Abstract
Background: Spasticity is a very common neurological sequelae that significantly impacts the quality of life of patients, affecting more than 12 million people worldwide. Botulinum toxin is considered a reversible treatment for spasticity, but due to the large amount of available evidence, synthesis seems necessary. Therefore, we conducted an overview of existing systematic reviews and meta-analyses to evaluate the effect of botulinum toxin injections in the treatment of spasticity of different etiologies. Methods: A systematic search of different databases, including Pubmed, Scopus, the Cochrane Library, and Web of Science, was performed from inception to February 2024. Standardized mean differences (SMDs) and their respective 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated to assess the effect of botulinum toxin compared to that of the control treatment using the Modified Ashworth Scale (MAS). All the statistical analyses were performed using STATA 15 software. Results: 28 studies were included in the umbrella review. The effect of botulinum toxin injections on spasticity, as measured by the MAS, was significantly lower in all but three studies, although these studies also supported the intervention. The SMDs reported by the meta-analyses ranged from −0.98 to −0.01. Conclusion: Botulinum toxin injections were effective at treating spasticity of different etiologies, as indicated by the measurements on the MAS. This implies an improvement in muscle tone and, consequently, in the patient’s mobility and quality of life.
1. Introduction
Spasticity is a highly prevalent neurological sequelae that significantly affects quality of life. It manifests as an intrinsic increase in muscle resistance related to the speed of the tonic reflex during passive stretching of a limb in individuals with upper motor neuron syndrome [1] (Figure 1). Spasticity leads to complications such as pain, a distorted joint position, postural and hygiene difficulties, joint contractures, and permanent deformities [2]. It is common in patients with central nervous system disorders such as stroke, multiple sclerosis, spinal cord injuries [3], traumatic brain injuries, and cerebral palsy (CP) [1]. Approximately 12 million people worldwide are estimated to suffer from spasticity [4].
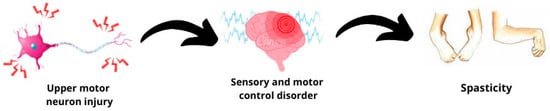
Figure 1.
Spasticity definition.
There are two scales used specifically to assess spasticity. The first is the Modified Ashworth Scale (MAS) [1,3], an ordinal scale that measures the intensity of muscle tone on a scale of 0 to 4 [3]. On this scale, 0 represents “no increase in tone,” while 4 indicates that the limb is “stiff in flexion or extension” [5] (Supplementary Table S1). The second is the Tardieu Scale or the Modified Tardieu Scale [1,3], which is also an ordinal scale that assesses the intensity of resistance to muscle stretch [3]. According to the Modified Tardieu Scale, each muscle group is rated for a specific stretching speed according to two parameters. The first is the quality of the muscle reaction, where 0 indicates no resistance to movement and 4 indicates that the occurrence of clonus lasted more than 10 s. The second parameter is the angle of muscle reaction, measured at the minimum stretching position of the muscle for all joints except the hip, where it is assessed in relation to the anatomical position at rest [5] (Supplementary Table S2).
The treatment of spasticity requires a multidisciplinary team, which includes medical specialists, occupational therapists, physiotherapists, nurses, and nutritionists, among others, to achieve the best results and improve patient quality of life [1]. There is evidence of the efficacy of different treatments for the improvement in spasticity, such as physiotherapy (stretching, use of orthoses, cryotherapy, heat, etc.), extracorporeal shock waves, oral medication, injections (such as botulinum toxin), intrathecal baclofen pumps, and surgical interventions [3]. In particular, botulinum toxin is considered a reversible treatment for spasticity and has been used for more than 30 years in patients with CP [6]. In poststroke patients, studies have shown an improvement in muscle tone, resulting in safe and effective therapy [7]. The different types of botulinum toxin injections used include Botox, Dysporter, Neurobloc, and Xenomin [6]. The administration dose depends on the patient’s weight, the number of muscles to be treated, the severity of spasticity, the size of the muscle, and the type of toxin [6,7].
