Intermedin Alleviates Diabetic Cardiomyopathy by Up-Regulating CPT-1β through Activation of the Phosphatidyl Inositol 3 Kinase/Protein Kinase B Signaling Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. IMD Levels Are Significantly Down-Regulated in Cardiac Tissues of DCM Rats, DCM Mice, and Hypertrophic Cardiomyocytes
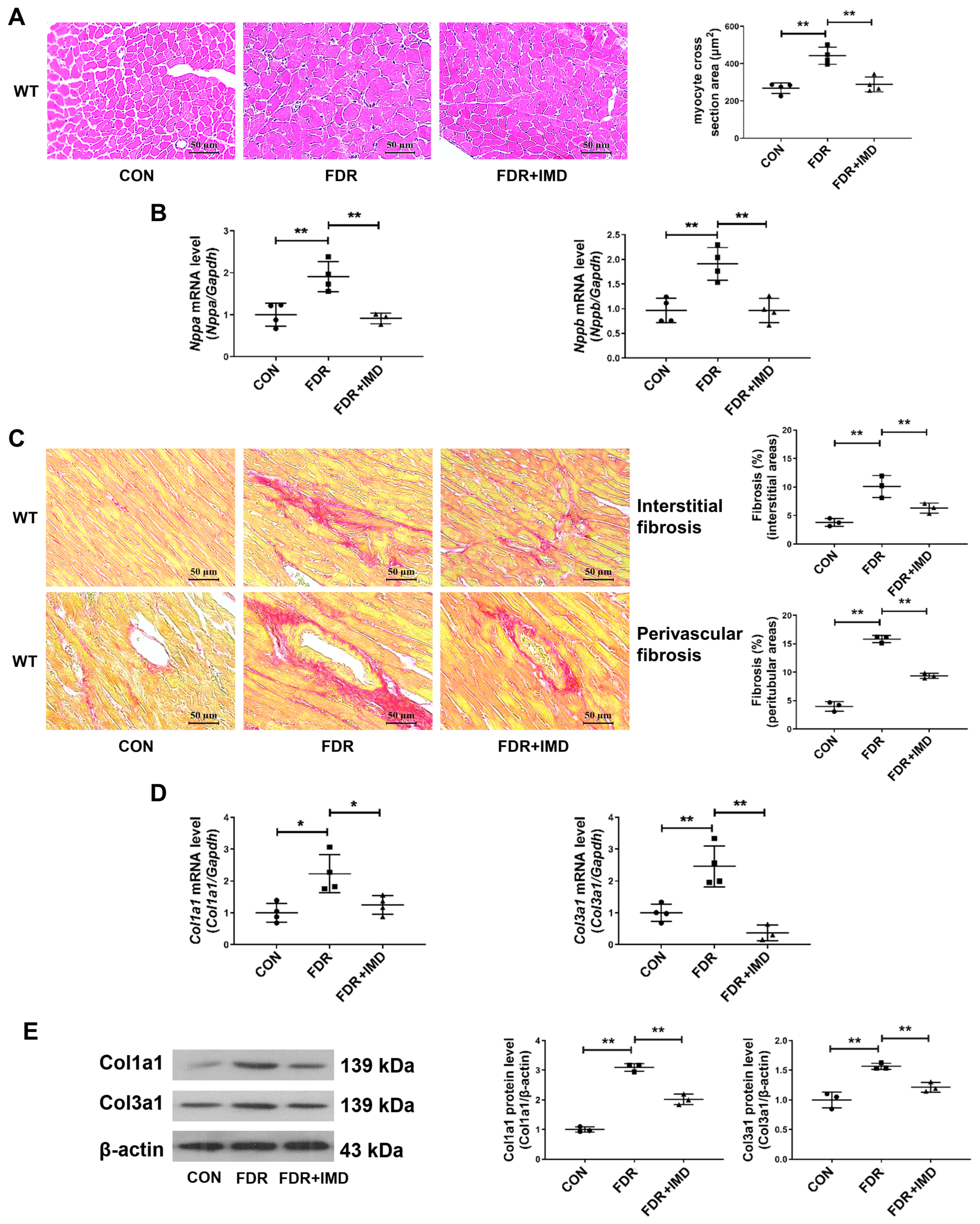
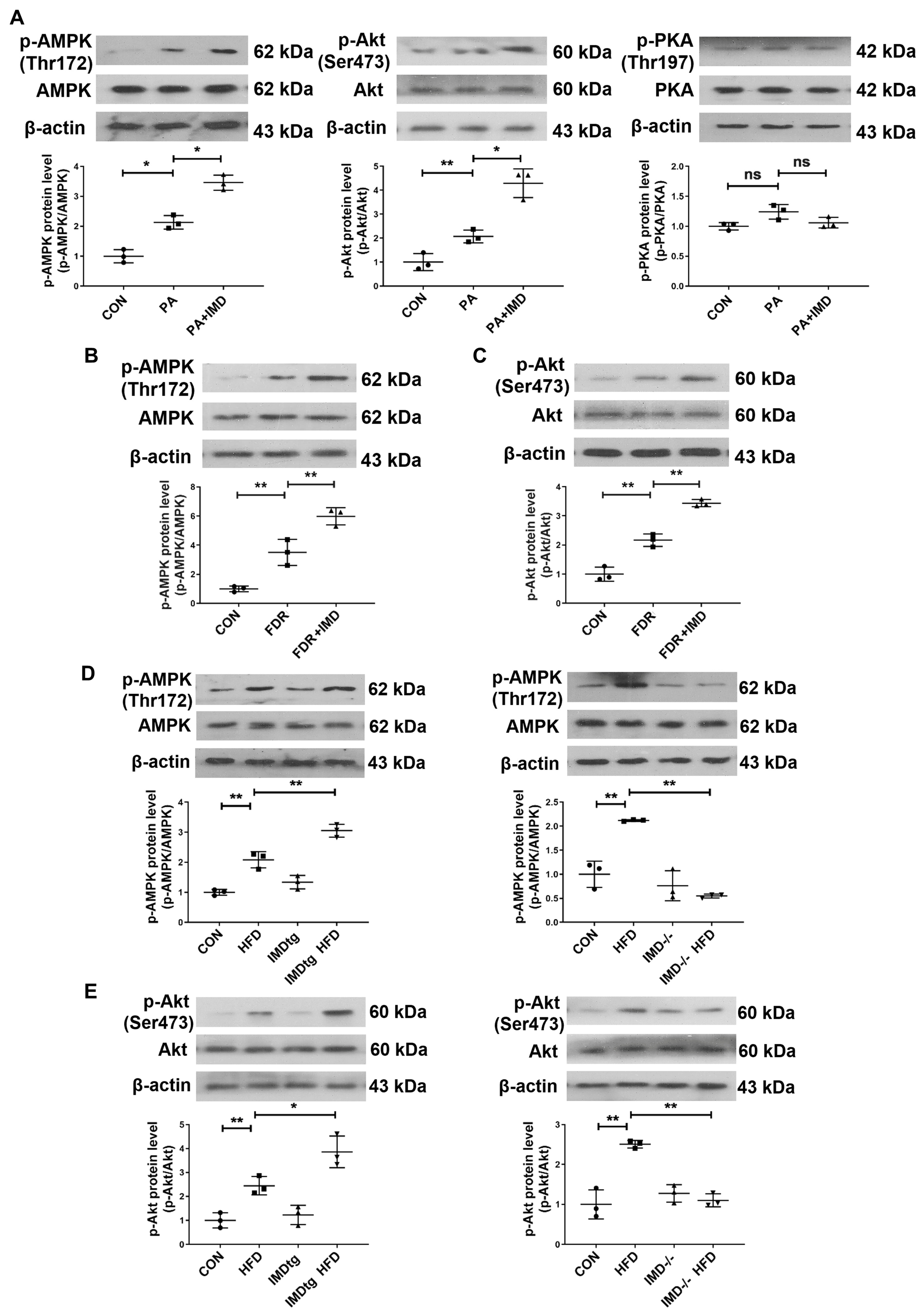
2.2. Exogenous IMD Alleviates DCM in Rats
2.3. IMD Overexpression Alleviates DCM in Mice
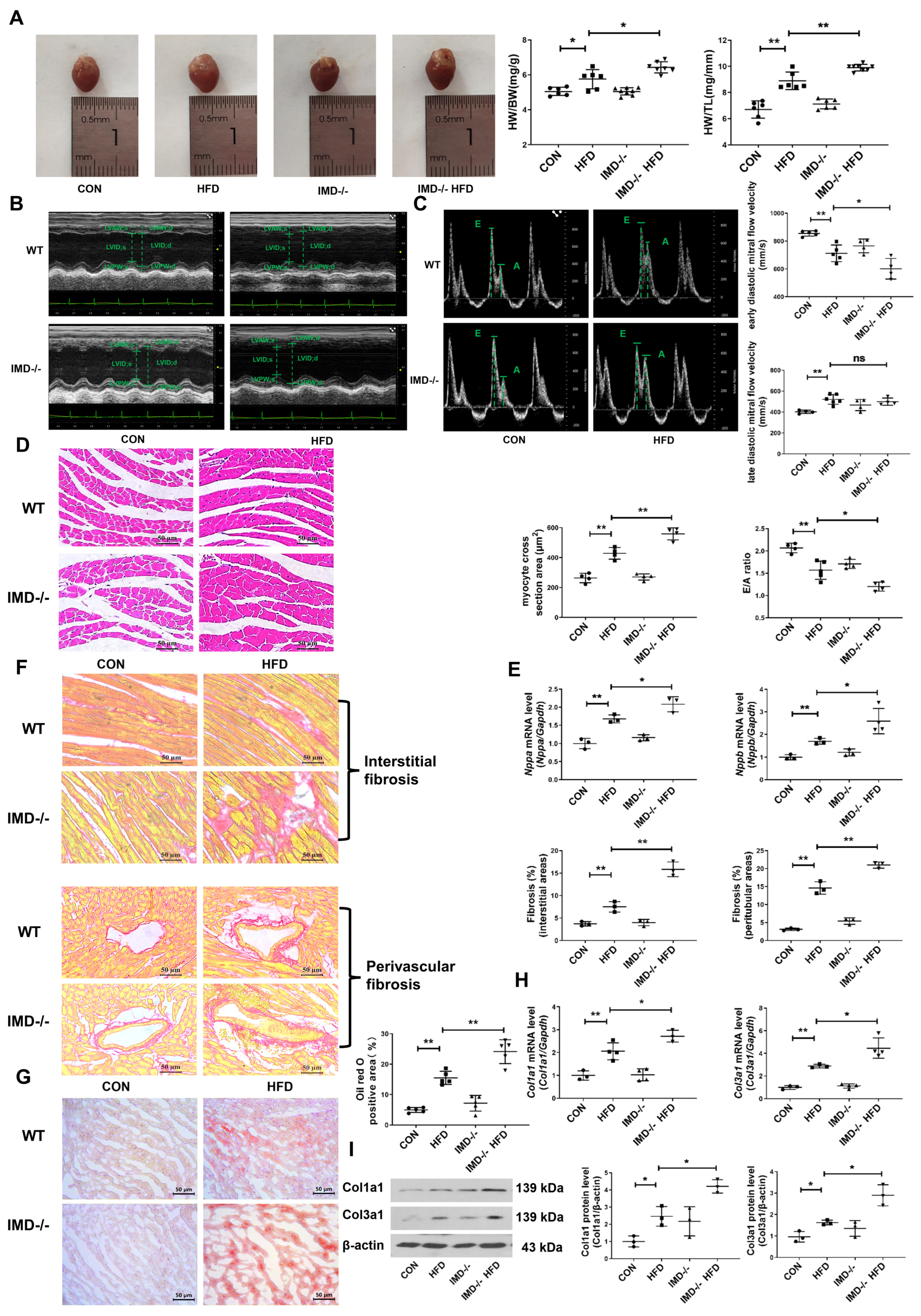
2.4. IMD Deficiency Exacerbates DCM in Mice
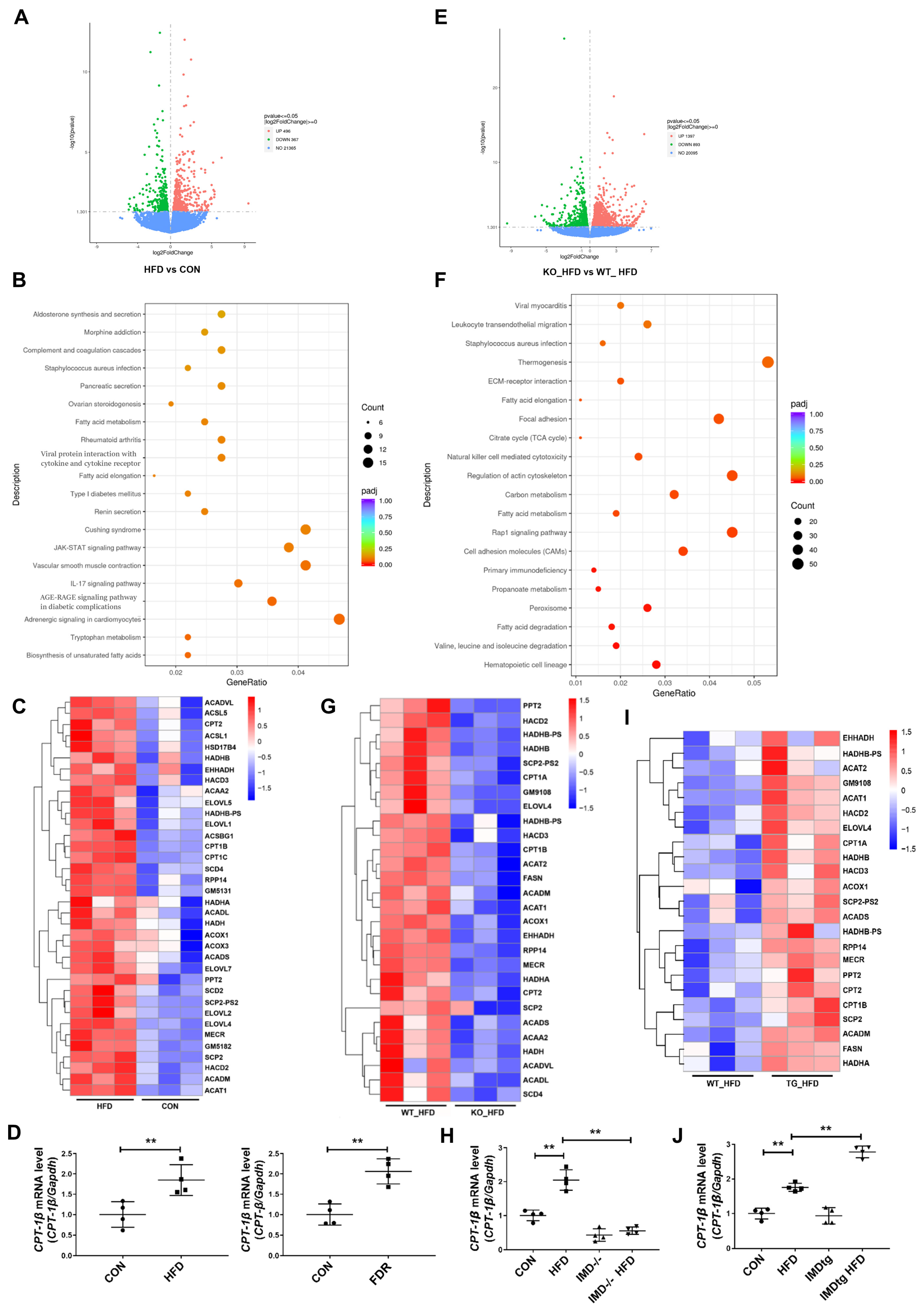
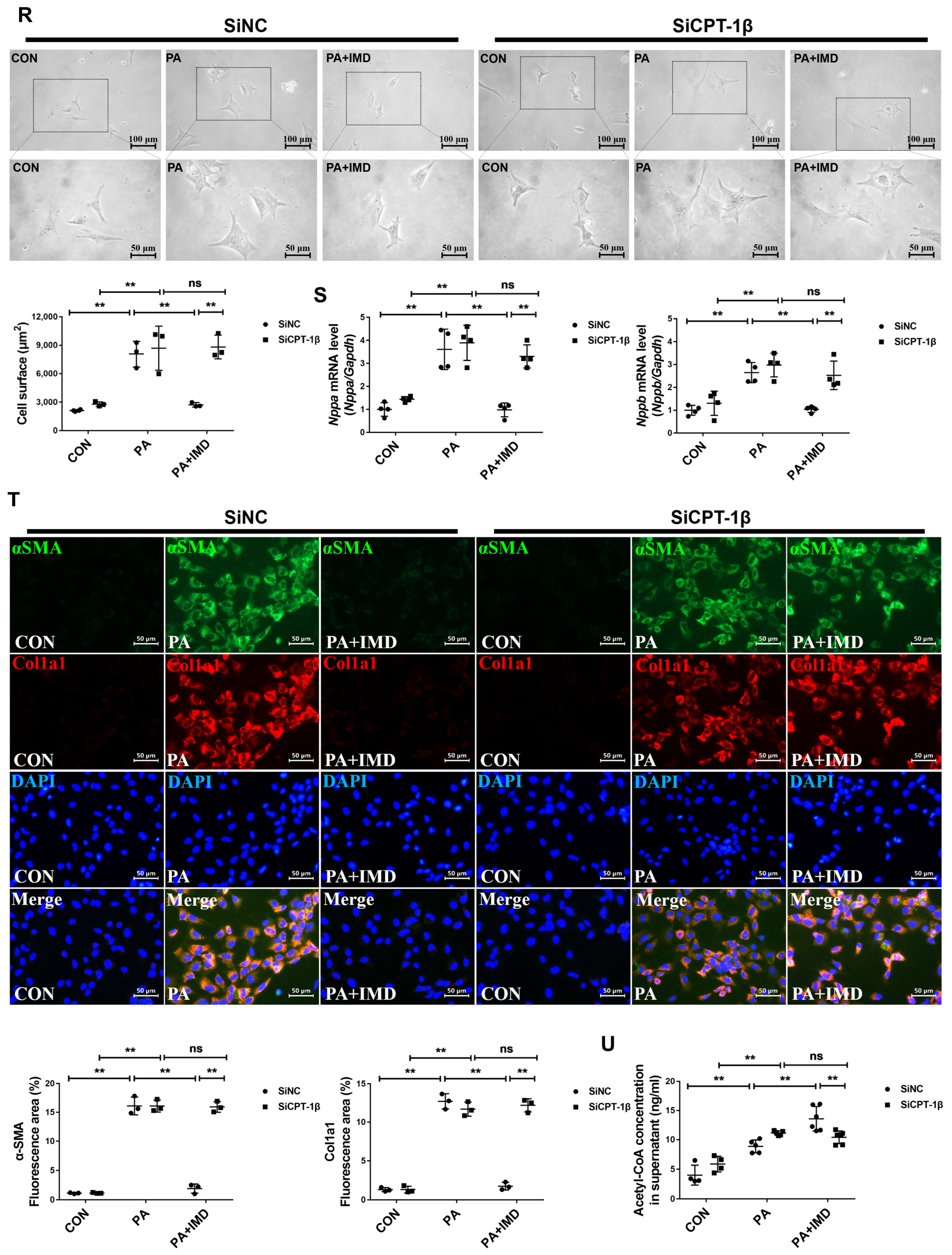
2.5. IMD Alleviates DCM by Up-Regulating CPT-1β
2.6. IMD Up-Regulates CPT-1β via the PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Human Subjects
4.2. Animals
4.3. DCM Models of Rats and Mice
4.4. Echocardiography
4.5. Blood Pressure Measurement
4.6. Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocyte (NRCM) and Cardiac Fibroblast Culture
4.7. H&E, Sirius Red, and Oil Red O Staining
4.8. Immunofluorescence Staining of Cardiac Fibroblast
4.9. Detection of Fasting Serum Glucose and Insulin and Homeostasis Model Assessment for Insulin Resistance (HOMA-IR) Analysis
4.10. Quantitation of Serum Lipids in Mice and Rats
4.11. ELISA
4.12. Western Blot Analysis
4.13. Quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis
4.14. RNA Sequencing
4.15. siRNA Transfection and Identification
4.16. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chan, J.C.N.; Lim, L.L.; Wareham, N.J.; Shaw, J.E.; Orchard, T.J.; Zhang, P.; Lau, E.S.H.; Eliasson, B.; Kong, A.P.S.; Ezzati, M.; et al. The lancet commission on diabetes: Using data to transform diabetes care and patient lives. Lancet 2021, 396, 2019–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, C.; Wintergerst, K.A.; Keller, B.B.; Cai, L. Mechanisms of diabetic cardiomyopathy and potential therapeutic strategies: Preclinical and clinical evidence. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2020, 17, 585–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Liu, C.; Chen, J.; Zhou, S.; Li, Y.; Zhao, X.; Xing, J.; Xue, J.; Liu, F.; Li, F. Endothelial MICU1 alleviates diabetic cardiomyopathy by attenuating nitrative stress-mediated cardiac microvascular injury. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2023, 22, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Geng, L.; Ying, L.; Shu, L.; Ye, K.; Yang, R.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cai, Y.; Jiang, X.; et al. FGF21-Sirtuin 3 axis confers the protective effects of exercise against diabetic cardiomyopathy by governing mitochondrial integrity. Circulation 2022, 146, 1537–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Einarson, T.R.; Acs, A.; Ludwig, C.; Panton, U.H. Prevalence of cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes: A systematic literature review of scientific evidence from across the world in 2007–2017. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2018, 17, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Quintana, M.T.; Sullivan, J.; Parry, T.L.; Grevengoed, T.J.; Schisler, J.C.; Hill, J.A.; Yates, C.C.; Mapanga, R.F.; Essop, M.F.; et al. MuRF2 regulates PPARγ1 activity to protect against diabetic cardiomyopathy and enhance weight gain induced by a high fat diet. