Identification of a Potential PGK1 Inhibitor with the Suppression of Breast Cancer Cells Using Virtual Screening and Molecular Docking
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
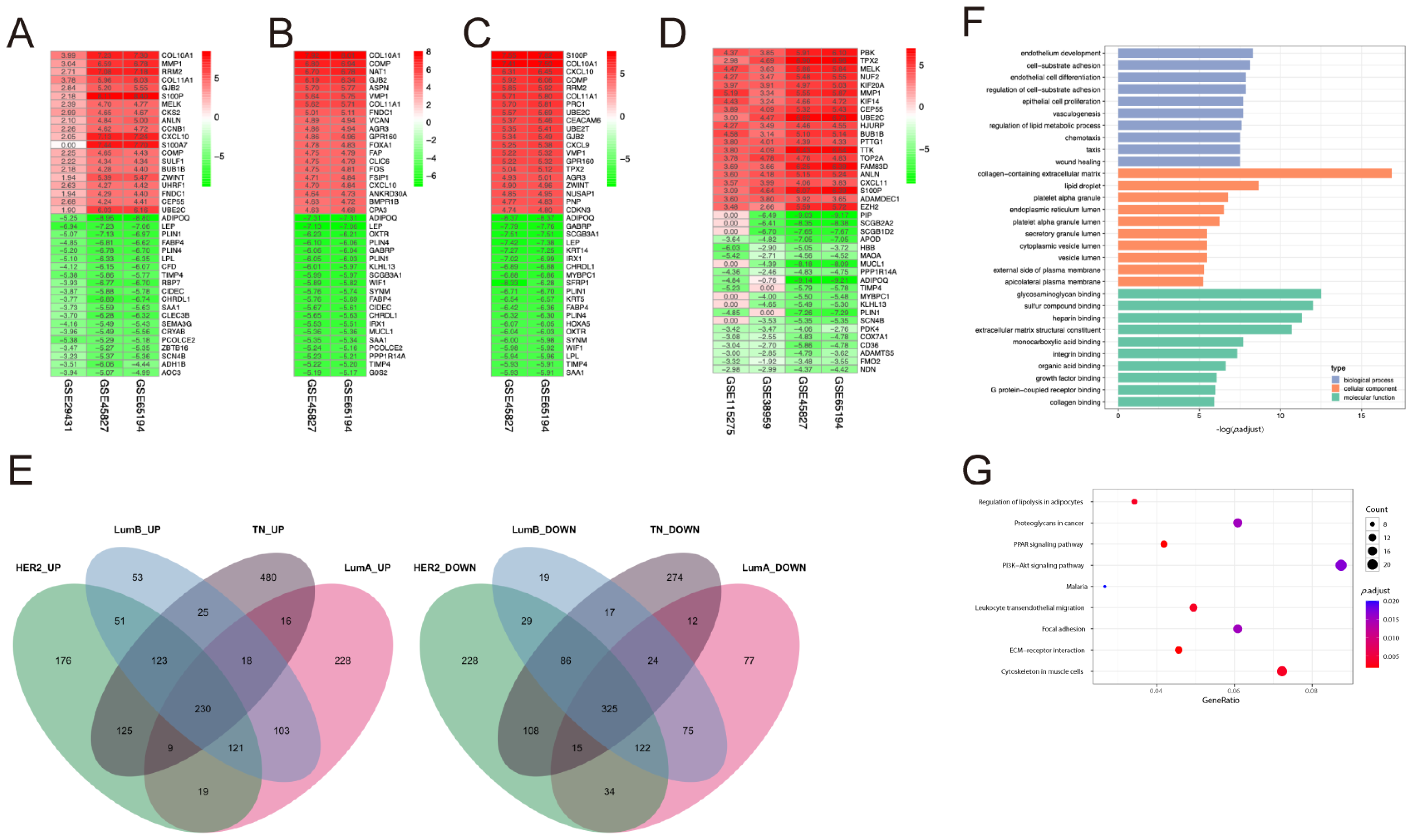
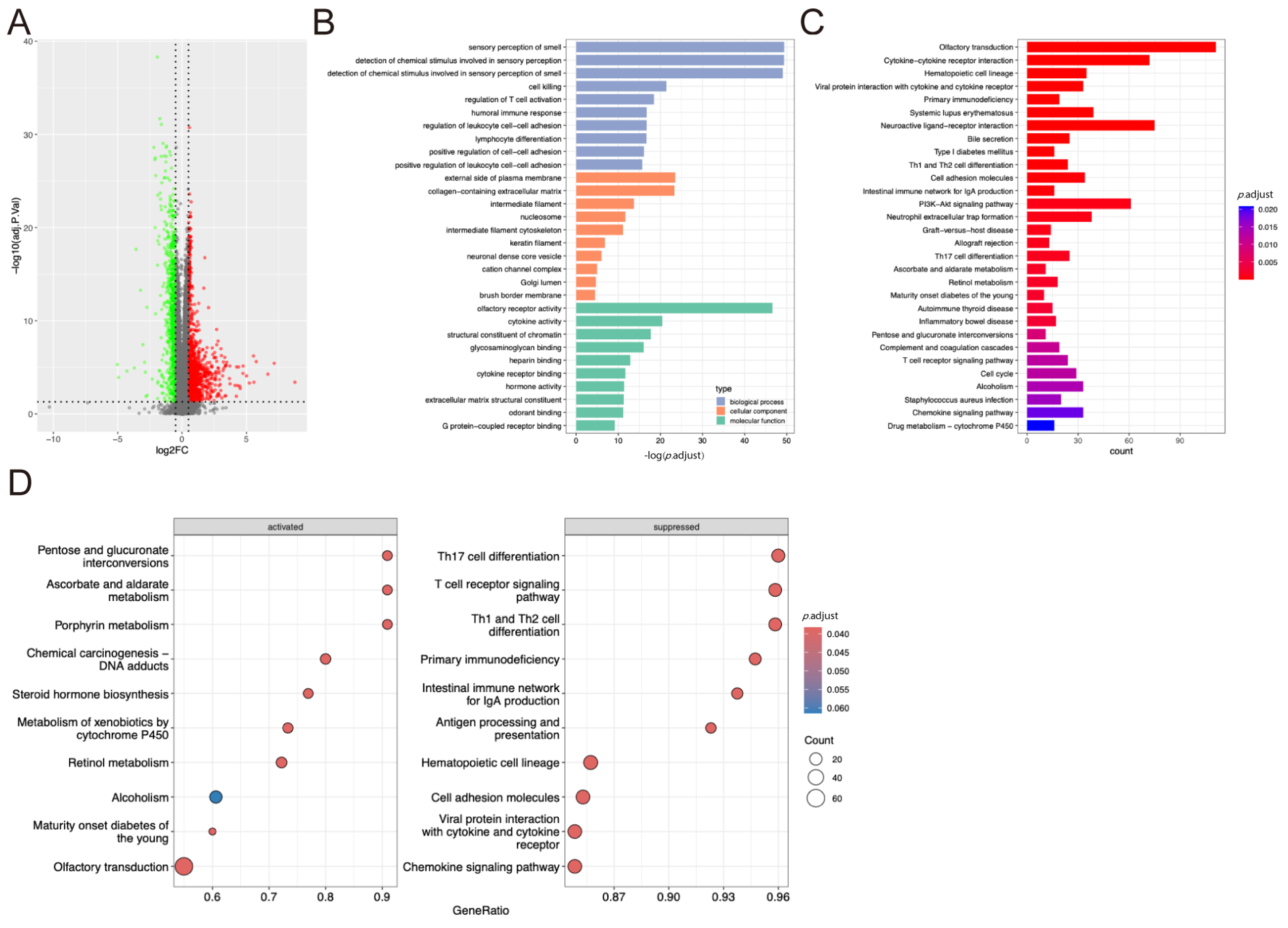
2.1. DEGs Identification and Functional Enrichment Analysis
2.2. Independent Prognostic Model Analysis
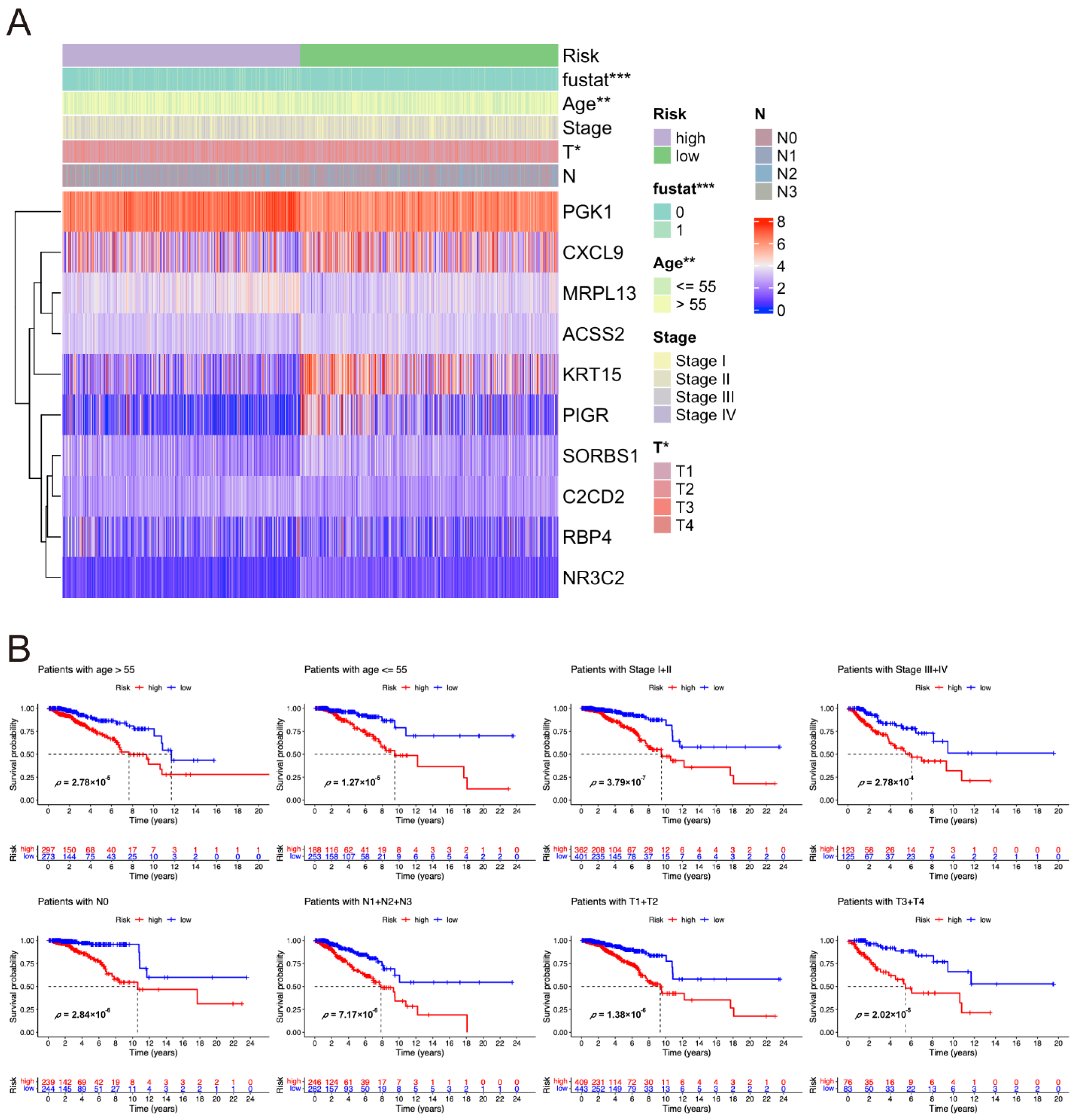
2.3. Correlation Between Risk Score and Clinical Characteristics of Breast Cancer Patients
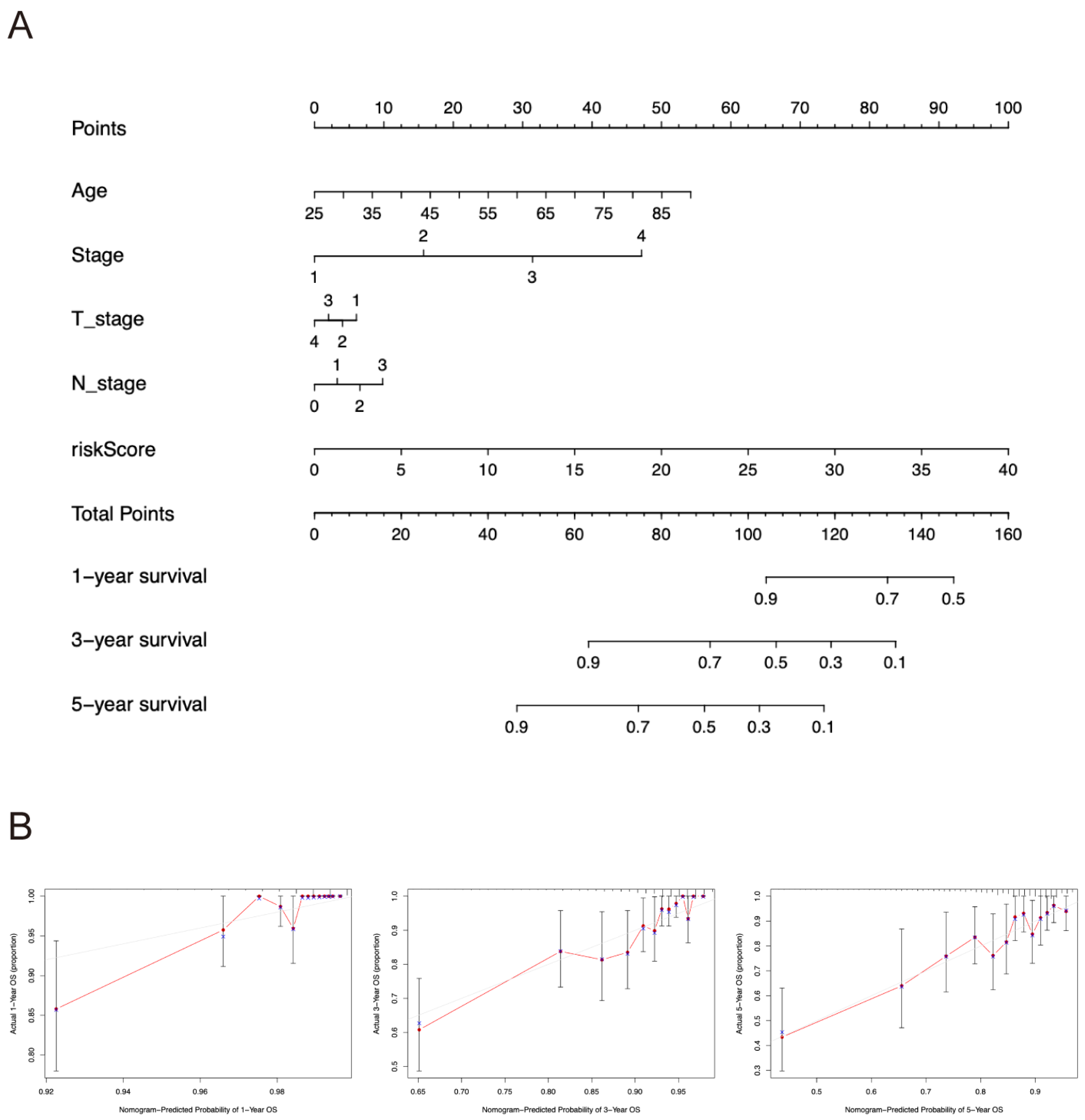
2.4. Nomogram Construction
2.5. Functional Enrichment Analyses
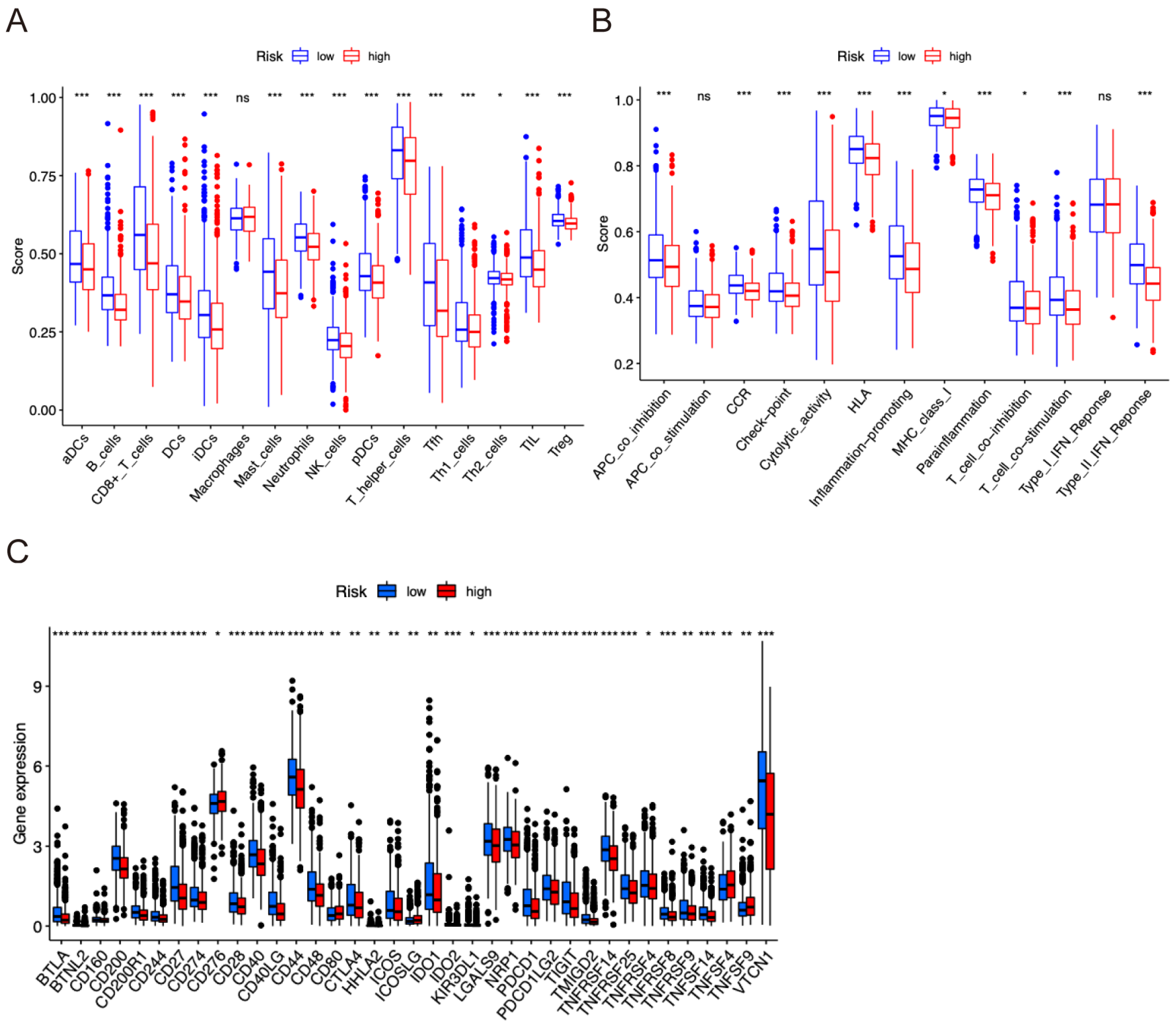
2.6. Tumor Immune Infiltration Correlation Analyses
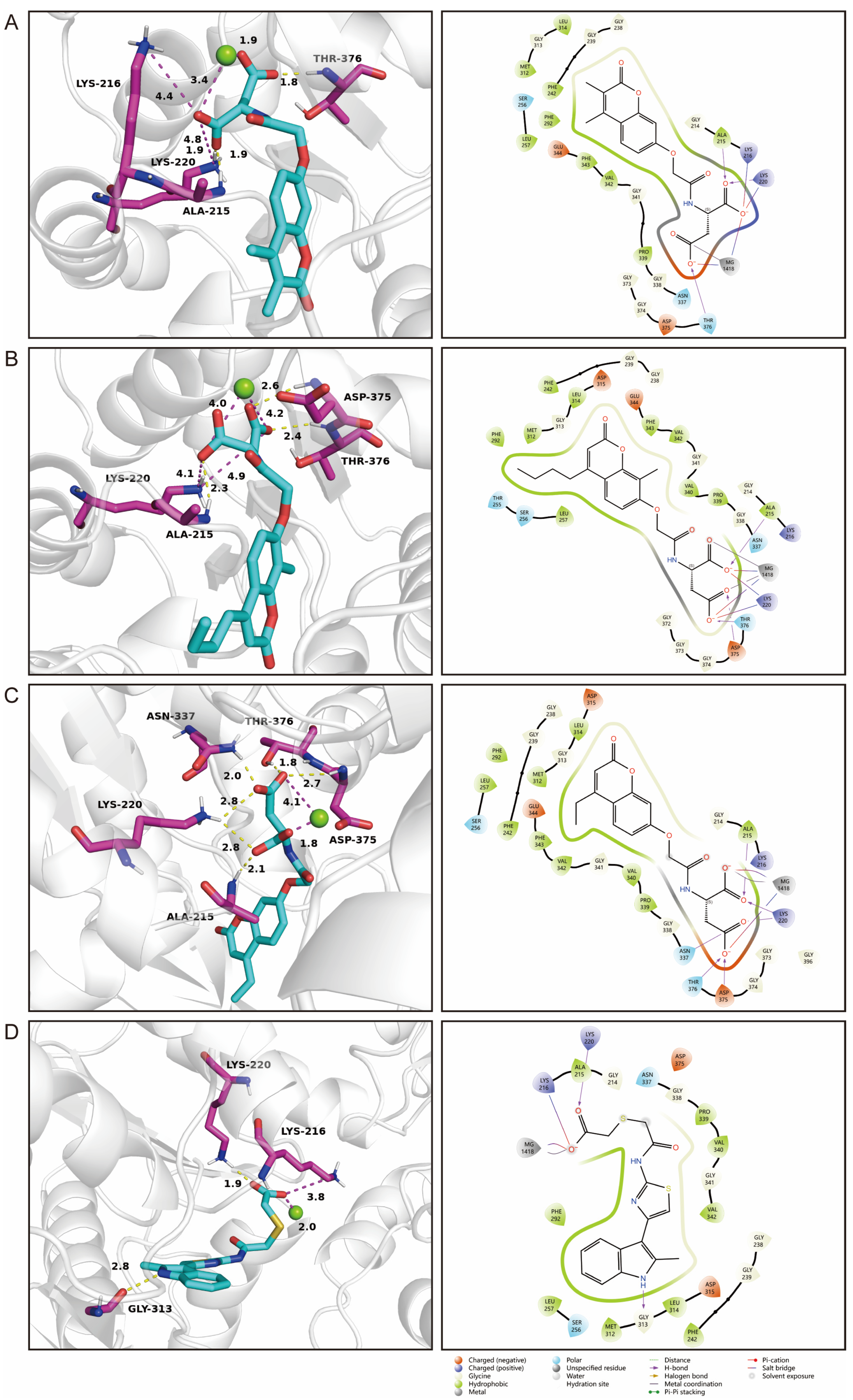
2.7. Identification of Novel Inhibitors of PGK1
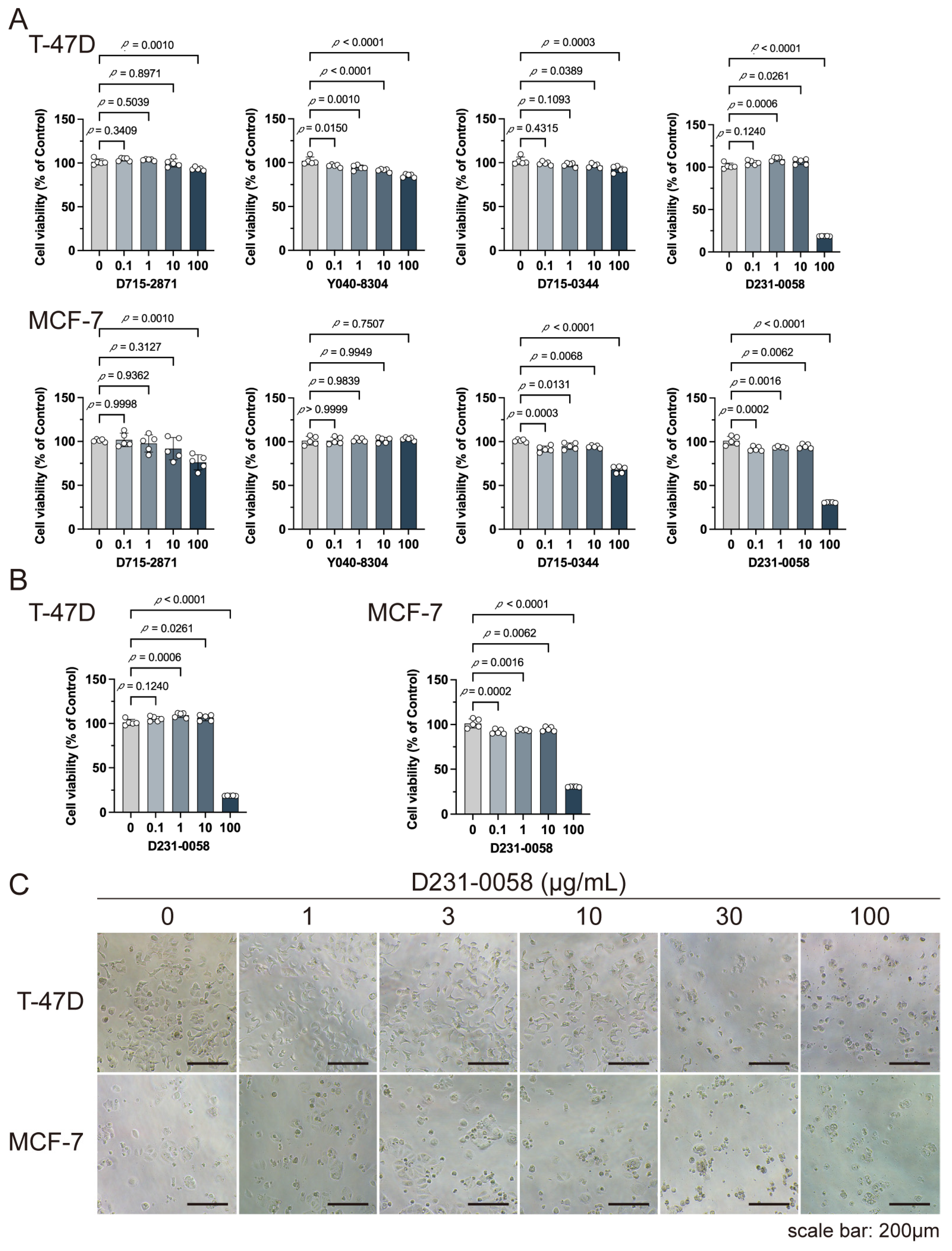
2.8. D231-0058 Inhibits the Growth of Breast Cancer Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Compounds and Cells
4.2. Data Source and Preprocessing
4.3. Differential Expression Analysis and Data Preprocessing
4.4. Functional Enrichment Analysis
4.5. Construction of the Prognostic Model
4.6. Molecular Docking
4.7. Cell Experiments
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Cancer Genome Atlas Network. Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 2012, 490, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.; Hasan, S.M.A.; Grouchy, S.; Gartia, M.R. DNA microarray analysis using a smartphone to detect the BRCA-1 gene. Analyst 2018, 144, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J. Identification of novel biomarkers, MUC5AC, MUC1, KRT7, GAPDH, CD44 for gastric cancer. Med. Oncol. 2020, 37, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.F.; Meng, L.B.; Wang, Q.Q.; He, Z.K.; Hu, C.H.; Shan, M.J.; Wang, D.Y.; Yu, X. Identification and functional enrichment analysis of potential diagnostic and therapeutic targets in adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma. J. Comput. Biol. 2020, 27, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wu, G.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Ruan, N.; Ma, L.; Han, X.; Wei, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, H.; et al. Screening and identification of key biomarkers for bladder cancer: A study based on TCGA and GEO data. Biomed. Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 8283401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, G.S.; Lou, W.Y.; Shen, Q.Y.; Yu, K.; Zheng, Y.J. Identification of key genes as potential biomarkers for triple-negative breast cancer using integrating genomics analysis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 21, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Guo, Y.; Feng, Y.M.; Zhang, N. Identification of triple-negative breast cancer genes and a novel high-risk breast cancer prediction model development based on PPI data and support vector machines. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Gao, C.; Liu, C.; Zhuang, J.; Su, P.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Sun, C. Identification of the key pathways and genes involved in HER2-positive breast cancer with brain metastasis. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2019, 215, 152475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Fu, F.; Lv, J.; Wang, M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, C. Identification of potential key genes for HER-2 positive breast cancer based on bioinformatics analysis. Medicine 2020, 99, e18445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Liu, J.; Song, Y.; Liu, Q.; Wang, C.; Qian, C.