Neuroendocrine Biomarkers of Herbal Medicine for Major Depressive Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
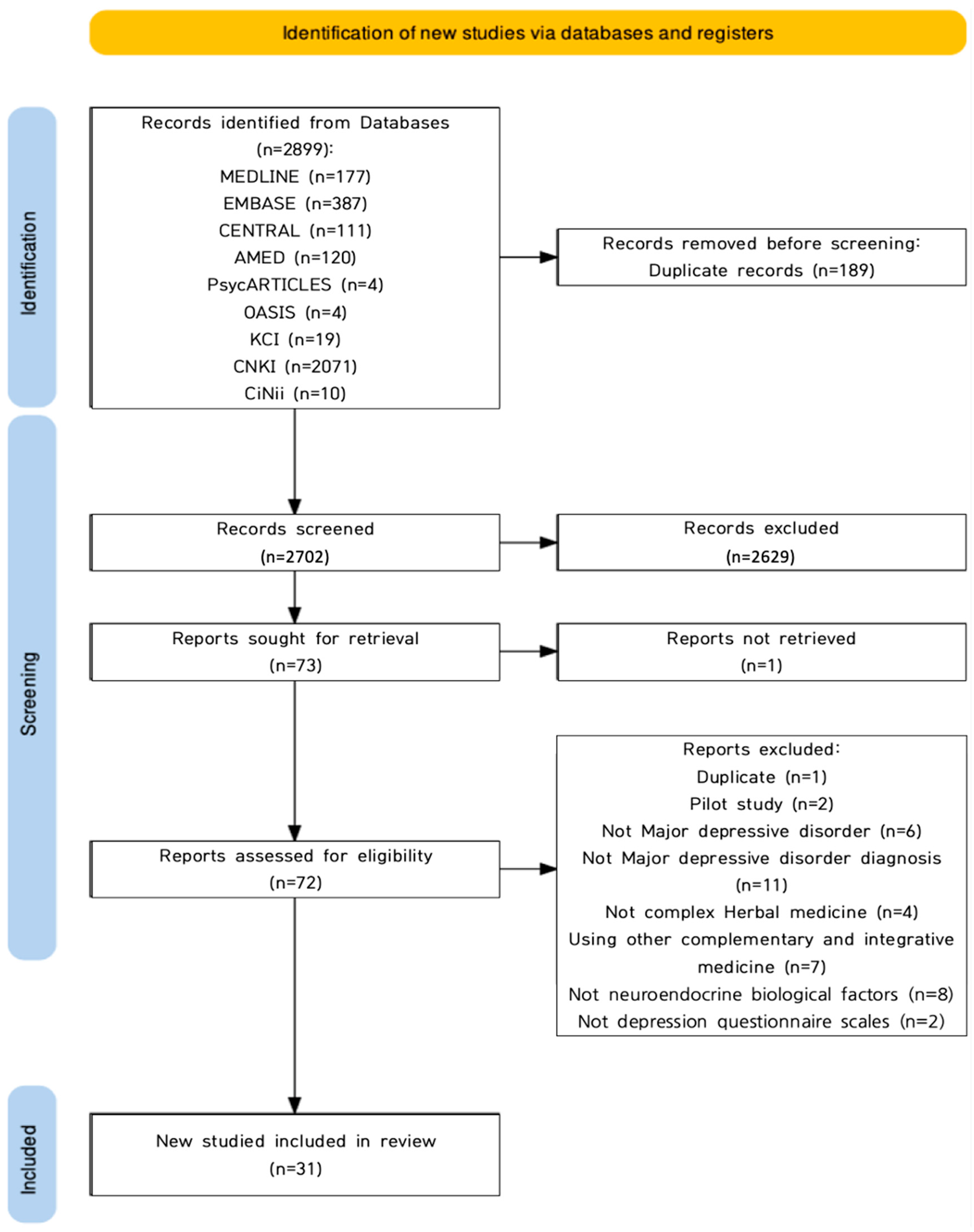
2.1. Study Description
2.2. Study Characteristics
2.2.1. Publication Years
2.2.2. Study Designs
2.2.3. Participants
2.2.4. Interventions
2.2.5. Treatment Periods
2.2.6. Outcome Measurements
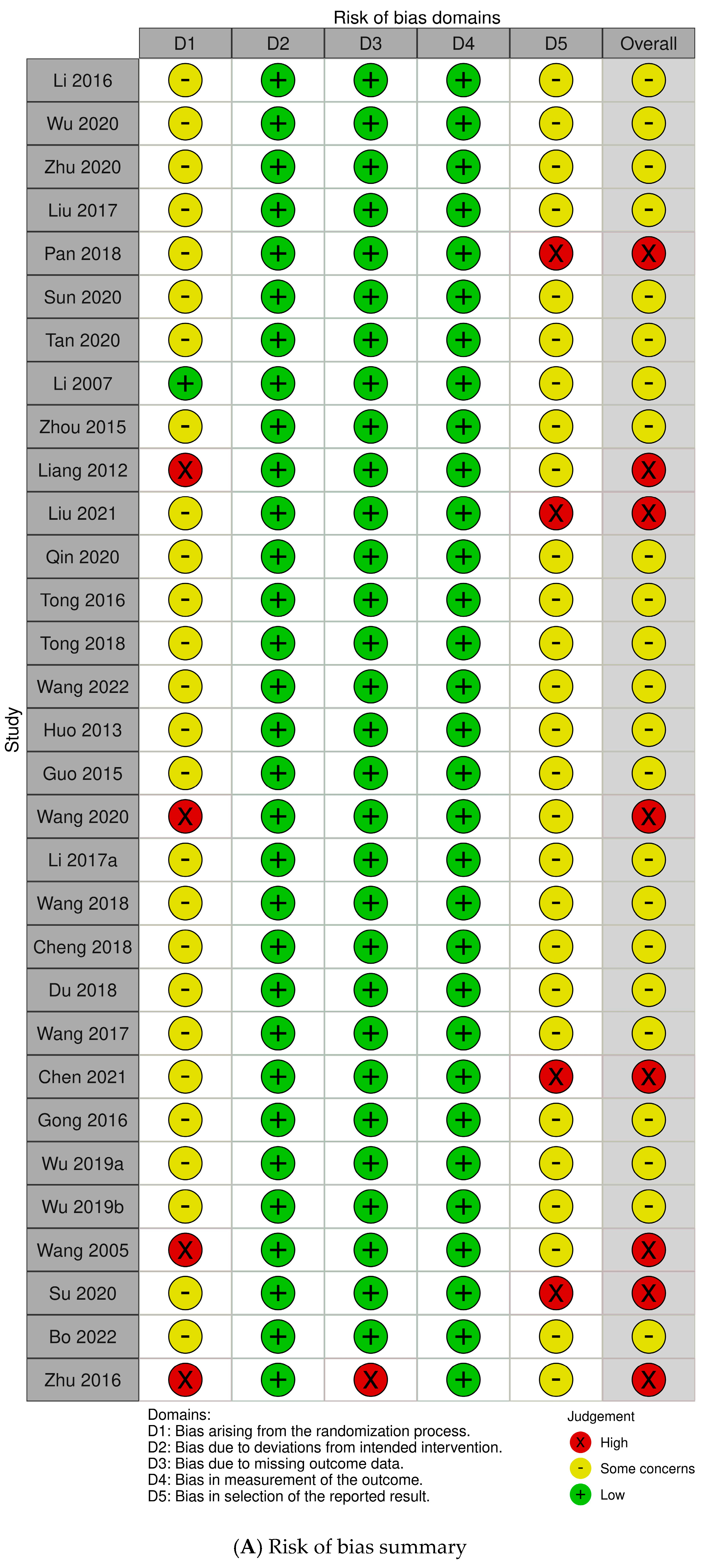
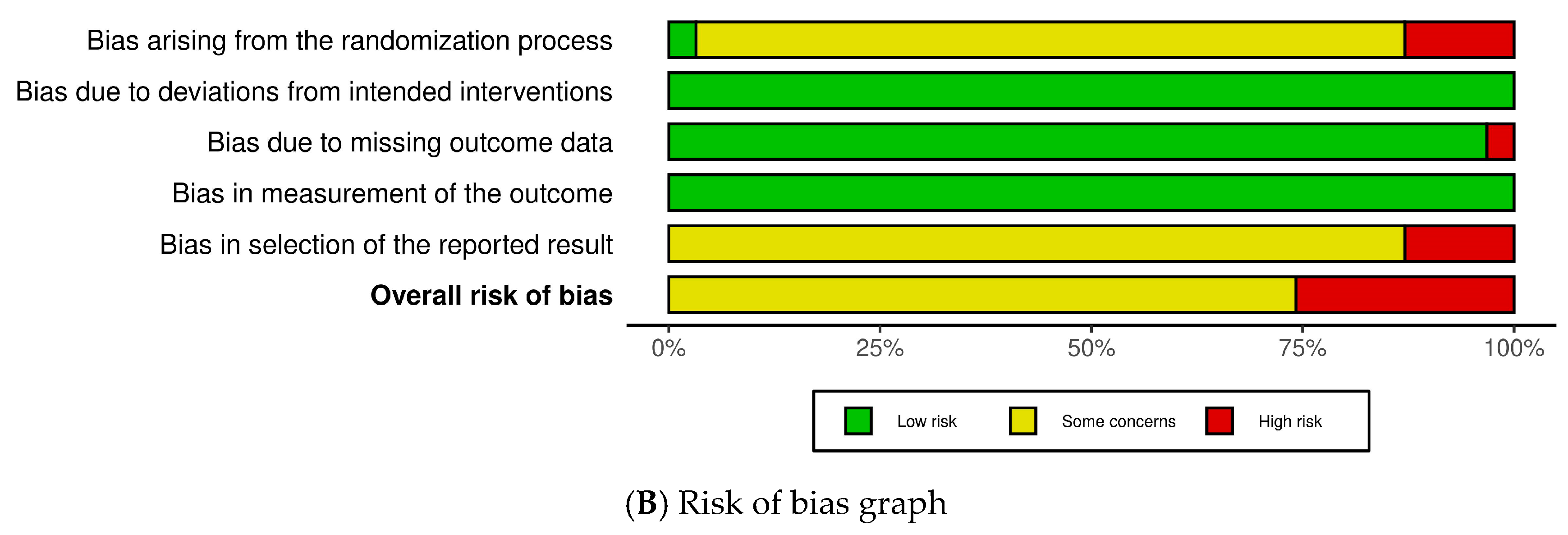
2.3. Risk of Bias (RoB)
2.4. Efficacy of HM Based on Neuroendocrine Biomarkers (Primary Outcome)
