Chitosan/Solid-Lipid Nanoparticles Hybrid Gels for Vaginal Delivery of Estradiol for Management of Vaginal Menopausal Symptoms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Compatibility Study
2.2. Preparation of Estradiol SLPs
2.3. Characterization of Estradiol-Loaded SLPs
2.4. In Vitro Release
2.5. Characterization of Some Selected SLPs Gels
2.6. Ex Vivo Permeation Study
2.7. In Vitro MTT Assay for Vaginal Irritation Using Hela Cell Lines
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Compatibility Study
3.2. Preparation of Estradiol SLPs
3.3. Characterization of Estradiol-Loaded SLPs
3.3.1. SLPs Size, PDI, and Zeta Potential Measurements
3.3.2. SEM
3.3.3. Entrapment Efficiency (EE) (%)
3.4. Preparation of SLPs-Loaded Chitosan Gels
3.5. Characterization of SLPs Gels
3.5.1. Viscosity Measurements
3.5.2. Gelation Temperature
3.5.3. Gelation Time
3.5.4. Mucoadhesive Strength
3.5.5. Gel Strength
3.6. Ex Vivo Permeation Study
3.7. In Vitro MTT Assay for Vaginal Irritation Using Hela Cell Lines
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paciuc, J. Hormone therapy in menopause. In Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Deligdisch-Schor, L., Miceli, A.M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 89–120. [Google Scholar]
- Huan, L.; Deng, X.; He, M.; Chen, S.; Niu, W. Meta-analysis: Early Age at Natural Menopause and Risk for All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 6636856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faubion, S.S.; Kuhle, C.L.; Shuster, L.T.; Rocca, W.A. Long-term health consequences of premature or early menopause and considerations for management. Climacteric 2015, 18, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikkola, T.S.; Tuomikoski, P.; Lyytinen, H.; Korhonen, P.; Hoti, F.; Vattulainen, P.; Gissler, M.; Ylikorkala, O. Vaginal estradiol use and the risk for cardiovascular mortalit. Hum. Reprod. 