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, W.; Yang, X.; Wan, F.; et al. Screening of immunosuppressive factors for biomarkers of breast cancer malignancy phenotypes and subtype-specific targeted therapy. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, B.; Hang, J.; Lei, T.; He, Y.; Kuang, Z.; Wang, L.; Chen, L.; He, J.; Zhang, W.; Liao, Y.; et al. Identification of key genes relevant to the prognosis of ER-positive and ER-negative breast cancer based on a prognostic prediction system. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2019, 46, 2111–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, S.Y.; Dai, H.X.; Li, R.J.; Liu, W.; Ye, R.F.; Ha, Y.P.; Di, X.Q.; Hu, W.H.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, Y.Q. Identification of key differentially expressed genes between ER-positive/HER2-negative breast cancer and ER-negative/HER2-negative breast cancer using integrated bioinformatics analysis. Gland Surg. 2020, 9, 661–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negri, M.; Gentile, A.; de Angelis, C.; Monto, T.; Patalano, R.; Colao, A.; Pivonello, R.; Pivonello, C. Vitamin D-induced molecular mechanisms to potentiate cancer therapy and to reverse drug-resistance in cancer cells. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, A.; Wen, X.; Zou, Q.; Yin, L.; Zhu, S.; Sheng, Y.; He, Y.; Liu, Q.; Luo, D.; Guo, Z. Phosphoglycerate kinase 1: An effective therapeutic target in cancer. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 2024, 29, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, C. Development and validation of a Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER)-based prognostic nomogram for predicting survival in elderly patients with gastric cancer after surgery. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2021, 12, 278–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Wu, H.; Wu, X.; You, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Liang, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, W.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Silencing of PGK1 promotes sensitivity to paclitaxel treatment by upregulating XAF1-mediated apoptosis in triple-negative breast cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 535230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Liu, L.L.; Shen, Q.; Cen, M. Integrating single-cell transcriptomics and machine learning to predict breast cancer prognosis: A study based on natural killer cell-related genes. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2024, 28, e18549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, J.; Mei, N.; Chen, H.; Niu, L.; He, J.; Wang, R. Identifying subtypes and developing prognostic models based on N6-methyladenosine and immune microenvironment related genes in breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 16586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miglietta, F.; Ragazzi, M.; Fernandes, B.; Griguolo, G.; Massa, D.; Girardi, F.; Bottosso, M.; Bisagni, A.; Zarrilli, G.; Porra, F.; et al. A prognostic model based on residual cancer burden and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes on residual disease after neoadjuvant therapy in HER2+ breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 29, 3429–3437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.N.; Qiu, X.T.; Xue, J.S.; Yi, L.M.; Chen, M.L.; Huang, Z.J. Predicting the prognosis and immunotherapeutic response of triple-negative breast cancer by constructing a prognostic model based on CD8+ T cell-related immune genes. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2024, 37, 581–593. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Wang, P.; Feng, R.; Chetry, M.; Li, E.; Wu, X.; Liu, Z.; Liao, S.; Lin, J. Prognostic model of ER-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer predicted by clinically relevant indicators. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2024, 26, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vosa, U.; Kolde, R.; Vilo, J.; Metspalu, A.; Annilo, T. Comprehensive meta-analysis of microRNA expression using a robust rank aggregation approach. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1182, 361–373. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, G.; Li, Y.; Peng, Y.; Lu, D.; Zhang, F.; Cui, X.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Z. Identification of differentially expressed genes and biological characteristics of colorectal cancer by integrated bioinformatics analysis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 15215–15224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.L.; Wang, L.; Shi, L.; Yun, F.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y.X.; Chen, C.; Ren, Y.N.; Jia, Y.F. Transcriptome profiling revealed multiple genes and ECM-receptor interaction pathways that may be associated with breast cancer. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2019, 24, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budczies, J.; Pfitzner, B.M.; Györffy, B.; Winzer, K.J.; Radke, C.; Dietel, M.; Fiehn, O.; Denkert, C. Glutamate enrichment as new diagnostic opportunity in breast cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, 1619–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Shen, X.; Li, Y.; Zou, W.; Hassan, S.S.U.; Feng, Y.; Wang, X.; Tian, J.; Shao, X.; Tao, Y.; et al. Proteomic and metabolomic characterization of bone, liver, and lung metastases in plasma of breast cancer patients. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2024, 3, e2300136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, J.Y.; Zhang, B. Developing four cuproptosis-related lncRNAs signature to predict prognosis and immune activity in ovarian cancer. J. Ovarian Res. 2023, 16, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.Y.; Yin, X.Z.; Wang, L.X.; Liu, K.L.; Liu, W.Y.; Bo, L.; Wang, L. Identifying tumour microenvironment-related signature that correlates with prognosis and immunotherapy response in breast cancer. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeaiter, N.; Belot, L.; Cunin, V.; Nahed, R.A.; Tokarska-Schlattner, M.; Le Gouellec, A.; Petosa, C.; Khochbin, S.; Schlattner, U. Acetyl-CoA synthetase (ACSS2) does not generate butyryl- and crotonyl-CoA. Mol. Metab. 