Zinc Oxide and Magnesium-Doped Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Ameliorate Murine Chronic Toxoplasmosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
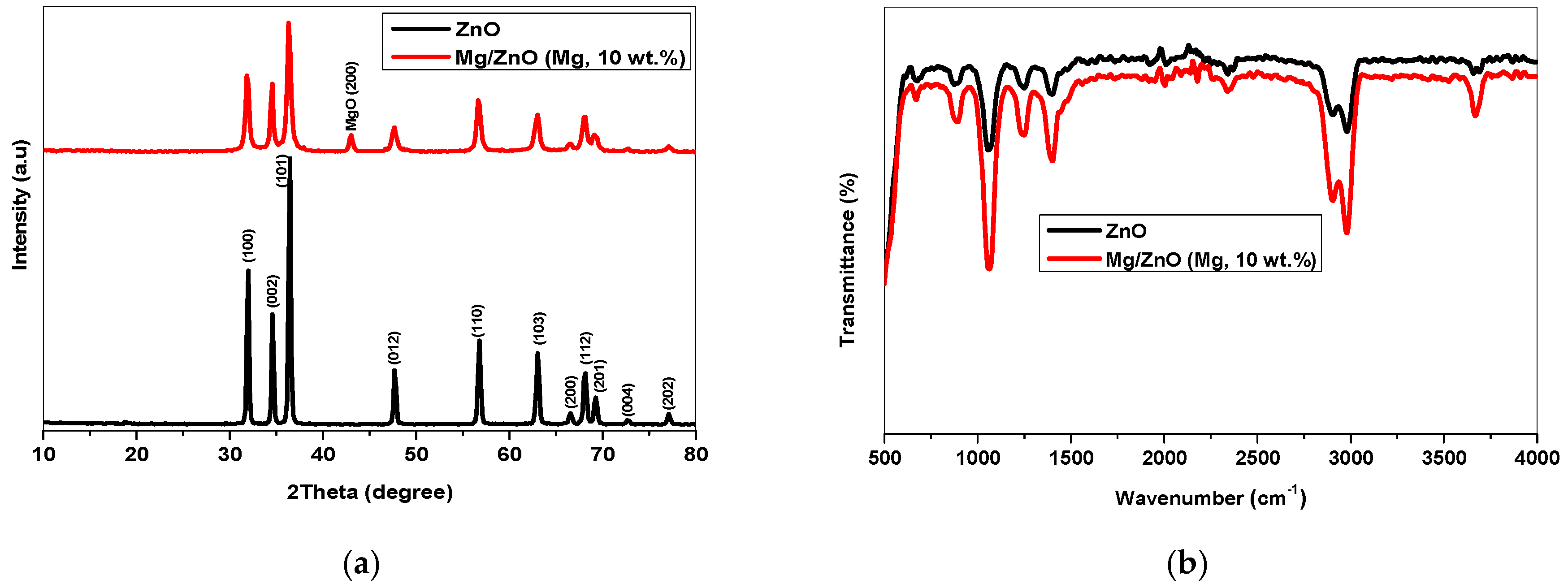
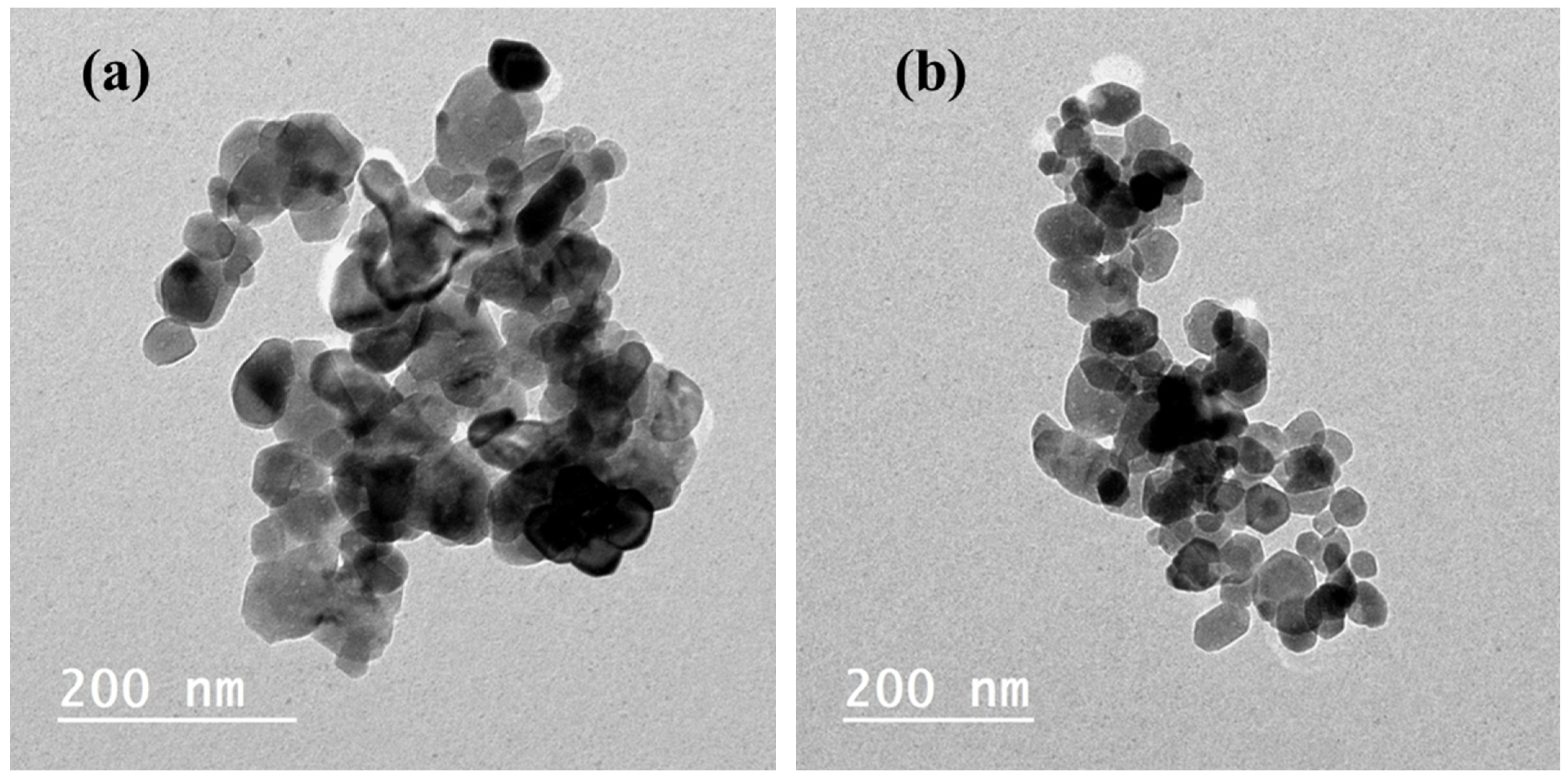
2.1. Crystal Structure, Functional Group, Chemical Valence, and Morphological Analysis
2.1.1. XRD Analysis
2.1.2. FTIR Analysis
2.1.3. XPS Analysis
2.1.4. TEM Analysis
2.2. Parasitological Assessment
2.2.1. Parasitic Burden Assessment
2.2.2. Histopathological Assessment
- Brain
- Liver
- Spleen
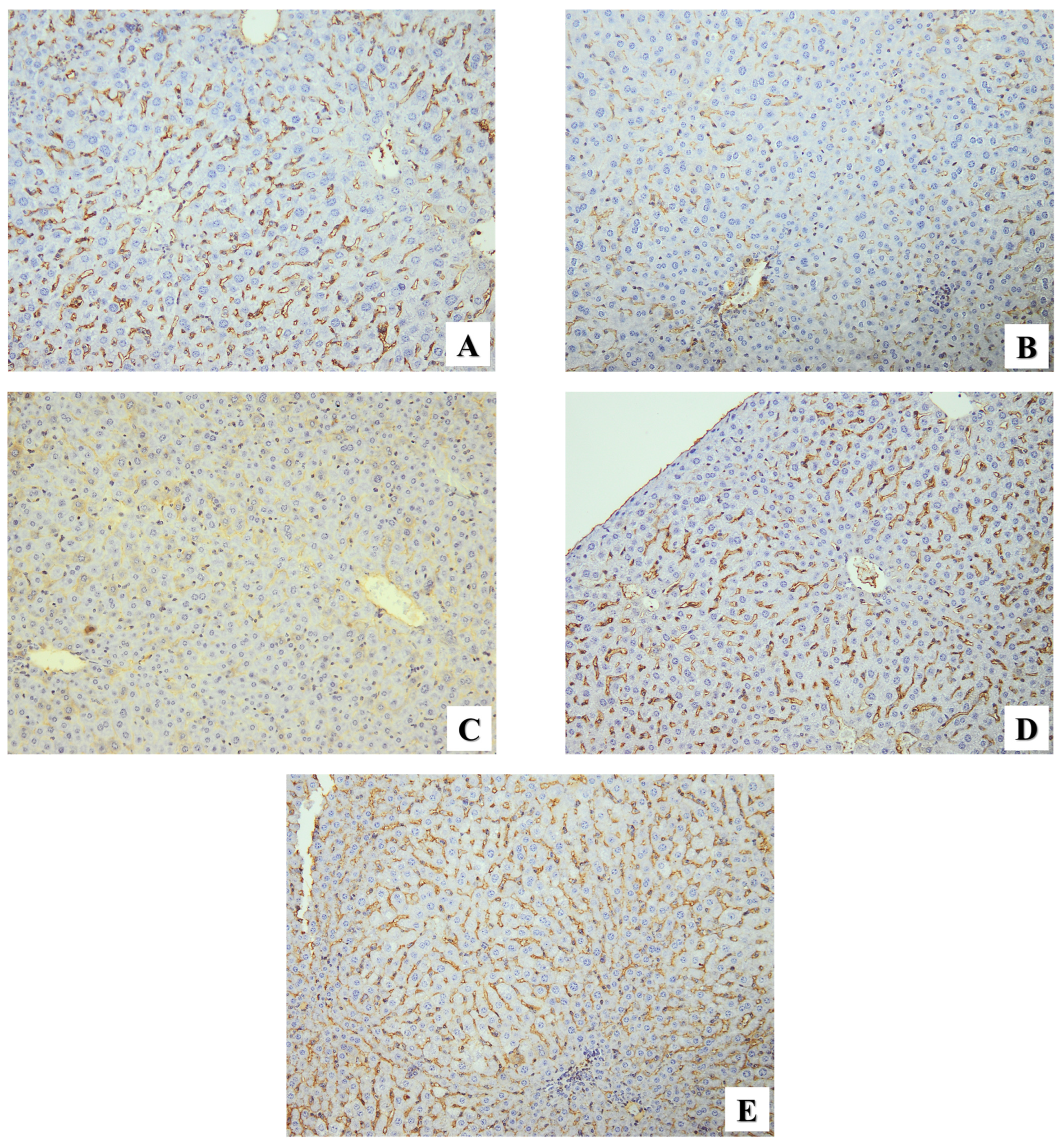
2.2.3. Immunohistochemical Assessment
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Proclamation
4.2. Synthesis of NPs
4.2.1. Materials for Synthesis of NPs
4.2.2. Synthesis of Un-Doped ZnO and Mg-Doped ZnO Using Co-Precipitation Method
4.3. Characterization of Un-Doped ZnO and Mg-Doped ZnO
4.4. Experimental Design
4.4.1. Parasite Strain and Infection
4.4.2. Animal Model
4.4.3. Treatment Schedule
4.4.4. Collecting Samples
4.5. Parasitological Assessment
4.5.1. Parasitic Burden Assessment
4.5.2. Histopathological Assessment
4.5.3. Immunohistochemistry Assessment
4.5.4. Inflammatory and Immunohistochemical Scoring
4.6. Analytical Statistics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Z.D.; Liu, H.H.; Ma, Z.X.; Ma, H.Y.; Li, Z.Y.; Yang, Z.B.; Liu, Q. Toxoplasma gondii infection in immunocompromised patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shammaa, A.M.; Powell, T.G.; Benmerzouga, I. Adverse outcomes associated with the treatment of Toxoplasma infections. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greigert, V.; Bittich-Fahmi, F.; Pfaff, A.W. Pathophysiology of ocular toxoplasmosis: Facts and open questions. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahighi, M.; Heidari, A.; Keshavarz, H.; Bairami, A.; Shojaee, S.; Sezavar, M.; Teimouri, A. Seroepidemiological study of toxoplasmosis in women referred to a pre-marriage counseling center in Alborz Province, Iran. BMC Res. Notes 2021, 14, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarean, M.; Shafiei, R.; Gholami, M.; Fata, A.; Balaghaleh, M.R.; Karimi, A.; Akhavan, A. Seroprevalence of anti–Toxoplasma Gondii antibodies in healthy voluntary blood Donors from Mashhad City, Iran. Arch. Iran. Med. 2017, 20, 441. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arnold, K.C.; Flint, C.J.; Arnold, K.C.; Flint, C.J. Cytomegalovirus, Parvovirus B19, Varicella Zoster, and Toxoplasmosis in Pregnancy. In Obstetrics Essentials: A Question-Based Review; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 199–207. [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson, F.; Stallings, C.; Origoni, A.; Katsafanas, E.; Schweinfurth, L.; Savage, C.; Yolken, R. Antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii and cognitive functioning in schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and nonpsychiatric controls. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 2014, 202, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Keefe, K.