Ginsenoside Rb1 Reduces Hyper-Vasoconstriction Induced by High Glucose and Endothelial Dysfunction in Rat Aorta
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
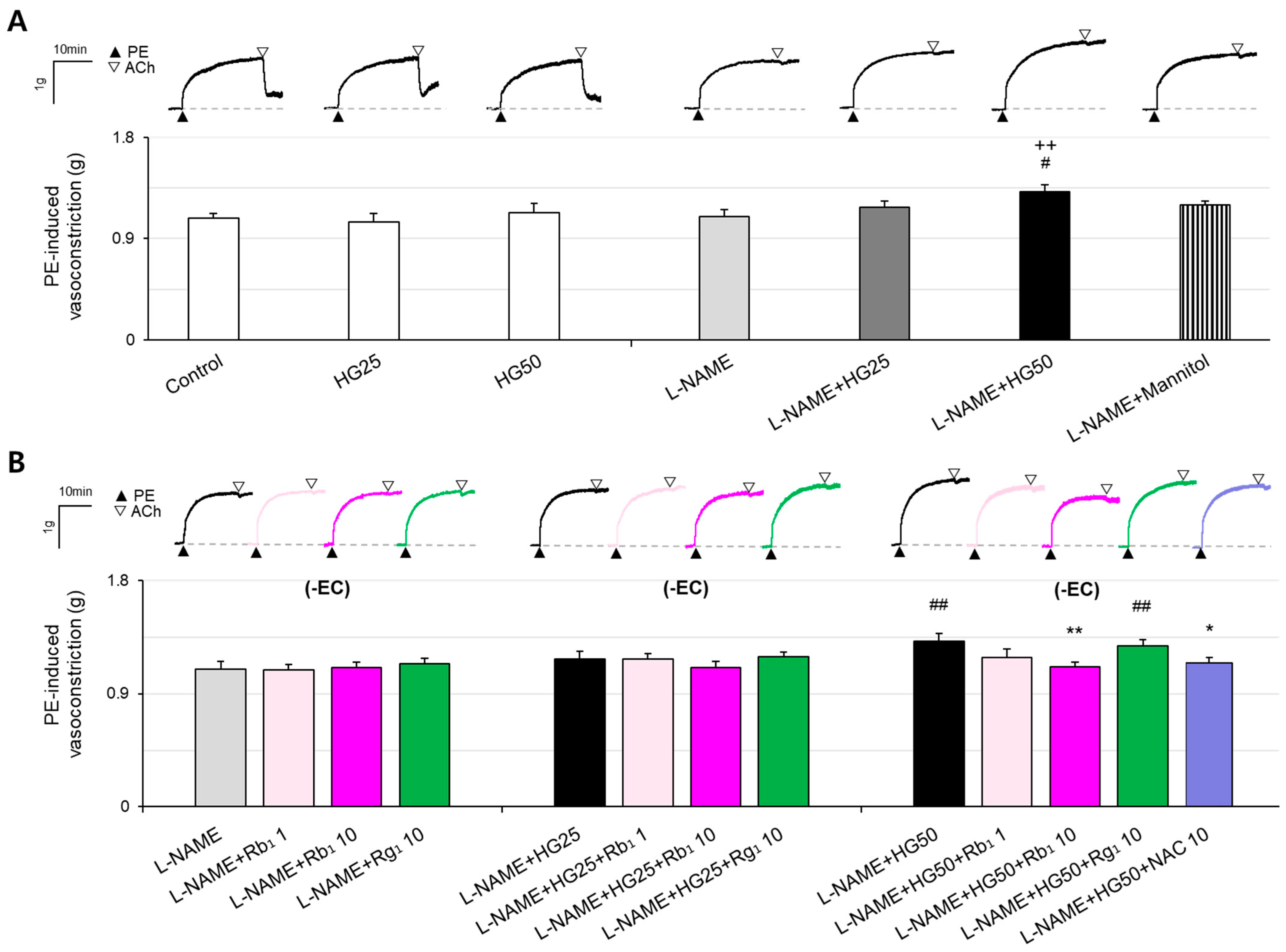
2.1. Effects of HG on Vasoconstriction in Rat Aorta
2.2. Effects of Rb1 on Hyper-Vasoconstriction Induced by HG and ED in Rat Aorta
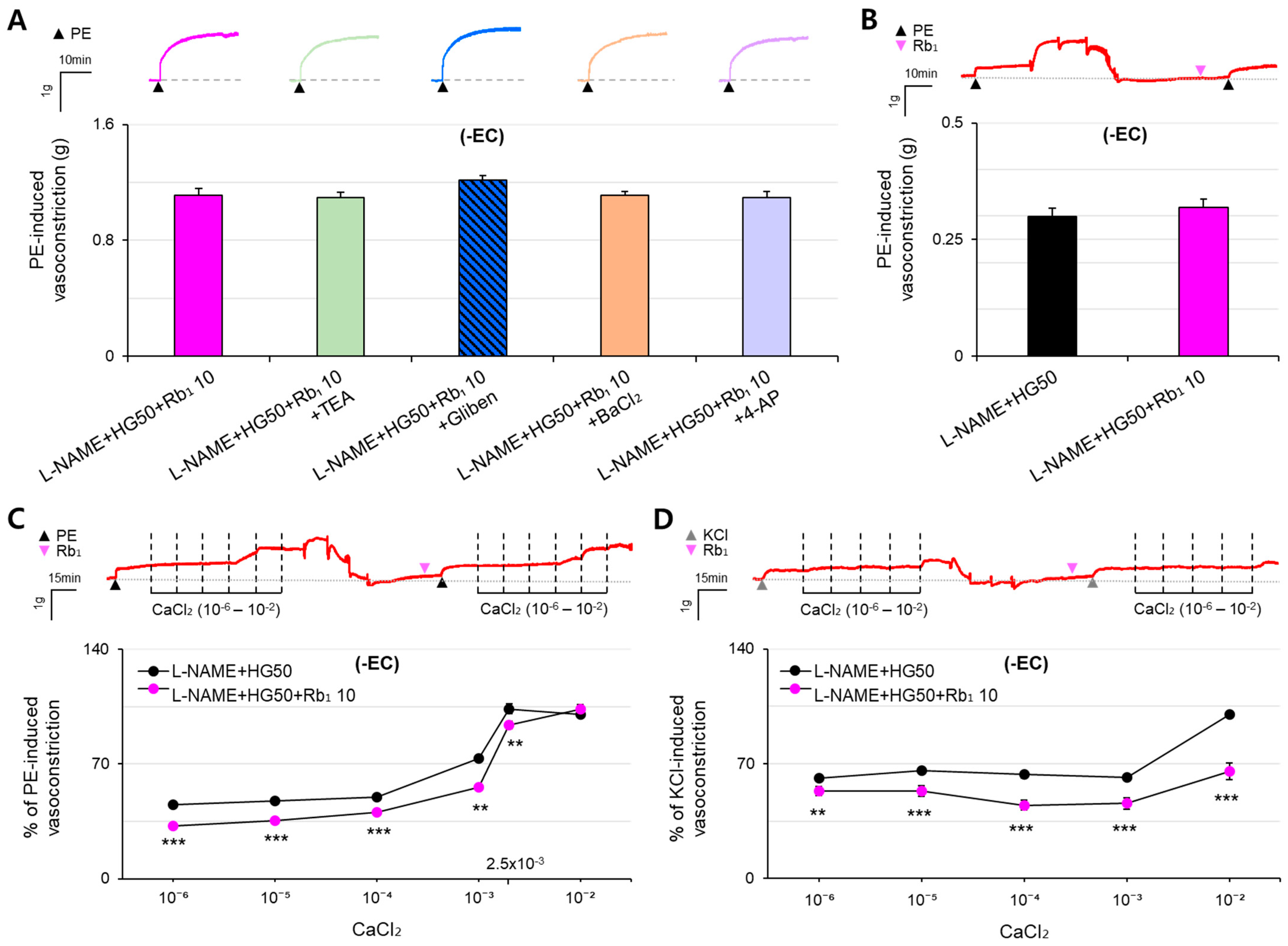
2.3. Effect of K+ Channel Blockers on Rb1-Treated Hyper-Vasoconstriction Induced by HG and ED in Rat Aorta
2.4. Effect of SR Ca2+ Release and Extracellular Ca2+ Influx on Rb1-Treated Hyper-Vasoconstriction Induced by HG and ED in Rat Aorta
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Preparation of Aortic Rings
4.3. Involvement of K+ Channel in Vasoconstriction
4.4. Measurement of SR Ca2+ Release-Induced Vasoconstriction
4.5. Measurement of Extracellular Ca2+ Influx-Induced Vasoconstriction
4.6. Chemicals
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Richardson, A.; Park, W.G. Acute pancreatitis and diabetes mellitus: A review. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2021, 36, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumnicka, P.; Maduzia, D.; Ceranowicz, P.; Olszanecki, R.; Drożdż, R.; Kuśnierz-Cabala, B. The interplay between inflammation, coagulation and endothelial injury in the early phase of acute pancreatitis: Clinical implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, A.; Vyavahare, N.R. High-glucose levels and elastin degradation products accelerate osteogenesis in vascular smooth muscle cells. Diab. Vasc. Dis. Res. 2013, 10, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo-Sepulveda, M.A.; Maddie, N.; Johnson, C.M.; Burke, C.; Lutz, O.; Yakoub, B.; Kramer, B.; Persand, D. Vascular hyperacetylation is associated with vascular smooth muscle dysfunction in a rat model of non-obese type 2 diabetes. Mol. Med. 2022, 28, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meza, C.A.; La Favor, J.D.; Kim, D.-H.; Hickner, R.C. Endothelial Dysfunction: Is There a Hyperglycemia-Induced Imbalance of NOX and NOS? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mah, E.; Noh, S.K.; Ballard, K.D.; Matos, M.E.; Volek, J.S.; Bruno, R.S. Postprandial hyperglycemia impairs vascular endothelial function in healthy men by inducing lipid peroxidation and increasing asymmetric dimethylarginine: Arginine. J. Nutr. 2011, 141, 1961–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Wu, J.H.; Mai, L.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Huang, Y. Association between prediabetes and risk of all cause mortality and cardiovascular disease: Updated meta-analysis. BMJ 2020, 370, m2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhong, C.; Pu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Bao, Y. Structure characteristics and immunomodulatory activities of a polysaccharide RGRP-1b from radix ginseng Rubra. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 189, 980–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Min, D.S.; Lee, C.W.; Song, K.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, H.P. Ginsenosides from Korean Red Ginseng ameliorate lung inflammatory responses: Inhibition of the MAPKs/NF-κB/c-Fos pathways. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.M.; Bae, B.S.; Park, H.W.; Ahn, N.G.; Cho, B.G.; Cho, Y.L.; Kwak, Y.S. Characterization of korean red ginseng (Panax ginseng Meyer): History, preparation method, and chemical composition. J. Ginseng Res. 2015, 39, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Zhou, X.; Li, F.; Xu, C.; Zheng, F.; Li, J.; Zhao, H.; Dai, Y.; Liu, S.; Feng, Y. Microbial transformation of ginsenoside Rb1, Re and Rg1 and its contribution to the improved anti-inflammatory activity of ginseng. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Shen, L.-h.; Zhang, J.-t. Anti-amnestic and anti-aging effects of ginsenoside Rg1 and Rb1 and its mechanism of action. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2005, 26, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Ma, Q.; Fan, C.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; Tang, M. Ginsenosides Rb1 and Rg1 protect primary cultured astrocytes against oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced injury via improving mitochondrial function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Xie, R.; Zhong, C.; Huang, J.; Shi, P.; Yao, H. Recent progress (2015–2020) in the investigation of the pharmacological effects and mechanisms of ginsenoside Rb1, a main active ingredient in Panax ginseng Meyer. J. Ginseng Res. 2022, 46, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; He, D.; Zhang, H.; Xie, J.; Zhang, S.; Tian, X.; Zeng, H.; Qin, Y.; Huang, L. Ginsenoside Rb1 protects against diabetes-associated metabolic disorders in Kkay mice by reshaping gut microbiota and fecal metabolic profiles. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 303, 115997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.T. Botanical characteristics, pharmacological effects and medicinal components of Korean Panax ginseng C A Meyer. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2008, 29, 1109–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanan, P.; Subramaniyam, S.; Mathiyalagan, R.; Yang, D.C. Molecular signaling of ginsenosides Rb1, Rg1, and Rg3 and their mode of actions. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Zhang, X.; Guo, M.; Guo, R.