Survival and Radiotherapy-Related Adverse Events in Patients Receiving Radiotherapy and Concurrent Metformin: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials and Cohort Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection Criteria
2.2. Types of Studies
2.3. Types of Participants
2.4. Types of Interventions
2.5. Types of Outcome Measures
2.6. Data Sources and Search Strategies
2.7. Study Selection
2.8. Data Extraction and Management
2.9. Risk of Bias Assessment
2.10. Data Analysis
3. Results
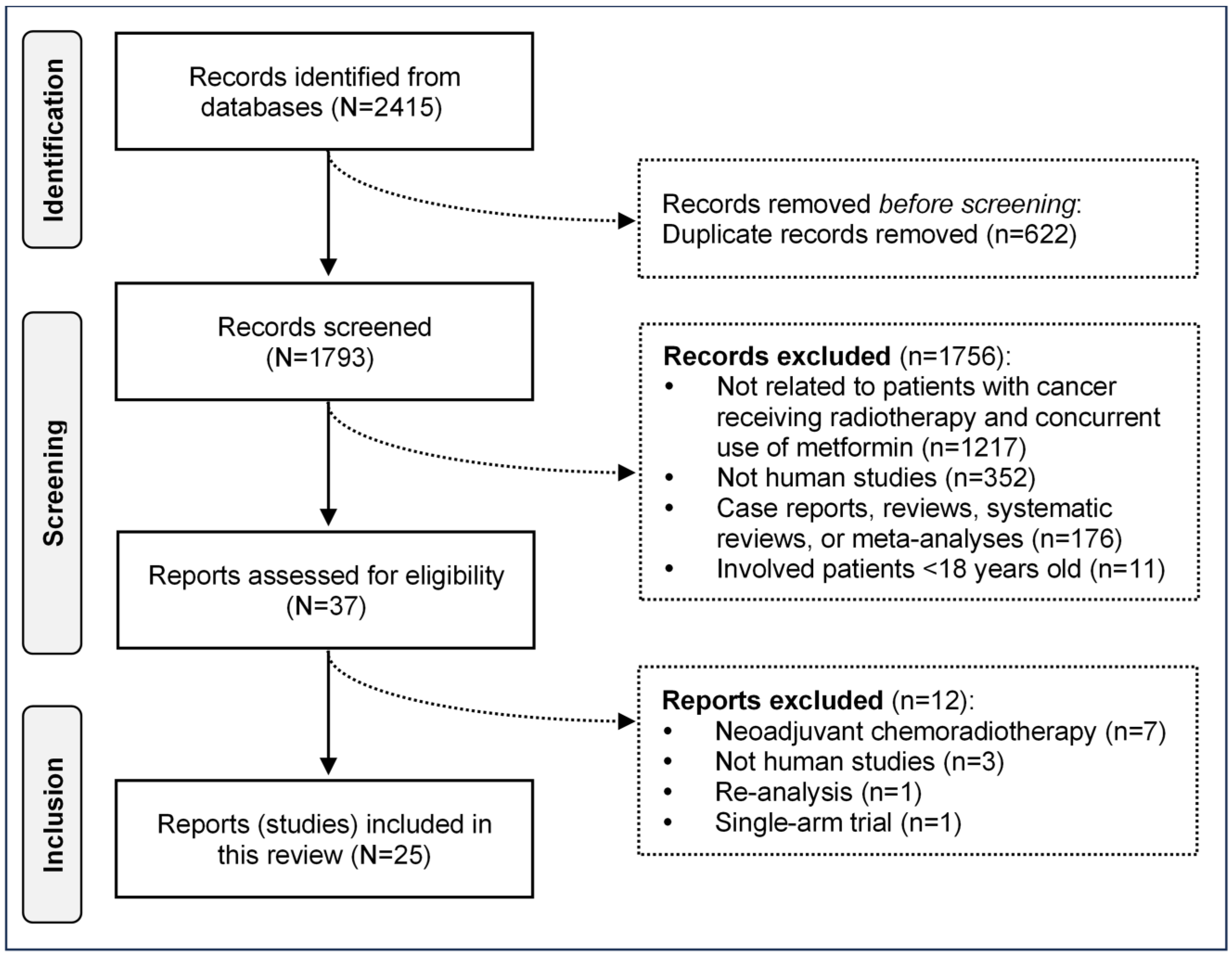
3.1. Selection of Study
3.2. Characteristics of Included Studies
3.3. Quality Assessment
3.4. Overall Survival Rates
3.5. Cancer Progression Outcomes
3.6. Other Survival Outcome Measures
3.7. Radiotherapy-Related Adverse Events
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baker, C.; Retzik-Stahr, C.; Singh, V.; Plomondon, R.; Anderson, V.; Rasouli, N. Should metformin remain the first-line therapy for treatment of type 2 diabetes? Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 12, 2042018820980225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alrashed, F.A.; Iqbal, M.; Alsubiheen, A.M.; Ahmad, T. Exploring determinants of sex and family history-based disparity in type 2 diabetes mellitus prevalence among clinical patients. BMC Public Health 2024, 24, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadakos, S.P.; Argyrou, A.; Lekakis, V.; Arvanitakis, K.; Kalisperati, P.; Stergiou, I.E.; Konstantinidis, I.; Schizas, D.; Koufakis, T.; Germanidis, G.; et al. Metformin in esophageal carcinoma: Exploring molecular mechanisms and therapeutic insights. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viollet, B.; Guigas, B.; Garcia, N.S.; Leclerc, J.; Foretz, M.; Andreelli, F. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of metformin: An overview. Clin. Sci. 2012, 122, 253–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalving, M.; Gietema, J.A.; Lefrandt, J.D.; de Jong, S.; Reyners, A.K.; Gans, R.O.; de Vries, E.G. Metformin: Taking away the candy for cancer? Eur. J. Cancer 2010, 46, 2369–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marini, C.; Cossu, V.; Bauckneht, M.; Lanfranchi, F.; Raffa, S.; Orengo, A.M.; Ravera, S.; Bruno, S.; Sambuceti, G. Metformin and cancer glucose metabolism: At the bench or at the bedside? Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbele, A.T.; Faromika, O.P.; Awe, O.O.; Amodu, F.R.; Edaogbogun, G.O.; Bello, K.A. Impact of metformin on the therapeutic effect of radiotherapy. Radiat. Med. Prot. 2021, 2, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, D.R.; Morris, A.D. Metformin in cancer treatment and prevention. Annu. Rev. Med. 2015, 66, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zi, F.; Zi, H.; Li, Y.; He, J.; Shi, Q.; Cai, Z. Metformin and cancer: An existing drug for cancer prevention and therapy. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraei, P.; Asadi, I.; Kakar, M.A.; Moradi-Kor, N. The beneficial effects of metformin on cancer prevention and therapy: A comprehensive review of recent advances. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 3295–3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeberg, S.; Bernhardt, D.; Ben Harrabi, S.; Bostel, T.; Mohr, A.; Koelsche, C.; Diehl, C.; Rieken, S.; Debus, J. Metformin influences progression in diabetic glioblastoma patients. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2015, 191, 928–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, O.H.Y.; Suissa, S. Metformin and cancer: Solutions to a real-world evidence failure. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, 904–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mee, T.; Kirkby, N.F.; Defourny, N.N.; Kirkby, K.J.; Burnet, N.G. The use of radiotherapy, surgery and chemotherapy in the curative treatment of cancer: Results from the FORTY (Favourable Outcomes from RadioTherapY) project. Br. J. Radiol. 2023, 96, 20230334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marks, L.B.; Yu, X.; Vujaskovic, Z.; Small, W., Jr.; Folz, R.; Anscher, M.S. Radiation-induced lung injury. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2003, 13, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Ruysscher, D.; Niedermann, G.; Burnet, N.G.; Siva, S.; Lee, A.W.M.; Hegi-Johnson, F. Radiotherapy toxicity. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 13, Erratum in Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner-Wasik, M.; Pequignot, E.; Leeper, D.; Hauck, W.; Curran, W. Predictors of severe esophagitis include use of concurrent chemotherapy, but not the length of irradiated esophagus: A multivariate analysis of patients with lung cancer treated with nonoperative therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2000, 48, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharath, L.P.; Nikolajczyk, B.S. The intersection of metformin and inflammation. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2021, 320, C873–C879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Bai, P.; Dai, H.; Deng, Z. Metformin and risk of cancer among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Prim. Care Diabetes 2021, 15, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.; Ferro, A.; Cohler, A.; Langenfeld, J.; Surakanti, S.G.; Aisner, J.; Zou, W.; Haffty, B.G.; Jabbour, S.K. Impact of metformin use on survival in locally-advanced, inoperable non-small cell lung cancer treated with definitive chemoradiation. J. Thorac. Dis. 2015, 7, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, S.G.; Liao, Z.; Jeter, M.D.; Chang, J.Y.; Lin, S.H.; Komaki, R.U.; Guerrero, T.M.; Mayo, R.C.; Korah, B.M.; Koshy, S.M.; et al. Metabolic responses to metformin in inoperable early-stage non–small cell lung cancer treated with stereotactic radiotherapy: Results of a randomised phase II clinical trial. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 43, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakiridis, T.; Pond, G.R.; Wright, J.; Ellis, P.M.; Ahmed, N.; Abdulkarim, B.; Roa, W.; Robinson, A.; Swaminath, A.; Okawara, G.; et al. Metformin in combination with chemoradiotherapy in locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer: The OCOG-ALMERA randomised clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2021, 7, 1333–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.M.; Hsieh, M.C.; Qin, L.; Zhang, J.; Wu, S.Y. Metformin reduces radiation-induced cardiac toxicity risk in patients having breast cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 9, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, P.H.; Yeh, K.Y.; Wang, C.H.; Chen, E.Y.; Yang, S.W.; Chou, W.C.; Hsieh, J.C. Impact of metformin on patients with advanced head and neck cancer undergoing concurrent chemoradiotherapy. Head Neck 2017, 39, 1573–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: Explanation and elaboration. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 151, W65–W94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A guideline of selecting and reporting intraclass correlation coefficients for reliability research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterne, J.A.; Hernán, M.A.; Reeves, B.C.; Savović, J.; Berkman, N.D.; Viswanathan, M.; Henry, D.; Altman, D.G.; Ansari, M.T.; Boutron, I.; et al. ROBINS-I: A tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions. BMJ 2016, 355, i4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Blencowe, N.S.; Boutron, I.; Cates, C.J.; Cheng, H.Y.; Corbett, M.S.; Eldridge, S.M.; et al. RoB 2: A revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2019, 366, l4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipitz-Snyderman, A.; Curry, M.A.; Rubin, D.M.; Li, D.G.; Duck, E.; Radzyner, M.H.; Bach, P. A conundrum in cancer quality measurement: Performance on long-term survival reflects performance a long time ago. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, e18222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontopantelis, E.; Reeves, D. Metaan: Random-effects meta-analysis. Stata J. 2010, 10, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadeddu, G.; Hervás-Morón, A.; Martín-Martín, M.; Pelari-Mici, L.; Ytuza-Charahua de Kirsch, K.; Hernández-Corrales, A.; Vallejo-Ocaña, C.; Sastre-Gallego, S.; Carrasco-Esteban, E.; Sancho-García, S.; et al. Metformin and statins: A possible role in high-risk prostate cancer. Rep. Pract. Oncol. Radiother. 2020, 25, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dağdelen, M.; Barlas, C.; Yıldırım, C.; Karaçam, S.