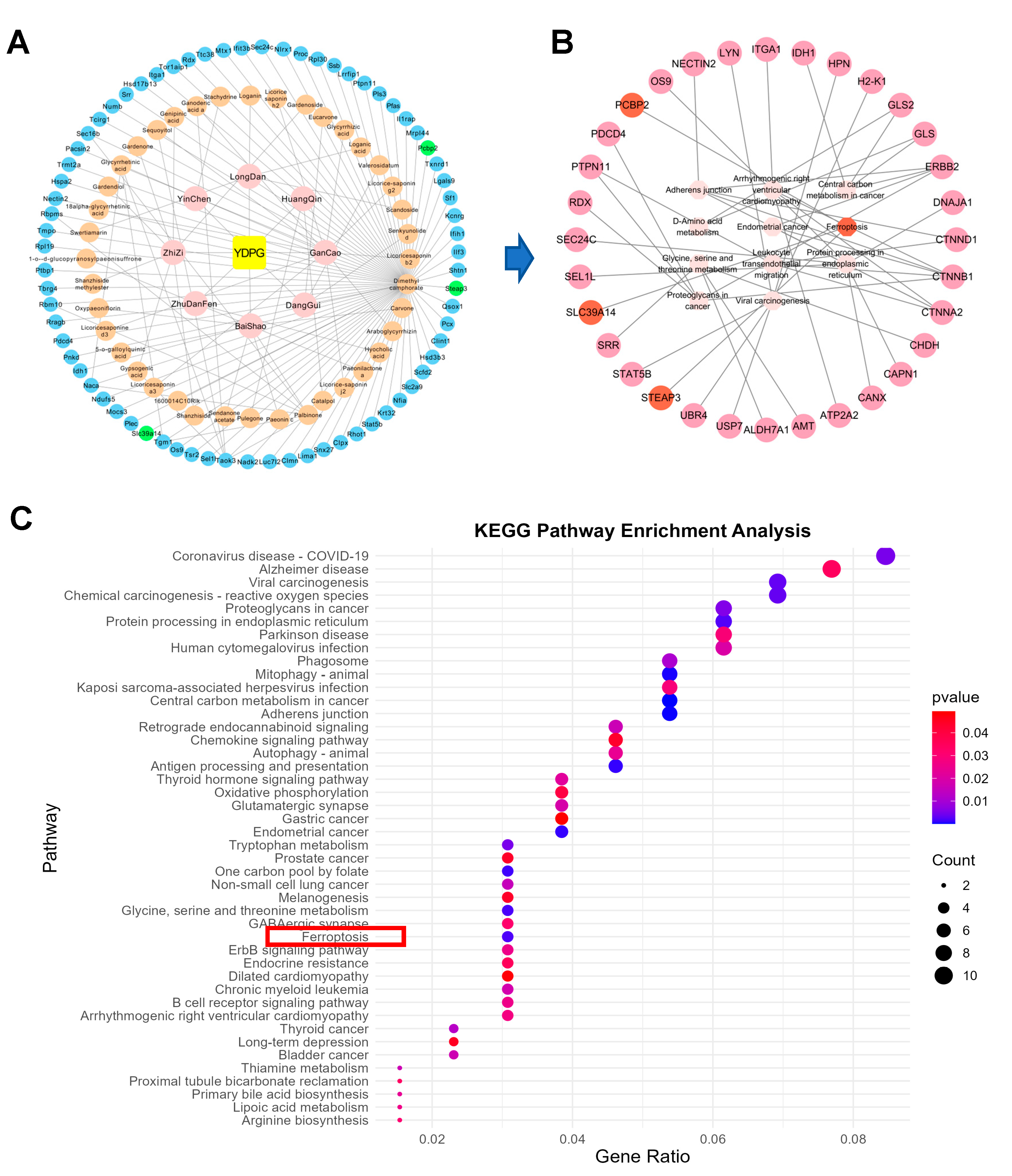
2.2. Analysis of Targets of YDPG for Improving Hepatic Fibrosis
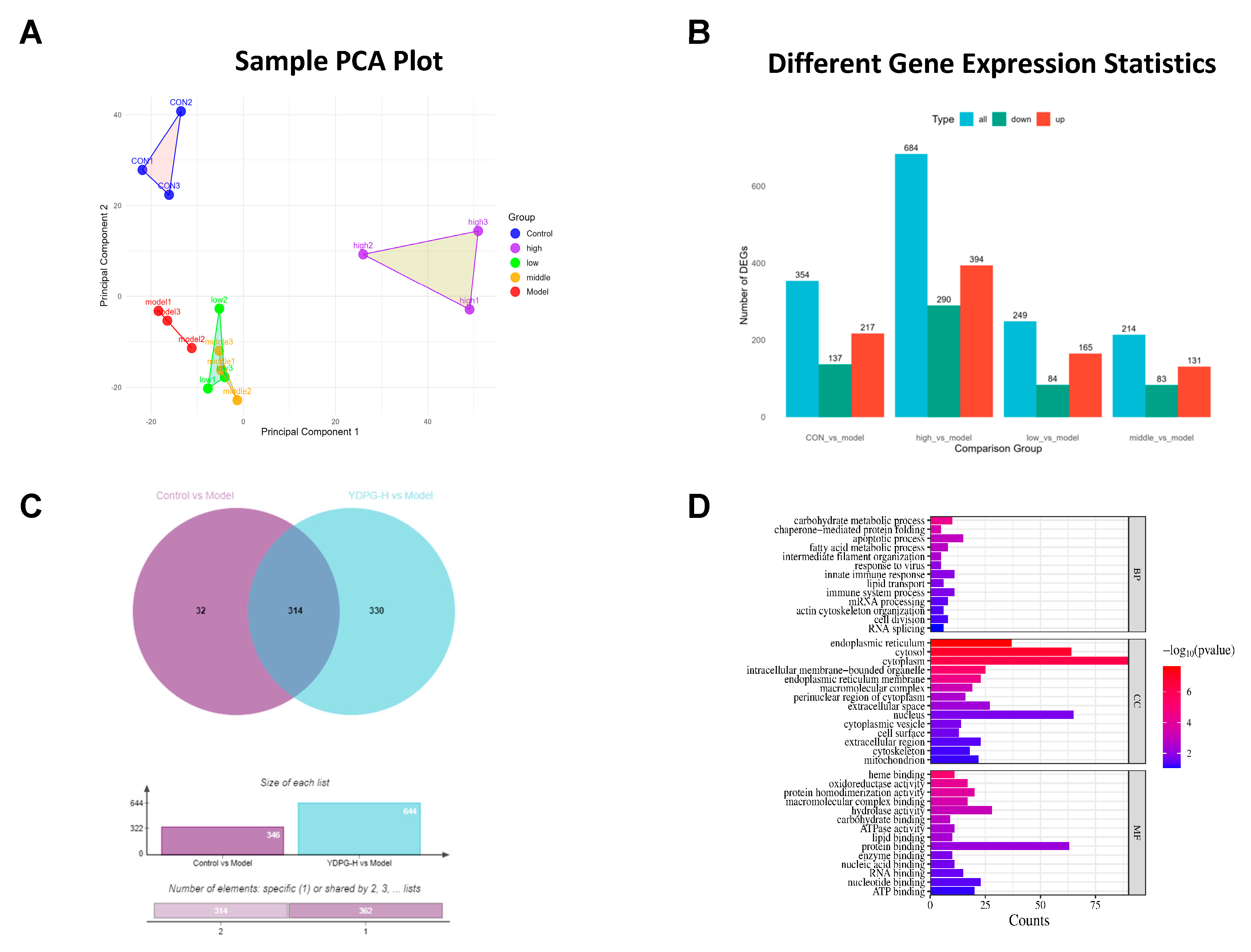
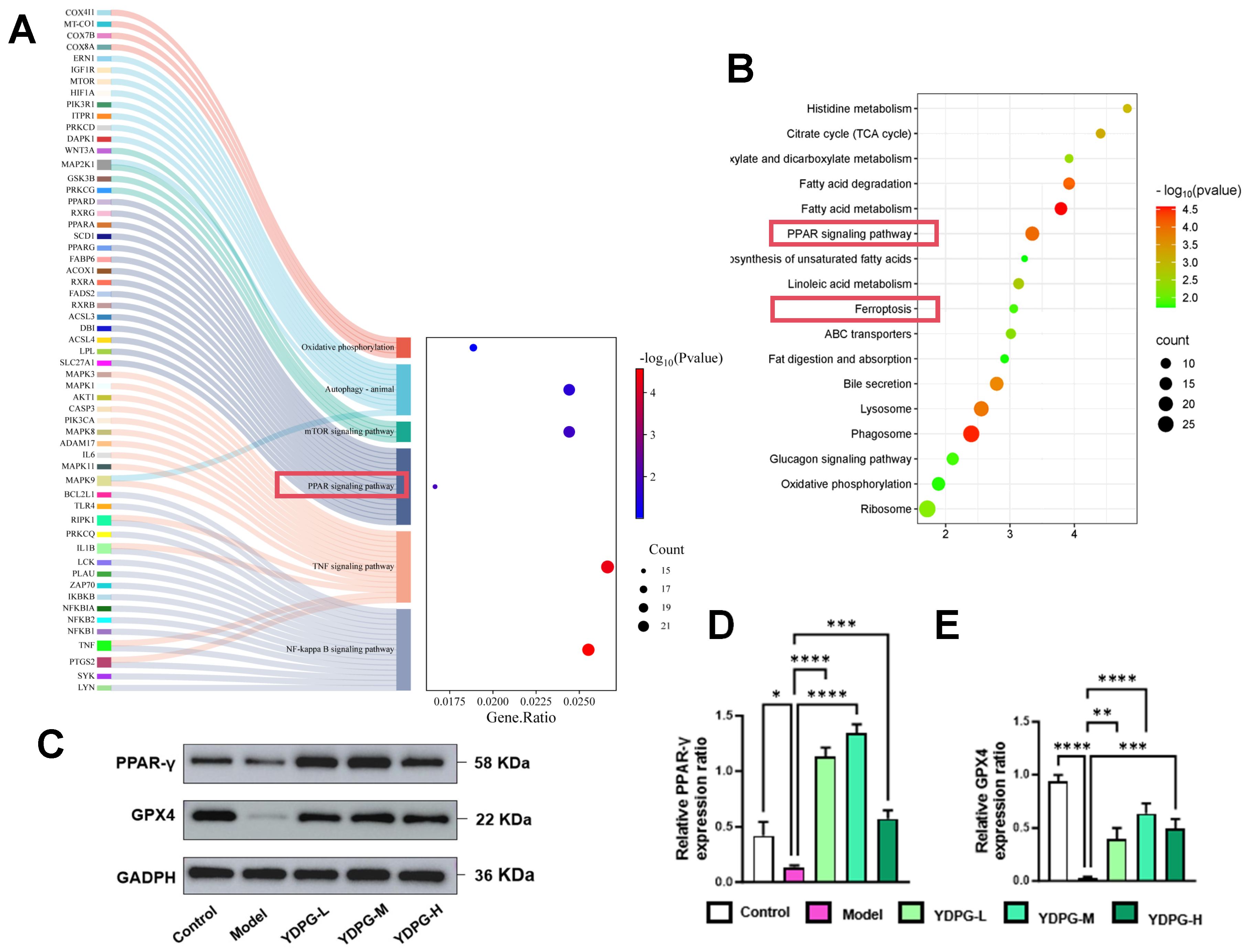
2.3. Proteomics Revealed YDPG Broadly Reprograms Liver Proteins and Activates PPAR γ/GPX4 in CCl4-Treated Mice
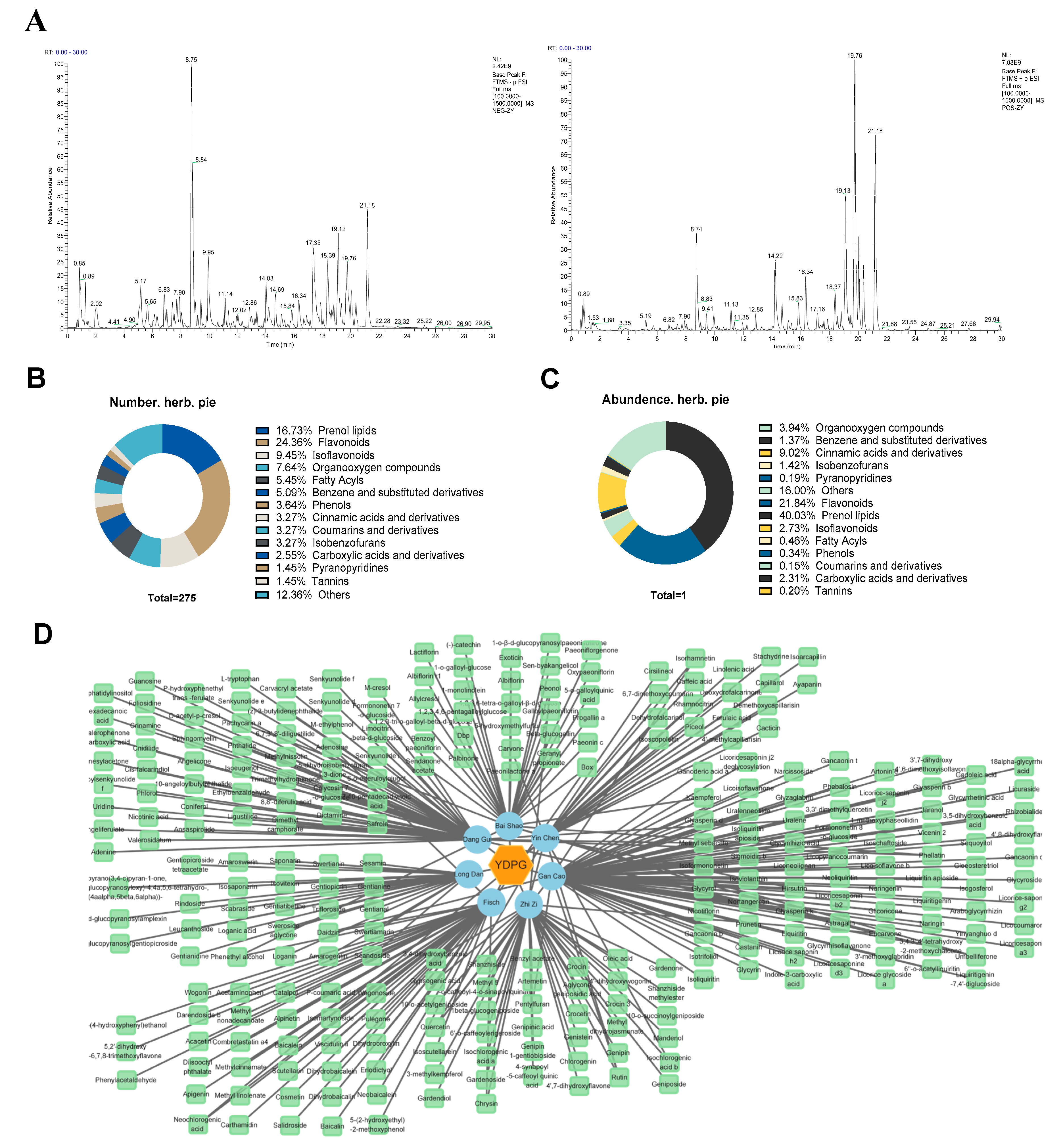
2.4. Identification of Chemical Constituents in YDPG
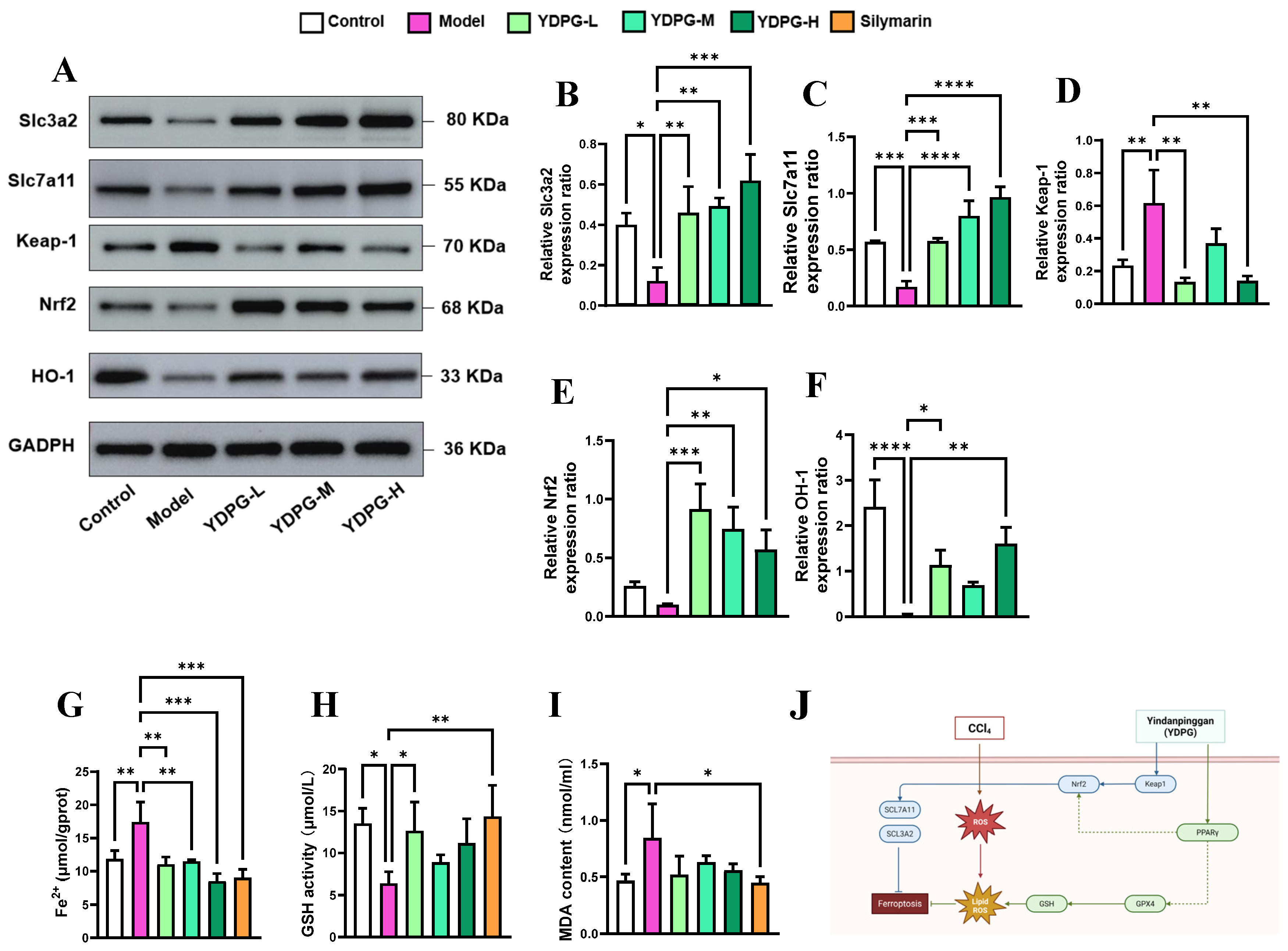
2.5. YDPG Prevents CCL4-Induced Hepatocyte Ferroptosis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemical and Material
4.2. Animals
4.3. Experimental Design
4.4. Evaluation of Blood and Liver Parameters
4.5. Histological Analysis
4.6. Network Pharmacology Research
4.6.1. Prediction of YDPG Component Targets
4.6.2. Prediction of Liver Fibrosis Targets
4.6.3. Construction of Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Network
4.6.4. Construction of Target-Pathway Network Diagrams
4.6.5. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) Pathway Enrichment Analysis and Gene Ontology (GO) Function
4.7. Drug Target Interaction Prediction
4.8. Proteome Analysis
4.9. Antioxidant Enzyme Activities and Fe2+ Levels Detection
4.10. Western Blot Assay
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| YDPG | Yin Dan Ping Gan |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| AST | Aspartate transaminase |
| DBIL | Direct bilirubin |
| TBIL | Total bilirubin |
| γ-GT | Gamma-glutamyl transferase |
| TBA | Total bile acid |
| CCl4 | Carbon tetrachloride |
| GSH | Glutathione |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| HO-1 | Heme oxygenase 1 |
| H&E | Hematoxylin and eosin |
| SLC7A11, LC3A2 | Solute carrier family 3 member 2; Solute carrier family 7 member 11 |