2016, 31, 804–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okeke, T.C.; Anyaehie, U.B.; Ezenyeaku, C.C. Premature menopause. Ann. Med. Health Sci. Res. 2013, 3, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luine, V. Estradiol and cognitive function: Past, present and future. Horm Behav. 2014, 66, 602–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, M.; Wheeler, T.L.; Snyder, T.E.; Richter, H.E. Local Effects of Vaginally Administered Estrogen Therapy: A Review. J. Pelvic Med. Surg. 2009, 15, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardozo, L.; Bachmann, G.; McClish, D.; Fonda, D.; Birgerson, L. Meta-analysis of estrogen therapy in the management of urogenital atrophy in postmenopausal women: Second report of the Hormones and Urogenital Therapy Committee. Obstet. Gynecol. 1998, 92, 722–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmałek, T.; Froelich, A.; Jadach, B.; Tatarek, A.; Gadziński, P.; Falana, A.; Gralińska, K.; Ekert, M.; Puri, V.; Wrotyńska-Barczyńska, J.; et al. Recent Advances in Polymer-Based Vaginal Drug Delivery Systems. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulletti, C.; de Ziegler, D.; Flamigni, C.; Giacomucci, E.; Polli, V.; Bolelli, G.; Franceschetti, F. Targeted drug delivery in gynaecology: The first uterine pass effect. Hum. Reprod. 