Adjuvant Chinese Medicine for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Combined with Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of a Randomised Controlled Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Research Subjects
2.2. Inclusion Criteria
2.3. Exclusion Criteria
2.4. Literature Search
2.5. Data Extraction
2.6. Quality Evaluation
2.7. Statistical Methods
3. Results
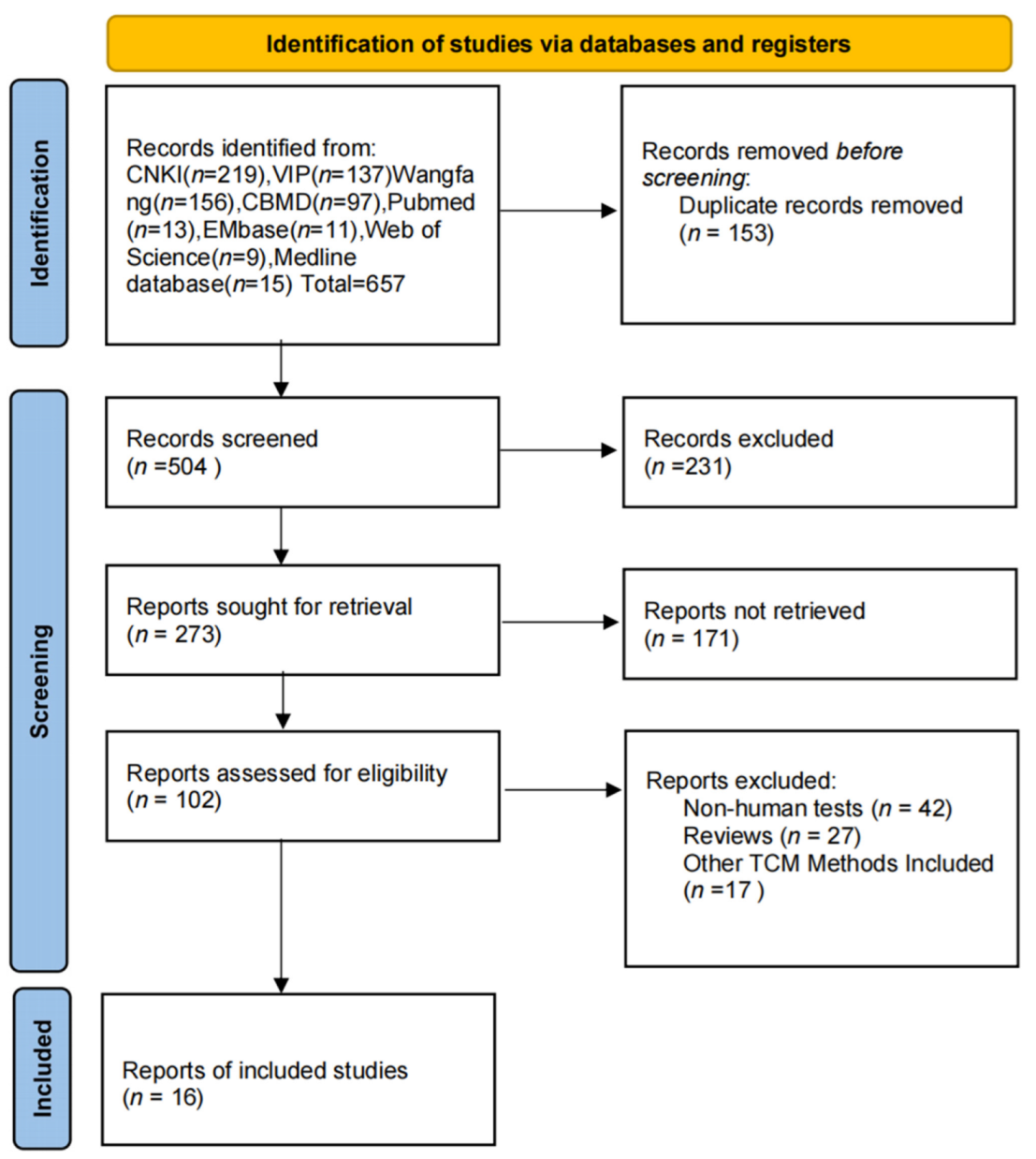
3.1. Literature Search Results and Basic Features
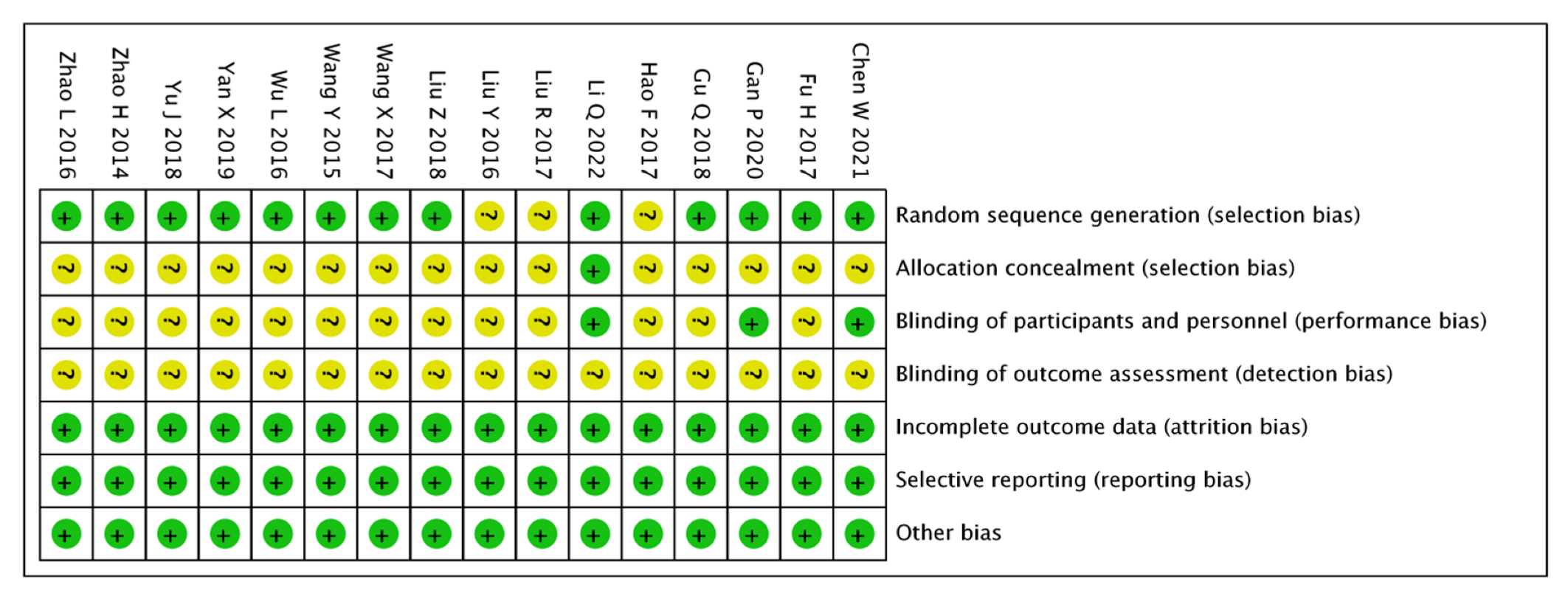
3.2. Risk of Bias Results
3.3. Meta-Analysis Results
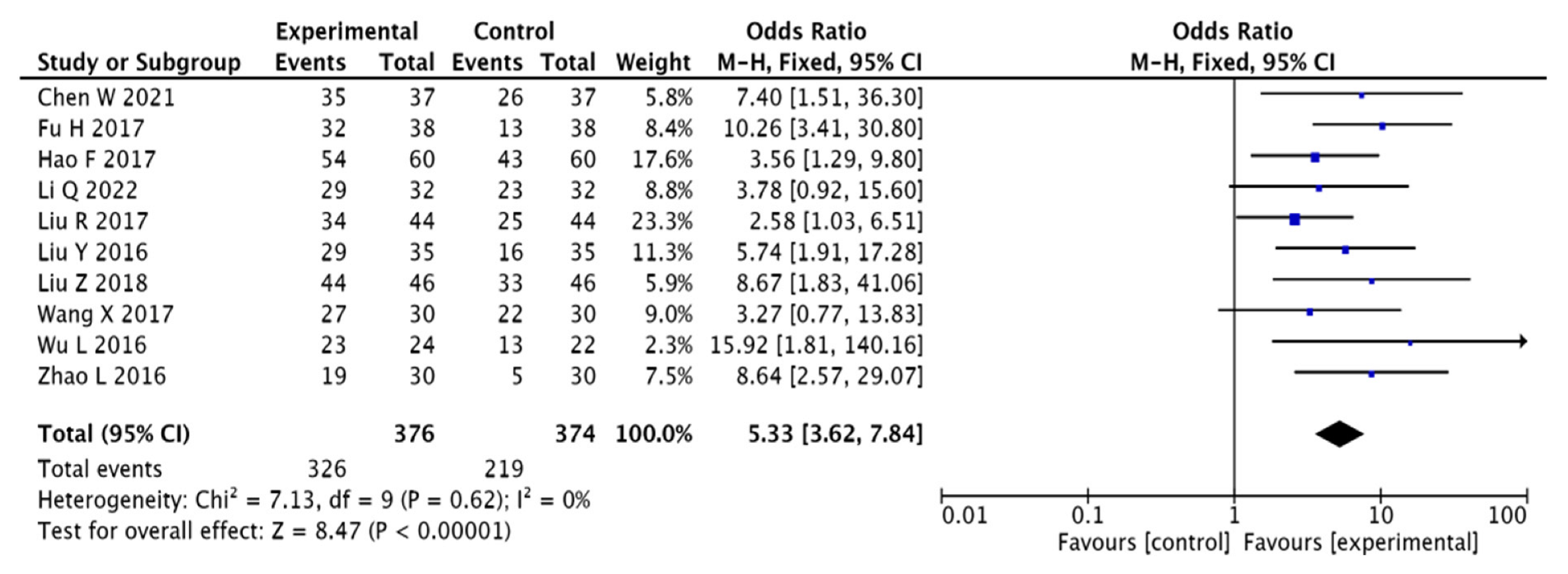
3.3.1. Clinical Effectiveness
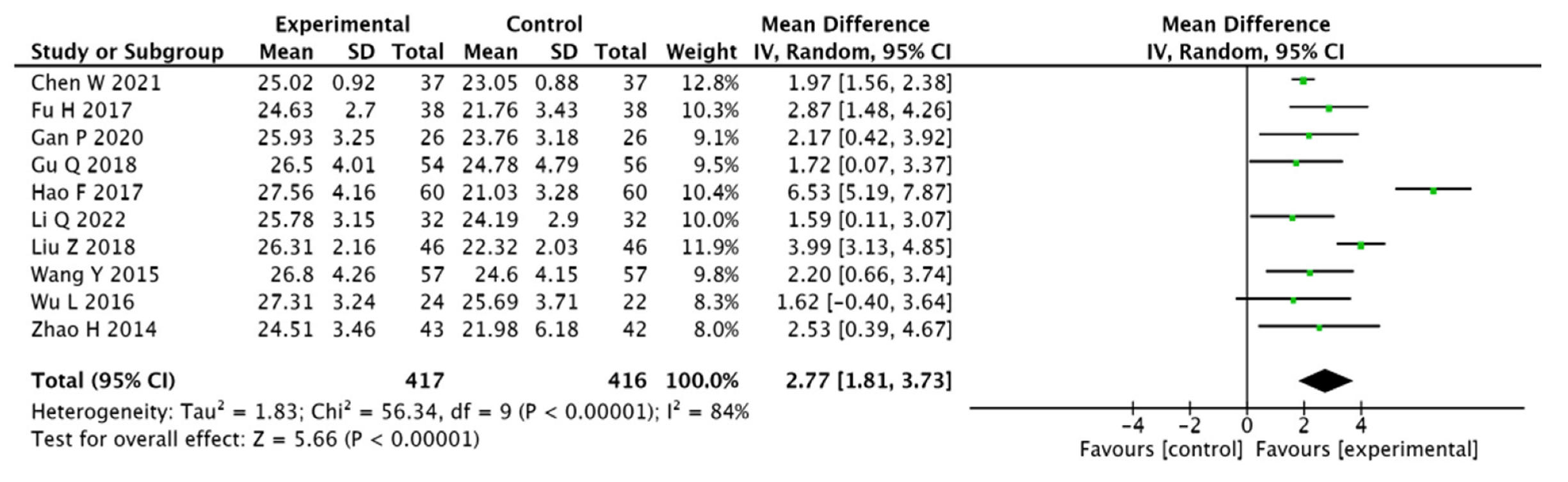
3.3.2. MoCA Scores
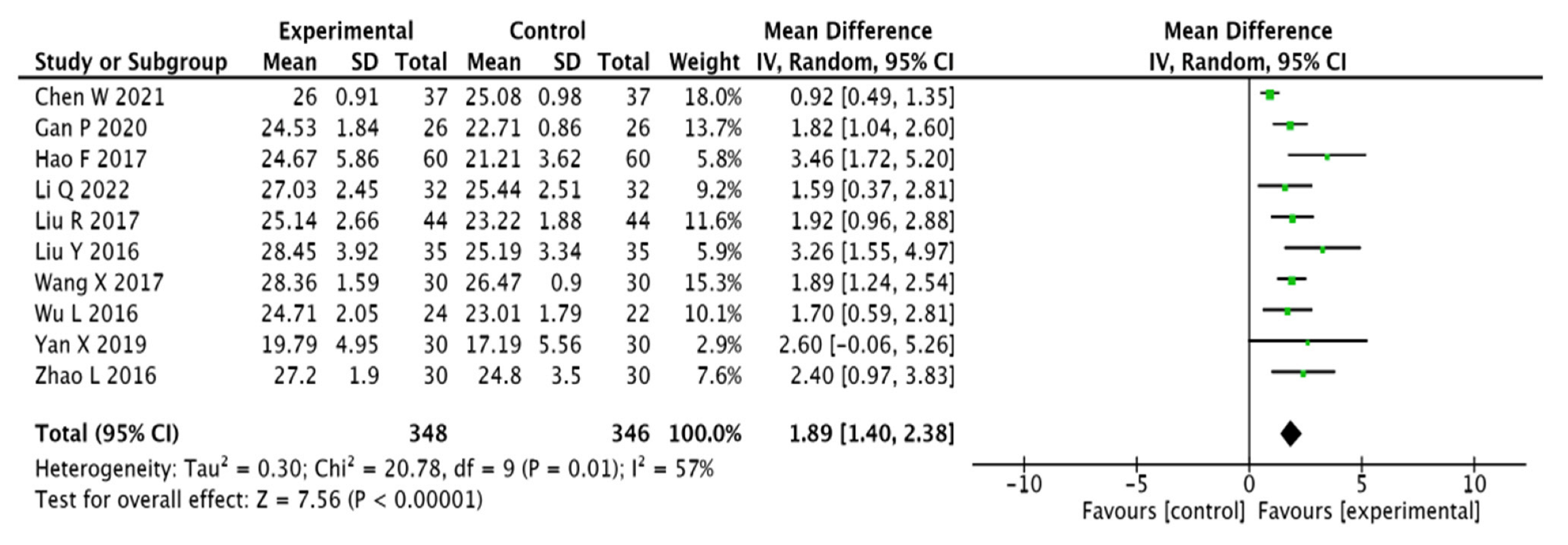
3.3.3. MMSE Scores
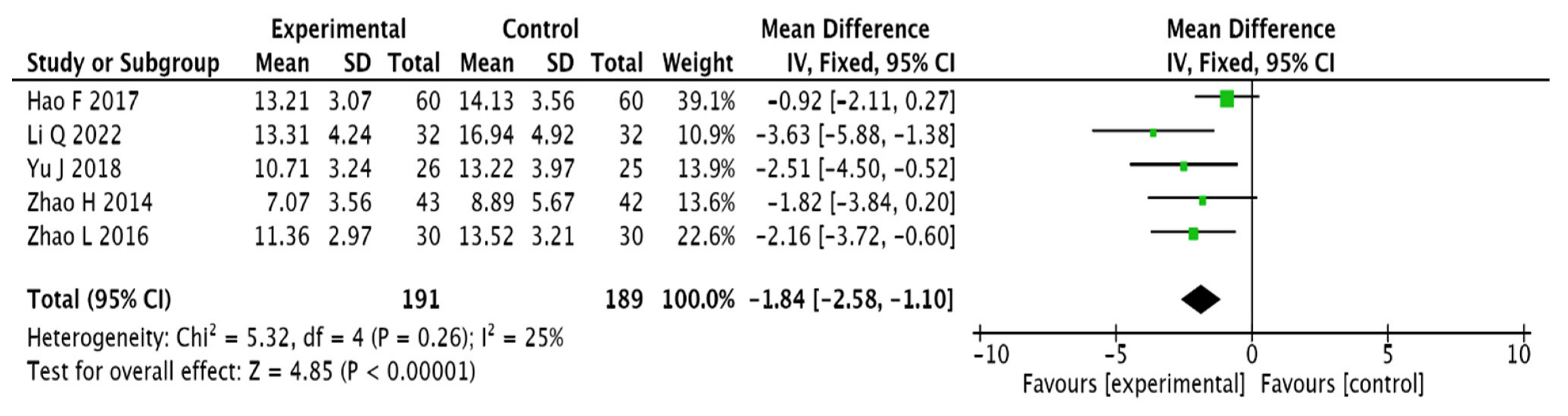
3.3.4. Chinese Medicine Symptom Score
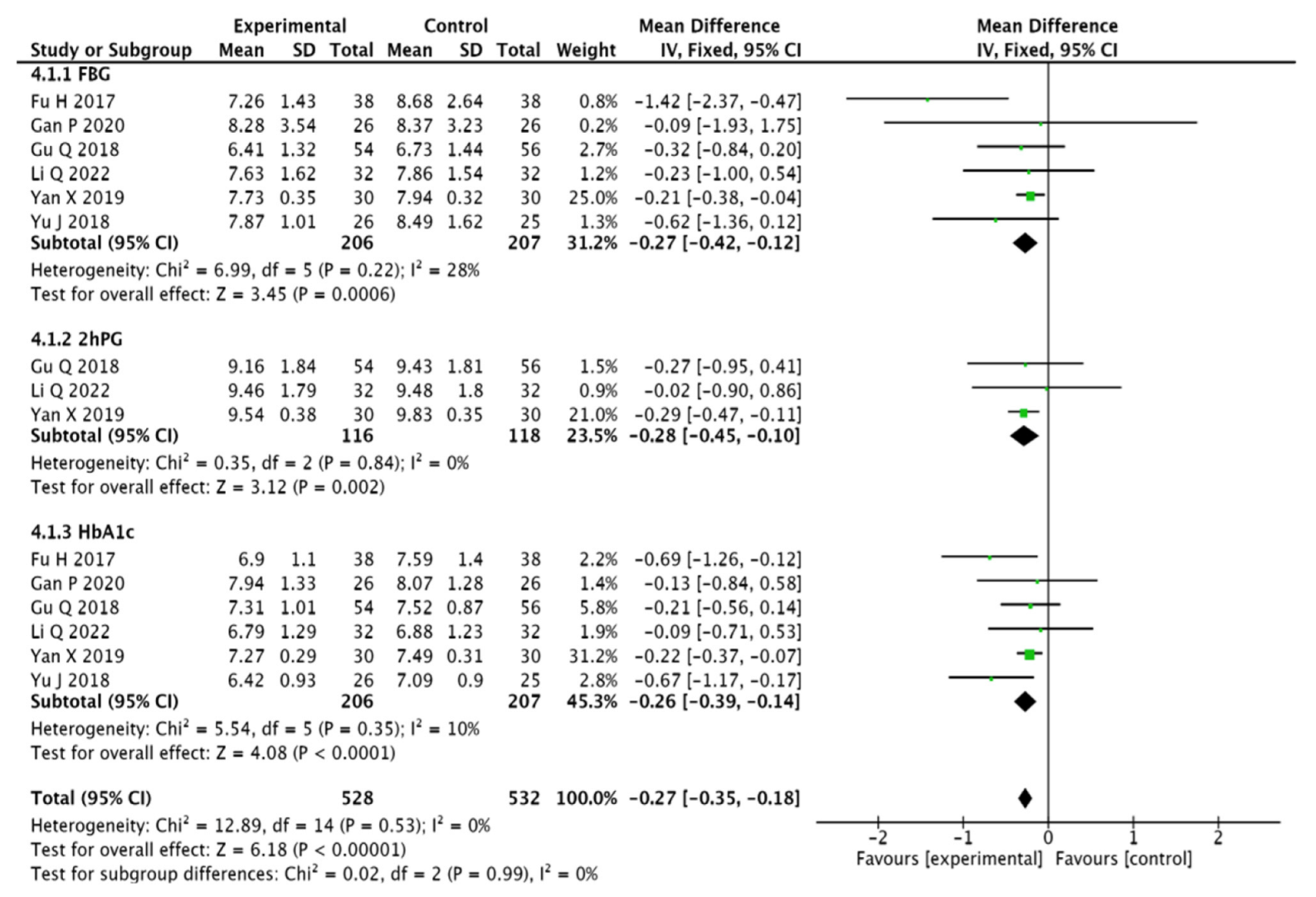
3.3.5. Blood Glucose Indicators
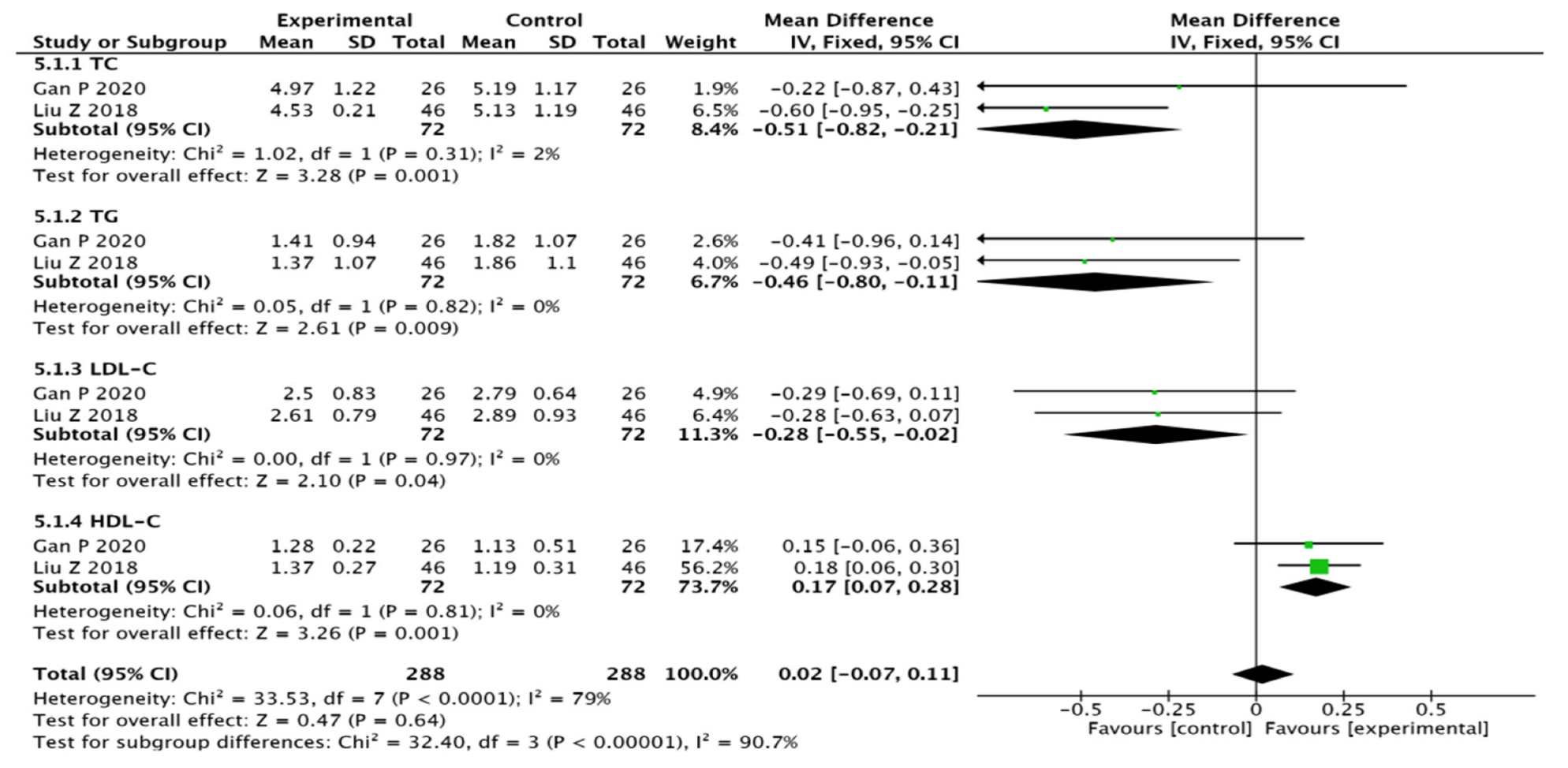
3.3.6. Blood Lipid Indicators
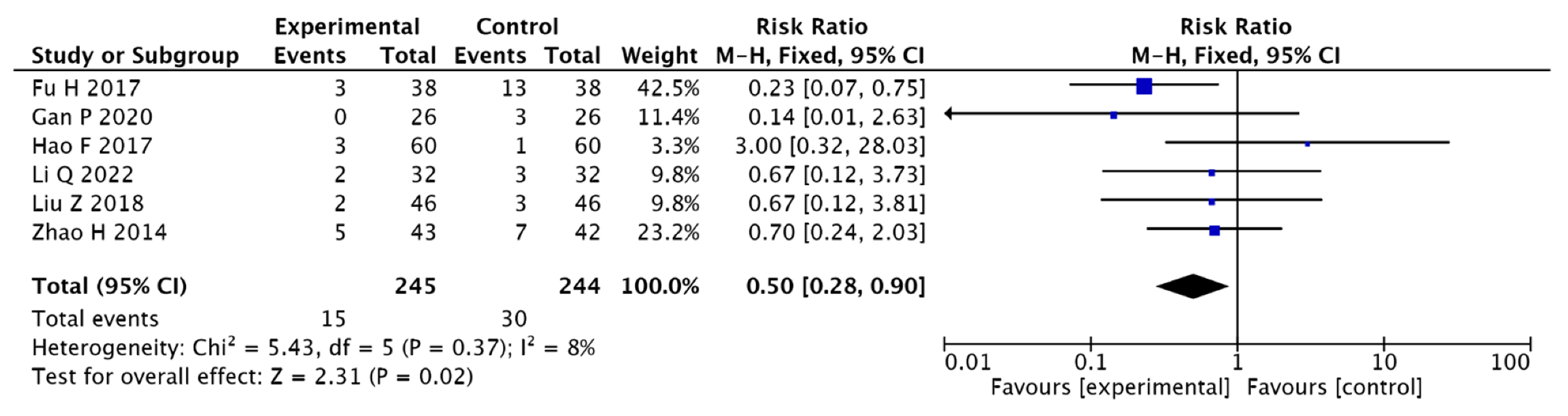
3.3.7. Adverse Reactions
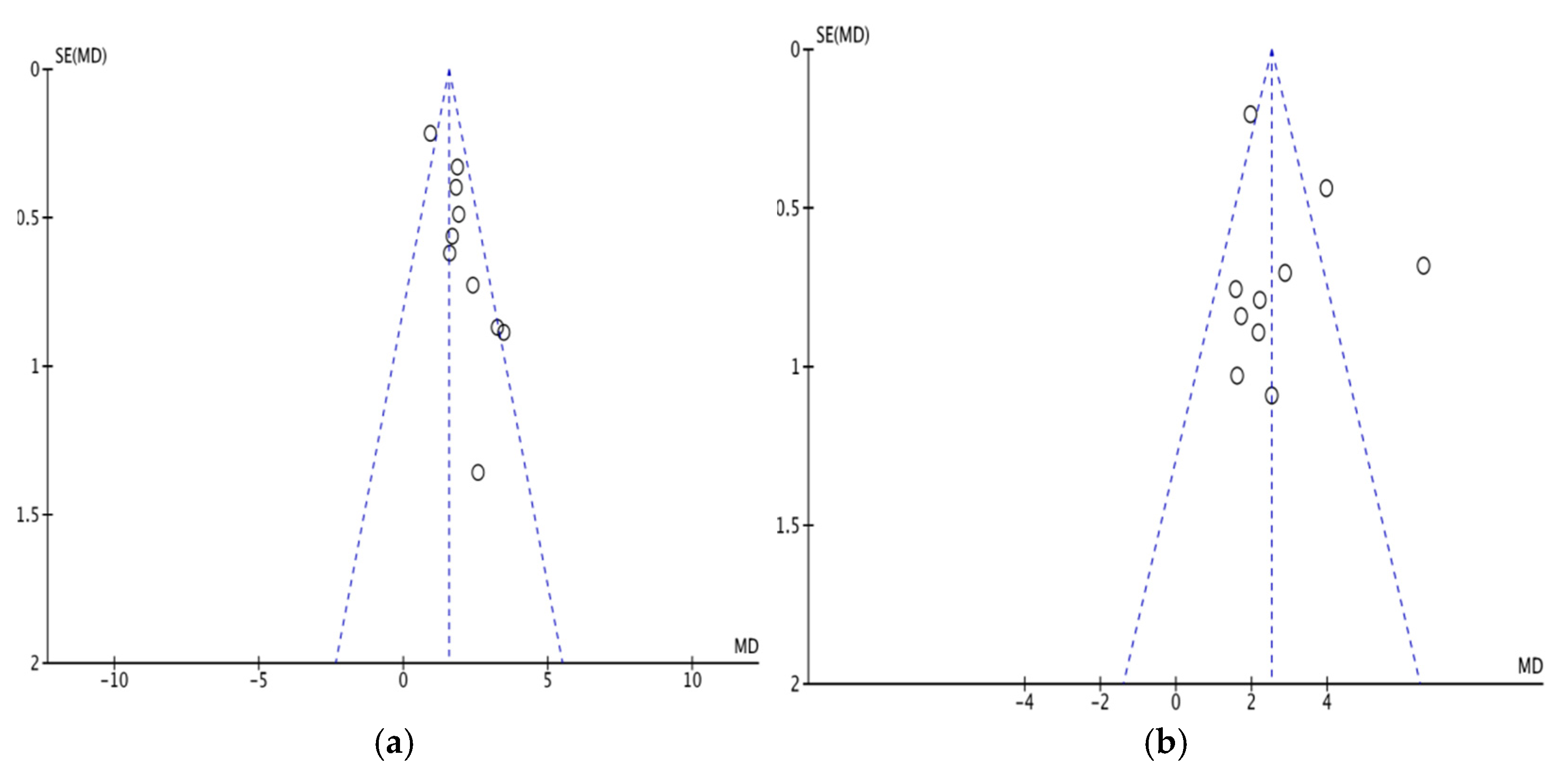
3.4. Publication Bias
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Teng, Z.; Feng, J.; Liu, R.; Dong, Y.; Chen, H.; Xu, J.; Jiang, X.; Li, R.; Lv, P. Cerebral Small Vessel Disease is Associated with Mild Cognitive Impairment