| GPX4 | Glutathione peroxidase 4 |
| TFR | Transferrin receptor |
| NRF2 | Nuclear factor erythroid 2 |
| PPAR γ | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ |
| DTI | Drug-target interaction |
| FASP | Filter-aided sample preparation |
| GO | Gene ontology |
| BP | Biological processes |
| CC | Cellular components |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| PPI | Protein–protein interaction |
| TCM | Traditional Chinese Medicine |
References
- Pradhan-Sundd, T.; Zhou, L.; Vats, R.; Jiang, A.; Molina, L.; Singh, S.; Poddar, M.; Russell, J.; Stolz, D.B.; Oertel, M.; et al. Dual catenin loss in murine liver causes tight junctional deregulation and progressive intrahepatic cholestasis. Hepatology 2018, 67, 2320–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Tsao, G.; Abraldes, J.G.; Berzigotti, A.; Bosch, J. Portal hypertensive bleeding in cirrhosis: Risk stratification, diagnosis, and management: 2016 practice guidance by the American Association for the study of liver diseases. Hepatology 2017, 65, 310–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyoğlu, D.; Idle, J.R. The metabolomic window into hepatobiliary disease. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 842–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmer, A.; VanWagner, L.B.; Ganger, D. Assessment of Advanced Liver Fibrosis and the Risk for Hepatic Decompensation in Patients With Congestive Hepatopathy. Hepatology 2018, 68, 1633–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, D.; Ditah, I.C.; Saeian, K.; Lalehzari, M.; Aronsohn, A.; Gorospe, E.C.; Charlton, M. Changes in the Prevalence of Hepatitis C Virus Infection, Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis, and Alcoholic Liver Disease Among Patients With Cirrhosis or Liver Failure on the Waitlist for Liver Transplantation. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 1090–1099.e1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Liu, S.; Qin, X.; Abudureyimu, M.; Wang, L.; Zou, R.; Ajoolabady, A.; Zhang, W.; Peng, H.; Ren, J.; et al. FUNDC1 interacts with GPx4 to govern hepatic ferroptosis and fibrotic injury through a mitophagy-dependent manner. J. Adv. Res. 2024, 55, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Tan, H.; Wan, J.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Lu, X. PPAR-γ signaling in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Pathogenesis and therapeutic targets. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 245, 108391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenan, B.P.; Fong, L.; Kelley, R.K. Immunotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma: The complex interface between inflammation, fibrosis, and the immune response. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, G.; Meng, L.; Cao, S.; Liu, S.; Wu, J.; Li, Q.; Huang, W.; Zhang, L. PPARα alleviates iron overload-induced ferroptosis in mouse liver. EMBO Rep. 2022, 23, e52280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Gao, C.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, J.; Zhang, X.; Gong, X.; Hao, Z. Mori fructus aqueous extracts attenuates liver injury by inhibiting ferroptosis via the Nrf2 pathway. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2023, 14, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Sun, P.; Zhao, T.; Cao, J.; Liu, Y.; Khan, A.; Zhou, W.; Cheng, G. E Se tea extract ameliorates CCl(4) induced liver fibrosis via regulating Nrf2/NF-κB/TGF-β1/Smad pathway. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2023, 115, 154854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.Y.; Wang, H.R.; Fan, Y.M.; Gu, J.H.; Zhang, X.Y.; Gong, X.H.; Hao, Z.H. Acute liver injury induced by carbon tetrachloride reversal by Gandankang aqueous extracts through nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 signaling pathway. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 251, 114527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J. Protective effect of Yindan Pinggan Capsules on liver inflammatory injury and oxidative stress induced by acute alcoholic intake. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi = Zhongguo Zhongyao Zazhi = China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2019, 44, 1233–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Fu, T.; Glass, L.M.; Zitnik, M.; Xiao, C.; Sun, J. DeepPurpose: A deep learning library for drug-target interaction prediction. Bioinformatics 2021, 36, 5545–5547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercado-Gómez, M.; Lopitz-Otsoa, F.; Azkargorta, M.; Serrano-Maciá, M.; Lachiondo-Ortega, S.; Goikoetxea-Usandizaga, N.; Rodríguez-Agudo, R.; Fernández-Ramos, D.; Bizkarguenaga, M.; Juan, V.G.; et al. Multi-Omics Integration Highlights the Role of Ubiquitination in CCl(4)-Induced Liver Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammoutene, A.; Rautou, P.E. Role of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 1278–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.Q.; Ruan, B.; Liu, J.J.; Duan, J.L.; Yue, Z.S.; Song, P.; Xu, H.; Ding, J.; Xu, C.; Dou, G.R.; et