Fucoidan-Mediated Inhibition of Fibrotic Properties in Oral Submucous Fibrosis via the MEG3/miR-181a/Egr1 Axis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
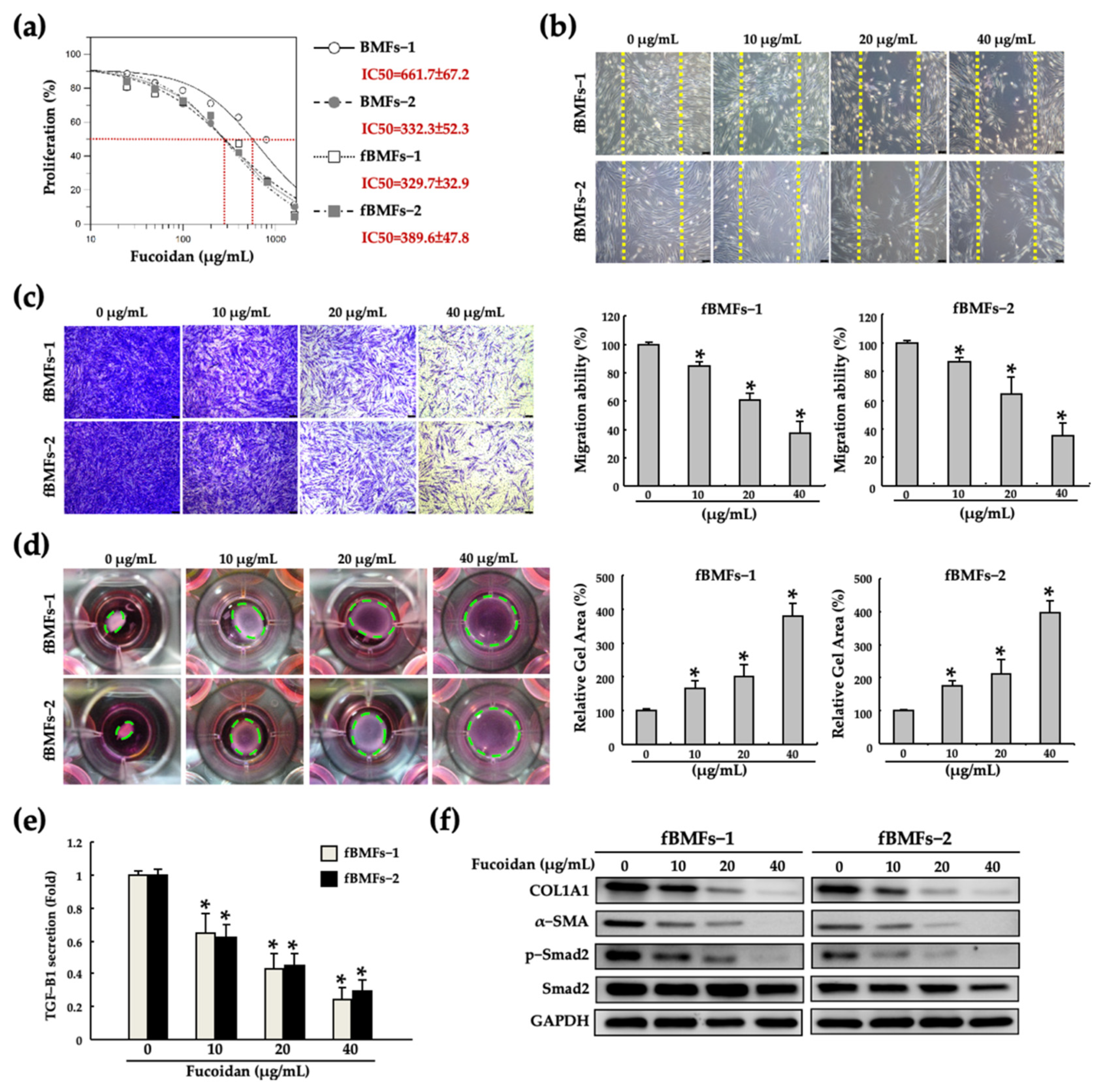
2.1. Fucoidan Inhibits the Myofibroblast Activities of Fibrotic BMFs (fBMFs)
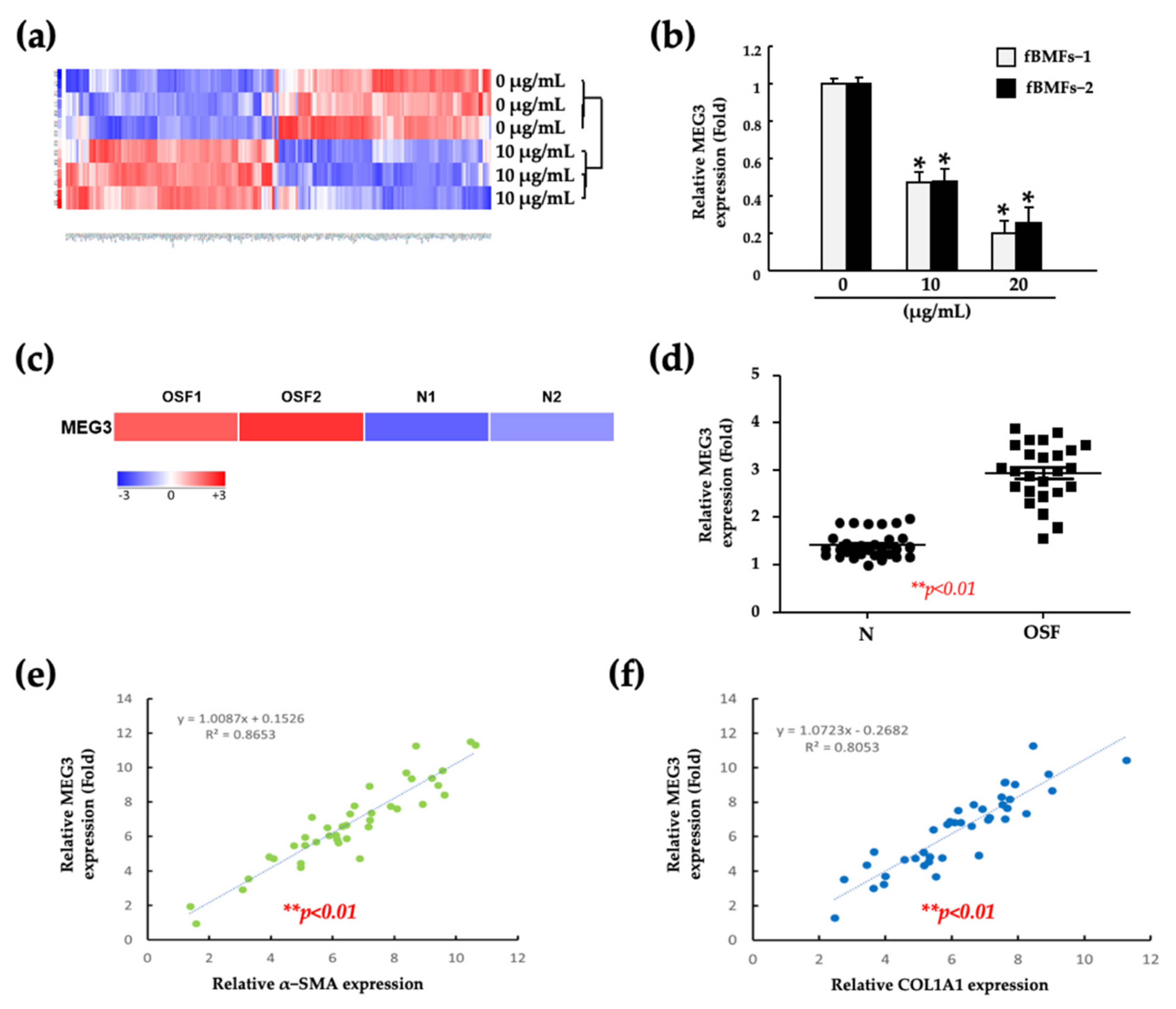
2.2. Fucoidan Suppresses the Myofibroblast Activities of fBMFs by Reducing the MEG3 Levels
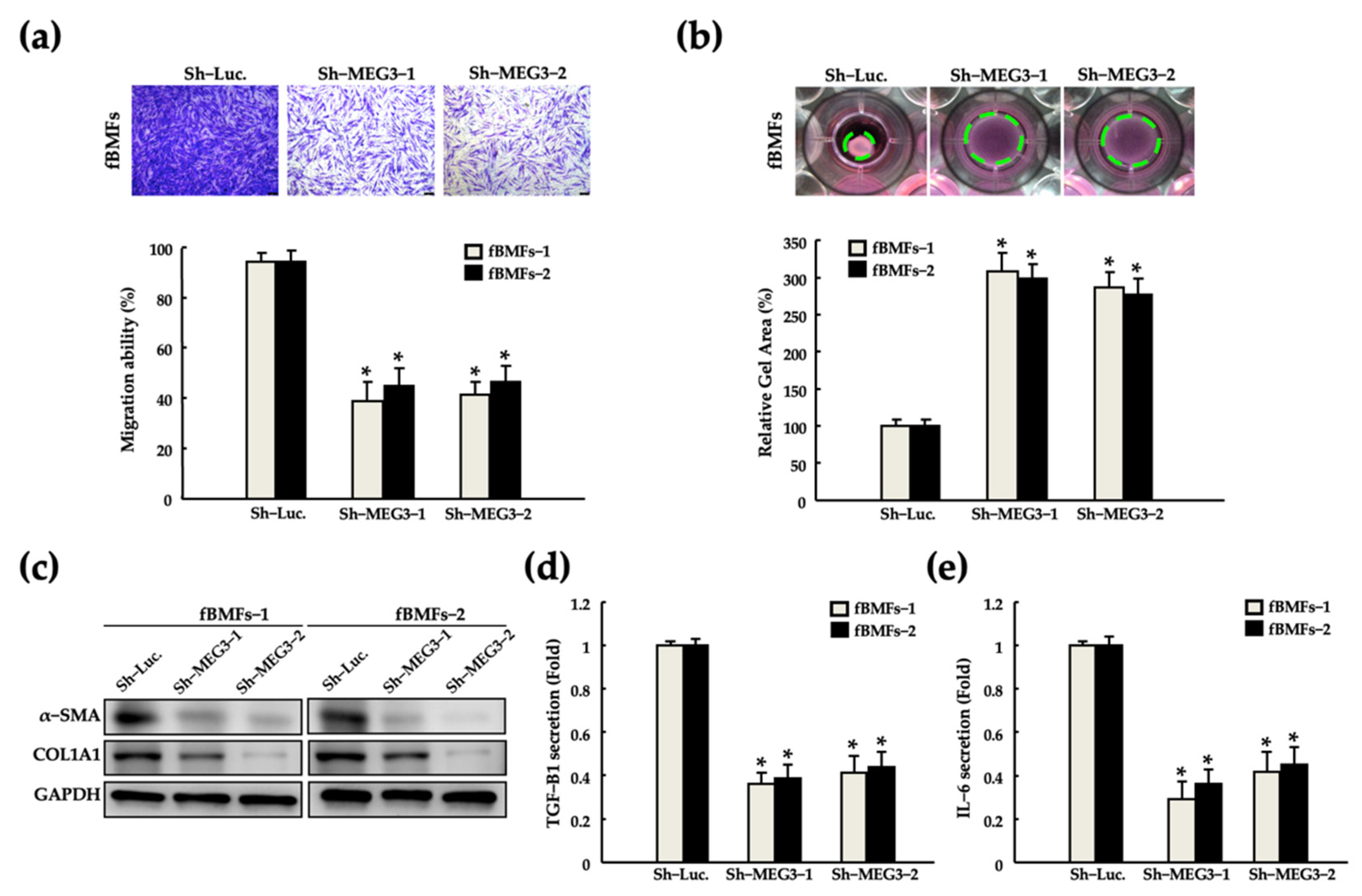
2.3. Silencing of MEG3 in fBMFs Suppresses the Myofibroblast Activities
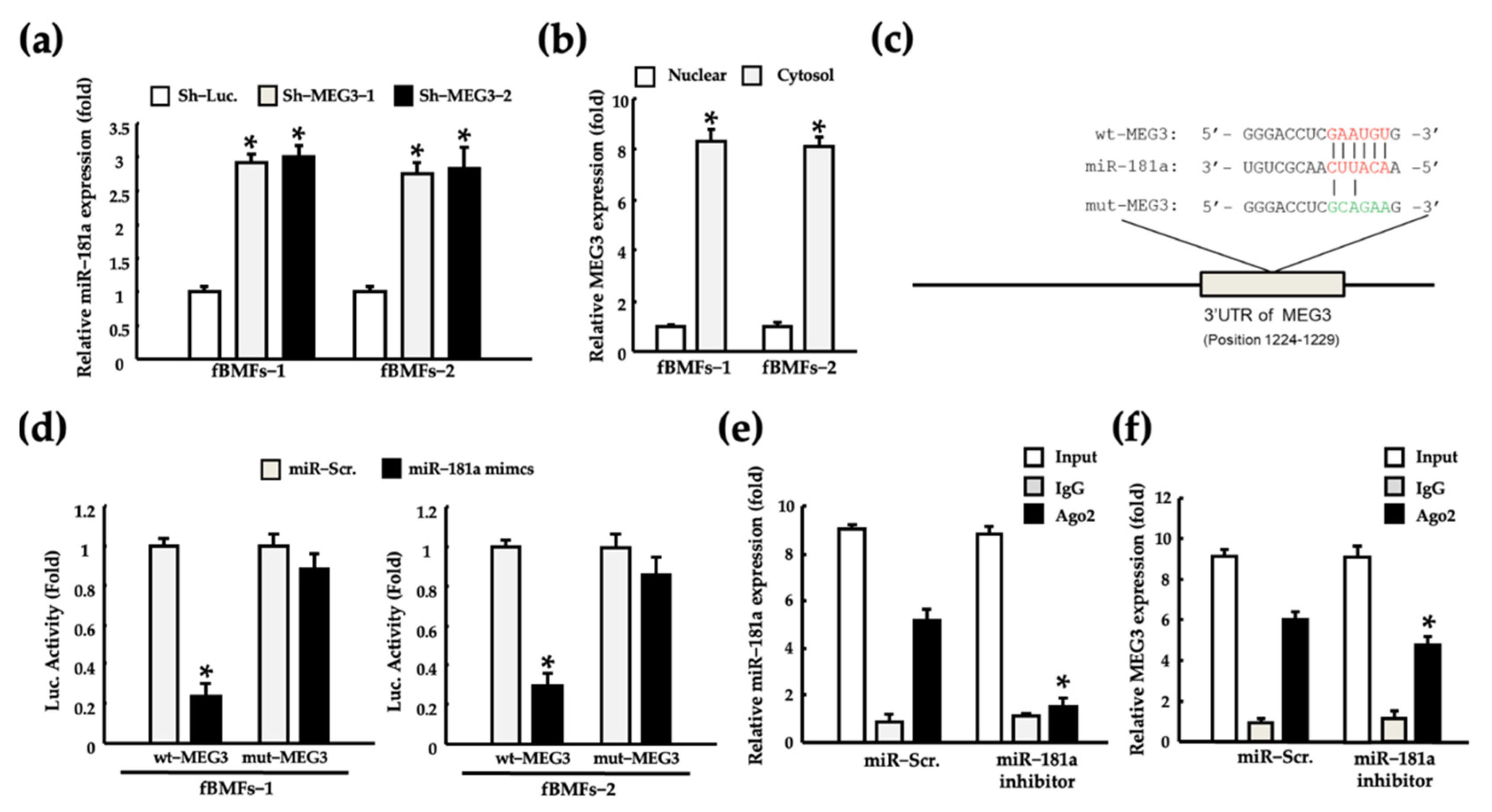
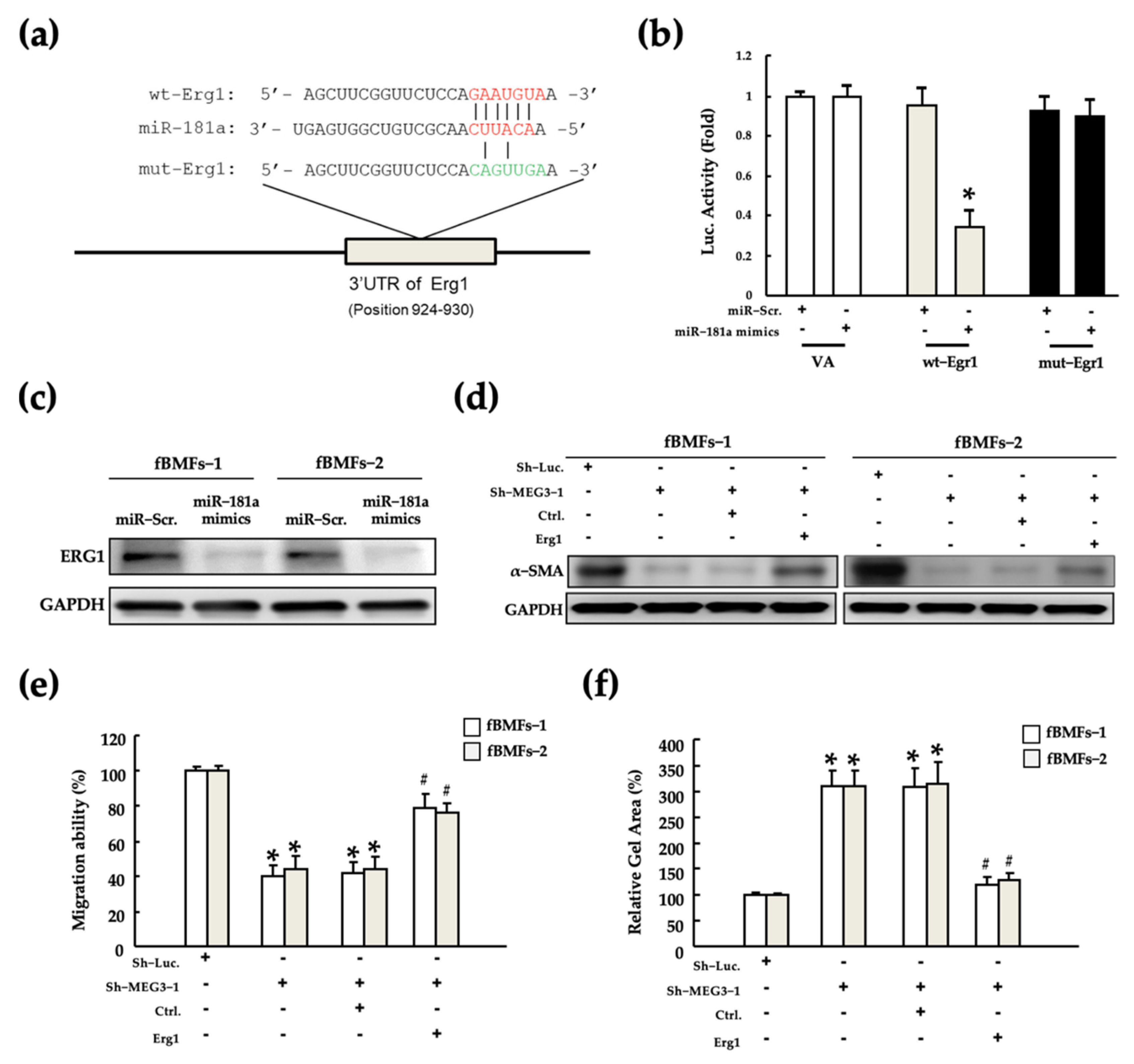
2.4. MEG3 Acts as a miR-181a Sponge in fBMFs
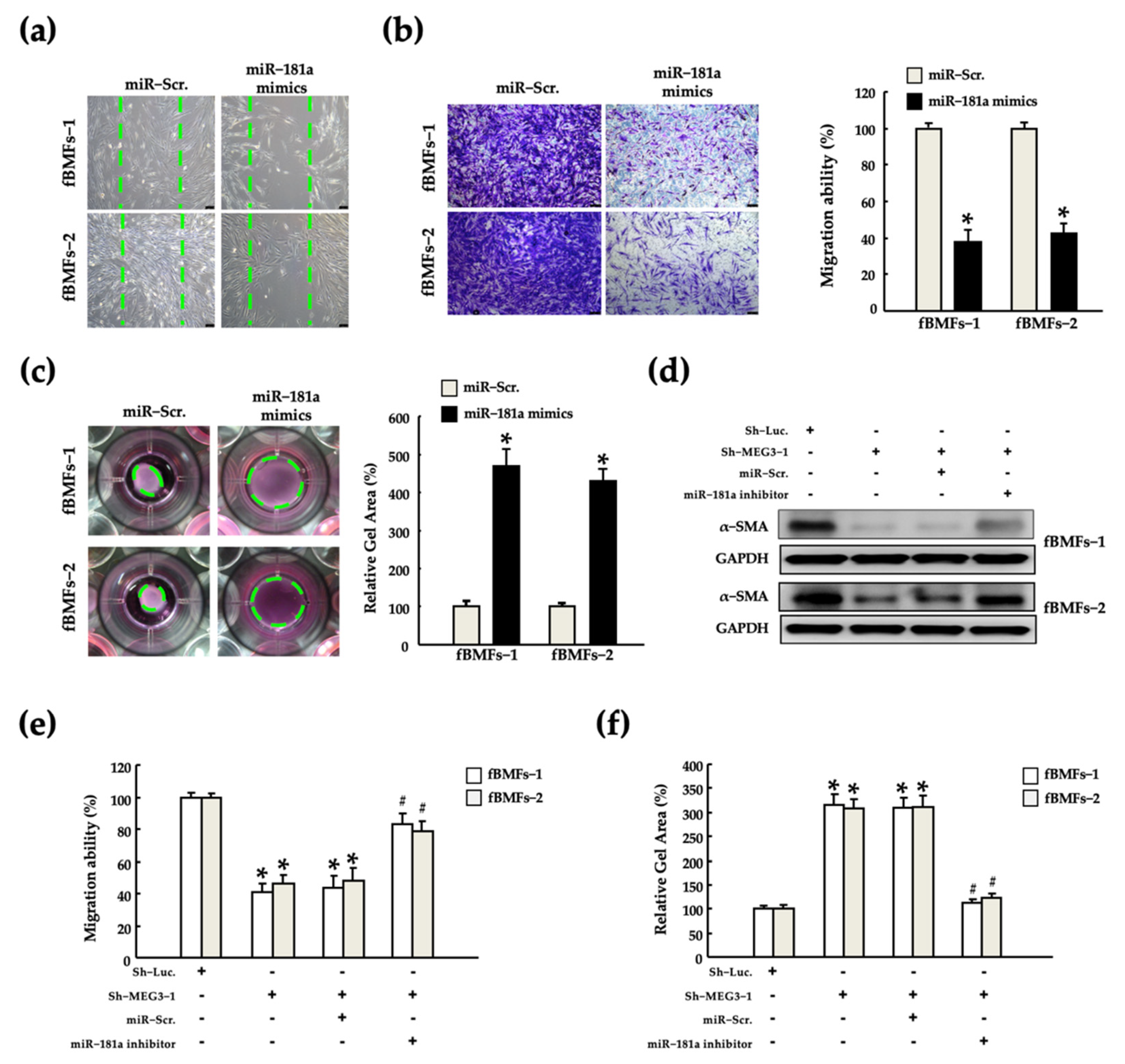
2.5. MEG3/miR-181a Axis Alters Myofibroblast Activites of fBMFs
2.6. MEG3/miR-181a/Erg1 Axis Alters the Myofibroblast Activities of fBMFs
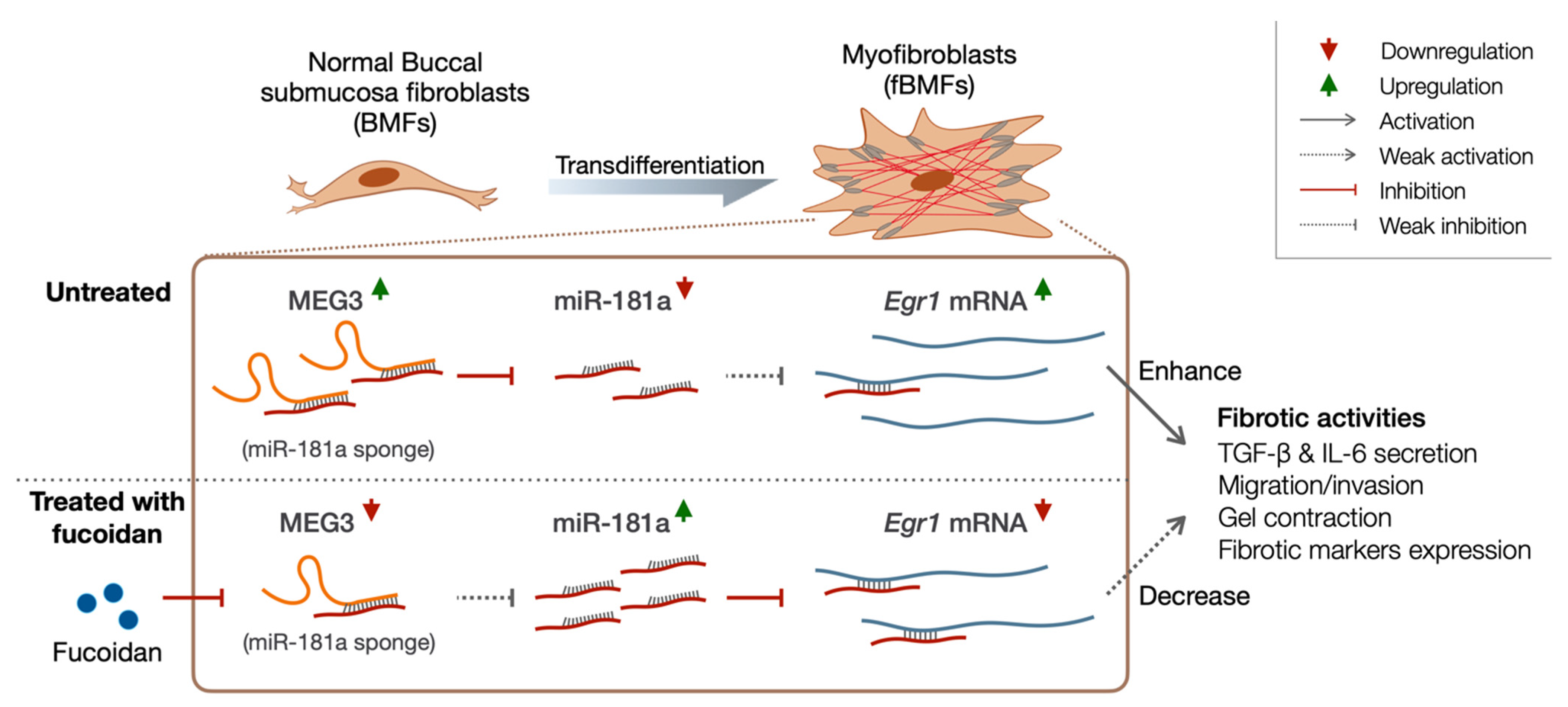
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Reagents
4.2. Cell Viability Assay
4.3. Cell Migration Assay
4.4. Collagen Gel Contraction Assay
4.5. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
4.6. Western Blotting
4.7. RNA Isolation and Sequencing
4.8. Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction
4.9. Lentiviral-Mediated Knockdown or Overexpression
4.10. Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay
4.11. RNA Immunoprecipitation Assay
4.12. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- van der Waal, I. Potentially malignant disorders of the oral and oropharyngeal mucosa; terminology, classification and present concepts of management. Oral Oncol. 2009, 45, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angadi, P.V.; Rao, S.S. Areca nut in pathogenesis of oral submucous fibrosis: Revisited. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2011, 15, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Tail, Y.H.; Wang, W.C.; Chen, C.Y.; Kao, Y.H.; Chen, Y.K.; Chen, C.H. Malignant transformation in 5071 southern Taiwanese patients with potentially malignant oral mucosal disorders. BMC Oral Health 2014, 14, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murti, P.R.; Bhonsle, R.B.; Pindborg, J.J.; Daftary, D.K.; Gupta, P.C.; Mehta, F.S. Malignant transformation rate in oral submucous fibrosis over a 17-year period. Community Dent. Oral Epidemiol. 1985, 13, 340–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pindborg, J.J.; Mehta, F.S.; Gupta, P.C.; Daftary, D.K. Prevalence of oral submucous fibrosis among 50,915 Indian villagers. Br. J. Cancer 1968, 22, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez, I.; Warnakulasuriya, S.; Varela-Centelles, P.I.; López-Jornet, P.; Suárez-Cunqueiro, M.; Diz-Dios, P.; Seoane, J. Is early diagnosis of oral cancer a feasible objective? Who is to blame for diagnostic delay? Oral Dis. 2010, 16, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, C.H.; Yang, Y.H.; Wang, T.Y.; Shieh, T.Y.; Warnakulasuriya, S. Oral precancerous disorders associated with areca quid chewing, smoking, and alcohol drinking in southern Taiwan. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2005, 34, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.H.; Lee, H.Y.; Tung, S.; Shieh, T.Y. Epidemiological survey of oral submucous fibrosis and leukoplakia in aborigines of Taiwan. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2001, 30, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichart, P.A.; Warnakulasuriya, S. Oral lichenoid contact lesions induced by areca nut and betel quid chewing: A mini review. J. Investig. Clin. Dent. 2012, 3, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Bijl, P.; van Eyk, A.D. Areca nut extract lowers the permeability of vaginal mucosa to reduced arecoline and arecaidine. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2001, 30, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Biji, P.; Van Eyk, A.D.; Van Wyk, C.W.; Stander, I.A. Diffusion of reduced arecoline and arecaidine through human vaginal and buccal mucosa. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2001, 30, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Q.T.; Wang, T.; Yu, D.H.; Wang, Z.R.; Sun, Y.; Liang, C.W. Development of a mouse model of arecoline-induced oral mucosal fibrosis. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2017, 10, 1177–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hande, A.H.; Chaudhary, M.S.; Gawande, M.N.; Gadbail, A.R.; Zade, P.R.; Bajaj, S.; Patil, S.K.; Tekade, S. Oral submucous fibrosis: An enigmatic morpho-insight. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2019, 15, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passi, D.; Bhanot, P.; Kacker, D.; Chahal, D.; Atri, M.; Panwar, Y. Oral submucous fibrosis: Newer proposed classification with critical updates in pathogenesis and management strategies. Natl. J. Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 8, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajendran, R.; Rajeesh, M.P.; Shaikh, S.; Shanthi; Pillai, M.R. Expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-1, MMP-2 and MMP-9) and their inhibitors (TIMP-1 and TIMP-2) in oral submucous fibrosis. Indian J. Dent. Res. 2006, 17, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, Y.H.; Wang, T.H.; Shieh, T.M.; Tseng, Y.H. Oral Submucous Fibrosis: A Review on Etiopathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.T.; Chen, H.M.; Cheng, S.J.; Chiang, C.P.; Kuo, M.Y. Arecoline-stimulated connective tissue growth factor production in human buccal mucosal fibroblasts: Modulation by curcumin. Oral Oncol. 2009, 45, e99–e105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.C.; Yang, S.F.; Tai, K.W.; Chou, M.Y.; Hsieh, Y.S. Increased tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 expression and inhibition of gelatinase A activity in buccal mucosal fibroblasts by arecoline as possible mechanisms for oral submucous fibrosis. Oral Oncol. 2002, 38, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.C.; Yang, S.F.; Tai, K.W.; Chou, M.Y.; Hsieh, Y.S. Increased plasminogen activator inhibitor-1/tissue type plasminogen activator ratio in oral submucous fibrosis. Oral Dis. 2007, 13, 234–238. [Google Scholar]