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y. Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of p53 is essential for MDM2-mediated cytoplasmic degradation but not ubiquitination. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 6396–6405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tousson, E.; Beltagy, D.M.; Gazia, M.A.; Al-Behbehani, B. Expressions of P53 and CD68 in mouse liver with Schistosoma mansoni infection and the protective role of silymarin. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2013, 29, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honnegowda, T.M.; Kumar, P.; Udupa, E.G.P.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, U.; Rao, P. Role of angiogenesis and angiogenic factors in acute and chronic wound healing. Plast. Aesthetic Res. 2015, 2, 243–249. [Google Scholar]
- Imhof, B.A.; Dunon, D. Leukocyte migration and adhesion. Adv. Immunol. 1995, 58, 345–416. [Google Scholar]
- Nishi, L.; Santana, P.L.; Evangelista, F.F.; Beletini, L.F.; Souza, A.H.; Mantelo, F.M.; Falavigna-Guilherme, A.L. Rosuvastatin reduced brain parasite burden in a chronic toxoplasmosis in vivo model and influenced the neuropathological pattern of ME-49 strain. Parasitology 2020, 147, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunay, I.R.; Gajurel, K.; Dhakal, R.; Liesenfeld, O.; Montoya, J.G. Treatment of toxoplasmosis: Historical perspective, animal models, and current clinical practice. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 31, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinovic, N.; Guegan, H.; Stäjner, T.; Belaz, S.; Robert-Gangneux, F. Treatment of toxoplasmosis: Current options and future perspectives. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2019, 15, e00036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azami, S.J.; Teimouri, A.; Keshavarz, H.; Amani, A.; Esmaeili, F.; Hasanpour, H.; Shojaee, S. Curcumin nanoemulsion as a novel chemical for the treatment of acute and chronic toxoplasmosis in mice. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 7363–7374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foroutan, M.; Ghaffarifar, F. Calcium-dependent protein kinases are potential targets for Toxoplasma gondii vaccine. Clin. Exp. Vaccine Res. 2018, 7, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azami, S.J.; Amani, A.; Keshavarz, H.; Najafi-Taher, R.; Mohebali, M.; Faramarzi, M.A.; Shojaee, S. Nanoemulsion of atovaquone as a promising approach for treatment of acute and chronic toxoplasmosis. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 117, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawab, R.; Iqbal, A.; Niazi, F.; Iqbal, G.; Khurshid, A.; Saleem, A.; Munis, M.F.H. Review featuring the use of inorganic nano-structured material for anti-microbial properties in textile. Polym. Bull. 2023, 80, 7221–7245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babayevska, N.; Przysiecka, L.; Iatsunskyi, I.; Nowaczyk, G.; Jarek, M.; Janiszewska, E.; Jurga, S. ZnO size and shape effect on antibacterial activity and cytotoxicity profile. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, D.J.; Duran, A.; Cabral, A.D.; Fonseca, F.L.; Bueno, R.F.; Rosa, D.S. Questioning ZnO, Ag, and Ag/ZnO nanoparticles as antimicrobial agents for textiles: Do they guarantee total protection against bacteria and SARS-CoV-2? J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2022, 234, 112538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, R.A.; Ghazali, N.M.; Kassem, L.M.; Elgazzar, E.; Mostafa, W.A. Synthesis of MnCoO/CNT nanoflakes for the photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange dye and the evaluation of their activity against Culex pipiens larvae in the purification of fresh water. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 29048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khashan, K.S.; Sulaiman, G.M.; Hussain, S.A.; Marzoog, T.R.; Jabir, M.S. Synthesis, characterization and evaluation of anti-bacterial, anti-parasitic and anti-cancer activities of aluminum-doped zinc oxide nanoparticles. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2020, 30, 3677–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batool, M.; Nazar, M.F.; Awan, A.; Tahir, M.B.; Rahdar, A.; Shalan, A.E.; Lanceros-Méndez, S.; Zafar, M.N. Bismuth-based heterojunction nanocomposites for photocatalysis and heavy metal detection applications. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2021, 27, 100762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kermanizadeh, A.; Balharry, D.; Wallin, H.; Loft, S.; Møller, P. Nanomaterial translocation–the biokinetics, tissue accumulation, toxicity and fate of materials in secondary organs–a review. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2015, 45, 837–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd El-Hack, M.E.; Alagawany, M.; Salah, A.S.; Abdel-Latif, M.A.; Farghly, M.F. Effects of dietary supplementation of zinc oxide and zinc methionine on layer performance, egg quality, and blood serum indices. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2018, 184, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd El-Hack, M.E.; Alagawany, M.; Arif, M.; Chaudhry, M.T.; Emam, M.; Patra, A. Organic or inorganic zinc in poultry nutrition: A review. World’s Poult. Sci. J. 2017, 73, 904–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brakat, R.M.; Sharaf-El-Deen, S.A.; Abd ElHafiz, H.I. Zinc oxide nanoparticles kill giardia and protect against intestinal damage. Egypt. J. Med. Microbiol. 2019, 28, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dkhil, M.A.; Al-Quraishy, S.; Wahab, R. Anticoccidial and antioxidant activities of zinc oxide nanoparticles on Eimeria papillata-induced infection in the jejunum. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 1961–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Humaidi, J.Y.; Hagar, M.; Bakr, B.A.; Elwakil, B.H.; Moneer, E.A.; El-Khatib, M. Decorative multi-walled carbon nanotubes by ZnO: Synthesis, characterization, and potent anti-toxoplasmosis activity. Metals 2022, 12, 1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadatmand, M.; Al-Awsi, G.R.L.; Alanazi, A.D.; Sepahvand, A.; Shakibaie, M.; Shojaee, S.; Mohammadi, R.; Mahmoudvand, H. Green synthesis of zinc nanoparticles using Lavandula angustifolia Vera. Extract by microwave method and its prophylactic effects on Toxoplasma gondii infection. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 6454–6460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Hack, M.E.; Alaidaroos, B.A.; Farsi, R.M.; Abou-Kassem, D.E.; El-Saadony, M.T.; Saad, A.M.; Ashour, E.A. Impacts of supplementing broiler diets with biological curcumin, zinc nanoparticles and Bacillus licheniformis on growth, carcass traits, blood indices, meat quality and cecal microbial load. Animals 2021, 11, 1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasi, G.; Seo, J. Influence of Mg doping on the structural, morphological, optical, thermal, and visible-light responsive antibacterial properties of ZnO nanoparticles synthesized via co-precipitation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 98, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdy, M.S.; Chandekar, K.V.; Shkir, M.; AlFaify, S.; Ibrahim, E.H.; Ahmad, Z.; Kilany, M.; Al-Shehri, B.M.; Al-Namshah, K.S. Novel Mg@ ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by facile one-step combustion route for anti-microbial, cytotoxicity and photocatalysis applications. J. Nanostructure Chem. 2021, 11, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, B.S.; Witola, W.H.; El Bissati, K.; Zhou, Y.; Mui, E.; Fomovska, A.; McLeod, R. Molecular target validation, antimicrobial delivery, and potential treatment of Toxoplasma gondii infections. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 14182–14187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsheikha, H.M.; Marra, C.M.; Zhu, X.Q. Epidemiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management of cerebral toxoplasmosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 34, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Shafey, A.A.; Hegab, M.H.; Seliem, M.M.; Barakat, A.M.; Mostafa, N.E.; Abdel-Maksoud, H.A.; Abdelhameed, R.M. Curcumin@ metal-organic frameworks nano-composite for treatment of chronic toxoplasmosis. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2020, 31, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tari, R.M.; Diallo, A.; Kouame, E.; Assogba, P.; Badjabaissi, E.; Povi, L.E.; Tona, K. Assessment of the Teratogenic Effect of Sulfadoxine-Pyrimethamine on the Chicken Embryo. J. Toxicol. 2022, 2022, 2995492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panchal, P.; Sharma, R.; Reddy, A.S.; Nehra, K.; Sharma, A.; Nehra, S.P. Eco-friendly synthesis of Ag-doped ZnO/MgO as a potential photocatalyst for antimicrobial and dye degradation applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 493, 215283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercan, F.; Alamroo, N.; Ghrib, T.; Kayed, T.; Ozcelik, B.; Ercan, I.; Alonizan, N.; Abubshait, S.A. Structural, optical, and electrical properties of Zn(1−x)MgxO nano-compounds and ZnO/Zn(1−x)MgxO heterostructures. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 290, 126479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldal’in, H.K.; Al-Otaibi, A.M.; Alaryani, F.S.; Alsharif, I.; Alghamdi, Y.S.; Abd El-Hack, M.E.; Abdelnour, S.A. Use of zinc nanoparticles and/or prodigiosin to mitigate heat stress in rabbits. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2023, 23, 1221–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okeke, I.S.; Agwu, K.K.; Ubachukwu, A.A.; Ezema, F.I. Influence of transition metal doping on physiochemical and antibacterial properties of ZnONanoparticles: A review. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, 100227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khyrun, S.F.; Riyas, Z.M.; Raja, V.; Sarbudeen, S.S.; Natesan, V.; Velsankar, K.; Selvaraj, T. Environmental and biomedical applications in the synthesis and structural, optical, elemental characterizations of Mg-doped ZnO nanoparticles using Coleus aromaticus leaf extract. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2022, 151, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochnev, N.D.; Tkachenko, D.S.; Kirsanov, D.O.; Bobrysheva, N.P.; Osmolowsky, M.G.; Voznesenskiy, M.A.; Osmolovskaya, O.M. Regulation and prediction of defect-related properties in ZnO nanosheets: Synthesis, morphological and structural parameters, DFT study and QSPR modeling. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 621, 156828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riyas, Z.M.; Gayathri, R.; Prabhu, M.R.; Velsankar, K.; Sudhahar, S. Green synthesis and biomedical behavior of Mg-doped ZnO nanoparticle using leaf extract of Ficus religiosa. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 24619–24628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Yu, X.; Yan, M.; Weng, T.; Chen, L.; Zhou, Y.; Wei, J. Lowering oxygen vacancies of ZnO nanorods via Mg-doping and their effect on polymeric diode behavior. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2020, 312, 112163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessien, M. Recent progress in zinc oxide nanomaterials and nanocomposites: From synthesis to applications. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 22609–22628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sa-Nguanprang, S.; Phuruangrat, A.; Thongtem, T.; Thongtem, S. Synthesis, analysis, and photocatalysis of Mg-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 64, 1841–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, A.; Al Jitan, S.; Garlisi, C.; Palmisano, G. A review of recent and emerging antimicrobial nanomaterials in wastewater treatment applications. Chemosphere 2021, 278, 130440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, O.S.; El Naggar, H.M.; Abdelmaksoud, H.F.; Barakat, A.M.; Abdelhameed, R.M.; Shehata, M.A.S. The effect of Nigella sativa oil-and wheat germ oil-loaded metal-organic frameworks on chronic murine toxoplasmosis. Acta Trop. 2023, 239, 106823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasai, M.; Pradipta, A.; Yamamoto, M. Host immune responses to Toxoplasma gondii. Int. Immunol. 