Several systematic reviews and meta-analyses have shown that botulinum toxin injections are effective at reducing spasticity [8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17], with a peak effect occurring at 5 weeks [17] and decreasing efficacy at 12 weeks postintervention [10]. It is considered a safe therapy and is likely to improve the quality of life of poststroke patients [15,16]. Furthermore, it is an effective intervention for reducing spasticity in children with spasticity [18], particularly in children with CP [19]. Since no study has synthesized all the existing information on the effect of botulinum toxin injections, an umbrella review is needed to synthesize this information and evaluate the effect of the treatment on the reduction in spasticity. Therefore, we conducted an overview of existing systematic reviews and meta-analyses to assess the effect of botulinum toxin injections in the treatment of spasticity of different etiologies.
2. Methods
This umbrella review was conducted following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines [20] and the Cochrane Collaboration Handbook [21]. This study was registered in PROSPERO (Registration Number: 502078).
To conduct this umbrella review, a search strategy has been implemented using keywords and Boolean operators, following inclusion and exclusion criteria to identify all available reviews on the treatment of spasticity with botulinum toxin injections. Once the studies were selected, two tables were created to classify them, and their quality was assessed. Finally, data synthesis was performed.
2.1. Search Strategy
A search was conducted in the Pubmed, Scopus, Cochrane, and Web of Science databases from their inception to February 2024. The selected keywords were combined using Boolean operators (AND, OR) following the population, intervention, comparator, outcomes (PICO) strategy to identify studies assessing the effect of botulinum toxin in the treatment of spasticity (Supplementary Table S3). The search strategy used was as follows: ((“general population”) OR (“children”) OR (“adults”)) AND ((“botox”) OR (“botulinum toxin”)) AND ((“spasticity”) OR (“cerebral palsy”) OR (“spastic paraplegia)) AND ((“systematic review”) OR (“meta-analysis”) OR (“network meta-analysis”)). In addition, reference lists of the retrieved systematic reviews and meta-analyses were checked for additional studies.
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
The inclusion criteria were as follows: (i) population: general population (children and adults); (ii) intervention: botulinum toxin injections; (iii) outcome: spasticity assessed with the MAS and/or Modified Tardieu Scale; (iv) study design: systematic reviews and/or meta-analyses; and (v) no language restriction. The exclusion criteria were as follows: (i) articles combining botulinum toxin injections with other treatments; and (ii) articles evaluating outcomes other than efficacy and effectiveness in improving spasticity.
2.3. Data Extraction
Two ad hoc tables were created, one for systematic reviews and one for meta-analyses, where the data from the selected studies were included as follows: (1) reference (first author and year of publication); (2) study design (only for meta-analyses); (3) number of included studies; (4) type of population; (5) age range; (6) intervention; (7) comparator; (8) length of intervention (weeks); (9) spasticity assessment scale; (10) effect; and (11) assessment of study quality using the AMSTAR 2 scale (Table 1 and Table 2).

Table 1.
Characteristics of the included systematic reviews.

Table 2.
Characteristics of the included meta-analyses.
2.4. Methodological Quality Assessment
The quality of the selected studies was assessed using the AMSTAR 2 tool [39]. This tool critically evaluates the risk of bias in systematic reviews and consists of 16 different domains that assess relevant methodological aspects, each of which is answered “yes”, “no”, “cannot answer”, or “partial yes”. The overall quality of the studies was rated as high when there were no deficiencies or only one non-critical deficiency; moderate when there was more than one non-critical deficiency; low when there was a critical deficiency with or without non-critical deficiencies; and critically low with more than one critical deficiency with or without non-critical deficiencies.
Two researchers (I.O-l and A.S-L) independently conducted the study selection, data extraction, and assessment of the methodological quality of the included studies. Disagreements were resolved through consensus or by a third reviewer (I.C-R.).