2024, 81, 101903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, K.D.; O’Connor, S.; Pniewski, K.A.; Kannan, T.; Acosta, R.; Mirji, G.; Papp, S.; Hulse, M.; Mukha, D.; Hlavaty, S.I.; et al. Acetate acts as a metabolic immunomodulator by bolstering T-cell effector function and potentiating antitumor immunity in breast cancer. Nat. Cancer 2023, 4, 1491–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esquea, E.M.; Ciraku, L.; Young, R.G.; Merzy, J.; Talarico, A.N.; Ahmed, N.N.; Karuppiah, M.; Ramesh, A.; Chatoff, A.; Crispim, C.V.; et al. Selective and brain-penetrant ACSS2 inhibitors target breast cancer brain metastatic cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1394685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.Q.; Li, J.; He, T.S.; Ding, J.Q. Bioinformatics identified 17 immune genes as prognostic biomarkers for breast cancer: Application study based on artificial intelligence algorithms. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozga, A.J.; Chow, M.T.; Luster, A.D. Chemokines and the immune response to cancer. Immunity 2021, 54, 859–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seitz, S.; Dreyer, T.F.; Stange, C.; Steiger, K.; Brauer, R.; Scheutz, L.; Multhoff, G.; Weichert, W.; Kiechle, M.; Magdolen, V.; et al. CXCL9 inhibits tumour growth and drives anti-PD-L1 therapy in ovarian cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 126, 1470–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.K.; Deng, Z.K.; Chen, M.T.; Qiu, S.Q.; Xiao, Y.S.; Qi, Y.Z.; Xie, Q.; Wang, Z.H.; Jia, S.C.; Zeng, D.; et al. CXCL9 is a potential biomarker of immune infiltration associated with favorable prognosis in ER-negative breast cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 710286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Sun, S.; Qu, F.; Sun, M.; Liu, X.; Sun, Q.; Cheng, L.; Zheng, Y.; Su, G. CXCL9 influences the tumor immune microenvironment by stimulating JAK/STAT pathway in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2023, 72, 1479–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moll, R.; Divo, M.; Langbein, L. The human keratins: Biology and pathology. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 129, 705–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Q.; Signoretti, S.; Whitaker-Menezes, D.; Friedman, T.M.; Korngold, R.; Murphy, G.F. Cytokeratin15-positive basal epithelial cells targeted in graft-versus-host disease express a constitutive antiapoptotic phenotype. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyashita, H.; Niwano, H.; Yoshida, S.; Hatou, S.; Inagaki, E.; Tsubota, K.; Shimmura, S. Long-term homeostasis and wound healing in an in vitro epithelial stem cell niche model. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.D.; Miao, C.L. KRT15 promotes colorectal cancer cell migration and invasion through β-catenin/MMP-7 signaling pathway. Med. Oncol. 2022, 39, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, P.C.; Shu, R.; Wu, H.W.; Liu, Z.W.; Shen, X.L.; Hu, Y.J. Low KRT15 expression is associated with poor prognosis in patients with breast invasive carcinoma. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 21, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummer, E.; Ban, N. Mechanisms and regulation of protein synthesis in mitochondria. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 307–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, C.Q.; Fu, R.; Wang, C.; Li, X.R.; Zhang, W. MRPL13 act as a novel therapeutic target and could promote cell proliferation in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2021, 13, 5535–5545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.G.; He, Z.J.; Fan, Y.; Yin, L.; Hong, Z.P.; Tong, Y.; Bi, Q.; Zhu, S.B. Multi-omics analysis of MRPL-13 as a tumor-promoting marker from pan-cancer to lung adenocarcinoma. Aging 2023, 15, 10640–10680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.M.; Li, H.N.; Chen, R.F.; Zhou, X. MRPL13 promotes tumor cell proliferation, migration and EMT process in breast cancer through the PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway. Cancer Manag. Res. 2021, 13, 2009–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.; Suo, H.D.; Zhang, L.; Jin, Z.N.