Impact of Concomitant Use of Proton Pump Inhibitors and Clopidogrel on Recurrent Stroke and Myocardial Infarction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Self-Controlled Case Series Analysis
2.1.1. Relative Risk of Recurrent Stroke in the PPI Co-Prescription Group
2.1.2. Relative Risk of Recurrent MI in the PPI Co-Prescription Group
2.2. Cohort Study
2.2.1. Incidence of Recurrent Stroke in the PPI Co-Prescription Group
2.2.2. Incidence of Recurrent MI in the PPI Co-Prescription Group
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Data Sources
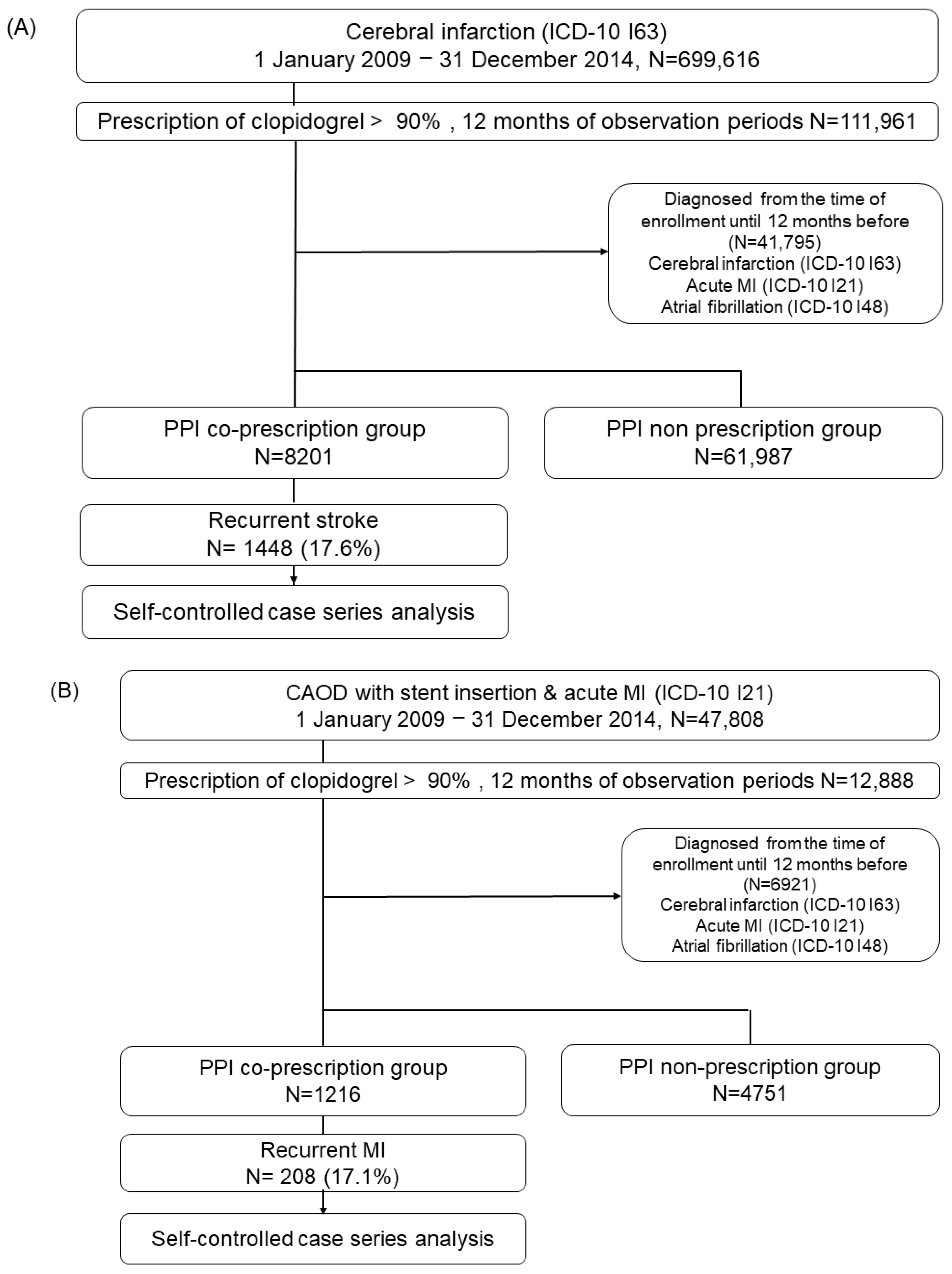
4.2. Study Design and Population
4.2.1. Self-Controlled Case Series Analysis
4.2.2. Cohort Study
4.3. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scally, B.; Emberson, J.R.; Spata, E.; Reith, C.; Davies, K.; Halls, H.; Holland, L.; Wilson, K.; Bhala, N.; Hawkey, C.; et al. Effects of gastroprotectant drugs for the prevention and treatment of peptic ulcer disease and its complications: A meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 3, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, P.O.; Dunbar, K.B.; Schnoll-Sussman, F.H.; Greer, K.B.; Yadlapati, R.; Spechler, S.J. ACG Clinical Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 117, 27–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwakiri, K.; Fujiwara, Y.; Manabe, N.; Ihara, E.; Kuribayashi, S.; Akiyama, J.; Kondo, T.; Yamashita, H.; Ishimura, N.; Kitasako, Y.; et al. Evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for gastroesophageal reflux disease 2021. J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 57, 267–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.K.; Tae, C.H.; Song, K.H.; Kang, S.J.; Park, J.K.; Gong, E.J.; Shin, J.E.; Lim, H.C.; Lee, S.K.; Jung, D.H.; et al. 2020 Seoul Consensus on the Diagnosis and Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2021, 27, 453–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, N.S.; Hlatky, M.A.; Antman, E.M.; Bhatt, D.L.; Bjorkman, D.J.; Clark, C.B.; Furberg, C.D.; Johnson, D.A.; Kahi, C.J.; Laine, L.; et al. ACCF/ACG/AHA 2010 expert consensus document on the concomitant use of proton pump inhibitors and thienopyridines: A focused update of the ACCF/ACG/AHA 2008 expert consensus document on reducing the gastrointestinal risks of antiplatelet therapy and NSAID use. A Report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation Task Force on Expert Consensus Documents. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 56, 2051–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Kandulski, A.; Venerito, M. Proton-pump inhibitors: Understanding the complications and risks. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 697–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaezi, M.F.; Yang, Y.X.; Howden, C.W. Complications of Proton Pump Inhibitor Therapy. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savarino, V.; Marabotto, E.; Zentilin, P.; Furnari, M.; Bodini, G.; De Maria, C.; Pellegatta, G.; Coppo, C.; Savarino, E. Proton pump inhibitors: Use and misuse in the clinical setting. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 11, 1123–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthiah, M.D.; Zheng, H.L.; Chew, N.W.S.; Xiao, J.L.; Lim, L.G.; Tan, H.C.; Lee, C.H.; Low, A.F.; Foo, L.L.; Richards, A.M.; et al. Outcomes of a multi-ethnic Asian population on combined treatment with clopidogrel and omeprazole in 12,440 patients. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2021, 52, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, D.L.; Cryer, B.L.; Contant, C.F.; Cohen, M.; Lanas, A.; Schnitzer, T.J.; Shook, T.L.; Lapuerta, P.; Goldsmith, M.A.; Laine, L.; et al. Clopidogrel with or without omeprazole in coronary artery disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1909–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaduganathan, M.; Cannon, C.P.; Cryer, B.L.; Liu, Y.; Hsieh, W.H.; Doros, G.; Cohen, M.; Lanas, A.; Schnitzer, T.J.; Shook, T.L.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Proton-Pump Inhibitors in High-Risk Cardiovascular Subsets of the COGENT Trial. Am. J. Med. 2016, 129, 1002–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, D.; Goh, K.L. East Asian perspective on the interaction between proton pump inhibitors and clopidogrel. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 32, 1152–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, S.G.; Clare, R.; Pieper, K.S.; Nicolau, J.C.; Storey, R.F.; Cantor, W.J.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Angiolillo, D.J.; Husted, S.; Cannon, C.P.; et al. Association of proton pump inhibitor use on cardiovascular outcomes with clopidogrel and ticagrelor: Insights from the platelet inhibition and patient outcomes trial. Circulation 2012, 125, 978–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, K.; Katsanos, A.H.; Bilal, M.; Ishfaq, M.F.; Goyal, N.; Tsivgoulis, G. Cerebrovascular Outcomes With Proton Pump Inhibitors and Thienopyridines: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Stroke 2018, 49, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, P.M.; Maddox, T.M.; Wang, L.; Fihn, S.D.; Jesse, R.L.; Peterson, E.D.; Rumsfeld, J.S. Risk of adverse outcomes associated with concomitant use of clopidogrel and proton pump inhibitors following acute coronary syndrome. JAMA 2009, 301, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassen, J.A.; Choudhry, N.K.; Avorn, J.; Schneeweiss, S. Cardiovascular outcomes and mortality in patients using clopidogrel with proton pump inhibitors after percutaneous coronary intervention or acute coronary syndrome. Circulation 2009, 120, 