2.5. Grading the Quality of Evidence
We used the Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) tool [40] to assess the quality of evidence and provide recommendations. Each outcome had a high, moderate, low, or very low evidence score, depending on the study design, risk of bias, inconsistency, indirect evidence, imprecision, and publication bias.
2.6. Data Synthesis
The DerSimonian and Laird random-effects method [41] was used to calculate pooled estimates of standardized mean differences (SMDs) and their respective 95% confidence intervals (95% CIs) to assess the effect of botulinum toxin injections compared to that of a control group using the MAS and they are displayed in a forest plot.
Heterogeneity was examined using the I2 statistic [42], which ranges from 0% to 100%. Based on the I2 values, heterogeneity was considered not important (0–30%), moderate (30–60%), substantial (60–75%), or considerable (75–100%). The corresponding p values were also considered.
A forest plot was generated using Stata SE software, version 15 (StataCorp, College Station, TX, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
The flowchart was created to summarize how the data extraction process was carried out in this manuscript.
Of the 519 manuscripts collected from different databases, 110 records were selected for full-text review after screening by title. Finally, 28 manuscripts were included in the umbrella review (Figure 2).
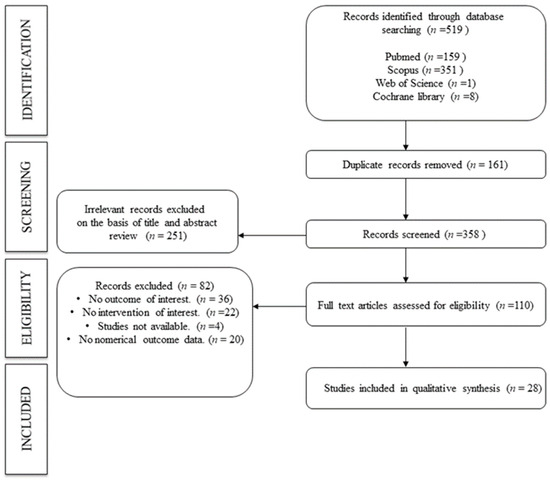
Figure 2.
Flowchart. Search strategy.
Two tables were created, one for systematic reviews (Table 1) and one for meta-analyses (Table 2), showing the characteristics of the studies included in this umbrella review. Of the total number of included studies, 12 were systematic reviews [22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33] and 16 were meta-analyses [8,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,34,35,36,37,38]. The studies included in this umbrella review were published between 2001 and 2023. The range of participants included in the studies was between 1 and 468. The study participants were children and adults with spasticity caused by CP or stroke aged between 8 months and 92 years. The duration of intervention ranged from 0 to 48 months. Almost all the included studies used the MAS [8,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,22,23,24,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,38,42], five used the Tardieu Scale [11,18,24,31,32], and five used the Modified Tardieu Scale [13,19,25,27,33].
In summary, two tables were created, one for systematic reviews and one for meta-analysis, which synthesize the data obtained from the records included in this study.
3.2. Methodological Quality Assessment and GRADE
To assess the quality of the studies, it is necessary to use a specific scale for systematic reviews and meta-analysis.
The methodological quality of the studies was assessed using the AMSTAR 2 tool. Of the total included studies, 35.71% were rated “high”, 50.00% were rated “moderate”, 7.14% were rated “low”, and 7.14% were rated “critically low” (Supplementary Tables S4 and S5).
When the GRADE was evaluated, 92.86 of the pairwise comparison studies were rated as low and 7.14 as very low (Supplementary Table S6).
In summary, most of the studies have achieved moderate quality in the AMSTAR 2 tool and most of the studies were rated as low in the GRADE tool.
3.3. Data Synthesis
A forest plot of the included meta-analyses has been conducted to assess the effectiveness of botulinum toxin injections on spasticity.