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D.Y.; Wu, M.; Peng, N.X.; Zhao, Y.J.; Chen, B. MRPL13 is a prognostic cancer biomarker and correlates with immune infiltrates in breast cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 12255–12268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, D.Y.; Bu, K.N.; Gao, J.D.; Zhang, B.L. Prognosis prediction and risk stratification of breast cancer patients based on a mitochondria-related gene signature. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horisberger, J.D.; Rossier, B.C. Aldosterone regulation of gene transcription leading to control of ion transport. Hypertension 1992, 19, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Xi, X.; Li, J.T.; Ni, J.; Yang, H.B.; Wen, C.Y.; Wen, M.L. miR-301b and NR3C2 co-regulate cells malignant properties and have the potential to be independent prognostic factors in breast cancer. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2021, 35, e22650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Zeng, M.; Pan, S.; Liu, H.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, H. Identification of a novel transcription factor prognostic index for breast cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 666505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadwal, A.; Purohit, P.; Khokhar, M.; Vishnoi, J.R.; Pareek, P.; Choudhary, R.; Elhence, P.; Banerjee, M.; Sharma, P. In silico analysis of differentially expressed-aberrantly methylated genes in breast cancer for prognostic and therapeutic targets. Clin. Exp. Med. 2023, 23, 3847–3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Q.; Yu, Z. Phosphoglycerate kinase 1 (PGK1) in cancer: A promising target for diagnosis and therapy. Life Sci. 2020, 256, 117863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Zhan, Q.; Su, D.; Cui, X.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Q.; Hong, B.; Ju, J.; Cheng, C.; Yang, E.; et al. HIF1alpha/ATF3 partake in PGK1 K191/K192 succinylation by modulating P4HA1/succinate signaling in glioblastoma. Neuro-Oncol. 2024, 26, 1405–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Z.; Huo, N.; Zhu, X.; Liu, H.X.; Cong, R.; Ma, L.Y.; Kang, X.F.; Xue, C.Y.; Li, J.T.; Li, Q.H.; et al. FOXO3A-induced LINC00926 suppresses breast tumor growth and metastasis through inhibition of PGK1-mediated Warburg effect. Mol. Ther. 2021, 29, 2737–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, M.; Komiyama, K. Polymeric immunoglobulin receptor. J. Oral Sci. 2011, 53, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, J.; Choi, J.; Chung, J. Polymeric immunoglobulin receptor (pIgR) in cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 149, 17683–17690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Chen, L.; Ke, Y.; Hang, J.; Cao, L.