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2015, 14, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riehle, C.; Bauersachs, J. Of mice and men: Models and mechanisms of diabetic cardiomyopathy. Basic. Res. Cardiol. 2018, 114, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopal, K.; Karwi, Q.G.; Dakhili, S.A.T.; Wagg, C.S.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Q.; Saed, C.T.; Panidarapu, S.; Perfetti, R.; Ramasamy, R.; et al. Aldose reductase inhibition alleviates diabetic cardiomyopathy and is associated with a decrease in myocardial fatty acid oxidation. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2023, 22, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, G.; Hill, M.A.; Sowers, J.R. Diabetic cardiomyopathy: An update of mechanisms contributing to this clinical entity. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 624–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, G.; DeMarco, V.G.; Sowers, J.R. Insulin resistance and hyperinsulinaemia in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2016, 12, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.L.; Karwi, Q.G.; Connolly, D.; Pherwani, S.; Ketema, E.B.; Ussher, J.R.; Lopaschuk, G.D. Metabolic, structural and biochemical changes in diabetes and the development of heart failure. Diabetologia 2022, 65, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, D.; Kolwicz, S.C., Jr.; Wang, P.; Roe, N.D.; Villet, O.; Nishi, K.; Hsu, Y.W.A.; Flint, G.V.; Caudal, A.; Wang, W.; et al. Increasing fatty acid oxidation prevents high-fat diet-induced cardiomyopathy through regulating parkin-mediated mitophagy. Circulation 2020, 142, 983–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drosatos, K.; Pollak, N.M.; Pol, C.J.; Ntziachristos, P.; Willecke, F.; Valenti, M.C.; Trent, C.M.; Hu, Y.; Guo, S.; Aifantis, I.; et al. Cardiac myocyte KLF5 regulates ppara expression and cardiac function. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wu, F.; Günther, S.; Looso, M.; Kuenne, C.; Zhang, T.; Wiesnet, M.; Klatt, S.; Zukunft, S.; Fleming, I.; et al. Inhibition of fatty acid oxidation enables heart regeneration in adult mice. Nature 2023, 622, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van-Weeghel, M.; Abdurrachim, D.; Nederlof, R.; Argmann, C.A.; Houtkooper, R.H.; Hagen, J.; Nabben, M.; Denis, S.; Ciapaite, J.; Kolwicz, S.C., Jr.; et al. Increased cardiac fatty acid oxidation in a mouse model with decreased malonyl-CoA sensitivity of CPT1B. Cardiovasc. Res. 2018, 114, 1324–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanley, W.C.; Recchia, F.A.; Lopaschuk, G.D. Myocardial substrate metabolism in the normal and failing heart. Physiol. Rev. 2005, 85, 1093–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Liu, T.; Husain, S.; Zhai, P.; Warren, J.S.; Hsu, C.P.; Matsuda, T.; Phiel, C.J.; Cox, J.E.; Tian, B.; et al. Glycogen synthase kinase-3α promotes fatty acid uptake and lipotoxic cardiomyopathy. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 1119–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, C.R.; Hoy, A.J.; Turner, N.; Watt, M.J.; Allen, T.L.; Carpenter, K.; Cooney, G.J.; Febbraio, M.A.; Kraegen, E.W. Overexpression of carnitine palmitoyltransferase-1 in skeletal muscle is sufficient to enhance fatty acid oxidation and improve high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance. Diabetes 2009, 58, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.M.; An, Z.N.; Ge, M.H.; Wei, D.Z.; Jiang, D.W.; Xing, X.J.; Shen, X.L.; Liu, C. Medium & long-chain acylcarnitine’s relation to lipid metabolism as potential predictors for diabetic cardiomyopathy: A metabolomic study. Lipids Health Dis. 2021, 20, 151. [Google Scholar]
- He, L.; Kim, T.; Long, Q.; Liu, J.; Wang, P.; Zhou, Y.; Ding, Y.; Prasain, J.; Wood, P.A.; Yang, Q. Carnitine palmitoyltransferase-1b deficiency aggravates pressure overload-induced cardiac hypertrophy caused by lipotoxicity. Circulation 2012, 126, 1705–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira-Lara, M.A.; Dommerholt, M.B.; Zhang, W.; Blankestijn, M.; Wolters, J.C.; Abegaz, F.; Gerding, A.; van der Veen, Y.T.; Thomas, R.; van Os, R.P.; et al. Age-related susceptibility to insulin resistance arises from a combination of CPT1B decline and lipid overload. BMC Biol. 2021, 19, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haynie, K.R.; Vandanmagsar, B.; Wicks, S.E.; Zhang, J.; Mynatt, R.L. Inhibition of carnitine palymitoyltransferase1b induces cardiac hypertrophy and mortality in mice. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2014, 16, 757–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yin, C.; Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; Zou, Y.; Wang, X.; An, Y.; Wu, F.; Zhang, G.; Yang, C.; et al. Cardiac-specific LRP6 knockout induces lipid accumulation through Drp1/CPT1b pathway in adult mice. Cell Tissue Res. 2020, 380, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora, C.; Pintado, C.; Rubio, B.; Mazuecos, L.; López, V.; Fernández, A.; Salamanca, A.; Bárcena, B.; Fernández-Agulló, T.; Arribas, C.; et al. Central leptin regulates heart lipid content by selectively increasing PPAR β/δ expression. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 236, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Yus, M.; Lopez-Perez, R.; Garcia-Sobreviela, M.P.; Moral-Bergos, R.D.; Lorente-Cebrian, S.; Arbones-Mainar, J.M. Adiponectin overexpression in C2C12 myocytes increases lipid oxidation and myofiber transition. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 78, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleckenstein-Elsen, M.; Dinnies, D.; Jelenik, T.; Roden, M.; Romacho, T.; Eckel, J. Eicosapentaenoic acid and arachidonic acid differentially regulate adipogenesis, acquisition of a brite phenotype and mitochondrial function in primary human adipocytes. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 60, 2065–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellieux, C.; Montessuit, C.; Papageorgiou, I.; Lerch, R. Angiotensin II downregulates the fatty acid oxidation pathway in adult rat cardiomyocytes via release of tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Cardiovasc. Res. 2009, 82, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, J.; Chang, C.L.; Bhalla, A.; Klein, C.; Hsu, S.Y.T. Intermedin is a calcitonin/calcitonin gene-related peptide family peptide acting through the calcitonin receptor-like receptor/receptor activity-modifying protein receptor complexes. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 7264–7274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takei, Y.; Inoue, K.; Ogoshi, M.; Kawahara, T.; Bannai, H.; Miyano, S. Identification of novel adrenomedullin in mammals: A potent cardiovascular and renal regulator. FEBS Lett. 2004, 556, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.Q.; Zhang, J.S.; Tang, C.S.; Qi, Y.F. Intermedin/adrenomedullin2: An autocrine/paracrine factor in vascular homeostasis and disease. Sci. China Life Sci. 2014, 57, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Xu, M.J.; Wang, X. Adrenomedullin 2/intermedin: A putative drug candidate for treatment of cardiometabolic diseases. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 1230–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Li, H.; Wu, P.; Li, Q.; Yu, C.Y.; Wang, D.; Li, W. Multi-biological functions of intermedin in diseases. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1233073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; Hay, D.L.; Quirion, R.; Poyner, D.R. The pharmacology of adrenomedullin 2/intermedin. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 166, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.S.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ren, J.L.; Zhang, Y.R.; Yu, Y.R.; Jia, M.Z.; Ning, Z.P.; Du, J.; Tang, C.S.; et al. Intermedin alleviates pathological cardiac remodeling by up-regulating klotho. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 159, 104926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.W.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J.S.; Hou, Y.L.; Yu, Y.R.; Jia, M.Z.; Tang, C.S.; Qi, Y.F. Intermedin1-53 protects against cardiac hypertrophy by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress via activating AMP-activated protein kinase. J. Hypertens. 2015, 33, 1676–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.S.; Zhang, J.S.; Hou, Y.L.; Lu, W.W.; Ni, X.Q.; Lin, F.; Liu, X.Y.; Wang, X.J.; Yu, Y.R.; Jia, M.Z.; et al. Intermedin1-53 inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation by targeting IRE1α in cardiac fibrosis. Inflammation 2022, 45, 1568–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.S.; Hou, Y.L.; Lu, W.W.; Ni, X.Q.; Lin, F.; Yu, Y.R.; Tang, C.S.; Qi, Y.F. Intermedin1-53 protects against myocardial fibrosis by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress and inflammation induced by homocysteine in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2016, 23, 1294–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, T.; Totsune, K.; Mori, N.; Morimoto, R.; Hashimoto, M.; Nakashige, Y.; Metoki, H.; Asayama, K.; Kikuya, M.; Ohkubo, T.; et al. Increased expression of adrenomedullin 2/intermedin in rat hearts with congestive heart failure. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2008, 10, 840–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tian, J.; Mi, Y.; Ren, X.; Lian, S.; Kang, J.; Wang, J.; Zang, H.; Wu, Z.; Yang, J.; et al. Experimental study on renoprotective effect of intermedin on diabetic nephropathy. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2021, 528, 111224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, S.Y.; Jiang, C.; Li, Y.; Xu, G.; Xu, M.J.; Wang, X. Intermedin/adrenomedullin 2 polypeptide promotes adipose tissue browning and reduces high-fat diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance in mice. Int. J. Obes. 2016, 40, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Li, Y.; Lv, Y.; Sun, L.