2322–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, I.J.; Evans, S.J.; Hingorani, A.D.; Grosso, A.M.; Timmis, A.; Hemingway, H.; Smeeth, L. Clopidogrel and interaction with proton pump inhibitors: Comparison between cohort and within person study designs. BMJ 2012, 345, e4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, T.Z.; Xiang, Q.; Zhang, P.; Liu, X.; Zhang, C.; Tan, H.; Huang, J.; et al. Efficacy and safety of clopidogrel only vs. clopidogrel added proton pump inhibitors in the treatment of patients with coronary heart disease after percutaneous coronary intervention: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Cardiol. Heart Vasc. 2019, 23, 100317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Luo, Y.; Yang, X. Inappropriate Use of Proton Pump Inhibitors Increases Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Coronary Heart Disease. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2022, 15, 8685–8691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Ni, L.; Yang, J.; Fan, X.; Yu, M.; Yang, H.; Yu, M.; Yang, Y.; China Acute Myocardial Infarction Registry study, g. The Clinical Impact of Proton Pump Inhibitors When Co-Administered With Dual Antiplatelet Therapy in Patients Having Acute Myocardial Infarction With Low Risk of Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Insights From the China Acute Myocardial Infarction Registry. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 685072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saven, H.; Zhong, L.; McFarlane, I.M. Co-prescription of Dual-Antiplatelet Therapy and Proton Pump Inhibitors: Current Guidelines. Cureus 2022, 14, e21885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, J.J.; Thomas, C.D.; Barbarino, J.; Desta, Z.; Van Driest, S.L.; El Rouby, N.; Johnson, J.A.; Cavallari, L.H.; Shakhnovich, V.; Thacker, D.L.; et al. Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guideline for CYP2C19 and Proton Pump Inhibitor Dosing. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 109, 1417–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibbing, D.; Morath, T.; Stegherr, J.; Braun, S.; Vogt, W.; Hadamitzky, M.; Schömig, A.; Kastrati, A.; von Beckerath, N. Impact of proton pump inhibitors on the antiplatelet effects of clopidogrel. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 101, 714–719. [Google Scholar]
- Siller-Matula, J.M.; Spiel, A.O.; Lang, I.M.; Kreiner, G.; Christ, G.; Jilma, B. Effects of pantoprazole and esomeprazole on platelet inhibition by clopidogrel. Am. Heart J. 2009, 157, 148.e1–148.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA. Early Communication about an Ongoing Safety Review of Clopidogrel Bisulfate (Marketed as Plavix). 2009. Available online: https://www.ktgh.com.tw/Public/Medicament_News/2009131945327055.pdf (accessed on 19 September 2021).