Ç.; Dinçbaş, H. Effect of diabetes mellitus and metformin usage on treatment outcomes and side effects on prostate cancer treated with radical radiotherapy. Üroonkoloji Bülteni 2021, 20, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, A.; Goyal, S.; Kim, S.; Wu, H.; Taunk, N.K.; Schiff, D.; Pirlamarla, A.; Haffty, B.G. Evaluation of diabetic patients with breast cancer treated with metformin during adjuvant radiotherapy. Int. J. Breast Cancer 2013, 2013, 659723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, W.I.; Kim, M.S.; Lim, J.S.; Yoo, H.J.; Seo, Y.S.; Han, C.J.; Park, S.C.; Kay, C.S.; Kim, M.; Jang, H.S. Survival advantage associated with metformin usage in hepatocellular carcinoma patients receiving radiotherapy: A propensity score matching analysis. Anticancer Res. 2015, 35, 5047–5054. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Si-Tu, J.; Qiu, J.; Lu, L.; Mao, Y.; Zeng, H.; Chen, M.; Lai, C.; Chang, H.-J.; Wang, D. Statin and metformin therapy in prostate cancer patients with hyperlipidemia who underwent radiotherapy: A population-based cohort study. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 1189–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Li, J.; Schild, S.E.; Schild, M.H.; Wong, W.; Vora, S.; Herman, M.G.; Fatyga, M. Statins and metformin use is associated with lower PSA levels in prostate cancer patients presenting for radiation therapy. J. Cancer Ther. 2017, 8, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranasinghe, W.K.; Williams, S.; Ischia, J.; Wetherell, D.; Baldwin, G.; Shulkes, A.; Sengupta, S.; Bolton, D.; Patel, O. Metformin may offer no protective effect in men undergoing external beam radiation therapy for prostate cancer. BJU Int. 2019, 123, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, H.D.; Crane, C.H.; Garrett, C.R.; Eng, C.; Chang, G.J.; Skibber, J.M.; Rodriguez-Bigas, M.A.; Kelly, P.; Sandulache, V.C.; Delclos, M.E. Metformin use and improved response to therapy in rectal cancer. Cancer Med. 2013, 2, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spratt, D.E.; Zhang, C.; Zumsteg, Z.S.; Pei, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zelefsky, M.J. Metformin and prostate cancer: Reduced development of castration-resistant disease and prostate cancer mortality. Eur. Urol. 2013, 63, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spratt, D.E.; Beadle, B.M.; Zumsteg, Z.S.; Rivera, A.; Skinner, H.D.; Osborne, J.R.; Garden, A.S.; Lee, N.Y. The influence of diabetes mellitus and metformin on distant metastases in oropharyngeal cancer: A multicenter study. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2016, 94, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stang, K.; Alite, F.; Adams, W.; Altoos, B.; Small, C.; Melian, E.; Emami, B.; Harkenrider, M. Impact of concurrent coincident use of metformin during lung stereotactic body radiation therapy. Cureus 2021, 13, e14157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taira, A.V.; Merrick, G.S.; Galbreath, R.W.; Morris, M.; Butler, W.M.; Adamovich, E. Metformin is not associated with improved biochemical free survival or cause-specific survival in men with prostate cancer treated with permanent interstitial brachytherapy. J. Contemp. Brachyther. 2014, 6, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takiuchi, T.; Machida, H.; Hom, M.S.; Mostofizadeh, S.; Frimer, M.; Brunette, L.L.; Matsuo, K. Association of metformin use and survival outcome in women with cervical cancer. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2017, 27, 1455–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsou, Y.A.; Chang, W.D.; Lu, J.J.; Wu, T.F.; Chen, H.L.; Chen, C.M.; Tsai, M.H. The effect of metformin use on hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma in diabetes mellitus patients. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van De Voorde, L.; Janssen, L.; Larue, R.; Houben, R.; Buijsen, J.; Sosef, M.; Vanneste, B.; Schraepen, M.-C.; Berbée, M.; Lambin, P. Can metformin improve ‘the tomorrow’of patients treated for oesophageal cancer? Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 41, 1333–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wink, K.C.; Belderbos, J.S.; Dieleman, E.M.; Rossi, M.; Rasch, C.R.; Damhuis, R.A.; Houben, R.M.; Troost, E.G. Improved progression free survival for patients with diabetes and locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) using metformin during concurrent chemoradiotherapy. Radiother. Oncol. 2016, 118, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.O.; McDonald, M.O.; Ong, A.; Koul, R.; Dubey, A.; Hunter, W.; Ahmed, S.; Quon, H.; Yee, D.; Parliament, M.; et al. Gastrointestinal and genitourinary toxicity profiles of metformin versus placebo in men with prostate cancer receiving prostate radiotherapy: Interim toxicity results of a double-blinded, multicenter, phase II randomised controlled trial. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 16, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, H.; Hu, C.; Tsakiridis, T.; Santana-Davila, R.; Lu, B.; Erasmus, J.J.; Doemer, A.J.; Videtic, G.M.; Coster, J.; Yang, A.X. Addition of metformin to concurrent chemoradiation in patients with locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer: The NRG-LU001 phase 2 randomised clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2021, 7, 1324–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tate, M.K.; Hernandez, M.; Chang, J.Y.; Lin, S.H.; Liao, Z.; Koshy, S.M.; Skinner, H.D.; Chun, S.G. Metformin in conjunction with stereotactic radiotherapy for early-stage non-small cell lung cancer: Long-term results of a prospective phase II clinical trial. Anticancer Res. 2024, 44, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsuri, N.A.B.; Leech, M.; Marignol, L. Metformin and improved treatment outcomes in radiation therapy—A review. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2017, 55, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevalier, B.; Pasquier, D.; Lartigau, E.F.; Chargari, C.; Schernberg, A.; Jannin, A.; Mirabel, X.; Vantyghem, M.-C.; Escande, A. Metformin: (future) best friend of the radiation oncologist? Radiother. Oncol. 2020, 151, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Yi, Z.; Chen, Y.; Huang, J.; Mao, X.; Zhang, L.; Zeng, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Ye, W.; Liu, Z.; et al. Efficacy of metformin therapy in patients with cancer: A meta-analysis of 22 randomised controlled trials. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coyle, C.; Cafferty, F.H.; Vale, C.; Langley, R.E. Metformin as an adjuvant treatment for cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 2184–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zannella, V.E.; Pra, A.D.; Muaddi, H.; McKee, T.D.; Stapleton, S.; Sykes, J.; Glicksman, R.; Chaib, S.; Zamiara, P.; Milosevic, M.; et al. Reprogramming metabolism with metformin improves tumor oxygenation and radiotherapy response. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 6741–6750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, X.; Liu, H.; Xu, H. The impact of metformin use with survival outcomes in urologic cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 5311828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzzai, M.; Jones, R.G.; Amaravadi, R.K.; Lum, J.J.; DeBerardinis, R.J.; Zhao, F.; Viollet, B.; Thompson, C.B. Systemic treatment with the antidiabetic drug metformin selectively impairs p53-deficient tumor cell growth. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 6745–6752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.; Gao, C.; Guo, M.; Law, B.Y.K.; Xu, Y. Effects of metformin treatment on radiotherapy efficacy in patients with cancer and diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 4881–4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulpitt, C.J. The advantages and disadvantages of randomised controlled trials. In Randomised Controlled Clinical Trials; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1996; pp. 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Component | Inclusion Criteria | Exclusion Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Population and conditions |
|
|
| Intervention and comparator | Oral administration of metformin, either alone or in combination with other drugs, such as chemotherapy. |
|
| Outcome |
|
|
| Study type | Human studies. | Animal or in vitro studies. |
| Language | English. | Other languages without English translation. |
| Publication | Full-text article on prospective or retrospective cohort study, cross-sectional study, and clinical trial. | Case-control study, case series, case report, systematic review, meta-analysis, conference abstract, abstract without full article, editorial, letter to editors, commentary, and grey literature. |
| Author, Year, Country | Cancer | Types of Radiation | Radiation Dose (Gy) | Number of Patients | Age of Patients (Year) | Outcome Category | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Metformin Users | Non-User | ||||||||
| DM (+) | DM (−) | DM (+) § | DM (−) | |||||||
