Transcriptomic Profiling after In Vitro Δ8-THC Exposure Shows Cytoskeletal Remodeling in Trauma-Injured NSC-34 Cell Line
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Transcriptomic Profiles Analysis
2.2. Gene Ontology Over-Representation Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Synthesis and Purification of Δ8-THC
4.2. NSC-34 Culture, Differentiation, and Treatment
4.3. Scratch Injury and Δ8-THC Administration
4.4. RNA Isolation from Cells Pellet and cDNA Library Preparation
4.5. Bioinformatics Analysis
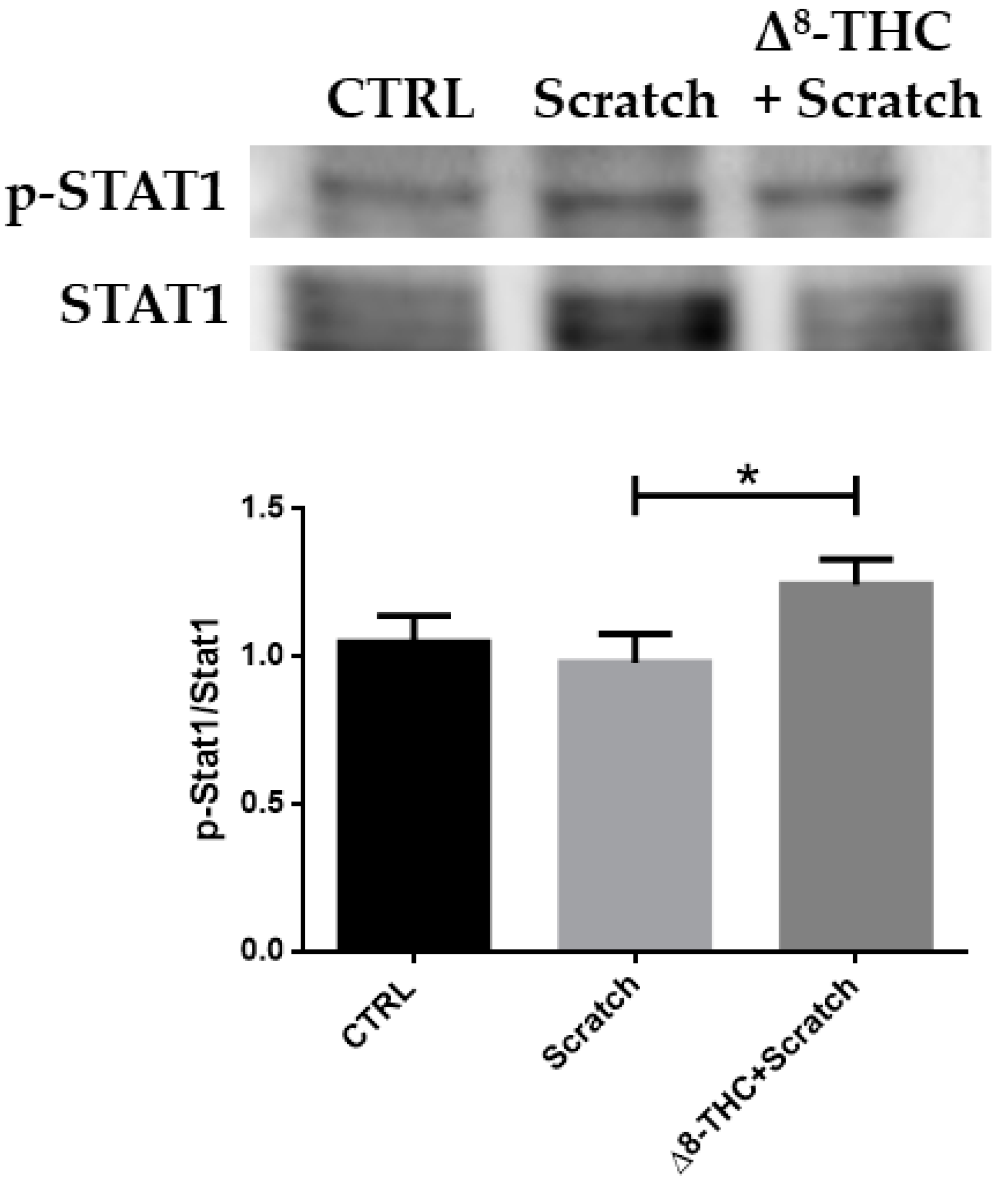
4.6. Protein Extraction and Western Blot
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chi, H.; Chang, H.Y.; Sang, T.K. Neuronal Cell Death Mechanisms in Major Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.; Yuan, S.; Shi, L.; Li, J.; Ning, G.; Kong, X.; Feng, S. Programmed cell death in spinal cord injury pathogenesis and therapy. Cell Prolif. 2021, 54, e12992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Fact Sheet N°384. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/spinal-cord-injury (accessed on 23 March 2023).