2018, 30, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emam, M.A.; Farouk, S.M.; Aljazzar, A.; Abdelhameed, A.A.; Eldeeb, A.A.; Gad, F.A.M. Curcumin and cinnamon mitigate lead acetate-induced oxidative damage in the spleen of rats. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 13, 1072760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Sharazly, B.M.; Asaad, I.A.A.; Yassen, N.A.; El Maghraby, G.M.; Carter, W.G.; Mohamed, D.A.; Ismail, H.I. Mefloquine-loaded niosomes as a promising approach for the treatment of acute and chronic toxoplasmosis. Acta Trop. 2023, 239, 106810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etewa, S.E.; El-Maaty, D.A.A.; Hamza, R.S.; Metwaly, A.S.; Sarhan, M.H.; Abdel-Rahman, S.A.; El-Shafey, M.A. Assessment of spiramycin-loaded chitosan nanoparticles treatment on acute and chronic toxoplasmosis in mice. J. Parasit. Dis. 2018, 42, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauomy, A.A. Zinc oxide nanoparticles and L-carnitine effects on neuro-schistosomiasis mansoni induced in mice. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 18699–18707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hamed, A.; Samy, N.; Abd-Rabou, A.; Salem, Z. Therapeutic Efficacy of Kumquat-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles against Toxoplasmosis in mice model. Egypt. J. Chem. 2022, 65, 609–622. [Google Scholar]
- Puetkasichonpasutha, J.; Namwat, N.; Sa-Ngiamwibool, P.; Titapun, A.; Suthiphongchai, T. Evaluation of p53 and its target gene expression as potential biomarkers of cholangiocarcinoma in Thai patients. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. APJCP 2020, 21, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.M.; Guha, R.; Portugal, S.; Skinner, J.; Ongoiba, A.; Bhardwaj, J.; Crompton, P.D. A molecular signature in blood reveals a role for p53 in regulating malaria-induced inflammation. Immunity 2019, 51, 750–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moshrefi, M.; Spotin, A.; Kafil, H.S.; Mahami-Oskouei, M.; Baradaran, B.; Ahmadpour, E.; Mansoori, B. Tumor suppressor p53 induces apoptosis of host lymphocytes experimentally infected by Leishmania major, by activation of Bax and caspase-3: A possible survival mechanism for the parasite. Parasitol. Res. 2017, 116, 2159–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeij, J.P.; Boyle, J.P.; Boothroyd, J.C. Differences among the three major strains of Toxoplasma gondii and their specific interactions with the infected host. Trends Parasitol. 2005, 21, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlog, A.; Schlüter, D.; Dunay, I.R. Toxoplasma gondii-induced neuronal alterations. Parasite Immunol. 