| Ferro, 2013, US [32] | Breast cancer | WBI or external-beam partial-breast irradiation | Range: 45, 50 | 130 | 51 | 51 | 28 | Mean (range): 60 (27, 83) | RT-related side effects | |
| Skinner, 2013, US [37] | Rectal cancer | CRT | Median (range): 50.4 (20, 63) | 482 | 20 | 40 | 422 | Median (range): 58 (19, 84) | Survival outcomes | |
| Spratt, 2013, US [38] | Prostate cancer | EBRT | NA | 2901 | 157 | 162 | 2582 | Median (IQR): 69 (64, 73) | Survival outcomes | |
| Taira, 2014, US [41] | Prostate cancer | Interstitial brachytherapy | NA | 2298 | 126 | 144 | 2028 | Mean ± SD: 65.3 ± 7.4 | Survival outcomes | |
| Adeberg, 2015, Germany [11] | Primary glioblastoma | RT | Median (range): 60.0 (36.0, 68.0) | 276 | 20 | 20 | 236 | Median (range): 63.0 (17.2, 86.6) | Survival outcomes | |
| Ahmed, 2015, US [19] | NSCLC | Thoracic RT | Median (range): 62 (60, 66) | 166 | 20 | 20 | 126 | Median (range): 65 (24, 86) | Survival outcomes | |
| Jang, 2015, Korea [33] | Hepatocellular carcinoma | SBRT or hypofractionated RT | Range: 25, 60 | 217 | 19 | 29 | 169 | NA | Survival outcomes | |
| Van De Voorde, 2015, Netherlands [44] | Oesophageal cancer | EBRT | Median (NA): 41.4 (NA) or 50.4 (NA) | 196 | 19 | 5 | 172 | Mean (range): 63 (37, 82) | Survival outcomes | |
| Spratt, 2016, US [39] | Oropharyngeal cancer | EBRT | Median (IQR): 69.96 (66, 70) | 1745 | 102 | 82 | 1561 | Median (range): 56 (25, 91) | Survival outcomes | |
| Wink, 2016, Germany [45] | Locally advanced NSCLC | CRT | Median (range): 66.1 (50, 129.6) | 682 | 59 | Non-user ¶: 623 | Median (range): 63 (29, 87) | Survival outcomes | ||
| Chang, 2017, Taiwan [23] | Head and neck SCC | CRT | Range: 70, 74 | 252 | 39 | Non-user ¶: 213 | Median (range): 55 (26, 83) | Survival outcomes RT-related side effects | ||
| Liu, 2017, US [35] | Prostate cancer | RT | Median (range): 2000–2005: 75.6 (NA); 2009–2012: 80.3 (NA) | 381 | 27 | Non-user ¶: 354 | Mean ± SD: 74.4 ± 6.0 | Survival outcomes | ||
| Takiuchi, 2017, US [42] | Cervical cancer | Whole pelvic RT | NA | 478 | Metformin user ¦: 41 | Non-user ¶: 437 | NA | Survival outcomes | ||
| Li, 2019, Taiwan [34] | Prostate cancer | RT | NA | 567 | Metformin user ¶: 180 | Non-user ¶: 387 | Mean ± SD: 71.8 ± 8.7 | Survival outcomes | ||
| Ranasinghe, 2019, Australia [36] | Prostate cancer | EBRT | NA | 2055 | 113 | Non-user ¶: 1942 | Median (range): 70 (54, 79) | Survival outcomes | ||
| Tsou, 2019, Taiwan [43] | Hypopharyngeal SCC | CRT | Range: 60, 70 | 141 | 49 | 43 | 49 | Mean ± SD: 63.64 ± NA | Survival outcomes | |
| Yu, 2019, Taiwan [22] | Early-stage breast cancer | Breast RT | Median (range): 50.4 (50, 59.4) | 6993 | Metformin user ¦: 2062 | Non-user ¶: 4931 | Median (range): metformin user: 59.89 (NA); non-user: 59.35 (NA) | RT-related side effects | ||
| Cadeddu, 2020, Spain [30] | High-risk prostate cancer | RT | Range: 72, 76 | 447 | Metformin users ¤: 70 | Non-user ¤: 377 | Median (range): 70 (46, 83) | Survival outcomes RT-related side effects | ||
| Chun, 2020, US [20] | Squamous or adenocarcinoma NSCLC | SBRT | Median (range): peripheral: 50 (NA); central: 70 (NA) | 15 | 14 | 1 | Median (range): 73 (51, 84) | Survival outcomes RT-related side effects | ||
| Dağdelen, 2021, Turkey [31] | Prostate cancer | Radical RT | Median (range): 78 (70, 80) | 94 | 22 | 72 | Median (range): 69 (53, 88) | Survival outcomes RT-related side effects | ||
| Kim, 2021, Canada [46] | Prostate cancer | Prostate/pelvic RT | Range: 76, 78 | 81 | 39 | 42 | Mean ± SD: 72 ± 7.1 | RT-related side effects | ||
| Skinner, 2021, US [47] | Locally advanced NSCLC | 3D conformal or intensity-modulated RT | Median (range): 60 (NA) | 167 | 86 | 81 | Median (range): 64 (43, 86) | Survival outcomes RT-related side effects | ||
| Stang, 2021, US [40] | Locally advanced NSCLC | SBRT | Range: 50, 60 | 120 | 31 | 11 | 78 | Mean ± SD: 71.38 ± 9.09 | Survival outcomes | |
| Tsakiridis, 2021, Canada [21] | Locally advanced NSCLC | Chest RT | Range: 60, 63 | 54 | 26 | 28 | Mean ± SD: 65.6 ± 7.6 | Survival outcomes RT-related side effects | ||
| Tate, 2024, US [48] | NSCLC | SBRT | Median (range): peripheral: 50 (NA); central: 70 (NA) | 15 | 14 | 1 | Median (range): 73 (51, 84) | Survival outcomes | ||
| Study | Cancer | Comparison | Event Rate | Odds Ratio (95%CI) | Effect Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1: metformin (NS) vs. non-user (NS) | 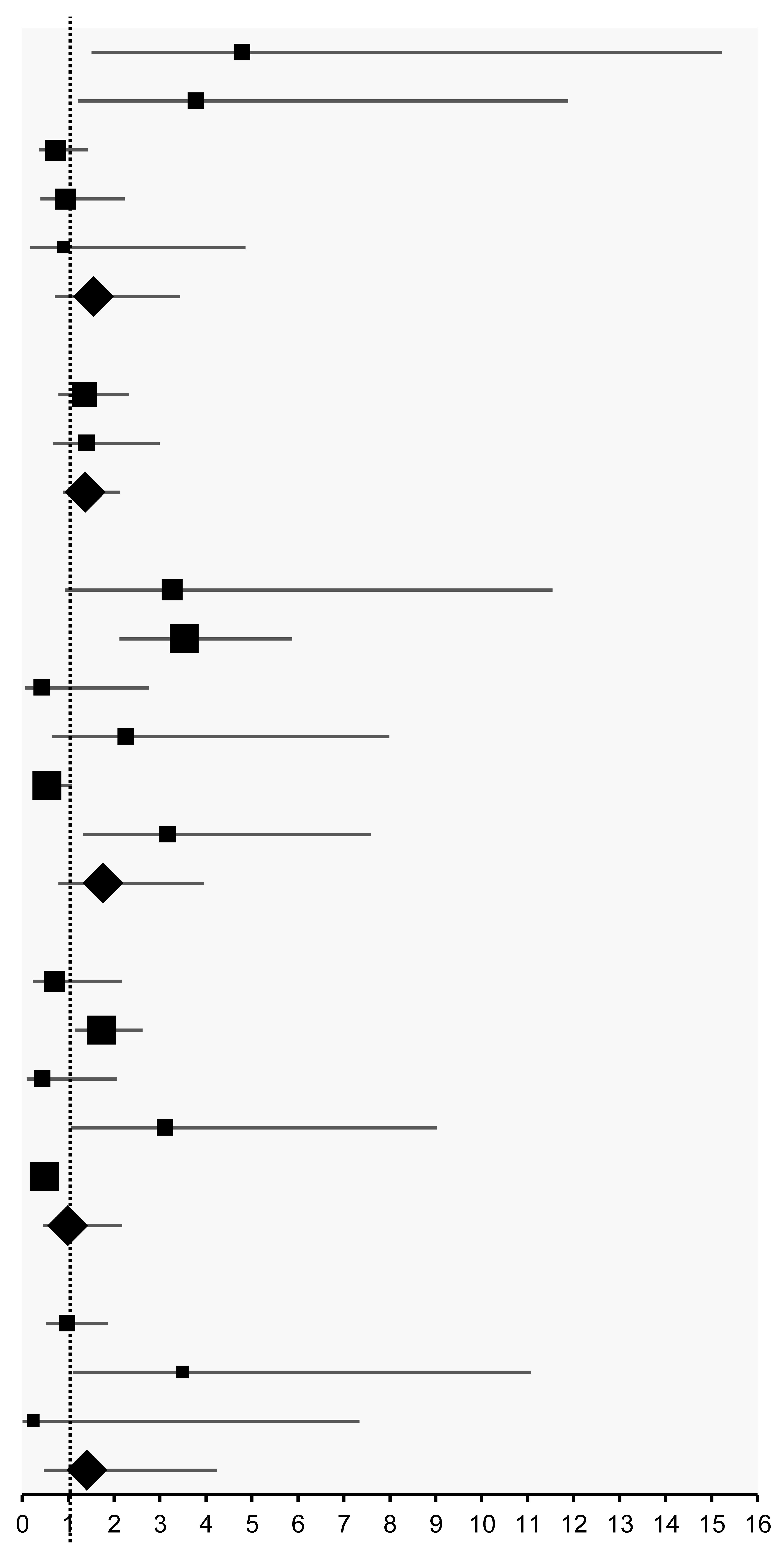 | ||||