- Bundhun, P.K.; Teeluck, A.R.; Bhurtu, A.; Huang, W.Q. Is the concomitant use of clopidogrel and Proton Pump Inhibitors still associated with increased adverse cardiovascular outcomes following coronary angioplasty?: A systematic review and meta-analysis of recently published studies (2012–2016). BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2017, 17, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.C.; Yan, L.; Yang, J.G.; Yu, M.Y. Ethnic variance on long term clinical outcomes of concomitant use of proton pump inhibitors and clopidogrel in patients with stent implantation A PRISMA-complaint systematic review with meta-analysis. Medicine 2021, 100, e24366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhat, N.; Haddad, N.; Crispo, J.; Birkett, N.; McNair, D.; Momoli, F.; Wen, S.W.; Mattison, D.R.; Krewski, D. Trends in concomitant clopidogrel and proton pump inhibitor treatment among ACS inpatients, 2000-2016. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 75, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, B.J.; Shin, S.Y.; Kim, D.B.; Ahn, H.S. Influence of individual proton pump inhibitors on clinical outcomes in patients receiving clopidogrel following percutaneous coronary intervention. Medicine 2021, 100, e27411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.J.; Kim, N.; Jang, I.J.; Cho, J.Y.; Nam, R.H.; Park, J.H.; Jo, H.J.; Yoon, H.; Shin, C.M.; Park, Y.S.; et al. Pantoprazole Does Not Reduce the Antiplatelet Effect of Clopidogrel: A Randomized Controlled Trial in Korea. Gut Liver 2017, 11, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitaker, H.J.; Hocine, M.N.; Farrington, C.P. The methodology of self-controlled case series studies. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 2009, 18, 7–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Schuemie, M.J.; Blei, D.M.; Hripcsak, G. Adjusting for indirectly measured confounding using large-scale propensity score. J. Biomed. Inform. 2022, 134, 104204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Schuemie, M.J.; Suchard, M.A. Evaluating large-scale propensity score performance through real-world and synthetic data experiments. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2018, 47, 2005–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, S.C.; Rho, Y.; Bikdeli, B.; Kim, J.; Siapos, A.; Weaver, J.; Londhe, A.; Cho, J.; Park, J.; Schuemie, M.; et al. Association of Ticagrelor vs Clopidogrel With Net Adverse Clinical Events in Patients With Acute Coronary Syndrome Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Intervention. JAMA 2020, 324, 1640–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suchard, M.A.; Schuemie, M.J.; Krumholz, H.M.; You, S.C.; Chen, R.; Pratt, N.; Reich, C.G.; Duke, J.; Madigan, D.; Hripcsak, G.; et al. Comprehensive comparative effectiveness and safety of first-line antihypertensive drug classes: A systematic, multinational, large-scale analysis. Lancet 2019, 394, 1816–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Requena, G.; Douglas, I.J.; Huerta, C.; de Abajo, F. Impact of pre-exposure time bias in self-controlled case series when the event conditions the exposure: Hip/femur fracture and use of benzodiazepines as a case study. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2020, 29, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.O.; Jung, C.H.; Song, Y.D.; Park, C.Y.; Kwon, H.S.; Cha, B.S.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, K.U.; Ko, K.S.; Lee, B.W. Background and data configuration process of a nationwide population-based study using the korean national health insurance system. Diabetes Metab. J. 2014, 38, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Han, K.; Ko, S.H.; Ko, K.S.; Lee, K.U. Data Analytic Process of a Nationwide Population-Based Study Using National Health Information Database Established by National Health Insurance Service. Diabetes Metab. J. 2016, 40, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, S.C.; Lee, S.; Cho, S.Y.; Park, H.; Jung, S.; Cho, J.; Yoon, D.; Park, R.W. Conversion of National Health Insurance Service-National Sample Cohort (NHIS-NSC) Database into Observational Medical Outcomes Partnership-Common Data Model (OMOP-CDM). Stud. Health Technol. Inform. 2017, 245, 467–470. [Google Scholar]
- Hripcsak, G.; Duke, J.D.; Shah, N.H.; Reich, C.G.; Huser, V.; Schuemie, M.J.; Suchard, M.A.; Park, R.W.; Wong, I.C.; Rijnbeek, P.R.; et al. Observational Health Data Sciences and Informatics (OHDSI): Opportunities for Observational Researchers. Stud. Health Technol. Inform. 2015, 216, 574–578. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, S.I.; Park, C.H.; You, S.C.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, K.J.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.; Yoo, J.J.; Seo, W.W.; Lee, H.S.; et al. Association between proton pump inhibitor use and gastric cancer: A population-based cohort study using two different types of nationwide databases in Korea. Gut 2021, 70, 2066–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.H.; Seo, S.I.; Lee, K.J.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.; Seo, W.W.; Lee, H.S.; Shin, W.G.; Yoo, J.J. Long-term proton pump inhibitor use and risk of osteoporosis and hip fractures: A nationwide population-based and multicenter cohort study using a common data model. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 37, 1534–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, S.I.; Park, C.H.; Kim, T.J.; Bang, C.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, K.J.; Kim, J.; Kim, H.H.; You, S.C.; Shin, W.G. Aspirin, metformin, and statin use on the risk of gastric cancer: A nationwide population-based cohort study in Korea with systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Med. 2022, 11, 1217–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Stroke | Myocardial Infarction | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | PPI Co-Prescription Groups (n = 8201) | PPI Non-Prescription Group (n = 61,987) | p-Value | PPI Co-Prescription Group (n = 1216) | PPI Non-Prescription Group (n = 4751) | p-Value |
| Sex | ||||||
| Women, n(%) | 3742 (45.8) | 25,662 (41.4) | <0.001 | 670 (55.1) | 3043 (64.0) | <0.001 |
| Age | 67.3 ± 10.9 | 66.1 ± 11.8 | <0.001 | 69.6 ± 10.2 | 68.1 ± 11.5 | <0.001 |
| Aspirin co-prescription | 3094 (37.8) | 22,810 (36.8) | 0.069 | 982 (80.8) | 3608 (75.9) | <0.001 |
| Comorbidity | ||||||
