Assessing the Antibacterial Potential and Biofilm Inhibition Capability of Atorvastatin-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers via Crystal Violet Assay
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Development and Characterization of NLC Formulations
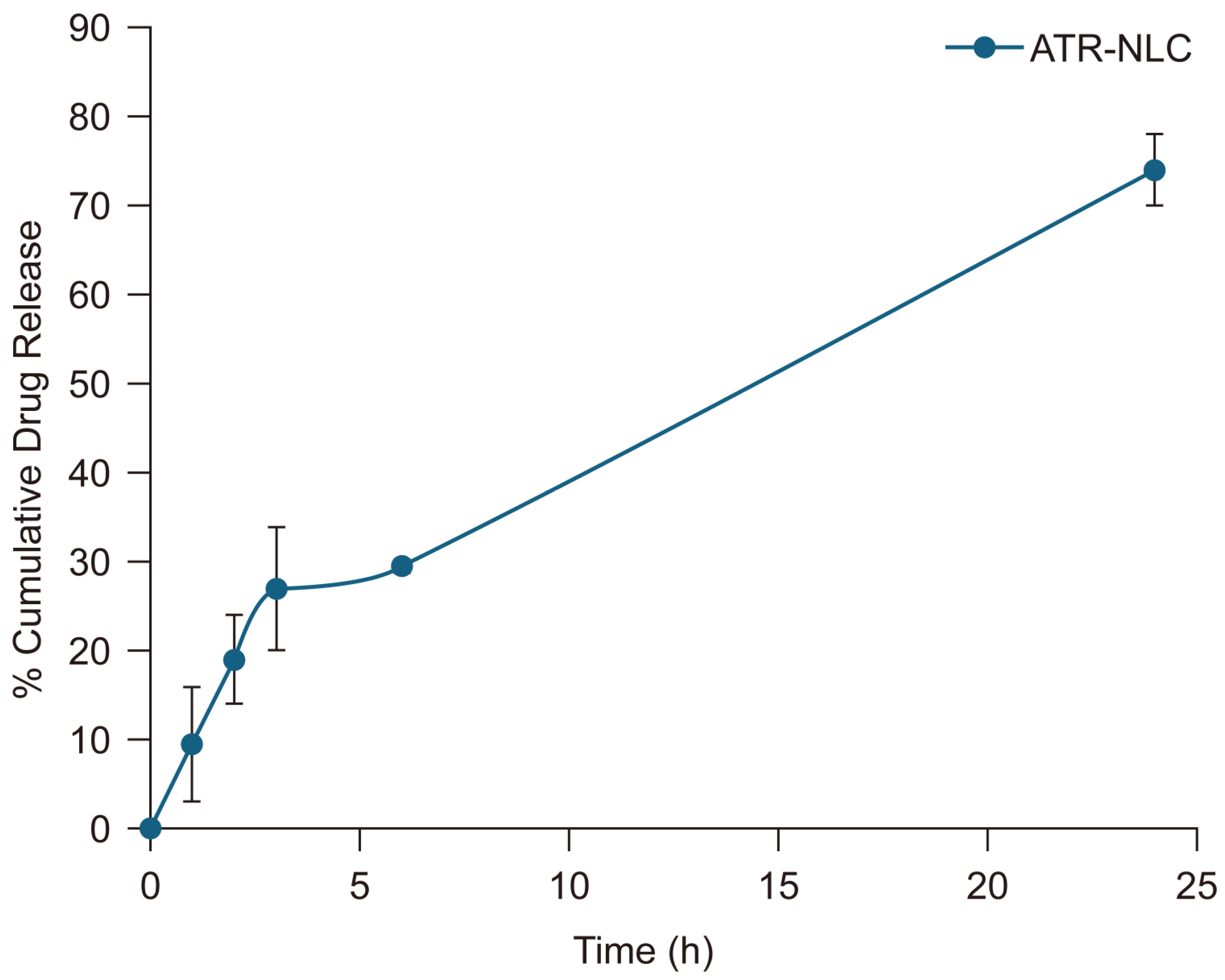
2.2. In Vitro Release Studies
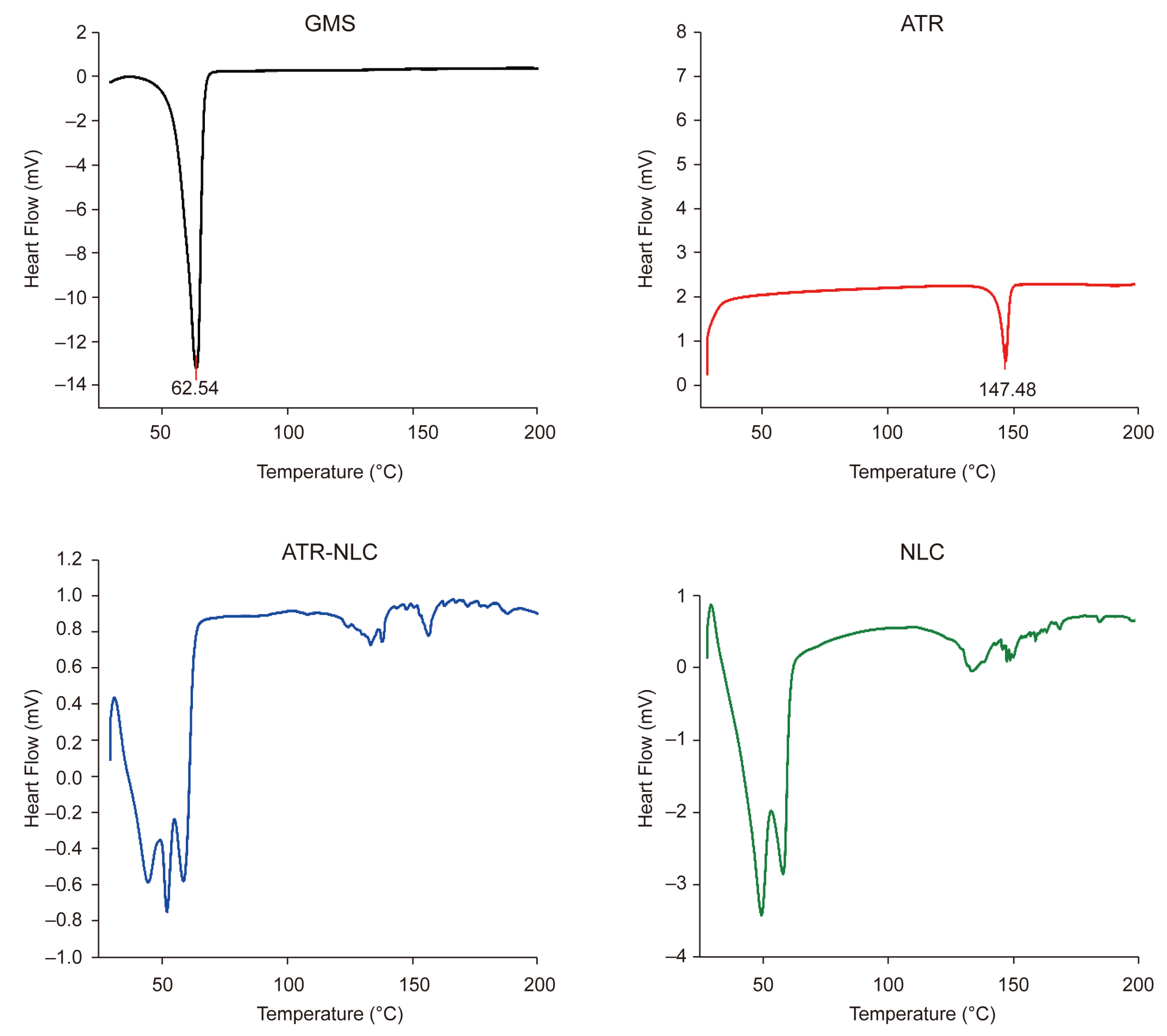
2.3. Thermal Analysis
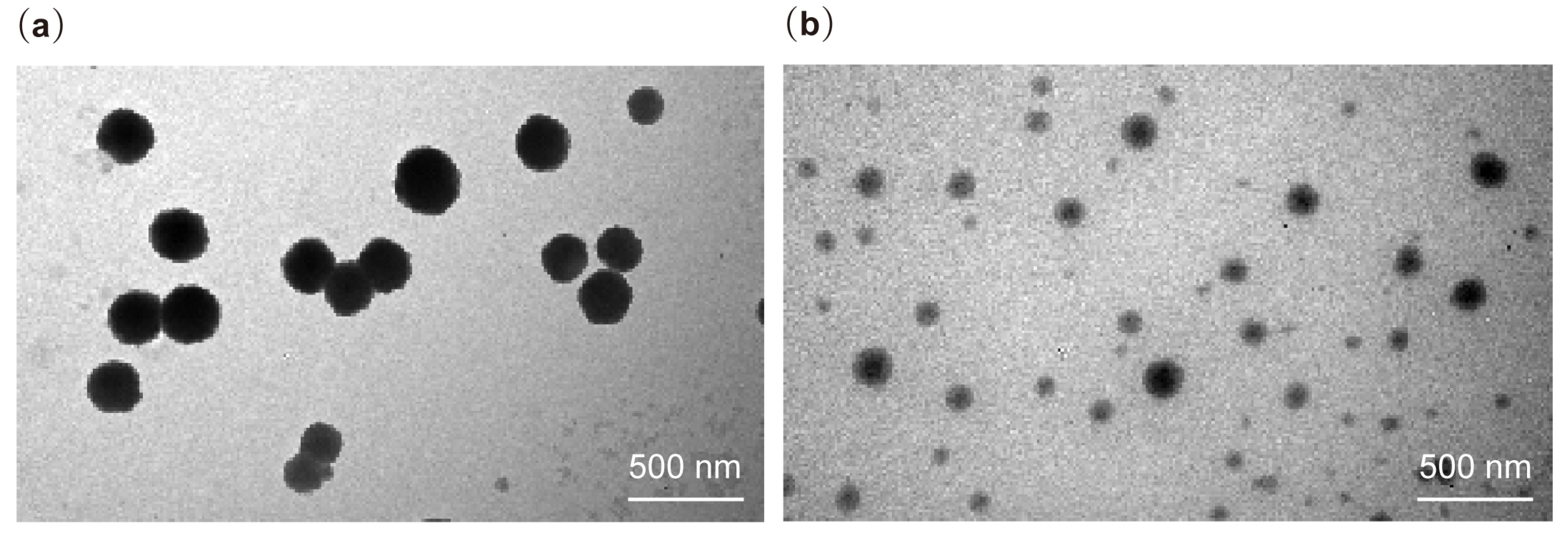
2.4. Morphology: Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