2015, 37, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besteiro, S. Toxoplasma control of host apoptosis: The art of not biting too hard the hand that feeds you. Microb. Cell 2015, 2, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kady, A.M.; Al-Megrin, W.A.I.; Abdel-Rahman, I.A.; Sayed, E.; Alshehri, E.A.; Wakid, M.H.; Younis, S.S. Ginger is a potential therapeutic for chronic toxoplasmosis. Pathogens 2022, 11, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoae-Hagh, P.; Rahimifard, M.; Navaei-Nigjeh, M.; Baeeri, M.; Gholami, M.; Mohammadirad, A.; Abdollahi, M. Zinc oxide nanoparticles reduce apoptosis and oxidative stress values in isolated rat pancreatic islets. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2014, 162, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dincel, G.C.; Atmaca, H.T. Increased expressions of ADAMTS-13 and apoptosis contribute to neuropathology during Toxoplasma gondii encephalitis in mice. Neuropathology 2016, 36, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahtzaz, S.; Nasir, M.; Shahzadi, L.; Amir, W.; Anjum, A.; Arshad, R.; Iqbal, F.; Chaudhry, A.A.; Yar, M.; ur Rehman, I. A study on the effect of zinc oxide and zinc peroxide nanoparticles to enhance angiogenesis-pro-angiogenic grafts for tissue regeneration applications. Mater. Des. 2017, 132, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djurković-Djaković, O.; Milenković, V.; Nikolić, A.; Bobić, B.; Grujić, J. Efficacy of atovaquone combined with clindamycin against murine infection with a cystogenic (Me49) strain of Toxoplasma gondii. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2002, 50, 981–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romand, S.; Pudney, M.; Derouin, F. In vitro and in vivo activities of the hydroxynaphthoquinone atovaquone alone or combined with pyrimethamine, sulfadiazine, clarithromycin, or minocycline against Toxoplasma gondii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1993, 37, 2371–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraei, M.; Ghaderi, Y.; Mosavi, T.; Shahnazi, M.; Keshavarz, H.; Shojaee, S. Brain cystogenesis capacity of Toxoplasma gondii, avirulent Tehran strain in mice. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Dis. 2014, 4, S739–S742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvarna, K.S.; Layton, C.; Bancroft, J.D. Bancroft’s Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Salem, M.L.; Shoukry, N.M.; Teleb, W.K.; Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Abdel-Rahman, M.A. In vitro and in vivo antitumor effects of the Egyptian scorpion Androctonus amoreuxi venom in an Ehrlich ascites tumor model. Springerplus 2016, 5, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdi, A.; Baharvand, H.; Javan, M. Enhanced remyelination following lysolecithin-induced demyelination in mice under treatment with fingolimod (FTY720). Neuroscience 2015, 311, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feeney, B.C. A Simple Guide to IBM SPSS® Statistics: For Version 23.0; Cengage Learning: Boston, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]