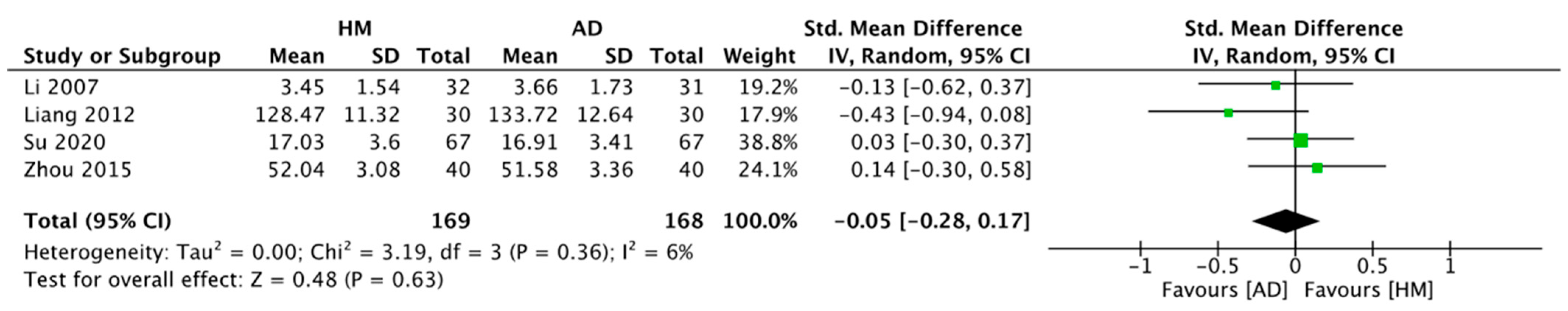
2.4.1. HM Alone vs. ADs Alone
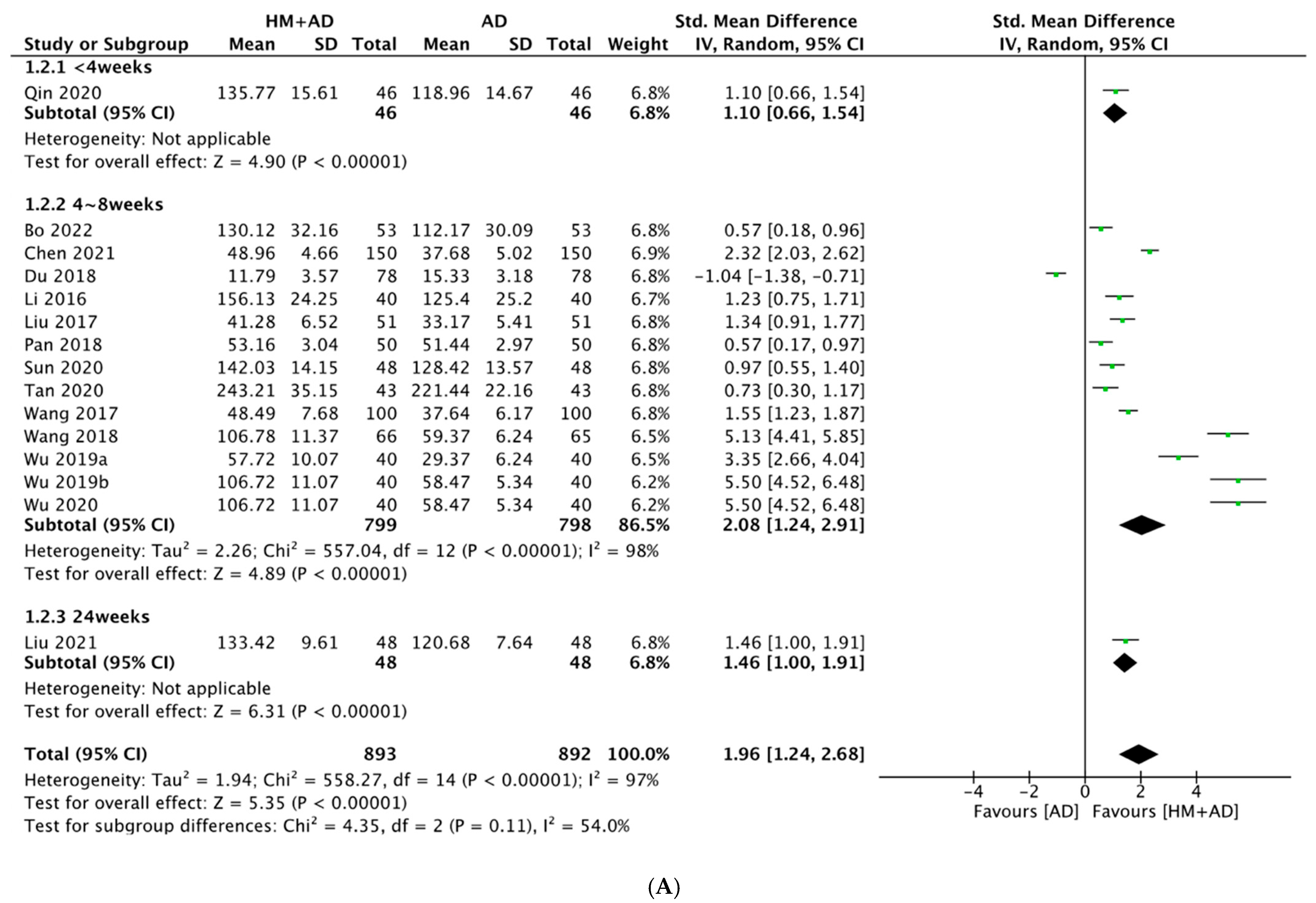
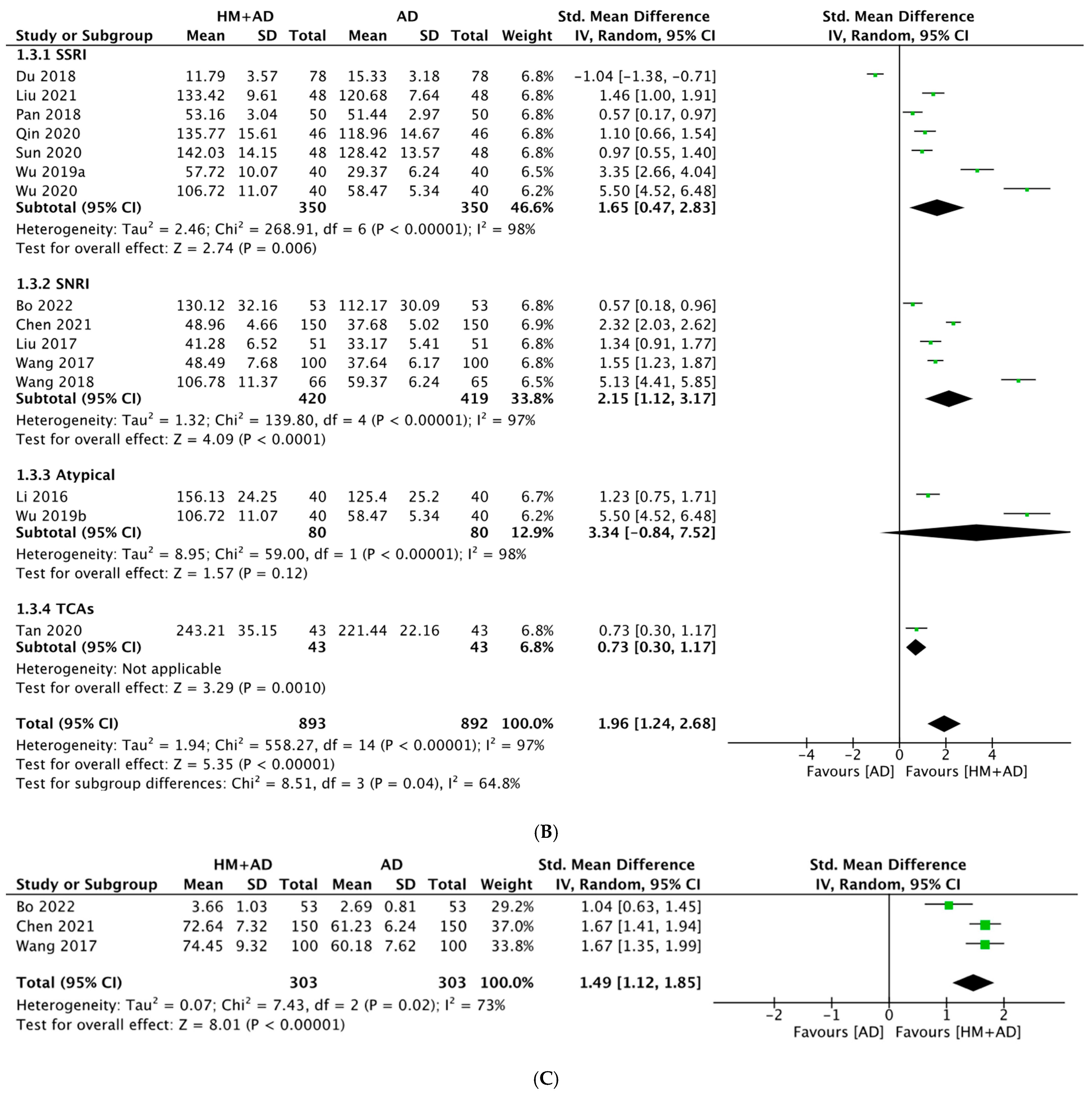
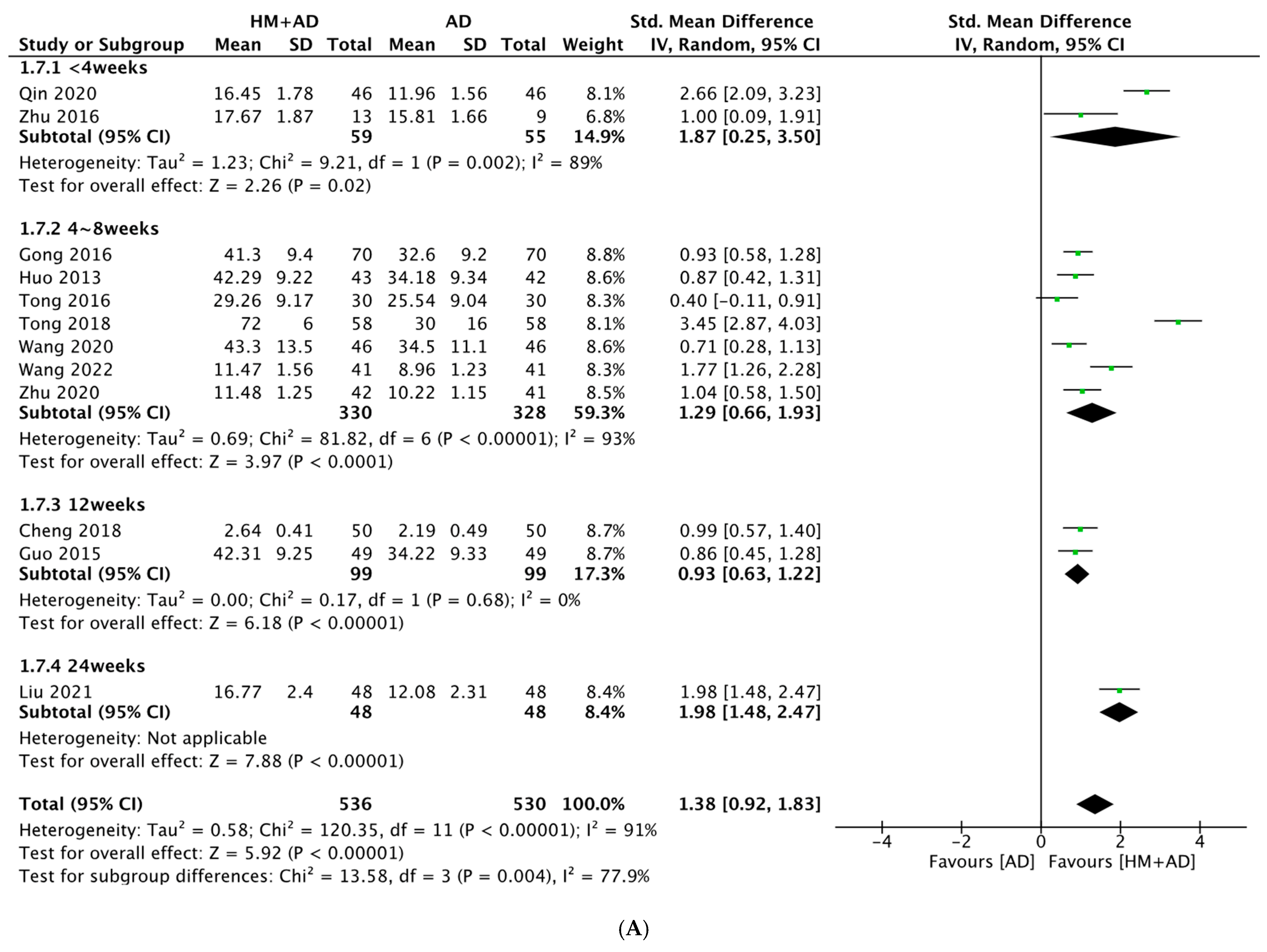
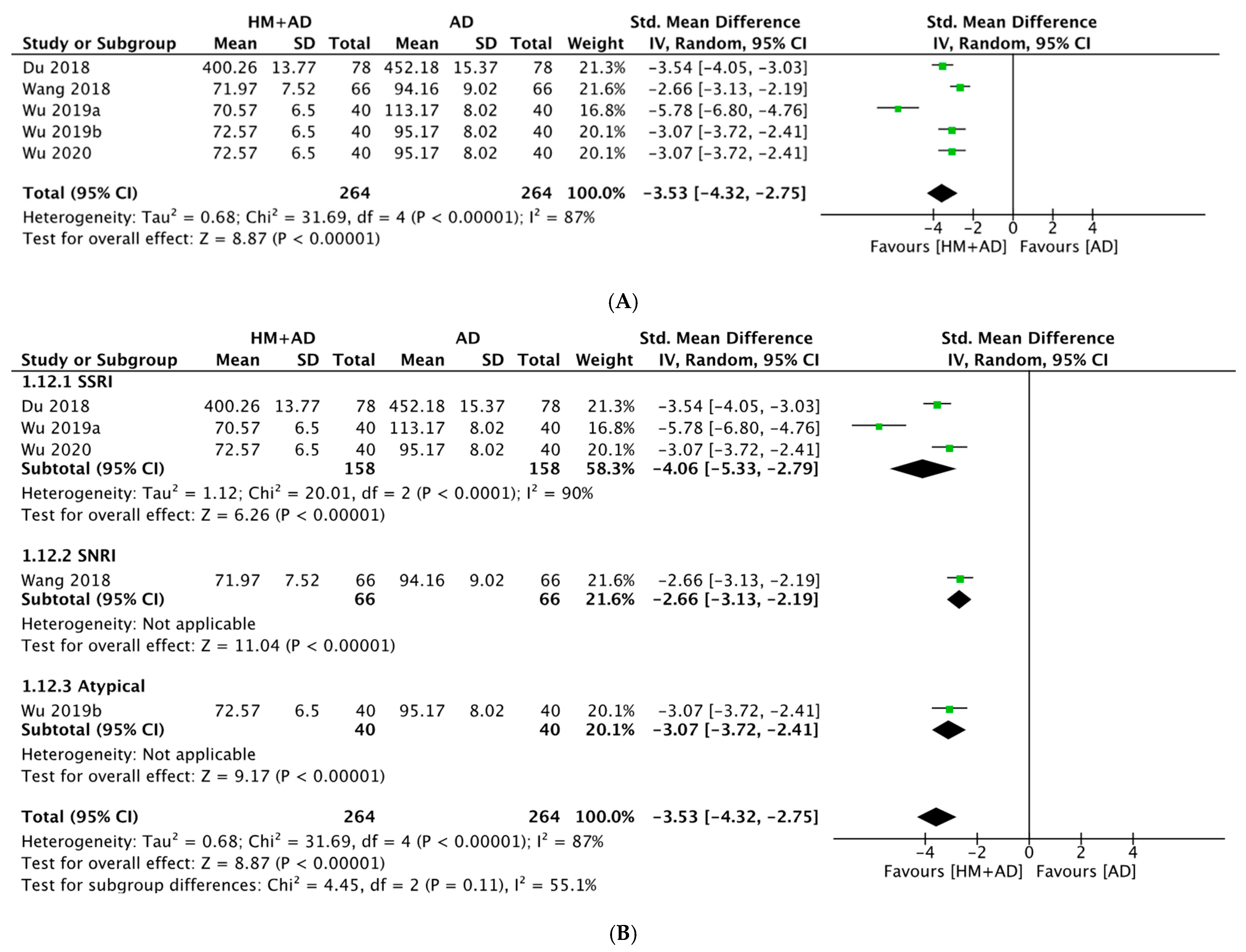
2.4.2. HM Plus ADs vs. ADs Alone
2.5. Efficacy of HM Based on Questionnaire Evaluation Scales (Secondary Outcome)
2.5.1. HM Alone vs. ADs Alone
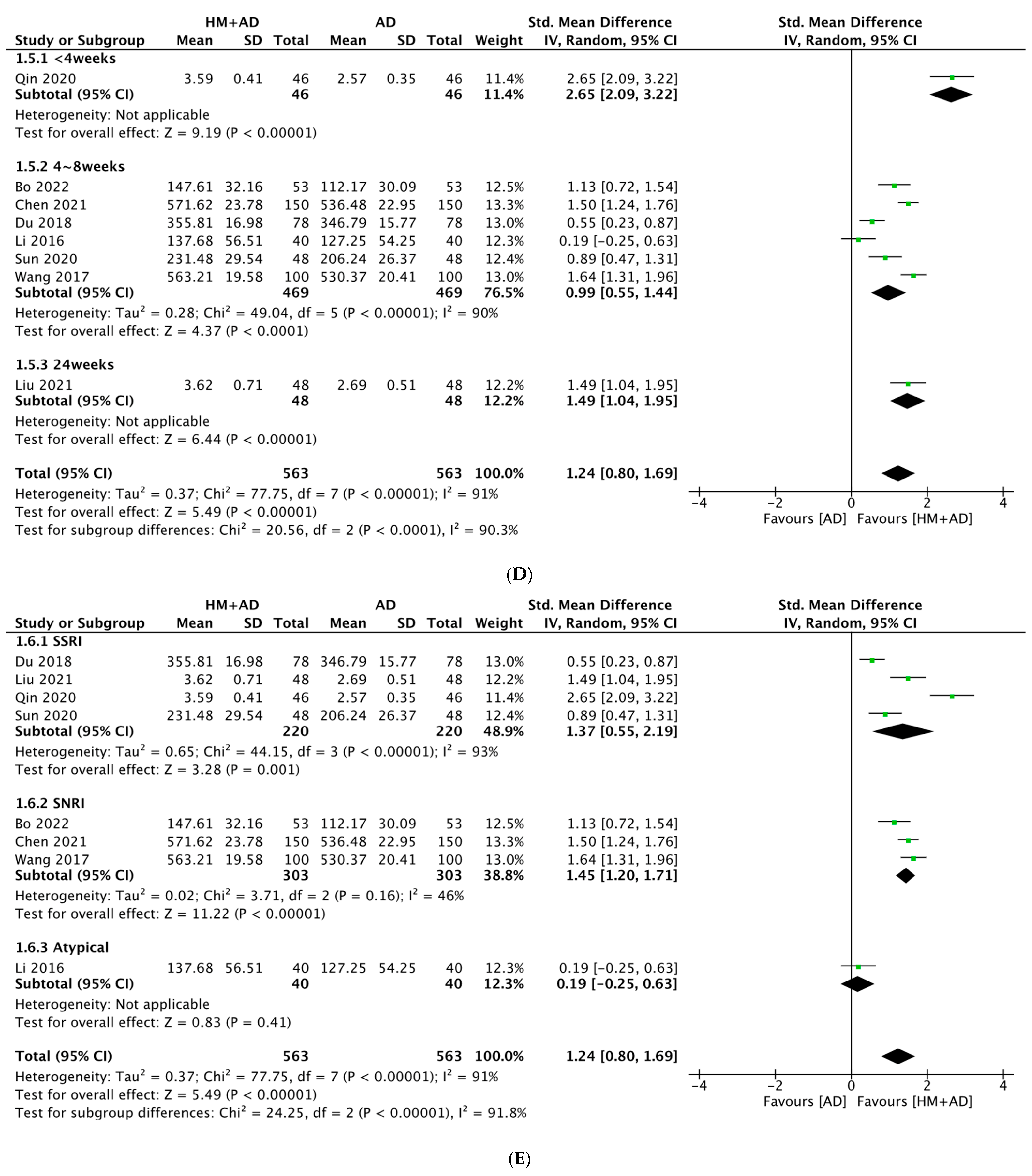
2.5.2. HM plus ADs vs. ADs Alone
2.6. Safety of HM