| Jang (2015) [33] | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Metformin (NS) vs. non-user (NS) | 14/19 vs. 21/57 | 4.80 (1.51, 15.22) | |
| Van De Voorde (2015) [44] | Oesophageal cancer | Metformin (NS) vs. non-user (NS) | 15/19 vs. 88/177 | 3.79 (1.21, 11.88) | |
| Takiuchi (2017) [42] | Cervical cancer | Metformin (NS) vs. non-user (NS) | 27/41 vs. 317/437 | 0.73 (0.37, 1.44) | |
| Cadeddu (2020) [30] | High-risk prostate cancer | Metformin (NS) vs. non-user (NS) | 63/70 vs. 341/377 | 0.95 (0.40, 2.23) | |
| Dağdelen (2021) [31] | Prostate cancer | Metformin (NS) vs. non-user (NS) | 20/22 vs. 66/72 | 0.91 (0.17, 4.86) | |
| Overall | Metformin (NS) vs. non-user (NS) | 139/171 vs. 833/1120 | 1.56 (0.71, 3.44), I2 = 66.0% | ||
| Group2: metformin (DM+) vs. non-user (NS) | |||||
| Wink (2016) [45] | Locally advanced NSCLC | Metformin (DM+) vs. non-user (NS) | 33/59 vs. 301/623 | 1.36 (0.79, 2.32) | |
| Chang (2017) [23] | Head and neck SCC | Metformin (DM+) vs. non-user (NS) | 28/39 vs. 137/213 | 1.41 (0.67, 2.99) | |
| Overall | Metformin (DM+) vs. non-user (NS) | 61/98 vs. 438/836 | 1.38 (0.89, 2.13), I2 < 0.1% | ||
| Group 3: metformin (DM+) vs. non-user (DM+) | |||||
| Skinner (2013) [37] | Rectal cancer | Metformin (DM+) vs. non-user (DM+) | 16/20 vs. 22/40 | 3.27 (0.93, 11.54) | |
| Spratt (2013) [38] | Prostate cancer | Metformin (DM+) vs. non-user (DM+) | 128/157 vs. 90/162 | 3.53 (2.12, 5.87) | |
| Ahmed (2015) [19] | NSCLC | Metformin (DM+) vs. non-user (DM+) | 2/20 vs. 4/20 | 0.44 (0.07, 2.76) | |
| Jang (2015) [33] | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Metformin (DM+) vs. non-user (DM+) | 14/19 vs. 16/29 | 2.27 (0.65, 7.99) | |
| Spratt (2016) [39] | Oropharyngeal cancer | Metformin (DM+) vs. non-user (DM+) | 72/102 vs. 67/82 | 0.54 (0.27, 1.09) | |
| Tsou (2019) [43] | Hypopharyngeal SCC | Metformin (DM+) vs. non-user (DM+) | 27/49 vs. 12/43 | 3.17 (1.33, 7.59) | |
| Overall | Metformin (DM+) vs. non-user (DM+) | 259/367 vs. 211/376 | 1.77 (0.79, 3.96), I2 = 77.8% | ||
| Group 4: metformin (DM+) vs. non-user (DM−) | |||||
| Skinner (2013) [37] | Rectal cancer | Metformin (DM+) vs. non-user (DM−) | 16/20 vs. 359/422 | 0.70 (0.23, 2.17) | |
| Spratt (2013) [38] | Prostate cancer | Metformin (DM+) vs. non-user (DM−) | 128/157 vs. 1854/2582 | 1.73 (1.15, 2.62) | |
| Ahmed (2015) [19] | NSCLC | Metformin (DM+) vs. non-user (DM−) | 2/20 vs. 25/126 | 0.45 (0.10, 2.06) | |
| Jang (2015) [33] | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Metformin (DM+) vs. non-user (DM−) | 14/19 vs. 80/169 | 3.12 (1.07, 9.03) | |
| Spratt (2016) [39] | Oropharyngeal cancer | Metformin (DM+) vs. non-user (DM−) | 72/102 vs. 1296/1561 | 0.49 (0.31, 0.77) | |
| Overall | Metformin (DM+) vs. non-user (DM−) | 232/318 vs. 3614/4860 | 1.00 (0.46, 2.18), I2 = 82.2% | ||
| Group 5: metformin (DM−) vs. non-user (DM−) | |||||
| Skinner (2021) [47] | Locally advanced NSCLC | Metformin (DM−) vs. non-user (DM−) | 56/86 vs. 53/81 | 0.99 (0.52, 1.87) | |
| Tsakiridis (2021) [21] | Locally advanced NSCLC | Metformin (DM−) vs. non-user (DM−) | 14/26 vs. 7/28 | 3.50 (1.11, 11.07) | |
| Tate (2024) [48] | NSCLC | Metformin (DM−) vs. non-user (DM−) | 6/14 vs. 1/1 | 0.25 (0.01, 7.34) | |
| Overall | Metformin (DM−) vs. non-user (DM−) | 76/126 vs. 61/110 | 1.41 (0.47, 4.24), I2 = 55.2% | ||
| Study | Cancer | Comparison | Event Rate | Odds Ratio (95%CI) | Effect Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pooled progression-free | 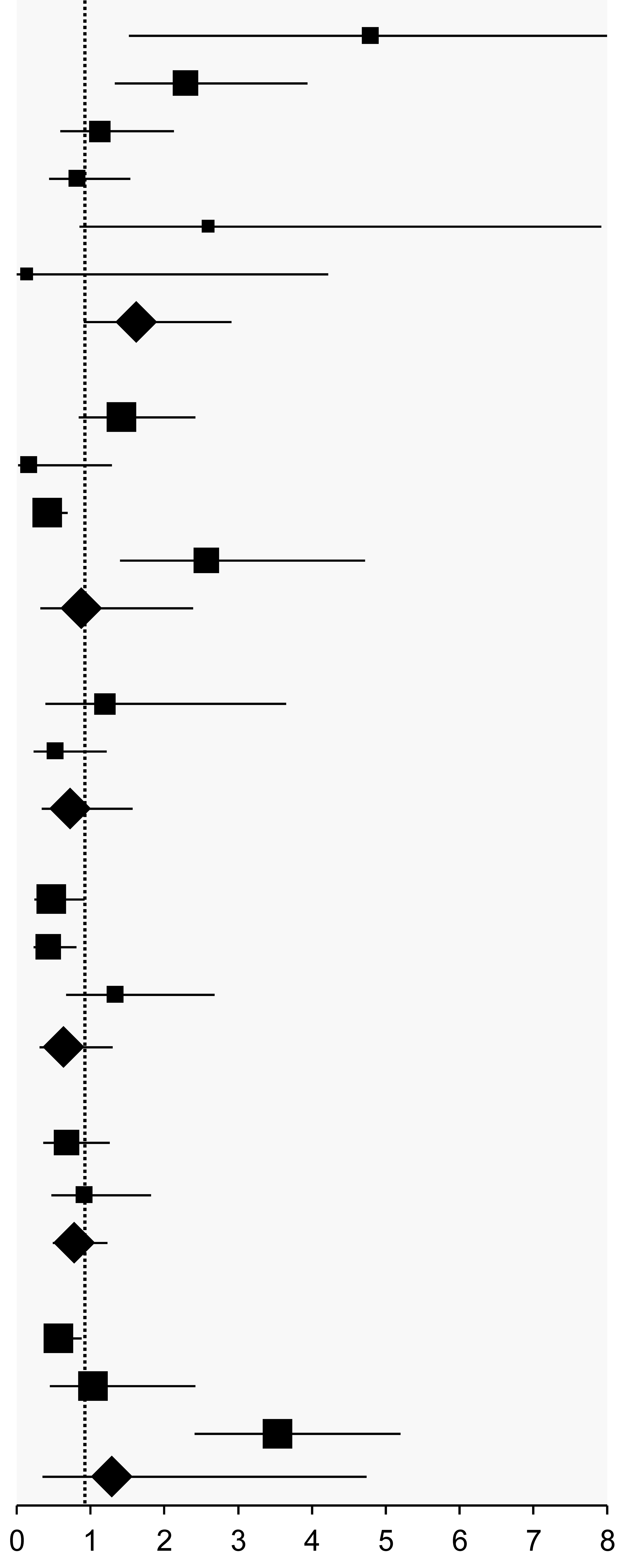 | ||||
| Jang (2015) [33] | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Metformin (NS) vs. non-user (NS) | 9/19 vs. 9/57 | 4.80 (1.52, 15.13) | |
| Wink (2016) [45] | Locally advanced NSCLC | Metformin (DM+) vs. non-user (NS) | 34/59 vs. 232/623 | 2.29 (1.33, 3.94) | |
| Takiuchi (2017) [42] | Cervical cancer | Metformin (NS) vs. non-user (NS) | 23/41 vs. 233/437 | 1.12 (0.59, 2.13) | |
| Skinner (2021) [47] | Locally advanced NSCLC | Metformin (DM−) vs. non-user (DM−) | 30/86 vs. 32/81 | 0.82 (0.44, 1.54) | |
| Tsakiridis (2021) [21] | Locally advanced NSCLC | Metformin (DM−) vs. non-user (DM−) | 18/26 vs. 13/28 | 2.60 (0.85, 7.92) | |
| Tate (2024) [48] | NSCLC | Metformin (DM−) vs. non-user (DM−) | 4/14 vs. 1/1 | 0.14 (0.00, 4.22) | |
| Overall | 118/245 vs. 520/1227 | 1.62 (0.91, 2.91), I2 = 62.6% | |||
| Distant metastasis-free survival rate | |||||
| Spratt (2013) [38] | Prostate cancer | Metformin (DM+) vs. non-user (DM−) | 141/157 vs. 2223/2582 | 1.42 (0.84, 2.42) | |