- Eckert, M.J.; Martin, M.J. Trauma: Spinal Cord Injury. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 97, 1031–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.R.; Cadotte, D.W.; Fehlings, M.G. Clinical predictors of neurological outcome, functional status, and survival after traumatic spinal cord injury: A systematic review. J. Neurosurg. Spine SPI 2012, 17, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, A.; Dyck, S.M.; Karimi-Abdolrezaee, S. Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury: An Overview of Pathophysiology, Models and Acute Injury Mechanisms. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Te Ao, B.; Brown, P.; Tobias, M.; Ameratunga, S.; Barker-Collo, S.; Theadom, A.; McPherson, K.; Starkey, N.; Dowell, A.; Jones, K.; et al. Cost of traumatic brain injury in New Zealand: Evidence from a population-based study. Neurology 2014, 83, 1645–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, C.S.; Nori, S.; Tetreault, L.; Wilson, J.; Kwon, B.; Harrop, J.; Choi, D.; Fehlings, M.G. Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury—Repair and Regeneration. Neurosurgery 2017, 80, S9–S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Ruiz, J.; Moro, M.A.; Martinez-Orgado, J. Cannabinoids in Neurodegenerative Disorders and Stroke/Brain Trauma: From Preclinical Models to Clinical Applications. Neurotherapeutics 2015, 12, 793–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhunia, S.; Kolishetti, N.; Arias, A.Y.; Vashist, A.; Nair, M. Cannabidiol for neurodegenerative disorders: A comprehensive review. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 989717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tagen, M.; Klumpers, L.E. Review of delta-8-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ8-THC): Comparative pharmacology with Δ9-THC. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 179, 3915–3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leas, E.C. The Hemp Loophole: A Need to Clarify the Legality of Delta-8-THC and Other Hemp-Derived Tetrahydrocannabinol Compounds. Am. J. Public Health 2021, 111, 1927–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LoParco, C.R.; Rossheim, M.E.; Walters, S.T.; Zhou, Z.; Olsson, S.; Sussman, S.Y. Delta-8 tetrahydrocannabinol: A scoping review and commentary. Addiction 2023, 118, 1011–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, F.I.; Mowforth, O.D.; Butler, M.B.; Bhatti, A.I.; Adeeko, S.; Akhbari, M.; Dilworth, R.; Grodzinski, B.; Osunronbi, T.; Ottewell, L.; et al. Systematic review of the impact of cannabinoids on neurobehavioral outcomes in preclinical models of traumatic and nontraumatic spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 2021, 59, 1221–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabata, K.J.; Tse, E.K.; Nightingale, T.E.; Lee, A.H.X.; Eng, J.J.; Querée, M.; Walter, M.; Krassioukov, A.V. The Therapeutic Potential and Usage Patterns of Cannabinoids in People with Spinal Cord Injuries: A Systematic Review. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2021, 19, 402–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anchesi, I.; Schepici, G.; Chiricosta, L.; Gugliandolo, A.; Salamone, S.; Caprioglio, D.; Pollastro, F.; Mazzon, E. Delta(8)-THC Induces Up-Regulation of Glutamatergic Pathway Genes in Differentiated SH-SY5Y: A Transcriptomic Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugliandolo, A.; Blando, S.; Salamone, S.; Caprioglio, D.; Pollastro, F.; Mazzon, E.; Chiricosta, L. Delta(8)-THC Protects against Amyloid Beta Toxicity Modulating ER Stress In Vitro: A Transcriptomic Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cory, G. Scratch-wound assay. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 769, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajan, T.S.; Diomede, F.; Bramanti, P.; Trubiani, O.; Mazzon, E. Conditioned medium from human gingival mesenchymal stem cells protects motor-neuron-like NSC-34 cells against scratch-injury-induced cell death. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2017, 30, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Citron, B.A.; Zhang, S.X.; Smirnova, I.V.; Festoff, B.W. Apoptotic, injury-induced cell death in cultured mouse murine motor neurons. Neurosci. Lett. 1997, 230, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payette, D.J.; Xie, J.; Shirwany, N.; Guo, Q. Exacerbation of apoptosis of cortical neurons following traumatic brain injury in par-4 transgenic mice. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2008, 1, 44–56. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Luo, P.; Guo, Q.; Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, M.; Xu, H.; Yang, Y.; Poon, W.; Fei, Z. Interactions between SIRT1 and MAPK/ERK regulate neuronal apoptosis induced by traumatic brain injury in vitro and in vivo. Exp. Neurol. 2012, 237, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Chen, F.; Ge, X.; Tan, J.; Lei, P.; Zhang, J. miR-21 alleviated apoptosis of cortical neurons through promoting PTEN-Akt signaling pathway in vitro after experimental traumatic brain injury. Brain Res. 2014, 1582, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darnell, J.E. STATs and Gene Regulation. Science 1997, 277, 1630–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, P.J. The JAK-STAT Signaling Pathway: Input and Output Integration. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 2623–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, D.A. The Jak/STAT pathway. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2012, 4, a011205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghoreschi, K.; Laurence, A.; O’Shea, J.J. Janus kinases in immune cell signaling. Immunol. Rev. 2009, 228, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlonka, J.; Rak, B.; Ambroziak, U. The regulation of cyclin D promoters—Review. Cancer Treat. Res. Commun. 2021, 27, 100338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacey, D.W. Cyclin D1 serves as a cell cycle regulatory switch in actively proliferating cells. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2003, 15, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platanitis, E.; Demiroz, D.; Schneller, A.; Fischer, K.; Capelle, C.; Hartl, M.; Gossenreiter, T.; Muller, M.; Novatchkova, M.; Decker, T. A molecular switch from STAT2-IRF9 to ISGF3 underlies interferon-induced gene transcription. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.Y.; Kessler, D.S.; Veals, S.A.; Levy, D.E.; Darnell, J.E., Jr. ISGF3, the transcriptional activator induced by interferon alpha, consists of multiple interacting polypeptide chains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 8555–8559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, K.; Stark, G.R.; Kerr, I.M.; Darnell, J.E., Jr. A single phosphotyrosine residue of Stat91 required for gene activation by interferon-gamma. Science 1993, 261, 1744–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivashkiv, L.B.; Donlin, L.T. Regulation of type I interferon responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kershaw, N.J.; Murphy, J.M.; Liau, N.P.; Varghese, L.N.; Laktyushin, A.; Whitlock, E.L.; Lucet, I.S.; Nicola, N.A.; Babon, J.J. SOCS3 binds specific receptor-JAK complexes to control cytokine signaling by direct kinase inhibition. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2013, 20, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.D.; Sun, F.; Park, K.K.; Cai, B.; Wang, C.; Kuwako, K.; Martinez-Carrasco, I.; Connolly, L.; He, Z. SOCS3 Deletion Promotes Optic Nerve Regeneration In Vivo. Neuron 2009, 64, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, D.; Liu, Y.; Sun, F.