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, W.; Liao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Chen, J.; et al. Identification of methylation sites and signature genes with prognostic value for luminal breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.T.; Zhou, Q. Identification of exosome-related gene signature as a promising diagnostic and therapeutic tool for breast cancer. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Graham, T.E.; Mody, N.; Preitner, F.; Peroni, O.D.; Zabolotny, J.M.; Kotani, K.; Quadro, L.; Kahn, B.B. Serum retinol binding protein 4 contributes to insulin resistance in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Nature 2005, 436, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, F.J.; Zhu, Y.J.; Wu, F.X.; Huang, X.J.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, H.T.; Liang, L.F.; Qin, L.R.; Wang, Q.; et al. Retinol-binding protein 4 as a promising serum biomarker for the diagnosis and prognosis of hepatocellular Carcinoma. Transl. Oncol. 2024, 45, 101979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.T.; Zhang, C.K.; Sun, Q.N.; Baral, S.; Ding, J.Y.; Zhao, F.Y.; Yao, Q.; Gao, S.Y.; Liu, B.; Wang, D.R. Retinol binding protein 4 serves as a potential tumor biomarker and promotes malignant behavior in gastric cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2024, 16, 891–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Li, Q.; Wang, H. Identification of novel biomarkers associated with the prognosis and potential pathogenesis of breast cancer via integrated bioinformatics analysis. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 20, 1533033821992081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.H.; Huang, C.J.; Liu, M.W.; Chang, H.M.; Chen, Y.J.; Tai, T.Y.; Chuang, L.M. Cloning, mapping, and characterization of the human sorbin and SH3 domain containing 1 (SORBS1) gene: A protein associated with c-Abl during insulin signaling in the hepatoma cell line Hep3B. Genomics 2001, 74, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, W.C.; Jang, J.E.; Kim, K.H.; Yoo, B.C.; Ku, J.L. SORBS1 serves a metastatic role via suppression of AHNAK in colorectal cancer cell lines. Int. J. Oncol. 2020, 56, 1140–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.X.; Li, D.W.; Zhang, Y.D.; Li, C.A.; Zhang, C.Z.; Wang, L.B. MiR-142-5p acts as a significant regulator through promoting proliferation, invasion, and migration in breast cancer modulated by targeting SORBS1. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 18, 1533033819892264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, K.; Di, Y.; Han, M.; Yan, W.; Wang, Y. SORBS1 inhibits epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) of breast cancer cells by regulating PI3K/AKT signaling and macrophage phenotypic polarization. Aging 2024, 16, 4789–4810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Gu, Y.; Li, L.; Chi, J.; Liu, X.; Xiong, Y.; Zhong, C. Development and validation of a prognostic classifier based on lipid metabolism-related genes for breast cancer. J. Inflamm. Res. 2022, 15, 3477–3499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, M.G.; Kim, S.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Jung, T.Y.; Jung, S.; Rhee, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, J.S.; Cho, J.H.; Moon, K.S.; et al. Evolution of the tumor microenvironment toward immune-suppressive seclusion during brain metastasis of breast cancer: Implications for targeted therapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 4895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteva, F.J.; Hubbard-Lucey, V.M.; Tang, J.; Pusztai, L. Immunotherapy and targeted therapy combinations in metastatic breast cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, e175–e186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Ren, J.