Case Report and Literature Review: Bisphosphonate, Sirolimus, and Atenolol Treatment in a 4-Year-Old Child Diagnosed with Gorham–Stout Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
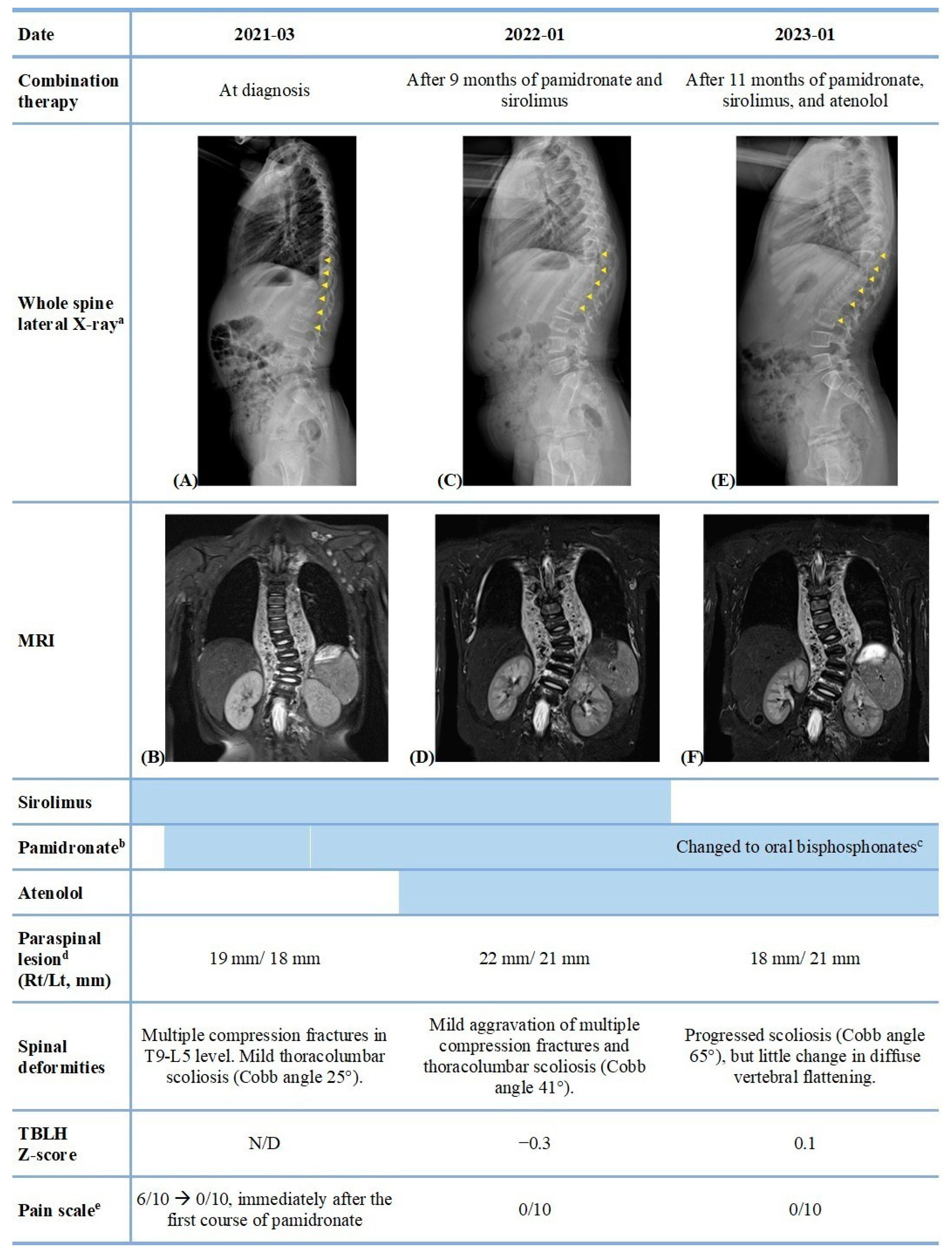
2. Case Report
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gorham, L.W.; Stout, A.P. Massive osteolysis (acute spontaneous absorption of bone, phantom bone, disappearing bone): Its relation to hemangiomatosis. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 1955, 37, 985–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaroli, D.A.; Cavarzere, P.; Cheli, M.; Provenzi, M.; Barillari, M.; Rodella, G.; Gaudino, R.; Antoniazzi, F. A child with early-onset gorham-stout disease complicated by chylothorax: Near-complete regression of bone lesions with interferon and bisphosphonate treatment. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2019, 91, 406–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelini, A.; Mosele, N.; Pagliarini, E.; Ruggieri, P. Current concepts from diagnosis to management in gorham-stout disease: A systematic narrative review of about 350 cases. EFORT Open Rev. 2022, 7, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momanu, A.; Caba, L.; Gorduza, N.C.; Arhire, O.E.; Popa, A.D.; Ianole, V.; Gorduza, E.V. Gorham-stout disease with multiple bone involvement-challenging diagnosis of a rare disease and literature review. Medicina 2021, 57, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Keyser, C.E.; Saltzherr, M.S.; Bos, E.M.; Zillikens, M.C. A large skull defect due to gorham-stout disease: Case report and literature review on pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heffez, L.; Doku, H.C.; Carter, B.L.; Feeney, J.E. Perspectives on massive osteolysis. Report of a case and review of the literature. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 1983, 55, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, S.L.; Wei, S.; Merrow, A.C.; Pressey, J.G. Gorham-stout disease successfully treated with sirolimus and zoledronic acid therapy. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2016, 38, e129–e132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Tian, R.; Wang, J.; Shan, Y.; Gao, H.; Xie, C.; Li, J.; Xu, M.; Gu, S. Gorham-stout disease successfully treated with sirolimus (rapamycin): A case report and review of the literature. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2020, 21, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forero Saldarriaga, S.; Vallejo, C.; Urrea Pineda, L.; Osma, A.; Bonilla Gonzalez, C. Gorham-stout disease with clinical response to sirolimus treatment. Eur. J. Case Rep. Intern. Med. 2021, 8, 002740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyness, S.P.; Roberts, W.L.; Straseski, J.A. Pediatric reference intervals for four serum bone markers using two automated immunoassays. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2013, 415, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.A.; Kwon, A.; Kim, J.H.; Nam, H.-K.; Yoo, J.-H.; Lim, J.S.; Cho, S.Y.; Cho, W.K.; Shim, K.S. Clinical practice guidelines for optimizing bone health in korean children and adolescents. Ann. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 27, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawson, S.L.; Hogg, M.M.; Moore, C.G.; Anderson, W.E.; Osipoff, P.S.; Runyon, M.S.; Reynolds, S.L. Pediatric pain assessment in the emergency department: Patient and caregiver agreement using the wong-baker faces and the faces pain scale–revised. Pediatr. Emerg. Care. 2021, 37, e950–e954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nir, V.; Guralnik, L.; Livnat, G.; Bar-Yoseph, R.; Hakim, F.; Ilivitzki, A.; Bentur, L. Propranolol as a treatment option in gorham-stout syndrome: A case report. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2014, 49, 417–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koto, K.; Inui, K.; Itoi, M.; Itoh, K. Gorham-stout disease in the rib and thoracic spine with spinal injury treated with radiotherapy, zoledronic acid, vitamin d, and propranolol: A case report and literature review. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 11, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baud, J.; Lomri, A.; Graber, D.; Bikfalvi, A. The therapeutic response in gorham’s syndrome to the beta-blocking agent propranolol is correlated to vegf-a, but not to vegf-c or flt1 expression. BMC Res. Notes 2015, 8, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wu, C.; Song, D.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; Guo, L. Atenolol vs. Propranolol for the treatment of infantile haemangiomas: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 20, 1644–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballona, R.; Zevallos, J.; Núñez, J. Clinical evaluation of infantile hemangiomas treated with atenolol. Dermatol. Online J. 2020, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.; Buonuomo, P.S.; Battafarano, G.; Conforti, A.; Mariani, E.; Algeri, M.; Pelle, S.; D’Agostini, M.; Macchiaiolo, M.; De Vito, R.; et al. Dissecting the mechanisms of bone loss in gorham-stout disease. Bone 2020, 130, 115068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Beek, E.R.; Cohen, L.H.; Leroy, I.M.; Ebetino, F.H.; Lowik, C.W.; Papapoulos, S.E. Differentiating the mechanisms of antiresorptive action of nitrogen containing bisphosphonates. Bone 2003, 33, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, R.G.; Rogers, M.J.; Frith, J.C.; Luckman, S.P.; Coxon, F.P.; Benford, H.L.; Croucher, P.I.; Shipman, C.; Fleisch, H.A. The pharmacology of bisphosphonates and new insights into their mechanisms of action. J. Bone Miner. Res. 1999, 14 (Suppl. S2), 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, M.T.; Clarke, B.L.; Khosla, S. Bisphosphonates: Mechanism of action and role in clinical practice. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2008, 83, 1032–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Hwang, S.; Kim, G.-H.; Lee, B.H.; Yoo, H.-W.; Choi, J.-H. Genotype-phenotype correlations and long-term efficacy of pamidronate therapy in patients with osteogenesis imperfecta. Ann. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 27, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santini, D.; Schiavon, G.; Angeletti, S.; Vincenzi, B.; Gasparro, S.; Grilli, C.; La Cesa, A.; Virzí, V.; Leoni, V.; Budillon, A.; et al. Last generation of amino-bisphosphonates (n-bps) and cancer angio-genesis: A new role for these drugs? Recent. Pat. Anticancer. Drug Discov. 2006, 1, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, F.; Kenn, W.; Wesselmann, U.; Hofbauer, L.C.; Delling, G.; Allolio, B.; Arlt, W. Gorham-stout disease—Stabilization during bisphosphonate treatment. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2005, 20, 350–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, K.N.; Masthoff, M.; Gosheger, G.; Klingebiel, S.; Schorn, D.; Roder, J.; Vogler, T.; Wildgruber, M.; Andreou, D. Gorham-stout disease: Good results of bisphosphonate treatment in 6 of 7 patients. Acta Orthop. 2020, 91, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoi, H.; Chakravarthy, V.; Whiting, B.; Kilpatrick, S.E.; Chen, T.; Krishnaney, A. Gorham-stout disease of the spine presenting with intracranial hypotension and cerebrospinal fluid leak: A case report and review of the literature. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2020, 11, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.