Determining the Oxidation Mechanism through Radical Intermediates in Polysorbates 80 and 20 by Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. EPR Spectroscopy Method Optimization
2.2. Radical Adduct Identification
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ionova, Y.; Wilson, L. Biologic excipients: Importance of clinical awareness of inactive ingredients. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0235076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekewe, A.; Connors, N.K.; Sainsbury, F.; Wibowo, N.; Lua, L.H.L.; Middelberg, A.P.J. A rapid and simple screening method to identify conditions for enhanced stability of modular vaccine candidates. Biochem. Eng. J. 2015, 100, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkert, C.; Freyburger, A.; Huber, V.; Touraud, D.; Kunz, W. Development of a fully water-dilutable mint concentrate based on a food-approved microemulsion. Food Chem. 2022, 372, 131230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarkhed, M.; O’Dell, C.; Hsieh, M.C.; Zhang, J.; Goldstein, J.; Srivastava, A. Effect of Surfactants on Mechanical, Thermal, and Photostability of a Monoclonal Antibody. AAPS PharmSciTech 2018, 19, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottrell, T.; Peij, J.V. Sorbitan Esters and Polysorbates. In Emulsifiers in Food Technology, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 271–296. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Hewitt, D.; Lentz, Y.K.; Ji, J.A.; Zhang, T.Y.; Zhang, K. Characterization and stability study of polysorbate 20 in therapeutic monoclonal antibody formulation by multidimensional ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography-charged aerosol detection-mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 5150–5157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerwin, B.A. Polysorbates 20 and 80 used in the formulation of protein biotherapeutics: Structure and degradation pathways. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 2924–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borisov, O.V.; Ji, J.A.; Wang, Y.J.; Vega, F.; Ling, V.T. Toward understanding molecular heterogeneity of polysorbates by application of liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry with computer-aided data analysis. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 3934–3942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishore, R.S.K.; Kiese, S.; Fischer, S.; Pappenberger, A.; Grauschopf, U.; Mahler, H.C. The degradation of polysorbates 20 and 80 and its potential impact on the stability of biotherapeutics. Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 1194–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishore, R.S.K.; Pappenberger, A.; Dauphin, I.B.; Ross, A.; Buergi, B.; Staempfli, A.; Mahler, H.C. Degradation of polysorbates 20 and 80: Studies on thermal autoxidation and hydrolysis. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yadav, S.; Demeule, B.; Wang, Y.J.; Mozziconacci, O.; Schöneich, C. Degradation Mechanisms of Polysorbate 20 Differentiated by 18O-labeling and Mass Spectrometry. Pharm. Res. 2017, 34, 84–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, L.M.; Sharma, A.N.; Gopalrathnam, G.; Huang, L.; Bradley, S. A mechanistic understanding of polysorbate 80 oxidation in histidine and citrate buffer systems—Part 2. PDA J. Pharm. Sci. Technol. 2019, 73, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmon, P.A.; Kosuda, K.; Nelson, E.; Mowery, M.; Reed, R.A. A novel peroxy radical based oxidative stressing system for ranking the oxidizability of drug substances. J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 95, 2014–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brovč, E.V.; Mravljak, J.; Šink, R.; Pajk, S. Degradation of polysorbates 20 and 80 catalysed by histidine chloride buffer. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2020, 154, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Yadav, S.; John Wang, Y.; Mozziconacci, O.; Schöneich, C. Dual Effect of Histidine on Polysorbate 20 Stability: Mechanistic Studies. Pharm. Res. 2018, 35, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bensaid, F.; Dagallier, C.; Authelin, J.R.; Audat, H.; Filipe, V.; Narradon, C.; Guibal, P.; Clavier, S.; Wils, P. Mechanistic understanding of metal-catalyzed oxidation of polysorbate 80 and monoclonal antibody in biotherapeutic formulations. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 615, 121496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, J.; Buske, J.; Mäder, K.; Garidel, P.; Diederichs, T. Oxidation of polysorbates—An underestimated degradation pathway? Int. J. Pharm. X 2023, 6, 100202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuchner, K.; Yi, L.; Chery, C.; Nikels, F.; Junge, F.; Crotts, G.; Rinaldi, G.; Starkey, J.A.; Bechtold-Peters, K.; Shuman, M.; et al. Industry Perspective on the Use and Characterization of Polysorbates for Biopharmaceutical Products Part 2: Survey Report on Control Strategy Preparing for the Future. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 111, 2955–2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donbrow, M.; Azaz, E.; Pillersdorf, A. Autoxidation of polysorbates. J. Pharm. Sci. 1978, 67, 1676–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Dokuru, D.K.; Noestheden, M.; Park, S.S.; Kerwin, B.A.; Jona, J.; Ostovic, D.; Reid, D.L. A quantitative kinetic study of polysorbate autoxidation: The role of unsaturated fatty acid ester substituents. Pharm. Res. 2009, 26, 2303–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittag, J.J.; Trutschel, M.L.; Kruschwitz, H.; Mäder, K.; Buske, J.; Garidel, P. Characterization