The Efficacy of Combined Use of Huaier Granules in the Treatment of Primary Liver Cancer: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search Strategy
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.2.1. Inclusion Criteria
2.2.2. Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Literature Screening and Data Extraction
2.4. Risk of Bias Assessment of the Included Studies
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Sensitivity and Subgroup Analyses
2.7. Compliance Statement
3. Results
3.1. Literature Retrieval Process and Results
3.2. Study Characteristics and Assessment of Risk of Bias
3.3. Meta-Analysis Results
3.3.1. Meta-Analysis of Total Recurrence Rate
3.3.2. Meta-Analysis of One-Year Survival Rate
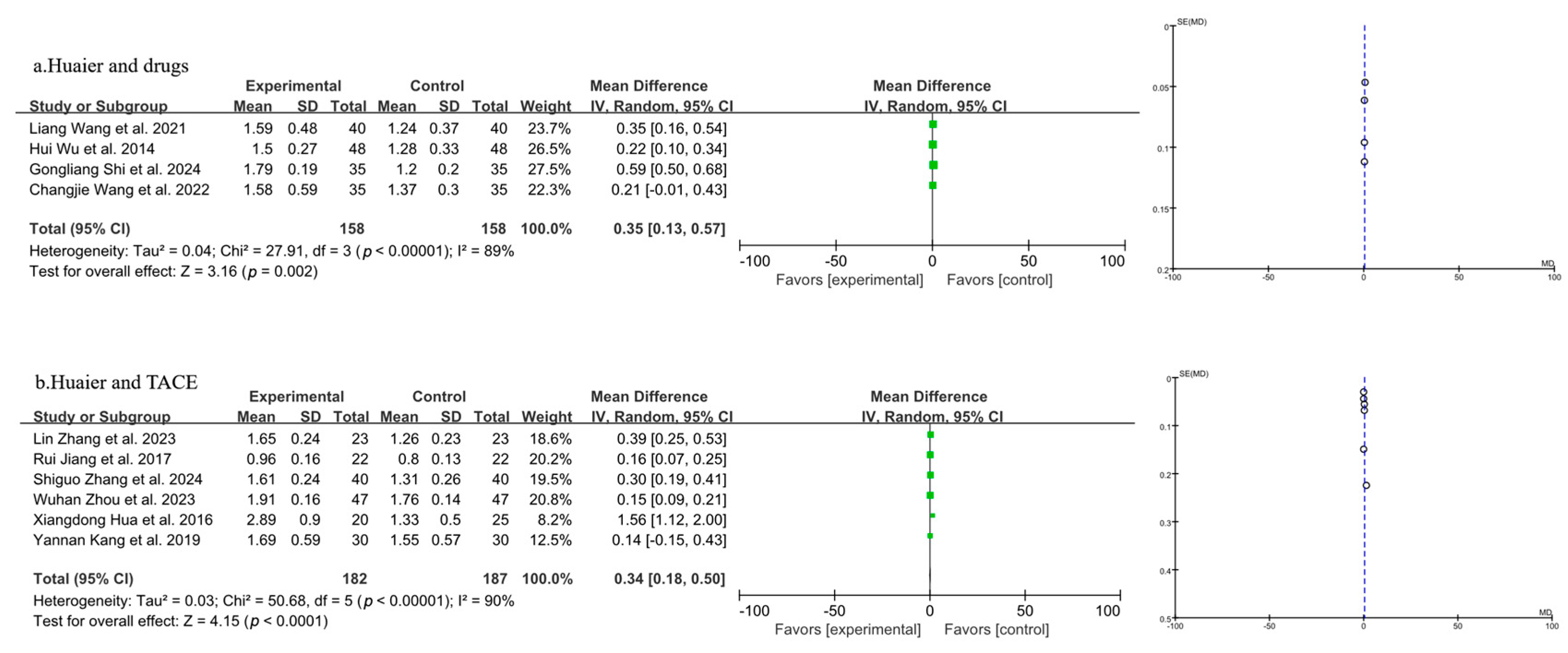
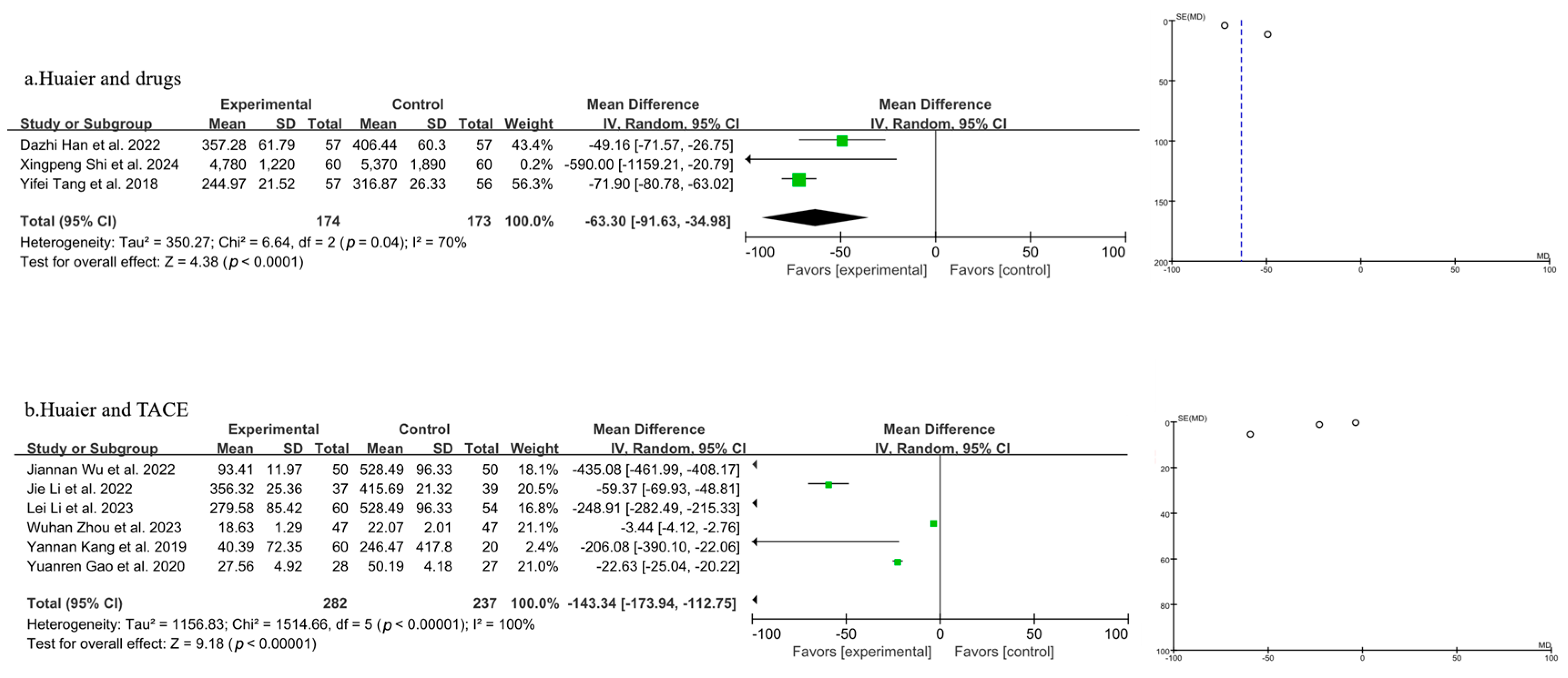
3.3.3. Meta-Analysis of Quality-of-Life Analysis
3.3.4. Meta-Analysis of T Lymphocyte Subtype CD3+
3.3.5. Meta-Analysis of T Lymphocyte Subtype CD4+
3.3.6. Meta-Analysis of T Lymphocyte Subtype CD8+
3.3.7. Meta-Analysis of CD4+/CD8+
3.3.8. Meta-Analysis of AFP
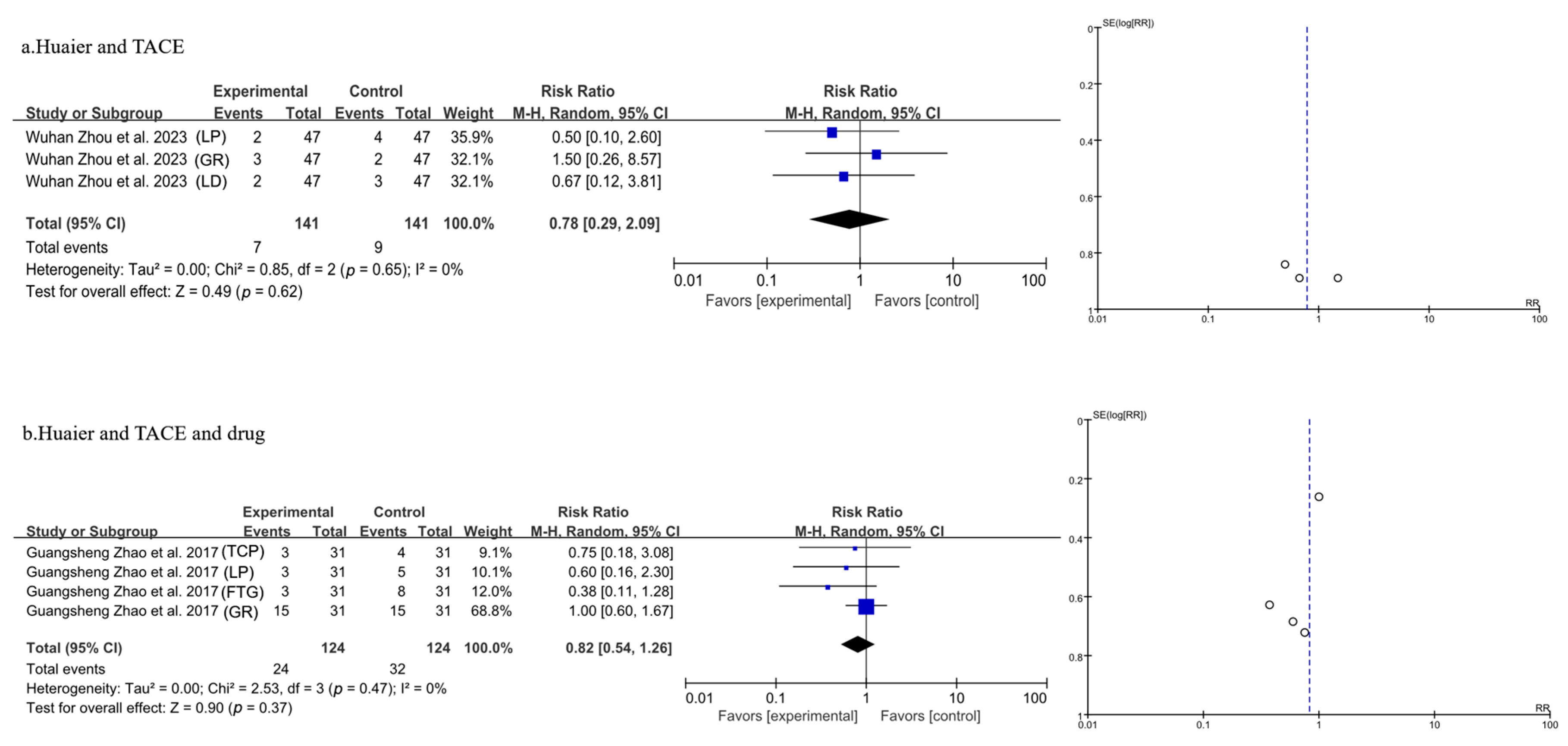
3.3.9. Meta-Analysis of Side Effects
4. Discussion
4.1. Summary of Main Findings
4.2. Comparison with Existing Literature
4.3. Advantages and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kazi, A.; Jahagirdar, V.; Kabir, W.; Syed, A.K.; Kabir, A.W.; Perisetti, A. Role of imaging in screening for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancers 2024, 16, 3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Zhu, X.; Beeraka, M.; Zhao, R.; Li, S.; Li, F.; Mahesh, P.A.; Nikolenko, V.N.; Fan, R.; Liu, J. Projected epidemiological trends and burden of liver cancer by 2040 based on GBD, CI5plus, and WHO data. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 28131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devarbhavi, H.; Asrani, K.; Arab, P.; Nartey, Y.A.; Pose, E.; Kamath, P.S. Global burden of liver disease: 2023 update. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 516–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Zheng, R.; Zeng, H.; Wang, S.; Sun, K.; Chen, R.; Li, L.; Wei, W.; He, J. Cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2022. J. Natl. Cancer Cent. 2024, 4, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, J.; Li, M.; Wang, L.; Hu, Y.; Liu, W.; Long, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Yin, P.; Zhou, M. National and subnational trends in cancer burden in China, 2005–2020: An analysis of national mortality surveillance data. Lancet Public Health 2023, 8, E943–E955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, G.; Zou, Y.; Lucatelli, P.; Tsilimigras, D.I.; Shimise, S.; Kawaguchi, T. Chinese expert consensus on technical recommendations for the standard operation of drug-eluting beads for transvascular embolization. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Ren, S.; Zhang, Y. Current status and treatment strategies for liver injury before targeted immunotherapy for liver cancer. Chin. J. Hepatol. 2023, 31, 1133–1136. [Google Scholar]