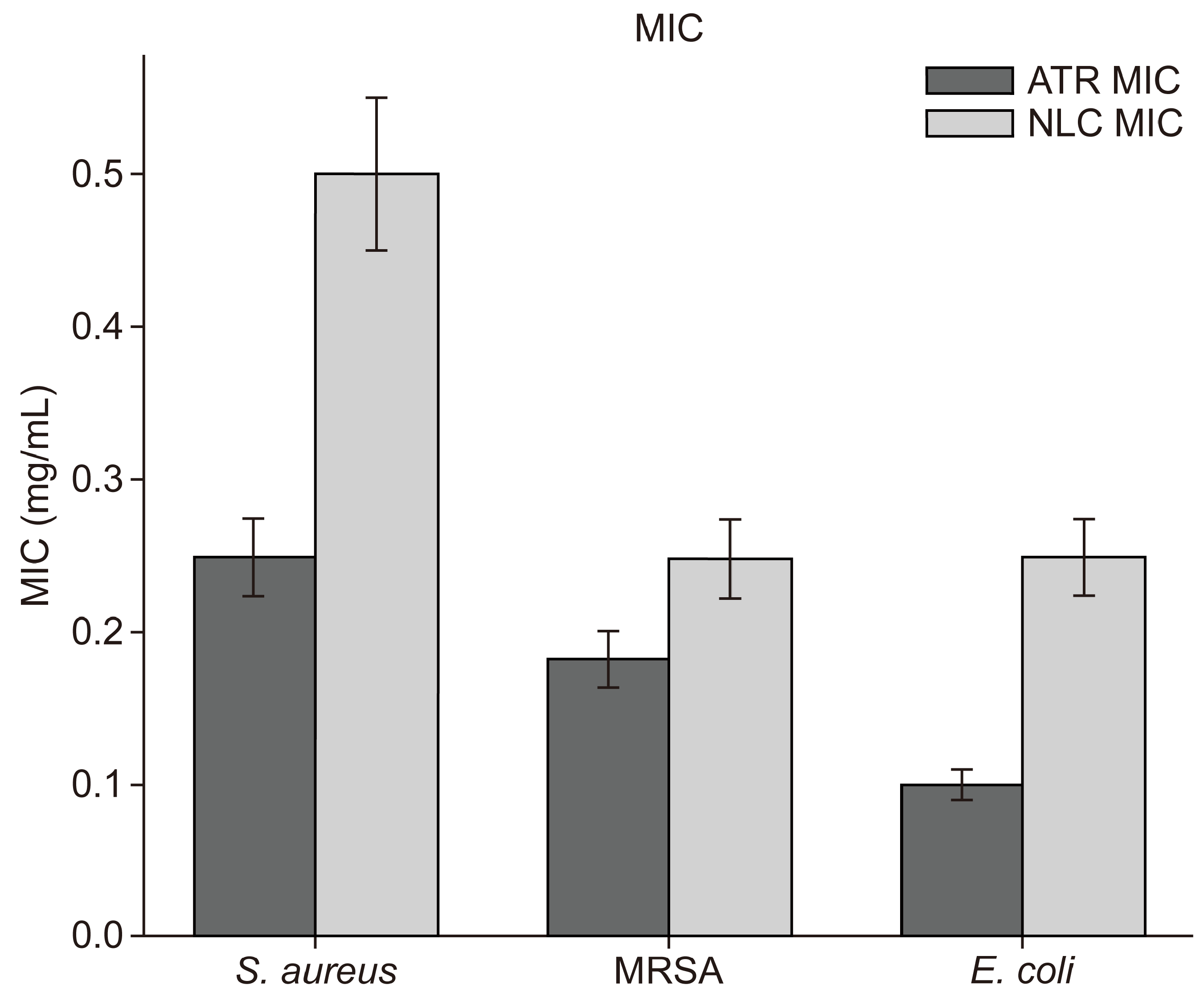
2.5. Sensitivity Testing Using Agar Well Diffusion Method
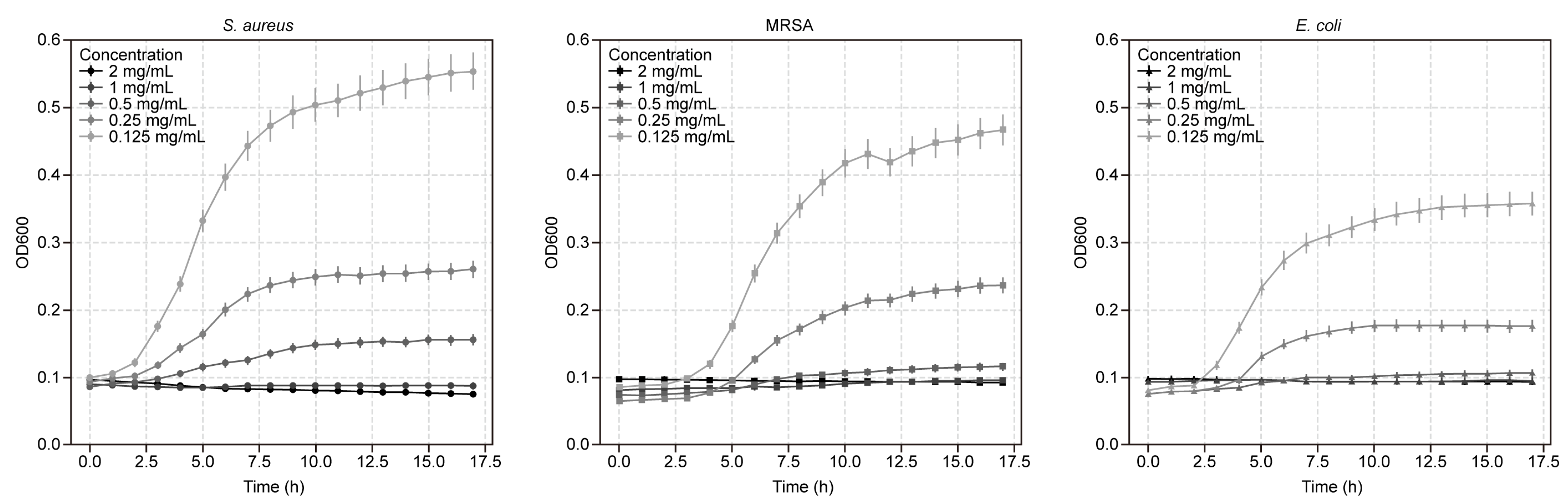
2.6. Growth Curve Analysis Using Microbroth Dilution Assay
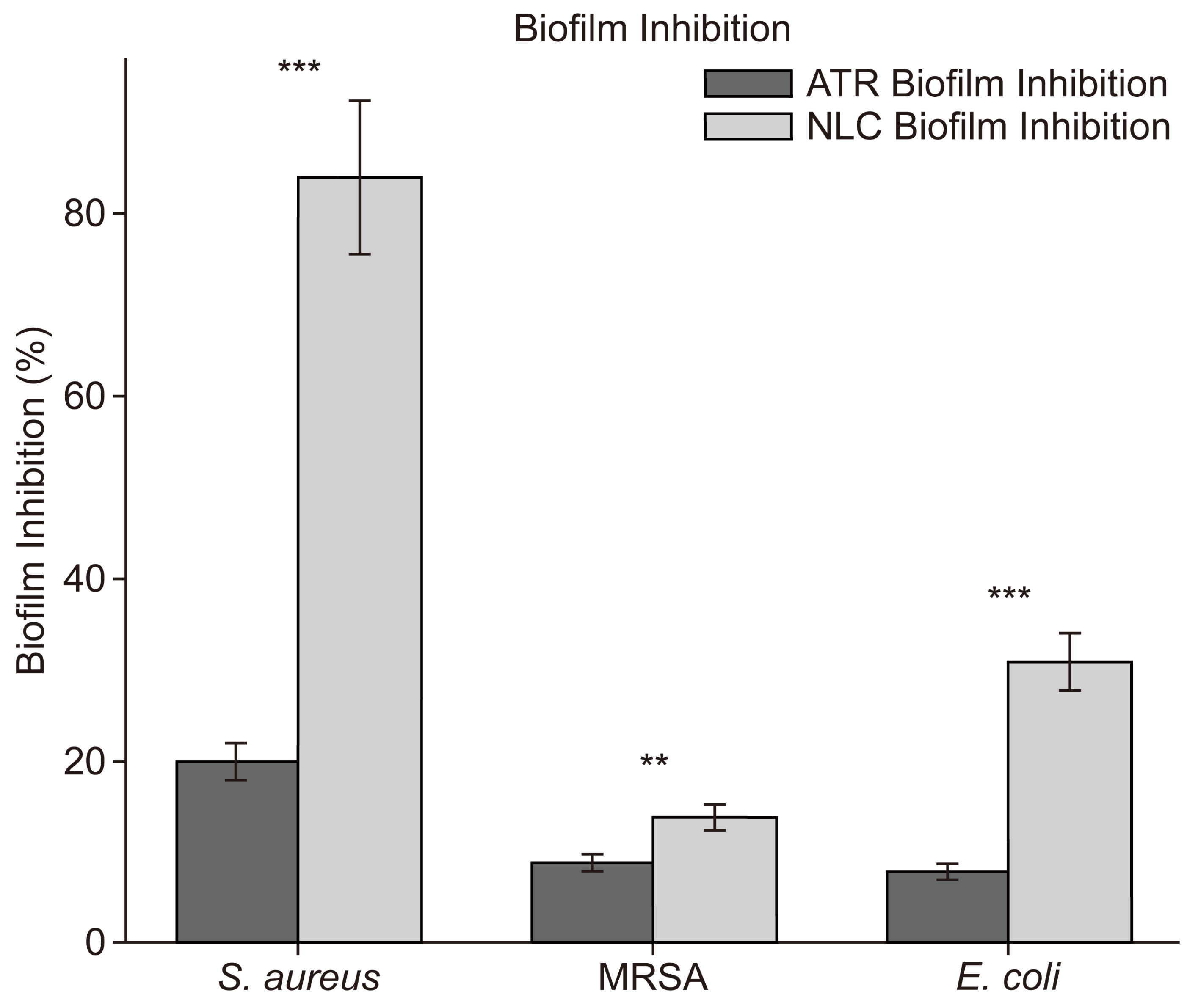
2.7. Biofilm Formation Using Crystal Violet Assay
3. Discussion
- Improved solubility and stability:The encapsulation of ATR in NLCs enhances its solubility and stability, allowing for higher effective concentrations at the site of infection [51].