of radicals in polysorbate 80 using electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectroscopy and spin trapping. Int. J. Pharm. X 2022, 4, 100123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Jin, Y.; Menon, R.; Laskowich, E.; Bareford, L.; de Vilmorin, P.; Kolwyck, D.; Yeung, B.; Yi, L. Characterization of Polysorbate 80 by Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry to Understand Its Susceptibility to Degradation and Its Oxidative Degradation Pathway. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 111, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, M.J.; Billiar, T.R.; Stoyanovsky, D.A. N-tert-butylmethanimine N-oxide is an efficient spin-trapping probe for EPR analysis of glutathione thiyl radical. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buettner, G.R. Spin Trapping: ESR parameters of spin adducts 1474 1528V. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1987, 3, 259–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potapenko, D.I.; Bagryanskaya, E.G.; Reznikov, V.V.; Clanton, T.L.; Khramtsov, V.V. NMR and EPR studies of the reaction of nucleophilic addition of (bi) sulfite to the nitrone spin trap DMPO. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2003, 41, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorio, C.; Campbell, S.J.; Bruschi, M.; Tampieri, F.; Barbon, A.; Toffoletti, A.; Tapparo, A.; Paijens, C.; Wedlake, A.J.; Grice, P.; et al. Online Quantification of Criegee Intermediates of α-Pinene Ozonolysis by Stabilization with Spin Traps and Proton-Transfer Reaction Mass Spectrometry Detection. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 3999–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Sutton, A.T.; Yang, R.S.; Miller, D.V.; Pagels, B.; Rustandi, R.R.; Welch, J.; Payne, A.; Haverick, M. Extensive Characterization of Polysorbate 80 Oxidative Degradation Under Stainless Steel Conditions. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 112, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Kutsuna, S.; Yamane, S.; Mizukado, J. ESR spin trapping determination of the hydroperoxide concentration in polyethylene oxide (PEO) in aqueous solution. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2017, 139, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroën, K.; Berton-Carabin, C.C. A unifying approach to lipid oxidation in emulsions: Modelling and experimental validation. Food Res. Int. 2022, 160, 111621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drouza, C.; Dieronitou, A.; Hadjiadamou, I.; Stylianou, M. Investigation of Phenols Activity in Early Stage Oxidation of Edible Oils by Electron Paramagnetic Resonance and 19F NMR Spectroscopies Using Novel Lipid Vanadium Complexes As Radical Initiators. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 4942–4951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoutas, D.; Haralabopoulos, D.; Avramiotis, S.; Sotiroudis, T.G.; Xenakis, A. Virgin olive oil: Free radical production studied with spin-trapping electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy. JAOCS J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2001, 78, 1121–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikalov, S.I.; Mason, R.P. Spin trapping of polyunsaturated fatty acid-derived peroxyl radicals: Reassignment to alkoxyl radical adducts. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2001, 30, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cao, P.; Liu, Y. Degradation of Edible Oil During Deep-Frying Process by Electron Spin Resonance Spectroscopy and Physicochemical Appreciation. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2018, 120, 1700376–1700386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, X.M.; Lai, W.G.; Chan, E.K.; Ling, V.; Hsu, C.C. Site-specific tryptophan oxidation induced by autocatalytic reaction of polysorbate 20 in protein formulation. Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 2543–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Cao, P.; Liu, Y. Thermal Oxidation Rate of Oleic Acid Increased Dramatically at 140 °C Studied using Electron Spin Resonance and GC–MS/MS. JAOCS J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2019, 96, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, B.K.; Eliot, H.M.; Kalayanaraman, B. Iron-dependent hydroxyl radical formation and DNA damage from a novel metabolite of the clinically active antitumor drug VP-16. FEBS Lett. 1988, 227, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, B.K.; Katki, A.G.; Batist, G.; Cowan, K.H.; Myers, C.E. Differential Formation of Hydroxyl Radicals by Adriamycin in Sensitive and Resistant MCF-7 Human Breast Tumor Cells: Implications for the Mechanism of Action. Biochemistry 1987, 26, 3776–3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sainte Claire, P. Degradation of PEO in the solid state: A theoretical kinetic model. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 3469–3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morlat, S.; Gardette, J.L. Phototransformation of water-soluble polymers. I: Photo- and thermooxidation of poly(ethylene oxide) in solid state. Polymer 2001, 42, 6071–6079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Xue, Y.; Lü, Z.G.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Q.; Shi, N.; Sun, F. Self-accelerating decomposition temperature and quantitative structure-property relationship of organic peroxides. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2015, 94, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozuch, B.; Weber, J.; Buske, J.; Mäder, K.; Garidel, P.; Diederichs, T. Comparative Stability Study of Polysorbate 20 and Polysorbate 80 Related to Oxidative Degradation. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talbot, G. The stability and shelf life of fats and oils. In The Stability and Shelf Life of Food; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; pp. 461–503. [Google Scholar]