1997, 12, 1073–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, D.F.; Kimble, T.D.; Lin, F.Y.; Battucci, S.; Sniukiene, V.; Liu, J.H. A Randomized, Multicenter, Double-Blind, Study to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of Estradiol Vaginal Cream 0.003% in Postmenopausal Women with Vaginal Dryness as the Most Bothersome Symptom. J. Women’s Health 2018, 27, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.E.; McLaughlin, E.M.; Pandya, L.K.; Hade, E.M.; Lynch, C.D.; Hudson, C.O. A pilot randomized controlled trial of vaginal estrogen on postpartum atrophy, perineal pain, and sexual function. Int. Urogynecology J. 2022, 33, 3383–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.; Pal, K.; Anis, A.; Pramanik, K.; Prabhakar, B. Polymers in Mucoadhesive Drug-Delivery Systems: A Brief Note. Des. Monomers Polym. 2009, 12, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathalla, Z.; Mustafa, W.W.; Abdelkader, H.; Moharram, H.; Sabry, A.M.; Alany, R.G. Hybrid thermosensitive-mucoadhesive in situ forming gels for enhanced corneal wound healing effect of L-carnosine. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 374–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Wen, J.; Sharma, M. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Topical Drug Delivery: Mechanisms, Dosage Form Perspectives, and Translational Status. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2020, 26, 3203–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassano, R.; Ferrarelli, T.; Mauro, M.V.; Cavalcanti, P.; Picci, N.; Trombino, S. Preparation, characterization and in vitro activities evaluation of solid lipid nanoparticles based on PEG-40 stearate for antifungal drugs vaginal delivery. Drug Deliv. 2014, 23, 1037–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassano, R.; Trombino, S. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles Based on L-Cysteine for Progesterone Intravaginal Delivery. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2019, 2019, 8690145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Madni, A.; Shah, H.; Jamshaid, T.; Jan, N.; Khan, S.; Khan, M.M.; Mahmood, M.A. Solid lipid-based nanoparticulate system for sustained release and enhanced in vitro cytotoxic effect of 5-fluorouracil on skin Melanoma and squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0281004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Jindal, S.; Singh, M.; Sharma, G.; Kaur, I.P. Nano-formulation of rifampicin with enhanced bioavailability: Development, characterization and in vivo safety. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 485, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, J.Y.; Mulet, X.; Waddington, L.J.; Boyd, B.J.; Drummond, C.J. Steric stabilisation of self-assembled cubic lyotropic liquid crystalline nanoparticles: High throughput evaluation of triblock polyethylene oxide-polypropylene oxide- polyethylene oxide copolymers. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 4768–4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göppert, T.M.; Müller, R.H. Polysorbate-stabilized solid lipid nanoparticles as colloidal carriers for intravenous targeting of drugs to the brain: Comparison of plasma protein adsorption patterns. J. Drug Target. 2005, 13, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, H.; Ahmad, S.; Madni, A.; Rao, I.; Ghazwani, M.; Hani, U.; Umair, M.; Ahmad, I.; Rai, N.; Ahmed, M.; et al. Compritol-Based Alprazolam Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Sustained Release of Alprazolam: Preparation by Hot Melt Encapsulation. Molecules 