- Criss, R.; Makary, S. Recent advances in image-guided locoregional therapies for primary liver tumours. Biology 2023, 12, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntellas, P.; Chau, I. Updates on systemic therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Annu. Meet. 2024, 44, e430028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Qin, S. Immune checkpoint inhibitors in hepatocellular carcinoma: Opportunities and challenges. Oncologist 2019, 24, S3–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Zhu, S.; Cao, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, W.; Liu, K.; Zhong, J.; Shang, C.; Chen, Y. Inhibition of MMP-2 expression enhances the antitumour effect of sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma by suppressing the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Oncol. Res. 2017, 25, 1543–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidensticker, M.; Oecal, O.; Schuette, K.; Malfertheiner, P.; Berg, T.; Loewe, C.; Klümpen, H.J.; van Delden, O.; Ümütlü, M.R.; Khaled, N.B.; et al. Impact of adjuvant sorafenib treatment after local ablation for HCC in the phase II soramic trial. Jhep Rep. 2023, 5, 100699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, S.; Yu, H.; Wang, H.; Song, J.; Yan, J. Hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy combined with sorafenib versus sorafenib alone for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 16, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Yang, C.; Jiang, Z.; Huang, J. Trametes robiniophila Murr: A traditional Chinese medicine with potent anti-tumor effects. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 1541–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Fan, Y. Immunomodulatory effects of Huaier granule in cancer therapy: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2024, 29, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, S.; Wu, W. Efficacy and safety of Huaier granule as an adjuvant therapy for cancer: An overview of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2022, 21, 15347354221083910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asif, M.; Asif, A.; Rahman, A.; Haseeb, A.; Jafar, U.; Farooq, H. Efficacy and safety of abatacept in preclinical rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2024, 69, 152562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Xiang, L.; Yin, X.; Song, H.; Chen, C.; Yang, B.; Ye, H.; Gu, Z. Efficacy and safety of coenzyme Q10 in heart failure: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord 2024, 24, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero, P.; Dans, L. Key concepts in clinical epidemiology: Detecting and dealing with heterogeneity in meta-analyses. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2021, 130, 149–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Yan, L.; Zhu, J.; Wang, W. Hepatocellular carcinoma patients may benefit from postoperative Huaier aqueous extract after liver transplantation. Transplant. Proc. 2015, 47, 2920–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, Z.