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; He, Z. Restoration of skilled locomotion by sprouting corticospinal axons induced by co-deletion of PTEN and SOCS3. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.A.R.; An, J.; Jeong, S. The Pleiotropic Face of CREB Family Transcription Factors. Mol. Cells 2023, 46, 399–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Cao, F.-j.; Xu, D.-d.; Xu, Y.-q.; Feng, S.-q. Upregulated Ras/Raf/ERK1/2 signaling pathway: A new hope in the repair of spinal cord injury. Neural Regen. Res. 2015, 10, 792–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Ghosh, P.; Prasad, R.; Ghosh, A.; Das, K.; Roy, A.; Mallik, S.; Sinha, D.K.; Sen, P. MAP Kinase driven actomyosin rearrangement is a crucial regulator of monocyte to macrophage differentiation. Cell. Signal. 2020, 73, 109691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Pasini, S.; Shelanski, M.L.; Greene, L.A. Activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4) modulates post-synaptic development and dendritic spine morphology. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, P.N.; Lasek, R.J. Axonal transport of the cytoskeleton in regenerating motor neurons: Constancy and change. Brain Res. 1980, 202, 317–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Xie, F.; Siedlak, S.L.; Nunomura, A.; Honda, K.; Moreira, P.I.; Zhua, X.; Smith, M.A.; Perry, G. Neurofilament proteins in neurodegenerative diseases. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2004, 61, 3057–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, A.; Rao, M.V.; Veeranna; Nixon, R.A. Neurofilaments at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 3257–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrot, R.; Lonchampt, P.; Peterson, A.C.; Eyer, J. Axonal neurofilaments control multiple fiber properties but do not influence structure or spacing of nodes of Ranvier. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 9573–9584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, G.; Yang, C.; Ellis, R.; Anderson, K.; Parker Mickle, J.; Scheff, S.; Pike, B.; Anderson, D.K.; Howland, D.R. Hyperphosphorylated neurofilament NF-H is a serum biomarker of axonal injury. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 336, 1268–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayakawa, K.; Okazaki, R.; Ishii, K.; Ueno, T.; Izawa, N.; Tanaka, Y.; Toyooka, S.; Matsuoka, N.; Morioka, K.; Ohori, Y.; et al. Phosphorylated neurofilament subunit NF-H as a biomarker for evaluating the severity of spinal cord injury patients, a pilot study. Spinal Cord 2012, 50, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, J.B.; Chen, A.; Kaminsky, S.M.; Crystal, R.G.; Sondhi, D. Advances in the Treatment of Neuronal Ceroid Lipofuscinosis. Expert Opin. Orphan Drugs 2019, 7, 473–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ching, G.Y.; Chien, C.-L.; Flores, R.; Liem, R.K.H. Overexpression of α-Internexin Causes Abnormal Neurofilamentous Accumulations and Motor Coordination Deficits in Transgenic Mice. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 2974–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugawara, T.; Lewén, A.; Gasche, Y.; Yu, F.; Chan, P.H. Overexpression of SOD1 protects vulnerable motor neurons after spinal cord injury by attenuating mitochondrial cytochrome c release. FASEB J. 2002, 16, 1997–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiricosta, L.; Silvestro, S.; Pizzicannella, J.; Diomede, F.; Bramanti, P.; Trubiani, O.; Mazzon, E. Transcriptomic Analysis of Stem Cells Treated with Moringin or Cannabidiol: Analogies and Differences in Inflammation Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Hu, E.; Xu, S.; Chen, M.; Guo, P.; Dai, Z.; Feng, T.; Zhou, L.; Tang, W.; Zhan, L.; et al. clusterProfiler 4.0: A universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. Innovation 2021, 2, 100141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, S.; Pyl, P.T.; Huber, W. HTSeq—A Python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbon, S.; Ireland, A.; Mungall, C.J.; Shu, S.; Marshall, B.; Lewis, S.; AmiGO Hub; Web Presence Working Group. AmiGO: Online access to ontology and annotation data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 288–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Gene | CTRL vs. Scratch | Scratch vs. Δ8-THC 20 μM + Scratch | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| log2 Fold Change | q-Value | log2 Fold Change | q-Value | |