-H.; Choi, Y.; Lee, Y.; Yoo, H.-W.; Choi, J.-H. Efficacy and safety of intravenous pamidronate infusion for treating osteoporosis in children and adolescents. Ann. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 26, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baroncelli, G.I.; Bertelloni, S. The use of bisphosphonates in pediatrics. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2014, 82, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreutle, V.; Blum, C.; Meier, C.; Past, M.; Müller, B.; Schütz, P.; Borm, K. Bisphosphonate induced hypocalcaemia-report of six cases and review of the literature. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2014, 144, w13979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, R.; Mishra, V.; Fraser, W.D. Severe hypocalcaemia after being given intravenous bisphosphonate. BMJ. 2004, 328, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, N.T.; Rech, B.O.; Martins, I.G.; Franco, J.B.; Ortega, K.L. Can children be affected by bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw? A systematic review. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 49, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celin, M.R.; Simon, J.C.; Krzak, J.J.; Fial, A.V.; Kruger, K.M.; Smith, P.A.; Harris, G.F. Do bisphosphonates alleviate pain in children? A systematic review. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2020, 18, 486–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagae, M.; Hiraga, T.; Wakabayashi, H.; Wang, L.; Iwata, K.; Yoneda, T. Osteoclasts play a part in pain due to the inflammation adjacent to bone. Bone 2006, 39, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneda, T.; Hata, K.; Nakanishi, M.; Nagae, M.; Nagayama, T.; Wakabayashi, H.; Nishisho, T.; Sakurai, T.; Hiraga, T. Involvement of acidic microenvironment in the pathophysiology of cancer-associated bone pain. Bone 2011, 48, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhen, G.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Ford, N.C.; Wu, X.; Wu, Q.; Yan, D.; Chen, X.; Cao, X.; Guan, Y. Mechanisms of bone pain: Progress in research from bench to bedside. Bone Res. 2022, 10, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maksymowych, P.W. Bisphosphonates-anti-inflammatory properties. Curr. Med. Chem.-Anti-Inflamm. Anti-Allergy Agents 2002, 1, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, P.; Bourgeois, P.; Boyer, O.; Catonné, Y.; Saillant, G. Massive gorham-stout syndrome of the pelvis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2005, 24, 551–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.; Almond, H.G.A.; Johnson, R. Massive osteolysis of the humerus with spontaneous recovery. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. Vol. 1975, 57-B, 238–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, K.W.; Hammill, A.M.; Mobberley-Schuman, P.; Nelson, S.C.; Blatt, J.; Bender, J.L.G.; McCuaig, C.C.; Synakiewicz, A.; Frieden, I.J.; Adams, D.M. Efficacy of systemic sirolimus in the treatment of generalized lymphatic anomaly and gorham-stout disease. Pediatr. Blood Cancer. 2019, 66, e27614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triana, P.; Dore, M.; Cerezo, V.N.; Cervantes, M.; Sánchez, A.V.; Ferrero, M.M.; González, M.D.; Lopez-Gutierrez, J.C. Sirolimus in the treatment of vascular anomalies. Eur. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2017, 27, 86–90. [Google Scholar]