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, M. Transarterial chemoembolization combined with Huaier granule for the treatment of primary hepatic carcinoma: Safety and efficacy. Medicine 2017, 96, e7589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Pan, L.; Zheng, Y.; Du, G.; Fu, X.; Zhu, Z.; Song, J.; Liu, Z.; Su, X.; Chen, W.; et al. Novel strategy of sirolimus plus thymalfasin and huaier granule on tumor recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma beyond the UCSF criteria following liver transplantation: A single center experience. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 4407–4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Yu, X.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, Z.; Han, Z.; Liu, F.; Dou, J.; Kong, Y.; Dong, X.; Zhao, Q.; et al. Huaier granule prevents the recurrence of early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma after thermal ablation: A cohort study. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 281, 114539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, S.; Hu, H. Huaier granule prolongs overall survival after curative resection of hepatocarcinoma carcinoma: A propensity score analysis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 301, 115774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Shu, C.; Laurence, A.D.; Chen, Y.; Peng, B.; Zhen, Z.; Cai, J.; Ding, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Effect of Huaier granule on recurrence after curative resection of HCC: A multicentre, randomised clinical trial. Gut 2018, 67, 2006–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J. Study on the effect of Huaier granules to prevent and treat tumor recurrence and metastasis after surgery for hepatocellular carcinoma. China Prac. Med. 2022, 17, 21–23. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, X.; Shang, H.; He, Z.; Hao, Z.; Ma, Z.; Fu, X. Analysis of curative effect of Huaier granule combined with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization following radical resection of primary hepatocellular carcinoma with microvascular invasion. Chin. J. Bases Clin. General Surg. 2016, 23, 982–986. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Cai, J.; Bi, X.; Yang, X. Observation of the clinical efficacy of Huaier granules in the treatment of postoperative metastasis and recurrence of primary liver cancer. In Proceedings of the 5th National Clinical Conference on Liver Diseases and the 10th Anniversary Academic Conference of the Chinese Journal of Hepatology, Dalian, China, 1 May 2006; p. 346. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.; Wang, J.; Chen, D.; Chen, J.; Guo, Y. Value of combining Huaier granules and lenvatinib for prevention of tumor recurrence/metastasis after laparoscopic hepatectomy. China & Foreign Med. Treat. 2023, 17, 26–34. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Liu, Z. Treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma with Huaier granule combined with TACE: Prospective cohort study. J. Chin. Clin. Med. Imaging. 