Is Anlotinib and Radiotherapy Combination Effective for Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer with Brain Metastases? A Systematic Scoping Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Information Sources and Search Strategy
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Research Questions
2.4. Trial Selection
2.5. Data Extraction
2.6. Outcome Measures
2.7. Quality Assessment
2.8. Data Synthesis
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection
Study Characteristics
3.2. Quality Assessment
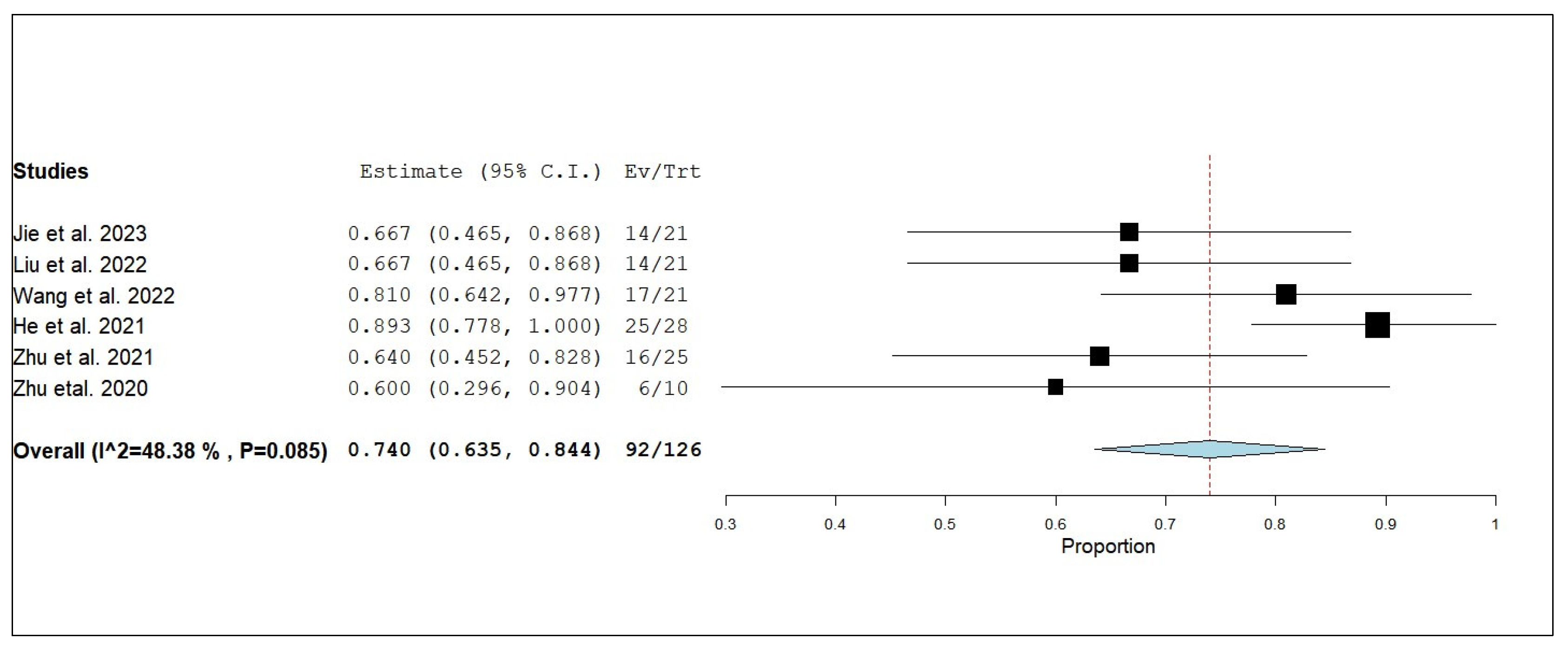
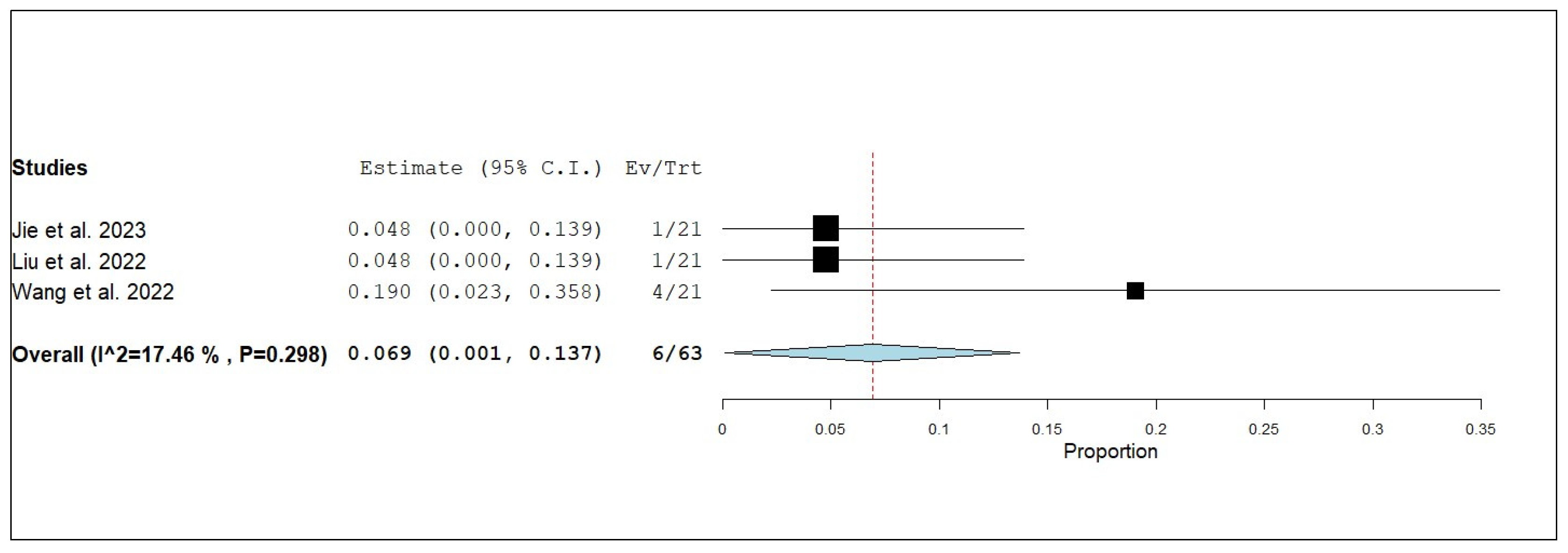
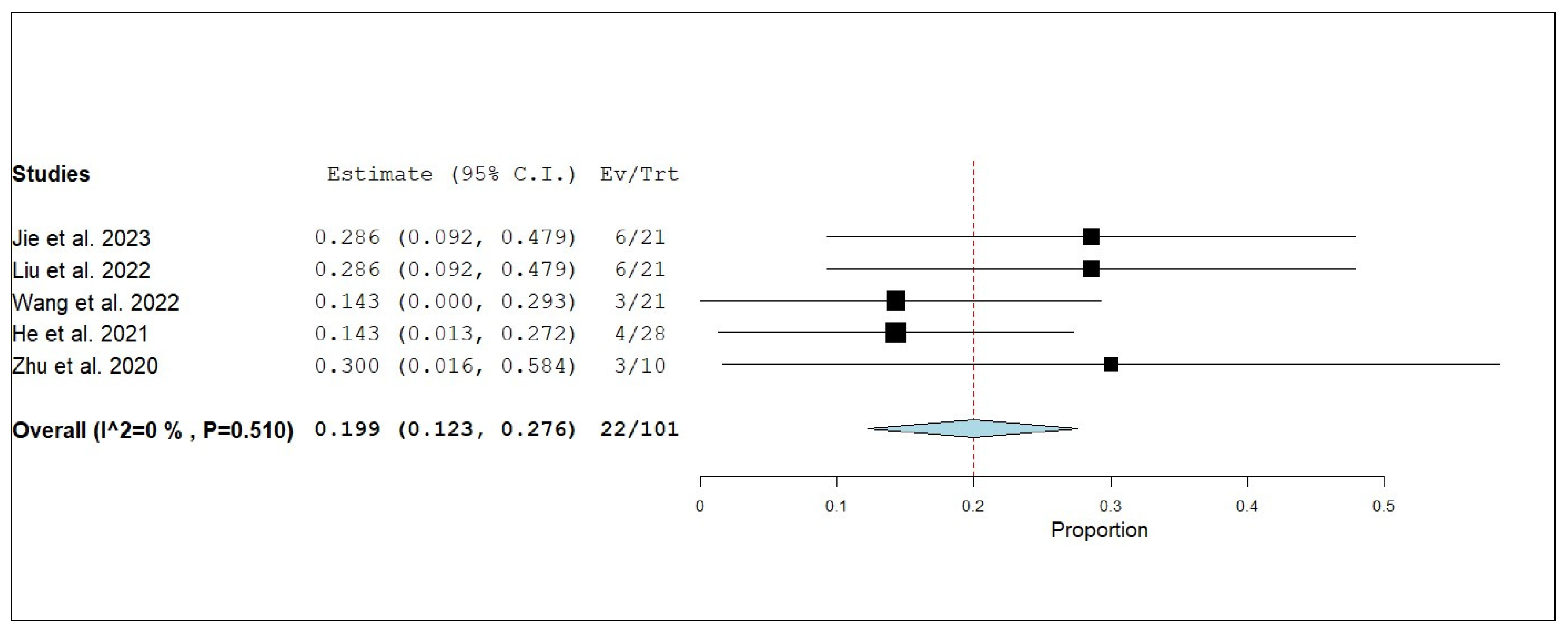
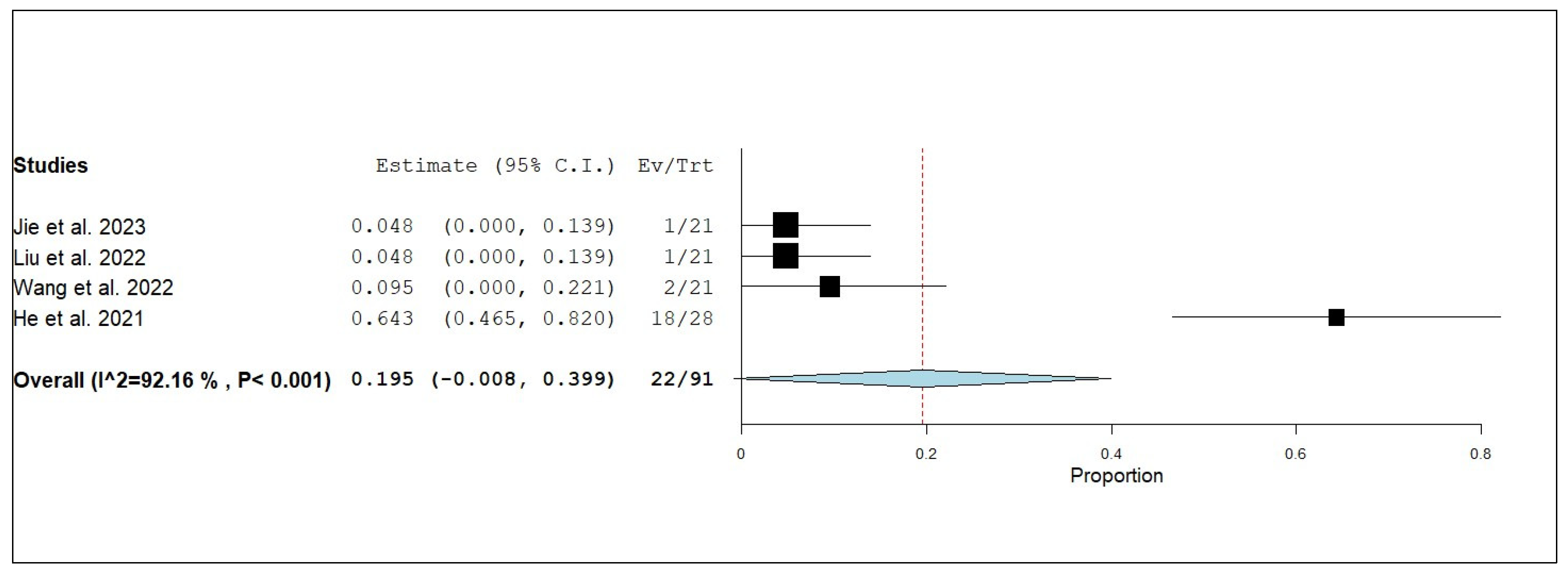
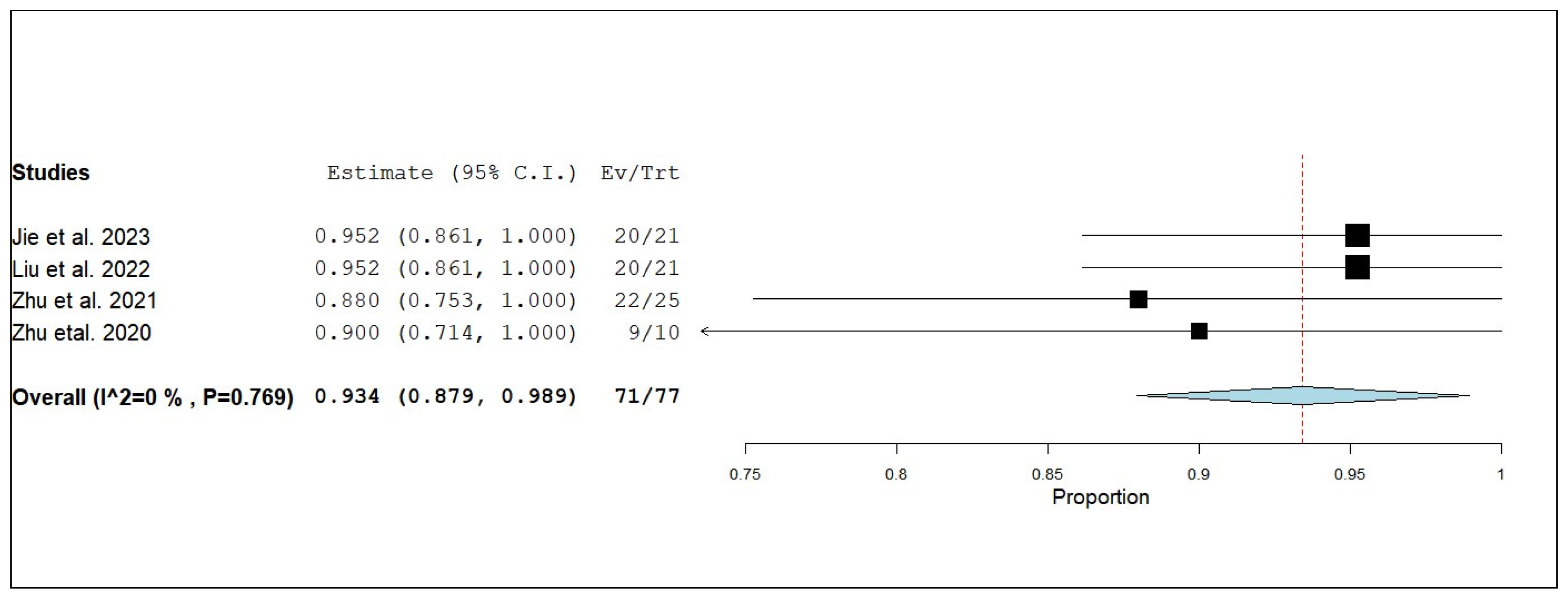
3.3. Primary and Secondary Outcomes
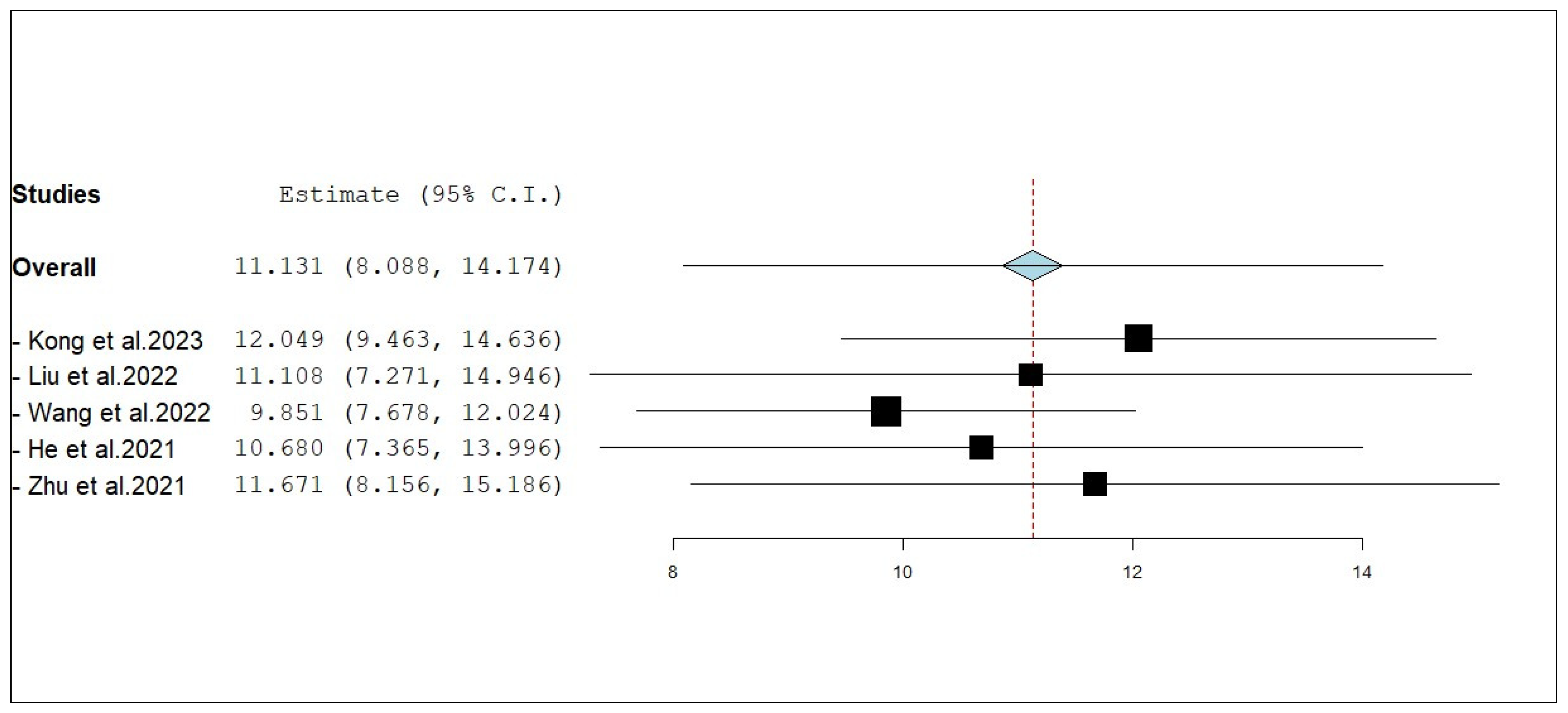
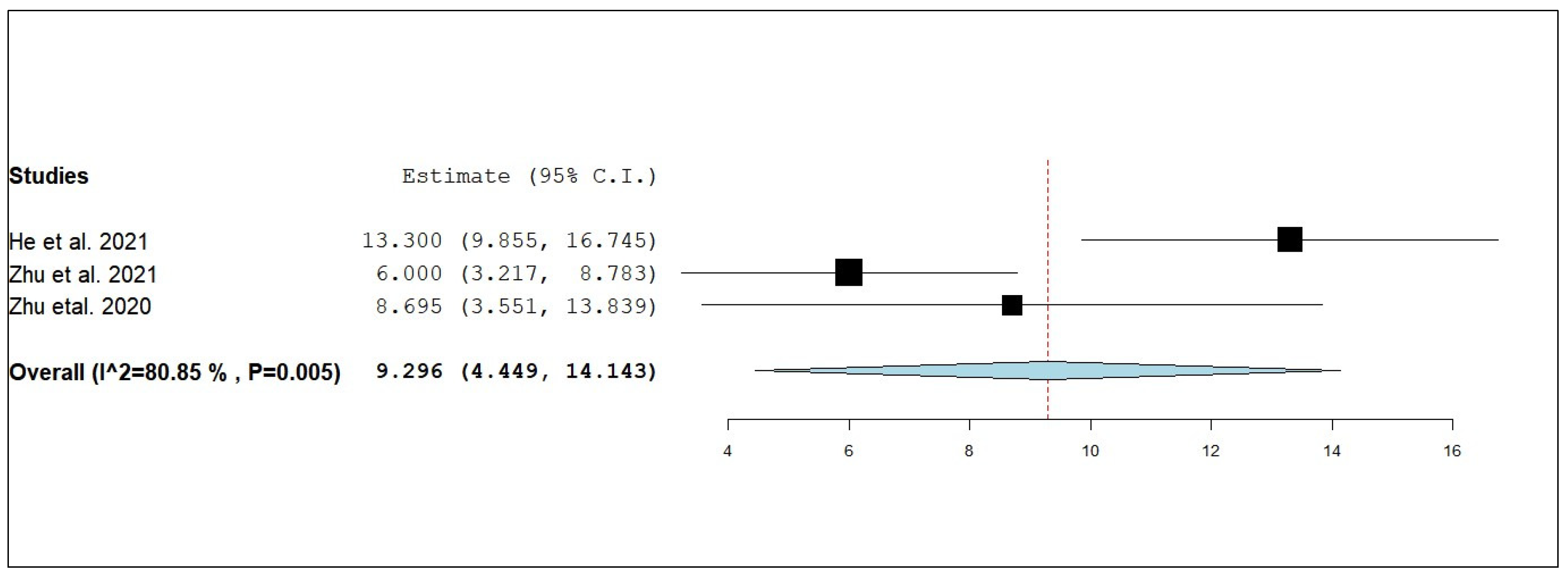
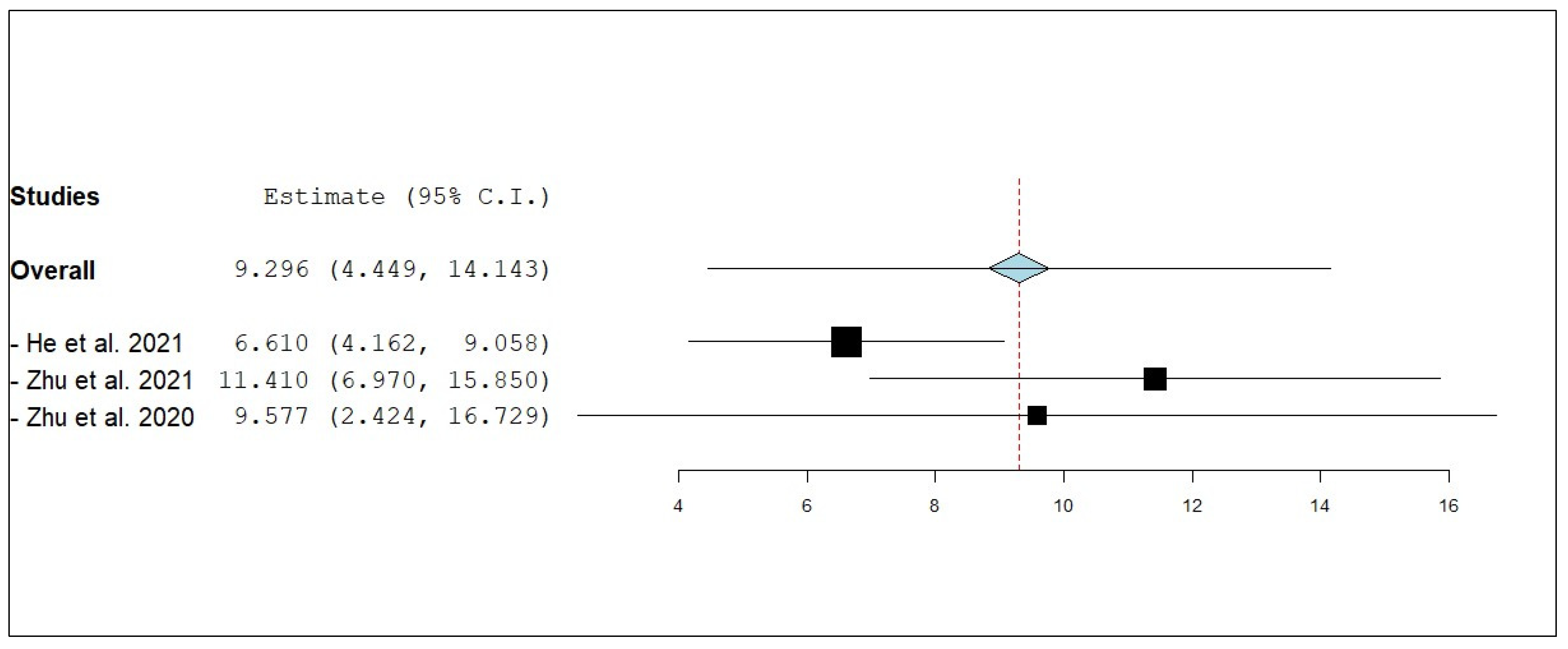
3.3.1. Overall Survival (OS)
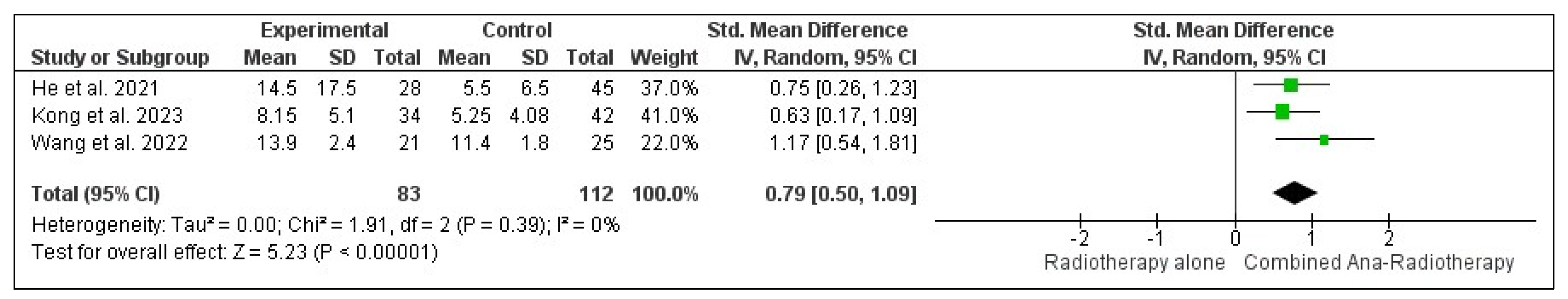
3.3.2. Internal Progression-Free Survival (iPFS)
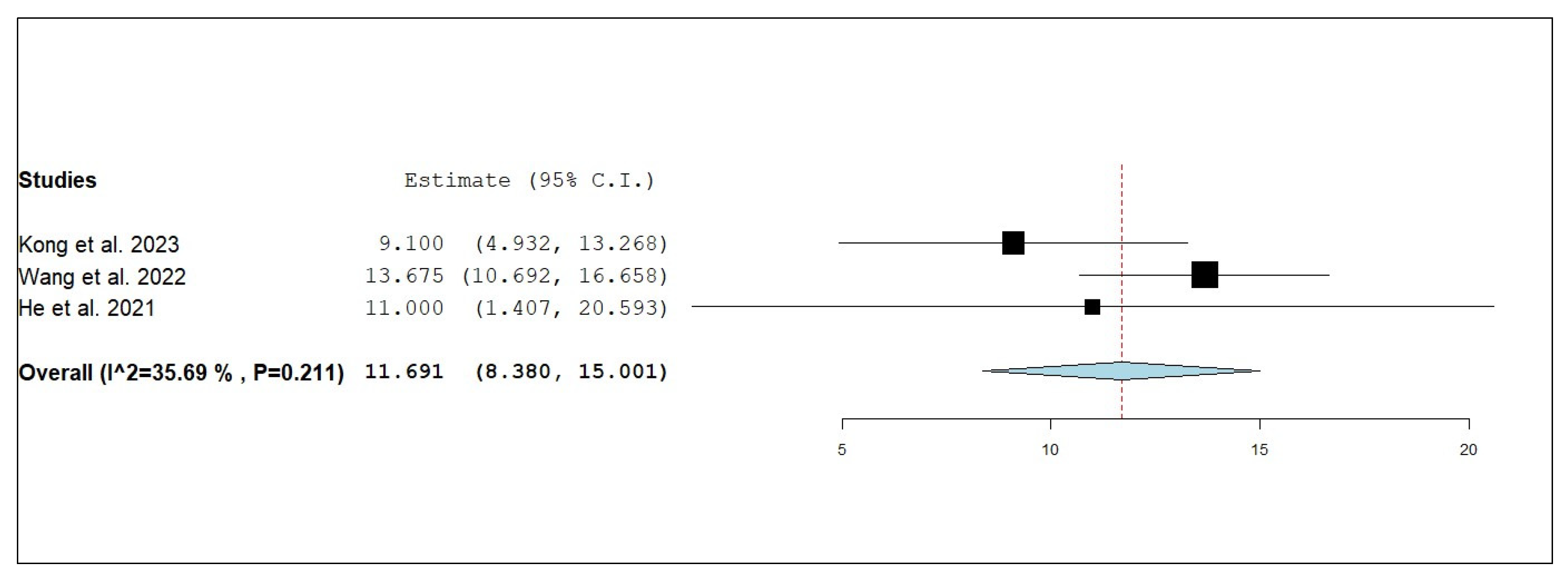
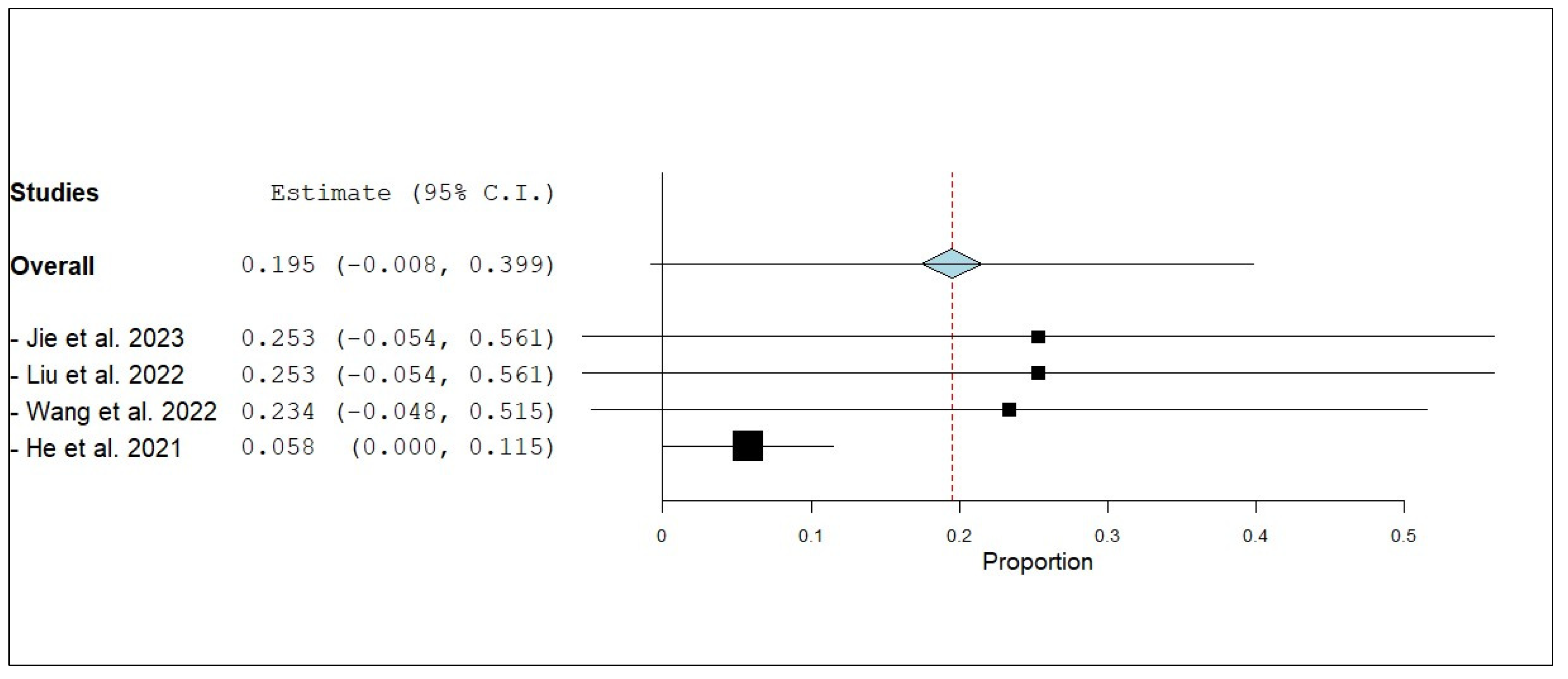
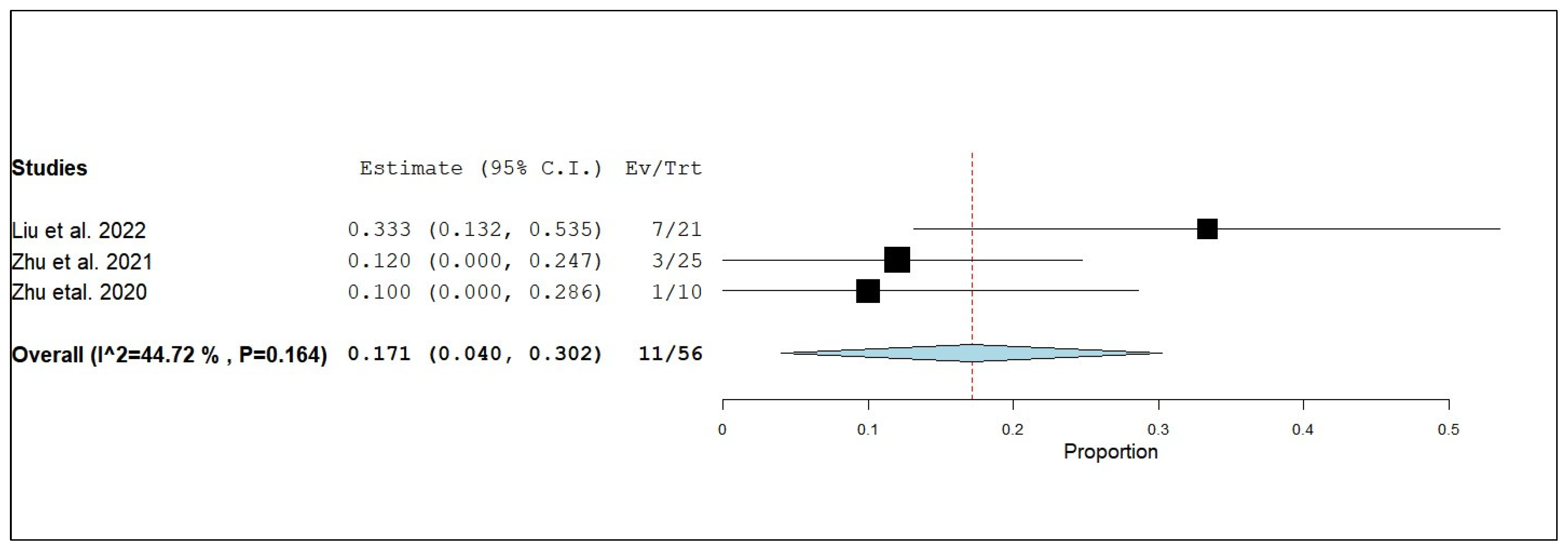
3.3.3. Internal Objective Response Rate (iORR)
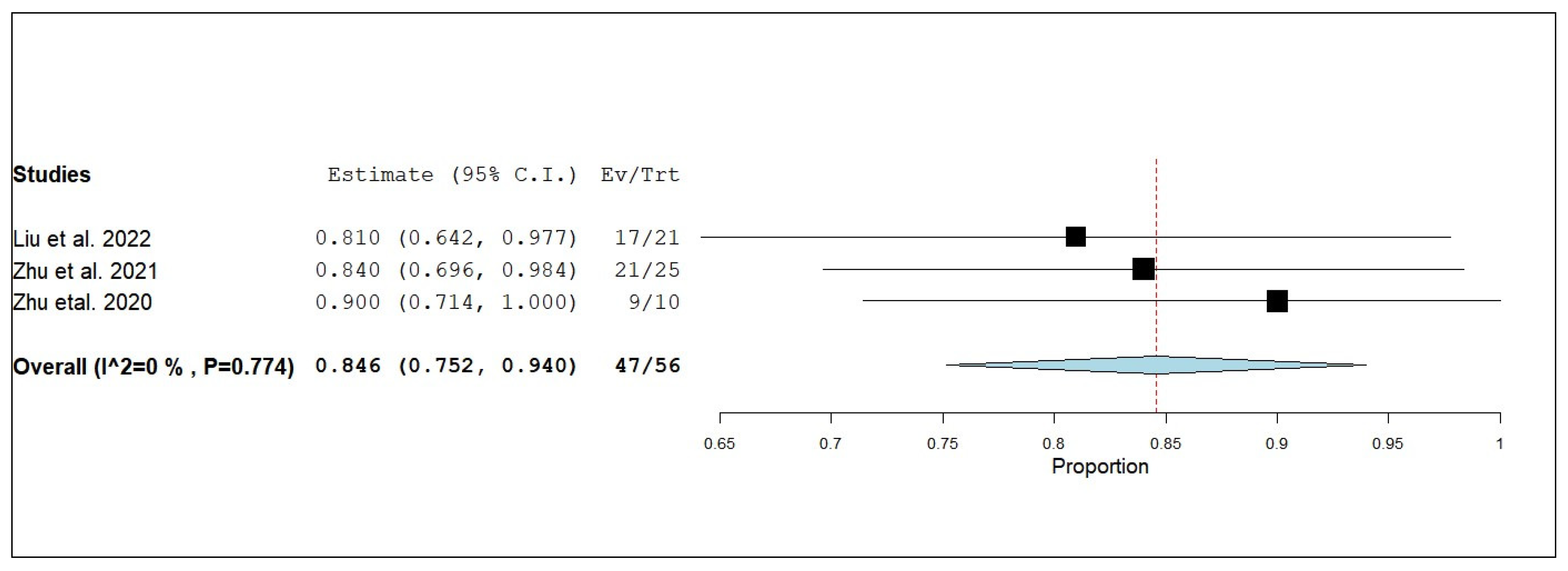
3.3.4. Internal Disease Control Rate (iDCR)
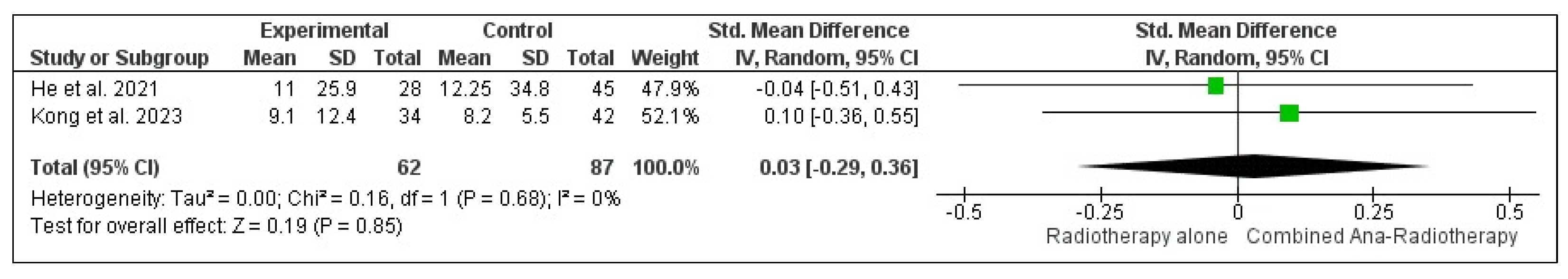
3.3.5. External Progression-Free Survival (ePFS)
3.3.6. External Objective Response Rate (eORR)
3.3.7. External Disease Control Rate (eDCR)
4. Discussion
4.1. Strengths and Limitations
4.2. Recommendations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carioli, G.; Malvezzi, M.; Bertuccio, P.; Boffetta, P.; Levi, F.; La Vecchia, C.; Negri, E. European cancer mortality predictions for the year 2021 with focus on pancreatic and female lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Cancer Society. Key Statistics for Lung Cancer; American Cancer Society: New York, NY, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S.; Sloan, A.E.; Davis, F.G.; Vigneau, F.D.; Lai, P.; Sawaya, R.E. Incidence proportions of brain metastases in patients diagnosed (1973 to 2001) in the Metropolitan Detroit Cancer Surveillance System. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 2865–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperduto, P.W.; Kased, N.; Roberge, D.; Xu, Z.; Shanley, R.; Luo, X.; Sneed, P.K.; Chao, S.T.; Weil, R.J.; Suh, J.; et al. Summary report on the graded prognostic assessment: An accurate and facile diagnosis-specific tool to estimate survival for patients with brain metastases. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoyama, H.; Tago, M.; Kato, N.; Toyoda, T.; Kenjyo, M.; Hirota, S.; Shioura, H.; Inomata, T.; Kunieda, E.; Hayakawa, K. Neurocognitive function of patients with brain metastasis who received either whole brain radiotherapy plus stereotactic radiosurgery or radiosurgery alone. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2007, 68, 1388–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soon, Y.Y.; Tham, I.W.; Lim, K.H.; Koh, W.Y.; Lu, J.J. Surgery or radiosurgery plus whole brain radiotherapy versus surgery or radiosurgery alone for brain metastases. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, 2014, Cd009454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, M.N.; Xu, W.; Wong, R.K.; Lloyd, N.; Laperriere, N.; Sahgal, A.; Rakovitch, E.; Chow, E. Whole brain radiotherapy for the treatment of newly diagnosed multiple brain metastases. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 1, Cd003869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, E.L.; Wefel, J.S.; Hess, K.R.; Allen, P.K.; Lang, F.F.; Kornguth, D.G.; Arbuckle, R.B.; Swint, J.M.; Shiu, A.S.; Maor, M.H.; et al. Neurocognition in patients with brain metastases treated with radiosurgery or radiosurgery plus whole-brain irradiation: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 1037–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.D.; Jaeckle, K.; Ballman, K.V.; Farace, E.; Cerhan, J.H.; Anderson, S.K.; Carrero, X.W.; Barker, F.G., 2nd; Deming, R.; Burri, S.H.; et al. Effect of Radiosurgery Alone vs. Radiosurgery with Whole Brain Radiation Therapy on Cognitive Function in Patients with 1 to 3 Brain Metastases: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2016, 316, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulvenna, P.; Nankivell, M.; Barton, R.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Wilson, P.; McColl, E.; Moore, B.; Brisbane, I.; Ardron, D.; Holt, T.; et al. Dexamethasone and supportive care with or without whole brain radiotherapy in treating patients with non-small cell lung cancer with brain metastases unsuitable for resection or stereotactic radiotherapy (QUARTZ): Results from a phase 3, non-inferiority, randomised trial. Lancet 2016, 388, 2004–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, C.; Allouache, D.; Lacroix, J.; Dugue, A.; Supiot, S.; Campone, M.; Mahe, M.; Kichou, S.; Leheurteur, M.; Hanzen, C. REBECA: A phase I study of bevacizumab and whole-brain radiation therapy for the treatment of brain metastasis from solid tumours. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 2351–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Zheng, F.; Ren, D.; Du, F.; Dong, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, F.; Ahmad, R.; Zhao, J. Anlotinib: A novel multi-targeting tyrosine kinase inhibitor in clinical development. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Mai, W.; Jiang, W.; Geng, Q. Sintilimab: A Promising Anti-Tumor PD-1 Antibody. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 594558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brun, L.; Dupic, G.; Chassin, V.; Chautard, E.; Moreau, J.; Dedieu, V.; Khalil, T.; Verrelle, P.; Lapeyre, M.; Biau, J. Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for large brain metastases: Optimizing the dosimetric parameters. Cancer Radiothér. 2021, 25, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahrom, A.; Grimley, R.; Jeffree, R.L. A case of delayed cyst formation post brain AVM stereotactic radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformation: Case report. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2021, 87, 17–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, Y.; Liu, J.; Mao, J.; Wu, D. Efficacy and safety of anlotinib combined with whole brain radiation therapy in treatment of driver gene mutation-negative non-small cell lung cancer patients with multiple brain metastases. Cancer Res. Clin. 2023, 35, 664–669. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, C.; Yu, S.; Qian, P.; Song, X.; Wen, J.; Jiang, M.; Zhu, J.; Xu, J.; Zhao, L.; Guo, Z.; et al. Anlotinib combined with whole-brain radiotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer with multiple brain metastases that progressed or developed after at least one lines of prior treatment. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1169333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xu, J.; Ye, W.; Zhong, W.; Zhang, X.; Mao, J.; Wu, D. Whole-brain radiotherapy combined with anlotinib for multiple brain metastases from non-small cell lung cancer without targetable driver mutation: A single-arm, phase II study. Clin. Med. Insights Oncol. 2022, 16, 11795549221079185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cheng, C.; Zhuang, H. The safety and efficacy of anlotinib in combination with stereotactic radiotherapy for the treatment of brain metastases from non-small cell lung cancer. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2022, 102, 930–934. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.; Liu, J.; Ma, Y.; Jiang, H.; Cui, Z.; Wang, G.; Wu, Y.; Liu, J.; Cai, X.; Qian, J. Anlotinib combined with cranial radiotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer patients with brain metastasis: A retrospectively, control study. Cancer Manag. Res. 2021, 13, 6101–6111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, C.; Zhu, X.; Jiang, M.; Song, X.; Qian, P.; Zhu, J.; Xu, J.; He, X. Anlotinib in combination with whole brain radiotherapy for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer with brain metastases progressive or developed after at least one lines of prior treatment. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2021, 111, e569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, H.; Wang, Y. FP04. 05 Anti-Vascular Drug Anlotinib Combined with SRS Versus SRS Alone for Brain Metastases From NSCLC: A Case Control Study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, S198–S199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Tao, H.; Jiang, M.; Shi, M.; Kong, C.; Song, X.; Zhang, N.; Chen, C.; Jiang, N.; Zhao, L. A phase II study of anlotinib plus whole brain radiation therapy (WBRT) for advanced non-small cell lung cancer with multiple brain metastases. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, e21063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Tao, H.; Kong, C.; Song, X.; Zhang, N.; Chen, C.; Jiang, N.; Zhao, L.; Yan, P.; He, X. 1386P Anlotinib combined with whole brain radiation therapy (WBRT) for advanced non-small cell lung cancer with multiple brain metastases: An open-label, single-arm phase II trial. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, S881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirriyeh, R.; Lawton, R.; Gardner, P.; Armitage, G. Reviewing studies with diverse designs: The development and evaluation of a new tool. J. Eval. Clin. Pract. 2012, 18, 746–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viechtbauer, W. Conducting meta-analyses in R with the metafor package. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 36, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, B.C.; Dahabreh, I.J.; Trikalinos, T.A.; Lau, J.; Trow, P.; Schmid, C.H. Closing the gap between methodologists and end-users: R as a computational back-end. J. Stat. Softw. 2012, 49, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetta, H.F.; Zahran, A.M.; Shafik, E.A.; El-Mahdy, R.I.; Mohamed, N.A.; Nabil, E.E.; Esmaeel, H.M.; Alkady, O.A.; Elkady, A.; Mohareb, D.A. Circulating miRNA-21 and miRNA-23a expression signature as potential biomarkers for early detection of non-small-cell lung cancer. Microrna 2019, 8, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetta, H.F.; Alqifari, S.F.; Alshehri, K.; Alhowiti, A.; Alharbi, S.S.; Mirghani, H.; Alrasheed, T.; Mostafa, M.E.; Sheikh, M.; Elodemi, M. Efficacy of Anlotinib Plus Docetaxel in Advanced NSCLC Previously Treated with Platinum-Based Chemotherapy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetta, H.F.; Aljohani, H.M.; Sirag, N.; Elfadil, H.; Salama, A.; Al-Twalhy, R.; Alanazi, D.; Al-Johani, M.D.; Albalawi, J.H.; Al-Otaibi, R.M. Synergizing Success: The Role of Anlotinib Combinations in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.-J.; Zhou, C.; Huang, Y.; Feng, J.; Lu, S.; Song, Y.; Huang, C.; Wu, G.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, Y. Icotinib versus whole-brain irradiation in patients with EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer and multiple brain metastases (BRAIN): A multicentre, phase 3, open-label, parallel, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2017, 5, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, I.; Zaorsky, N.G.; Palmer, J.D.; Mehra, R.; Lu, B. Targeting brain metastases in ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, e510–e521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnuson, W.J.; Lester-Coll, N.H.; Wu, A.J.; Yang, T.J.; Lockney, N.A.; Gerber, N.K.; Beal, K.; Amini, A.; Patil, T.; Kavanagh, B.D. Management of brain metastases in tyrosine kinase inhibitor–naïve epidermal growth factor receptor–mutant non–small-cell lung cancer: A retrospective multi-institutional analysis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1070–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, T.; Huang, S.; Armstrong, E.; Eickhoff, J.C.; Harari, P.M. Enhancement of radiation response with bevacizumab. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 31, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Dicker, A.P. CNS Metastases in Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer and ALK Gene Rearrangement. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 34, 107–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Authors | Year | Study Design | Setting | Date (Period of the Study) | Group(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jie et al., 2023 [17] | 2023 | Retrospective Analysis | Shaoxing People’s Hospital, China | From March 2018 to March 2022 | Combined anlotinib and WBRT |
| Single WBRT group | |||||
| Kong et al., 2023 [18] | 2023 | Retrospective Control Study | Jiangsu Cancer Hospital, Nanjing, China | From 2019 to 2021 | Concurrent WBRT and anlotinib |
| WBRT alone or in combination with other systemic agents | |||||