al. Notch-triggered maladaptation of liver sinusoidal endothelium aggravates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis through endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Hepatology 2022, 76, 742–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesh, M.; Hemalatha, P.; Mei, P.M.; Rajasekar, K.; Jang, H.T. A new fluoride mediated synthesis of mesoporous silica and their usefulness in controlled delivery of duloxetine hydrochloride a serotonin re-uptake inhibitor. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2012, 18, 684–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Dong, M.Q.; Liu, Z.M.; Xu, M.; Huang, Z.H.; Liu, H.J.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, W.J. A strategy of vascular-targeted therapy for liver fibrosis. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 660–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Huo, Q.; Wu, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, T.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.Y.; et al. Phosphorylation of FOXN3 by NEK6 promotes pulmonary fibrosis through Smad signaling. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuiqiong, W.; Chao, X.; Xinling, F.; Yinyan, J. Schisandrin B suppresses liver fibrosis in rats by targeting miR-101-5p through the TGF-β signaling pathway. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2020, 48, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, S.; Gupta, S.C.; Chaturvedi, M.M.; Aggarwal, B.B. Oxidative stress, inflammation, and cancer: How are they linked? Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 49, 1603–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.; Chung, S.W. ROS-mediated autophagy increases intracellular iron levels and ferroptosis by ferritin and transferrin receptor regulation. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, S.J.; Lemberg, K.M.; Lamprecht, M.R.; Skouta, R.; Zaitsev, E.M.; Gleason, C.E.; Patel, D.N.; Bauer, A.J.; Cantley, A.M.; Yang, W.S.; et al. Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 2012, 149, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodson, M.; Castro-Portuguez, R.; Zhang, D.D. NRF2 plays a critical role in mitigating lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis. Redox Biol. 2019, 23, 101107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.S.; SriRamaratnam, R.; Welsch, M.E.; Shimada, K.; Skouta, R.; Viswanathan, V.S.; Cheah, J.H.; Clemons, P.A.; Shamji, A.F.; Clish, C.B.; et al. Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by GPX4. Cell 2014, 156, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.; Zhang, P.; Liu, J.; Wang, R.; Kaufman, R.J.; Yaden, B.C.; Karin, M. ATF4 suppresses hepatocarcinogenesis by inducing SLC7A11 (xCT) to block stress-related ferroptosis. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 362–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higdon, A.; Diers, A.R.; Oh, J.Y.; Landar, A.; Darley-Usmar, V.M. Cell signalling by reactive lipid species: New concepts and molecular mechanisms. Biochem. J. 2012, 442, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Huo, X.; Li, R.; Xing, J.; Xu, L.; Yu, D. piR-16404 drives ferroptotic liver injury via CASTOR1/mTORC1/GPX4 dysregulation in HepG2 cells and mice: A novel toxicity mechanism of N, N-dimethylformamide. Arch. Toxicol. 2025. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agyeman, A.S.; Chaerkady, R.; Shaw, P.G.; Davidson, N.E.; Visvanathan, K.; Pandey, A.; Kensler, T.W. Transcriptomic and proteomic profiling of KEAP1 disrupted and sulforaphane-treated human breast epithelial cells reveals common expression profiles. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 132, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osburn, W.O.; Wakabayashi, N.; Misra, V.; Nilles, T.; Biswal, S.; Trush, M.A.; Kensler, T.W. Nrf2 regulates an adaptive response protecting against oxidative damage following diquat-mediated formation of superoxide anion. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2006, 454, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, X.; Fan, Y.Z.; Deng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gao, J.; Zhu, G.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Ge, G.; Liu, H.X. Pectolinarigenin mitigates 5-FU-induced intestinal mucositis via suppressing ferroptosis through activating PPARγ/GPX4 signaling. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2025, 143, 156843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sporn, M.B.; Liby, K.T. NRF2 and cancer: The good, the bad and the importance of context. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Kostov, R.V.; Canning, P. Keap1, the cysteine-based mammalian intracellular sensor for electrophiles and oxidants. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2017, 617, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Xiao, X.; Li, D.; Tun, S.; Wang, Y.; Velkov, T.; Tang, S. Chloroquine ameliorates carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver injury in mice via the concomitant inhibition of inflammation and induction of apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishak, K.; Baptista, A.; Bianchi, L.; Callea, F.; De Groote, J.; Gudat, F.; Denk, H.; Desmet, V.; Korb, G.; MacSween, R.N.; et al. Histological grading and staging of chronic hepatitis. J. Hepatol. 