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, Z.; Dong, M.; Dai, H.; Ji, X.; et al. Ginsenoside Rb1 ameliorates CKD-associated vascular calcification by inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 7088–7098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.X.; He, R.L.; Jiao, H.X.; Dai, M.; Mu, Y.P.; Hu, Y.; Wu, Z.J.; Sham, J.S.K.; Lin, M.J. Ginsenoside Rb1 attenuates agonist-induced contractile response via inhibition of store-operated calcium entry in pulmonary arteries of normal and pulmonary hypertensive rats. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 35, 1467–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.-X.; He, R.-L.; Jiao, H.-X.; Zhang, R.-T.; Guo, J.-Y.; Liu, X.-R.; Gui, L.-X.; Lin, M.-J.; Wu, Z.-J. Preventive treatment with ginsenoside Rb1 ameliorates monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension in rats and involves store-operated calcium entry inhibition. Pharm. Biol. 2020, 58, 1055–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turpin, B.P.; Duckworth, W.C.; Solomon, S.S. Simulated hyperglycemic hyperosmolar syndrome. Impaired insulin and epinephrine effects upon lipolysis in the isolated rat fat cell. J. Clin. Investig. 1979, 63, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shor, D.; Harrison, S.; Anacker, K.; Wiley, J. Acute pancreatitis as a sequela of hypertriglyceridemia due to hyperosmolar hyperglycemic syndrome. Cureus 2021, 13, e19640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanhoutte, P.M.; Shimokawa, H.; Feletou, M.; Tang, E.H.C. Endothelial dysfunction and vascular disease—A 30th anniversary update. Acta Physiol. 2017, 219, 22–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Yang, H.; Yang, L.; Wang, Z.; Qin, X.; Zhou, J.; Dong, L.; Li, J.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, X.; et al. Acute glucose influx-induced mitochondrial hyperpolarization inactivates myosin phosphatase as a novel mechanism of vascular smooth muscle contraction. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, A.Y.; Ha, S.M.; Shin, Y.K.; Seol, G.H. Ginsenoside Rg-1 prevents elevated cytosolic Ca2+ via store-operated Ca2+ entry in high-glucose–stimulated vascular endothelial and smooth muscle cells. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2022, 22, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Lou, J. Blood glucose-related indicators are associated with in-hospital mortality in critically ill patients with acute pancreatitis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-J.; He, C.; Tian, K.; Li, P.; Su, H.; Wan, J.-B. Ginsenoside Rb1 attenuates angiotensin II-induced abdominal aortic aneurysm through inactivation of the JNK and p38 signaling pathways. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2015, 73, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Wan, J.-B.; Chan, S.-W.; Deng, Y.-H.; Yu, N.; Zhang, Q.-W.; Wang, Y.-T.; Lee, S.M.-Y. Comparative study on saponin fractions from Panax notoginseng inhibiting inflammation-induced endothelial adhesion molecule expression and monocyte adhesion. Chin. Med. 2011, 6, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, H.; Azma, T.; Nakahata, K.; Iranami, H.; Kimoto, Y.; Dojo, M.; Yuge, O.; Hatano, Y. Inhibitory effect of high concentration of glucose on relaxations to activation of ATP-sensitive K+ channels in human omental artery. Arter. Thromb Vasc. Biol. 2004, 24, 2290–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flechtner, I.; De Lonlay, P.; Polak, M. Diabetes and hypoglycaemia in young children and mutations in the Kir6.2 subunit of the potassium channel: Therapeutic consequences. Diabetes Metab. 2006, 32, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Bryan, L.; John, P.; Clement, I.; Gonzalez, G.; Kunjilwar, K.; Babenko, A.; Bryan, J. Toward understanding the assembly and structure of KATP channels. Physiol. Rev. 1998, 78, 227–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.J.; Li, J.L.; Zhou, Q.M.; Cai, F.F.; Chen, X.L.; Lu, Y.Y.; Zhao, M.; Su, S.B. Ginsenoside Rb1 pretreatment attenuates myocardial ischemia by reducing calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II-medicated calcium release. World J. Trad. Chin. Med. 2020, 6, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.Y.; Chen, L.M.; Zhang, J.; Pan, X.D.; Zhu, Y.G.; Ye, Q.Y.; Huang, H.P.; Chen, X.C. Ginsenoside Rb1 selectively inhibits the activity of L-type voltage-gated calcium channels in cultured rat hippocampal neurons. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2012, 33, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabatini, P.V.; Speckmann, T.; Lynn, F.C. Friend and foe: β-cell Ca2+ signaling and the development of diabetes. Mol. Metab. 2019, 21, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Xu, Z.Y.; Lin, C.C.; Li, H.; Sun, J.H.; Chen, J.G.; Wang, C.M. Schisantherin A causes endothelium-dependent and -independent vasorelaxation in isolated rat thoracic aorta. Life Sci. 2020, 245, 117357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Xing, Y.F.; Ye, Z.C.; Li, C.M.; Luo, P.L.; Li, M.; Lou, T.Q. High glucose induces activation of the local renin-angiotensin system in glomerular endothelial cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 9, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosentino, F.; Eto, M.; Paolis, P.D.; Loo, B.v.d.; Bachschmid, M.; Ullrich, V.; Kouroedov, A.; Gatti, C.D.; Joch, H.; Volpe, M.; et