| Liu et al., 2022 [19] | 2022 | Prospective Single-Arm, Phase II Study | Shaoxing People’s Hospital, Zhejiang Province, China | From April 2019 to March 2021 | Combined WBRT and anlotinib |
| Wang et al., 2022 [20] | 2022 | Retrospective Cohort | Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing, China | From October 2017 to June 2019 | Combined anlotinib and SRS |
| Single SRS group | |||||
| He et al., 2021 [21] | 2021 | Retrospective Control Study | Hospital of Bengbu Medical College, China | From September 2016 to June 2020 | Combined anlotinib and CRT |
| CRT alone | |||||
| Kong et al., 2021 [22] | 2021 | Retrospective Control Study | Jiangsu Cancer Hospital, Nanjing, China | From 2019 to 2020 | Concurrent WBRT and anlotinib |
| WBRT alone or in combination with other systemic agents | |||||
| Zhuang et al., 2021 [23] | 2021 | Case–Control Study | Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing, China | From October 2017 to June 2019 | Combined anlotinib and SRS |
| Single SRS group | |||||
| Zhu et al., 2021 [24] | 2021 | Phase II Clinical Study | Jiangsu Cancer Hospital, Nanjing, China | At data cut-off 25 Jan 2021 | Combined anlotinib and WBRT |
| Zhu et al., 2020 [25] | 2020 | Open-Label, Single-Arm Phase II Trial | NA | At data cut-off 30 April 2020 | Combined anlotinib and WBRT |
| Authors | Group(s) | Regimen of Treatment | Sequence of Follow-Up | Sample Size | Median Age (years) * | Male Population N (%) | Pathological Types N (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jie et al., 2023 [17] | Combined anlotinib and WBRT | Oral anlotinib (12 mg/d, day 1 to day 14, 21 days per cycle) at the same time at the start of radiotherapy for two cycles, combined with 30 Gy/10 times (5 times/week). | Tumor response was assessed every 8 weeks using brain MRI until PD. All patients were followed up by a combination of telephone and outpatient visits. | 21 | 12 pts (57.1%) were aged > 60 years | 13 (61.9) | Adenocarcinoma 18 (85.7) Squamous cell carcinoma 3 (14.3) |
| Single WBRT group | WBRT in the form of 30 Gy/10 times (5 times/week). | 21 | 15 pts (71.4%) were aged > 60 years | 14 (66.7) | Adenocarcinoma 17 (81.0) Squamous cell carcinoma 4 (19.0) | ||
| Kong et al., 2023 [18] | Concurrent WBRT and anlotinib | Anlotinib (8–12 mg daily for 14 days) orally per 3-week cycle, combined with WBRT 30 Gy in 10–12 daily fractions, ideally given over 2–2.5 weeks with a 6-MV linear accelerator with two parallel opposed fields. | Brain MRIs were used to evaluate the intracranial disease at baseline and during a follow-up period every 2–3 months. Median follow-up: 21 (IQR: 14–22) months | 34 | 61 | 18 (53) | Adenocarcinoma 29 (85) Others 5 (15) |