Figure 3 shows the forest plot of the meta-analyses included in the umbrella review assessing the effectiveness of botulinum toxin injections compared to the control group. The SMD reported by the meta-analyses ranged from −0.98 to −0.01. All the studies except three showed a significant reduction in spasticity measured with the MAS (18,38,39), which, although not significant, was in favor of the intervention (standardized mean difference (SMD): −0.04; 95% CI: −0.14, 0.05; SMD: −0.27; 95% CI: −0.80, 0.26; and SMD: −0.1; 95% CI: −0.3, 0.1). Overall heterogeneity in the forest plot was considerable (94.9%). Therefore, there is a significant reduction in spasticity and a reduction in muscle tone according to the MAS.
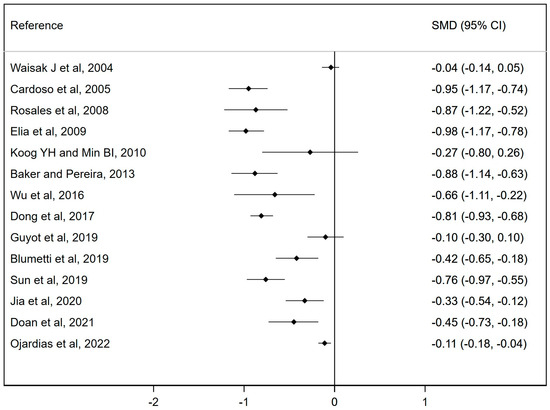
Figure 3.
Forest plot for the effect of botulinum toxin injections on spasticity measured by the MAS [10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,35,36,37,38].
In summary, in all studies, the results were favourable to the intervention, showing significant results in 78.57% of the studies.
3.4. Effectiveness of Botulinum Toxin Injection
The impact of botulinum toxin injections in clinical practice needs to be evaluated, as shown below. Our results indicate that botulinum toxin decreases spasticity assessed by the MAS. Studies suggest that in clinical practice, this therapy reduces spasticity, decreasing muscle tone, resulting in a reduction in the MAS [15,19]. This reduction occurs both in poststroke patients [15] and in children with CP [19].
In summary, both in the results obtained and in clinical practice, a reduction in spasticity is shown.
4. Discussion
4.1. Main Findings
This umbrella review aimed to analyze the effect of botulinum toxin injections in the treatment of spasticity of different etiologies using the MAS. This study provided significant evidence on the effectiveness of botulinum toxin injections in reducing muscle tone, as measured by the MAS, as indicated by a decrease in spasticity.
4.2. Interpretation
According to the studies reviewed, botulinum toxin injections can improve lower limb spasticity in children with CP [19] and can be used in combination with other therapies, such as physiotherapy [29,38] or physical activity [27]. One study supported the efficacy of botulinum toxin injections in children under two years of age with CP and highlighted the safety of its use [33]. Regarding patients with poststroke spasticity, the authors reported that botulinum toxin injections reduce spasticity in both the upper and lower limbs, suggesting that botulinum toxin is a safe treatment option [11,12,14,15,22,26]. However, according to one study, the effects of the treatment decreased 12 weeks after application [10].
Botulinum toxin, when injected at high concentrations, strongly affects the management of spasticity by blocking the release of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine from the neuromuscular junction to various muscle groups, resulting in what is known as “chemical denervation” [3]. Neuromuscular blockade affects both intrafusal and extrafusal muscle fibers. The decrease in activity of intrafusal muscle fibers (reduction in afferent input) peaks at 2 weeks and gradually decreases by 12 weeks post-injection. This blockade reduces the flow of muscle spindles to spinal stretch reflex circuits, reducing spasticity [2] (Figure 4). Botulinum toxin doses are usually adjusted according to factors such as the severity of spasticity, number of muscles affected, age, previous response to botulinum toxin treatment, and the use of adjuvant therapy. The development of antibodies against botulinum toxin proteins can lead to therapeutic failure. To avoid this, increasing the dose of botulinum toxin, avoiding short intervals between injections, and using different botulinum toxin serotypes are suggested [7]. Based on the studies reviewed, this therapy is generally well tolerated and safe, although botulinum toxin injections can cause fatigue, tiredness, pain, skin rashes, flu-like symptoms, worsening of spasms, weakness, convulsions, and incoordination [12,26]. Compared to other therapies, such as intrathecal baclofen, the incidence of treatment-related adverse effects is low [27].