al. High Glucose Causes Upregulation of Cyclooxygenase-2 and Alters Prostanoid Profile in Human Endothelial Cells. Circulation 2003, 107, 1017–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, J.; Carpenter, A.J.; Das, N.A.; Kandikattu, H.K.; López-Ongil, S.; Martinez-Lemus, L.A.; Siebenlist, U.; DeMarco, V.G.; Chandrasekar, B. TRAF3IP2 mediates high glucose-induced endothelin-1 production as well as endothelin-1-induced inflammation in endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2018, 314, H52–H64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Xie, W.; He, S.; Sun, Y.; Meng, X.; Sun, G.; Sun, X. Ginsenoside Rb1 as an Anti-Diabetic Agent and Its Underlying Mechanism Analysis. Cells 2019, 8, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Chan, D.K.; Haugrud, A.B.; Miskimins, W.K. Mechanisms by which low glucose enhances the cytotoxicity of metformin to cancer cells both in vitro and in vivo. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, N.L.; Achike, F.I. Gender discrimination in the influence of hyperglycemia and hyperosmolarity on rat aortic tissue responses to insulin. Regul. Pept. 2010, 163, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, S.-S.; Lin, Y.-S.; Chio, L.-M.; Liang, W.-Z. Evaluation of the mycotoxin patulin on cytotoxicity and oxidative stress in human glioblastoma cells and investigation of protective effect of the antioxidant N-acetylcysteine (NAC). Toxicon 2023, 221, 106957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, J.; Shin, Y.K.; Kim, U.; Seol, G.H. Ginsenoside Rb1 Reduces Hyper-Vasoconstriction Induced by High Glucose and Endothelial Dysfunction in Rat Aorta. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1238. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091238
Park J, Shin YK, Kim U, Seol GH. Ginsenoside Rb1 Reduces Hyper-Vasoconstriction Induced by High Glucose and Endothelial Dysfunction in Rat Aorta. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(9):1238. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091238
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Jubin, You Kyoung Shin, Uihwan Kim, and Geun Hee Seol. 2023. "Ginsenoside Rb1 Reduces Hyper-Vasoconstriction Induced by High Glucose and Endothelial Dysfunction in Rat Aorta" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 9: 1238. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091238
APA StylePark, J., Shin, Y. K., Kim, U., & Seol, G. H. (2023). Ginsenoside Rb1 Reduces Hyper-Vasoconstriction Induced by High Glucose and Endothelial Dysfunction in Rat Aorta. Pharmaceuticals, 16(9), 1238. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091238