2020, 31, 490–494. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H. Huaier granules combined with chemoembolization in treating primary liver cancer in 96 cases. China Pharm. 2014, 23, 16–18. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Lu, H. Clinical observation of Huaier granules in the treatment of postoperative patients with hepatitis B-related liver cancer. Mod. Med. and Health Res. 2023, 7, 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Xu, Y. Changes in cellular immunity induced by oral administration of Huaier granules combined with interventional therapy for primary liver cancer. Med. J. of Chin. People’s Health 2009, 21, 2196–2230. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, G.; He, Y.; Yan, Y. Clinical efficacy of locust ear granules combined with molecular targeted drugs in treating spleen deficiency type of primary liver cancer. Med. J. West China 2024, 36, 120–124. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, R. Exploration on the influence of Huaier granules on patients after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) for liver cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2017, 4, 12423–12425. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Y. Effect of Huaier Granules Combined with Thymosinα1 on Cellular Immune Function in Patients with Primary Liver Cancer After TACE; Zhengzhou University: Zhengzhou, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Q.; Cao, H. Effect of Huaier granule combined with sorafenib on immune function and quality of life in patients with advanced liver cancer. Oncol. Prog. 2021, 19, 507–510. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; He, D.; Wang, B. Clinical efficacy analysis of Huaier granule combined with interventional treatment on patients with HBV DNA-negative hepatitis B. World J. Chin. Med. 2018, 13, 1597–1600. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Li, L.; Sun, C. Effect of Huaier granules on liver function, T lymphocytes and quality of life in patients with liver cancer after operation. Chin. J. Integr. Tradit. West. Med. Liver Dis. 2022, 32, 610–613. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S. Effect of Huaier granules combined with thymosinα1 on Th1/Th2 balance and liver function in patients with primary liver cancer. Proc. Clin. Med. 2024, 33, 14–17. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Wang, C.; Sun, C. The short-term curative effect of Huaier granule combined with S-TACE on advanced liver cancer and its effect on serum TGF-β1 and B7-H3. Chin. J. Integr. Tradit. West. Med. Liver Dis. 2023, 33, 106–110. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Zhen, Z. Clinical study on Huaier granules combined with transarterial chemoembolization for unresectable liver cancer. New Chin. Med. 2022, 54, 149–152. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Chen, S.; Hou, Y.; Hou, X.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y. Clinical effect of Huaier granule sequential with radiofrequency ablation and TACE in treating primary hepatic carcinoma. J. Changchun University Chin. Med. 2020, 36, 684–687. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Huang, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhen, C.; Gao, Y. Clinical study on Huaier granules combined with sorafenib in treatment of advanced liver cancer. Drugs Clin. 2018, 33, 1732–1735. [Google Scholar]
- Han, D. Effects of Huaier granules combined with sorafenib on postoperative recurrence patients with primary hepatocellular carcinoma and its effects on alpha-fetoprotein-L3 level. China J. Pharm. Econ. 2022, 17, 64–67. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.; Lu, J. Clinical study on Huaier granules combined with western medicine for patients with advanced primary liver cancer undergoing transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. New Chin. Med. 2024, 56, 191–195. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Zeng, J.; Zeng, J.; Huang, Y. Huaier granule improves liver inflammation and fibrosis and prevents recurrence in hepatitis B virus related hepatocellular carcinoma. Transl. Cancer Res. 2024, 13, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Yi, Y.; Yang, Y.; Dai, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Jiang, N.; Wang, H.; Li, K.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; et al. The potential therapeutic benefits of Huaier in digestive system cancer: Its chemical components, pharmacological applications and future direction. J. Funct. Foods 2024, 118, 106267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.; Zhou, X.; Wu, W.; Tian, Y.; Jiang, J.; Wang, M.H. Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic applications of huaier in breast cancer treatment. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1269096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, D.; Jiang, B.; Yang, Y.; Miao, Y.; Fu, Q.; Zhang, F. Effect of huaier on melanoma invasion, metastasis, and angiogenesis. Biomed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 8163839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Yuan, L.; Xu, J.; Xu, H.; Wang, L.; Huang, L.; Xu, Z.; Cheng, X. Huaier inhibits gastric cancer growth and hepatic metastasis by reducing syntenin expression and STAT3 phosphorylation. J. Oncol. 2022, 2022, 6065516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Wu, Z. Immunoregulatory effects of Huaier (Trametes robiniophila Murr) and relevant clinical applications. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1147098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.; Mi, T.; Alli, S.; Guy, C.; Djekidel, M.N.; Liu, X.; Boi, S.; Chowdhury, P.; He, M.; Zehn, D.; et al. Antitumour progenitor exhausted CD8(+) T cells are sustained by TCR engagement. Nat. Immunol. 