- Musakhanian, J.; Rodier, J.D.; Dave, M. Oxidative Stability in Lipid Formulations: A Review of the Mechanisms, Drivers, and Inhibitors of Oxidation. AAPS PharmSciTech 2022, 23, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borisov, O.V.; Ji, J.A.; Wang, Y.J. Oxidative degradation of polysorbate surfactants studied by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 1005–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
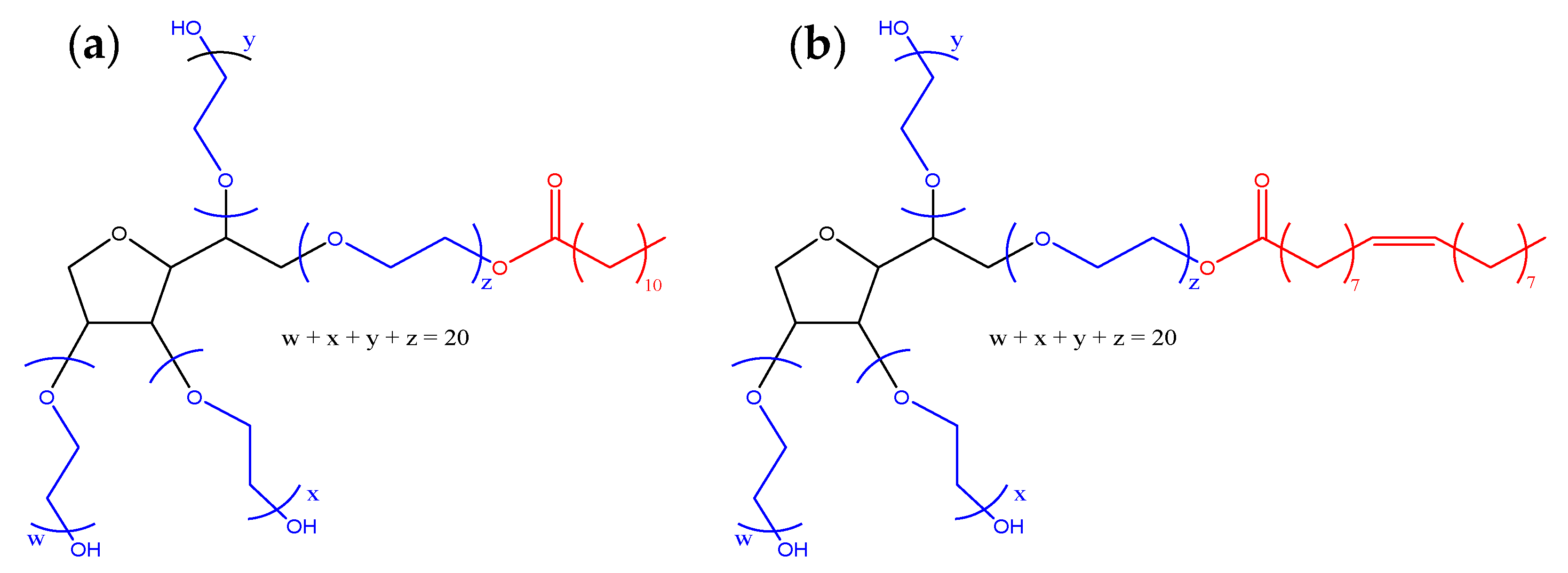

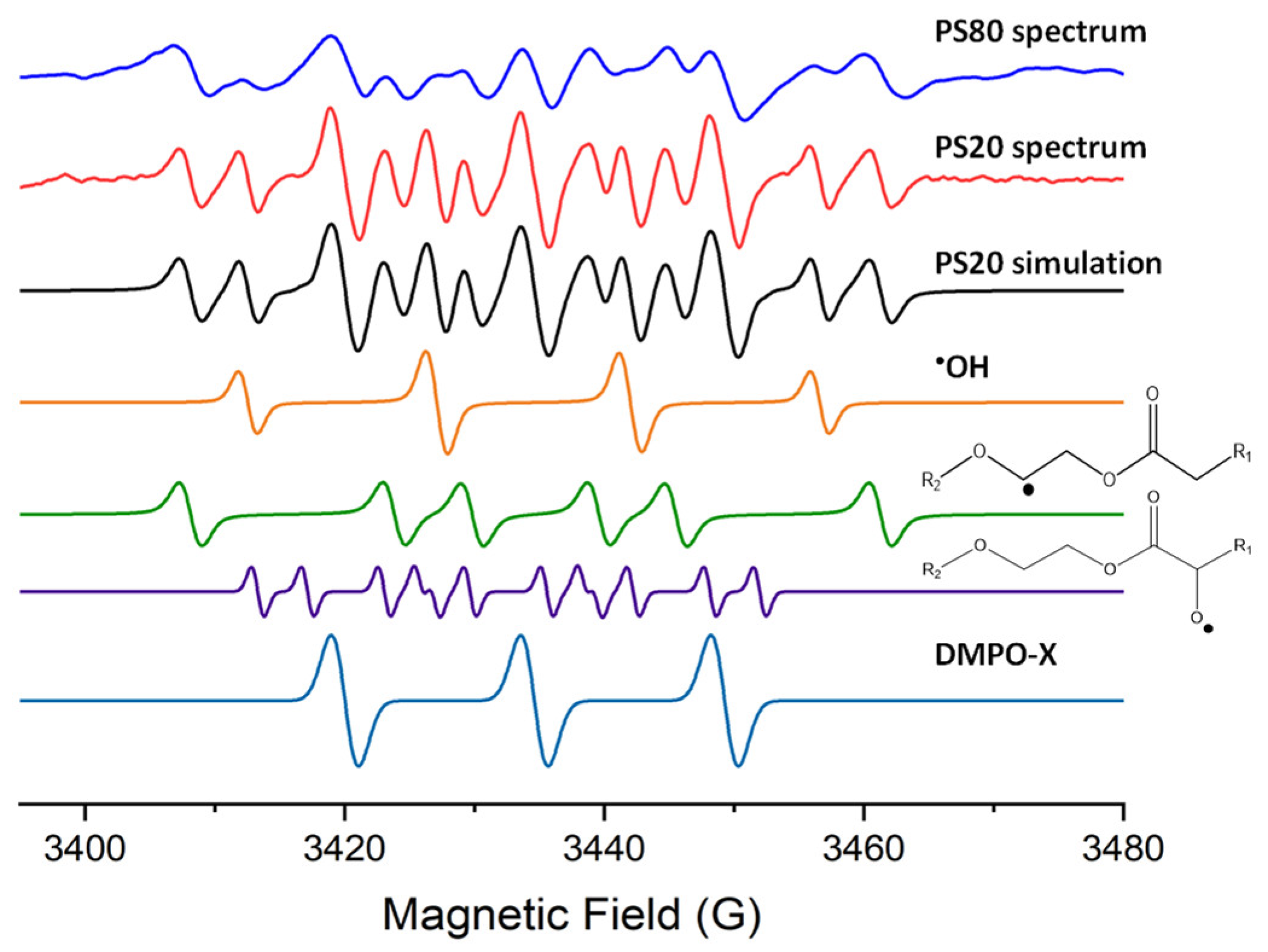

| Radical Species | Hyperfine Coupling Constant (G) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| aN | aHβ | aHγ | References | |
| PS stocks | ||||
| R-OO• | 13.8 ± 0.1 | 11.2 ± 0.2 | 0.7 ± 0.2 | [30,31] |
| R-O• | 13.4 ± 0.1 | 8.2 ± 0.8 | 1.4 ± 0.1 | [30,31,32,33,35] |
| R• | 14.7 ± 0.2 | 19.8 ± 0.3 | - | [33,35] |
| DMPO-X | 14.3 ± 0.5 | - | - | [28,31] |
| 10% aqueous PS solutions | ||||
| HO• | 15.0 ± 0.1 | 14.3 ± 0.2 | - | [28] |
| R-O• | 12.6 ± 0.1 | 9.5 ± 0.3 | 3.9 ± 1.5 | [30,31,32,33,35] |
| PEO-R• | 15.8 ± 0.1 | 22.3 ± 0.3 | - | [28,36,37] |
| DMPO-X | 14.6 ± 0.1 | - | - | [28,31] |
| Adduct Species | Hyperfine Coupling Constant (G) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| aN | aHβ | aHγ | |
| 1 | 14.3 | 20.2 | |
| 2 | 13.9 | ||
| 3 | 14.7 | 19.5 | |
| 4 | 13.2 | 7.7 | 1.5 |
| 5 | 13.7 | 11 | 1.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sutton, A.T.; Rustandi, R.R. Determining the Oxidation Mechanism through Radical Intermediates in Polysorbates 80 and 20 by Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17020233
Sutton AT, Rustandi RR. Determining the Oxidation Mechanism through Radical Intermediates in Polysorbates 80 and 20 by Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(2):233. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17020233
Chicago/Turabian StyleSutton, Adam T., and Richard R. Rustandi. 2024. "Determining the Oxidation Mechanism through Radical Intermediates in Polysorbates 80 and 20 by Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Spectroscopy" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 2: 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17020233
APA StyleSutton, A. T., & Rustandi, R. R. (2024). Determining the Oxidation Mechanism through Radical Intermediates in Polysorbates 80 and 20 by Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Pharmaceuticals, 17(2), 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17020233