2022, 27, 8894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mura, P.; Maestrelli, F.; D’ambrosio, M.; Luceri, C.; Cirri, M. Evaluation and Comparison of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLNs) and Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLCs) as Vectors to Develop Hydrochlorothiazide Effective and Safe Pediatric Oral Liquid Formulations. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrams, R.M.; Royston, J.P. Some Properties of Rectum and Vagina as Sites for Basal Body Temperature Measurement. Fertil. Steril. 1981, 35, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mura, P.; Mennini, N.; Nativi, C.; Richichi, B. In situ mucoadhesive-thermosensitive liposomal gel as a novel vehicle for nasal extended delivery of opiorphin. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 122, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemiyeh, P.; Mohammadi-Samani, S. Potential of Nanoparticles as Permeation Enhancers and Targeted Delivery Options for Skin: Advantages and Disadvantages. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 3271–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasir, M.; Som, I.; Bhatia, K. Status of surfactants as penetration enhancers in transdermal drug delivery. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2012, 4, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, N.; Rehman, M.U.; Khan, H.M.S.; Rasool, F.; Saeed, T.; Murtaz, G. Penetration Enhancing Effect of Polysorbate 20 and 80 on the In Vitro Percutaneous Absorption of LAscorbic Acid. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2011, 10, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayehunie, S.; Cannon, C.; LaRosa, K.; Pudney, J.; Anderson, D.J.; Klausner, M. Development of an in vitro alternative assay method for vaginal irritation. Toxicology 2011, 279, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigaard, J.; Jensen, J.L.; Galtung, H.K.; Hiorth, M. The Potential of Chitosan in Nanomedicine: An Overview of the Cytotoxicity of Chitosan Based Nanoparticles. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 880377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabi-Meibodi, M.; Vatanara, A.; Najafabadi, A.R.; Rouini, M.R.; Ramezani, V.; Gilani, K.; Etemadzadeh, S.M.H.; Azadmanesh, K. The effective encapsulation of a hydrophobic lipid-insoluble drug in solid lipid nanoparticles using a modified double emulsion solvent evaporation method. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 112, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad, S.A.; Mustafa, W.W.; Salem, H.; Elrehany, M.; Rofaeil, R.R.; Abdelkader, H. Physicochemical characteristics and ex vivo skin permeability for three phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors (sildenafil, tadalafil and vardenafil): A proof-of-concept study for topical penile therapy. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 70, 103166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
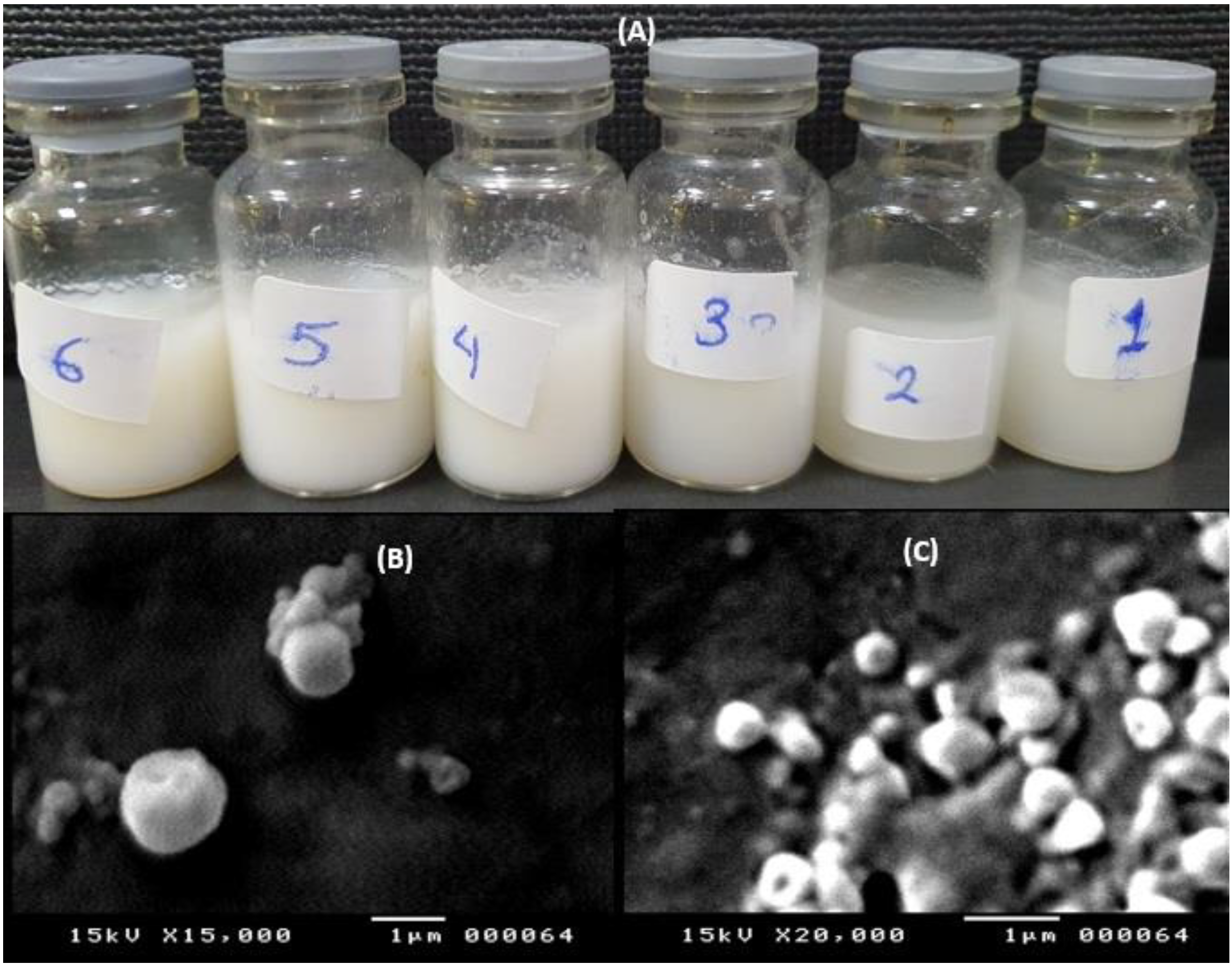

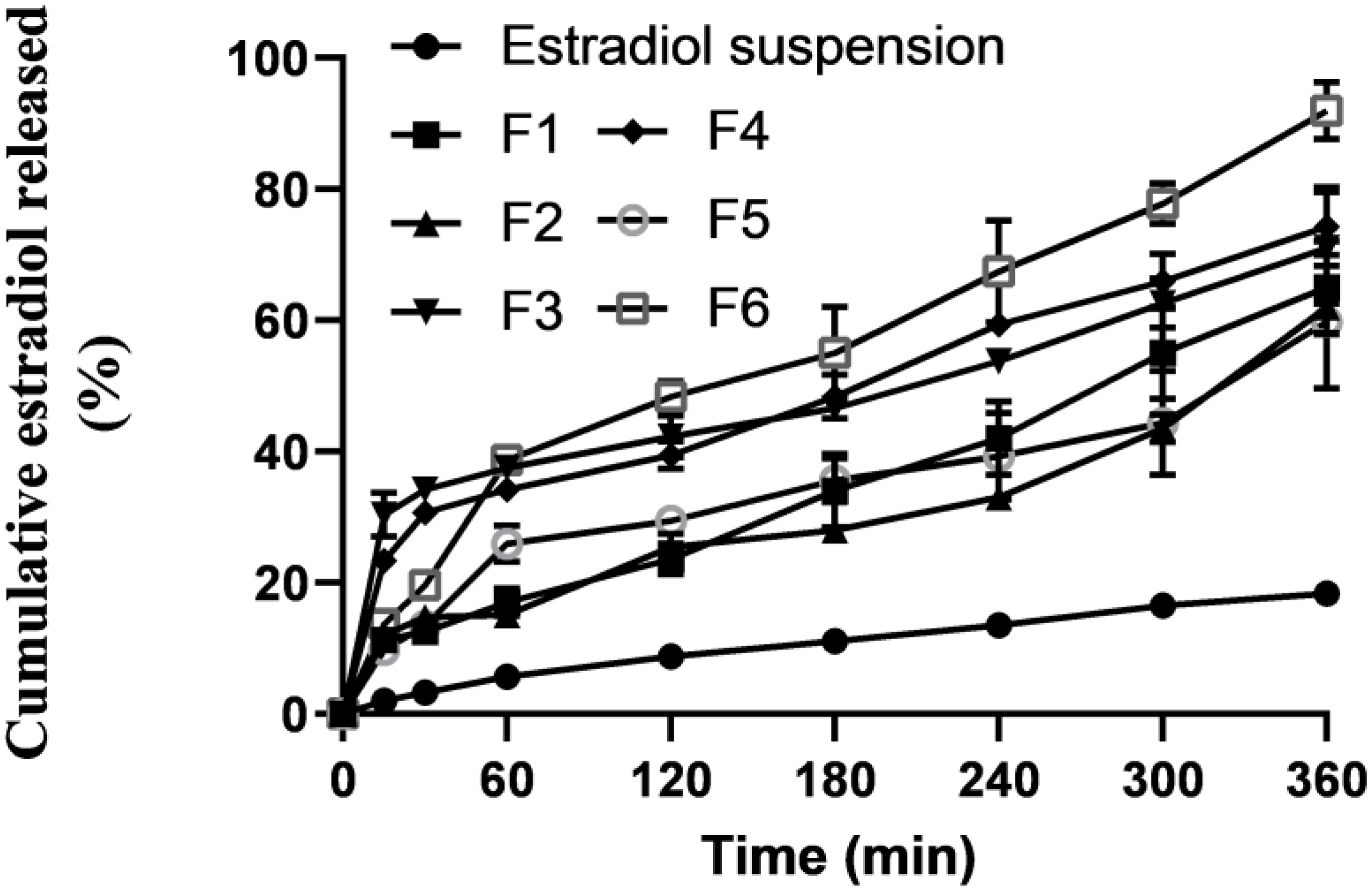
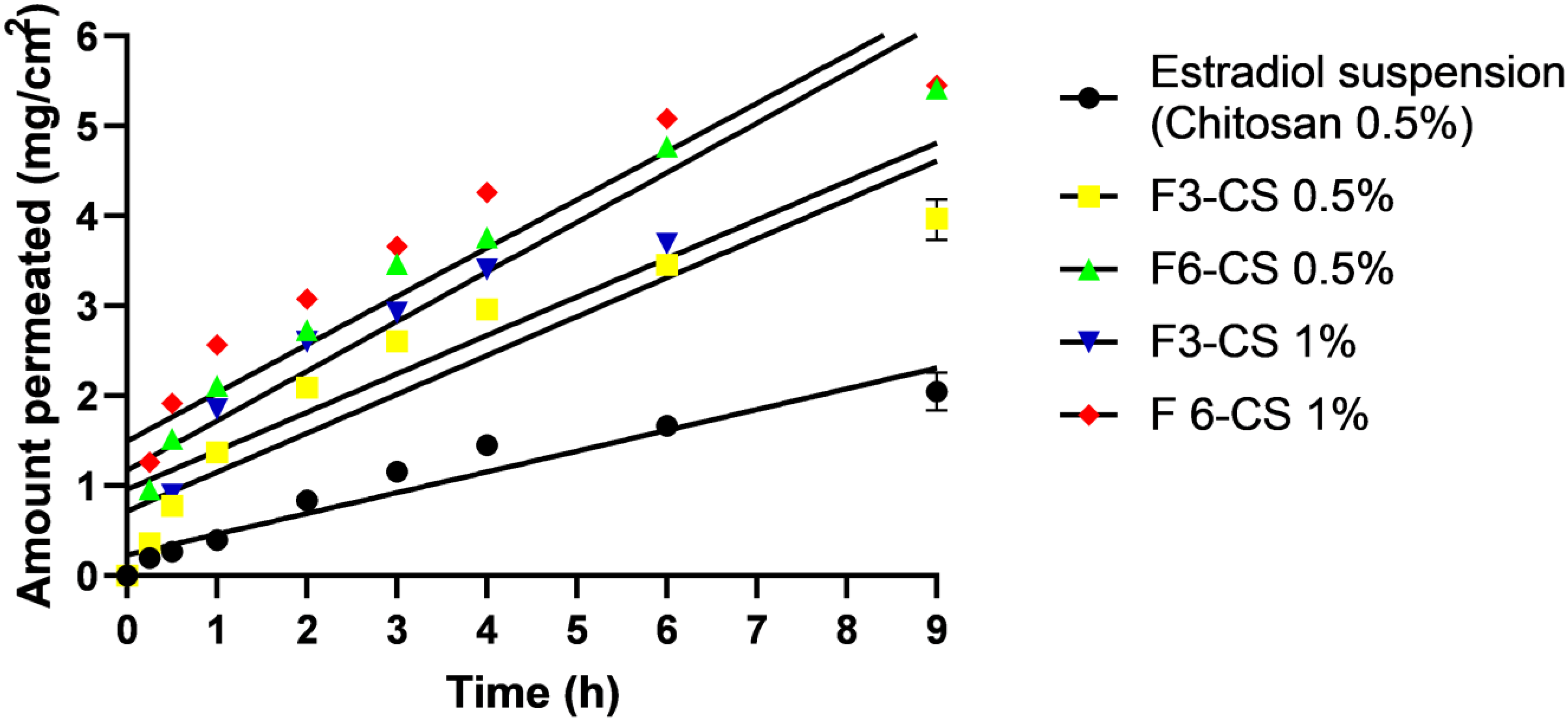
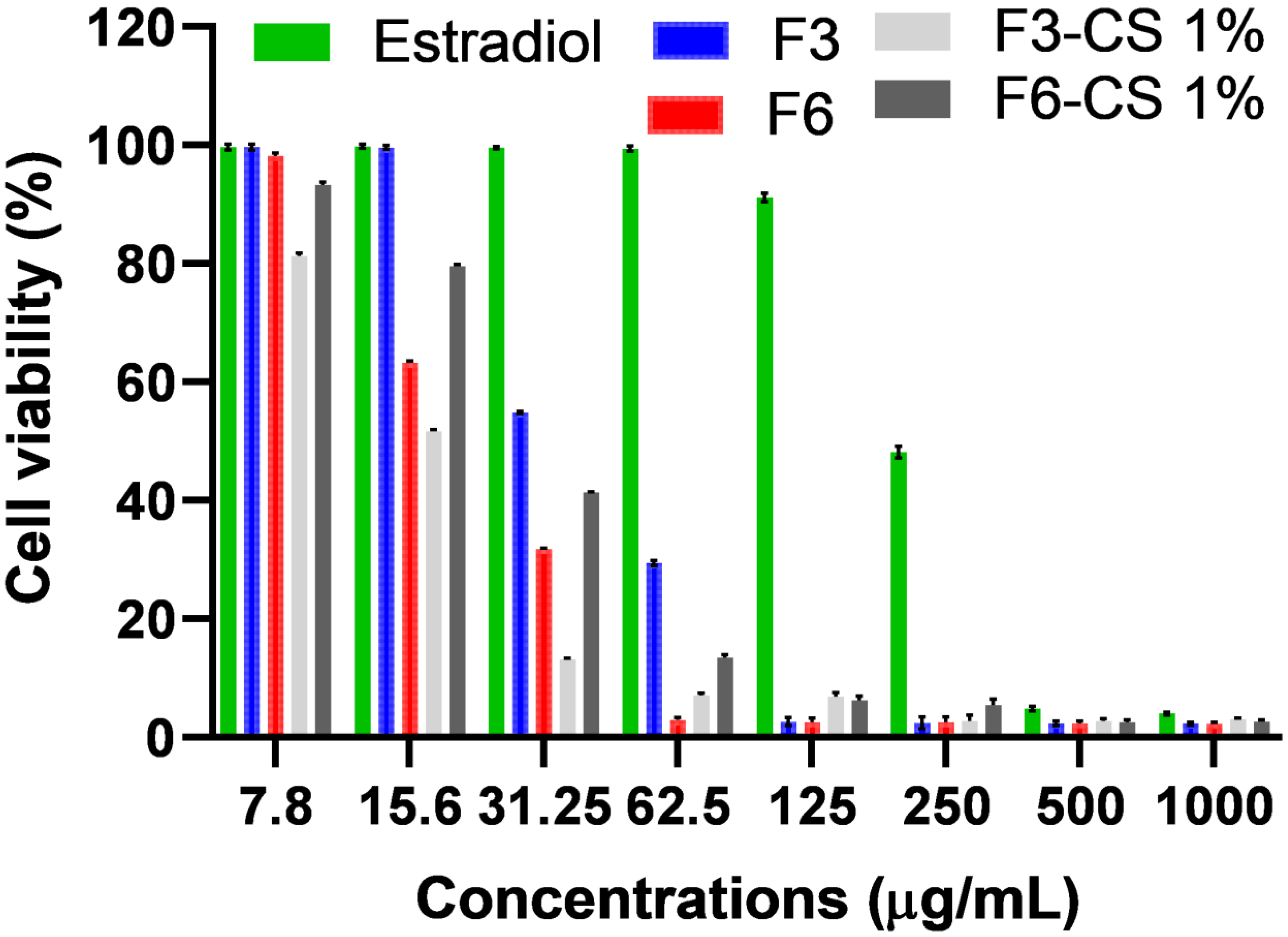
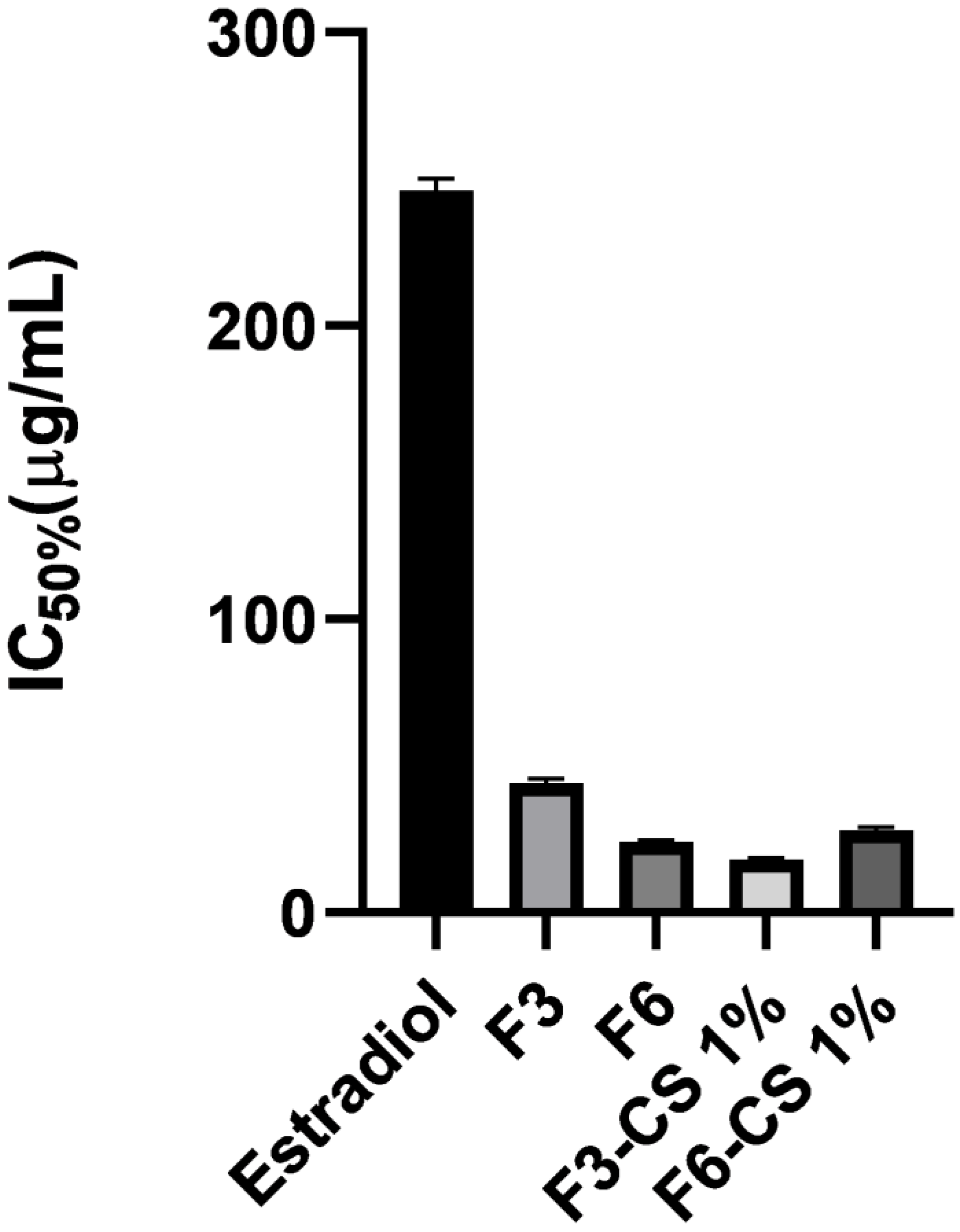
| Formula No. | % EE | % Cumulative Release | Size (nm) | PDI | Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 82.72 ± 2.0 | 68.90 ± 4.3 | 849.9 ± 5.5 | 0.64 ± 0.2 | −10.9 ± 1.4 |
| F2 | 70.67 ± 2.5 | 59.06 ± 3.4 | 713.5 ± 5.7 | 0.55 ± 0.25 | −9.9 ± 1.0 |