| Hypertension | 6357 (77.7) | 46,388 (74.8) | <0.001 | 1080 (58.1) | 4103 (86.4) | 0.023 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 4041 (49.4) | 32,432 (52.3) | <0.001 | 707 (58.1) | 2662 (56.0) | 0.185 |
| Dyslipidemia | 5499 (67.3) | 38,245 (61.7) | <0.001 | 917 (75.4) | 3534 (74.4) | 0.463 |
| Smoking history | ||||||
| Never smoker | 2610 (31.9) | 16,837 (27.1) | <0.001 | 341 (28.0) | 1146 (24.1) | 0.020 |
| Ex-smoker | 728 (8.9) | 4643 (7.5) | 106 (8.7) | 389 (8.2) | ||
| Current smoker | 1137 (13.9) | 8531 (13.8) | 159 (13.1) | 625 (13.2) | ||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.43 ± 3.09 | 24.39 ± 3.05 | 0.479 | 24.11 ± 3.1 | 24.41 ± 3.08 | 0.032 |
| Total cholesterol level (mg/dL) | 202.52 ± 42.01 | 204.96 ± 45.07 | <0.001 | 205.94 ± 44.95 | 207.52 ± 53.37 | 0.460 |
| Recurrent Stroke (n = 1448) | Recurrent MI (n = 208) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N (%) | Relative Risk (95% CI) | N (%) | Relative Risk (95% CI) | |
| RR of PPIs exposed periods (PPIs co-prescribed periods only) | ||||
| PPIs unexposed | 795 (54.9) | 1 (reference) | 113 (54.3) | 1 (reference) |
| PPIs exposed | 653 (45.1) | 2.09 (1.83–2.38) | 95 (45.7) | 1.47 (1.02–2.11) |
| Time from beginning of PPI co-prescription | ||||
| 0~2 weeks | 254 (17.6) | 1.76 (1.50–2.07) | 32 (15.4) | 1.30 (0.83–2.04) |
| 2~4 weeks | 187 (12.9) | 2.02 (1.68–2.43) | 16 (7.7) | 0.95 (0.54–1.69) |
| 4~6weeks | 90 (6.2) | 3.02 (2.36–3.86) | 19 (9.1) | 2.33 (1.32–4.13) |
| 6~8 weeks | 47 (3.2) | 2.81 (2.02–3.92) | 11 (5.3) | 1.99 (0.98–4.03) |
| >8weeks | 75 (5.2) | 5.57 (4.06–7.64) | 17 (8.2) | 3.80 (1.93–7.45) |
| RR of PPIs exposed periods (included PPIs washout periods) | ||||
| Non-risk periods | 594 (41.0) | 1 (reference) | 85 (40.9) | 1 (reference) |
| Risk periods | 854 (59.0) | 2.47 (2.16–2.81) | 123 (59.1) | 1.87 (1.31–2.65) |
| Type of PPIs | Recurrent Stroke | Recurrent MI | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Events (%) | Relative Risk (95% CI) | Number of Events (%) | Relative Risk (95% CI) | ||
| Omeprazole | PPIs unexposed | 83 (60.6) | 1 (reference) | 7 (77.8) | 1 (reference) |
| PPIs exposed | 54 (39.4) | 1.84 (1.18–2.86) | 2 (22.2) | 0.33 (0.47–2.34) | |
| Non-risk periods | 64 (46.7) | 1 (reference) | 5 (55.6) | 1 (reference) | |
| Risk periods including washout periods | 73 (53.3) | 2.03 (1.34–3.08) | 4 (44.4) | 1.04 (0.13–8.40) | |
| Esomeprazole | PPIs unexposed | 181 (48.5) | 1 (reference) | 29 (58.0) | 1 (reference) |
| PPIs exposed | 192 (51.5) | 2.75 (2.12–3.57) | 21 (42.0) | 0.89 (0.36–2.18) | |
| Non-risk periods | 128 (34.3) | 1 (reference) | 23 (46.0) | 1 (reference) | |
| Risk periods including washout periods | 245 (65.7) | 3.18 (2.45–4.11) | 27 (54.0) | 1.18 (0.52–2.65) | |
| Pantoprazole | PPIs unexposed | 213 (58.5) | 1 (reference) | 42 (51.2) | 1 (reference) |
| PPIs exposed | 151 (41.5) | 1.61 (1.21–2.13) | 40 (48.8) | 2.56 (1.46–4.50) | |
| Non-risk periods | 175 (48.1) | 1 (reference) | 35 (42.7) | 1 (reference) | |
| Risk periods including washout periods | 189 (51.9) | 1.80 (1.37–2.35) | 47 (57.3) | 2.53 (1.47–4.36) | |
| Rabeprazole | PPIs unexposed | 295 (60.0) | 1 (reference) | 39 (67.2) | 1 (reference) |
| PPIs exposed | 197 (40.0) | 1.88 (1.49–2.36) | 19 (32.8) | 1.11 (0.54–2.24) | |