| Nanoparticles | D (nm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZnO | 29.00 | 1.05 | 12.00 | 52.00 |
| Mg-doped ZnO (10 wt.%) | 23.00 | 1.52 | 20.00 | 41.00 |
| Groups | Tissue Cysts (Mean ± SD) | Std. Error | Reduction (%) | F | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GII | 4205.00 ± 136.32 | 43.11 | - | 1036.82 | <0.001 * |
| GIII | 1202.00 ± 107.48 | 33.99 | 71.41 | ||
| GIV | 2973.00 ± 94.64 | 29.93 | 29.30 | ||
| GV | 2730.00 ± 139.84 | 44.22 | 35.08 |
| Groups | IS in Brain (mean ± SD) | IS in Liver (mean ± SD) | IS in Spleen (mean ± SD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GI | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| GII | 2.50 ± 0.71 | 2.85 ± 0.42 | 2.60 ± 0.70 |
| GIII | 2.65 ± 0.70 | 2.70 ± 0.48 | 2.70 ± 0.68 |
| GIV | 0.70 a ± 0.68 | 1.00 a ± 0.94 | 1.20 ± 1.23 |
| GV | 0.50 a ± 0.71 | 0.80 a ± 0.79 | 1.20 ± 1.14 |
| H | 37.26 | 37.62 | 29.75 |
| p-value | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| Groups | IHS of P53 (mean ± SD) | IHS of CD31 (mean ± SD) |
|---|---|---|
| GI | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 3.00 ± 0.00 |
| GII | 1.80 ± 0.63 | 1.60 ± 0.52 |
| GIII | 2.70 ± 0.48 | 0.70 ± 0.48 |
| GIV | 0.50 ± 0.53 | 2.70 a ± 0.48 |
| GV | 0.40 a ± 0.67 | 2.80 a ± 0.42 |
| H | 38.49 | 40.23 |
| p-value | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sarhan, M.H.; Felemban, S.G.; Alelwani, W.; Sharaf, H.M.; Abd El-Latif, Y.A.; Elgazzar, E.; Kandil, A.M.; Tellez-Isaias, G.; Mohamed, A.A. Zinc Oxide and Magnesium-Doped Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Ameliorate Murine Chronic Toxoplasmosis. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17010113
Sarhan MH, Felemban SG, Alelwani W, Sharaf HM, Abd El-Latif YA, Elgazzar E, Kandil AM, Tellez-Isaias G, Mohamed AA. Zinc Oxide and Magnesium-Doped Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Ameliorate Murine Chronic Toxoplasmosis. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(1):113. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17010113
Chicago/Turabian StyleSarhan, Mohamed H., Shatha G. Felemban, Walla Alelwani, Hesham M. Sharaf, Yasmin A. Abd El-Latif, Elsayed Elgazzar, Ahmad M. Kandil, Guillermo Tellez-Isaias, and Aya A. Mohamed. 2024. "Zinc Oxide and Magnesium-Doped Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Ameliorate Murine Chronic Toxoplasmosis" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 1: 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17010113
APA StyleSarhan, M. H., Felemban, S. G., Alelwani, W., Sharaf, H. M., Abd El-Latif, Y. A., Elgazzar, E., Kandil, A. M., Tellez-Isaias, G., & Mohamed, A. A. (2024). Zinc Oxide and Magnesium-Doped Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Ameliorate Murine Chronic Toxoplasmosis. Pharmaceuticals, 17(1), 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17010113