in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2022, 15, 1985–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kullmann, S.; Heni, M.; Hallschmid, M.; Fritsche, A.; Preissl, H.; Häring, H.U. Brain Insulin Resistance at the Crossroads of Metabolic and Cognitive Disorders in Humans. Physiol. Rev. 2016, 96, 1169–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koekkoek, P.S.; Rutten, G.E.; Biessels, G.J. Cognitive disorders in diabetic patients. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2014, 126, 145–166. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rawlings, A.M.; Sharrett, A.R.; Albert, M.S.; Coresh, J.; Windham, B.G.; Power, M.C.; Knopman, D.S.; Walker, K.; Burgard, S.; Mosley, T.H.; et al. The Association of Late-Life Diabetes Status and Hyperglycemia with Incident Mild Cognitive Impairment and Dementia: The ARIC Study. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 1248–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese Society of Endocrinology; Chinese Expert Consensus on the Prevention and Treatment of Cognitive Dysfunction in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Chin. J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 38, 453–464.
- Liang, J.; Jin, S.; Wu, L.; Yang, D. Analysis of the etiology and pathogenesis of cognitive dysfunction in diabetes mellitus in Chinese medicine. J. Pract. Clin. Med. 2015, 19, 149–151. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, D.; Feng, L.; Wu, X.C.; Gao, Q. Exploring the Chinese medical mechanism and treatment of diabetic encephalopathy based on Sirt1. J. Chin. Med. 2019, 34, 1621–1624. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, S.; Xu, W. Recent research on the treatment of cognitive dysfunction in type 2 diabetes mellitus in Chinese medicine. Jiangsu Trad. Chin. Med. 2020, 52, 87–89. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Guo, X.; Liu, B.; Wu, S.; Hu, Y.; Hu, H.; Wang, Y.; Gong, Y. Current status and progress of Chinese medicine research on diabetes mellitus combined with cognitive dysfunction. J. Liaoning Univ. Trad. Chin. Med. 2022, 6, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Chinese Medical Association, Diabetes Branch. Chinese guidelines for the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus (2010 edition). Chin. J. Diabetes 2012, 20, 81–117. [Google Scholar]
- Albert, M.S.; Dekosky, S.T.; Dickson, D. The diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Instituteon Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on di-agnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Associat. 2011, 7, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Diagnostic and Efficacy Criteria for Chinese Medicine Illnesses; Nanjing University Press: Nanjing, China, 1994; pp. 132–133. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Jia, S.; Guan, H. Clinical efficacy of Dihuang Drinking Zi in the treatment of mild cognitive dysfunction associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus with kidney deficiency and reduced medulla. Lishizhen Med. Mater. Med. Res. 2022, 33, 410–412. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.M.; Li, J.; Huo, L.L.; Yang, J.; Li, L. Clinical efficacy of Brain Ling Tang in the treatment of cognitive impairment in diabetes mellitus. J. Guangzhou Univ. Chin. Med. 2021, 38, 449–454. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, P.; Wu, S.; Huang, L.; Liu, L. Clinical study on the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus combined with mild cognitive dysfunction with kidney-clearing brain-breaking tablets. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2020, 40, 422–426. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, S.Y.; Guan, X.J. The efficacy of the treatment of cognitive dysfunction combined with type 2 diabetes mellitus in the elderly with the treatment of puzzle combination. Chin. Med. Her. 2019, 14, 97–100. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.X. Clinical efficacy of Hemifu Bangyu Tang in the treatment of cognitive dysfunction in elderly type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin. Res. Trad. Chin. Med. 2018, 34, 86–88. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.H.; Wang, X.J.; Wang, X.D. Efficacy of combining Yi Qi, Shu Feng and Tongluo formula with atorvastatin in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus combined with coronary atherosclerotic heart disease. J. Chin. Med. 2018, 5, 751–755. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Q.S.; Wang, Y.; Xu, H.J.; Zhu, Z. Exploring the effect and mechanism of combining pioglitazone with kidney and brain granules in the treatment of cognitive impairment in diabetes mellitus. Chin. Trad. Med. Sci. Tech. 2018, 2, 235–238, 241. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, F.Q.; Ji, Y.H.; Cao, H.G.; Wang, H.G. Efficacy of nourishing the kidney, dispelling dampness and resolving phlegm in the treatment of vascular mild cognitive dysfunction secondary to diabetes mellitus in the elderly and the effects on oxidative stress indicators and acetylcholinesterase levels. J. Mod. Trad. Chin. West. Med. 2017, 30, 3324–3327. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, H.; Lai, W.W.; Wang, H.; Yang, J.X.; Chu, S.L.; Hong, J.N.; Wang, X.M. Clinical study on the treatment of mild cognitive dysfunction in type 2 diabetes mellitus with the formula of tonifying the kidney and activating blood. Chin. J. Integr. Trad. Chin. West. Med. 2017, 6, 661–665. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.P. Comparison of the efficacy of tonifying the kidney and dispelling stasis and puzzle soup and nimodipine in the treatment of cognitive dysfunction in diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Rat. Drug Use 2017, 11, 50–51. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.Y. Clinical study on the treatment of mild cognitive dysfunction in diabetes mellitus with Awakening Brain Puzzle Formula. Elec. J. Integr. Med. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2017, 18, 43, 45. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.J.; Liang, J.T.; Yang, D.D.; Li, Y.D. Clinical study on the prevention of cognitive impairment due to diabetes mellitus by tonifying the kidney, activating blood and opening the orifices. Elec. J. Integr. Med. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2016, 28, 160–161, 163. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.F.; Li, X.L.; Sun, L.; Zhao, L.H. Clinical study on the treatment of 35 cases of mild cognitive dysfunction in elderly people with diabetes mellitus by Yi Qi, tonifying the kidney and activating blood formula. Chin. Contemp. Med. 2016, 6, 100–102. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.H.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, Y.Q.; Sun, L. Effects of tonic deficiency and elimination of turbidity on ISI, leptin and lipocalin in elderly patients with mild cognitive impairment in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Mod. Distance Educ. Chin. Trad. Med. 2016, 19, 52–56. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Jin, W.B.; Liu, L.; Li, Z.Y. Clinical analysis of tonifying kidney and invigorating blood soup in the treatment of diabetic cognitive dysfunction. Chin. J. Exp. Formula 2015, 9, 196–199. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Guo, Q.; Yang, D.D.; Shi, M. Study on secondary prevention of vascular mild cognitive dysfunction due to diabetes mellitus (kidney deficiency and blood stasis type) by tonifying kidney and activating blood to open the orifice formula. Chin. J. Exp. Formula 2014, 19, 181–184. [Google Scholar]
- Guariguata, L.; Whiting, D.R.; Hambleton, I.; Beagley, J.; Linnenkamp, U.; Shaw, J.E. Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2013 and projections for 2035. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2014, 103, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, R.J.; Kato, A.; Yu, C.Y.; Fleet, G.W.J. Iminosugars as therapeutic agents: Recent advances and promising trends. Future Med. Chem. 2011, 3, 1513–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.F.; Shimadate, Y.; Kato, A.; Li, Y.X.; Jia, Y.M.; Fleet, G.W.J.; Yu, C.Y. Synthesis and glycosidase inhibition of N-substituted derivatives of DIM. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2020, 18, 999–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chennaiah, A.; Bhowmick, S.; Vankar, Y.D. Conversion of glycals into vicinal-1,2-diazides and 1,2-(or 2,1)-azidoacetates using hypervalent iodine reagents and Me3SiN3. Application in the synthesis of N-glycopeptides, pseudo-trisaccharides and an iminosugar. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 41755–41762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekaran, P.; Ande, C.; Vankar, Y.D. Synthesis of (5,6 & 6,6)-oxa-oxa annulated sugars as glycosidase inhibitors from 2-formyl galactal using iodocyclization as a key step. ARKIVOC 2022, 6, 5–23. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, G.; Huang, C.; Deng, H.; Wang, H. Diabetes as a risk factor for dementia and mild cognitive impairment: A meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. Intern. Med. J. 2012, 5, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biessels, G.J.; De Leeuw, F.E.; Lindeboom, J.; Barkhof, F.; Scheltens, P. Increased cortical atrophy in patients with Alzheimer’s disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2006, 3, 304–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honig, L.S.; Vellas, B.; Woodward, M.; Boada, M.; Bullock, R.; Borrie, M.; