Exploring the In Vitro Mechanism of Action of β-Acetoxyisovalerylalkannin on Inflammatory Skin Diseases Using Network-Based Pharmacology and Non-Targeted Metabolomics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
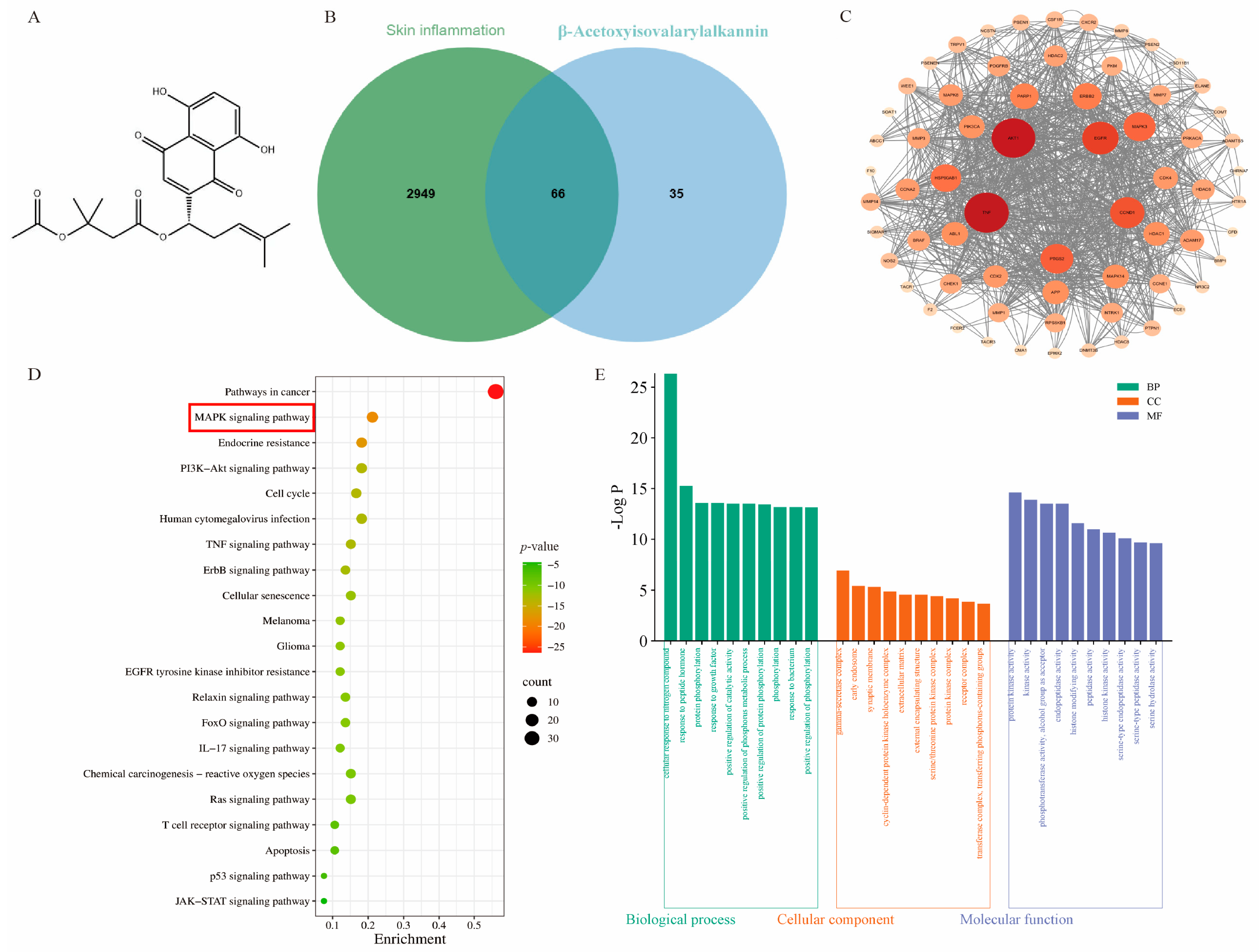
2.1. Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Analysis of β-Acetoxyisovalerylalkannin
2.2. Effect of β-Acetoxyisovalerylalkannin on HaCaT Cell Proliferation
2.3. Impact of β-Acetoxyisovalerylalkannin-Induced Apoptosis on HaCaTs
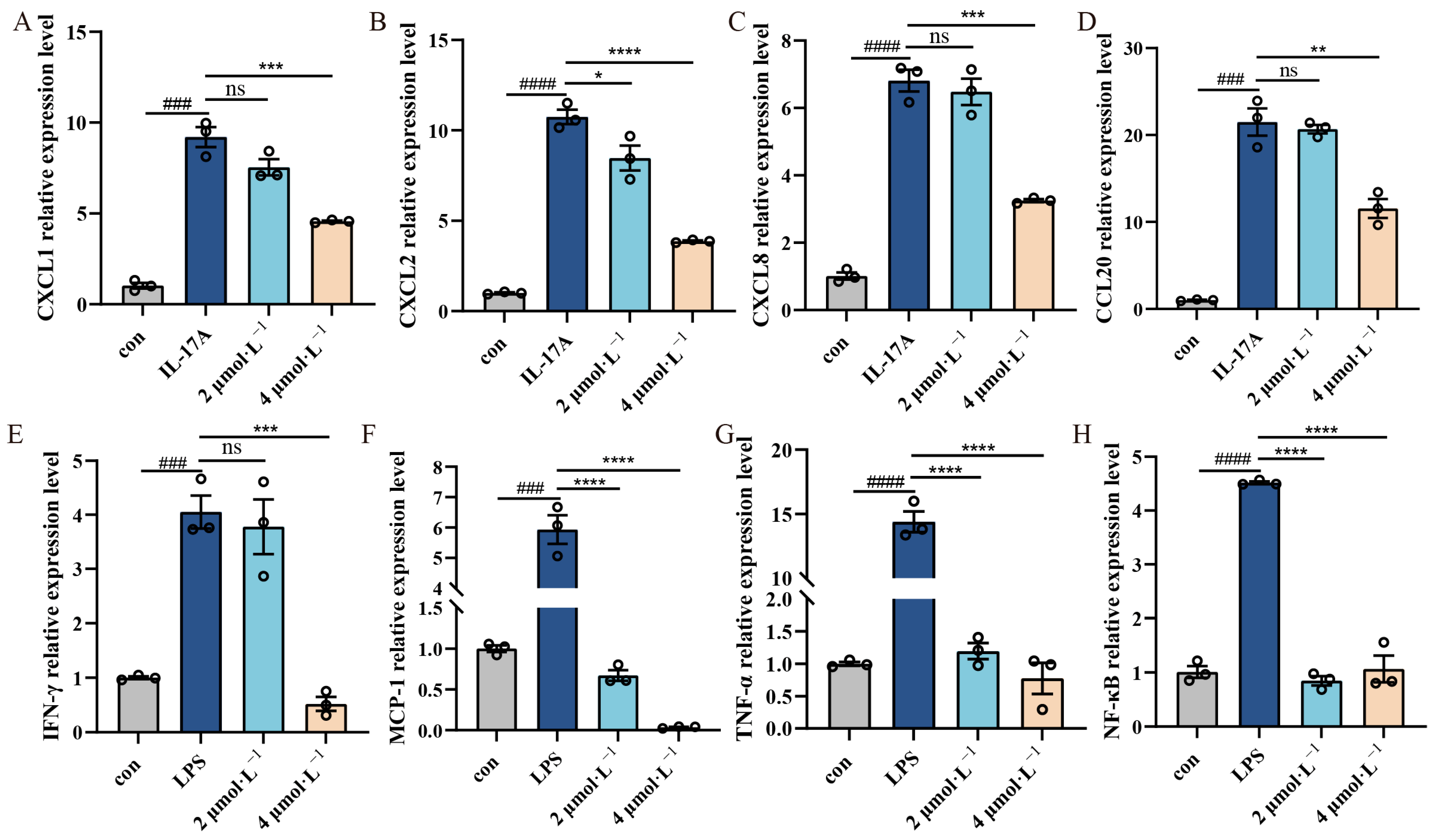
2.4. Effect of β-Acetoxyisovalerylalkannin on Inflammatory Factors
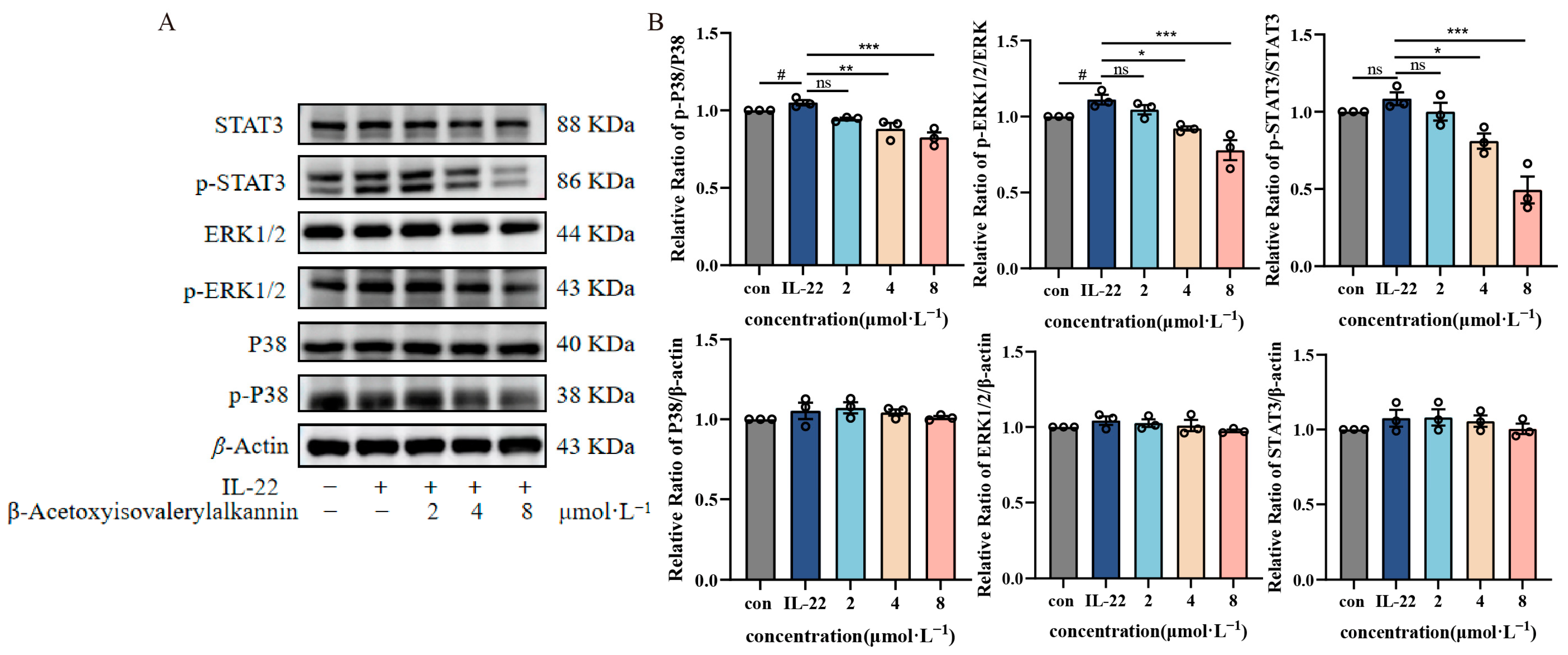
2.5. β-Acetoxyisovalerylalkannin-Inhibited MAPK/STAT3 Signaling Pathway
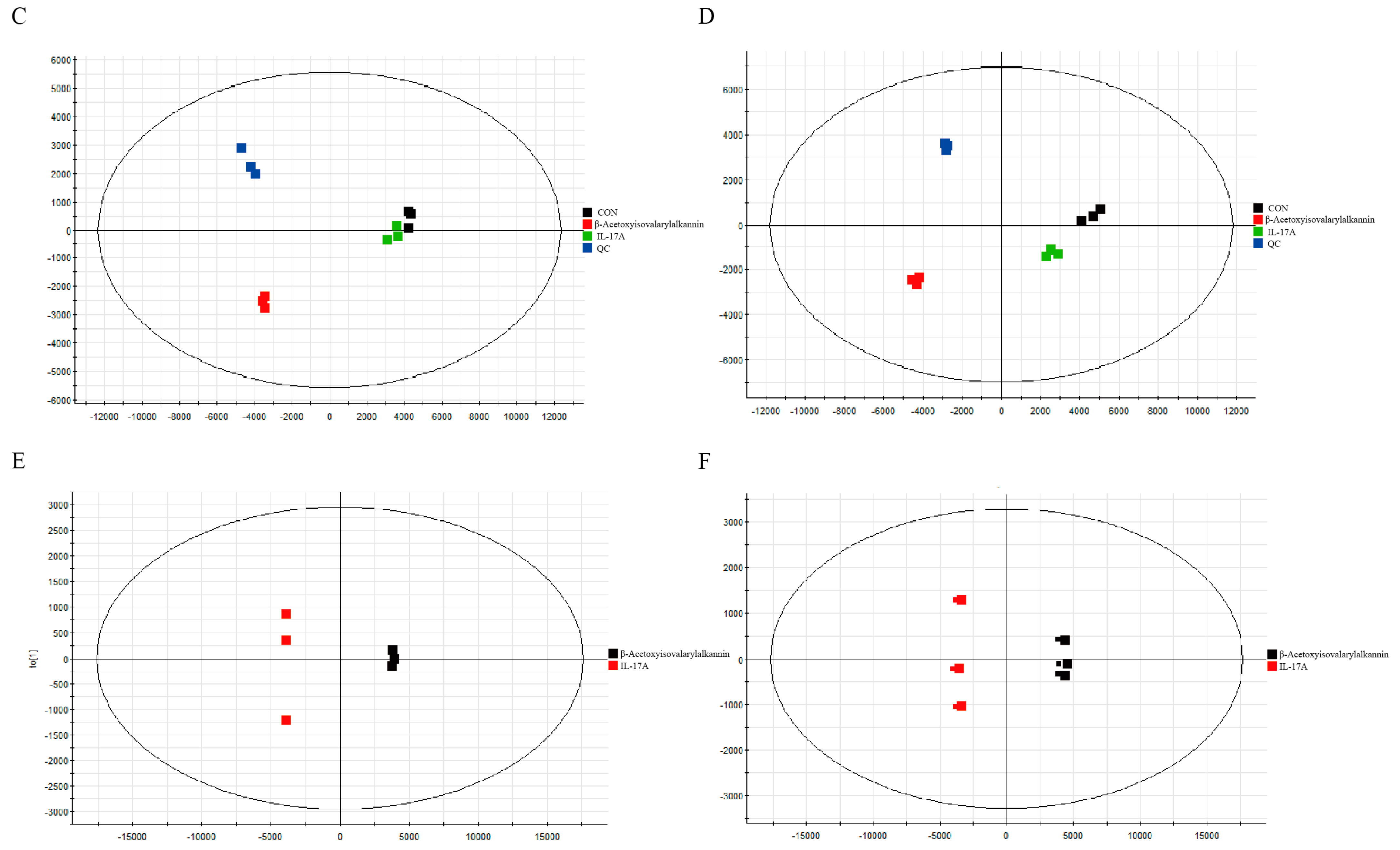
2.6. Non-Targeted Metabolomics Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Drugs and Reagents
4.1.1. Cells
4.1.2. Reagents
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking
4.2.2. Preparation of β-Acetoxyisovalerylalkannin Stock Solution
4.2.3. Cell Viability Assay (CCK-8 Method)
4.2.4. Clone Formation Assay for Assessing Cell Proliferation
4.2.5. Scratch Assay for Evaluating Cell Migration
4.2.6. Flow Cytometry
4.2.7. Immunofluorescence Detection of Apoptosis
4.2.8. Determination of HaCaT Cell-Associated Inflammatory Factors via RT-qPCR
4.2.9. Western Blot Detection of MAPK/STAT3 Signaling Pathway Protein Expression
4.2.10. Non-Targeted Metabolomics
4.2.11. Data Analysis and Processing
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boarder, E.; Rumberger, B.; Howell, M.D. Modeling Skin Inflammation Using Human In Vitro Models. Curr. Protoc. 2021, 1, e72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diotallevi, F.; Campanati, A.; Martina, E.; Radi, G.; Paolinelli, M.; Marani, A.; Molinelli, E.; Candelora, M.; Taus, M.; Galeazzi, T.; et al. The Role of Nutrition in Immune-Mediated, Inflammatory Skin Disease: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirley, S.N.; Watson, A.E.; Yusuf, N. Pathogenesis of Inflammation in Skin Disease: From Molecular Mechanisms to Pathology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.Y.; Jiang, Y.P.; Shu, Y.Q.; Liao, S.Y.; Chen, Z.C.; Tang, Q.F.; Shao, M. Extraction and Decolorization Process Optimization for Polysaccharides from Arnebia euchroma. Chin. Tradit. Pat. Med. 2024, 46, 2898–2903. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.Y.; Jiang, Y.P.; Feng, H.W.; Shu, Y.Q.; Liao, S.Y.; Liao, Y.; Shao, M. Research Progress of Traditional External Preparations and Novel Nanoformulations of Arnebiae Radix. China Pharm. 2023, 34, 1909–1914. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, S.; Sharma, A.; Nayik, G.A.; Cooper, R.; Bhardwaj, G.; Sohal, H.S.; Mutreja, V.; Kaur, R.; Areche, F.O.; AlOudat, M.; et al. Review of Shikonin and Derivatives: Isolation, Chemistry, Biosynthesis, Pharmacology and Toxicology. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 905755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; He, J.; Song, X.; Tan, L.; Wang, M.; Jiang, P.; Li, Y.; Cao, Z.; Peng, C. Pharmacological Properties and Derivatives of Shikonin—A Review in Recent Years. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 149, 104463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Li, M.; Qian, Q.; Chen, L.; Yang, Y.; Ji, T.F.; Li, J.G. β-Acetoxyisovalerylalkannin Suppresses Proliferation and Induces ROS-Based Mitochondria-Mediated Apoptosis in Human Melanoma Cells. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2024, 26, 372–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Fan, W.; Huang, R.; Liu, G. β-Acetoxyisovaleryl Alkannin (AAN-II) from Alkanna tinctoria Promotes the Healing of Pressure-Induced Venous Ulcers in a Rabbit Model through the Activation of TGF-β/Smad3 Signaling. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2021, 26, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.Y.; Fu, H.L.; Tang, H.Q.; Yin, Z.Q.; Zhang, W.; Shu, G.; Yin, L.Z.; Zhao, L.; Yan, X.R.; Lin, J.C. Optimization Extraction of Shikonin Using Ultrasound-Assisted Response Surface Methodology and Antibacterial Studies. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 1208617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.Y.; Deng, Y.H.; Feng, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhou, D.; Wang, H.L. Studies of Anti-Human Papillomavirus Activity of Herba Arnebia. Tradit. Chin. Drug Res. Clin. Pharm. 2005, 4, 259–260. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.Q.; Jin, C.H. Research Progress on Pharmacological Effects of Shikonin Compound β-Acetoxyisovalerylshikonin. Hortic. Seed 2023, 43, 108–110. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Q.; Guo, F.; Tao, S.; Huang, R.; Ma, L.; Fu, P. Flavonoid Fisetin Alleviates Kidney Inflammation and Apoptosis via Inhibiting Src-Mediated NF-κB p65 and MAPK Signaling Pathways in Septic AKI Mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 122, 109772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Guo, T.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, D.; Hou, L.; Ma, C.; Xing, M. Endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation as a novel mechanism of polystyrene microplastics (PS-MPs)-induced pulmonary inflammation in chickens. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2024, 25, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, C.; Qiao, X.H.; Gao, J.J.; Tian, F.; Zhou, K.L.; Wang, C.C.; Wang, J.P. Shikonin Inhibits Inflammation of Psoriasis Cell Model by Regulating cGAS/STING Signaling Pathway. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae 2024, 30, 114–120. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, X.; Wang, H.; Qi, R.; Xu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Guo, H.; Gao, X.H.; Geng, L. Shikonin inhibits CEBPD downregulation in IL-17-treated HaCaT cells and in an imiquimod-induced psoriasis model. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 2263–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Lan, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Gao, X.; Geng, L. Shikonin induces apoptosis and suppresses growth in keratinocytes via CEBP-δ upregulation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 72, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xu, X.; Gao, X.; Chen, H.; Geng, L. Shikonin suppresses IL-17-induced VEGF expression via blockage of JAK2/STAT3 pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 19, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Yan, G.; Li, F.; Tang, Y.; Xu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Ze, K. Qingxiong Ointment and its Active Ingredient, Shikonin Treat Psoriasis through HIF-1 Signaling Pathway. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2024, 30, 1927–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Xie, Y.; Zhong, J.; Chen, W.; Fang, S.; Chen, X.; Peng, S.; Liu, W.; Liu, C. Improving shikonin solubility and stability by encapsulation in natural surfactant-coated shikonin nanoparticles. J. Food Sci. 2023, 88, 825–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, X.; Xu, T.; Ren, M.; Gao, M.; Lin, H. Quercetin antagonizes apoptosis, autophagy and immune dysfunction induced by di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate via ROS/ASK1/JNK pathway. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2024, 285, 109991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, H.; Hou, L.; Guo, T.; Zhao, H.; Xing, M. Polystyrene microplastics promote liver inflammation by inducing the formation of macrophages extracellular traps. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 452, 131236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, A.V.Q.; Na, Y.; Suk, G.; Yang, C.; Kang, S.M.; Lee, J.; Choi, H.; Kim, W.; Chi, S.W.; Han, S.; et al. Identification of Tie2 as a Sensor for Reactive Oxygen Species and Its Therapeutic Implication. Redox Biol. 2025, 81, 103555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakis, J.M.; Avruch, J. Mammalian MAPK Signal Transduction Pathways Activated by Stress and Inflammation: A 10-Year Update. Physiol. Rev. 2012, 92, 689–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.Q.; Wu, P.; Dong, X.M.; Cheng, L.H.; Lu, H.Q.; Lin, Y.Y.; Tang, W.Y.; Xie, T.; Zhou, J.L. Elemene Induces Cell Apoptosis via Inhibiting Glutathione Synthesis in Lung Adenocarcinoma. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 311, 116409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrés, R.M.; Hald, A.; Johansen, C.; Kragballe, K.; Iversen, L. Studies of Jak/STAT3 Expression and Signaling in Psoriasis Identifies STAT3-Ser727 Phosphorylation as a Modulator of Transcriptional Activity. Exp. Dermatol. 2013, 22, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, D.; Du, B.; Li, P. Dendrobium officinale Kimura et Migo Polysaccharide Ameliorated DNFB-Induced Atopic Dermatitis in Mice Associated with Suppressing MAPK/NF-κB/STAT3 Signaling Pathways. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 335, 118677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.W.; Hsu, C.Y.; Aljuffali, I.A.; Alalaiwe, A.; Lai, W.N.; Gu, P.Y.; Tseng, C.H.; Fang, J.Y. Skin Delivery of Synthetic Benzoyl Pterostilbenes Suppresses Atopic Dermatitis-Like Inflammation through the Inhibition of Keratinocyte and Macrophage Activation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 170, 116073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Xiong, H.; Zhao, Z.; Luo, M.; Ju, Y.; Yang, G.; Mei, Z. Genistein Suppresses Allergic Contact Dermatitis through Regulating the MAP2K2/ERK Pathway. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 4556–4569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.; Yu, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, F.; Wei, W.; Zhang, L.; Chen, W.; Lin, N.; Wu, Y. Hyperforin Ameliorates Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-Like Murine Skin Inflammation by Modulating IL-17A-Producing γδ T Cells. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 635076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Lv, H.; Tang, B.; Zhong, Y.; Luo, Q.; Bi, Y.; Yang, K.; Zhong, H.; Chen, H.; et al. The Causal Relationship Between Serum Metabolites and the Risk of Psoriasis: A Mendelian Randomization and Meta-Analysis Study. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1343301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Li, H.; Zhou, X. Tryptanthrin Ameliorates Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis in Mice by Suppressing Inflammation and Oxidative Stress via NF-κB/MAPK/Nrf2 Pathways. J. Nat. Med. 2023, 77, 188–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.; Xiao, K.; Lin, P.; Lin, J. Five Rutaceae Family Ethanol Extracts Alleviate H2O2 and LPS-Induced Inflammation via NF-κB and JAK-STAT3 Pathway in HaCaT Cells. Chinese J. Nat. Med. 2022, 20, 937–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Gao, S.; Wei, Y.; Wu, G.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Kuang, H.; Han, W. Combined Untargeted Metabolomics and Network Pharmacology Approaches to Reveal the Therapeutic Role of Withanolide B in Psoriasis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2024, 245, 116163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navik, U.; Sheth, V.G.; Sharma, N.; Tikoo, K. L-Methionine Supplementation Attenuates High-Fat Fructose Diet-Induced Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis by Modulating Lipid Metabolism, Fibrosis, and Inflammation in Rats. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 4941–4953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Qin, S.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, S. L-Proline Protects Mice Challenged by Klebsiella pneumoniae Bacteremia. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2021, 54, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Deng, Z.; Huang, J.; Li, T.; Jiang, J.; Wang, W.; Sun, Y.; Deng, Y. Zearalenone-Induced Hepatointestinal Toxicity in Laying Hens: Unveiling the Role of Gut Microbiota and Fecal Metabolites. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 104221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Yang, F.; Zheng, J.; Wang, K. Intracellular Proton-Mediated Activation of TRPV3 Channels Accounts for the Exfoliation Effect of Alpha-Hydroxyl Acids on Keratinocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 25905–25916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhou, R.; Yan, H.; Yin, H.; Wu, X.; Tan, Y.; Li, L. Metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 modulates calcium oscillation and innate immune response induced by lipopolysaccharide in microglial cell. Neuroscience 2014, 281, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wautier, J.L.; Wautier, M.P. Pro- and Anti-Inflammatory Prostaglandins and Cytokines in Humans: A Mini Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, M.; Ribeiro, D.; Janela, J.S.; Varela, C.L.; Costa, S.C.; Da Silva, E.T.; Fernandes, E.; Roleira, F.M.F. Plant-derived and dietary phenolic cinnamic acid derivatives: Anti-inflammatory properties. Food Chem. 2024, 459, 140080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H. Sphingosine-1-phosphate and immune regulation: Trafficking and beyond. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2011, 32, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feingold, K.R. Thematic review series: Skin lipids. The role of epidermal lipids in cutaneous permeability barrier homeostasis. J. Lipid. Res. 2007, 48, 2531–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, W.Y.; Yang, W.K.; Peng, C.T.; Pai, W.Y.; Wang, H.J. MicroRNA-200a/200b Modulate High Glucose-Induced Endothelial Inflammation by Targeting O-linked N-Acetylglucosamine Transferase Expression. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 355. [Google Scholar]





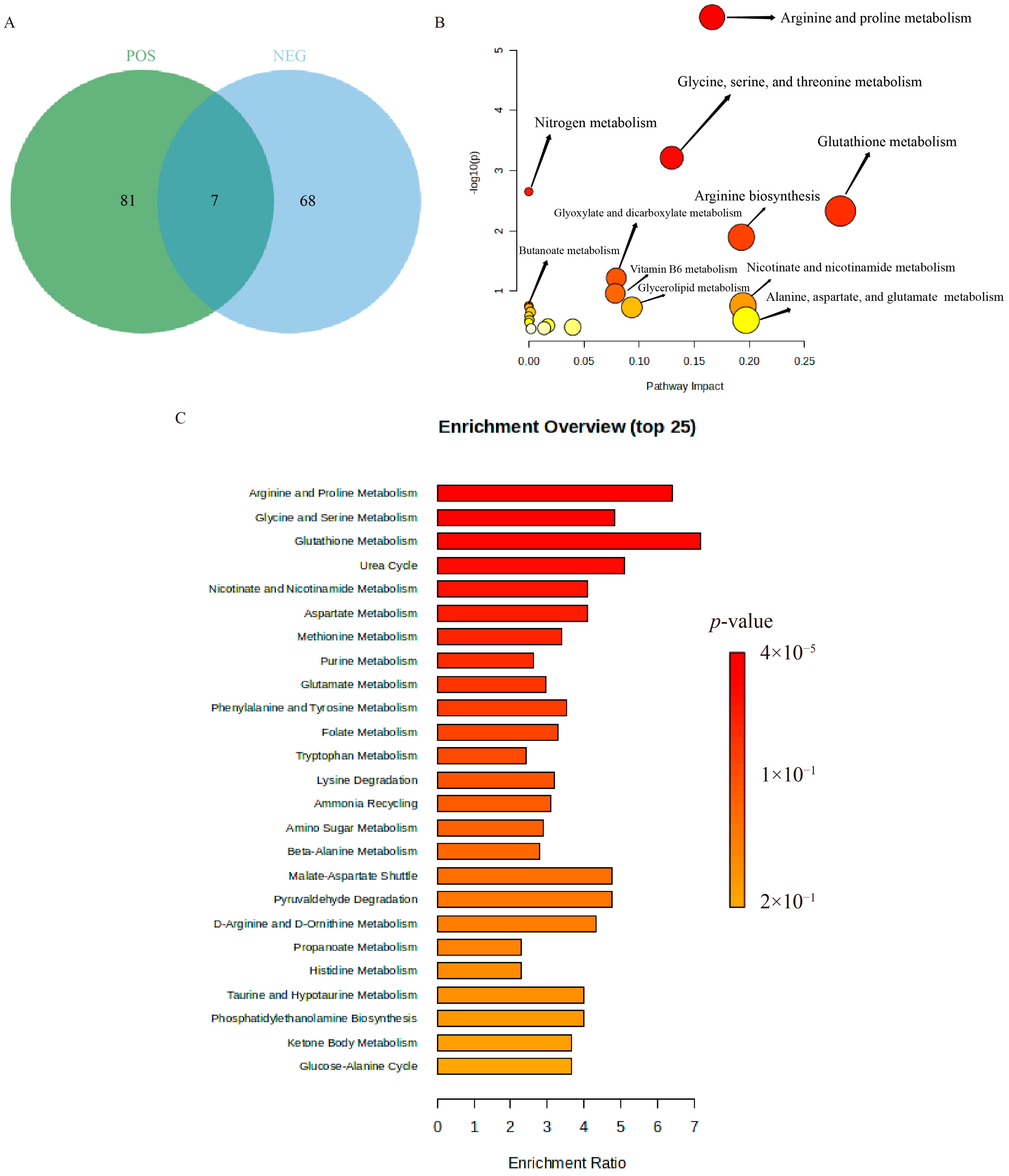
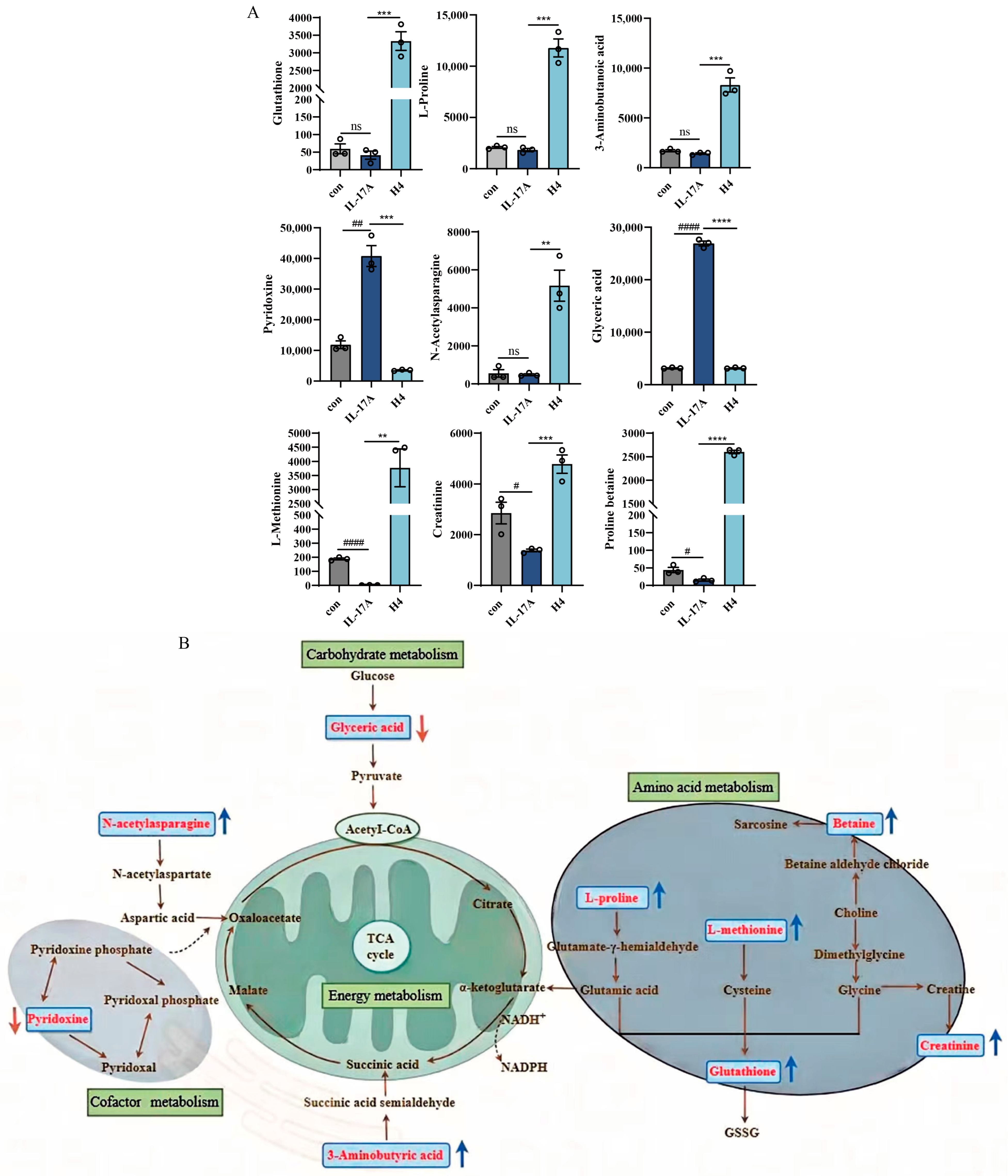
| Serial Number | Retention Time (min) | Mass-to-Charge Ratio m/z | Metabolite Name | Molecular Formula | One-Way ANOVA (p) | β-Acetoxyisovalerylalkannin Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.004383 | 415.2105 | Armillarin | C24H30O6 | 0.000243 | ↑ |
| 2 | 1.65725 | 792.5764 | PG(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)) | C42H79O10P | 0.00014 | ↑ |
| 3 | 9.9014 | 182.0808 | Coumarinic acid | C9H8O3 | 0.011782 | ↑ |
| 4 | 6.342983 | 116.107 | (Z)-4-Hexenal | C6H10O | 3.21 × 10−7 | ↓ |
| 5 | 1.969567 | 359.3147 | MG(18:0/0:0/0:0) | C21H42O4 | 3.56 × 10−5 | ↑ |
| 6 | 10.36602 | 608.0886 | Uridine diphosphate-N-acetylglucosamine | C17H27N3O17P2 | 0.005755 | ↑ |
| 7 | 10.73917 | 130.0499 | Pyroglutamic acid | C5H7NO3 | 7.80 × 10−6 | ↑ |
| 8 | 2.833333 | 138.1274 | 1,2,4-Tris(methylene)cyclohexane | C9H12 | 0.000432 | ↓ |
| 9 | 9.24125 | 166.0859 | Cinnamic acid | C9H8O2 | 0.000894 | ↑ |
| 10 | 10.33287 | 308.0913 | 1-[4,9-Dihydro-2-(methylthio)-1,3-thiazino[6,5-b]indol-4-yl]-2-propanone | C14H14N2OS2 | 0.005284 | ↑ |
| 11 | 1.787267 | 391.2838 | 12-Ketodeoxycholic acid | C24H38O4 | 0.001827 | ↑ |
| 12 | 14.50635 | 161.128 | L-2-Amino-3-methylenehexanoic acid | C7H13NO2 | 0.014649 | ↑ |
| 13 | 14.3875 | 130.0862 | L-trans-4-Methyl-2-pyrrolidinecarboxylic acid | C6H11NO2 | 1.65 × 10−5 | ↑ |
| 14 | 2.548467 | 675.5417 | SM(d18:1/14:0) | C37H75N2O6P | 0.017606 | ↑ |
| 15 | 1.969567 | 331.2832 | MG(0:0/16:0/0:0) | C19H38O4 | 0.00129 | ↑ |
| 16 | 10.89645 | 508.0031 | dGTP | C10H16N5O13P3 | 0.000442 | ↑ |
| 17 | 10.33287 | 615.1723 | Safflomin C | C30H30O14 | 0.000167 | ↑ |
| 18 | 10.36602 | 148.0603 | L-Glutamic acid | C5H9NO4 | 3.72 × 10−7 | ↑ |
| 19 | 10.36602 | 130.0498 | 1-Pyrroline-4-hydroxy-2-carboxylate | C5H7NO3 | 0.000189 | ↑ |
| 20 | 10.77292 | 86.09667 | Piperidine | C5H11N | 4.85 × 10−6 | ↓ |
| Primers | Forward Sequence (5′-3′) | Reverse Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| IL-17A | TCAGCGTGTCCAAACACTGAG | CGCCAAGGGAGTTAAAGACTT |
| CXCL1 | CTGGGATTCACCTCAAGAACATC | CAGGGTCAAGGCAAGCCTC |
| CXCL2 | ATGCCTCACTCGTACCCAG | TTTCCACCCCAATTTGGCTCA |
| CXCL8 | ACTGAGAGTGATTGAGAGTGGAC | AACCCTCTGCACCCAGTTTTC |
| CCL20 | ACTGTTGCCTCTCGTACATACA | GAGGAGGTTCACAGCCCTTTT |
| IFN-γ | GTGATGGCTGAACTGTCGCC | CTGGGATGCTCTTCGACCTC |
| MCP-1 | CAGCCAGATGCAATCAATGCC | TGGAATCCTGAACCCACT |
| NF-κB | ACACCCACAAACCAACTCTGG | TGCTGAACACTGGAGGAAGTC |
| TNF-α | TCCAGTGTGTCCTTCCGAAGT | TGCCTCCGCCAGAACTGTA |
| β-actin | GGCTGTATTCCCCTCCATCG | CCAGTTGGTAACAATGCCATGT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Y.; Ma, X.; Ma, Y.; Peng, L.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, J. Exploring the In Vitro Mechanism of Action of β-Acetoxyisovalerylalkannin on Inflammatory Skin Diseases Using Network-Based Pharmacology and Non-Targeted Metabolomics. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091249
Ma Y, Ma X, Ma Y, Peng L, Zhang Z, Li J, Zhang L, Li J. Exploring the In Vitro Mechanism of Action of β-Acetoxyisovalerylalkannin on Inflammatory Skin Diseases Using Network-Based Pharmacology and Non-Targeted Metabolomics. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(9):1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091249
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Yinglan, Xuehong Ma, Yue Ma, Liuqian Peng, Zixin Zhang, Jinyan Li, Lu Zhang, and Jianguang Li. 2025. "Exploring the In Vitro Mechanism of Action of β-Acetoxyisovalerylalkannin on Inflammatory Skin Diseases Using Network-Based Pharmacology and Non-Targeted Metabolomics" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 9: 1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091249
APA StyleMa, Y., Ma, X., Ma, Y., Peng, L., Zhang, Z., Li, J., Zhang, L., & Li, J. (2025). Exploring the In Vitro Mechanism of Action of β-Acetoxyisovalerylalkannin on Inflammatory Skin Diseases Using Network-Based Pharmacology and Non-Targeted Metabolomics. Pharmaceuticals, 18(9), 1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091249