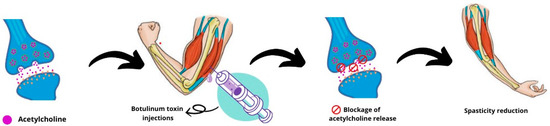
Figure 4.
Mechanism of action of botulinum toxin injections on spasticity.
Botulinum toxin is the most widespread treatment for spasticity [43], although there are other effective treatments, such as intrathecal baclofen pumps; surgical procedures, such as selective dorsal rhizotomy; physiotherapy, such as extracorporeal shockwave therapy; and oral medication [3]. Botulinum toxin is a very versatile treatment option because it can be combined with other agents, such as extracorporeal shockwave therapy, physiotherapy and rehabilitation, and splints and casts [2].
A study in poststroke patients, in which different doses were analyzed, reports that regardless of the dose and type of botulinum toxin used, there was a reduction in the MAS, with the maximum reduction occurring between weeks 4 and 6 post-injection [16]. One of the reviewed studies reports that there was no difference in spasticity reduction between the application of 100 U of botulinum toxin combined with short-term electrical stimulation and the application of a high dose of 400 U [12]. Another study mentions that the number of muscles treated and the dose per patient vary depending on the spasticity pattern, patient size, and the residual function of the affected limb [26]. A study in children with CP concluded that the efficacy of injections was not significantly better when higher doses of botulinum toxin were used [32]
4.3. Clinical Implications
Based on the evidence reviewed, botulinum toxin injections effectively decrease muscle tone in both limbs in poststroke spasticity, improving quality of life and showing to be a safe therapeutic agent [13,15]. In addition, botulinum toxin injections are effective in improving gait, range of motion, spasticity, and caregiver satisfaction in patients with CP, mainly when assessed in the medium- to short-term [19]. Despite the abundance of evidence on botulinum toxin injections, randomized clinical trials in different etiologies, adjusting for dosage, injection site, and age, are needed to adequately assess the efficacy of this therapy and generalize it to daily clinical practice.
4.4. Limitations
This study has several limitations. Firstly, several meta-analyses were conducted with a limited number of studies due to the low prevalence of disease spasticity-associated conditions. Secondly, there is variability in botulinum toxin doses and application sites among studies, which influences the results and complicates the generation of generalizable conclusions. Thirdly, several primary studies were included in more than one meta-analysis, potentially increasing the influence of these studies. Although these overlapping studies provided the most rigorous and consistent evidence, the possible presence of regression-to-mean bias prevents us from making a pooled estimate of the estimates from the analyses. Fourthly, the results presented in our umbrella review showed considerable heterogeneity, which may be due to differences between population groups, age ranges, types of botulinum toxin, and injection protocols, so these conclusions should be interpreted with caution.