- Moriceau, G.; Ory, B.; Mitrofan, L.; Riganti, C.; Blanchard, F.; Brion, R.; Charrier, C.; Battaglia, S.; Pilet, P.; Denis, M.G.; et al. Zoledronic acid potentiates mtor inhibition and abolishes the resistance of osteosarcoma cells to rad001 (everolimus): Pivotal role of the prenylation process. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 10329–10339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storch, C.H.; Hoeger, P.H. Propranolol for infantile haemangiomas: Insights into the molecular mechanisms of action. Br. J. Dermatol. 2010, 163, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozeki, M.; Fukao, T.; Kondo, N. Propranolol for intractable diffuse lymphangiomatosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1380–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, L.M.; Konji, V.N.; Ma, J. The management of osteoporosis in children. Osteoporos. Int. 2016, 27, 2147–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowden, S.A.; Mahan, J.D. Zoledronic acid in pediatric metabolic bone disorders. Transl. Pediatr. 2017, 6, 256–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuorimies, I.; Toiviainen-Salo, S.; Hero, M.; Mäkitie, O. Zoledronic acid treatment in children with osteogenesis imperfecta. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2011, 75, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barros, E.R.; Saraiva, G.L.; de Oliveira, T.P.; Lazaretti-Castro, M. Safety and efficacy of a 1-year treatment with zoledronic acid compared with pamidronate in children with osteogenesis imperfecta. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 25, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glorieux, F.; Bishop, N.; Bober, M.; Brain, C.; Devogelaer, J.; Fekete, G.; Forin, V.; Hopkin, R.; Kaitila, I.; Lee, B.; et al. Intravenous zoledronic acid (zol) compared to iv pamidronate (pam) in children with severe osteogenesis imperfecta (oi). Calcif. Tissue Int. 2008, 82, S85. [Google Scholar]
- Green, J.R. Zoledronic acid: Pharmacologic profile of a potent bisphosphonate. J. Organomet. Chem. 2005, 690, 2439–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scala, R.; Maqoud, F.; Antonacci, M.; Dibenedetto, J.R.; Perrone, M.G.; Scilimati, A.; Castillo, K.; Latorre, R.; Conte, D.; Bendahhou, S.; et al. Bisphosphonates targeting ion channels and musculoskeletal effects. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 837534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scala, R.; Maqoud, F.; Angelelli, M.; Latorre, R.; Perrone, M.G.; Scilimati, A.; Tricarico, D. Zoledronic acid modulation of trpv1 channel currents in osteoblast cell line and native rat and mouse bone marrow-derived osteoblasts: Cell proliferation and mineralization effect. Cancers 2019, 11, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, S.J.; Yoo, J.W.; Ahn, M.B. Case Report and Literature Review: Bisphosphonate, Sirolimus, and Atenolol Treatment in a 4-Year-Old Child Diagnosed with Gorham–Stout Disease. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1504. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16101504
Park SJ, Yoo JW, Ahn MB. Case Report and Literature Review: Bisphosphonate, Sirolimus, and Atenolol Treatment in a 4-Year-Old Child Diagnosed with Gorham–Stout Disease. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(10):1504. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16101504
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Su Jin, Jae Won Yoo, and Moon Bae Ahn. 2023. "Case Report and Literature Review: Bisphosphonate, Sirolimus, and Atenolol Treatment in a 4-Year-Old Child Diagnosed with Gorham–Stout Disease" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 10: 1504. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16101504
APA StylePark, S. J., Yoo, J. W., & Ahn, M. B. (2023). Case Report and Literature Review: Bisphosphonate, Sirolimus, and Atenolol Treatment in a 4-Year-Old Child Diagnosed with Gorham–Stout Disease. Pharmaceuticals, 16(10), 1504. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16101504