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.1.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.1.2. Bacterial Strains
4.2. Preparation of NLC
4.3. Characterization of NLCs
4.4. Encapsulation Efficiency
4.5. In Vitro Release Studies
4.6. Thermal Analysis
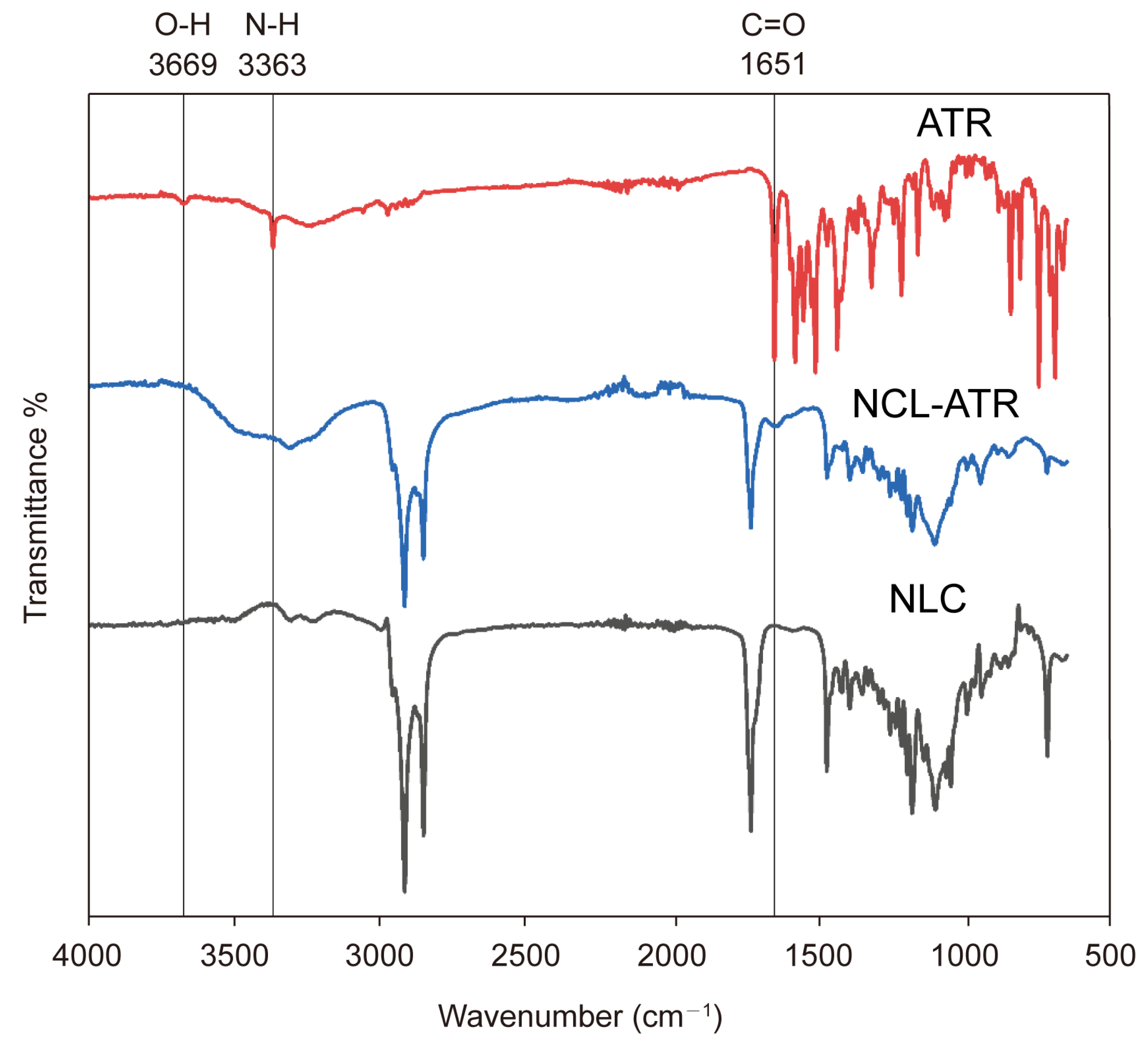
4.7. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
4.8. Morphology Evaluation
4.9. Antibacterial Activity
4.9.1. Sensitivity Testing Using Well Diffusion Method
4.9.2. Growth Curve Analysis Using Microbroth Dilution Assay
4.9.3. Crystal Violet Assay
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Global Antimicrobial Resistance and Use Surveillance System (GLASS) Report 2022; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Su, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, W.; Wang, M.; Wang, Y. A retrospective study on the effect of statins on mortality and antimicrobial resistance among patients with Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infection. Arch. Med. Sci. AMS 2024, 20, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, J. Tackling Drug-Resistant Infections Globally: Final Report and Recommendations; Government of the United Kingdom: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ashburn, T.T.; Thor, K.B. Drug repositioning: Identifying and developing new uses for existing drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennessy, E.; Adams, C.; Reen, F.J.; O’Gara, F. Is there potential for repurposing statins as novel antimicrobials? Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 5111–5121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmowafy, M.; Ibrahim, H.M.; Ahmed, M.A.; Shalaby, K.; Salama, A.; Hefesha, H. Atorvastatin-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs): Strategy to overcome oral delivery drawbacks. Drug Deliv. 2017, 24, 932–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masadeh, M.; Mhaidat, N.; Alzoubi, K.; Al-Azzam, S.; Alnasser, Z. Antibacterial activity of statins: A comparative study of atorvastatin, simvastatin, and rosuvastatin. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2012, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davuluri, K.S.; Singh, A.K.; Singh, A.V.; Chaudhary, P.; Raman, S.K.; Kushwaha, S.; Singh, S.V.; Chauhan, D.S. Atorvastatin potentially reduces mycobacterial severity through its action on Lipoarabinomannan and Drug Permeability in Granulomas. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e03197-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannachi, N.; Fournier, P.-E.; Martel, H.; Habib, G.; Camoin-Jau, L. Statins potentiate the antibacterial effect of platelets on Staphylococcus aureus. Platelets 2021, 32, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manalo, R.V.M.; Josol, V.J.D.; Gloriani, N.G. The differential effects of atorvastatin co-administered with ampicillin on the bacterial growth and biofilm formation of Staphylococcus aureus. Curr. Med. Res. Pract. 2017, 7, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajal Sarabhai, S.S.; Dhaliwal, L.; Neena Capalash, N.C.; Prince Sharma, P.S. Effect of atorvastatin and rosuvastatin on quorum sensing, biofilm formation and bacterial motilities of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int. J. Pharma Bio Sci. 2015, 6, B-1–B-8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.L.; Casey, P.J. Protein prenylation: Molecular mechanisms and functional consequences. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1996, 65, 241–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, M.D.; McDowell, S.A. Pleiotropic effects of statins: New therapeutic approaches to chronic, recurrent infection by Staphylococcus aureus. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirtori, C.R. The pharmacology of statins. Pharmacol. Res. 2014, 88, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Xie, Q.; Sun, Y. Advances in nanomaterial-based targeted drug delivery systems. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1177151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, J.; Taratula, O.; Minko, T. Nanocarrier-based systems for targeted and site specific therapeutic delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 144, 57–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, M.; Guo, H.; Gao, S.; Hu, Y.; Zeng, G.; Yang, D. Nanotechnology-driven strategies to enhance the treatment of drug-resistant bacterial infections. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 16, e1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Smitha, M.; Singh, S.P. The role of nanotechnology in combating multi-drug resistant bacteria. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 14, 4745–4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makabenta, J.M.V.; Nabawy, A.; Li, C.-H.; Schmidt-Malan, S.; Patel, R.; Rotello, V.M. Nanomaterial-based therapeutics for antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R.H.; Shegokar, R.; Keck, C.M. 20 years of lipid nanoparticles (SLN & NLC): Present state of development & industrial applications. Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 2011, 8, 207–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R.; Radtke, M.; Wissing, S. Nanostructured lipid matrices for improved microencapsulation of drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 242, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Chaudhury, A. Recent advances in lipid nanoparticle formulations with solid matrix for oral drug delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech 2011, 12, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Sharma, A.; Jain, V. An overview of nanostructured lipid carriers and its application in drug delivery through different routes. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2023, 13, 446–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvi, V.; Pawar, P. Nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) system: A novel drug targeting carrier. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 51, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomaa, E.; Fathi, H.A.; Eissa, N.G.; Elsabahy, M. Methods for preparation of nanostructured lipid carriers. Methods 2022, 199, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beloqui, A.; Solinís, M.Á.; Rodríguez-Gascón, A.; Almeida, A.J.; Préat, V. Nanostructured lipid carriers: Promising drug delivery systems for future clinics. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2016, 12, 143–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haider, M.; Abdin, S.M.; Kamal, L.; Orive, G. Nanostructured lipid carriers for delivery of chemotherapeutics: A review. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabale, V.; Jiwankar, M. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers in Chemotherapeutics: An Overview. Indian J. Pharm. Educ. Res. 2023, 57, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viegas, C.; Patrício, A.; Prata, J.; Nadhman, A.; Chintamaneni, P.; Fonte, P. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles vs. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers: A Comparative Review. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sütő, B.; Berkó, S.; Kozma, G.; Kukovecz, Á.; Budai-Szűcs, M.; Erős, G.; Kemény, L.; Sztojkov-Ivanov, A.; Gáspár, R.; Csányi, E. Development of ibuprofen-loaded nanostructured lipid carrier-based gels: Characterization and investigation of in vitro and in vivo penetration through the skin. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 1201–1212. [Google Scholar]
- Cortesi, R.; Valacchi, G.; Muresan, X.M.; Drechsler, M.; Contado, C.; Esposito, E.; Grandini, A.; Guerrini, A.; Forlani, G.; Sacchetti, G. Nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) for the delivery of natural molecules with antimicrobial activity: Production, characterisation and in vitro studies. J. Microencapsul. 2017, 34, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondì, M.L.; Craparo, E.F.; Giammona, G.; Cervello, M.; Azzolina, A.; Diana, P.; Martorana, A.; Cirrincione, G. Nanostructured lipid carriers-containing anticancer compounds: Preparation, characterization, and cytotoxicity studies. Drug Deliv. 2007, 14, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albekery, M.; Alharbi, K.; Alarifi, S.; Ahmad, D.; Omer, M.; Massadeh, S.; Yassin, A. Optimization of a nanostructured lipid carriers system for enhancing the biopharmaceutical properties of valsartan. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 2017, 12, 381–389. [Google Scholar]