| Ccnd1 | −0.51 | 9.49 × 10−26 | 0.20 | 5.06 × 10−5 |
| Hras | −0.88 | 1.16 × 10−19 | 0.37 | 3.29 × 10−4 |
| Irf9 | −0.79 | 6.00 × 10−3 | 1.25 | 4.80 × 10−7 |
| Jak1 | −0.32 | 7.47 × 10−10 | 0.42 | 8.36 × 10−19 |
| Jak2 | −1.07 | 4.29 × 10−10 | 0.75 | 9.20 × 10−6 |
| Ptpn11 | −0.27 | 4.55 × 10−5 | 0.14 | 2.74 × 10−2 |
| Raf1 | −0.46 | 2.51 × 10−15 | 0.38 | 7.62 × 10−12 |
| Socs3 | 1.88 | 3.99 × 10−2 | −3.35 | 4.67 × 10−3 |
| Socs7 | 0.40 | 1.70 × 10−3 | −0.32 | 5.00 × 10−3 |
| Sos2 | −0.40 | 3.25 × 10−11 | 0.34 | 2.90 × 10−9 |
| Stat2 | −1.25 | 3.62 × 10−3 | 1.28 | 1.50 × 10−3 |
| Gene | Ctrl vs. Scratch | Scratch vs. DELTA8-20-Scratch | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fold_Change | q-Value | Fold_Change | q-Value | |
| Atf4 | - | >0.05 | 0.14 | 3.94 × 10−6 |
| Erbb3 | - | >0.05 | 0.74 | 6.75 × 10−10 |
| Grb2 | - | >0.05 | 0.27 | 3.76 × 10−3 |
| Hras | - | >0.05 | 0.37 | 3.29 × 10−4 |
| Igf1r | 0.09 | 3.76 × 10−2 | 0.10 | 4.52 × 10−3 |
| Kras | - | >0.05 | 0.34 | 1.72 × 10−5 |
| Map2k1 | - | >0.05 | 0.2 | 2.11 × 10−7 |
| Mknk1 | - | >0.05 | 0.75 | 3.39 × 10−7 |
| Ngfr | - | >0.05 | 0.35 | 3.13 × 10−3 |
| Pdgfrb | - | >0.05 | 1.42 | 9.52 × 10−6 |
| Raf1 | - | >0.05 | 0.38 | 7.62 × 10−12 |
| Rps6ka2 | - | >0.05 | 0.38 | 8.24 × 10−17 |
| Sos2 | - | >0.05 | 0.34 | 2.90 × 10−9 |
| Gene | CTRL vs. Scratch | Scratch vs. Δ8-THC 20 μM + Scratch | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fold Change | q-Value | Fold Change | q-Value | |
| Atf2 | −0.11 | 1.40 × 10−2 | - | - |
| Atp8a2 | −3.12 | 9.86 × 10−3 | - | - |
| Cln8 | −5.14 | 1.89 × 10−3 | 5.90 | 1.94 × 10−4 |
| Ina | 0.44 | 3.75 × 10−5 | −0.64 | 3.89 × 10−11 |
| Ndel1 | 0.31 | 9.24 × 10−6 | 0.21 | 4.10 × 10−4 |
| Nefh | - | - | 0.20 | 4.51 × 10−3 |
| Nefl | - | - | −0.32 | 2.28 × 10−3 |
| Sod1 | −1.30 | 5.83 × 10−87 | 1.35 | 2.06 × 10−102 |
| Vps54 | −0.41 | 2.86 × 10−13 | 0.13 | 2.60 × 10−2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chiricosta, L.; D’Angiolini, S.; Gugliandolo, A.; Salamone, S.; Pollastro, F.; Mazzon, E. Transcriptomic Profiling after In Vitro Δ8-THC Exposure Shows Cytoskeletal Remodeling in Trauma-Injured NSC-34 Cell Line. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1268. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091268
Chiricosta L, D’Angiolini S, Gugliandolo A, Salamone S, Pollastro F, Mazzon E. Transcriptomic Profiling after In Vitro Δ8-THC Exposure Shows Cytoskeletal Remodeling in Trauma-Injured NSC-34 Cell Line. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(9):1268. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091268
Chicago/Turabian StyleChiricosta, Luigi, Simone D’Angiolini, Agnese Gugliandolo, Stefano Salamone, Federica Pollastro, and Emanuela Mazzon. 2023. "Transcriptomic Profiling after In Vitro Δ8-THC Exposure Shows Cytoskeletal Remodeling in Trauma-Injured NSC-34 Cell Line" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 9: 1268. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091268
APA StyleChiricosta, L., D’Angiolini, S., Gugliandolo, A., Salamone, S., Pollastro, F., & Mazzon, E. (2023). Transcriptomic Profiling after In Vitro Δ8-THC Exposure Shows Cytoskeletal Remodeling in Trauma-Injured NSC-34 Cell Line. Pharmaceuticals, 16(9), 1268. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091268







