Tolerogenic Lipid Nanoparticles for Delivering Self-Antigen mRNA for the Treatment of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
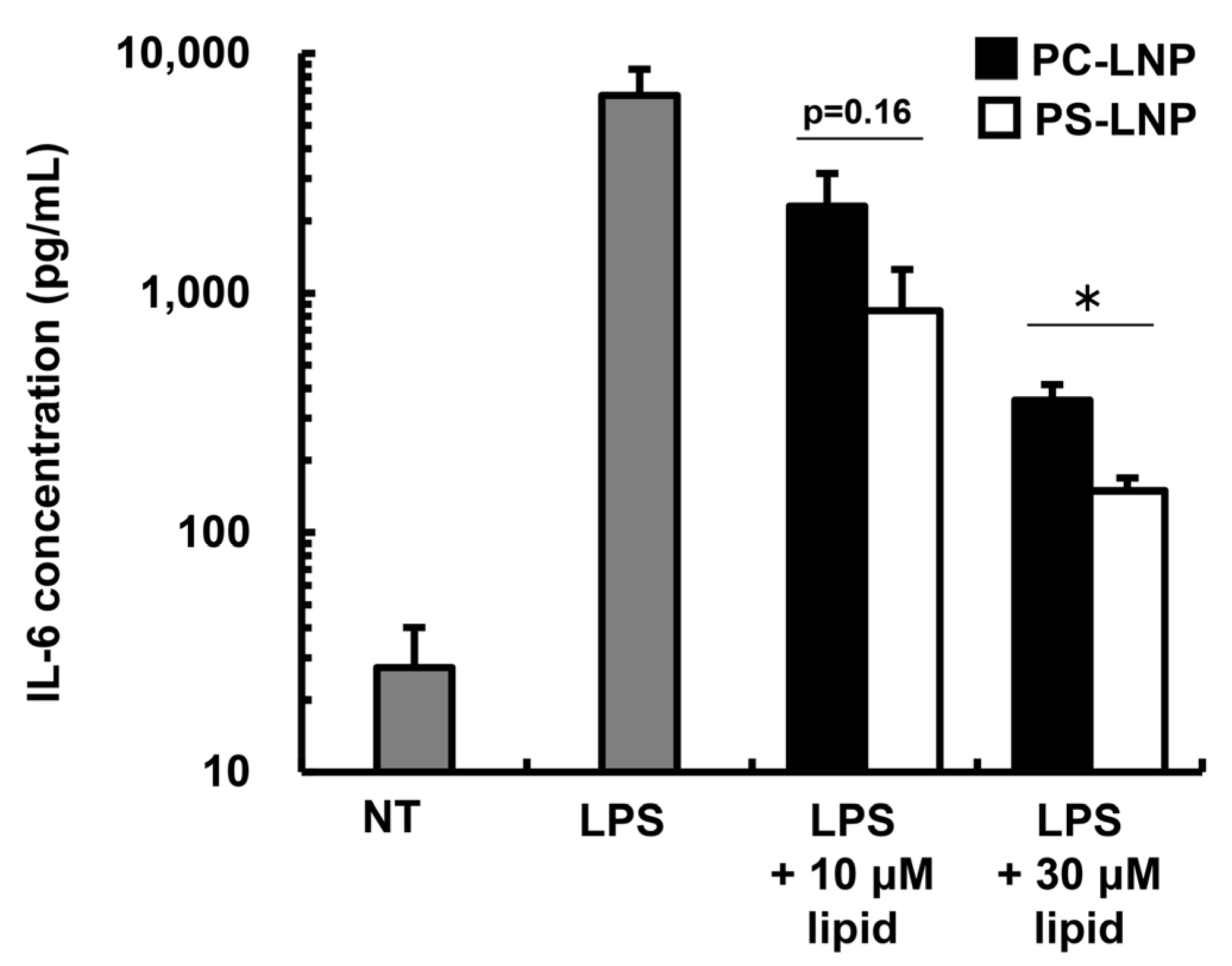
2.1. The Immune-Suppressive Effect of the PS-LNP
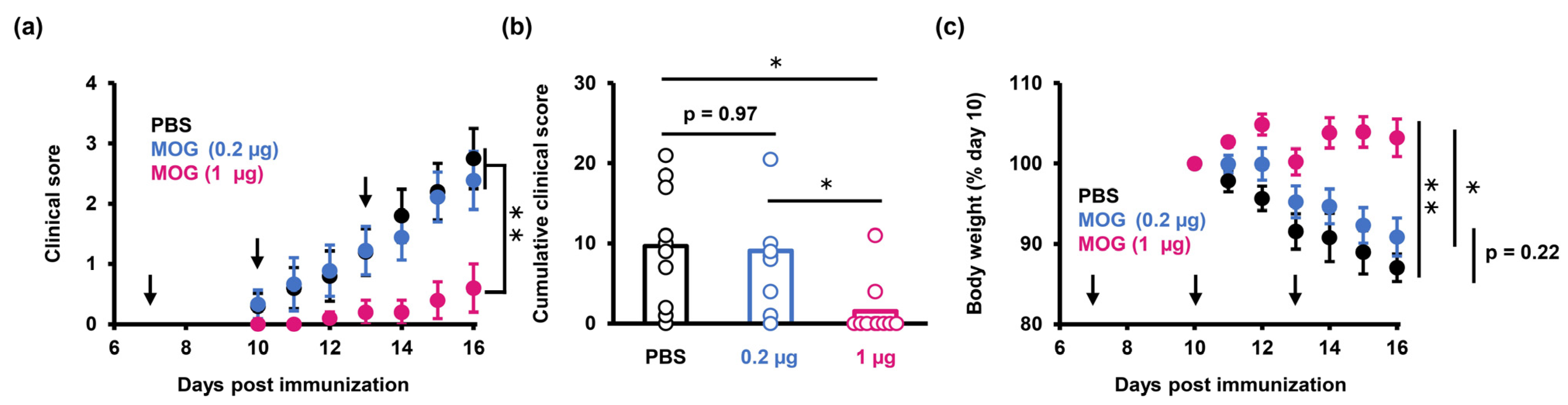
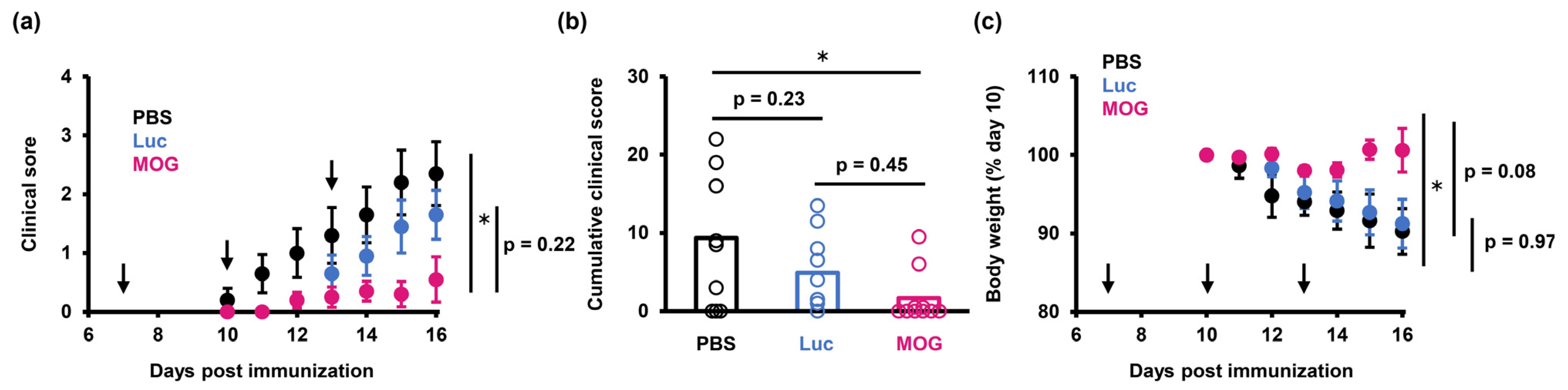
2.2. PS-LNP Loaded with MOG27–63 mRNA Ameliorates EAE
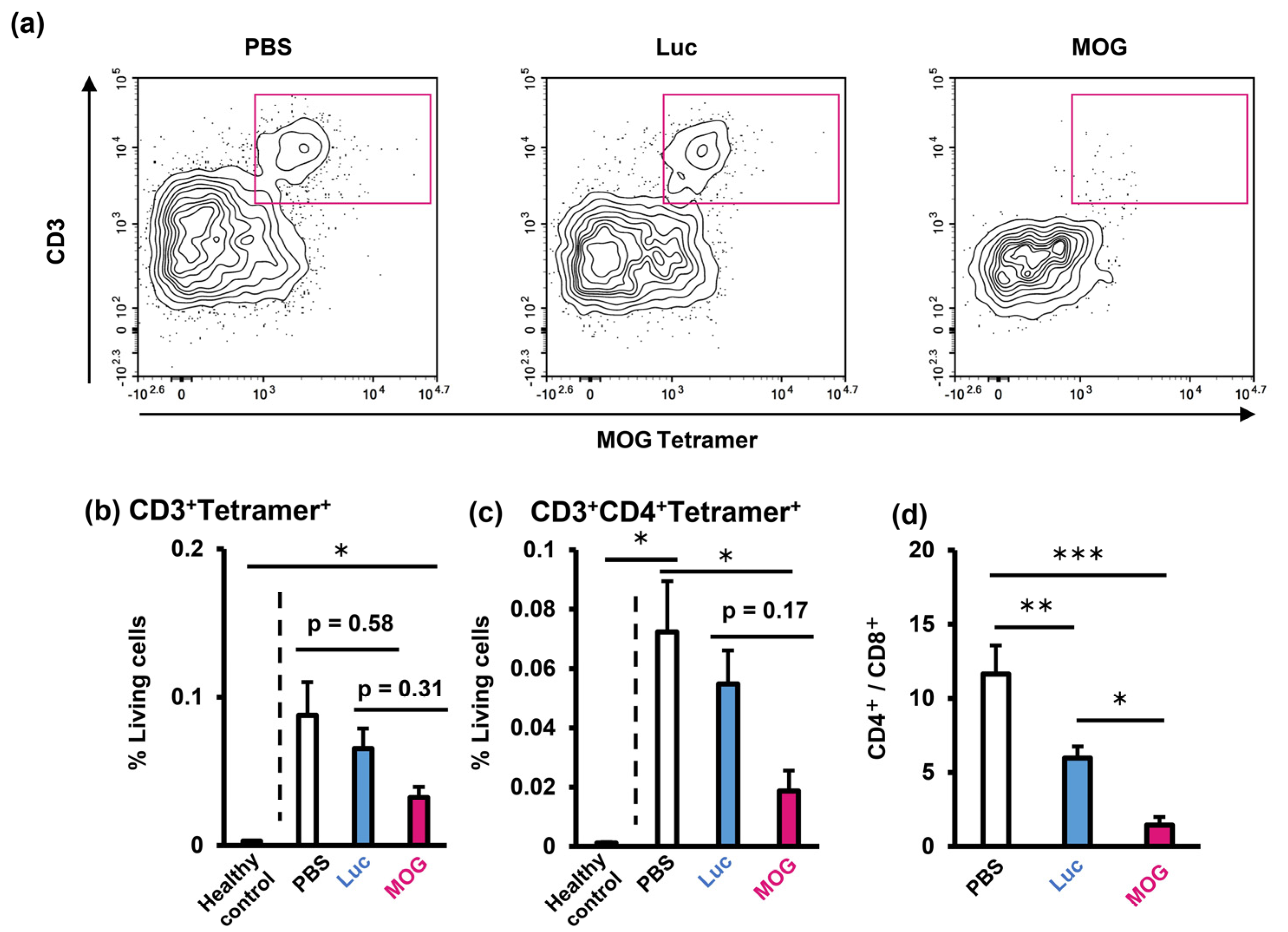
2.3. Evaluation of Infiltrating Immune Cells in the Central Nervous System
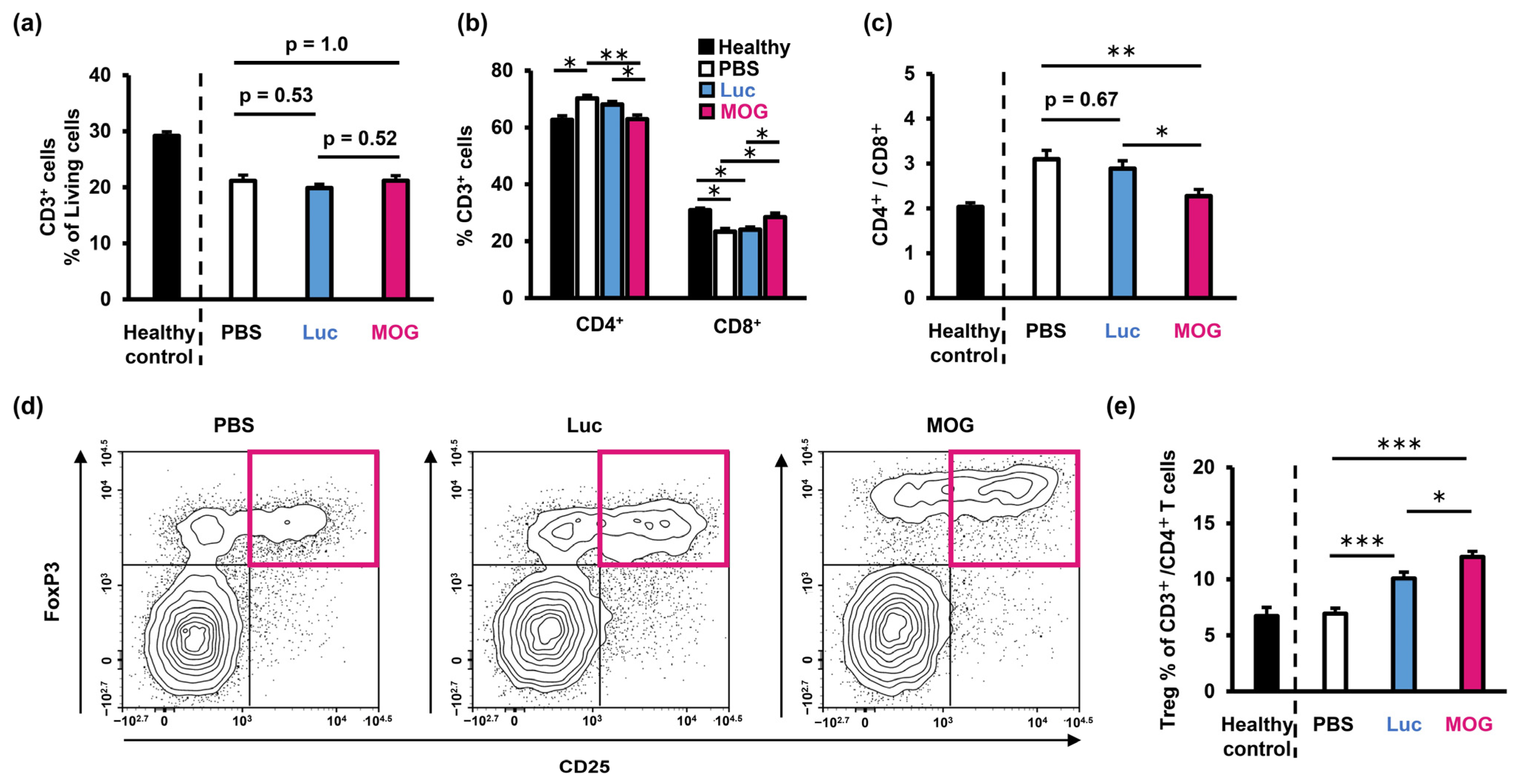
2.4. Evaluation of Immune Status in the Spleen
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Mice
4.3. Induction of EAE
4.4. In Vitro Transcription of mRNA
4.5. Preparation of mRNA-Loaded LNPs
4.6. Effect of PS-LNP on a Production of IL-6 from Activated Macrophages
4.7. LNP-Based Treatment of EAE Mice
4.8. Cell Isolation from Mouse Tissues
4.9. Flow Cytometry
4.10. Ex Vivo Stimulation of Splenocytes
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boster, A.; Edan, G.; Frohman, E.; Javed, A.; Stuve, O.; Tselis, A.; Weiner, H.; Weinstock-Guttman, B.; Khan, O. Multiple Sclerosis Clinical Research Center, Department of Neurology, Wayne State University School of Medicine. Intense immunosuppression in patients with rapidly worsening multiple sclerosis: Treatment guidelines for the clinician. Lancet Neurol. 2008, 7, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra, P.; Santamaria, P. Antigen-specific therapeutic approaches for autoimmunity. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 238–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iberg, C.A.; Jones, A.; Hawiger, D. Dendritic Cells As Inducers of Peripheral Tolerance. Trends Immunol. 2017, 38, 793–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benne, N.; Ter Braake, D.; Stoppelenburg, A.J.; Broere, F. Nanoparticles for Inducing Antigen-Specific T Cell Tolerance in Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 864403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahtinen, S.; Tong, A.J.; Himmels, P.; Oh, J.; Paler-Martinez, A.; Kim, L.; Wichner, S.; Oei, Y.; McCarron, M.J.; Freund, E.C.; et al. IL-1 and IL-1ra are key regulators of the inflammatory response to RNA vaccines. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 532–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, M.; Nakamura, T.; Miura, N.; Maeta, M.; Tanaka, H.; Ueda, K.; Higashi, K.; Moribe, K.; Tange, K.; Nakai, Y.; et al. DNA-loaded nano-adjuvant formed with a vitamin E-scaffold intracellular environmentally-responsive lipid-like material for cancer immunotherapy. Nanomedicine 2018, 14, 2587–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenison, J.E.; Jhaveri, A.; Li, Z.; Khadse, N.; Tjon, E.; Tezza, S.; Nowakowska, D.; Plasencia, A.; Stanton, V.P., Jr.; Sherr, D.H.; et al. Tolerogenic nanoparticles suppress central nervous system inflammation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 32017–32028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, E.; Gurczynski, S.J.; Kramer, K.R.; Wilke, C.A.; Miller, S.D.; Moore, B.B.; Shea, L.D. Modulating lung immune cells by pulmonary delivery of antigen-specific nanoparticles to treat autoimmune disease. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabc9317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomi, M.; Sakurai, Y.; Okada, T.; Miura, N.; Tanaka, H.; Akita, H. Development of Sentinel LN Imaging with a Combination of HAase Based on a Comprehensive Analysis of the Intra-lymphatic Kinetics of LPs. Mol. Ther. 2021, 29, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, Y.; Suzuoki, M.; Gomi, M.; Tanaka, H.; Akita, H. Optimization of Sentinel Lymph Node Imaging Methodology Using Anionic Liposome and Hyaluronidase. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomi, M.; Sakurai, Y.; Sato, M.; Tanaka, H.; Miyatake, Y.; Fujiwara, K.; Watanabe, M.; Shuto, S.; Nakai, Y.; Tange, K.; et al. Delivering mRNA to Secondary Lymphoid Tissues by Phosphatidylserine-Loaded Lipid Nanoparticles. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2022, 12, e2202528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeini, M.B.; Bianconi, V.; Pirro, M.; Sahebkar, A. The role of phosphatidylserine recognition receptors in multiple biological functions. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2020, 25, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segawa, K.; Nagata, S. An Apoptotic ‘Eat Me’ Signal: Phosphatidylserine Exposure. Trends Cell Biol. 2015, 25, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sliwa, K.; Ansari, A.A. Immunosuppression as therapy for congestive heart failure. Lancet 2008, 371, 184–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Xu, L.; Liang, X.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, C.; Gao, L. Tim-4 in Health and Disease: Friend or Foe? Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawano, M.; Nagata, S. Lupus-like autoimmune disease caused by a lack of Xkr8, a caspase-dependent phospholipid scramblase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 2132–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benne, N.; van Duijn, J.; Lozano Vigario, F.; Leboux, R.J.T.; van Veelen, P.; Kuiper, J.; Jiskoot, W.; Slutter, B. Anionic 1,2-distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoglycerol (DSPG) liposomes induce antigen-specific regulatory T cells and prevent atherosclerosis in mice. J. Control. Release 2018, 291, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pujol-Autonell, I.; Mansilla, M.J.; Rodriguez-Fernandez, S.; Cano-Sarabia, M.; Navarro-Barriuso, J.; Ampudia, R.M.; Rius, A.; Garcia-Jimeno, S.; Perna-Barrull, D.; Martinez-Caceres, E.; et al. Liposome-based immunotherapy against autoimmune diseases: Therapeutic effect on multiple sclerosis. Nanomedicine 2017, 12, 1231–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pujol-Autonell, I.; Serracant-Prat, A.; Cano-Sarabia, M.; Ampudia, R.M.; Rodriguez-Fernandez, S.; Sanchez, A.; Izquierdo, C.; Stratmann, T.; Puig-Domingo, M.; Maspoch, D.; et al. Use of autoantigen-loaded phosphatidylserine-liposomes to arrest autoimmunity in type 1 diabetes. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krienke, C.; Kolb, L.; Diken, E.; Streuber, M.; Kirchhoff, S.; Bukur, T.; Akilli-Ozturk, O.; Kranz, L.M.; Berger, H.; Petschenka, J.; et al. A noninflammatory mRNA vaccine for treatment of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Science 2021, 371, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toita, R.; Kawano, T.; Murata, M.; Kang, J.H. Anti-obesity and anti-inflammatory effects of macrophage-targeted interleukin-10-conjugated liposomes in obese mice. Biomaterials 2016, 110, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadok, V.A.; Bratton, D.L.; Rose, D.M.; Pearson, A.; Ezekewitz, R.A.; Henson, P.M. A receptor for phosphatidylserine-specific clearance of apoptotic cells. Nature 2000, 405, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, R.A.; Eitas, T.K.; Byrne, J.D.; Johnson, B.M.; Short, P.J.; McKinnon, K.P.; Reisdorf, S.; Luft, J.C.; DeSimone, J.M.; Ting, J.P. Towards programming immune tolerance through geometric manipulation of phosphatidylserine. Biomaterials 2015, 72, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blankenhorn, E.P.; Butterfield, R.; Case, L.K.; Wall, E.H.; del Rio, R.; Diehl, S.A.; Krementsov, D.N.; Saligrama, N.; Teuscher, C. Genetics of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis supports the role of T helper cells in multiple sclerosis pathogenesis. Ann. Neurol. 2011, 70, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, T.; Akgun, K.; Proschmann, U.; Sellner, J.; Ziemssen, T. The role of TH17 cells in multiple sclerosis: Therapeutic implications. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Economopoulos, V.; Noad, J.C.; Krishnamoorthy, S.; Rutt, B.K.; Foster, P.J. Comparing the MRI appearance of the lymph nodes and spleen in wild-type and immuno-deficient mouse strains. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alameh, M.G.; Tombacz, I.; Bettini, E.; Lederer, K.; Sittplangkoon, C.; Wilmore, J.R.; Gaudette, B.T.; Soliman, O.Y.; Pine, M.; Hicks, P.; et al. Lipid nanoparticles enhance the efficacy of mRNA and protein subunit vaccines by inducing robust T follicular helper cell and humoral responses. Immunity 2021, 54, 2877–2892 e2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevers, S.; Kooijmans, S.A.A.; Van de Velde, E.; Evers, M.J.W.; Seghers, S.; Gitz-Francois, J.; van Kronenburg, N.C.H.; Fens, M.; Mastrobattista, E.; Hassler, L.; et al. mRNA-LNP vaccines tuned for systemic immunization induce strong antitumor immunity by engaging splenic immune cells. Mol. Ther. 2022, 30, 3078–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, C.H.; Choi, J.H.; Byun, M.S.; Jue, D.M. Chloroquine inhibits production of TNF-alpha, IL-1beta and IL-6 from lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human monocytes/macrophages by different modes. Rheumatology 2006, 45, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Watanabe, A.; Konishi, M.; Nakai, Y.; Yoshioka, H.; Ohkawara, T.; Takeda, H.; Harashima, H.; Akita, H. The delivery of mRNA to colon inflammatory lesions by lipid-nano-particles containing environmentally-sensitive lipid-like materials with oleic acid scaffolds. Heliyon 2018, 4, e00959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGaha, T.L.; Karlsson, M.C. Apoptotic cell responses in the splenic marginal zone: A paradigm for immunologic reactions to apoptotic antigens with implications for autoimmunity. Immunol. Rev. 2016, 269, 26–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vignali, D.A.; Collison, L.W.; Workman, C.J. How regulatory T cells work. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A.C.; Chandwaskar, R.; Lee, D.H.; Sullivan, J.M.; Solomon, A.; Rodriguez-Manzanet, R.; Greve, B.; Sobel, R.A.; Kuchroo, V.K. A transgenic model of central nervous system autoimmunity mediated by CD4+ and CD8+ T and B cells. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 2084–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montero, E.; Nussbaum, G.; Kaye, J.F.; Perez, R.; Lage, A.; Ben-Nun, A.; Cohen, I.R. Regulation of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by CD4+, CD25+ and CD8+ T cells: Analysis using depleting antibodies. J. Autoimmun. 