Early Detection of Vulnerable Plaques Using Targeted Biosynthetic Nanobubbles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
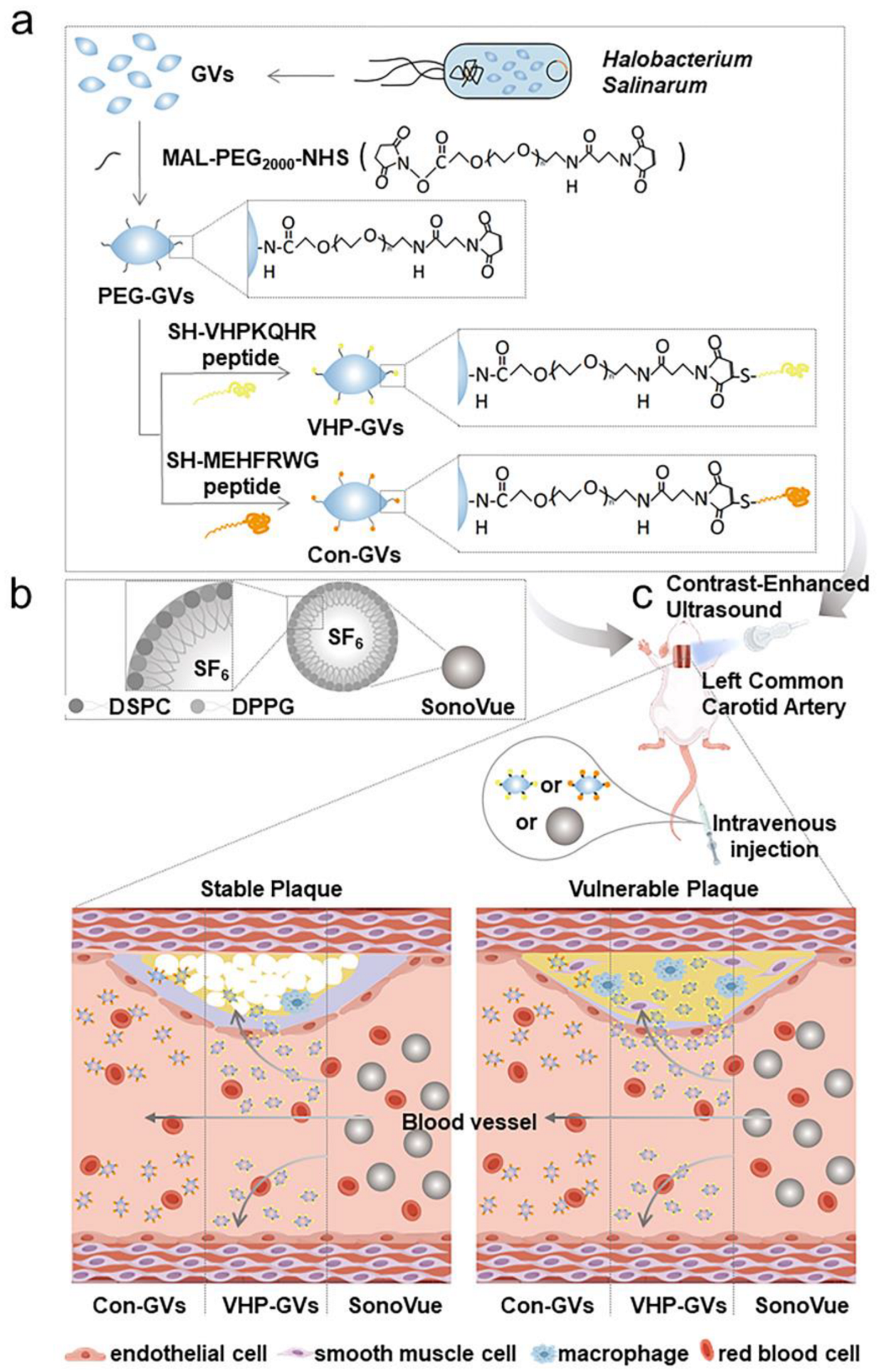
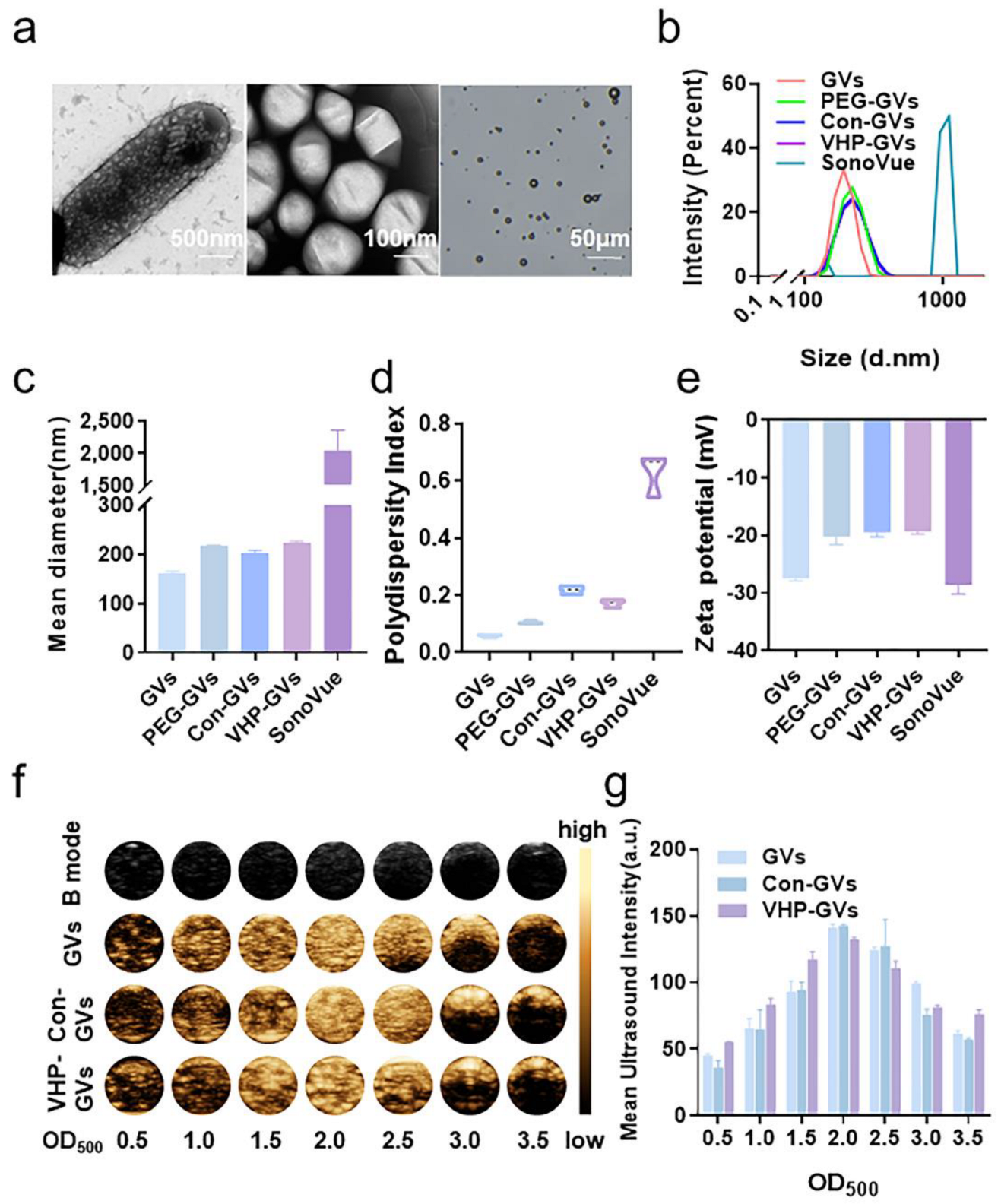
2.1. Characterization Results of Gas Vesicles
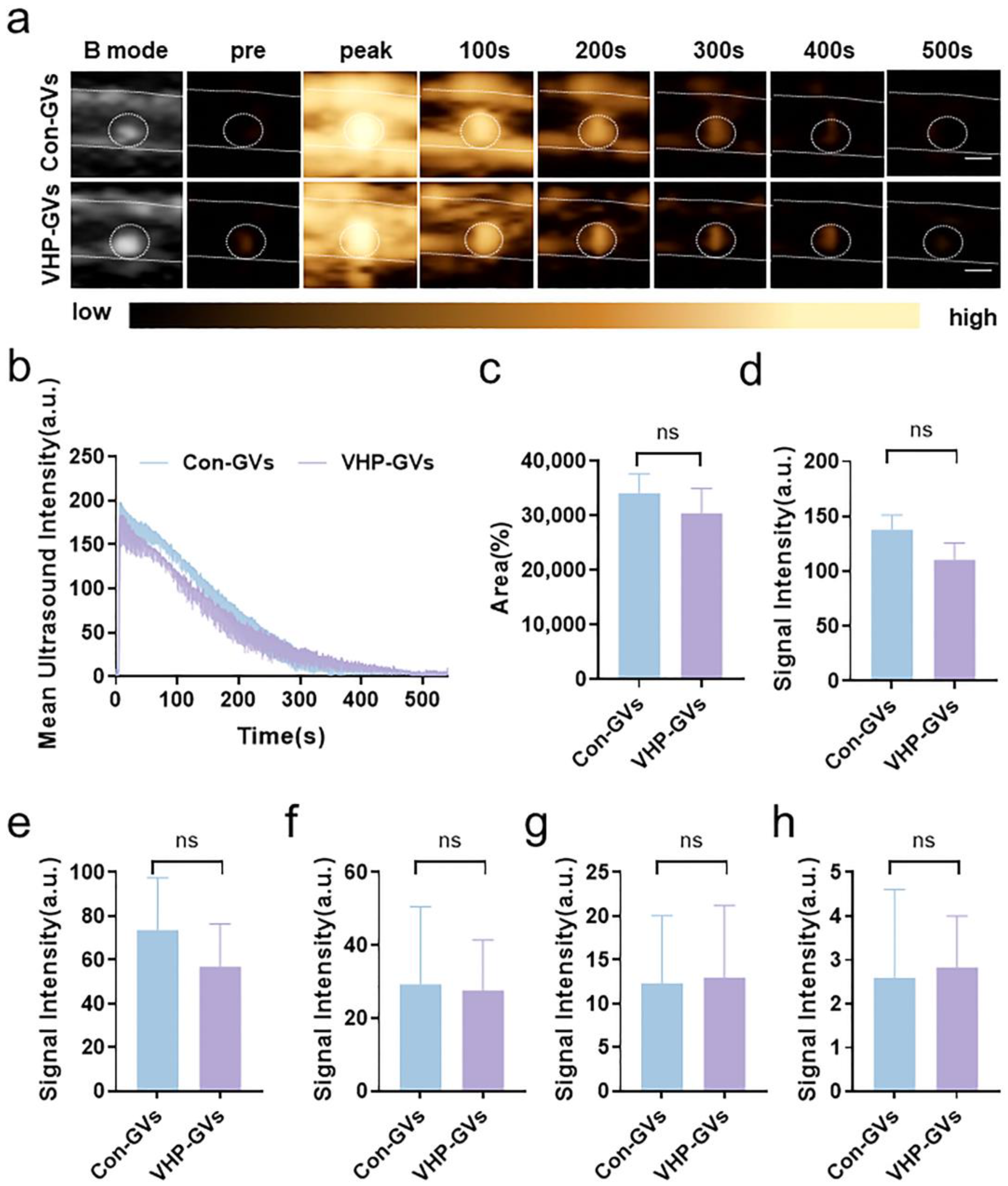
2.2. In Vitro Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound Imaging Results of GVs
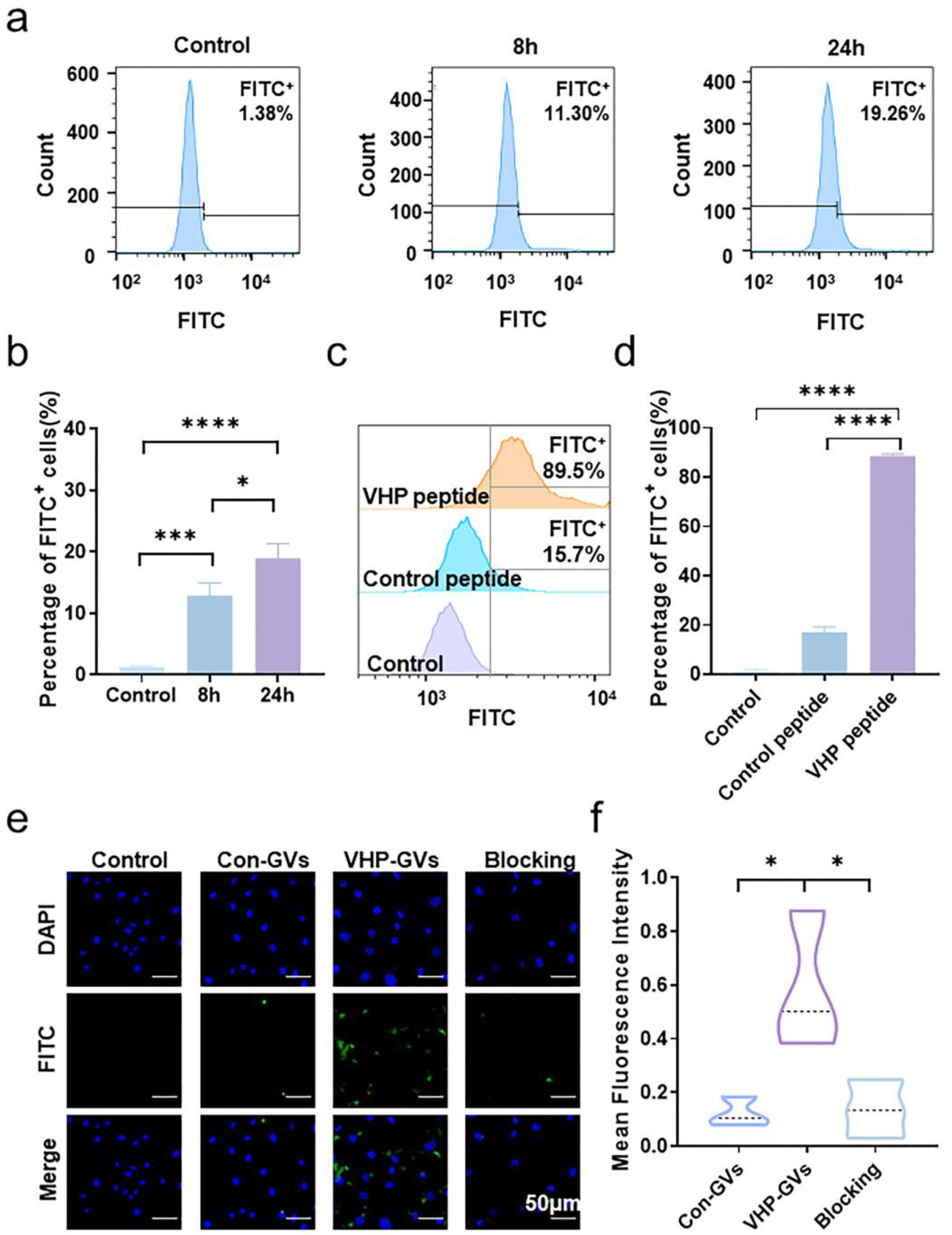
2.3. In Vitro Cell Targeting of VHPs and VHP-GVs
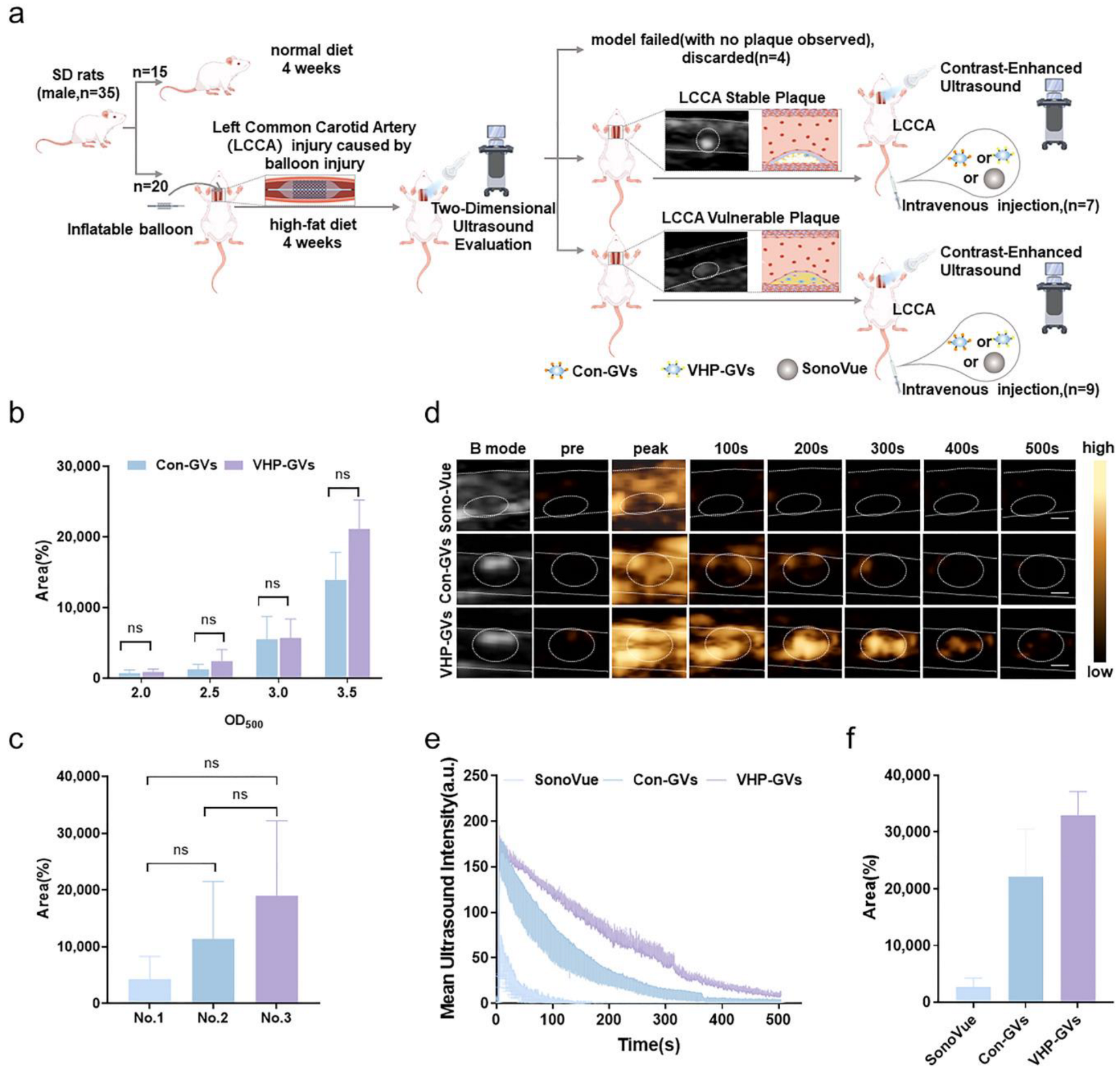
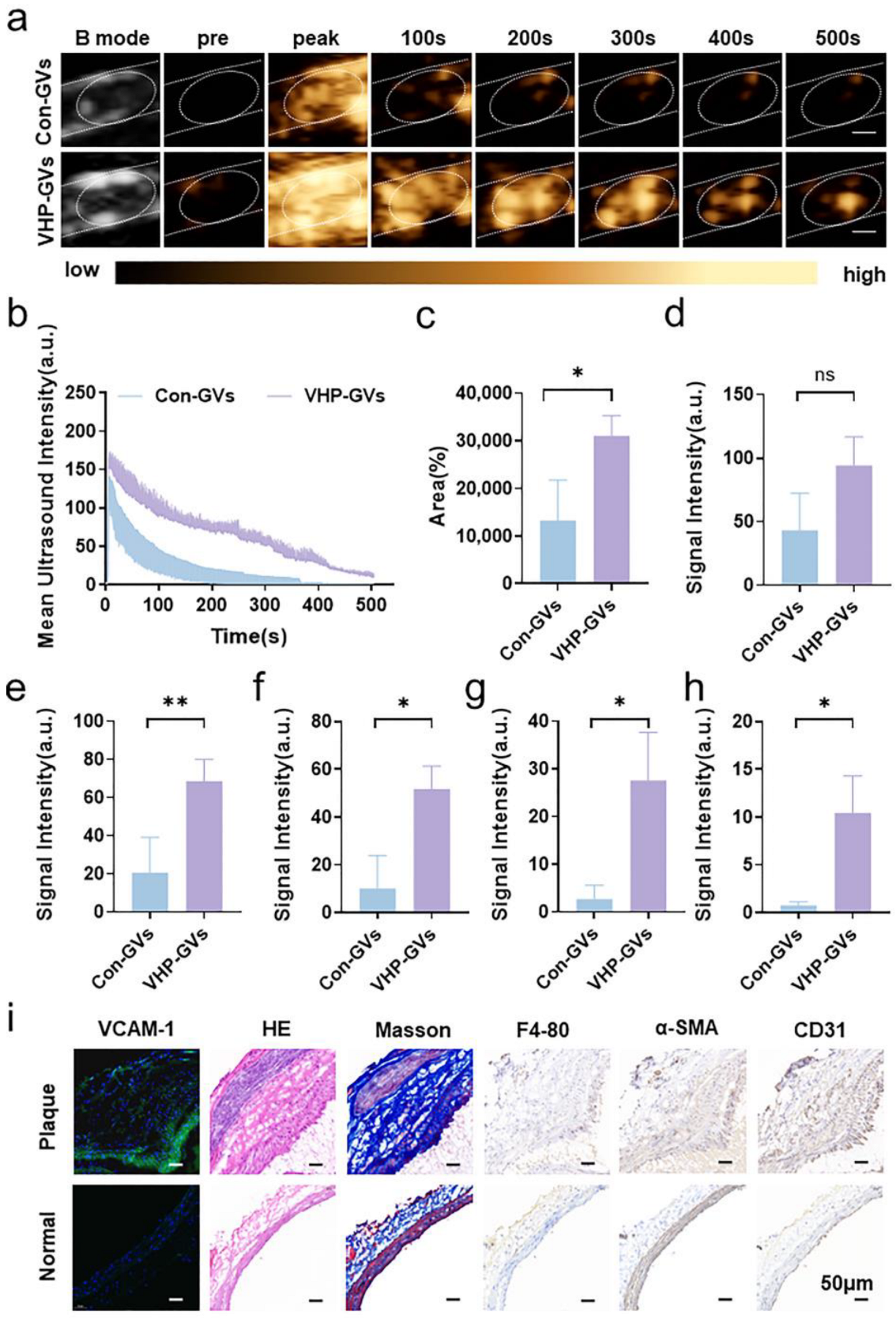
2.4. In Vivo Ultrasound Molecular Imaging Results
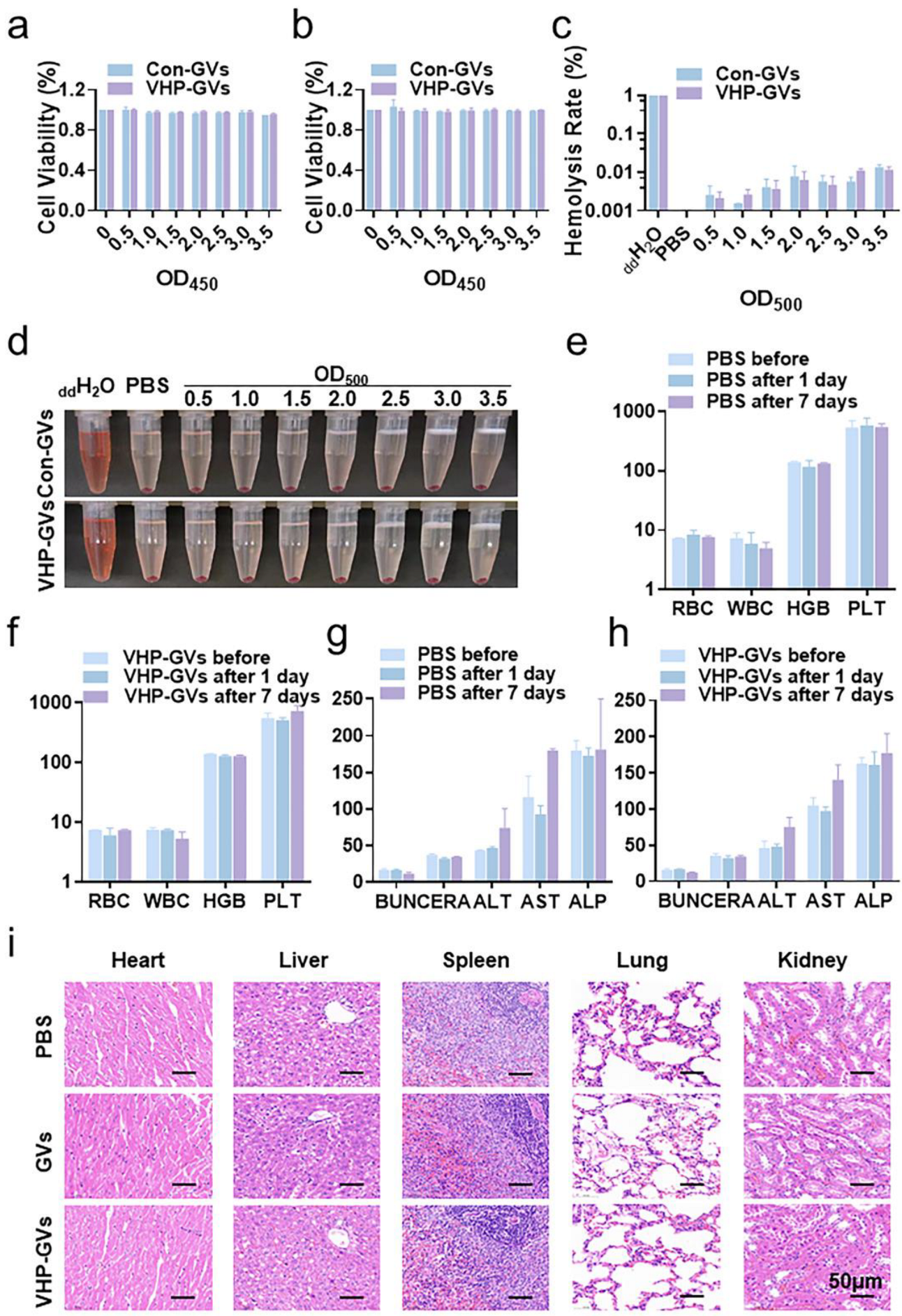
2.5. Biosafety Assessment
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of Gas Vesicles
4.3. Characterization of Gas Vesicles
4.4. In Vitro Ultrasound Contrast Imaging of GVs
4.5. Cell Culture and Inflammation Model
4.6. In Vitro Cell Adhesion Assay of VHP Peptides
4.7. In Vitro Cell Adhesion Assay of VHP-GVs
4.8. In Vivo Ultrasound Molecular Imaging
4.9. Histological Examination
4.10. Toxicity Assay
4.10.1. Cell Viability Assay
4.10.2. Hemolysis Assay
4.10.3. In Vivo Biosafety Assay
4.10.4. Repeat-Dose and Long-Term Organ Retention Assessment
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frostegård, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, J.; Yan, K.; Liu, A. Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein (OxLDL)-Treated Dendritic Cells Promote Activation of T Cells in Human Atherosclerotic Plaque and Blood, Which Is Repressed by Statins: microRNA let-7c Is Integral to the Effect. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2016, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Su, J.; Yang, C. Molecular imaging of atherosclerotic plaque with lipid nanobubbles as targeted ultrasound contrast agents. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 189, 110861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.; Kaur, R.; Kumari, P.; Pasricha, C.; Singh, R. ICAM-1 and VCAM-1: Gatekeepers in various inflammatory and cardiovascular disorders. Clin. Chim. Acta Int. J. Clin. Chem. 2023, 548, 117487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preiss, D.J.; Sattar, N. Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1: A viable therapeutic target for atherosclerosis? Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2007, 61, 697–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinkauf, C.C.; Concha-Moore, K.; Lindner, J.R.; Marinelli, E.R.; Hadinger, K.P.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Berman, S.S.; Goshima, K.; Leon, L.R., Jr.; Matsunaga, T.O.; et al. Endothelial vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 is a marker for high-risk carotid plaques and target for ultrasound molecular imaging. J. Vasc. Surg. 2018, 68, 105S–113S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.K.; Thavornpattanapong, P.; Cheung, S.C.; Sun, Z.; Tu, J. Effect of calcification on the mechanical stability of plaque based on a three-dimensional carotid bifurcation model. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2012, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahagi, K.; Kolodgie, F.D.; Lutter, C.; Mori, H.; Romero, M.E.; Finn, A.V.; Virmani, R. Pathology of Human Coronary and Carotid Artery Atherosclerosis and Vascular Calcification in Diabetes Mellitus. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2017, 37, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libby, P.; Buring, J.E.; Badimon, L.; Hansson, G.K.; Deanfield, J.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Tokgözoğlu, L.; Lewis, E.F. Atherosclerosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Yang, S.; Chen, X.; He, Q.; Zhao, K.; Hu, J. Molecular imaging diagnosis of atherosclerotic vulnerable plaque in rabbit carotid artery using a self-assembled nanoscale ultrasound microbubble contrast agent. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 22, 1657–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köse, G.; Darguzyte, M.; Kiessling, F. Molecular Ultrasound Imaging. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajmal, S. Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasonography: Review and Applications. Cureus 2021, 13, e18243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versluis, M.; Stride, E.; Lajoinie, G.; Dollet, B.; Segers, T. Ultrasound Contrast Agent Modeling: A Review. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2020, 46, 2117–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, M.J.; Stretanski, M.F. Ultrasound Therapy. In StatPearls; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, H.; Hu, H.; Sun, J.; Shi, M.; Yu, H.; Li, C.; Sun, Y.U.; Yang, Z.; Hoffman, R.M. Ultrasound Microbubble Delivery Targeting Intraplaque Neovascularization Inhibits Atherosclerotic Plaque in an APOE-deficient Mouse Model. In Vivo 2018, 32, 1025–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Sun, Y.; Wei, J.; Xu, L.; Tang, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, X.; Lu, Y. The effects of ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction (UTMD) carrying IL-8 monoclonal antibody on the inflammatory responses and stability of atherosclerotic plaques. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 118, 109161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, A.; Maki, G.; Johnson, P. TNF-alpha induction of CD44-mediated leukocyte adhesion by sulfation. Science 1998, 282, 941–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Sun, Y.; Mao, Y.; Wu, M.; Deng, Z.; Li, S.; Liu, X.; Xue, L.; Zheng, H. Ultrasound Molecular Imaging of Atherosclerosis for Early Diagnosis and Therapeutic Evaluation through Leucocyte-like Multiple Targeted Microbubbles. Theranostics 2018, 8, 1879–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo-Takahashi, Y.; Negishi, Y. Microbubbles and Nanobubbles with Ultrasound for Systemic Gene Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, F.; Du, M.; Chen, Z. Nanosized Contrast Agents in Ultrasound Molecular Imaging. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 758084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandhyala, S.; Van Namen, A.; Spatarelu, C.P.; Luke, G.P. EGFR-Targeted Perfluorohexane Nanodroplets for Molecular Ultrasound Imaging. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sax, N.; Kodama, T. Optimization of acoustic liposomes for improved in vitro and in vivo stability. Pharm. Res. 2013, 30, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Ma, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, F.; Chern, S.X.; Zhao, E.R.; Jhunjhunwala, A.; Darmadi, S.; Chen, H.; Jokerst, J.V. Exosome-like silica nanoparticles: A novel ultrasound contrast agent for stem cell imaging. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Cornel, E.J.; Du, J. Ultrasound-responsive polymer-based drug delivery systems. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2021, 11, 1323–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyman, S.A.; McLaughlan, J.R.; Abou-Saleh, R.H.; Marston, G.; Johnson, B.R.; Freear, S.; Coletta, P.L.; Markham, A.F.; Evans, S.D. On-chip preparation of nanoscale contrast agents towards high-resolution ultrasound imaging. Lab A Chip 2016, 16, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Yan, F.; Zhang, W.; He, L.; Li, Y.; Zheng, S.; Wang, Y.; Yu, T.; Du, L.; Shen, Y.; et al. Biosynthetic Gas Vesicles Combined with Focused Ultrasound for Blood-Brain Barrier Opening. Int. J. Nanomed. 2022, 17, 6759–6772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Li, F.; Chen, J.; Yibulayin, M.; Zhang, S.; Su, Z.; et al. PEGylated gas vesicles: A promising novel ultrasound contrast agent for diagnosis and guiding radiofrequency ablation of liver tumor. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2025, 23, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Hao, Y.; Zeng, F.; Zhang, Z.; Du, J.; Long, H.; Yan, F. Genetic Modulation of Biosynthetic Gas Vesicles for Ultrasound Imaging. Small (Weinh. Der Bergstr. Ger.) 2024, 20, e2310008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Lai, M.; Zhang, J.; Pei, X.; Yan, F. Biosynthetic Gas Vesicles from Halobacteria NRC-1: A Potential Ultrasound Contrast Agent for Tumor Imaging. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Huang, W.; Huang, C.; Zhou, C.; Tang, Y.; Wei, W.; Li, Y.; Tang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, Q.; et al. VHPKQHR Peptide Modified Ultrasmall Paramagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Targeting Rheumatoid Arthritis for T(1)-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 821256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, W. VHPKQHR peptide modified magnetic mesoporous nanoparticles for MRI detection of atherosclerosis lesions. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 2440–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Yeh, C.F.; Mellas, M.; Oh, M.J.; Zhu, J.; Li, J.; Huang, R.T.; Harrison, D.L.; Shentu, T.P.; Wu, D.; et al. Targeted polyelectrolyte complex micelles treat vascular complications in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2114842118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Huang, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, C.; Wei, W.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, W.; Tang, Y. Targeting Peptide, Fluorescent Reagent Modified Magnetic Liposomes Coated with Rapamycin Target Early Atherosclerotic Plaque and Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahrendorf, M.; Jaffer, F.A.; Kelly, K.A.; Sosnovik, D.E.; Aikawa, E.; Libby, P.; Weissleder, R. Noninvasive vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 imaging identifies inflammatory activation of cells in atherosclerosis. Circulation 2006, 114, 1504–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, K.A.; Nahrendorf, M.; Yu, A.M.; Reynolds, F.; Weissleder, R. In vivo phage display selection yields atherosclerotic plaque targeted peptides for imaging. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2006, 8, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piepoli, M.F.; Hoes, A.W.; Agewall, S.; Albus, C.; Brotons, C.; Catapano, A.L.; Cooney, M.T.; Corrà, U.; Cosyns, B.; Deaton, C.; et al. 2016 European Guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice: The Sixth Joint Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and Other Societies on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention in Clinical Practice (constituted by representatives of 10 societies and by invited experts) Developed with the special contribution of the European Association for Cardiovascular Prevention & Rehabilitation (EACPR). Atherosclerosis 2016, 252, 207–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobatto, M.E.; Calcagno, C.; Millon, A.; Senders, M.L.; Fay, F.; Robson, P.M.; Ramachandran, S.; Binderup, T.; Paridaans, M.P.; Sensarn, S.; et al. Atherosclerotic plaque targeting mechanism of long-circulating nanoparticles established by multimodal imaging. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 1837–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strunk, T.; Hamacher, K.; Hoffgaard, F.; Engelhardt, H.; Zillig, M.D.; Faist, K.; Wenzel, W.; Pfeifer, F. Structural model of the gas vesicle protein GvpA and analysis of GvpA mutants in vivo. Mol. Microbiol. 2011, 81, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, S.T.; Terwiel, D.; Evers, W.H.; Maresca, D.; Jakobi, A.J. Cryo-EM structure of gas vesicles for buoyancy-controlled motility. Cell 2023, 186, 975–986.e913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, A.; Pfeifer, F. Interaction of the gas vesicle proteins GvpA, GvpC, GvpN, and GvpO of Halobacterium salinarum. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 971917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DasSarma, S.; DasSarma, P. Gas Vesicle Nanoparticles for Antigen Display. Vaccines 2015, 3, 686–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Fu, M.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xiao, J.; Zhou, Y.; Yan, F. Modification of PEG reduces the immunogenicity of biosynthetic gas vesicles. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1128268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, T.; Luo, Y.; Jiao, L. Identification Markers of Carotid Vulnerable Plaques: An Update. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, L.; Saam, T.; Jäger, H.R.; Yuan, C.; Hatsukami, T.S.; Saloner, D.; Wasserman, B.A.; Bonati, L.H.; Wintermark, M. Imaging biomarkers of vulnerable carotid plaques for stroke risk prediction and their potential clinical implications. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, K.; Kawakami, R.; Finn, A.V.; Virmani, R. Differences in Stable and Unstable Atherosclerotic Plaque. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2024, 44, 1474–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubrano, V.; Balzan, S. Status of biomarkers for the identification of stable or vulnerable plaques in atherosclerosis. Clin. Sci. (Lond. Engl. 1979) 2021, 135, 1981–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gianopoulos, I.; Daskalopoulou, S.S. Macrophage profiling in atherosclerosis: Understanding the unstable plaque. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2024, 119, 35–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, P.; Fang, J.; Liu, Z.; Shi, Y.; Agostini, M.; Bernassola, F.; Bove, P.; Candi, E.; Rovella, V.; Sica, G.; et al. Macrophage polarization and metabolism in atherosclerosis. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schinkel, A.F.; Kaspar, M.; Staub, D. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound: Clinical applications in patients with atherosclerosis. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2016, 32, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindner, J.R.; Song, J.; Jayaweera, A.R.; Sklenar, J.; Kaul, S. Microvascular rheology of Definity microbubbles after intra-arterial and intravenous administration. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. Off. Publ. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2002, 15, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz, J.; Fayad, Z.A. Imaging of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Nature 2008, 451, 953–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Oord, S.C.; ten Kate, G.L.; Akkus, Z.; Renaud, G.; Sijbrands, E.J.; ten Cate, F.J.; van der Lugt, A.; Bosch, J.G.; de Jong, N.; van der Steen, A.F.; et al. Assessment of subclinical atherosclerosis using contrast-enhanced ultrasound. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2013, 14, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiangdong, L.; Yuanwu, L.; Hua, Z.; Liming, R.; Qiuyan, L.; Ning, L. Animal models for the atherosclerosis research: A review. Protein Cell 2011, 2, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, D.; Yang, P.; Liu, J.; Dai, F.; Xiao, Y.; Zhao, A.; Huang, N. Constructing Mal-Efferocytic Macrophage Model and Its Atherosclerotic Spheroids and Rat Model for Therapeutic Evaluation. Adv. Biol. 2023, 7, e2200277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priyadharsini, R.P. Animal models to evaluate anti-atherosclerotic drugs. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 29, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Yin, H.; Zhang, R.; Yu, D.; Wang, J.; Liu, T.; Shen, X.; Xue, L.; Yan, F. Early Detection of Vulnerable Plaques Using Targeted Biosynthetic Nanobubbles. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1285. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091285
Wang Y, Yin H, Zhang R, Yu D, Wang J, Liu T, Shen X, Xue L, Yan F. Early Detection of Vulnerable Plaques Using Targeted Biosynthetic Nanobubbles. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(9):1285. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091285
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yan, Huang Yin, Rui Zhang, Dan Yu, Jieqiong Wang, Tingting Liu, Xiong Shen, Li Xue, and Fei Yan. 2025. "Early Detection of Vulnerable Plaques Using Targeted Biosynthetic Nanobubbles" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 9: 1285. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091285
APA StyleWang, Y., Yin, H., Zhang, R., Yu, D., Wang, J., Liu, T., Shen, X., Xue, L., & Yan, F. (2025). Early Detection of Vulnerable Plaques Using Targeted Biosynthetic Nanobubbles. Pharmaceuticals, 18(9), 1285. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091285