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, G.; Xu, M.J.; Wang, X.; et al. Intermedin restores hyperhomocysteinemia-induced macrophage polarization and improves insulin resistance in mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 12336–12345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.L.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.S.; Zhang, Y.R.; Liu, S.M.; Yu, Y.R.; Jia, M.Z.; Tang, C.S.; Qi, Y.F.; Lu, W.W. Intermedin1-53 attenuates atherosclerotic plaque vulnerability by inhibiting CHOP-mediated apoptosis and inflammasome in macrophages. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sowers, J.R. Diabetes mellitus and vascular disease. Hypertension 2013, 61, 943–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Przezak, A.; Bielka, W.; Pawlik, A. Hypertension and type 2 diabetes-the novel treatment possibilities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.M.; Zhang, Y.R.; Chen, Y.; Ji, D.R.; Zhao, J.; Fu, S.; Jia, M.Z.; Yu, Y.R.; Tang, C.S.; Huang, W.; et al. Intermedin alleviates vascular calcification in CKD through Sirtuin 3-mediated inhibition of mitochondrial oxidative stress. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, C.; Du, Q.; Li, M.; Wang, R.; Ouyang, Q.; Su, S.; Zhu, S.; Chen, Q.; Sheng, Y.; Chen, L.; et al. A PKB-SPEG signaling nexus links insulin resistance with diabetic cardiomyopathy by regulating calcium homeostasis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Diepen, J.A.; Robben, J.H.; Hooiveld, G.J.; Carmone, C.; Alsady, M.; Boutens, L.; Bekkenkamp-Grovenstein, M.; Hijmans, A.; Engelke, U.F.H.; Wevers, R.A.; et al. SUCNR1-mediated chemotaxis of macrophages aggravates obesity-induced inflammation and diabetes. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 1304–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Salloum, F.N.; Filippone, S.M.; Durrant, D.E.; Rokosh, G.; Bolli, R.; Kukreja, R.C. Inhibition of mammalian target of rapamycin protects against reperfusion injury in diabetic heart through STAT3 signaling. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2015, 110, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydemann, A. An overview of murine high fat diet as a model for type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Diabetes Res. 2016, 2016, 2902351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, M.V.; Silljé, H.H.W.; Sijbesma, J.W.A.; Khan, M.A.F.; Steffensen, K.R.; van-Gilst, W.H.; de Boer, R.A. LXRα improves myocardial glucose tolerance and reduces cardiac hypertrophy in a mouse model of obesity-induced type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.R.; Liu, S.M.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.S.; Ji, D.R.; Zhao, J.; Yu, Y.R.; Jia, M.Z.; Tang, C.S.; Huang, W.; et al. Intermedin alleviates diabetic vascular calcification by inhibiting GLUT1 through activation of the cAMP/PKA signaling pathway. Atherosclerosis 2023, 385, 117342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakihara, S.; Matsuda, Y.; Hirabayashi, K.; Imai, A.; Iesato, Y.; Sakurai, T.; Kamiyoshi, A.; Tanaka, M.; Ichikawa-Shindo, Y.; Kawate, H.; et al. Role of adrenomedullin 2/intermedin in the pathogenesis of neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Lab. Investig. 