| WBRT alone or in combination with other systemic agents | WBRT was defined as 30 Gy in 10–12 daily fractions, ideally given over 2–2.5 weeks with a 6-MV linear accelerator with two parallel opposed fields. | 42 | 60.5 | 20 (48) | Adenocarcinoma 37 (88) Others 5 (12) | ||
| Liu et al., 2022 [19] | Combined WBRT and anlotinib | WBRT (30Gy/10 f, 5 f/week) and anlotinib (12 mg/day, day 1–14 of 21 days per cycle, 2 cycles) until disease progression or treatment intolerance. | The median follow-up time was 10.37 (3.27–26.13) months. | 21 | 12 pts (57.1%) were aged ≥ 60 years | 13 (61.9) | Adenocarcinoma 18 (85.7) Squamous cell carcinoma 3 (14.3) |
| Wang et al., 2022 [20] | Combined anlotinib and SRS | CyberKnife SRS + Oral anlotinib (12 mg/d) were taken for 2 weeks, 1 week off, and 21 days | A routine brain MRI examination was performed 1.5 to 2 months after treatment and then the patients were reexamined once every 2 to 3 months. | 21 | 61 (32, 74) | 12 (57.14) | Adenocarcinoma 16 (76.19) Squamous cell carcinoma 4 (19.047) Undifferentiated carcinoma 1 (4.7) |
| Single SRS group | CyberKnife SRS | 25 | 55 (39, 71) | 13 (52) | Adenocarcinoma 20 (80) Squamous cell carcinoma 4 (16) Undifferentiated carcinoma 1 (4) | ||
| He et al., 2021 [21] | Combined anlotinib and CRT | Anlotinib (8–12 mg daily for 14 days) orally and then 7 days off, combined with CRT treatment (6 MV X-ray) | Clinical follow-up was carried out every 3–6 months and included imaging, physical, and routine laboratory tests. Median follow-up 8 months | 28 | 63.5 (30–75) | 15 (53.57) | Adenocarcinoma 21 (75) Squamous carcinoma 7 (25) |
| CRT alone | CRT treatment (6 MV X-rays) included WBRT, WBRT plus LCRT, or LCRT. | 45 | 56 (41–73) | 24 (53.33) | Adenocarcinoma 38 (84.44) Squamous carcinoma 7 (15.56) | ||
| Kong et al., 2021 [22] | Concurrent WBRT and anlotinib | Anlotinib (8–12 mg daily for 14 days) orally per 3-week cycle, combined with WBRT 30 Gy in 10–12 daily fractions, ideally given over 2–2.5 weeks with a 6-MV linear accelerator with two parallel opposed fields. | NA | 26 | NA | NA | NA |
| WBRT alone or in combination with other systemic agents | WBRT was defined as 30 Gy in 10–12 daily fractions, ideally given over 2–2.5 weeks with a 6-MV linear accelerator with two parallel opposed fields. | 70 | |||||
| Zhuang et al., 2021 [23] | Combined anlotinib and SRS | CyberKnife SRS + Oral anlotinib 12 mg/d was taken for 2 weeks, 1 week off, 21 days. | NA | 21 | NA | NA | NA |