| F3 | 80.58 ± 3.0 | 77.05 ± 4.4 | 504 ± 3.0 | 0.59 ± 0.15 | −5.7 ± 2.2 |
| F4 | 63.60 ± 2.0 | 78.56 ± 5.4 | 423.3 ± 4.5 | 0.52 ± 0.12 | −4.6 ± 1.3 |
| F5 | 72.87 ± 2.4 | 52.56 ± 4.5 | 680.5 ± 4.3 | 0.57 ± 0.08 | −12.0 ± 1.4 |
| F6 | 50.82 ± 3.5 | 88.92 ± 5.5 | 450.7 ± 3.5 | 0.54 ± 0.1 | −15.1 ± 1.2 |
| Formulation | 0th Order | 1st Order | Higuchi | Korsmeyer-Peppas | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | K (%.min−1) | R2 | K (min−1) | R2 | K (%.min−0.5) | R2 | K (%.min−n) | n * | |
| F1 | 0.984 | 0.14 | 0.96 | 0.01 | 0.94 | 2.6 | 0.6 | 0.42 | 1 |
| F2 | 0.955 | 0.09 | 0.952 | 0.009 | 0.929 | 2.1 | 0.56 | 0.7 | 0.99 |
| F3 | 0.94 | 0.18 | 0.899 | 0.01 | 0.887 | 2.1 | 0.55 | 2.7 | 0.98 |
| F4 | 0.989 | 0.148 | 0.978 | 0.013 | 0.967 | 3.1 | 0.669 | 1.7 | 1.5 |
| F5 | 0.960 | 0.14 | 0.981 | 0.01 | 0.986 | 3.03 | 0.72 | 1.7 | 1.4 |
| F6 | 0.95 | 0.23 | 0.990 | 0.022 | 0.992 | 4.91 | 0.74 | 2.5 | 1.5 |
| SLPs Hybrid Gels | Gelation Time (s) | Gelation Temp | Mucoadhesion Force (g/cm2) | Gel Strength (S) | Viscosity (mPa.S) | Permeation Parameters | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 °C | 37 °C | Flux | Papp × 10−2 Cm/min) | |||||
| F3-CS 0.5% | 23 ± 2.0 | 33.7 ± 1.6 | 31.72 ± | 26 ± 2.0 | 540 ± 20 | 16,165 ± 100 | 0.43 ± 0.02 | 43 ± 2.0 |
| F6-CS 0.5% | 25 ± 3.0 | 34.2 ± 1.4 | 32.21 ± | 28 ± 2.0 | 517 ± 18 | 14,812 ± 150 | 0.55 ± 0.03 | 54.6 ± 3.5 |
| F3-CS 1% | 30 ± 4.0 | 31.5 ± 1.2 | 36.92 ± | 32 ± 4.0 | 872 ± 35 | 20,865 ± 200 | 0.44 ± 0.01 | 43.86 ± 2.4 |
| F6-CS 1% | 34 ± 5.0 | 31.9 ± 2.1 | 36.13 ± | 31 ± 3.0 | 923 ± 40 | 21,322 ± 250 | 0.53 ± 0.02 | 52.78 ± 4.3 |