- Apostolou, M.; Assi, S.; Fatokun, A.A.; Khan, I. The effects of solid and liquid lipids on the physicochemical properties of nanostructured lipid carriers. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 110, 2859–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemiyeh, P.; Mohammadi-Samani, S. Solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers as novel drug delivery systems: Applications, advantages and disadvantages. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 13, 288–303. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.-H.; Kim, K.-T.; Sohn, S.-Y.; Lee, J.-Y.; Lee, C.H.; Yang, H.; Lee, B.K.; Lee, K.W.; Kim, D.-D. Formulation and evaluation of nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) of 20 (S)-protopanaxadiol (PPD) by Box-Behnken design. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 8509–8520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, A.P.; Chavan, T.T.; Khandelwal, K.R. Enhancement of solubility, dissolution rate and bioavailability of atorvastatin using solid lipid: In vitro and in vivo characterization. J. Pharm. Investig. 2015, 45, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahor, A.K.; Singh, P.P.; Gupta, R.; Bhardwaj, P.; Rathore, P.; Kishore, A.; Goyal, R.; Sharma, N.; Verma, J.; Rosenholm, J.M. Nanostructured lipid carriers for improved delivery of therapeutics via the oral route. J. Nanotechnol. 2023, 2023, 4687959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unnisa, A.; Chettupalli, A.K.; Alazragi, R.S.; Alelwani, W.; Bannunah, A.M.; Barnawi, J.; Amarachinta, P.R.; Jandrajupalli, S.B.; Elamine, B.A.; Mohamed, O.A. Nanostructured lipid carriers to enhance the bioavailability and solubility of ranolazine: Statistical optimization and pharmacological evaluations. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanem, H.A.; Nasr, A.M.; Hassan, T.H.; Elkhoudary, M.M.; Alshaman, R.; Alattar, A.; Gad, S. Comprehensive study of atorvastatin nanostructured lipid carriers through multivariate conceptualization and optimization. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreedhar, R.; Kumar, V.; Bhaskaran Pillai, A.; Mangalathillam, S. Omega-3 Fatty Acid Based Nanolipid Formulation of Atorvastatin for Treating Hyperlipidemia. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 9, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raschi, E.; Casula, M.; Cicero, A.F.; Corsini, A.; Borghi, C.; Catapano, A. Beyond statins: New pharmacological targets to decrease LDL-cholesterol and cardiovascular events. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 250, 108507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KM, A.S.; Angolkar, M.; Rahamathulla, M.; Thajudeen, K.Y.; Ahmed, M.M.; Farhana, S.A.; Shivanandappa, T.B.; Paramshetti, S.; Osmani, R.A.M.; Natarajan, J. Box-Behnken Design-Based Optimization and Evaluation of Lipid-Based Nano Drug Delivery System for Brain Targeting of Bromocriptine. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibesh, S.; Bitar, Y.; Trefi, S. A New method for simultaneous qualitative and quantitative determination of amlodipine besylate and atorvastatin calcium in bulk and pharmaceutical formulations using transmission FT-IR spectroscopy. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Isha, M. Surface stabilized atorvastatin nanocrystals with improved bioavailability, safety and antihyperlipidemic potential. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamińska, M.; Aliko, A.; Hellvard, A.; Bielecka, E.; Binder, V.; Marczyk, A.; Potempa, J.; Delaleu, N.; Kantyka, T.; Mydel, P. Effects of statins on multispecies oral biofilm identify simvastatin as a drug candidate targeting Porphyromonas gingivalis. J. Periodontol. 2019, 90, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuon, F.F.; Suss, P.H.; Telles, J.P.; Dantas, L.R.; Borges, N.H.; Ribeiro, V.S.T. Antimicrobial treatment of Staphylococcus aureus biofilms. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahsan, A.; Thomas, N.; Barnes, T.J.; Subramaniam, S.; Loh, T.C.; Joyce, P.; Prestidge, C.A. Lipid Nanocarriers-Enabled Delivery of Antibiotics and Antimicrobial Adjuvants to Overcome Bacterial Biofilms. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.-Y.; Van der Mei, H.C.; Ren, Y.; Busscher, H.J.; Shi, L. Lipid-based antimicrobial delivery-systems for the treatment of bacterial infections. Front. Chem. 2020, 7, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Kang, F.; Yang, B.; Zhang, W.; Qin, C.; Gao, Y. Extracellular polymeric substances acting as a permeable barrier hinder the lateral transfer of antibiotic resistance genes. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmowafy, M.; Al-Sanea, M.M. Nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) as drug delivery platform: Advances in formulation and delivery strategies. Saudi Pharm. J. 2021, 29, 999–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penesyan, A.; Nagy, S.S.; Kjelleberg, S.; Gillings, M.R.; Paulsen, I.T. Rapid microevolution of biofilm cells in response to antibiotics. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2019, 5, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, G.; Hu, C.; Fang, K.; Li, Y.; Wang, L. How nanoparticles help in combating chronic wound biofilm infection? Int. J. Nanomed. 2024, 19, 11883–11921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawas, S.; Verderosa, A.D.; Totsika, M. Combination therapies for biofilm inhibition and eradication: A comparative review of laboratory and preclinical studies. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 850030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasr, M.; Ramzy, M.; Abdel-moneum, R.; Abdel-Rashid, R.S. Optimization of nano-structured lipid carriers for enhanced salbutamol delivery via buccal mucoadhesive film. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2025, 104, 106468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Formulation | GMS: Labrasol | Surfactant (Tween 80) | Particle Size | PDI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 70:30 | 1% | >1 µm | --- |
| B | 70:30 | 2% | >1 µm | --- |
| C | 50:50 | 1% | >300 nm | 0.4 |
| D 1 | 50:50 | 2% | 130 ± 8.39 nm | 0.3 ± 0.5 |
| Formulation | Particle Size (nm) | PDI | Zeta Potential (mV) | EE% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank NLC | 130 ± 8.39 | 0.3 ± 0.5 | −35 ± 0.5 | --- |
| ATR-NLC | 142 ± 52.20 | 0.4 ± 0.05 | −31 ± 1.41 | 94% |
| Bacteria | Zone of Inhibition (cm) |
|---|---|
| S. aureus | 2.3 ± 0.1 |
| MRSA | 1.8 ± 0.1 |
| E. coli | 2.2 ± 0.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Altuwaijri, N.; Fitaihi, R.; Alkathiri, F.A.; Bukhari, S.I.; Altalal, A.M.; Alsalhi, A.; Alsulaiman, L.; Alomran, A.O.; Aldosari, N.S.; Alqhafi, S.A.; et al. Assessing the Antibacterial Potential and Biofilm Inhibition Capability of Atorvastatin-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers via Crystal Violet Assay. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 417. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18030417
Altuwaijri N, Fitaihi R, Alkathiri FA, Bukhari SI, Altalal AM, Alsalhi A, Alsulaiman L, Alomran AO, Aldosari NS, Alqhafi SA, et al. Assessing the Antibacterial Potential and Biofilm Inhibition Capability of Atorvastatin-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers via Crystal Violet Assay. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(3):417. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18030417
Chicago/Turabian StyleAltuwaijri, Njoud, Rawan Fitaihi, Fai A. Alkathiri, Sarah I. Bukhari, Alanoud M. Altalal, Alyaa Alsalhi, Lama Alsulaiman, Aljawhara O. Alomran, Noura S. Aldosari, Safa A. Alqhafi, and et al. 2025. "Assessing the Antibacterial Potential and Biofilm Inhibition Capability of Atorvastatin-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers via Crystal Violet Assay" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 3: 417. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18030417
APA StyleAltuwaijri, N., Fitaihi, R., Alkathiri, F. A., Bukhari, S. I., Altalal, A. M., Alsalhi, A., Alsulaiman, L., Alomran, A. O., Aldosari, N. S., Alqhafi, S. A., Alhamdan, M., & Alfaraj, R. (2025). Assessing the Antibacterial Potential and Biofilm Inhibition Capability of Atorvastatin-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers via Crystal Violet Assay. Pharmaceuticals, 18(3), 417. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18030417