| Van De Voorde (2015) [44] | Oesophageal cancer | Metformin (NS) vs. non-user (NS) | 1/19 vs. 44/177 | 0.17 (0.02, 1.29) | |
| Spratt (2016) [39] | Oropharyngeal cancer | Metformin (DM+) vs. non-user (DM−) | 80/102 vs. 1399/1561 | 0.42 (0.26, 0.69) | |
| Wink (2016) [45] | Locally advanced NSCLC | Metformin (DM+) vs. non-user (NS) | 44/59 vs. 332/623 | 2.57 (1.40, 4.72) | |
| Overall | 266/337 vs. 3998/4943 | 0.88 (0.32, 2.39), I2 = 88.2% | |||
| Disease-free survival rate | |||||
| Skinner (2013) [37] | Rectal cancer | Metformin (DM+) vs. non-user (DM−) | 16/20 vs. 325/422 | 1.19 (0.39, 3.65) | |
| Tsou (2019) [43] | Hypopharyngeal SCC | Metformin (DM+) vs. non-user (DM+) | 22/49 vs. 26/43 | 0.53 (0.23, 1.22) | |
| Overall | 38/69 vs. 351/465 | 0.73 (0.34, 1.57), I2 = 22.3% | |||
| Distant metastasis rate | |||||
| Spratt (2013) [38] | Prostate cancer | Metformin (DM+) vs. non-user (DM−) | 9/157 vs. 298/2582 | 0.47 (0.24, 0.92) | |
| Wink (2016) [45] | Locally advanced NSCLC | Metformin (DM+) vs. non-user (NS) | 13/59 vs. 248/623 | 0.43 (0.23, 0.81) | |
| Skinner (2021) [47] | Locally advanced NSCLC | Metformin (DM−) vs. non-user (DM−) | 25/86 vs. 19/81 | 1.34 (0.67, 2.68) | |
| Overall | 47/302 vs. 565/3286 | 0.64 (0.31, 1.30), I2 = 70.2% | |||
| Locoregional recurrence rate | |||||
| Wink (2016) [45] | Locally advanced NSCLC | Metformin (DM+) vs. non-user (NS) | 14/59 vs. 196/623 | 0.68 (0.36, 1.26) | |
| Skinner (2021) [47] | Locally advanced NSCLC | Metformin (DM−) vs. non-user (DM−) | 23/86 vs. 23/81 | 0.92 (0.47, 1.82) | |
| Overall | 37/145 vs. 219/704 | 0.78 (0.49, 1.23), I2 < 0.1% | |||
| Biochemical failure rate | |||||
| Spratt (2013) [38] | Prostate cancer | Metformin (DM+) vs. non-user (DM−) | 26/157 vs. 666/2582 | 0.57 (0.37, 0.88) | |
| Taira (2014) [41] | Prostate cancer | Metformin (DM+) vs. non-user (DM−) | 6/126 vs. 93/2028 | 1.04 (0.45, 2.42) | |
| Ranasinghe (2019) [36] | Prostate cancer | Metformin (DM+) vs. non-user (NS) | 61/113 vs. 483/1942 | 3.54 (2.41, 5.20) | |
| Overall | 93/396 vs. 1242/6552 | 1.29 (0.35, 4.74), I2 = 94.9% | |||
| Adverse Event | Study | Comparison | Follow-Up (Months) | Event Rate | Odds Ratio (95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prostate cancer | |||||
| Acute gastrointestinal toxicity | Cadeddu (2020) [30] | Metformin (NS) vs. non-user (NS) | Median (range): 88 (1–194) | NA/70 vs. NA/377 ¦ | 1.00 (0.50, 1.60) † |
| Acute gastrointestinal toxicity | Dağdelen (2021) [31] | Metformin (NS) vs. non-user (NS) | Median (range): 57 (15–128) | 6/22 vs. 18/72 | 1.13 (0.38, 3.31) † |
| Acute genitourinary toxicity | Cadeddu (2020) [30] | Metformin (NS) vs. non-user (NS) | Median (range): 88 (1–194) | NA/70 vs. NA/377 ¦ | 1.4 (0.30, 0.90) § |
| Acute genitourinary toxicity | Dağdelen (2021) [31] | Metformin (NS) vs. non-user (NS) | Median (range): 57 (15–128) | 20/22 vs. 54/72 | 3.33 (0.71, 15.68) § |
| Chronic gastrointestinal toxicity | Cadeddu (2020) [30] | Metformin (NS) vs. non-user (NS) | Median (range): 88 (1–194) | NA/70 vs. NA/377 ¦ | 1.10 (0.30, 2.30) |
| Chronic genitourinary toxicity | Cadeddu (2020) [30] | Metformin (NS) vs. non-user (NS) | Median (range): 88 (1–194) | NA/70 vs. NA/377 ¦ | 1.0 (0.50, 1.80) |
| Late genitourinary side effects | Dağdelen (2021) [31] | Metformin (NS) vs. non-user (NS) | Median (range): 57 (15–128) | 4/22 vs. 9/72 | 1.56 (0.43, 5.65) |
| Late gastrointestinal side effects | Dağdelen (2021) [31] | Metformin (NS) vs. non-user (NS) | Median (range): 57 (15–128) | 3/22 vs. 3/72 | 3.63 (0.68, 19.47) |
| Overall genitourinary toxicity | Kim (2021) [46] | Metformin (DM−) vs. non-user (DM−) | Mean (range): 27.3 (0.5–63.2) | 2/29 vs. 1/28 | 2.00 (0.17, 23.39) |
| Overall gastrointestinal toxicity | Kim (2021) [46] | Metformin (DM−) vs. non-user (DM−) | Mean (range): 27.3 (0.5–63.2) | 1/29 vs. 0/28 | 2.00 (0.06, 62.06) |
| Head and neck SCC | |||||
| Feeding tube placement | Chang (2017) [23] | Metformin (DM+) vs. non-user (NS) | NA | 29/39 vs. 125/213 | 2.04 (0.95, 4.40) |
| Toxic death (grade 5 toxicity) | Chang (2017) [23] | Metformin (DM+) vs. non-user (NS) | NA | 2/39 vs. 9/213 | 1.23 (0.25, 5.90) |
| ≥grade 3 mucositis/pharyngitis | Chang (2017) [23] | Metformin (DM+) vs. non-user (NS) | NA | 16/39 vs. 116/213 | 0.58 (0.29, 1.16) |
| ≥grade 3 nausea/vomiting | Chang (2017) [23] | Metformin (DM+) vs. non-user (NS) | NA | 11/39 vs. 33/213 | 2.14 (0.97, 4.72) ¶¤ |