1995, 22, 696–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Jiang, X.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ouyang, Z.; Zhao, C.; Lin, L.; Li, X.; Huang, L. Yin-Dan-Ping-Gan Capsule Mitigates CCL4-Induced Liver Fibrosis via Regulating PPAR γ/GPX4 Signaling and Suppressing Ferroptosis. Pharmaceuticals 2026, 19, 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph19020251
Jiang X, Yang J, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Ouyang Z, Zhao C, Lin L, Li X, Huang L. Yin-Dan-Ping-Gan Capsule Mitigates CCL4-Induced Liver Fibrosis via Regulating PPAR γ/GPX4 Signaling and Suppressing Ferroptosis. Pharmaceuticals. 2026; 19(2):251. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph19020251
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Xue, Jicheng Yang, Yusheng Zhang, Ying Zhang, Zhen Ouyang, Chen Zhao, Limin Lin, Xianyu Li, and Luqi Huang. 2026. "Yin-Dan-Ping-Gan Capsule Mitigates CCL4-Induced Liver Fibrosis via Regulating PPAR γ/GPX4 Signaling and Suppressing Ferroptosis" Pharmaceuticals 19, no. 2: 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph19020251
APA StyleJiang, X., Yang, J., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Y., Ouyang, Z., Zhao, C., Lin, L., Li, X., & Huang, L. (2026). Yin-Dan-Ping-Gan Capsule Mitigates CCL4-Induced Liver Fibrosis via Regulating PPAR γ/GPX4 Signaling and Suppressing Ferroptosis. Pharmaceuticals, 19(2), 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph19020251