- Verrecchia, F.; Chu, M.L.; Mauviel, A. Identification of novel TGF-beta /Smad gene targets in dermal fibroblasts using a combined cDNA microarray/promoter transactivation approach. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 17058–17062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, I.; Kumar, N.; Khan, I.; Rao, S.G.; Kondaiah, P. Role of Areca Nut Induced TGF-β and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Interaction in the Pathogenesis of Oral Submucous Fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Kumar, N.; Pant, I.; Narra, S.; Kondaiah, P. Activation of TGF-β pathway by areca nut constituents: A possible cause of oral submucous fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moutasim, K.A.; Jenei, V.; Sapienza, K.; Marsh, D.; Weinreb, P.H.; Violette, S.M.; Lewis, M.P.; Marshall, J.F.; Fortune, F.; Tilakaratne, W.M.; et al. Betel-derived alkaloid up-regulates keratinocyte alphavbeta6 integrin expression and promotes oral submucous fibrosis. J. Pathol. 2011, 223, 366–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, C.Y.; Hsia, S.M.; Hsieh, P.L.; Liao, Y.W.; Peng, C.Y.; Wu, C.Z.; Lin, K.C.; Tsai, L.L.; Yu, C.C. Slug mediates myofibroblastic differentiation to promote fibrogenesis in buccal mucosa. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 6721–6730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, R.; Chen, Z.; Ding, Y.; Hao, J.; Hu, J.; Guo, F. Long non-coding RNA MEG3 inhibits the proliferation of cervical carcinoma cells through the induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Neoplasma 2013, 60, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.H.; Li, W.; Liu, X.H.; Sun, M.; Zhang, M.L.; Wu, W.Q.; Xie, W.P.; Hou, Y.Y. Long non-coding RNA MEG3 inhibits NSCLC cells proliferation and induces apoptosis by affecting p53 expression. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wu, Y.T.; Huang, C.; Meng, X.M.; Ma, T.T.; Wu, B.M.; Xu, F.Y.; Zhang, L.; Lv, X.W.; Li, J. Inhibitory effects of long noncoding RNA MEG3 on hepatic stellate cells activation and liver fibrogenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1842, 2204–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, R.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Ma, J.; An, C.; Ma, Z. miR-185 affected the EMT, cell viability, and proliferation via DNMT1/MEG3 pathway in TGF-β1-induced renal fibrosis. Cell Biol. Int. 2019, 43, 1152–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zha, F.; Qu, X.; Tang, B.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, P.; Ji, T.; Zhu, C.; Bai, S. Long non-coding RNA MEG3 promotes fibrosis and inflammatory response in diabetic nephropathy via miR-181a/Egr-1/TLR4 axis. Aging (Albany NY) 2019, 11, 3716–3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolova, E.; Lukova, P.; Baldzhieva, A.; Katsarov, P.; Nikolova, M.; Iliev, I.; Peychev, L.; Trica, B.; Oancea, F.; Delattre, C.; et al. Immunomodulatory and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Fucoidan: A Review. Polymers 2020, 12, 2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, T.S. The role of algal fucoidans in potential anti-allergic therapeutics. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 165, 1093–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cumashi, A.; Ushakova, N.A.; Preobrazhenskaya, M.E.; D’Incecco, A.; Piccoli, A.; Totani, L.; Tinari, N.; Morozevich, G.E.; Berman, A.E.; Bilan, M.I.; et al. A comparative study of the anti-inflammatory, anticoagulant, antiangiogenic, and antiadhesive activities of nine different fucoidans from brown seaweeds. Glycobiology 2007, 17, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gueven, N.; Spring, K.J.; Holmes, S.; Ahuja, K.; Eri, R.; Park, A.Y.; Fitton, J.H. Micro RNA Expression after Ingestion of Fucoidan; A Clinical Study. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, M.D.; Lin, H.Y.; Hwang, P.A. The anti-tumor activity of brown seaweed oligo-fucoidan via lncRNA expression modulation in HepG2 cells. Cytotechnology 2019, 71, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Sue, Y.M.; Cheng, C.Y.; Chen, Y.C.; Liu, C.T.; Hsu, Y.H.; Hwang, P.A.; Huang, N.J.; Chen, T.H. Oligo-fucoidan prevents renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis by inhibiting the CD44 signal pathway. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.H.; Chengchuan Ko, E.; Chang, C.L.; Yuan, K.S.; Wu, A.T.H.; Shan, Y.S.; Wu, S.Y. Fucoidan Inhibits Radiation-Induced Pneumonitis and Lung Fibrosis by Reducing Inflammatory Cytokine Expression in Lung Tissues. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, P.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhan, Q.; Wang, C. Low-molecular-weight fucoidan attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis: Possible role in inhibiting TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition through ERK pathway. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 2590–2602. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.C.; Huang, R.Y.; Chou, T.C. Oligo-Fucoidan Improves Diabetes-Induced Renal Fibrosis via Activation of Sirt-1, GLP-1R, and Nrf2/HO-1: An In Vitro and In Vivo Study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wu, N.; Chen, Y.; Tan, J.; Wang, J.; Geng, L.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, Q. Degradation of different molecular weight fucoidans and their inhibition of TGF-beta1 induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in mouse renal tubular epithelial cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 151, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.Y.; Chen, Y.T.; Tsai, G.Y.; Hsu, F.Y.; Hwang, P.A. Protective Effect of Low-Molecular-Weight Fucoidan on Radiation-Induced Fibrosis Through TGF-beta1/Smad Pathway-Mediated Inhibition of Collagen I Accumulation. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angadi, P.V.; Kale, A.D.; Hallikerimath, S. Evaluation of myofibroblasts in oral submucous fibrosis: Correlation with disease severity. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2011, 40, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dufour, A.M.; Alvarez, M.; Russo, B.; Chizzolini, C. Interleukin-6 and Type-I Collagen Production by Systemic Sclerosis Fibroblasts Are Differentially Regulated by Interleukin-17A in the Presence of Transforming Growth Factor-Beta 1. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.H.; Liu, Y.; Feng, L.; Yang, Y.S.; Liu, S.G.; Guo, W.; Zhou, H.X.; Li, Z.Q.; Zhang, L.; Meng, W.X. Interleukin-6 released by oral lichen planus myofibroblasts promotes angiogenesis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 21, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, M.; Andoh, A.; Hata, K.; Tasaki, K.; Araki, Y.; Fujiyama, Y.; Bamba, T. IL-6 secretion by human pancreatic periacinar myofibroblasts in response to inflammatory mediators. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shintani, Y.; Fujiwara, A.; Kimura, T.; Kawamura, T.; Funaki, S.; Minami, M.; Okumura, M. IL-6 Secreted from Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Mediates Chemoresistance in NSCLC by Increasing Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Signaling. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 1482–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derdak, Z.; Villegas, K.A.; Wands, J.R. Early growth response-1 transcription factor promotes hepatic fibrosis and steatosis in long-term ethanol-fed Long-Evans rats. Liver Int. 2012, 32, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, L.C.; Sung, J.M.; Shen, Y.T.; Jheng, H.F.; Chen, S.H.; Tsai, P.J.; Tsai, Y.S. Egr-1 deficiency protects from renal inflammation and fibrosis. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 94, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, Z.; Heng, Y.; Miao, C. MicroRNA181 exerts an inhibitory role during renal fibrosis by targeting early growth response factor1 and attenuating the expression of profibrotic markers. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 19, 3305–3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.G.; Zheng, J.F.; Li, Q.; Bao, S.Y.; Yu, X.F.; Xu, P.; Liao, C.X. MicroRNA-181a-5p suppresses cell proliferation by targeting Egr1 and inhibiting Egr1/TGF-beta/Smad pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2019, 106, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verduci, L.; Azzalin, G.; Gioiosa, S.; Carissimi, C.; Laudadio, I.; Fulci, V.; Macino, G. microRNA-181a enhances cell proliferation in acute lymphoblastic leukemia by targeting EGR1. Leuk. Res. 2015, 39, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Jiao, J.; Wang, Y.; Mai, Z.; Ren, J.; He, S.; Li, X.; Chen, Z. Egr-1 mediates low-dose arecoline induced human oral mucosa fibroblast proliferation via transactivation of Wnt5a expression. BMC Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.C.; Hung, P.S.; Wang, P.W.; Liu, C.J.; Chu, T.H.; Cheng, H.W.; Lin, S.C. miR-181 as a putative biomarker for lymph-node metastasis of oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2011, 40, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pessi, T.; Viiri, L.E.; Raitoharju, E.; Astola, N.; Seppala, I.; Waldenberger, M.; Lounatmaa, K.; Davies, A.H.; Lehtimaki, T.; Karhunen, P.J.; et al. Interleukin-6 and microRNA profiles induced by oral bacteria in human atheroma derived and healthy smooth muscle cells. Springerplus 2015, 4, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes, M.E.; Riquelme, I.; Salvo, T.; Zanella, L.; Letelier, P.; Brebi, P. Brown Seaweed Fucoidan in Cancer: Implications in Metastasis and Drug Resistance. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.M.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, J.W.; Choi, M.E.; Kim, S.K.; Choi, J.S. Fucoidan attenuates radioiodine-induced salivary gland dysfunction in mice. BMC Oral Health 2019, 19, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, S.H. Biology of fibroblasts and myofibroblasts. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2008, 5, 334–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, K.; Li, S.; Feng, J.; Liu, T.; Wang, F.; Zhang, R.; Xu, S.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, S.; et al. Protective effect of fucoidan from Fucus vesiculosus on liver fibrosis via the TGF-beta1/Smad pathway-mediated inhibition of extracellular matrix and autophagy. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2016, 10, 619–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Du, H.; Yu, X.; Zhu, J. Fucoidan attenuates hyperoxia-induced lung injury in newborn rats by mediating lung fibroblasts differentiate into myofibroblasts. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.S.; Li, H.; Balcos, M.C.; Yun, H.Y.; Baek, K.J.; Kwon, N.S.; Choi, H.R.; Park, K.C.; Kim, D.S. Fucoidan promotes the reconstruction of skin equivalents. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2014, 18, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Choi, S.H.; Park, S.J.; Lee, Y.J.; Park, J.H.; Song, P.H.; Cho, C.M.; Ku, S.K.; Song, C.H. Promoting Wound Healing Using Low Molecular Weight Fucoidan in a Full-Thickness Dermal Excision Rat Model. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccoli, M.T.; Gupta, S.K.; Viereck, J.; Foinquinos, A.; Samolovac, S.; Kramer, F.L.; Garg, A.; Remke, J.; Zimmer, K.; Batkai, S.; et al. Inhibition of the Cardiac Fibroblast-Enriched lncRNA Meg3 Prevents Cardiac Fibrosis and Diastolic Dysfunction. Circ. Res. 2017, 121, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gokey, J.J.; Snowball, J.; Sridharan, A.; Speth, J.P.; Black, K.E.; Hariri, L.P.; Perl, A.T.; Xu, Y.; Whitsett, J.A. MEG3 is increased in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and regulates epithelial cell differentiation. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e122490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Li, Y.; Cui, S.; Liu, J.; Tan, L.; Xia, H.; Zhang, C. Se alleviates homocysteine-induced fibrosis in cardiac fibroblasts via downregulation of lncRNA MEG3. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuppe, C.; Ibrahim, M.M.; Kranz, J.; Zhang, X.; Ziegler, S.; Perales-Paton, J.; Jansen, J.; Reimer, K.C.; Smith, J.R.; Dobie, R.; et al. Decoding myofibroblast origins in human kidney fibrosis. Nature 2021, 589, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, T.; Wang, Y.; Deng, N.; Huang, G.; Taghavifar, F.; Geng, Y.; Liu, N.; Kulur, V.; Yao, C.; Chen, P.; et al. Single-Cell Deconvolution of Fibroblast Heterogeneity in Mouse Pulmonary Fibrosis. Cell Rep. 2018, 22, 3625–3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albulescu, R. TGF-beta upregulates miR-181a expression to promote breast cancer metastasis. Biomark. Med. 2013, 7, 204. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, C.; Ye, Z.; Weyand, C.M.; Goronzy, J.J. miR-181a-regulated pathways in T-cell differentiation and aging. Immun. Ageing 2021, 18, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indrieri, A.; Carrella, S.; Carotenuto, P.; Banfi, S.; Franco, B. The Pervasive Role of the miR-181 Family in Development, Neurodegeneration, and Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Sata, T.N.; Yadav, A.K.; Mishra, A.; Vats, N.; Hossain, M.M.; Sanal, M.G.; Venugopal, S.K. TGF-beta induces liver fibrosis via miRNA-181a-mediated down regulation of augmenter of liver regeneration in hepatic stellate cells. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockhausen, J.; Tay, S.S.; Grzelak, C.A.; Bertolino, P.; Bowen, D.G.; d’Avigdor, W.M.; Teoh, N.; Pok, S.; Shackel, N.; Gamble, J.R.; et al. miR-181a mediates TGF-beta-induced hepatocyte EMT and is dysregulated in cirrhosis and hepatocellular cancer. Liver Int. 2015, 35, 240–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.P.; Chen, H.M.; Chang, J.Z.; Chiang, C.P.; Deng, Y.T.; Kuo, M.Y. Arecoline stimulated early growth response-1 production in human buccal fibroblasts: Suppression by epigallocatechin-3-gallate. Head Neck 2015, 37, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Melichian, D.S.; de la Garza, M.; Gruner, K.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Barr, L.; Nair, A.; Shahrara, S.; Sporn, P.H.; Mustoe, T.A.; et al. Essential roles for early growth response transcription factor Egr-1 in tissue fibrosis and wound healing. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 175, 1041–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Zheng, S.; Ge, D.; Xia, M.; Li, H.; Tang, J. LncRNA-COX2 inhibits Fibroblast Activation and Epidural Fibrosis by Targeting EGR1. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 1347–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Guan, M.P.; Zheng, Z.J.; Li, W.Q.; Lyv, F.P.; Pang, R.Y.; Xue, Y.M. Transcription Factor Egr1 is Involved in High Glucose-Induced Proliferation and Fibrosis in Rat Glomerular Mesangial Cells. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 36, 2093–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Ning, X.; Zhai, Y.; Du, R.; Lu, Y.; He, L.; Li, R.; Wu, W.; Sun, W.; Wang, H. Egr-1 mediates chronic hypoxia-induced renal interstitial fibrosis via the PKC/ERK pathway. Am. J. Nephrol. 2014, 39, 436–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.; Guan, M.P.; Bi, J.G.; Wang, D.; Zheng, Z.J.; Xue, Y.M. High glucose down-regulates microRNA-181a-5p to increase pro-fibrotic gene expression by targeting early growth response factor 1 in HK-2 cells. Cell Signal. 2017, 31, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Ma, X.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shao, Y.; Wang, Q. Klotho Restraining Egr1/TLR4/mTOR Axis to Reducing the Expression of Fibrosis and Inflammatory Cytokines in High Glucose Cultured Rat Mesangial Cells. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2019, 127, 630–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramani, T.; Rathnavelu, V.; Alitheen, N.B.; Padmanabhan, P. Cellular crosstalk mechanism of Toll-like receptors in gingival overgrowth (review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2015, 35, 1151–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Elsharkawy, A.M.; Mann, D.A. Nuclear factor-kappaB and the hepatic inflammation-fibrosis-cancer axis. Hepatology 2007, 46, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momtazi, G.; Elbanna, A.; Finnegan, S.; Héritier, M.; Lavery, L.; Mccollum, K.; Naranjo, J.; Schock, B. NF-kB activation in cystic fibrosis: The dream of A20. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 54, PA2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, W.F.; Tsai, C.H.; Yang, S.F.; Chang, Y.C. Elevated expression of NF-kappaB in oral submucous fibrosis--evidence for NF-kappaB induction by safrole in human buccal mucosal fibroblasts. Oral Oncol. 2007, 43, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Mou, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, L. MALAT1 promotes liver fibrosis by sponging miR181a and activating TLR4NFkappaB signaling. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 48, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.W.; Shih, Y.H.; Fuh, L.J.; Shieh, T.M. Oral Submucous Fibrosis: A Review on Biomarkers, Pathogenic Mechanisms, and Treatments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.C.; Liao, Y.W.; Hsieh, P.L.; Chang, Y.C. Targeting lncRNA H19/miR-29b/COL1A1 Axis Impedes Myofibroblast Activities of Precancerous Oral Submucous Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.Y.; Liao, Y.W.; Lu, M.Y.; Yang, C.M.; Hsieh, P.L.; Yu, C.C. Positive Feedback Loop of SNAIL-IL-6 Mediates Myofibroblastic Differentiation Activity in Precancerous Oral Submucous Fibrosis. Cancers 2020, 12, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, C.-Y.; Chen, S.-H.; Huang, C.-C.; Liao, Y.-W.; Chao, S.-C.; Yu, C.-C. Fucoidan-Mediated Inhibition of Fibrotic Properties in Oral Submucous Fibrosis via the MEG3/miR-181a/Egr1 Axis. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 833. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15070833
Fang C-Y, Chen S-H, Huang C-C, Liao Y-W, Chao S-C, Yu C-C. Fucoidan-Mediated Inhibition of Fibrotic Properties in Oral Submucous Fibrosis via the MEG3/miR-181a/Egr1 Axis. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(7):833. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15070833
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Chih-Yuan, Szu-Han Chen, Chun-Chung Huang, Yi-Wen Liao, Shih-Chi Chao, and Cheng-Chia Yu. 2022. "Fucoidan-Mediated Inhibition of Fibrotic Properties in Oral Submucous Fibrosis via the MEG3/miR-181a/Egr1 Axis" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 7: 833. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15070833
APA StyleFang, C.-Y., Chen, S.-H., Huang, C.-C., Liao, Y.-W., Chao, S.-C., & Yu, C.-C. (2022). Fucoidan-Mediated Inhibition of Fibrotic Properties in Oral Submucous Fibrosis via the MEG3/miR-181a/Egr1 Axis. Pharmaceuticals, 15(7), 833. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15070833