5. Conclusions
In summary, the analyses in this umbrella review demonstrate the efficacy of botulinum toxin injections in reducing spasticity as measured by the MAS, both in patients with CP and poststroke, leading to an improvement in the patient’s quality of life. Botulinum toxin injection therapy is considered reversible and safe and can be used in conjunction with other treatments such as physiotherapy and physical activity. However, further randomized clinical trials conducted in populations with different etiologies and adjusted for dosage, injection site, and age are needed to generalize this therapy to daily clinical practice.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ph17030310/s1, Supplementary Table S1: Modified Ashworth Scale; Supplementary Table S2: Modified Tardieu Scale; Supplementary Table S3: search strategy; Supplementary Table S4: assessment of the methodological quality of the included systematic reviews using the AMSTAR 2 tool; Supplementary Table S5: assessment of the methodological quality of the included meta-analyses using the AMSTAR 2 tool; Supplementary Table S6: Quality grading of evidence.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.O.-L., A.S.-L. and I.C.-R.; methodology, I.O.-L., I.M.-G. and I.C.-R.; software, I.C.-R. and I.M.-G.; validation, A.S.-L. and N.M.-H.; formal analysis, I.O.-L. and A.M.-R.; investigation, I.O.-L. and I.C.-R.; resources, I.O.-L., A.S.-L. and N.M.-H.; data curation, I.C.-R. and I.M.-G.; writing—original draft preparation, I.O.-L. and I.C.-R.; writing—review and editing, A.M.-R.; visualization, A.S.-L. and A.M.-R.; supervision, I.C.-R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by ERDF funds and partially supported by Castilla-La Mancha Regional Government/FEDER, UE, Grant/Award Number SBPLY/21/180501/000186. N.M.-H. is supported by a grant from Junta de Comunidades de Castilla-La Mancha (2023-PREJCCM-000062). I.M.-G.is supported by a Grant from the science, innovation, and universities (FPU21/06866).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Gómez-Vega, J.C.; Ocampo-Navia, M.I.; Acevedo-González, J.C. Espasticidad. Univ. Med. 2021, 62, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Francisco, G.E. The Use of Botulinum Toxin for Treatment of Spasticity. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2021, 263, 127–146. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, I.M.; Patel, A.T. Spasticity evaluation and management tools. Muscle Nerve 2023, 67, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spasticity. Jhon Hopkins Medicine. Available online: https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/spasticity (accessed on 4 January 2024).
- Yam, W.K.L.; Leung, M.S.M. Interrater Reliability of Modified Ashworth Scale and Modified Tardieu Scale in Children with Spastic Cerebral Palsy. J. Child Neurol. 2006, 21, 1031–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hareb, F.; Bertoncelli, C.M.; Rosello, O.; Rampal, V.; Solla, F. Botulinum Toxin in Children with Cerebral Palsy: An Update. Neuropediatrics 2020, 51, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcakir, S.; Sivrioglu, K. Botulinum toxin in poststroke spasticity. Clin. Med. Res. 2007, 5, 132–138. Available online: https://www.scopus.com/inwards/record.uri?eid=2-s2.0-38949130542&doi=10.3121%2Fcmr.2007.716&partnerID=40&md5=e5cfa8bd4fe44da9aa059bf02eb7ad15 (accessed on 4 January 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varvarousis, D.N.; Martzivanou, C.; Dimopoulos, D.; Dimakopoulos, G.; Vasileiadis, G.I.; Ploumis, A. The effectiveness of botulinum toxin on spasticity and gait of hemiplegic patients after stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Toxicon 2021, 203, 74–84. Available online: https://www.scopus.com/inwards/record.uri?eid=2-s2.0-85116759676&doi=10.1016%2Fj.toxicon.2021.09.020&partnerID=40&md5=aaf19f612382da8660283ad6df767429 (accessed on 5 January 2024). [CrossRef]