2024, 25, 1046–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrido, V.; Herrero, I.; Castro, J.; Castillo, A.; Rosado-Sánchez, I.; Galvá, M.I.; Ramos, R.; Olivas-Martínez, I.; Bulnes-Ramos, Á.; Cañizares, J.; et al. Immunological features beyond CD4/CD8 ratio values in older individuals. Aging 2021, 13, 13443–13459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanif, H.; Ali, J.; Susheela, T.; Khan, I.W.; Luna-Cuadros, M.A.; Khan, M.M.; Lau, D.T.Y. Update on the applications and limitations of alpha-fetoprotein for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 216–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Zhu, M.; Wang, W.; Li, W.; Dong, X.; Chen, Y.; Lu, Y.; Guo, J.; Li, M. Structural basis for alpha fetoprotein-mediated inhibition of caspase-3 activity in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 141, 1413–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Zhu, C.; Chen, Y.; Li, M.; Li, G.; Zu, Y.; Gao, Q.; Shang, T.; Liu, D.; Zhang, C.; et al. Huaier relieves oxaliplatin-induced hepatotoxicity through activation of the PI3K/AKT/Nrf2 signaling pathway in C57BL/6 mice. Heliyon 2024, 10, e37010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Yang, A.; Fan, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zha, X.; Zhang, H.; Tu, P. Huaier aqueous extract sensitizes cells to rapamycin and cisplatin through activating mTOR signaling. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 186, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Hernandez, M.O.; Zhao, Y.; Mehta, M.; Tran, B.; Kelly, M.; Rae, Z.; Hernandez, J.M.; Davis, J.L.; Martin, S.P.; et al. Tumor cell biodiversity drives microenvironmental reprogramming in liver cancer. Cancer Cell 2019, 36, 418–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
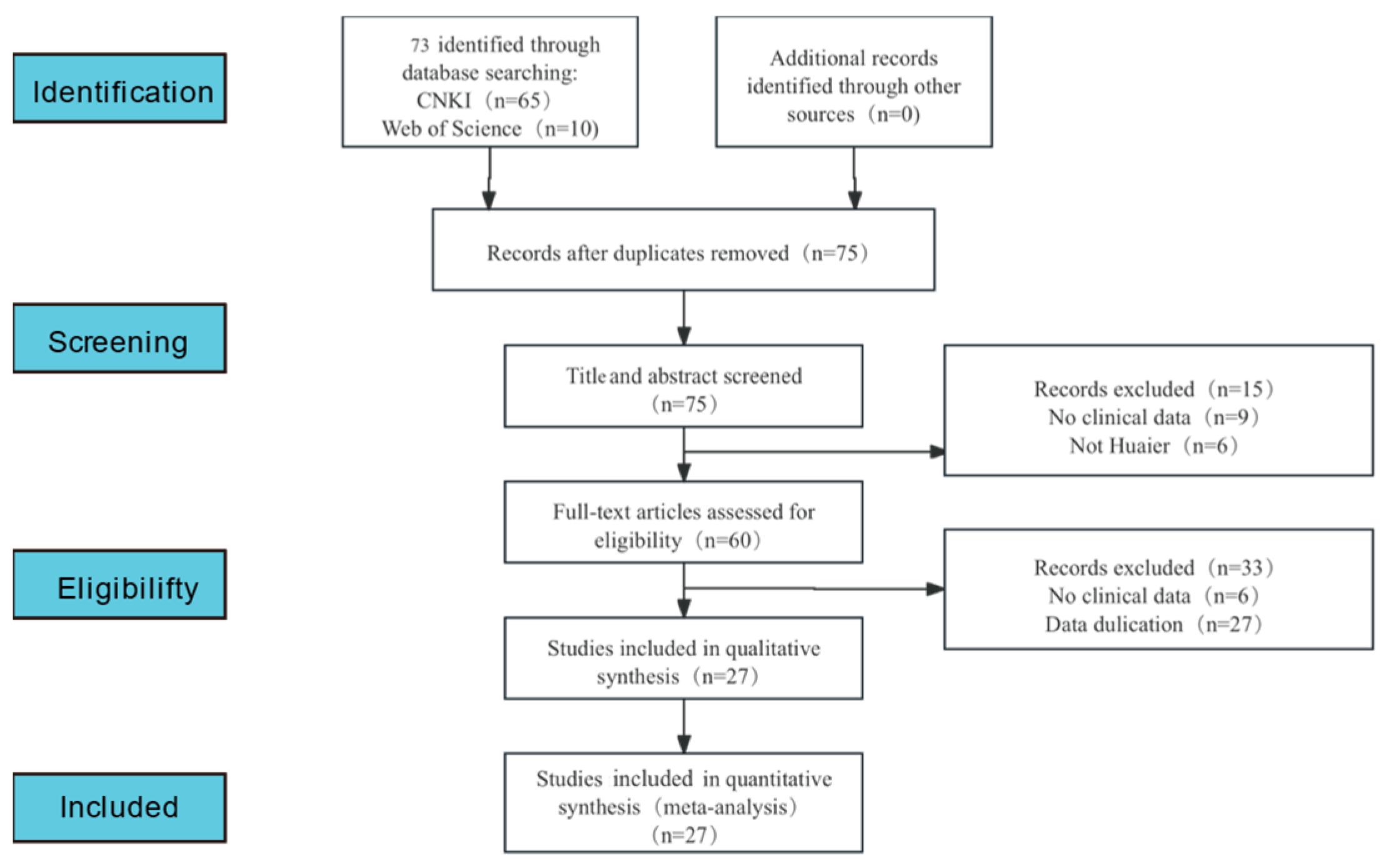
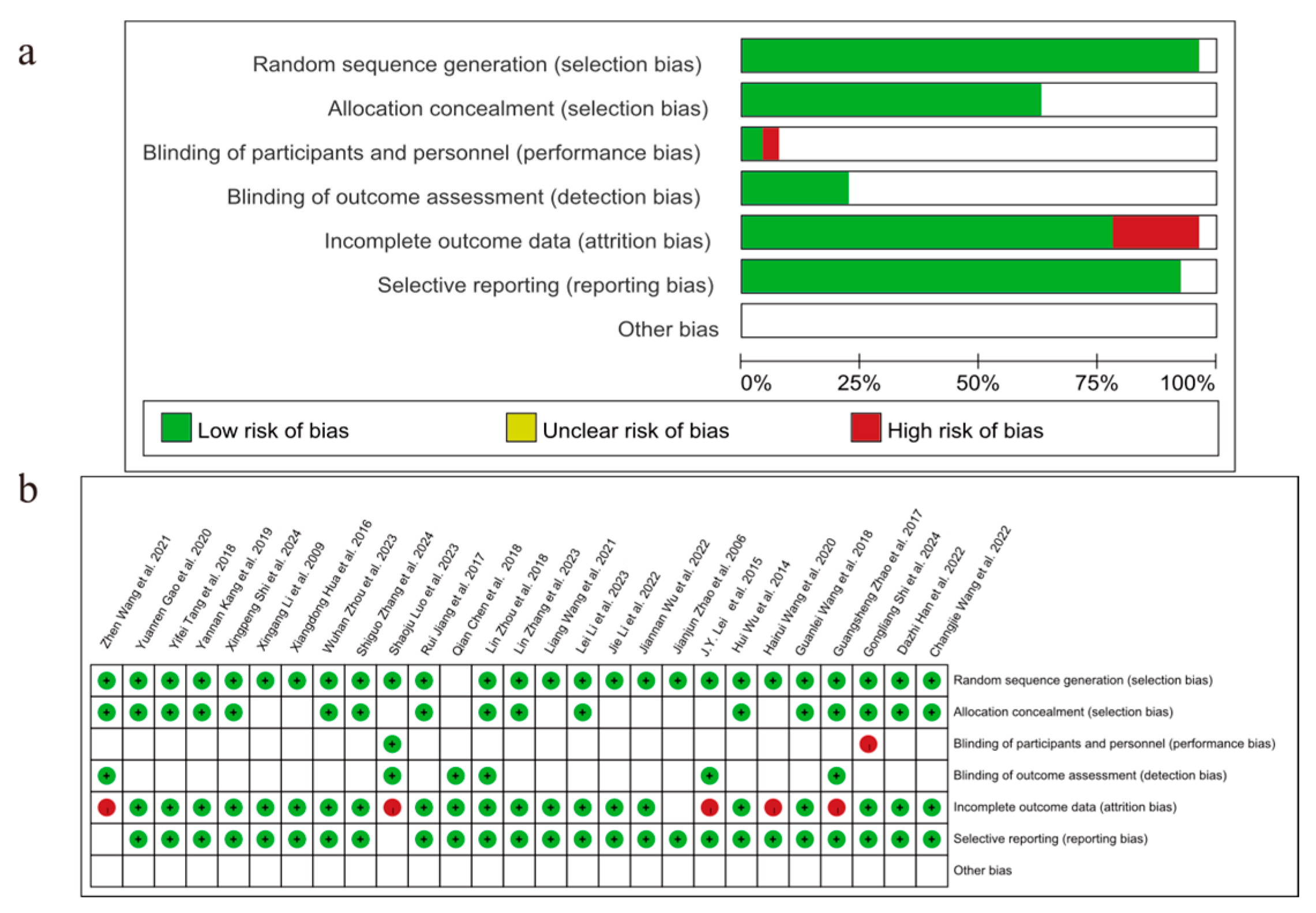
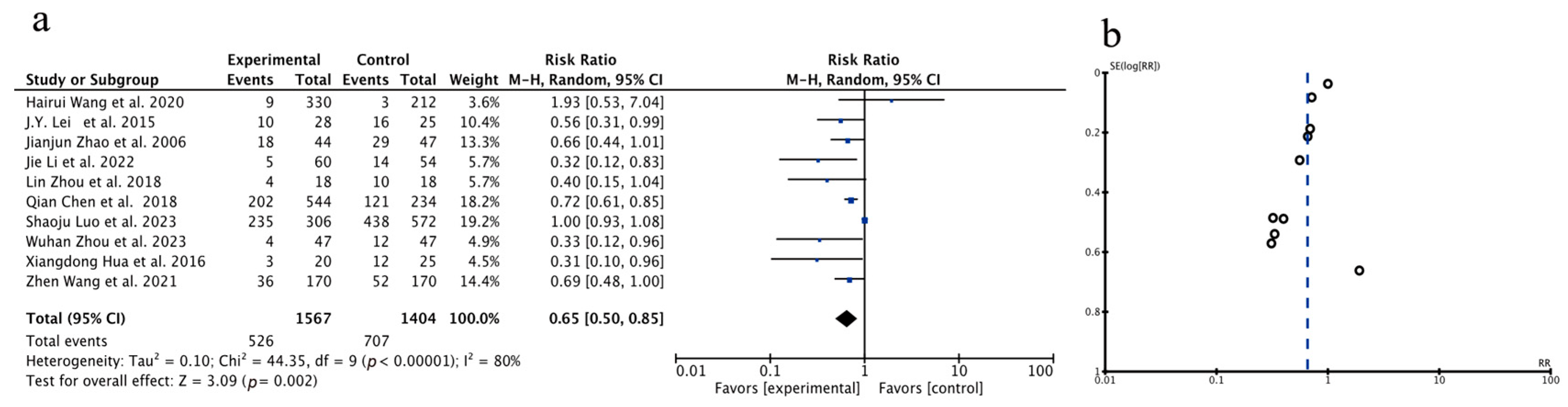
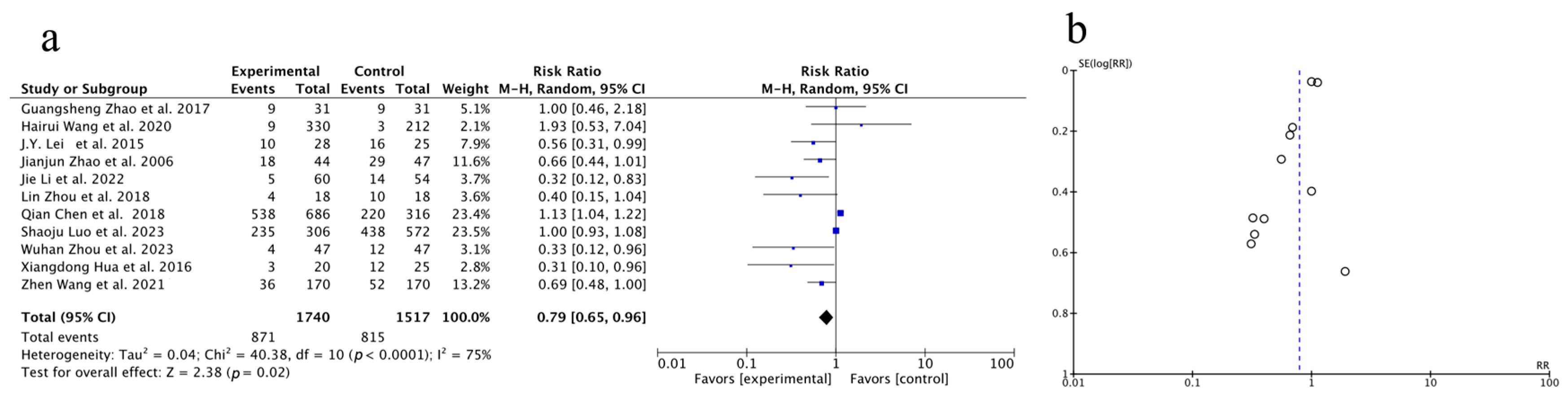
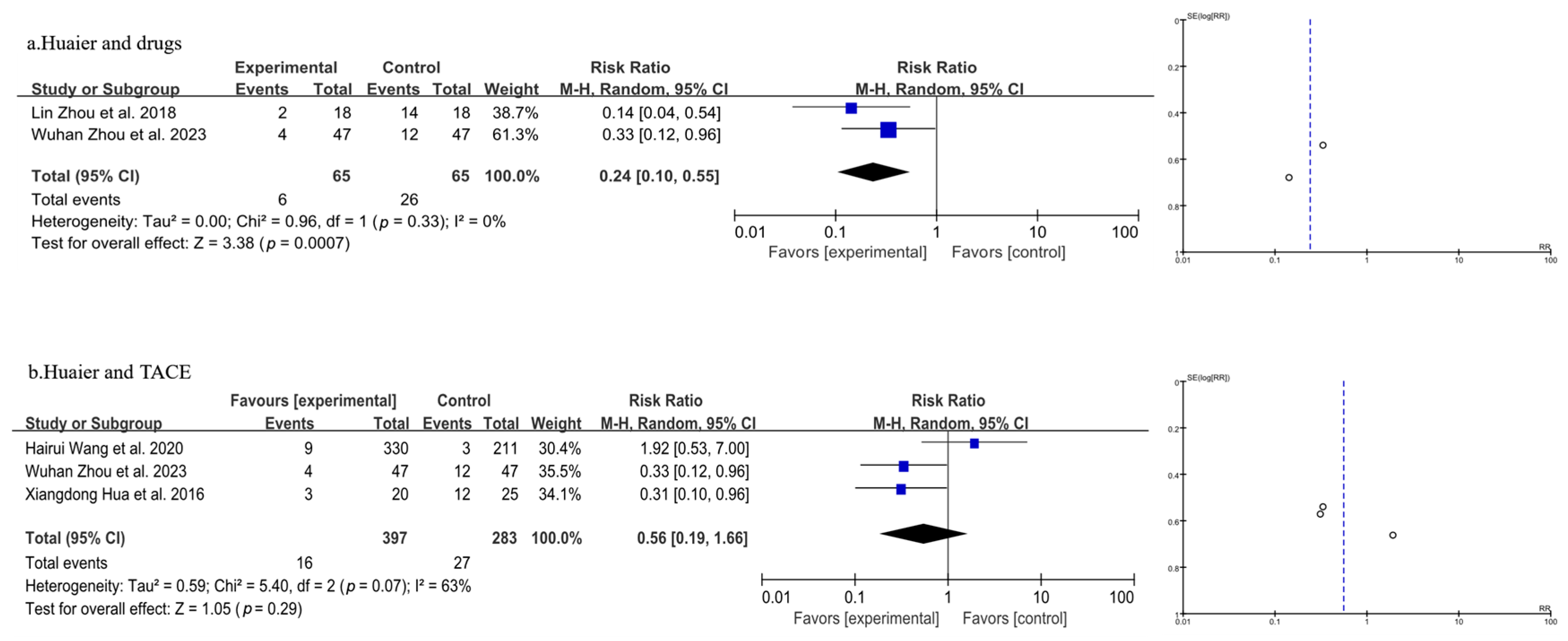
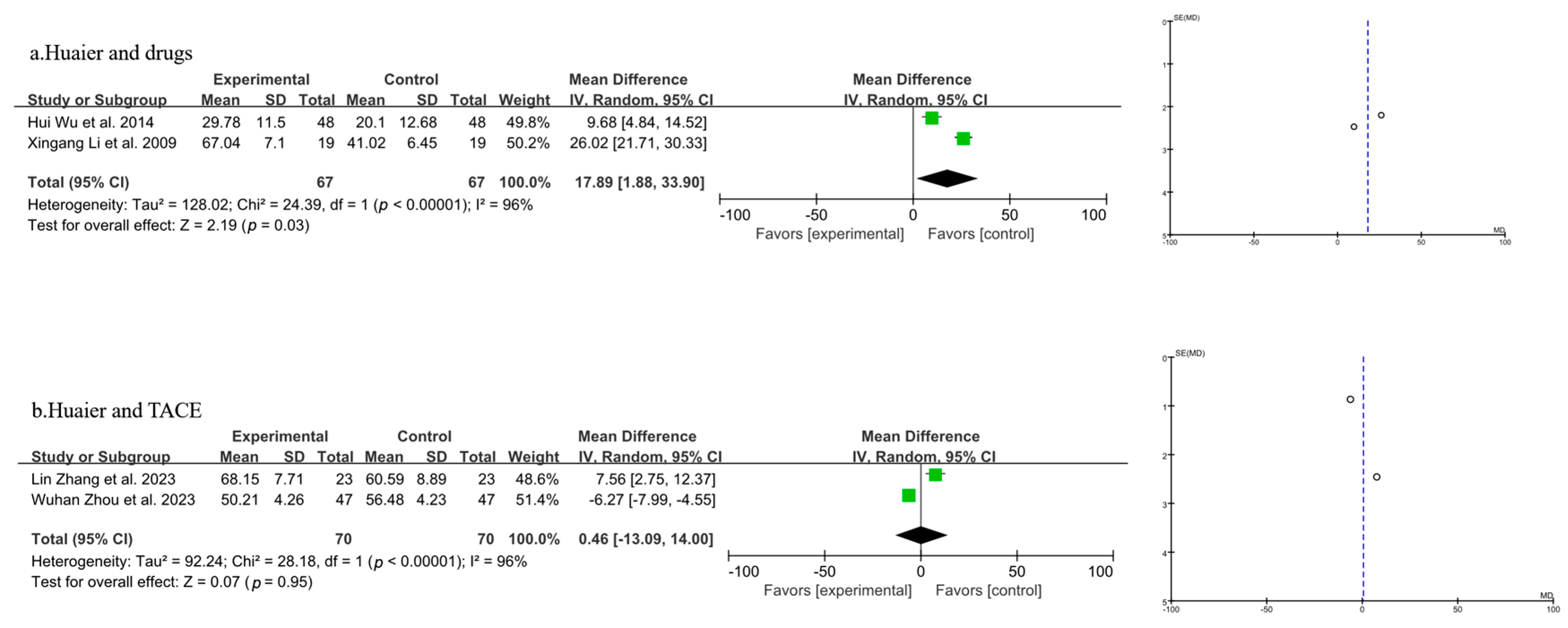
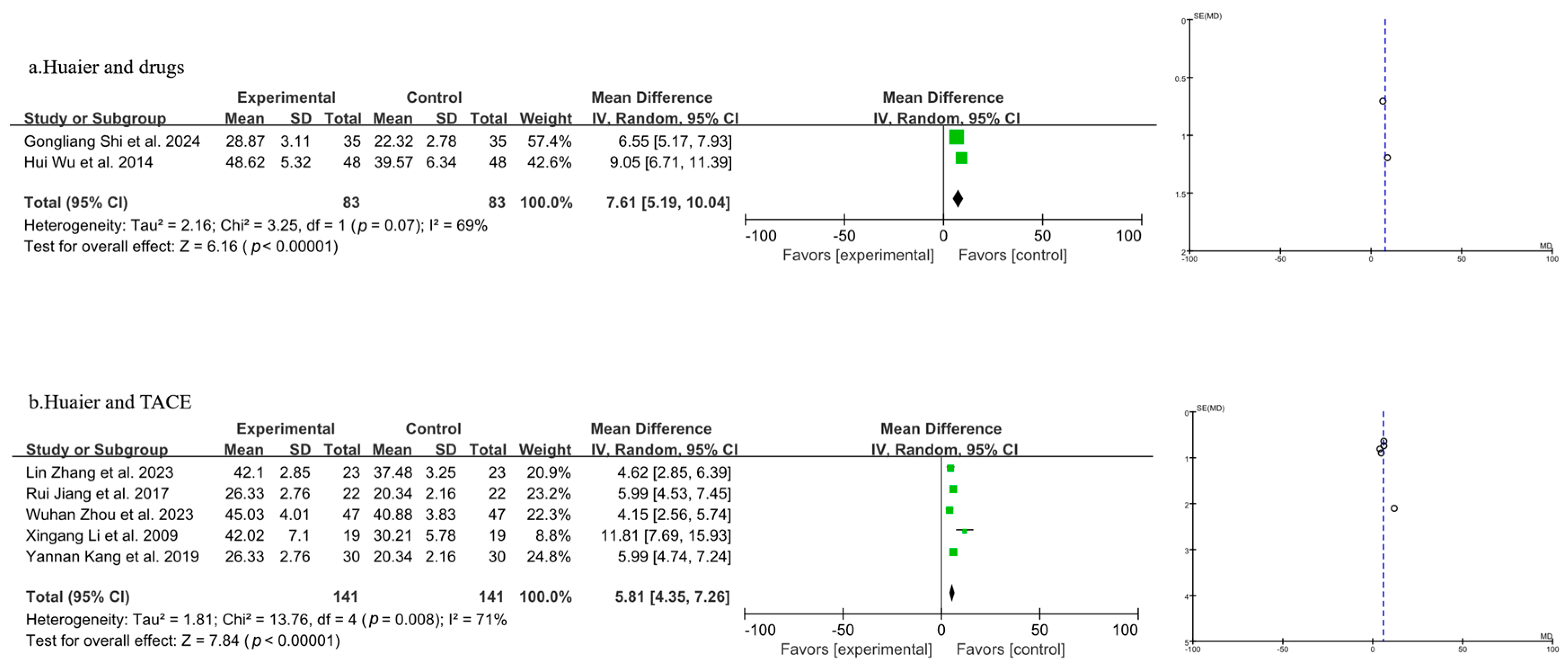
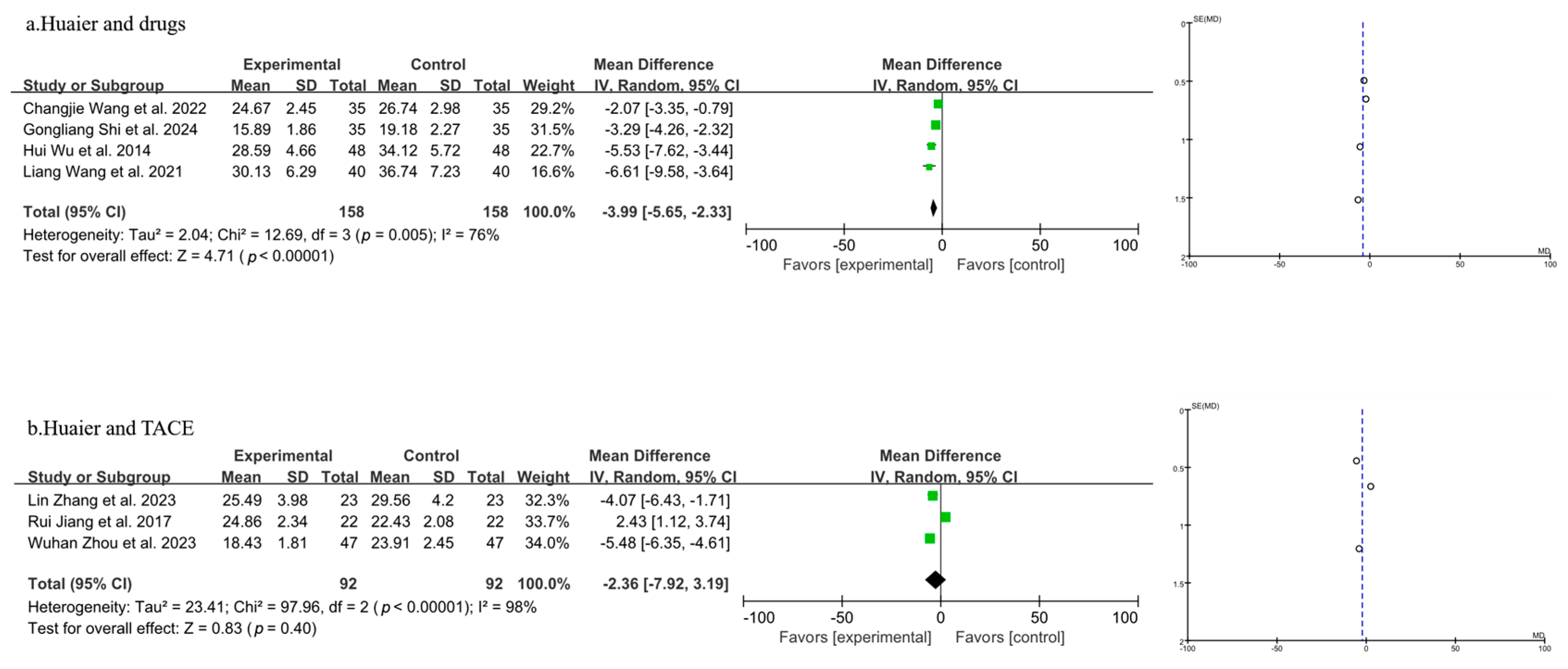
| Author, Year | Source | Sample Size | Age | Gender (Male/Female) | Surgery Type | Clinical Intervention | Time of Assessment (Months) | Outcome | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | C | I | C | I | C | I | C | I | C | ||||
| J.Y. Lei et al. 2015 [20] | West China Hospital of Sichuan University | 28 | 25 | 49.9 ± 8.4 | 50.3 ± 10.1 | (27/1) | (25/0) | / | Liver transplantation | Huaier granule | / | 30 | ①② |
| Guangsheng Zhao et al. 2017 [21] | Affiliated Zhongshan Hospital of Dalian University | 31 | 31 | average age 64.9 | average age 62.7 | (27/4) | (29/2) | TACE | TACE | Huaier granule | Lobaplatin chemotherapy | 12 | ②⑨ |
| Lin Zhou et al. 2018 [22] | Organ Transplant Institute, Chinese PLA 309th Hospital | 18 | 18 | 53.94 ± 7.40 | 49.72 ± 7.00 | (17/1) | (15/3) | / | / | Thymalfasin+Huaier granule | Tacrolimus | 12 | ①②③ |
| Zhen Wang et al. 2021 [23] | Chinese PLA General Hospital and Jining First People’s Hospital, Jining, Shandong Province | 170 | 170 | 30~86 | 34~86 | (143/27) | (129/41) | Thermal ablation | Thermal ablation | TCM | / | 12 | ①② |
| Shaoju Luo et al. 2023 [24] | The First Affiliated Hospital of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine | 405 | 706 | 49.62 (48.48, 50.74) | 50.17 (49.28, 51.05) | (354/51) | (629/77) | Radical surgery | Radical surgery | Huaier granule | / | 12 | ①② |