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, F.; Han, M. Prognosis of tumor microenvironment in luminal B-type breast cancer. Dis. Markers 2022, 2022, 5621441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galimberti, D.; Fenoglio, C.; Scarpini, E. Progranulin as a therapeutic target for dementia. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2018, 22, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.L.; Xiang, M.; Zhou, J.Q.; Ren, Z.J.; Shi, W.J.; Du, X.H.; Fu, X.Y.; Li, P.P.; Wang, H.Y. Progranulin inhibits autophagy to facilitate intracellular colonization of Helicobacter pylori through the PGRN/mTOR/DCN axis in gastric epithelial cells. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1425367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Zhou, T.; Shi, H.; Yao, M.; Zhang, D.; Qian, H.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, Y.; Jin, F.; Chai, C.; et al. Progranulin induces immune escape in breast cancer via up-regulating PD-L1 expression on tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) and promoting CD8(+) T cell exclusion. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shashni, B.; Sakharkar, K.R.; Nagasaki, Y.; Sakharkar, M.K. Glycolytic enzymes PGK1 and PKM2 as novel transcriptional targets of PPARγ in breast cancer pathophysiology. J. Drug Target. 2013, 21, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.J.; Zheng, Y.H.; Lu, Z.M. PGK1 is a new member of the protein kinome. Cell Cycle 2016, 15, 1803–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.P.; Zhao, C.Y.; Li, X.L.; Wang, T.; Li, Y.Z.; Cao, C.; Ding, Y.H.; Dong, M.Q.; Finci, L.; Wang, J.H.; et al. Terazosin activates Pgk1 and Hsp90 to promote stress resistance. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2015, 11, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Luo, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhang, D.; Hou, H.; Liang, Y.; Deng, S.; Zhang, P.; Liang, S. Novel inhibitors targeting the PGK1 metabolic enzyme in glycolysis exhibit effective antitumor activity against kidney renal clear cell carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 267, 116209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.; Dang, W.; Lin, T.; Yu, J.; Liu, T.; Li, W.; Xiao, S.; Feng, L.; Huang, J.; Fu, R.; et al. A potent PGK1 antagonist reveals PGK1 regulates the production of IL-1beta and IL-6. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 4180–4192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, L.; Yu, G.; Qi, X.; Zhang, A.; Lu, Z.; Li, D.; Li, J. Identification of a novel non-ATP-competitive protein kinase inhibitor of PGK1 from marine nature products. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 183, 114343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, A.; Qi, X.; Yu, R.; Li, J. A novel inhibitor of PGK1 suppresses the aerobic glycolysis and proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 158, 114115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forli, S.; Huey, R.; Pique, M.E.; Sanner, M.F.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. Computational protein-ligand docking and virtual drug screening with the AutoDock suite. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 905–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baell, J.; Walters, M.A. Chemistry: Chemical con artists foil drug discovery. Nature 2014, 513, 481–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, J.; Guo, Z.; Li, Q.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, X. Immunomodulatory Effect of Cordyceps militaris Polysaccharide on RAW 264.7 Macrophages by Regulating MAPK Signaling Pathways. Molecules 2024, 29, 3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
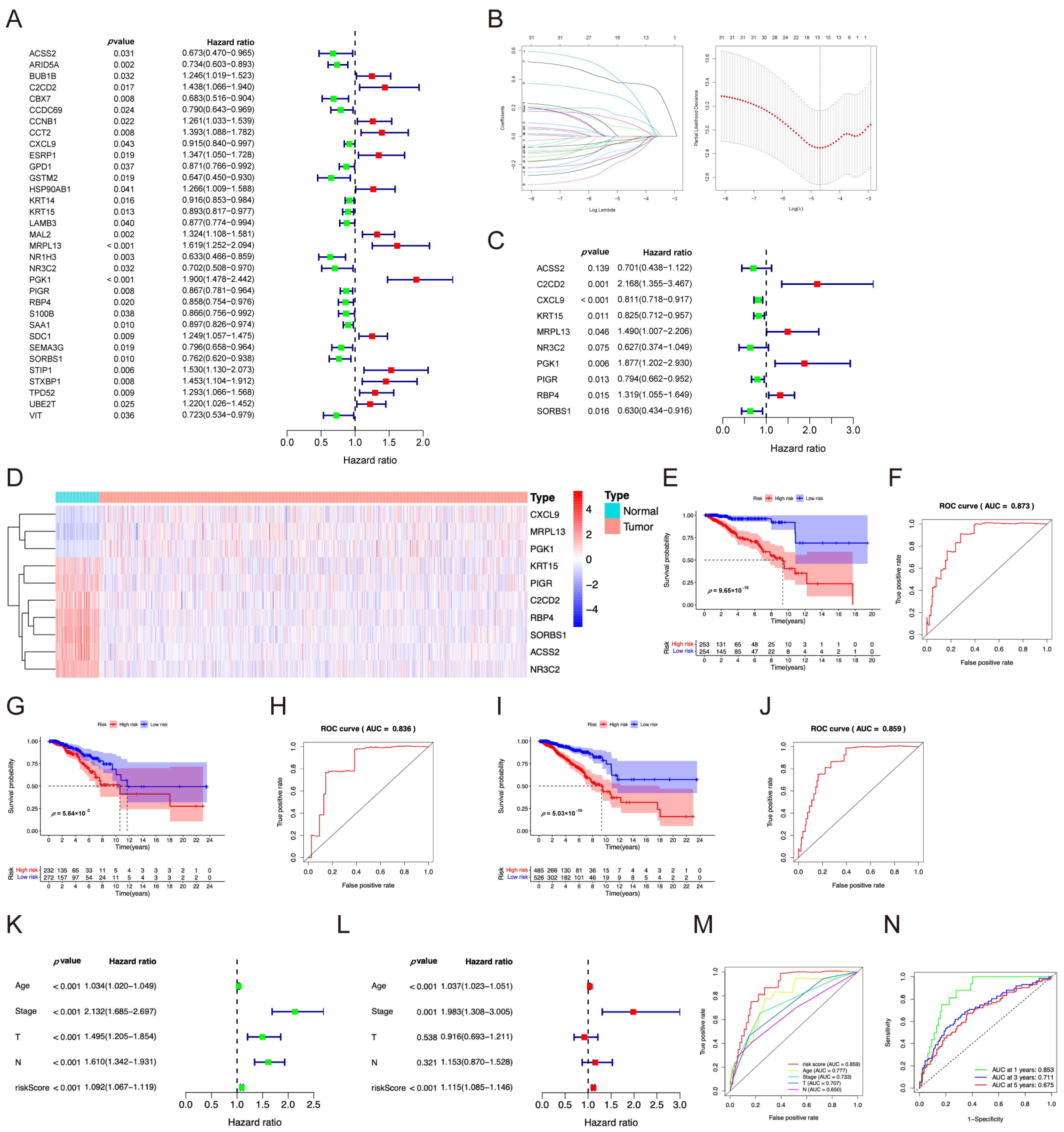
| ID | Coef | HR | HR.95L | HR.95H | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACSS2 | −0.3552 | 0.7010 | 0.4379 | 1.1222 | 0.1389 |
| C2CD2 | 0.7737 | 2.1677 | 1.3553 | 3.4672 | 0.0012 |
| CXCL9 | −0.2091 | 0.8113 | 0.7176 | 0.9173 | 0.0008 |
| KRT15 | −0.1919 | 0.8254 | 0.7122 | 0.9566 | 0.0108 |
| MRPL13 | 0.3990 | 1.4903 | 1.0068 | 2.2061 | 0.0462 |
| NR3C2 | −0.4672 | 0.6268 | 0.3745 | 1.0491 | 0.0755 |
| PGK1 | 0.6295 | 1.8767 | 1.2022 | 2.9297 | 0.0056 |
| PIGR | −0.2308 | 0.7939 | 0.6619 | 0.9522 | 0.0129 |
| RBP4 | 0.2766 | 1.3187 | 1.0548 | 1.6486 | 0.0152 |
| SORBS1 | −0.4613 | 0.6304 | 0.4339 | 0.9161 | 0.0155 |
| CAS No. | Structure | Name | Formula | Docking Score | dGBind (kcal/mol) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D715-2871 | / | 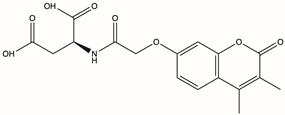 | 2-{2-[(3,4-dimethyl-2-oxo-2H-chromen-7-yl)oxy]acetamido}butanedioic acid | C17H17NO8 | −16.709 | −53.47 |
| Y040-8304 | 957001-29-5 | 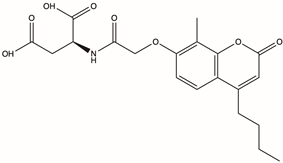 | 2-{2-[(4-butyl-8-methyl-2-oxo-2H-chromen-7-yl)oxy]acetamido}butanedioic acid | C20H23NO8 | −16.417 | −89.62 |
| D715-0344 | / | 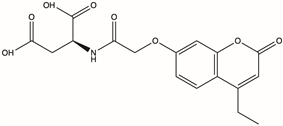 | 2-{2-[(4-ethyl-2-oxo-2H-chromen-7-yl)oxy]acetamido}butanedioic acid | C17H17NO8 | −16.314 | −87.54 |
| D231-0058 | 775298-43-6 | 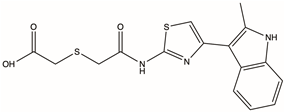 | 2-[({[4-(2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)-1,3-thiazol-2-yl]carbamoyl}methyl)sulfanyl]acetic acid | C16H15N3O3S2 | −16.232 | −77.19 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Zuo, Z.; Li, X.; Li, Q.; Zhang, L. Identification of a Potential PGK1 Inhibitor with the Suppression of Breast Cancer Cells Using Virtual Screening and Molecular Docking. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1636. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17121636
Chen X, Zuo Z, Li X, Li Q, Zhang L. Identification of a Potential PGK1 Inhibitor with the Suppression of Breast Cancer Cells Using Virtual Screening and Molecular Docking. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(12):1636. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17121636
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xianghui, Zanwen Zuo, Xianbin Li, Qizhang Li, and Lei Zhang. 2024. "Identification of a Potential PGK1 Inhibitor with the Suppression of Breast Cancer Cells Using Virtual Screening and Molecular Docking" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 12: 1636. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17121636
APA StyleChen, X., Zuo, Z., Li, X., Li, Q., & Zhang, L. (2024). Identification of a Potential PGK1 Inhibitor with the Suppression of Breast Cancer Cells Using Virtual Screening and Molecular Docking. Pharmaceuticals, 17(12), 1636. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17121636






