6-Shogaol Abrogates Parkinson’s Disease in Rotenone-Induced Rodents: Based on In Silico Study and Inhibiting TNF-α/NF-κB/IL-1β/MAO-B
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effect of 6-Shogaol on Behavioral Paradigms
2.1.1. Effect of 6-Shogaol on Open Field Test
2.1.2. Effect of 6-Shogaol on Forced Swim Test
2.1.3. Effect of 6-Shogaol on Rotarod Test
2.1.4. Effect of 6-Shogaol on Catalepsy
2.2. Biochemical Estimations
Effect of 6-Shogaol on AChE Activity
2.3. Antioxidant Levels
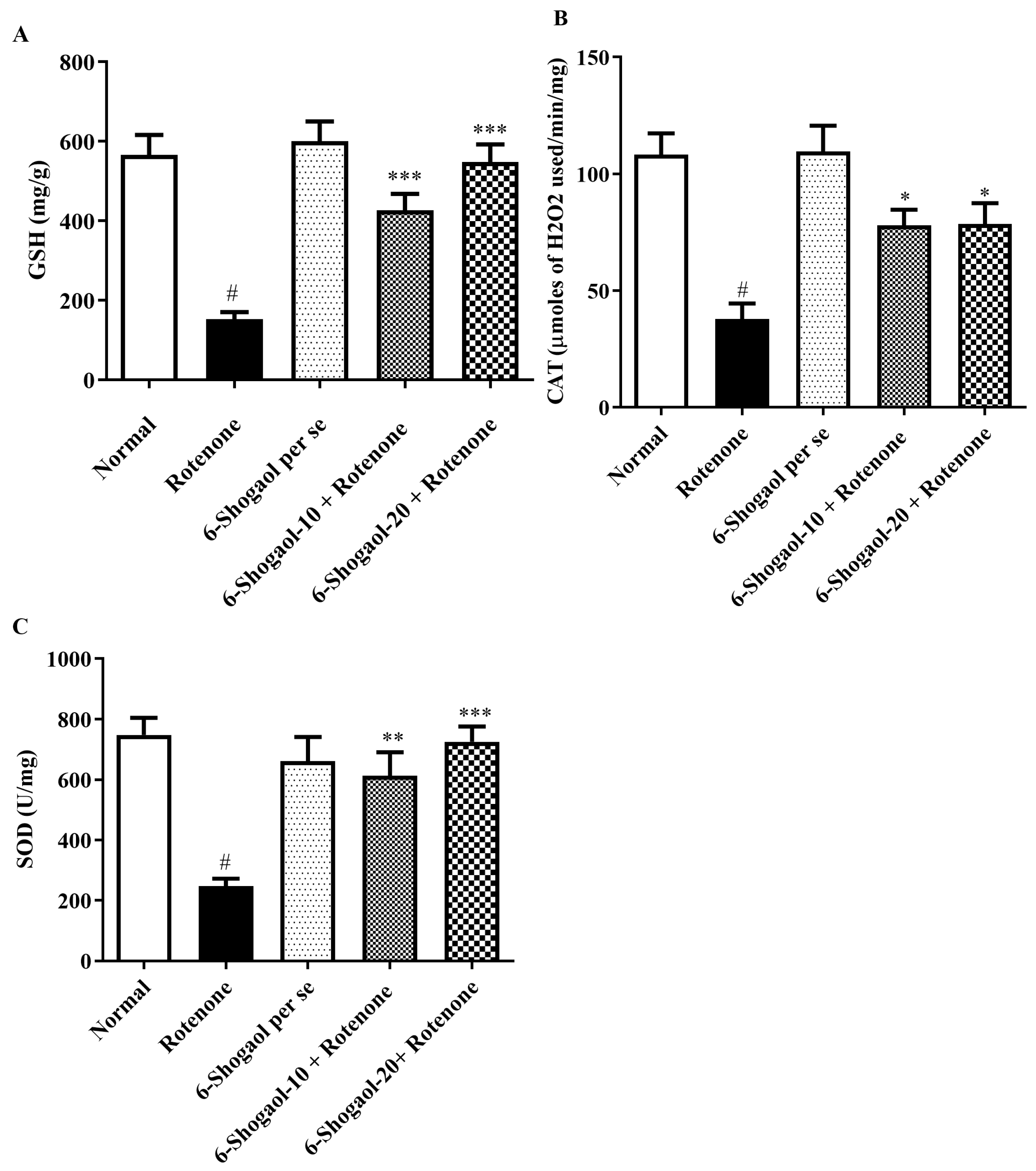
2.3.1. Effect of 6-Shogaol on GSH Level
2.3.2. Effect of 6-Shogaol on CAT Level
2.3.3. Effect of 6-Shogaol on SOD Level
2.4. MDA and Nitrite Oxide Level
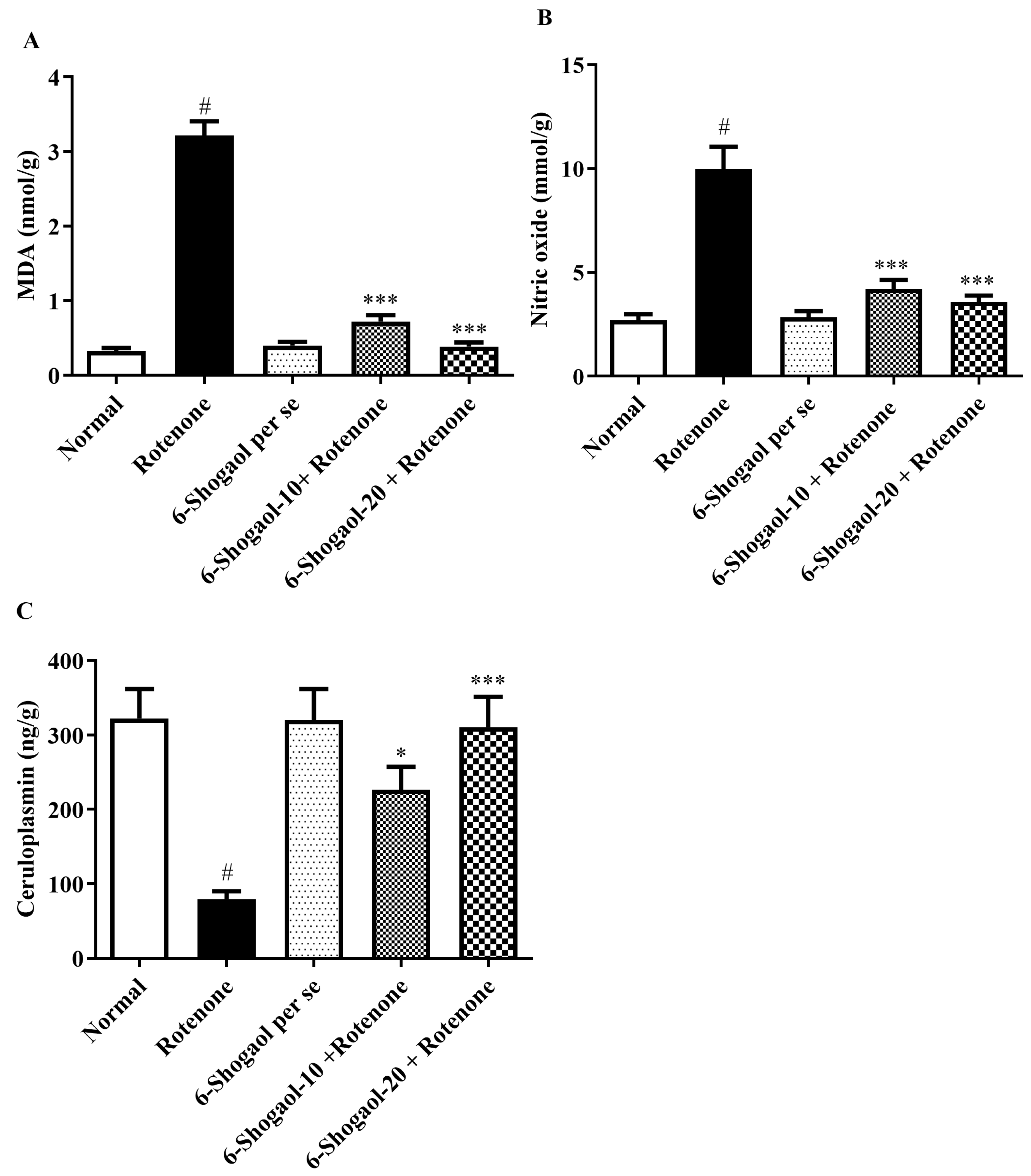
2.4.1. Effect of 6-Shogaol on MDA Level
2.4.2. Effect of 6-Shogaol on Nitrite Oxide Level
2.4.3. Effect of 6-Shogaol on CP Level
2.5. Effect of 6-Shogaol on Proinflammatory Levels
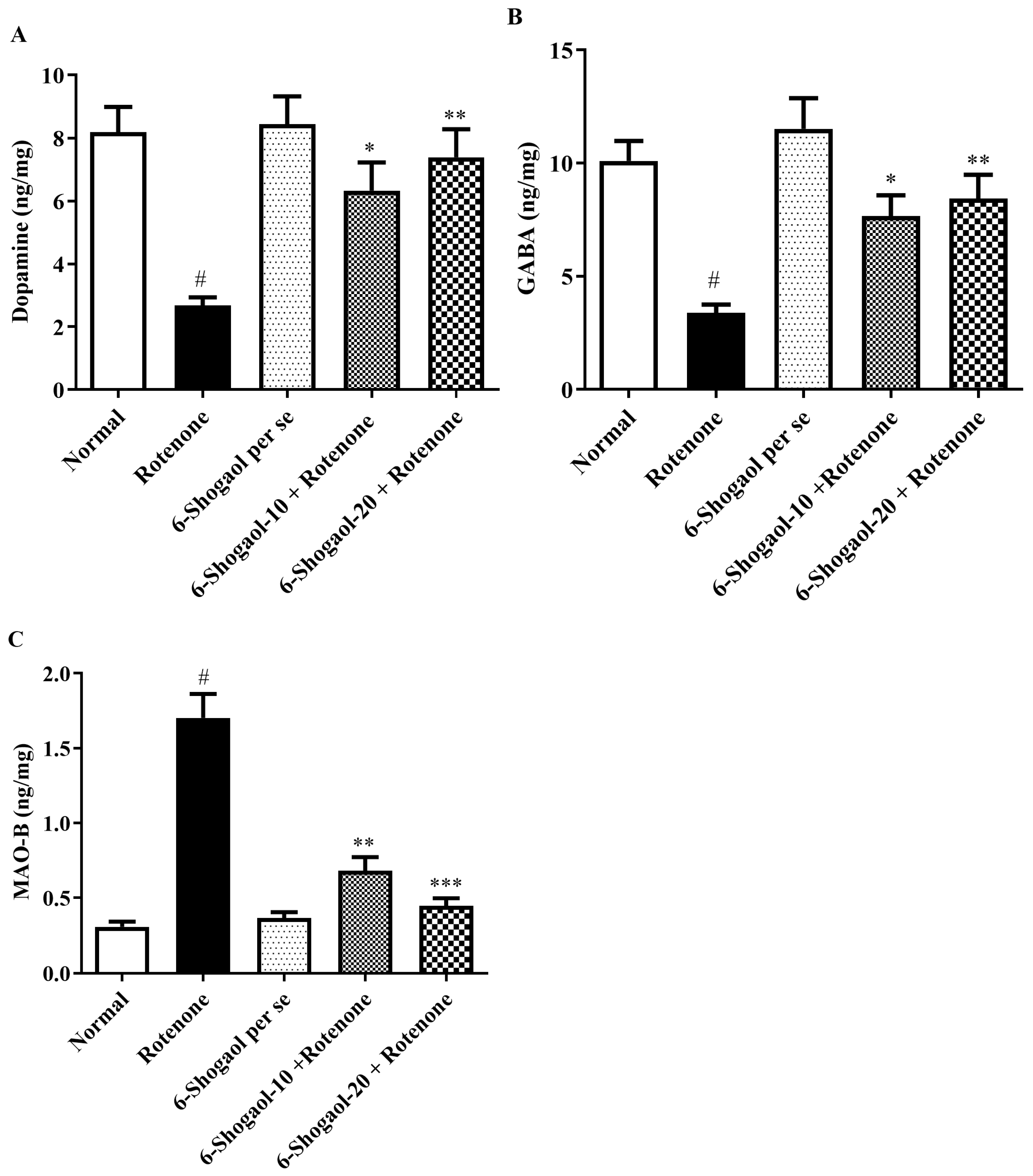
2.6. Effect of 6-Shogaol on Neurochemical Markers
2.7. Effects of 6-Shogaol on Brain Tissue
2.8. Molecular Docking of the 6-Shogaol
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Animals
4.3. Research Design
4.4. Behavioral Test
4.4.1. Open Field Test
4.4.2. Forced Swim Test
4.4.3. Rotarod Test
4.4.4. Catalepsy
4.5. Biochemical Evaluations
4.5.1. Brain Tissue Homogenate Preparation
4.5.2. AChE Activity
4.6. Endogenous Antioxidant Levels
4.6.1. GSH Level
4.6.2. CAT Level
4.6.3. SOD Level
4.7. Oxidative and Nitrative Stress Markers
4.7.1. MDA Level
4.7.2. Nitric Oxide Level
4.7.3. Ceruloplasmin (CP) Level
4.8. Proinflammatory Markers
4.9. Neurotransmitters Markers
4.10. Histopathology of the Brain
4.11. Molecular Docking
4.12. Statistics Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salari, N.; Kazeminia, M.; Sagha, H.; Daneshkhah, A.; Ahmadi, A.; Mohammadi, M. The performance of various machine learning methods for Parkinson’s disease recognition: A systematic review. Curr. Psychol. 2022, 42, 16637–16660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tysnes, O.-B.; Storstein, A. Epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease. J. Neural Transm. 2017, 124, 901–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura-Aguilar, J. Clinical Studies and Therapies in Parkinson’s Disease: Translations from Preclinical Models; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal, N.; Saini, B.S.; Gupta, S. The impact of clinical scales in Parkinson’s disease: A systematic review. Egypt. J. Neurol. Psychiatry Neurosurg. 2021, 57, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, S.; Bhartia, S.; Yadav, A.; Seeja, K. Predicting severity of Parkinson’s disease using deep learning. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 132, 1788–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garabadu, D.; Agrawal, N. Naringin exhibits neuroprotection against rotenone-induced neurotoxicity in experimental rodents. NeuroMolecular Med. 2020, 22, 314–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ntchapda, F.; Barama, J.; Azambou, D.R.K.; Etet, P.F.S.; Dimo, T. Diuretic and antioxidant activities of the aqueous extract of leaves of Cassia occidentalis (Linn.) in rats. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2015, 8, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betarbet, R.; Sherer, T.B.; MacKenzie, G.; Garcia-Osuna, M.; Panov, A.V.; Greenamyre, J.T. Chronic systemic pesticide exposure reproduces features of Parkinson’s disease. Nat. Neurosci. 2000, 3, 1301–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naughton, C.; O’Toole, D.; Kirik, D.; Dowd, E. Interaction between subclinical doses of the Parkinson’s disease associated gene, α-synuclein, and the pesticide, rotenone, precipitates motor dysfunction and nigrostriatal neurodegeneration in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2017, 316, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Salam, O.M.; Youness, E.R.; Ahmed, N.A.; El-Toumy, S.A.; Souleman, A.M.; Shaffie, N.; Abouelfadl, D.M. Bougainvillea spectabilis flowers extract protects against the rotenone-induced toxicity. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2017, 10, 478–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.; Schmidt, W. Rotenone destroys dopaminergic neurons and induces parkinsonian symptoms in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2002, 136, 317–324. [Google Scholar]
- Karch, A.M. Focus on Nursing Pharmacology; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, N.; Bafna, P. Effect of Cynodon dactylon on rotenone induced Parkinson’s disease. Orient. Pharm. Exp. Med. 2012, 12, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Q.Q.; Xu, X.Y.; Cao, S.Y.; Gan, R.Y.; Corke, H.; Beta, T.; Li, H.B. Bioactive Compounds and Bioactivities of Ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe). Foods 2019, 8, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jambi, E.J.; Alamri, A.; Afzal, M.; Al-Abbasi, F.A.; Al-Qahtani, S.D.; Almalki, N.A.R.; Bawadood, A.S.; Alzarea, S.I.; Sayyed, N.; Kazmi, I. 6-shogaol against 3-Nitropropionic acid-induced Huntington’s disease in rodents: Based on molecular docking/targeting pro-inflammatory cytokines/NF-κB-BDNF-Nrf2 pathway. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0305358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Afzal, M.; Kazmi, I.; Quazi, A.M.; Khan, S.A.; Zafar, A.; Al-Abbasi, F.A.; Imam, F.; Alharbi, K.S.; Alzarea, S.I.; Yadav, N. 6-Shogaol attenuates traumatic brain injury-induced anxiety/depression-like behavior via inhibition of oxidative stress-influenced expressions of inflammatory mediators TNF-α, IL-1β, and BDNF: Insight into the mechanism. ACS Omega 2021, 7, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.; Kim, H.G.; Ju, M.S.; Ha, S.K.; Park, Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Oh, M.S. 6-Shogaol, an active compound of ginger, protects dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson’s disease models via anti-neuroinflammation. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2013, 34, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brigo, F.; Erro, R.; Marangi, A.; Bhatia, K.; Tinazzi, M. Differentiating drug-induced parkinsonism from Parkinson’s disease: An update on non-motor symptoms and investigations. Park. Relat. Disord. 2014, 20, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapointe, J.; Li, C.; Higgins, J.P.; Van De Rijn, M.; Bair, E.; Montgomery, K.; Ferrari, M.; Egevad, L.; Rayford, W.; Bergerheim, U. Gene expression profiling identifies clinically relevant subtypes of prostate cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramkumar, M.; Rajasankar, S.; Swaminathan Johnson, W.M.S.; Prabu, K.; Venkateshgobi, V. Demethoxycurcumin ameliorates rotenone-induced toxicity in rats. Front. Biosci. Elite 2019, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Sherer, N.M.; Lehmann, M.J.; Jimenez-Soto, L.F.; Horensavitz, C.; Pypaert, M.; Mothes, W. Retroviruses can establish filopodial bridges for efficient cell-to-cell transmission. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid Nadeem, M.; Khan, J.A.; Al-Abbasi, F.A.; AlGhamdi, S.A.; Alghamdi, A.M.; Sayyed, N.; Gupta, G.; Kazmi, I. Protective effect of hirsutidin against rotenone-induced parkinsonism via inhibition of caspase-3/interleukins-6 and 1β. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 13016–13025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, R.; Borah, A. Global loss of acetylcholinesterase activity with mitochondrial complexes inhibition and inflammation in brain of hypercholesterolemic mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Salam, O.M.; Mohammed, N.A.; Youness, E.R.; Khadrawy, Y.A.; Omara, E.A.; Sleem, A.A. Cerebrolysin protects against rotenone-induced oxidative stress and neurodegeneration. J. Neurorestoratology 2014, 2, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Altharawi, A.; Alharthy, K.M.; Althurwi, H.N.; Albaqami, F.F.; Alzarea, S.I.; Al-Abbasi, F.A.; Nadeem, M.S.; Kazmi, I. Europinidin Inhibits Rotenone-Activated Parkinson’s Disease in Rodents by Decreasing Lipid Peroxidation and Inflammatory Cytokines Pathways. Molecules 2022, 27, 7159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fikry, H.; Saleh, L.A.; Abdel Gawad, S. Neuroprotective effects of curcumin on the cerebellum in a rotenone-induced Parkinson’s Disease Model. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2022, 28, 732–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saggu, H.; Cooksey, J.; Dexter, D.; Wells, F.; Lees, A.; Jenner, P.; Marsden, C. A selective increase in particulate superoxide dismutase activity in parkinsonian substantia nigra. J. Neurochem. 1989, 53, 692–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadrawy, Y.A.; Salem, A.M.; El-Shamy, K.A.; Ahmed, E.K.; Fadl, N.N.; Hosny, E.N. Neuroprotective and therapeutic effect of caffeine on the rat model of Parkinson’s disease induced by rotenone. J. Diet. Suppl. 2017, 14, 553–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dexter, D.T.; Holley, A.E.; Flitter, W.D.; Slater, T.F.; Wells, F.R.; Daniel, S.E.; Lees, A.J.; Jenner, P.; Marsden, C.D. Increased levels of lipid hydroperoxides in the parkinsonian substantia nigra: An HPLC and ESR study. Mov. Disord. 1994, 9, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes, S.; Rivera-Mancia, S.; Diaz-Ruiz, A.; Tristan-Lopez, L.; Rios, C. Copper and copper proteins in Parkinson’s disease. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2014, 2014, 147251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeser, H.; Lee, G.; Nacht, S.; Cartwright, G. The role of ceruloplasmin in iron metabolism. J. Clin. Investig. 1970, 49, 2408–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoilova, I.; Krastanov, A.; Stoyanova, A.; Denev, P.; Gargova, S. Antioxidant activity of a ginger extract (Zingiber officinale). Food Chem. 2007, 102, 764–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeena, K.; Liju, V.B.; Kuttan, R. Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive activities of essential oil from ginger. Indian J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2013, 57, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qi, H.; Han, B. Protective effect of 6-shogaol against endotoxin-induced periodontitis in rats. Acta Pol. Pharm. Drug Res. 2018, 75, 1391–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- More, S.V.; Kumar, H.; Kim, I.S.; Song, S.-Y.; Choi, D.-K. Cellular and molecular mediators of neuroinflammation in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 952375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Chen, X.; Zhang, N.; Song, Y.; Mu, Y. Gastrodin inhibits neuroinflammation in rotenone-induced Parkinson’s disease model rats. Neural Regen. Res. 2012, 7, 325. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mansour, R.M.; Ahmed, M.A.; El-Sahar, A.E.; El Sayed, N.S. Montelukast attenuates rotenone-induced microglial activation/p38 MAPK expression in rats: Possible role of its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and antiapoptotic effects. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2018, 358, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alabi, A.O.; Ajayi, A.M.; Ben-Azu, B.; Bakre, A.G.; Umukoro, S. Methyl jasmonate abrogates rotenone-induced parkinsonian-like symptoms through inhibition of oxidative stress, release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and down-regulation of immnopositive cells of NF-κB and α-synuclein expressions in mice. NeuroToxicology 2019, 74, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzarea, S.I.; Afzal, M.; Alharbi, K.S.; Alzarea, A.I.; Alenezi, S.K.; Alshammari, M.S.; Alquraini, A.; Kazmi, I. Hibiscetin attenuates oxidative, nitrative stress and neuroinflammation via suppression of TNF-α signaling in rotenone induced parkinsonism in rats. Saudi Pharm. J. 2022, 30, 1710–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, A.M.; Al-Abbasi, F.A.; AlGhamdi, S.A.; Fatima, F.; Alzarea, S.I.; Kazmi, I. Rosinidin inhibits NF-κB/Nrf2/caspase-3 expression and restores neurotransmitter levels in rotenone-activated Parkinson’s disease. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 30, 103656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazmi, I.; Al-Abbasi, F.A.; Almalki, N.A.; Sheikh, R.A.; Al-Qahtani, S.D.; Nadeem, M.S.; Beg, S.; Afzal, M. Malvidin attenuates behavioral and inhibits the TNF-α/Caspase-3/Nrf-2 expression in rotenone-induced Parkinson’s disease in rats: Insights from molecular docking. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2024, 28, 3330–3346. [Google Scholar]
- Veloso, C.C.; Bitencourt, A.D.; Cabral, L.D.; Franqui, L.S.; Dias, D.F.; dos Santos, M.H.; Soncini, R.; Giusti-Paiva, A. Pyrostegia venusta attenuate the sickness behavior induced by lipopolysaccharide in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 132, 355–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soncini, R.; de Souza, D.F.; Neves, A.P.; Braga, D.S.; Andrade, C.A.; Giusti-Paiva, A. Dipyrone attenuates acute sickness response to lipopolysaccharide in mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2012, 516, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshehri, S.; Imam, S.S. Rosinidin Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Memory Impairment in Rats: Possible Mechanisms of Action Include Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Can, A.; Dao, D.T.; Arad, M.; Terrillion, C.E.; Piantadosi, S.C.; Gould, T.D. The mouse forced swim test. J. Vis. Exp. 2012, 59, e3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateshgobi, V.; Rajasankar, S.; Johnson, W.; Prabu, K.; Ramkumar, M. Neuroprotective Effect of Agaricus Blazei Extract Against Rotenone-Induced Motor and Nonmotor Symptoms in Experimental Model of Parkinsons Disease. Int. J. Nutr. Pharmacol. Neurol. Dis. 2018, 8, 59–65. [Google Scholar]