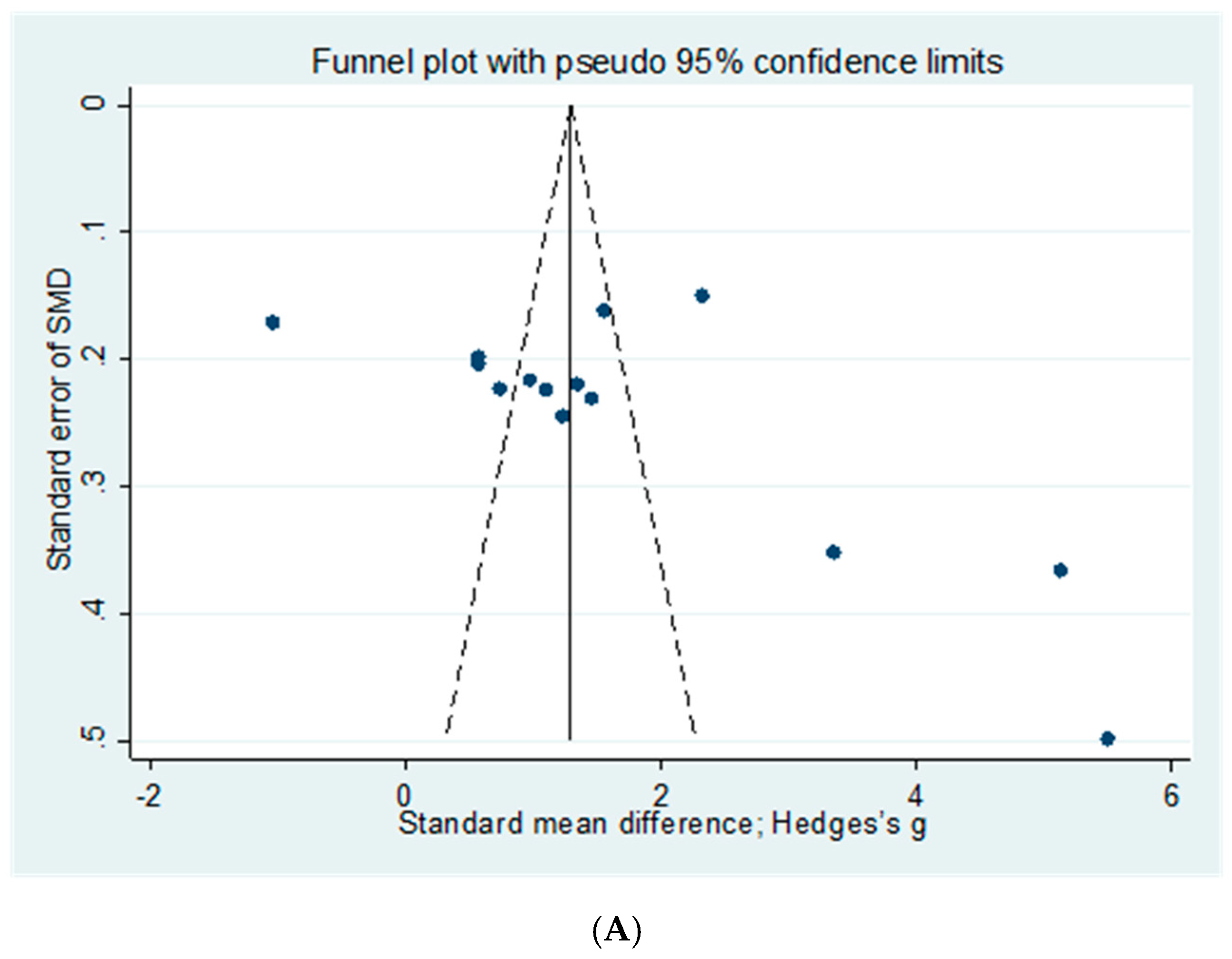
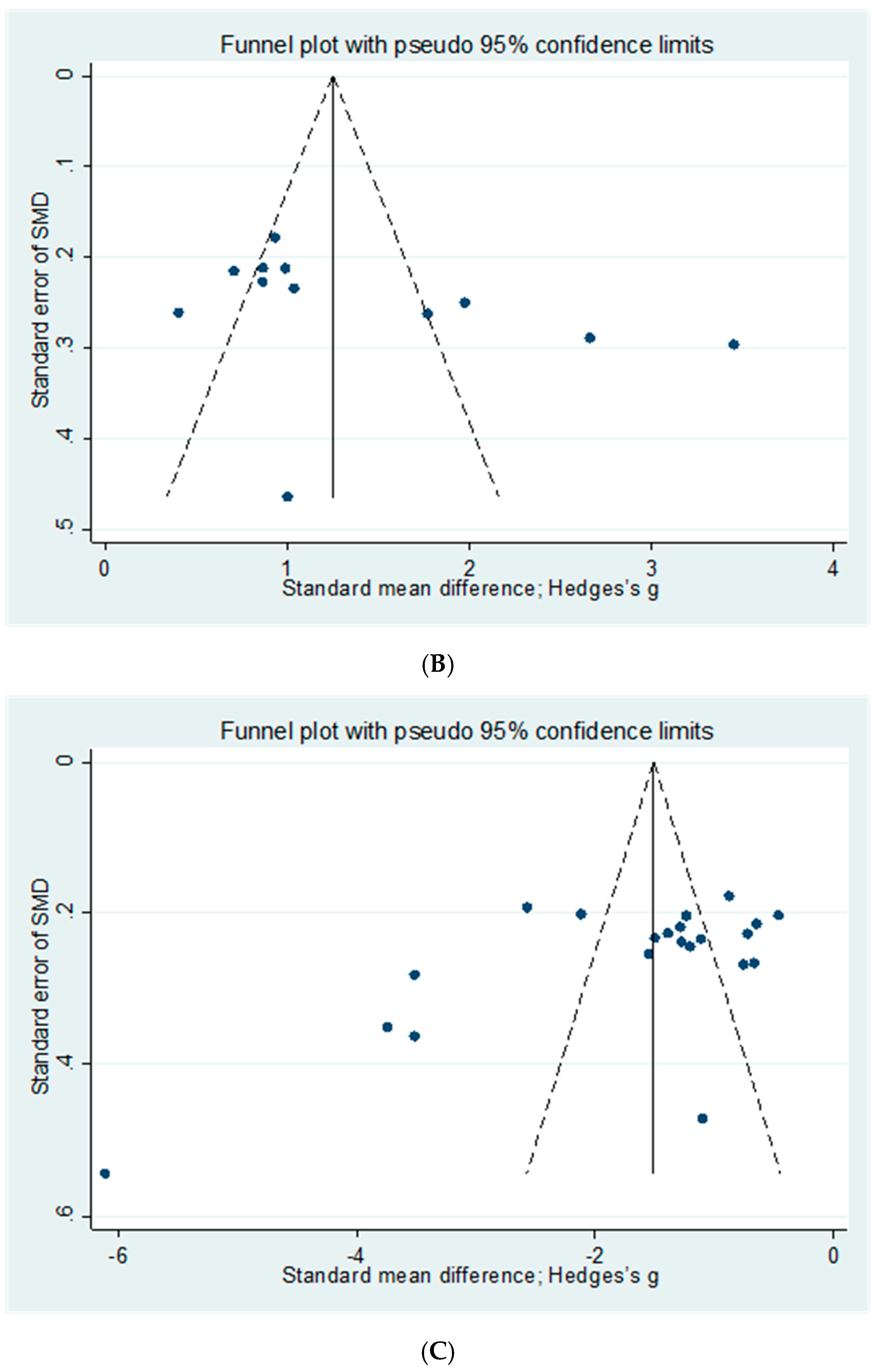
2.7. Publication Bias
3. Discussion
3.1. Summary of Evidence
3.2. Neuroendocrine Mechanisms of HM in the Treatment of MDD (Table 2)
3.2.1. Monoamine Neurotransmitters
3.2.2. Neurotrophic Factors
3.2.3. Hypothalamic–Pituitary–Adrenal (HPA) Axis Hormones
3.3. Clinical Implications
3.4. Limitations and Implications for Further Research
3.5. Implications for Further Research
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Registration
4.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
4.2.1. Types of Included Studies
4.2.2. Participants
4.2.3. Types of Intervention
4.2.4. Outcome Measures
4.3. Search Methods
4.4. Data Collection and Quality Assessment
4.4.1. Literature Selection
4.4.2. Data Extraction
4.4.3. Assessment of the RoB and Quality of Included Studies
4.5. Statistical Analysis
4.5.1. Strategy for Data Synthesis
4.5.2. Subgroup Analysis
4.5.3. Publication Bias and Sensitivity Analysis
5. Conclusions
- HM alone showed improvements similar to ADs for neuroendocrine biomarkers (5-HT) and the depression questionnaire scale (HAMD).
- HM combined with ADs significantly improved neuroendocrine biomarkers (5-HT, BDNF, DA, NE, NGF, and CORT) and the depression questionnaire scale (HAMD) compared with ADs alone.
- HM combined with ADs had a significantly lower incidence of adverse events than ADs alone.
- HM can treat depression by improving the expression of a patient’s neurotransmitters, neurotrophic factors, and HPA-axis hormones.