| Formulation No. | Composition (mg) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compritol 888 ATO (mg) | Precirol ATO 5 (mg) | Pluronic F127 (mg) | Tween 80 (%) | |
| F1 | 200 | - | 100 | 0.5 |
| F2 | 200 | - | 200 | 0.5 |
| F3 | - | 200 | 100 | 0.5 |
| F4 | - | 200 | 200 | 0.5 |
| F5 | 200 | 200 | 200 | 0.5 |
| F6 | 200 | 200 | 100 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abou-Taleb, H.A.; Fathalla, Z.; Naguib, D.M.; Fatease, A.A.; Abdelkader, H. Chitosan/Solid-Lipid Nanoparticles Hybrid Gels for Vaginal Delivery of Estradiol for Management of Vaginal Menopausal Symptoms. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1284. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091284
Abou-Taleb HA, Fathalla Z, Naguib DM, Fatease AA, Abdelkader H. Chitosan/Solid-Lipid Nanoparticles Hybrid Gels for Vaginal Delivery of Estradiol for Management of Vaginal Menopausal Symptoms. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(9):1284. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091284
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbou-Taleb, Heba A., Zeinab Fathalla, Demiana M. Naguib, Adel Al Fatease, and Hamdy Abdelkader. 2023. "Chitosan/Solid-Lipid Nanoparticles Hybrid Gels for Vaginal Delivery of Estradiol for Management of Vaginal Menopausal Symptoms" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 9: 1284. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091284
APA StyleAbou-Taleb, H. A., Fathalla, Z., Naguib, D. M., Fatease, A. A., & Abdelkader, H. (2023). Chitosan/Solid-Lipid Nanoparticles Hybrid Gels for Vaginal Delivery of Estradiol for Management of Vaginal Menopausal Symptoms. Pharmaceuticals, 16(9), 1284. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091284