| Non-risk periods | 232 (47.2) | 1 (reference) | 34 (58.6) | 1 (reference) | |
| Risk periods including washout periods | 260 (52.8) | 2.02 (1.62–2.52) | 24 (41.4) | 1.14 (0.54–1.98) | |
| Lansoprazole | PPIs unexposed | 121 (71.2) | 1 (reference) | 21 (65.6) | 1 (reference) |
| PPIs exposed | 49 (28.8) | 1.32 (0.87–2.01) | 11 (34.4) | 0.58 (0.22–1.52) | |
| Non-risk periods | 99 (58.2) | 1 (reference) | 16 (50.0) | 1 (reference) | |
| Risk periods including washout periods | 71 (41.8) | 1.63 (1.12–2.38) | 16 (50.0) | 0.87 (0.33–2.24) | |
| Dexlansoprazole | PPIs unexposed | 9 (75.0) | 1 (reference) | 0 | 1 (reference) |
| PPIs exposed | 3 (25.0) | 1.08 (0.18–6.49) | 2 | NA | |
| Non-risk periods | 6 (50.0) | 1 (reference) | 0 | 1 (reference) | |
| Risk periods including washout periods | 6 (50.0) | 3.65 (0.71–8.78) | 2 | NA | |
| Outcome | Cohort | Patients, n | Observation, Person years | Events | Incidence Rate a | HR (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stroke | PPI | 373 | 240 | 81 | 337.5 | 1.34 (1.01–1.76) | 0.04 |
| Non-PPI | 1051 | 740 | 189 | 255.2 | Reference | ||
| MI | PPI | 179 | 133 | 23 | 171.7 | 1.42 (0.79–2.49) | 0.23 |
| Non-PPI | 439 | 336 | 43 | 127.8 | Reference |
| Analysis | Observation Period | Stroke HR (95% CI) | MI HR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PS matching 1:4 (main analysis) | 12 months | 1.34 (1.01–1.76) | 1.42 (0.79–2.49) |
| 1:4 | 6 months | 1.42 (1.05–1.90) | 2.15 (1.10–4.13) |
| 1:1 | 12 months | 1.52 (1.06–2.20) | 1.33 (0.69–2.65) |
| 1:1 | 6 months | 1.56 (1.07–2.30) | 2.12 (0.95–5.21) |
| PS stratification | 12 months | 1.37 (1.08–1.73) | 1.15 (0.71–1.81) |
| 6 months | 1.43 (1.10–1.84) | 1.69 (0.96–2.92) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, Y.K.; Lim, H.S.; Choi, Y.I.; Choe, E.J.; Kim, S.; You, S.C.; Lee, K.J.; Kim, Y.; Park, D.H.; Shin, W.G.; et al. Impact of Concomitant Use of Proton Pump Inhibitors and Clopidogrel on Recurrent Stroke and Myocardial Infarction. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1213. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091213
Lee YK, Lim HS, Choi YI, Choe EJ, Kim S, You SC, Lee KJ, Kim Y, Park DH, Shin WG, et al. Impact of Concomitant Use of Proton Pump Inhibitors and Clopidogrel on Recurrent Stroke and Myocardial Infarction. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(9):1213. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091213
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Yong Kang, Hyun Sun Lim, Youn I Choi, Eun Ju Choe, Seonji Kim, Seng Chan You, Kyung Joo Lee, Yerim Kim, Da Hee Park, Woon Geon Shin, and et al. 2023. "Impact of Concomitant Use of Proton Pump Inhibitors and Clopidogrel on Recurrent Stroke and Myocardial Infarction" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 9: 1213. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091213
APA StyleLee, Y. K., Lim, H. S., Choi, Y. I., Choe, E. J., Kim, S., You, S. C., Lee, K. J., Kim, Y., Park, D. H., Shin, W. G., & Seo, S. I. (2023). Impact of Concomitant Use of Proton Pump Inhibitors and Clopidogrel on Recurrent Stroke and Myocardial Infarction. Pharmaceuticals, 16(9), 1213. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16091213