- In the future, conducting a high-quality multicenter large-scale RCT study using various neuroendocrine biomarkers is necessary.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; p. DSM-5. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez-Rojas, L.; Porras-Segovia, A.; Dunne, H.; Andrade-González, N.; Cervilla, J.A. Prevalence and Correlates of Major Depressive Disorder: A Systematic Review. Braz. J. Psychiatry 2020, 42, 657–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, A.J.; Charlson, F.J.; Norman, R.E.; Patten, S.B.; Freedman, G.; Murray, C.J.; Vos, T.; Whiteford, H.A. Burden of Depressive Disorders by Country, Sex, Age, and Year: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. PLoS Med. 2013, 10, e1001547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2019 Mental Disorders Collaborators. Global, Regional, and National Burden of 12 Mental Disorders in 204 Countries and Territories, 1990–2019: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Psychiatry 2022, 9, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, P.E.; Fournier, A.A.; Sisitsky, T.; Simes, M.; Berman, R.; Koenigsberg, S.H.; Kessler, R.C. The Economic Burden of Adults with Major Depressive Disorder in the United States (2010 and 2018). Pharmacoeconomics 2021, 39, 653–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, A.J.; Norman, R.E.; Freedman, G.; Baxter, A.J.; Pirkis, J.E.; Harris, M.G.; Page, A.; Carnahan, E.; Degenhardt, L.; Vos, T.; et al. The Burden Attributable to Mental and Substance Use Disorders as Risk Factors for Suicide: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, H.; Jin, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Cheung, T.; Balbuena, L.; Xiang, Y.T. Prevalence of Suicidal Ideation and Planning in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder: A Meta-analysis of Observation Studies. J. Affect. Disord. 2021, 293, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COVID-19 Mental Disorders Collaborators. Global Prevalence and Burden of Depressive and Anxiety Disorders in 204 Countries and Territories in 2020 Due to the COVID-19 Pandemic. Lancet 2021, 398, 1700–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaseem, A.; Barry, M.J.; Kansagara, D.; Clinical Guidelines Committee of the American College of Physicians. Nonpharmacologic Versus Pharmacologic Treatment of Adult Patients with Major Depressive Disorder: A Clinical Practice Guideline from the American College of Physicians. Ann. Intern. Med. 2016, 164, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Undurraga, J.; Baldessarini, R.J. Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trials of Antidepressants for Acute Major Depression: Thirty-Year Meta-analytic Review. Neuropsychopharmacology 2012, 37, 851–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, A.F.; Sharma, M.S.; Brunoni, A.R.; Vieta, E.; Fava, G.A. The Safety, Tolerability and Risks Associated with the Use of Newer Generation Antidepressant Drugs: A Critical Review of the Literature. Psychother. Psychosom. 2016, 85, 270–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, J.; Read, J. A Systematic Review into the Incidence, Severity and Duration of Antidepressant Withdrawal Effects: Are Guidelines Evidence-Based? Addict. Behav. 2019, 97, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubovicky, M.; Belovicova, K.; Csatlosova, K.; Bogi, E. Risks of Using SSRI/SNRI Antidepressants During Pregnancy and Lactation. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2017, 10, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kok, R.M.; Reynolds, C.F., 3rd. Management of Depression in Older Adults: A Review. JAMA 2017, 317, 2114–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payne, K.A.; Myhr, G. Increasing Access to Cognitive-Behavioural Therapy (CBT) for the Treatment of Mental Illness in Canada: A Research Framework and Call for Action. Healthc. Policy 2010, 5, e173–e185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kessler, R.C.; Soukup, J.; Davis, R.B.; Foster, D.F.; Wilkey, S.A.; Van Rompay, M.I.; Eisenberg, D.M. The Use of Complementary and Alternative Therapies to Treat Anxiety and Depression in the United States. Am. J. Psychiatry 2001, 158, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, J.Y.; Nazir, Z.; Nault, H. Complementary and Alternative Medicine Recommendations for Depression: A Systematic Review and Assessment of Clinical Practice Guidelines. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2020, 20, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, W.F.; Chung, K.F.; Ng, K.Y.; Yu, Y.M.; Ziea, E.T.; Ng, B.F. A Systematic Review on the Efficacy, Safety and Types of Chinese Herbal Medicine for Depression. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2014, 57, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhoury, M. Revisiting the Serotonin Hypothesis: Implications for Major Depressive Disorders. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 2778–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amidfar, M.; Réus, G.Z.; de Moura, A.B.; Quevedo, J.; Kim, Y.K. The Role of Neurotrophic Factors in Pathophysiology of Major Depressive Disorder. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2021, 1305, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Huang, J.; Cheng, Y.C.; Zhang, Y.W. Traditional Chinese Medicine in Depression Treatment: From Molecules to Systems. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Liang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yao, K.; Chen, Z.; Zhai, S. Chinese Herbal Medicine for the Treatment of Depression: Applications, Efficacies and Mechanisms. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 5180–5190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.J.; Luo, H.C.; Qian, R.Q. Effect of Danzhi Xiaoyao Powder on Neuro-Immuno-Endocrine System in Patients with Depression. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2007, 27, 197–200. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, R.; Zhu, D.; Xia, Y.; Wang, H.; Tao, W.; Xue, W.; Xia, B.; Ren, L.; Zhou, X.; Li, G.; et al. A Role of Yueju in Fast-Onset Antidepressant Action on Major Depressive Disorder and Serum BDNF Expression: A Randomly Double-Blind, Fluoxetine-Adjunct, Placebo-Controlled, Pilot Clinical Study. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2015, 11, 2013–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.P.; Chey, W.D.; Singh, S.; Gong, H.; Shringarpure, R.; Hoe, N.; Chuang, E.; Talley, N.J. A Biomarker Panel and Psychological Morbidity Differentiates the Irritable Bowel Syndrome from Health and Provides Novel Pathophysiological Leads. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 39, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Z.; Hui, K.; Liu, L.J. Influence of Chaifu Depression-Relieving Prescription Combined with Mirtazapine on the Levels of NE and 5-HT in the Serum of Patients with Depression Due to Liver Qi Stagnation Chinese. Henan Tradit. Chin. Med. 2016, 36, 1984–1986. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.L.; Pan, K.; Wu, A.L. Clinical Study of Chaihu Longgu Muli Decoction Combined with Paroxetine in the Treatment of Depression. J. Cardiovasc. Cerebrovasc. Dis. Integr. Trad. Chin. West. Med. 2020, 18, 1994–1996. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.C. Clinical Observation on the Treatment of Depression with Stagnation of Liver Li by Chaihu Plus Keel Oyster Decoction; Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine: Nanjing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C. Efficacy of Chaihu Shugan Powder Combined with Western Medicine in the Treatment of Depression Patients and Its Effect on Inflammatory Factors and 5-HT. Shaanxi Tradit. Chin. Med. 2017, 38, 873–874. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Z.Y.; Zhao, J.; Chen, J.S. Effect of Chaihu Shugan Powder Combined with Paroxetine on Serum Levels of 5-HT and Its Safety Analysis in Depression Patient. Tradit. Chin. Med. Inf. 2018, 35, 54–57. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.X. Clinical Study on Chaihu Shugan Powder Combined with Escitalopram Oxalate for Depression of Liver Qi Stagnation Type. New Chin. Med. 2020, 52, 37–40. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, C.H.; Chen, S.G.; Lin, J.X.; Zhao, Y.H. Clinical Effect of Chaihu Shugan Decoction in Treating Depression Patients with Qi Depression Syndrome. Inn. Mong. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2020, 39, 11–13. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.F.; Xia, Y.; Zhou, Z.H.; Chen, L.L. Clinical Study of the Effect on 5- Hydroxytryptamine in Serum from Depression Patients Treated with Fu Yang Shu Gan Jian Pi Fang. J. Guiyang Coll. Trad. Chin. Med. 2015, 37, 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, W.H. Study on Clinical Efficacy and the Influence on the 5-HT Level by Bupiyangxin Treatment in the Treating Depression; Chinese Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine: Jinan, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, S.Y.; Tong, X.X. Effect of Jiawei Chaihu Decoction and Paroxetine on Serum Levels of IL-2 and TNF-α in Patients with Depression. Chin. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2020, 38, 105–108. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Sun, Q.M. Effects of Jiawei Chaihu Decoction Assisted by Paroxetine on Serum Neurocytokines and Monoamine Transmitters in Patients with Depression. Mediterr. J. Commun. 2021, 35, 377–379. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, Z.S.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Y. A Randomized Controlled Trial of Paroxetine Combined with Jiawei Xiaoyaosan for Patients with Depression. Sichuan Ment. Health 2016, 29, 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, Z.S.; Liu, Y.; Huang, J.D. Clinical Study of Jiawei Xiaoyao Powder Combined with Fluoxetine Hydrochloride in the Treatment of Depression. Lab. Med. Clin. 2018, 15, 1249–1251. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.J.; Zuo, W.B. Effects of Jiawei Xiaoyao Powder Combined with Fluoxetine in Treatment of Patients with Depression. China Minkang Med. 2022, 34, 57–59+66. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, Z.H.; Zhang, D.Y.; Han, Z.G. Clinical Observation on the Treatment of Depression and the Influence to Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor with Jieyu Anshen Decoction Paroxetine. Chin. J. Exp. Formulas 2013, 19, 337–340. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.M.; Li, H.Z. Study on the the Clinical Effects of Mental Depression by Jieyu Anshen Dingzhi Combine with Paroxetine. Tradit. Chin. Med. Pharmacol. Clin. 2015, 31, 264–266. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.J.; Cao, W.; Li, Q.G.; Zhou, Y.S.; Yang, R.N.; Xin, Q. Effects of Agomelatine Combined with Jieyu Pills on Inflammatory Factors and Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Patients with Depression. Chronic Dis. Prev. Control China 2020, 28, 61–63. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M. Study of Jinkui Shenqi Pill on Improving the Fatigue of Depression Patients; Nanjing Medical University: Nanjing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.D.; Chen, L.J.; Liu, G.; Jin, Z.M.; Xu, M.W.; Li, P. Clinical Study on Jiuwei Zhenxin Granules Combined with Duloxetine in Treatment of Depression. Mod. Med. Clin. 2018, 33, 2848–2851. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.R.; Yang, C.Y. Effect of Traditional Chinese Medicine Combined with Western Medicine in Treatment of Depression and Effect on Serum Monoamine Neurotransmitters. Chin. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2017, 35, 1336–1339. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, H.Y. Clinical Observation of Combination Therapy of Traditional Chinese Medicine Xinshu Mixture and Sertraline Hydrochloride for the Treatment of Depression. Tianjin Tradit. Chin. Med. 2018, 35, 895–897. [Google Scholar]
- Du, M.J.; Xiao, W.X.; Shen, L.J.; Jiang, Y.S. Influence on the Scores of HAMD, HAMA, MADS and Safety for the Patients with Depression by Citalopram Combine with Chinese Traditional Medicine. Int. J. Psychiatry Med. 2018, 45, 72–74+99. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, J.B.; Kang, Y.H.; Wu, C.D. Effect of Shuganjieyu Capsule Combined with Duloxetine on Cognitive Function in Patients with Depression. Lab. Med. Clin. 2016, 13, 3539–3541. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Dai, S. Clinical Study on Shuganjieyu Capsule Combined with Venlafaxine in the Treatment of Depression. New Tradit. Chin. Med. 2021, 53, 59–62. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.L.; Meng, H.; Wu, A.L.; Peng, W.F.; Su, Q.H.; Li, G.Z. Clinical Study on Sini Powder Combined with Paroxetine in Treatment of Depression. J. Pract. Chin. Med. 2019, 33, 21–23. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.L.; Wu, A. Observation on the Effect of Sini Powder Combined with Mirtazapine in the Treatment of 40 Cases of Depression. Chin. Med. Forum 2019, 34, 31–33. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.H. The Clininal Study of Wangyou Decocton on Depression; Fujian College of Traditional Chinese Medicine: Fuzhou, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Su, L.J.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, Q.G. Study on Antidepression Effect of Xiaochaihu Decoction and Its Effect on Neurotransmitters, Neurotrophic Factor and Estrogen in Brai. Chin. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2020, 38, 38–40. [Google Scholar]
- Bo, D.Y.; Kou, M.; Meng, Y.; Zhou, X.L. Clinical Study on Xiaoyao Pill Combined with Venlafaxine in the Treatment of Depression of Liver Depression and Spleen Deficiency. J. Liaoning Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2022, 178–181. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.D. Clinical Study of Yueju Pill in Improving Depressive Symptoms Rapidly; Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine: Nanjing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Maurer-Spurej, E.; Pittendreigh, C.; Misri, S. Platelet Serotonin Levels Support Depression Scores for Women with Postpartum Depression. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2007, 32, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Carr, G.V.; Lucki, I. The Role of Serotonin Receptor Subtypes in Treating Depression: A Review of Animal Studies. Psychopharmacology 2011, 213, 265–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Z.; Zhang, C.; Du, Y.; Huang, W.; Xing, Z.; Cao, H.; Nie, K.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, X.; Yang, B. The Effect of Traditional Chinese Medicine Zhike-Houpu Herbal Pair on Depressive Behaviors and Hippocampal Serotonin 1A Receptors in Rats After Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress. Psychosom. Med. 2019, 81, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Wang, P.; Wu, L.; Liu, J.; Fang, Y.; Tian, J.; Zhou, Y.; Du, G.; Qin, X. Pharmacokinetics-Pharmacodynamics and Tissue Distribution Analysis of Low Polar Extract of Xiaoyao Powder Combined with Rat Model of Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2019, 42, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarting, R.K.; Huston, J.P. Behavioral Concomitants of Regional Changes in the Brain’s Biogenic Amines After Apomorphine and Amphetamine. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1992, 41, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.L.; Liu, Y.; Yan, C.; Pan, Y.; Su, J.F.; Wu, W.K. Antidepressant-Like Effects of Fractions Prepared from Danzhi-Xiaoyao-San Decoction in Rats with Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress: Effects on Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis, Arginine Vasopressin, and Neurotransmitters. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2016, 2016, 6784689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grace, A.A. Dysregulation of the Dopamine System in the Pathophysiology of Schizophrenia and Depression. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2016, 17, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.H.; Grace, A.A. Amygdala-Ventral pallidum Pathway Decreases Dopamine Activity After Chronic Mild Stress in Rats. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 76, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, C. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor, Depression, and Physical Activity: Making the Neuroplastic Connection. Neural Plast. 2017, 2017, 7260130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autry, A.E.; Monteggia, L.M. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Pharmacol. Rev. 2012, 64, 238–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Xu, X.; He, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhao, L.; Qiu, J.; Wang, D.; Gong, Z.; Qiu, X.; Huang, H. Antidepressant-Like Effects and Cognitive Enhancement of Coadministration of Chaihu Shugan San and Fluoxetine: Dependent on the BDNF-ERK-CREB Signaling Pathway in the Hippocampus and Frontal Cortex. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 2794263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.X.; Cheng, K.C.; Hsu, C.T.; Cheng, J.T.; Yang, T.T. Major Plant in Herbal Mixture Gan-Mai-Da-Zao for the Alleviation of Depression in Rat Models. Plants 2022, 11, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiener, C.D.; de Mello Ferreira, S.; Pedrotti Moreira, F.; Bittencourt, G.; de Oliveira, J.F.; Lopez Molina, M.; Jansen, K.; de Mattos Souza, L.D.; Rizzato Lara, D.; Portela, L.V.; et al. Serum Levels of Nerve Growth Factor (NGF) in Patients with Major Depression Disorder and Suicide Risk. J. Affect. Disord. 2015, 184, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciafrè, S.; Ferraguti, G.; Tirassa, P.; Iannitelli, A.; Ralli, M.; Greco, A.; Chaldakov, G.N.; Rosso, P.; Fico, E.; Messina, M.P.; et al. Nerve Growth Factor in the Psychiatric Brain. Riv. Psichiatr. 2020, 55, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, A.X.; Xia, T.C.; Mak, M.S.; Zhu, K.Y.; Dong, T.T.; Tsim, K.W. A Herbal Mixture of Sesami Semen nigrum and Longan Arillus Induces Neurite Outgrowth in Cultured Neurons and Shows Anti-depression in Chronic Mild Stress-Induced Rats. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2022, 2022, 8809546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.; Moon, M.; Oh, H.; Kim, H.G.; Kim, S.Y.; Oh, M.S. Ginger Improves Cognitive Function via NGF-Induced ERK/CREB Activation in the Hippocampus of the Mouse. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2014, 25, 1058–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weitzman, E.D.; Fukushima, D.; Nogeire, C.; Roffwarg, H.; Gallagher, T.F.; Hellman, L. Twenty-Four Hour Pattern of the Episodic Secretion of Cortisol in Normal Subjects. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1971, 33, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, H.M.; Davis, M.C.; Otte, C.; Mohr, D.C. Depression and Cortisol Responses to Psychological Stress: A Meta-analysis. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2005, 30, 846–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, B.E. Stress, Norepinephrine and Depression. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2001, 26, S11–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, H.; Sun, L.; Liu, X.; Peng, B.; Wang, Q.; Jia, W.; Chen, Y.; Pan, A.; Xiao, P. Preventive Action of Kai Xin San Aqueous Extract on Depressive-Like Symptoms and Cognition Deficit Induced by Chronic Mild Stress. Exp. Biol. Med. 2009, 234, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, C.; Tian, J.; Gao, X.; Li, K.; Du, G.; Qin, X. Plasma Metabolomics of Depressed Patients and Treatment with Xiaoyaosan Based on Mass Spectrometry Technique. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 246, 112219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Mao, J.J.; Vertosick, E.; Seluzicki, C.; Yang, Y. Evaluating Cancer Patients’ Expectations and Barriers Toward Traditional Chinese Medicine Utilization in China: A Patient-Support Group-Based Cross-Sectional Survey. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.; Ma, Q.; Cui, H.; Liu, G.; Zhao, X.; Li, W.; Piao, G. How Can Synergism of Traditional Medicines Benefit from Network Pharmacology? Molecules 2017, 22, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Blencowe, N.S.; Boutron, I.; Cates, C.J.; Cheng, H.Y.; Corbett, M.S.; Eldridge, S.M.; et al. RoB 2: A revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2019, 366, l4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, S.; Shin, I.; Bae, J. Intervention Meta-analysis Using Stata Software. J. Health Inform. Stat. 2016, 41, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
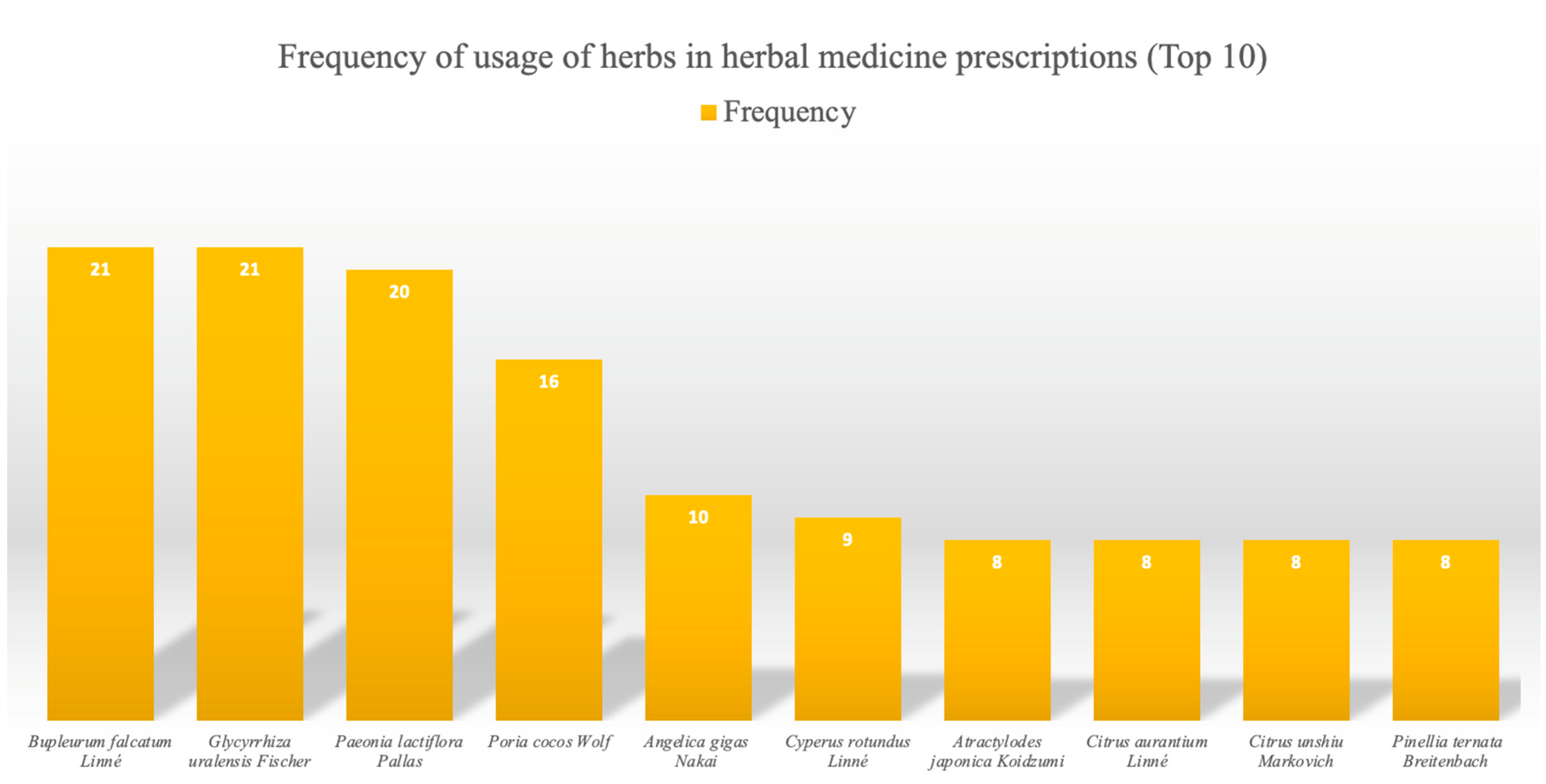

| Frequency | Herb |
|---|---|
| 21 | Bupleurum falcatum Linné, Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fischer |
| 20 | Paeonia lactiflora Pallas |
| 16 | Poria cocos Wolf |
| 10 | Angelica gigas Nakai |
| 9 | Cyperus rotundus Linné |
| 8 | Atractylodes japonica Koidzumi, Citrus aurantium Linné, Citrus unshiu Markovich, Pinellia ternata Breitenbach |
| 7 | Curcuma aromatica Salisb, Polygala tenuifolia Willdenow, Zizyphus jujuba Mill |
| 6 | Cnidium officinale Makino |
| 5 | Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi |
| 4 | Citrus aurantium Linné, Gardenia jasminoides Ellis, fossilia ossis mastodi |
| 3 | Albizia julibrissin Durazz, Aucklandia lappa Decne, Polygonum multiflorum Thumb, Cinnamomum cassia Presl, Ostrea gigas Thunberg, Lilium lancifolium Thunb, Hypericum perforatum, Paeonia suffruticosa Andrews, Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer, Rheum palmatum Linne, Zizyphus jujuba Miller var. inermis Rehder |
| 2 | Aconitum carmichaeli Debeaux, Acorus gramineus Solander, Astragalus membranaceus Bunge, Platycladus orientalis Franco, Codonopsis pilosula Nannfeldt, Mentha arvensis Linné var. piperascens Malinvaud ex Holmes, Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge, Zingiber officinale Roscoe |
| Main Mechanism | Outcome Raised | Outcome Reduced |
|---|---|---|
| Monoamine neurotransmitter | 5-HT, DA, NE | 5-HIAA |
| Neurotrophic factor | BDNF, NGF, NF | - |
| HPA-axis hormone | - | CORT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seung, H.-B.; Kwon, H.-J.; Kwon, C.-Y.; Kim, S.-H. Neuroendocrine Biomarkers of Herbal Medicine for Major Depressive Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16081176
Seung H-B, Kwon H-J, Kwon C-Y, Kim S-H. Neuroendocrine Biomarkers of Herbal Medicine for Major Depressive Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(8):1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16081176
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeung, Hye-Bin, Hui-Ju Kwon, Chan-Young Kwon, and Sang-Ho Kim. 2023. "Neuroendocrine Biomarkers of Herbal Medicine for Major Depressive Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 8: 1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16081176
APA StyleSeung, H.-B., Kwon, H.-J., Kwon, C.-Y., & Kim, S.-H. (2023). Neuroendocrine Biomarkers of Herbal Medicine for Major Depressive Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pharmaceuticals, 16(8), 1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16081176