2004, 23, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leuenberger, T.; Paterka, M.; Reuter, E.; Herz, J.; Niesner, R.A.; Radbruch, H.; Bopp, T.; Zipp, F.; Siffrin, V. The role of CD8+ T cells and their local interaction with CD4+ T cells in myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein35–55-induced experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 4960–4968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashi, V.P.; Ortega, S.B.; Karandikar, N.J. Neuroantigen-specific autoregulatory CD8+ T cells inhibit autoimmune demyelination through modulation of dendritic cell function. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delarasse, C.; Smith, P.; Baker, D.; Amor, S. Novel pathogenic epitopes of myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein induce experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in C57BL/6 mice. Immunology 2013, 140, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendel, I.; Kerlero de Rosbo, N.; Ben-Nun, A. A myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein peptide induces typical chronic experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in H-2b mice: Fine specificity and T cell receptor V beta expression of encephalitogenic T cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 1995, 25, 1951–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariko, K.; Muramatsu, H.; Welsh, F.A.; Ludwig, J.; Kato, H.; Akira, S.; Weissman, D. Incorporation of pseudouridine into mRNA yields superior nonimmunogenic vector with increased translational capacity and biological stability. Mol. Ther. 2008, 16, 1833–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, N.; Maeki, M.; Sato, Y.; Note, Y.; Ishida, A.; Tani, H.; Harashima, H.; Tokeshi, M. Development of the iLiNP Device: Fine Tuning the Lipid Nanoparticle Size within 10 nm for Drug Delivery. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 5044–5051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krotova, K.; Day, A.; Aslanidi, G. An Engineered AAV6-Based Vaccine Induces High Cytolytic Anti-Tumor Activity by Directly Targeting DCs and Improves Ag Presentation. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2019, 15, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Sample | Z-Average (nm) | PdI | Zeta-Potential (mV) | RR (%) | EE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC-LNPLuc | 126.7 ± 2.3 | 0.14 ± 0.06 | −2.1 ± 2.0 | 80.6 ± 17.5 | 71.4 ± 9.6 |
| PS-LNPLuc | 131.4 ± 5.2 | 0.12 ± 0.02 | −18.7 ± 1.3 | 82.1 ± 9.8 | 61.7 ± 3.3 |
| PS-LNPMOG | 133.1 ± 0.9 | 0.15 ± 0.04 | −21.2 ± 2.3 | 94.7 ± 6.5 | 40.8 ± 4.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gomi, M.; Nakayama, Y.; Sakurai, Y.; Oyama, R.; Iwasaki, K.; Doi, M.; Liu, Y.; Hori, M.; Watanabe, H.; Hashimoto, K.; et al. Tolerogenic Lipid Nanoparticles for Delivering Self-Antigen mRNA for the Treatment of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1270. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091270
Gomi M, Nakayama Y, Sakurai Y, Oyama R, Iwasaki K, Doi M, Liu Y, Hori M, Watanabe H, Hashimoto K, et al. Tolerogenic Lipid Nanoparticles for Delivering Self-Antigen mRNA for the Treatment of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(9):1270. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091270
Chicago/Turabian StyleGomi, Masaki, Yuka Nakayama, Yu Sakurai, Ryotaro Oyama, Koki Iwasaki, Mizuki Doi, Yi Liu, Mizuho Hori, Himeka Watanabe, Kohei Hashimoto, and et al. 2023. "Tolerogenic Lipid Nanoparticles for Delivering Self-Antigen mRNA for the Treatment of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 9: 1270. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091270
APA StyleGomi, M., Nakayama, Y., Sakurai, Y., Oyama, R., Iwasaki, K., Doi, M., Liu, Y., Hori, M., Watanabe, H., Hashimoto, K., Tanaka, H., Tange, K., Nakai, Y., & Akita, H. (2023). Tolerogenic Lipid Nanoparticles for Delivering Self-Antigen mRNA for the Treatment of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. Pharmaceuticals, 16(9), 1270. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091270