- Yankelevitch-Yahav, R.; Franko, M.; Huly, A.; Doron, R. The forced swim test as a model of depressive-like behavior. J. Vis. Exp. 2015, 97, 52587. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.; Kalonia, H.; Kumar, A. Novel protective mechanisms of antidepressants against 3-nitropropionic acid induced Huntington’s-like symptoms: A comparative study. J. Psychopharmacol. 2011, 25, 1399–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, H.-C.; Wang, M.-H.; Chang, K.-C.; Soung, H.-S.; Fang, C.-H.; Lin, Y.-W.; Li, K.-Y.; Yang, C.-C.; Tsai, C.-C. Protective effect of (−) epigallocatechin-3-gallate on rotenone-induced parkinsonism-like symptoms in rats. Neurotox. Res. 2020, 37, 669–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, M.M.; Bellissimo, M.I.; Anselmo-Franci, J.A.; Angellucci, M.E.M.; Canteras, N.S.; Da Cunha, C. Comparison of bilaterally 6-OHDA-and MPTP-lesioned rats as models of the early phase of Parkinson’s disease: Histological, neurochemical, motor and memory alterations. J. Neurosci. Methods 2005, 148, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Kandhare, A.D.; Mukherjee, A.A.; Bodhankar, S.L. Hesperidin, a plant flavonoid accelerated the cutaneous wound healing in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: Role of TGF-ß/Smads and Ang-1/Tie-2 signaling pathways. EXCLI J. 2018, 17, 399. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.; Kumar, A. Protective effect of rivastigmine against 3-nitropropionic acid-induced Huntington’s disease like symptoms: Possible behavioural, biochemical and cellular alterations. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 615, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeyadi, M.; Al-Abbasi, F.A.; Afzal, M.; Bawadood, A.S.; Sheikh, R.A.; Alzarea, S.I.; Sayyed, N.; Kazmi, I. Butin attenuates behavioral disorders via cholinergic/BDNF/Caspase-3 pathway in scopolamine-evoked memory deficits in rats. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2024, 3, 981–994. [Google Scholar]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.D.; Andres Jr, V.; Featherstone, R.M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyagi, E.; Agrawal, R.; Nath, C.; Shukla, R. Effect of melatonin on neuroinflammation and acetylcholinesterase activity induced by LPS in rat brain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 640, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wysocka, A.; Cybulski, M.; Berbeć, H.; Wysokiński, A.; Stążka, J.; Daniluk, J.; Zapolski, T. Dynamic changes of paraoxonase 1 activity towards paroxon and phenyl acetate during coronary artery surgery. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2017, 17, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alharthy, K.M.; Althurwi, H.N.; Albaqami, F.F.; Altharawi, A.; Alzarea, S.I.; Al-Abbasi, F.A.; Nadeem, M.S.; Kazmi, I. Barbigerone Potentially Alleviates Rotenone-Activated Parkinson’s Disease in a Rodent Model by Reducing Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammatory Cytokines. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 4608–4615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Aebi, H.; Wyss, S.R.; Scherz, B.; Skvaril, F. Heterogeneity of erythrocyte catalase II: Isolation and characterization of normal and variant erythrocyte catalase and their subunits. Eur. J. Biochem. 1974, 48, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wills, E. Mechanisms of lipid peroxide formation in animal tissues. Biochem. J. 1966, 99, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, S. Measurement of nitric oxide in biological models. FASEB J. 1993, 7, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, L.C.; Wagner, D.A.; Glogowski, J.; Skipper, P.L.; Wishnok, J.S.; Tannenbaum, S.R. Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and [15N] nitrate in biological fluids. Anal. Biochem. 1982, 126, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagakannan, P.; Shivasharan, B.; Thippeswamy, B.; Veerapur, V. Restoration of brain antioxidant status by hydroalcoholic extract of Mimusops elengi flowers in rats treated with monosodium glutamate. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. Oncol. 2012, 31, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraf, S.L.; Lin, X.; Lee, G.; Adjei, E.A.; Kumari, N.; Gordeuk, V.R.; Jerebtsova, M.; Nekhai, S.A. Urinary ceruloplasmin concentration predicts development of kidney disease in sickle cell disease patients. Blood 2016, 128, 4865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; El-Sayed, M.M.; Kandeil, M.A.; Khalaf, M.M. Empagliflozin attenuates neurodegeneration through antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and modulation of α-synuclein and Parkin levels in rotenone-induced Parkinson’s disease in rats. Saudi Pharm. J. 2022, 30, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
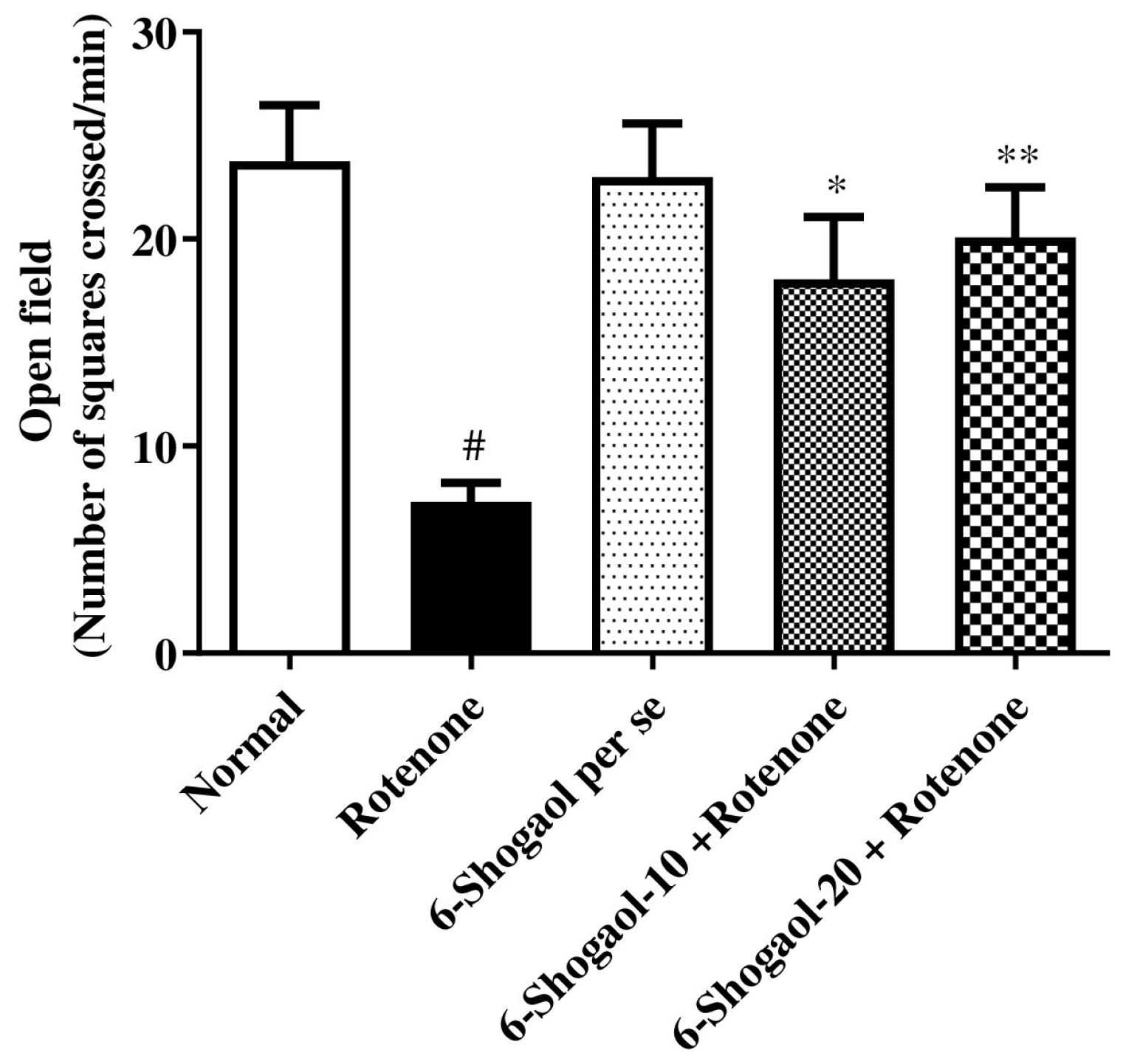

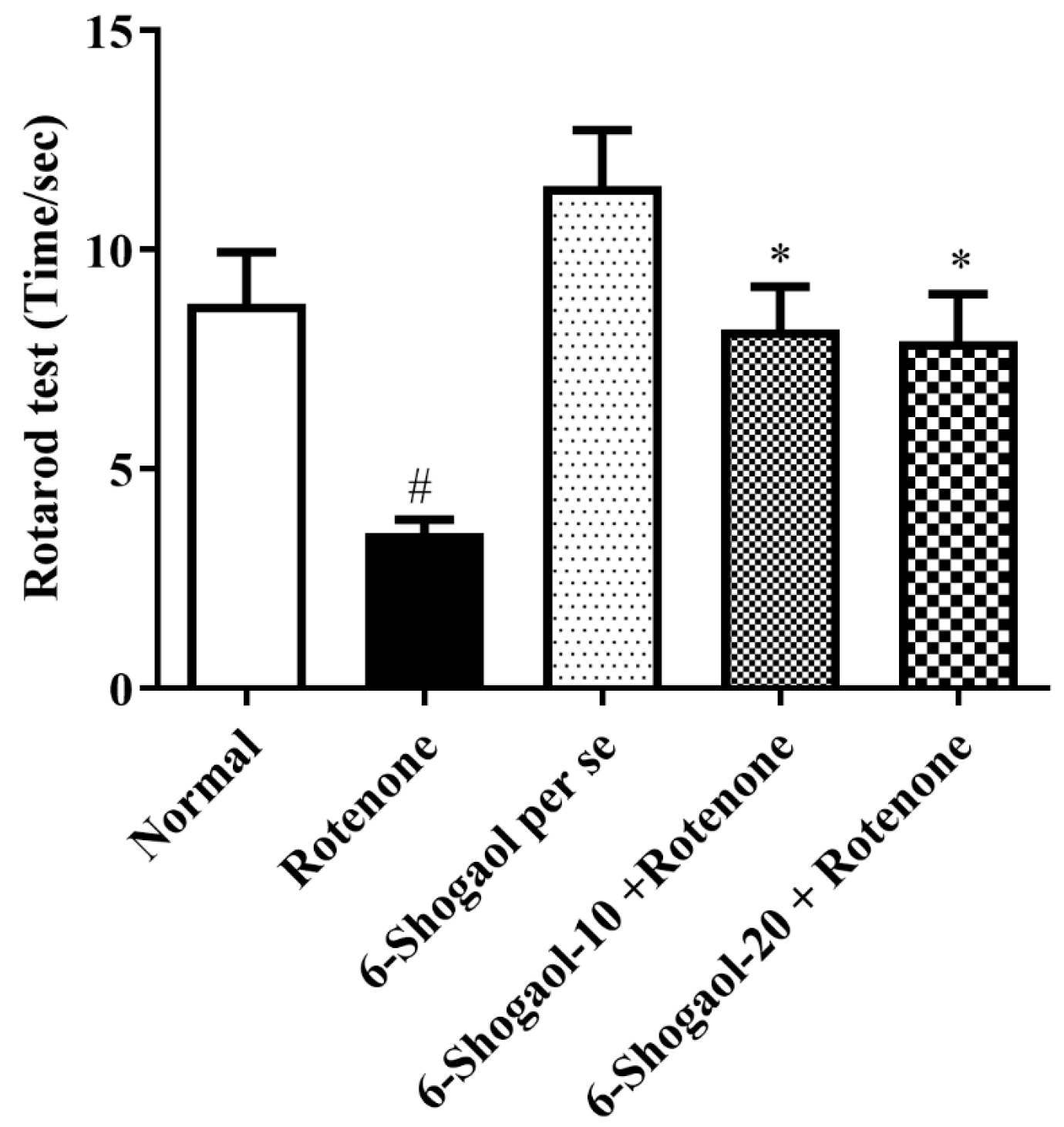
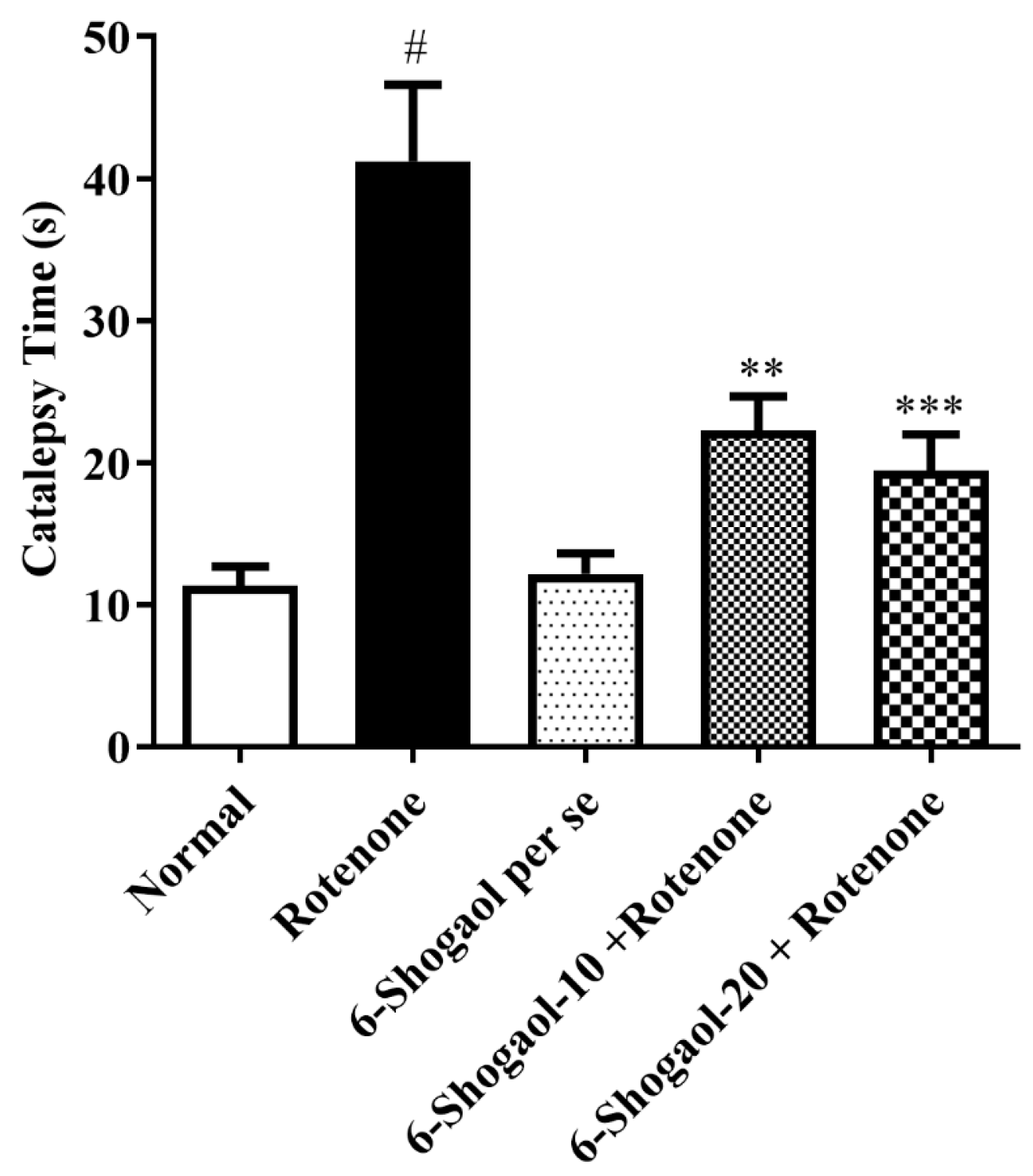
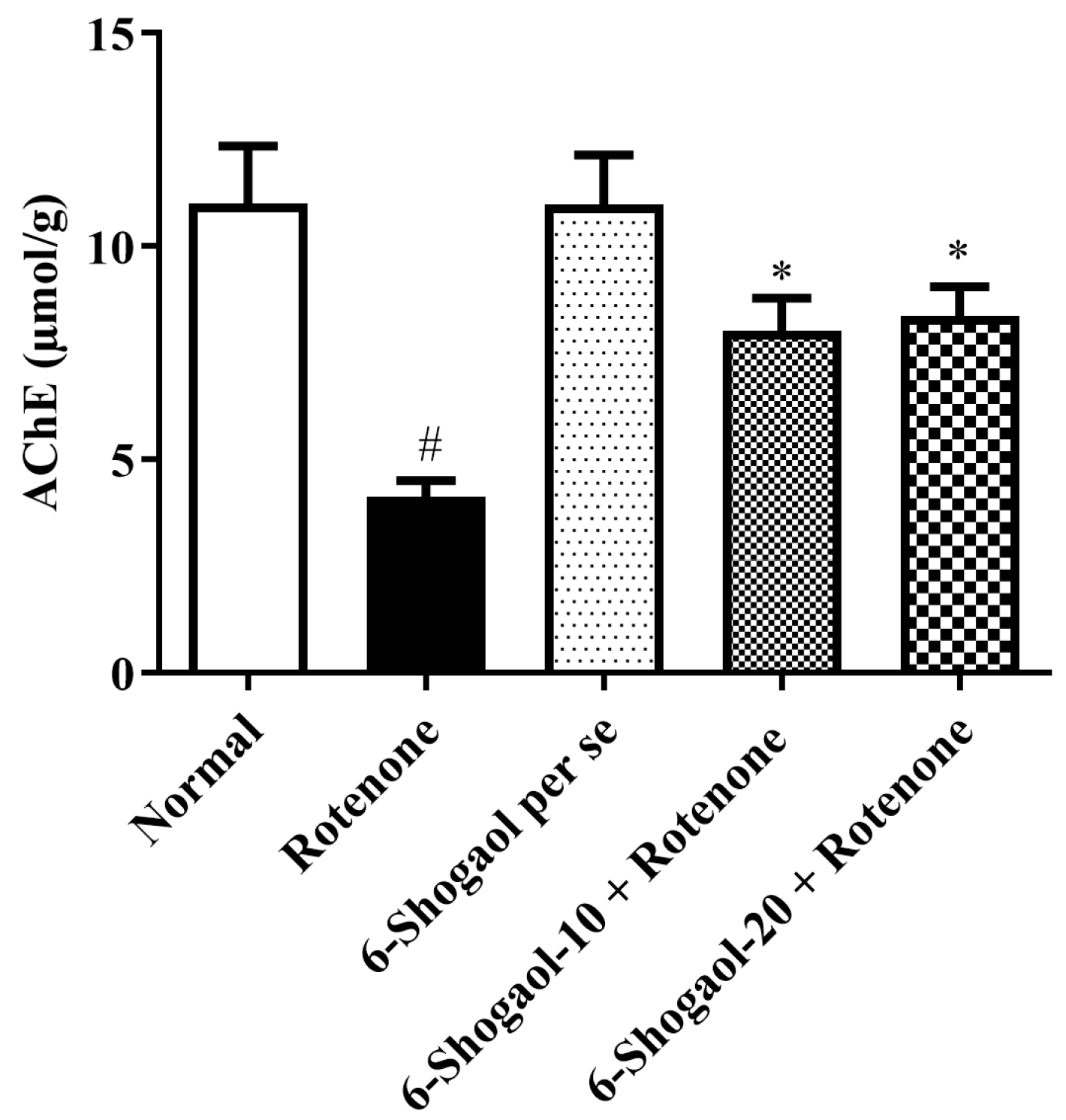


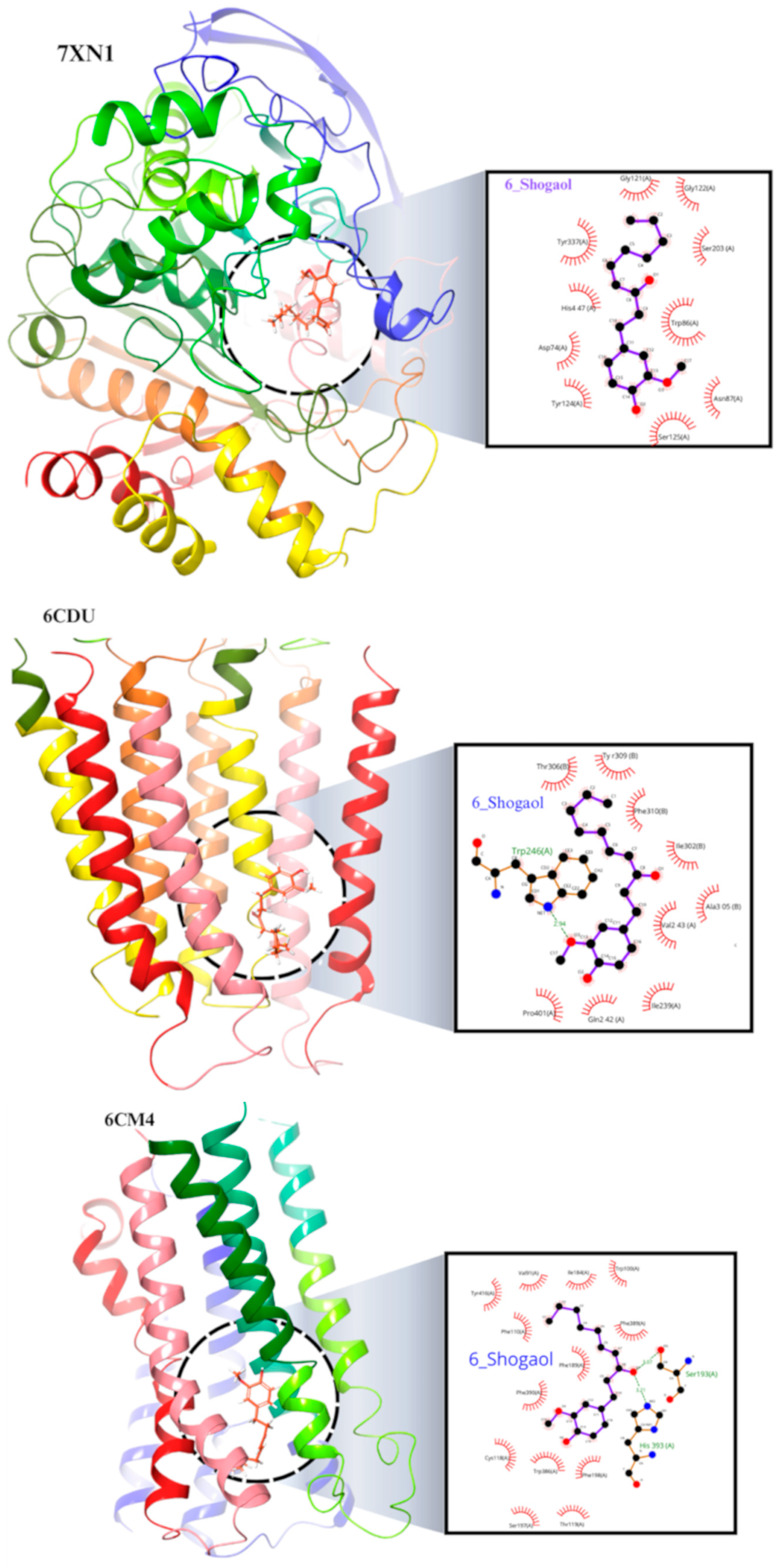

| Sr. No | Name of Compound | Binding Energy | Type of Interaction | Residue ID | Distance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 7xn1_6-Shogaol | −8.214 | Hydrophobic Interactions | ASP74A | 3.51 |
| TRP86A | 3.66 | ||||
| TRP86A | 3.65 | ||||
| TRP86A | 3.99 | ||||
| TYR337A | 3.97 | ||||
| TYR337A | 3.94 | ||||