| Qian Chen et al. 2018 [25] | Tongji Hospital of Tongji Medical College of HUST | 686 | 316 | 18~75 | (565/121) | (255/61) | Radical surgery | Radical surgery | Huaier granule | / | 48 | ①② | |
| Jie Li et al. 2022 [26] | Tongji Hospital of Tongji | 60 | 54 | 18~73, average age (50.12 ± 10.71) | (37/23) | Radical surgery | Radical surgery | Huaier granule | / | 12 | ①②⑧ | ||
| Xiangdong Hua et al. 2016 [27] | Medical College of HUS | 20 | 25 | 28~72, average age 55 | (15/5) | (16/9) | TACE | TACE | Huaier granule | / | 12 | ①②⑦ | |
| Jianjun Zhao et al. 2006 [28] | Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Chinese Union Medical University, Beijing | 44 | 47 | / | / | / | / | Radical surgery | Radical surgery | Huaier granule | / | 6 | ①② |
| Wuhan Zhou et al. 2023 [29] | Putian First Hospital, Putian, Fujian Province | 47 | 47 | 37~72, average age 57.98 ± 5.31 | (21/26) | (27/20) | Laparoscopic hepatectomy | Laparoscopic hepatectomy | Lenvatinib+Huaier granule | Lenvatinib | 6 | ①②③④⑤⑥⑦⑧⑨ | |
| Hairui Wang et al. 2020 [30] | Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang | 330 | 212 | 18~75 | (272/58) | (168/44) | TACE | TACE | Huaier granule | Targeted drug therapy, immunotherapy, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, etc. | 54 | ①② | |
| Hui Wu et al. 2014 [31] | Affiliated Nanjing Hospital, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, Jiangsu | 48 | 48 | 21~68, average age 43.02 ± 7.63 | (59/37) | TACE | TACE | Huaier granule | / | 3 | ④⑤⑥⑦ | ||
| Lin Zhang et al. 2023 [32] | Changshu First People’s Hospital | 23 | 23 | 48~81, average age 61.83 ± 12.04 | (13/10) | (15/8) | TACE | TACE | Huaier granule | / | 6 | ④⑤⑥⑦ | |
| Xingang Li et al. 2009 [33] | Beihua University Affiliated Hospital, Jilin Province | 19 | 19 | 48~75, average age 58.5 | (29/9) | TACE | TACE | Huaier granule | / | 2 | ⑤ | ||
| Gongliang Shi et al. 2024 [34] | Chenzhou First People’s Hospital | 35 | 35 | 42~68, average age 52.45 ± 3.53 | (19/16) | (20/15) | / | / | Drug+Huaier granule | Drug | 2 | ⑤⑥⑦ | |
| Rui Jiang et al. 2017 [35] | Huishan District People’s Hospital of Wuxi | 22 | 22 | 36~72, average age 50.13 ± 9.76 | (16/6) | (14/8) | TACE | TACE | Huaier granule | / | 0.25 | ⑤⑥⑦ | |
| Yannan Kang et al. 2019 [36] | The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University | 30 | 30 | 60.93 ± 11.00 | 56.76 ± 8.83 | (18/12) | (19/11) | TACE | TACE | Thymosin α1+Huaier granule | Thymosin α1 | 1 | ⑤⑦⑧ |
| Liang Wang et al. 2021 [37] | Affiliated Hospital of Shaanxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Xi’an and Yulin No.2 Hospital | 40 | 40 | 40~71, average age 53.21 ± 8.06 | (26/14) | (28/12) | / | / | Sorafenib toluenesulfonate+Huaier granule | Sorafenib toluenesulfonate | 2 | ⑥⑦ | |
| Guanlei Wang et al. 2018 [38] | The First Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang | 49 | 47 | 33~72 | (25/24) | (24/23) | / | / | Drug+Huaier granule | Drug | 6 | ⑥⑦ | |