- Andringa, A.; van de Port, I.; van Wegen, E.; Ket, J.; Meskers, C.; Kwakkel, G. Effectiveness of Botulinum Toxin Treatment for Upper Limb Spasticity Poststroke Over Different ICF Domains: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2019, 100, 1703–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.-C.; Chen, R.; Fu, C.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Q.; Chen, R.; Lin, X.; Luo, S. Efficacy and Safety of Botulinum Toxin Type A for Limb Spasticity after Stroke: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 8329306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Wu, T.; Hu, X.; Wang, T. Efficacy and safety of botulinum toxin type A for upper limb spasticity after stroke or traumatic brain injury: A systematic review with meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2017, 53, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Li, J.H.; Song, H.X.; Dong, Y. Effectiveness of Botulinum Toxin for Lower Limbs Spasticity after Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Top. Stroke Rehabil. 2016, 23, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J.A.; Pereira, G. The efficacy of Botulinum Toxin A for spasticity and pain in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis using the Grades of Recommendation, Assessment, Development and Evaluation approach. Clin. Rehabil. 2013, 27, 1084–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elia, A.E.; Filippini, G.; Calandrella, D.; Albanese, A. Botulinum neurotoxins for poststroke spasticity in adults: A systematic review. Mov. Disord. 2009, 24, 801–812. Available online: https://www.scopus.com/inwards/record.uri?eid=2-s2.0-67651159120&doi=10.1002%2Fmds.22452&partnerID=40&md5=be6e58937f4e53e1d93b40def20038ec (accessed on 5 January 2024). [CrossRef]
- Rosales, R.L.; Chua-Yap, A.S. Evidence-based systematic review on the efficacy and safety of botulinum toxin-A therapy in poststroke spasticity. J. Neural Transm. 2008, 115, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, E.; Rodrigues, B.; Lucena, R.; Oliveira, I.R.; Pedreira, G.; Melo, A. Botulinum toxin type a for the treatment of the upper limb spasticity after stroke: A meta-analysis. Arq. Neuro-Psiquiatr. 2005, 63, 30–33. Available online: https://www.cochranelibrary.com/central/doi/10.1002/central/CN-01733102/full (accessed on 5 January 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojardias, E.; Ollier, E.; Lafaie, L.; Celarier, T.; Giraux, P.; Bertoletti, L. Time course response after single injection of botulinum toxin to treat spasticity after stroke: Systematic review with pharmacodynamic model-based meta-analysis. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2022, 5, 101579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guyot, P.; Kalyvas, C.; Mamane, C.; Danchenko, N. Botulinum Toxins Type A (Bont-A) in the Management of Lower Limb Spasticity in Children: A Systematic Literature Review and Bayesian Network Meta-analysis. J. Child. Neurol. 2019, 34, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blumetti, F.C.; Belloti, J.C.; Tamaoki, M.J.S.; Pinto, J.A. Botulinum toxin type A in the treatment of lower limb spasticity in children with cerebral palsy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 10, 1465–1858. Available online: https://www.scopus.com/inwards/record.uri?eid=2-s2.0-85081238483&doi=10.1002%2F14651858.CD001408.pub2&partnerID=40&md5=77afa62b48aaa38abb4593c77c67d248 (accessed on 5 January 2024).
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, 2020–2021. [Google Scholar]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Green, S. Selecting studies and collecting data. In Cochrane Handbook of Systematic Reviews of Interventions; Version 5.1.0; The Cochrane Collaboration: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Reeuwijk, A.; van Schie, P.E.M.; Becher, J.G.; Kwakkel, G. Effects of botulinum toxin type A on upper limb function in children with cerebral palsy: A systematic review. Clin. Rehabil. 2006, 20, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demetrios, M.; Khan, F.; Turner-Stokes, L.; Brand, C.; McSweeney, S. Multidisciplinary rehabilitation following botulinum toxin and other focal intramuscular treatment for poststroke spasticity. Cochrane database Syst. Rev. 2013, CD009689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phadke, C.P.; Ismail, F.; Boulias, C.; Gage, W.; Mochizuki, G. The impact of poststroke spasticity and botulinum toxin on standing balance: A systematic review. Expert. Rev. Neurother. 2014, 14, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garciá Salazar, L.F.; Santos, G.L.D.; Pavaõ, S.L.; Rocha, N.A.C.F.; Russo, T.L.D. Intrinsic properties and functional changes in spastic muscle after application of BTX-A in children with cerebral palsy: Systematic review. Dev. Neurorehabil. 2015, 18, 1–14. Available online: https://www.scopus.com/inwards/record.uri?eid=2-s2.0-84920997967&doi=10.3109%2F17518423.2014.948640&partnerID=40&md5=87218f9e6a1ee5b51a8bf9bc1c9fe04d (accessed on 5 January 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dashtipour, K.; Chen, J.J.; Walker, H.W.; Lee, M.Y. Systematic literature review of abobotulinumtoxinA in clinical trials for adult upper limb spasticity. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2015, 94, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Fonseca, P.R.J.; Calhes Franco de Moura, R.; Galli, M.; Santos Oliveira, C. Effect of physiotherapeutic intervention on the gait after the application of botulinum toxin in children with cerebral palsy: Systematic review. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2017, 54, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.D.; Chu, W.H.; Howell, S.; Chakraborty, S.; Koblar, S.; Visvanathan, R.; Cameron, I.; Wilson, D. A systematic review: Efficacy of botulinum toxin in walking and quality of life in poststroke lower limb spasticity. Syst. Rev. 2018, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yana, M.; Tutuola, F.; Westwater-Wood, S.; Kavlak, E. The efficacy of botulinum toxin A lower limb injections in addition to physiotherapy approaches in children with cerebral palsy: A systematic review. NeuroRehabilitation 2019, 44, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, T.; Momosaki, R.; Niimi, M.; Yamada, N.; Hara, H.; Abo, M. Botulinum Toxin Therapy Combined with Rehabilitation for Stroke: A Systematic Review of Effect on Motor Function. Toxins 2019, 11, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, S.M.; Mohammed, M.O.; El-Sobky, T.A.; ElKadery, N.A.; ElZohiery, A.K. Botulinum Toxin a Injection in Treatment of Upper Limb Spasticity in Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. JBJS Rev. 2020, 8, e0119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, C.; Gouron, R.; Barbier, V. Effects of botulinum toxin injections in the upper limbs of children with cerebral palsy: A systematic review of the literature. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2023, 103578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Chen, S.; Shen, J.; Chen, Y.; Lai, M.; Chen, L.; Fang, S. Safety and Efficacy of Botulinum Toxin Type A in Children with Spastic Cerebral Palsy Aged < 2 Years: A Systematic Review. J. Child. Neurol. 2023, 38, 454–465. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boyd, R.N.; Hays, R.M. Current evidence for the use of botulinum toxin type A in the management of children with cerebral palsy: A systematic review. Eur. J. Neurol. 2001, 8, 1–20. Available online: https://www.scopus.com/inwards/record.uri?eid=2-s2.0-0035502461&doi=10.1046%2Fj.1468-1331.2001.00034.x&partnerID=40&md5=2430a1c0dc0110a9fd929296314ce53e (accessed on 5 January 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasiak, J.; Hoare, B.; Wallen, M. Botulinum toxin A as an adjunct to treatment in the management of the upper limb in children with spastic cerebral palsy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2004, CD003469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koog, Y.H.; Min, B.-I. Effects of botulinum toxin A on calf muscles in children with cerebral palsy: A systematic review. Clin. Rehabil. 2010, 24, 685–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, S.; Liu, Y.; Shen, L.; Liang, X.; Xu, X.; Wei, Y. Botulinum Toxin Type A for Upper Limb Spasticity in Poststroke Patients: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. Off. J. Natl. Stroke Assoc. 2020, 29, 104682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doan, T.-N.; Kuo, M.-Y.; Chou, L.-W. Efficacy and Optimal Dose of Botulinum Toxin A in Post-Stroke Lower Extremity Spasticity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Toxins 2021, 13, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shea, B.J.; Reeves, B.C.; Wells, G.; Thuku, M.; Hamel, C.; Moran, J.; Moher, D.; Tugwell, P.; Welch, V.; Kristjansson, E.; et al. AMSTAR 2: A critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomized or nonrandomized studies of healthcare interventions, or both. BMJ 2017, 358, j4008.23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guyatt, G.H.; Oxman, A.D.; Schünemann, H.J.; Tugwell PKnottnerus, A. GRADE guidelines: A new series of articles in the Journal of Clinical Epidemiology. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2011, 64, 380–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DerSimonian, R.; Kacker, R. Random-effects model for meta-analysis of clinical trials: An update. Contemp. Clin. Trials. 2007, 28, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 2002, 21, 1539–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, O.; Yelnik, A. Managing spasticity with drugs. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2010, 46, 401–410. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).