| Locally advanced NSCLC | |||||
| ≥grade 3 toxicities | Chun (2020) [20] | Metformin (DM−) vs. non-user (DM−) | Median (range): 6 (NA) | 0/14 vs. 0/1 | 0.07 (0.00, 5.90) |
| ≥grade 3 nausea | Skinner (2021) [47] | Metformin (DM−) vs. non-user (DM−) | Median (range): 27.7 (0.03–47.21) | 2/86 vs. 1/81 | 1.90 (0.17, 21.42) ¶ |
| ≥grade 3 nausea | Tsakiridis (2021) [21] | Metformin (DM−) vs. non-user (DM−) | NA | 0/26 vs. 1/28 | 0.52 (0.02, 16.15) ¶ |
| ≥grade 3 vomiting | Skinner (2021) [47] | Metformin (DM−) vs. non-user (DM−) | Median (range): 27.7 (0.03–47.21) | 1/86 vs. 1/81 | 0.94 (0.06, 15.30) ¤ |
| ≥grade 3 vomiting | Tsakiridis (2021) [21] | Metformin (DM−) vs. non-user (DM−) | NA | 0/26 vs. 1/28 | 0.52 (0.02, 16.15) ¤ |
| ≥grade 3 diarrhoea | Skinner (2021) [47] | Metformin (DM−) vs. non-user (DM−) | Median (range): 27.7 (0.03–47.21) | 1/86 vs. 2/81 | 0.46 (0.04, 5.23) |
| ≥grade 3 pneumonitis | Skinner (2021) [47] | Metformin (DM−) vs. non-user (DM−) | Median (range): 27.7 (0.03–47.21) | 1/86 vs. 2/81 | 0.46 (0.04, 5.23) |
| ≥grade 3 anaemia | Tsakiridis (2021) [21] | Metformin (DM−) vs. non-user (DM−) | NA | 1/26 vs. 1/28 | 1.08 (0.06, 18.21) |
| ≥grade 3 body odour | Tsakiridis (2021) [21] | Metformin (DM−) vs. non-user (DM−) | NA | 1/26 vs. 0/28 | 2.24 (0.07, 69.68) |
| ≥grade 3 dysphagia | Tsakiridis (2021) [21] | Metformin (DM−) vs. non-user (DM−) | NA | 2/26 vs. 0/28 | 4.67 (0.20, 108.54) |
| ≥grade 3 esophagitis | Tsakiridis (2021) [21] | Metformin (DM−) vs. non-user (DM−) | NA | 0/26 vs. 1/28 | 0.52 (0.02, 16.15) |
| ≥grade 3 lymphocyte count decreased | Tsakiridis (2021) [21] | Metformin (DM−) vs. non-user (DM−) | NA | 5/26 vs. 1/28 | 6.43 (0.70, 59.28) |
| ≥grade 3 neutrophil count decreased | Tsakiridis (2021) [21] | Metformin (DM−) vs. non-user (DM−) | NA | 2/26 vs. 1/28 | 2.25 (0.19, 26.41) |
| ≥grade 3 white blood cell count decreased | Tsakiridis (2021) [21] | Metformin (DM−) vs. non-user (DM−) | NA | 3/26 vs. 1/28 | 3.52 (0.34, 36.22) |
| ≥grade 3 respiratory failure | Tsakiridis (2021) [21] | Metformin (DM−) vs. non-user (DM−) | NA | 1/26 vs. 0/28 | 2.24 (0.07, 69.68) |
| Breast cancer | |||||
| Treatment breaks secondary to skin toxicity | Ferro (2013) [32] | Metformin (DM+) vs. non-user (DM+) | NA | 9/51 vs. 1/28 | 5.79 (0.69, 48.29) |
| Desquamation | Ferro (2013) [32] | Metformin (DM+) vs. non-user (DM+) | NA | 28/51 vs. 9/28 | 2.57 (0.98, 6.75) |
| Heart failure | Yu (2019) [22] | Metformin (NS) vs. non-user (NS) | Mean ± SD: 61.68 ± 17.28 | 74/2062 vs. 241/4931 | 0.72 (0.56, 0.94) * |
| All heart events | Yu (2019) [22] | Metformin (NS) vs. non-user (NS) | Mean ± SD: 61.68 ± 17.28 | 129/2062 vs. 419/4931 | 0.72 (0.59, 0.88) * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liao, W.-C.; Shokr, H.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Dempsey, C.; Williams, K.J.; Chen, L.-C. Survival and Radiotherapy-Related Adverse Events in Patients Receiving Radiotherapy and Concurrent Metformin: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials and Cohort Studies. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1390. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091390
Liao W-C, Shokr H, Faivre-Finn C, Dempsey C, Williams KJ, Chen L-C. Survival and Radiotherapy-Related Adverse Events in Patients Receiving Radiotherapy and Concurrent Metformin: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials and Cohort Studies. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(9):1390. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091390
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiao, Wan-Chuen, Hala Shokr, Corinne Faivre-Finn, Clare Dempsey, Kaye Janine Williams, and Li-Chia Chen. 2025. "Survival and Radiotherapy-Related Adverse Events in Patients Receiving Radiotherapy and Concurrent Metformin: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials and Cohort Studies" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 9: 1390. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091390
APA StyleLiao, W.-C., Shokr, H., Faivre-Finn, C., Dempsey, C., Williams, K. J., & Chen, L.-C. (2025). Survival and Radiotherapy-Related Adverse Events in Patients Receiving Radiotherapy and Concurrent Metformin: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials and Cohort Studies. Pharmaceuticals, 18(9), 1390. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091390