2023, 103, 100038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.; Li, M.; Ma, A.; Wei, Y.; Huang, L.; Kong, L.; Kang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, F.; Zhang, W. Intermedin (adrenomedullin 2) plays a protective role in sepsis by regulating T- and B-cell proliferation and activity. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 121, 110488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Xiao, F.; Wang, L.; Li, M.; Wang, D.; Feng, Z.; Huang, L.; Wei, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, F.; et al. Intermedin promotes vessel fusion by inducing VE-cadherin accumulation at potential fusion sites and to achieve a dynamic balance between VE-cadherin-complex dissociation/reconstitution. MedComm 2020, 1, 84–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, F.; Wang, D.; Kong, L.; Li, M.; Feng, Z.; Shuai, B.; Wang, L.; Wei, Y.; Li, H.; Wu, S.; et al. Intermedin protects against sepsis by concurrently re-establishing the endothelial barrier and alleviating inflammatory responses. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Xiao, F.; Kong, L.M.; Wang, D.N.; Li, H.Y.; Wei, Y.G.; Tan, C.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, T.; Cao, G.Q.; et al. Intermedin enlarges the vascular lumen by inducing the quiescent endothelial cell proliferation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2018, 38, 398–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, M.A.; Birnbaum, M.J. Molecular aspects of fructose metabolism and metabolic disease. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 2329–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, S.S.; Rezq, S.; Alsemeh, A.A.; Han, Y.; Mahmoud, M.F. Moxonidine ameliorates cardiac injury in rats with metabolic syndrome by regulating autophagy. Life Sci. 2023, 312, 121210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, D.; Campbell, M.; Ferguson, M.; Sayers, L.; Donaghy, L.; O’Regan, A.; Jewhurst, V.; Harbinson, M. AM₁-receptor-dependent protection by intermedin of human vascular and cardiac non-vascular cells from ischaemia-reperfusion injury. J. Physiol. 2012, 590, 1181–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Bian, Y.F.; Zhang, N.N.; Guo, J.; Wang, C.; Bond Lau, W.; Xiao, C.S. Intermedin protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in diabetic rats. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2013, 12, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.X.; Gu, C.L.; Shen, F.; Zhang, X.M. Changes in expression of adrenomedullin in the myocardium of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Chin. Med. J. 2007, 120, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Guo, Z.; Liu, C.J.; Li, M.R.; Li, T.P.; Wang, X.; Yuan, D.J. Preservation of CGRP in myocardium attenuates development of cardiac dysfunction in diabetic rats. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 220, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Xu, H.; Cao, H.; Liu, X.X.; Qin, C.H.; Zhao, Y.Z.; Han, X.L.; Li, H.L. Intermedin improves cardiac function and sympathetic neural remodeling in a rat model of post myocardial infarction heart failure. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 1723–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Savova, M.S.; Mihaylova, L.V.; Tews, D.; Wabitsch, M.; Georgiev, M.I. Targeting PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in obesity. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 159, 114244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramasubbu, K.; Devi-Rajeswari, V. Impairment of insulin signaling pathway PI3K/Akt/mTOR and insulin resistance induced AGEs on diabetes mellitus and neurodegenerative diseases: A perspective review. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2023, 478, 1307–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultze, S.M.; Hemmings, B.A.; Niessen, M.; Tschopp, O. PI3K/AKT, MAPK and AMPK signalling: Protein kinases in glucose homeostasis. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2012, 14, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Mu, J.; Kim, J.K.; Thorvaldsen, J.L.; Chu, Q.; Crenshaw, E.B.; Kaestner, K.H.; Bartolomei, M.S.; Shulman, G.I.; Birnbaum, M.J. Insulin resistance and a diabetes mellitus-like syndrome in mice lacking the protein kinase Akt2 (PKB beta). Science 2001, 292, 1728–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H.; Ta, A.P.; Chen, Y.; Lee, H.C.; Fan, W.; Chen, P.L.; Jordan, M.C.; Roos, K.P.; MacGregor, G.R.; Yang, Q.; et al. Dual roles of myocardial mitochondrial AKT on diabetic cardiomyopathy and whole body metabolism. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2023, 22, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, M.; Okagawa, S.; Okubo, Y.; Otsuka, Y.; Fukuda, K.; Igata, M.; Kondo, T.; Sato, Y.; Yoshizawa, T.; Fukuda, T.; et al. Phosphatase protector alpha4 (α4) is involved in adipocyte maintenance and mitochondrial homeostasis through regulation of insulin signaling. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora, M.; Villena, J.A. Contribution of impaired insulin signaling to the pathogenesis of diabetic cardiomyopathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tate, M.; Deo, M.; Cao, A.H.; Hood, S.G.; Huynh, K.; Kiriazis, H.; Du, X.J.; Julius, T.L.; Figtree, G.A.; Dusting, G.J.; et al. Insulin replacement limits progression of diabetic cardiomyopathy in the low-dose streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat. Diab. Vasc. Dis. Res. 2017, 14, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krüger, M.; Babicz, K.; Frieling-Salewsky, M.V.; Linke, W.A. Insulin signaling regulates cardiac titin properties in heart development and diabetic cardiomyopathy. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2010, 48, 910–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouwens, D.M.; Diamant, M. Myocardial insulin action and the contribution of insulin resistance to the pathogenesis of diabetic cardiomyopathy. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2007, 113, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fein, F.S.; Strobeck, J.E.; Malhotra, A.; Scheuer, J.; Sonnenblick, E.H. Reversibility of diabetic cardiomyopathy with insulin in rats. Circ. Res. 1981, 49, 1251–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrzynski, E.; Montanari, D.; Agata, J.; Zhu, J.; Chao, J.; Chao, L. Adrenomedullin improves cardiac function and prevents renal damage in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 283, E1291–E1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.Q.; Zhang, Y.R.; Jia, L.X.; Lu, W.W.; Zhu, Q.; Ren, J.L.