| Single SRS group | CyberKnife SRS | 25 | |||||
| Zhu et al., 2021 [24] | Combined anlotinib and WBRT | Anlotinib (12 mg, QD, day 1 to 14 of a 21-day cycle) combined with WBRT (DT 30 Gy/12f), followed by maintenance therapy with anlotinib until disease progression or treatment intolerance. | NA | 28 | 57.5 | 13 (46.4) | Adenocarcinoma 25 (89.3) EGFR mutation 6 (21.4) |
| Zhu et al., 2020 [25] | Combined anlotinib and WBRT | Anlotinib (12 mg, QD, day 1 to 14 of a 21-day cycle) combined with WBRT (DT 30 Gy/12 times). | NA | 10 | NA | NA | NA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hetta, H.F.; Ali, M.A.S.; Alqifari, S.F.; Salem, H.A.; Qasem, K.A.; Alanazi, F.E.; Alhowiti, A.; Alatawi, A.M.; Mirghani, H.; Alrasheed, T.; et al. Is Anlotinib and Radiotherapy Combination Effective for Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer with Brain Metastases? A Systematic Scoping Review and Meta-Analysis. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 974. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18070974
Hetta HF, Ali MAS, Alqifari SF, Salem HA, Qasem KA, Alanazi FE, Alhowiti A, Alatawi AM, Mirghani H, Alrasheed T, et al. Is Anlotinib and Radiotherapy Combination Effective for Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer with Brain Metastases? A Systematic Scoping Review and Meta-Analysis. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(7):974. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18070974
Chicago/Turabian StyleHetta, Helal F., Mostafa A. Sayed Ali, Saleh F. Alqifari, Hoda A. Salem, Khulood A. Qasem, Fawaz E. Alanazi, Amirah Alhowiti, Amirah M. Alatawi, Hyder Mirghani, Tariq Alrasheed, and et al. 2025. "Is Anlotinib and Radiotherapy Combination Effective for Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer with Brain Metastases? A Systematic Scoping Review and Meta-Analysis" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 7: 974. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18070974
APA StyleHetta, H. F., Ali, M. A. S., Alqifari, S. F., Salem, H. A., Qasem, K. A., Alanazi, F. E., Alhowiti, A., Alatawi, A. M., Mirghani, H., Alrasheed, T., Bukhari, S. Q., Almazyad, K. A., Alhumaid, S. A., Abd Ellah, N. H., Aljohani, H. M., Ramadan, Y. N., & Sayad, R. (2025). Is Anlotinib and Radiotherapy Combination Effective for Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer with Brain Metastases? A Systematic Scoping Review and Meta-Analysis. Pharmaceuticals, 18(7), 974. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18070974