| Hydrogen Bonds | TRP86A | 2.09 | |||
| TYR337A | 3.52 | ||||
| 2 | 6cm4_6-Shogaol | −7.396 | Hydrophobic Interactions | VAL91A | 3.75 |
| LEU94A | 3.98 | ||||
| TRP100A | 3.83 | ||||
| PHE110A | 3.77 | ||||
| ILE184A | 3.42 | ||||
| PHE189A | 3.76 | ||||
| PHE189A | 3.98 | ||||
| PHE389A | 3.76 | ||||
| PHE389A | 3.43 | ||||
| PHE390A | 3.63 | ||||
| THR412A | 3.99 | ||||
| Hydrogen Bonds | SER193A | 2.47 | |||
| SER197A | 2.81 | ||||
| HIS393A | 2.45 | ||||
| π-Stacking | TRP386A | 5.34 | |||
| 3 | 6CDU_6-Shogaol | −6.189 | Hydrophobic Interactions | ILE239A | 3.63 |
| VAL243A | 3.77 | ||||
| VAL243A | 3.48 | ||||
| TRP246A | 3.3 | ||||
| TRP246A | 3.83 | ||||
| ILE302B | 3.88 | ||||
| THR306B | 3.53 | ||||
| TYR309B | 3.7 | ||||
| PHE310B | 3.68 | ||||
| Hydrogen Bonds | TRP246A | 2.22 | |||
| THR306B | 3.65 | ||||
| 4 | 2v5z_6-Shogaol | −8.133 | Hydrophobic Interactions | LEU171A | 3.74 |
| LEU171A | 3.75 | ||||
| GLN206A | 4 | ||||
| TYR326A | 3.84 | ||||
| PHE343A | 3.33 | ||||
| TYR398A | 3.39 | ||||
| TYR398A | 3.7 | ||||
| TYR398A | 3.84 | ||||
| TYR398A | 3.6 | ||||
| TYR435A | 3.67 | ||||
| TYR435A | 3.61 | ||||
| Hydrogen Bonds | ILE198A | 2.24 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rafeeq, M.; Al-Abbasi, F.A.; Afzal, M.; Moglad, E.; Al-Qahtani, S.D.; Alzrea, S.I.; Almalki, N.A.R.; Imam, F.; Sayyed, N.; Kazmi, I. 6-Shogaol Abrogates Parkinson’s Disease in Rotenone-Induced Rodents: Based on In Silico Study and Inhibiting TNF-α/NF-κB/IL-1β/MAO-B. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17101348
Rafeeq M, Al-Abbasi FA, Afzal M, Moglad E, Al-Qahtani SD, Alzrea SI, Almalki NAR, Imam F, Sayyed N, Kazmi I. 6-Shogaol Abrogates Parkinson’s Disease in Rotenone-Induced Rodents: Based on In Silico Study and Inhibiting TNF-α/NF-κB/IL-1β/MAO-B. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(10):1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17101348
Chicago/Turabian StyleRafeeq, Misbahuddin, Fahad A. Al-Abbasi, Muhammad Afzal, Ehssan Moglad, Salwa D. Al-Qahtani, Sami I. Alzrea, Naif A. R. Almalki, Faisal Imam, Nadeem Sayyed, and Imran Kazmi. 2024. "6-Shogaol Abrogates Parkinson’s Disease in Rotenone-Induced Rodents: Based on In Silico Study and Inhibiting TNF-α/NF-κB/IL-1β/MAO-B" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 10: 1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17101348
APA StyleRafeeq, M., Al-Abbasi, F. A., Afzal, M., Moglad, E., Al-Qahtani, S. D., Alzrea, S. I., Almalki, N. A. R., Imam, F., Sayyed, N., & Kazmi, I. (2024). 6-Shogaol Abrogates Parkinson’s Disease in Rotenone-Induced Rodents: Based on In Silico Study and Inhibiting TNF-α/NF-κB/IL-1β/MAO-B. Pharmaceuticals, 17(10), 1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17101348