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.S.; Liu, X.; Yu, Y.R.; et al. Inhibition of Notch1-mediated inflammation by intermedin protects against abdominal aortic aneurysm via PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Aging 2021, 13, 5164–5184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Zhao, Y.; He, M.; Li, H.; Fan, J.; Nie, X.; Yan, M.; Chen, C.; Wang, D.W. MiR-30c/PGC-1β protects against diabetic cardiomyopathy via PPARα. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2019, 18, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhou, L.; Fan, Z.; Liu, S.; Fang, W. Palmitic acid, but not high-glucose, induced myocardial apoptosis is alleviated by N-acetylcysteine due to attenuated mitochondrial-derived ROS accumulation-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.H.; Ma, C.G.; Cai, Y.; Pan, C.S.; Zhao, J.; Tang, C.S.; Qi, Y.F. Effect of intermedin1-53 on angiotensin II-induced hypertrophy in neonatal rat ventricular myocytes. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2010, 56, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelini, A.; Saha, P.K.; Jain, A.; Jung, S.Y.; Mynatt, R.L.; Pi, X.; Xie, L. PHDs/CPT1B/VDAC1 axis regulates long-chain fatty acid oxidation in cardiomyocytes. Cell Rep. 2021, 37, 109767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haffner, S.M.; Miettinen, H.; Stern, M.P. The homeostasis model in the san antonio heart study. Diabetes Care 1997, 20, 1087–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, J.; Han, L.; Zhang, Y.-R.; Liu, S.-M.; Ji, D.-R.; Wang, R.; Yu, Y.-R.; Jia, M.-Z.; Chai, S.-B.; Tang, H.-F.; et al. Intermedin Alleviates Diabetic Cardiomyopathy by Up-Regulating CPT-1β through Activation of the Phosphatidyl Inositol 3 Kinase/Protein Kinase B Signaling Pathway. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1204. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091204
Zhao J, Han L, Zhang Y-R, Liu S-M, Ji D-R, Wang R, Yu Y-R, Jia M-Z, Chai S-B, Tang H-F, et al. Intermedin Alleviates Diabetic Cardiomyopathy by Up-Regulating CPT-1β through Activation of the Phosphatidyl Inositol 3 Kinase/Protein Kinase B Signaling Pathway. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(9):1204. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091204
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Jie, Ling Han, Ya-Rong Zhang, Shi-Meng Liu, Deng-Ren Ji, Rui Wang, Yan-Rong Yu, Mo-Zhi Jia, San-Bao Chai, Hui-Fang Tang, and et al. 2024. "Intermedin Alleviates Diabetic Cardiomyopathy by Up-Regulating CPT-1β through Activation of the Phosphatidyl Inositol 3 Kinase/Protein Kinase B Signaling Pathway" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 9: 1204. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091204
APA StyleZhao, J., Han, L., Zhang, Y.-R., Liu, S.-M., Ji, D.-R., Wang, R., Yu, Y.-R., Jia, M.-Z., Chai, S.-B., Tang, H.-F., Huang, W., & Qi, Y.-F. (2024). Intermedin Alleviates Diabetic Cardiomyopathy by Up-Regulating CPT-1β through Activation of the Phosphatidyl Inositol 3 Kinase/Protein Kinase B Signaling Pathway. Pharmaceuticals, 17(9), 1204. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091204