| Changjie Wang et al. 2022 [39] | Tangshan Central Hospital | 35 | 35 | average age 50.48 ± 6.37 | (31/4) | (29/6) | / | / | Drug+Huaier granule | Drug | 3 | ⑥⑦ | |
| Shiguo Zhang et al. 2024 [40] | Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital of Hengyang | 40 | 40 | average age 48.32 ± 3.28 | (22/18) | (23/17) | TACE | TACE | Thymosin α1+Huaier granule | Thymosin α1 | 1 | ⑦ | |
| Lei Li et al. 2023 [41] | Tangshan People’s Hospital | 38 | 38 | 25~75, average age 50.75 ± 4.38 | (28/10) | (30/8) | TACE | TACE | Huaier granule | / | 1 | ⑧ | |
| Jiannan Wu et al. 2022 [42] | Putuo District People’s Hospital of Zhoushan City | 50 | 50 | average age 52.60 ± 6.15 | (37/13) | (35/15) | TACE | TACE | Huaier granule | / | 3 | ⑧ | |
| Yuanren Gao et al. 2020 [43] | Harbin Medical University Cancer Hospital | 28 | 27 | 38~72, average age 51.21 ± 11.48 | (19/9) | (16/11) | TACE+RFA | TACE+RFA | Huaier granule | / | 3 | ⑧ | |
| Yifei Tang et al. 2018 [44] | Shuguang Hospital Affiliated with Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine | 57 | 56 | 35~74, average age 52.16 ± 7.33 | (40/17) | (41/15) | / | / | Sorafenib Tosylate+Huaier granule | Sorafenib Tosylate | 2 | ⑧ | |
| Dazhi Han et al. 2022 [45] | Chaoyang Central Hospital | 57 | 57 | 41~59, average age 46.57 ± 1.34 | (37/20) | (39/18) | / | / | Solafenib+Huaier granule | Solafenib | 2 | ⑧ | |
| Xingpeng Shi et al. 2024 [46] | Taizhou Hospital | 60 | 60 | average age 58.3 ± 8.1 | (36/24) | (31/29) | TACE | TACE | Drug+Huaier granule | Drug | 2 | ⑧ | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, T.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Sun, Z.; Wang, D.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, X.; et al. The Efficacy of Combined Use of Huaier Granules in the Treatment of Primary Liver Cancer: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 884. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18060884
Zhou T, Zhang Y, Lu Y, Sun Z, Wang D, Zhang X, Wang Y, Wei Y, Zhang T, Zhang X, et al. The Efficacy of Combined Use of Huaier Granules in the Treatment of Primary Liver Cancer: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(6):884. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18060884
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Tianhui, Yingying Zhang, Yuqing Lu, Zhaodong Sun, Dehui Wang, Xiaolong Zhang, Yu Wang, Yinuo Wei, Tiange Zhang, Xin Zhang, and et al. 2025. "The Efficacy of Combined Use of Huaier Granules in the Treatment of Primary Liver Cancer: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 6: 884. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18060884
APA StyleZhou, T., Zhang, Y., Lu, Y., Sun, Z., Wang, D., Zhang, X., Wang, Y., Wei, Y., Zhang, T., Zhang, X., Wei, R., Hu, P., Yang, G., Wang, X., & Pan, Y. (2025). The Efficacy of Combined Use of Huaier Granules in the Treatment of Primary Liver Cancer: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pharmaceuticals, 18(6), 884. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18060884







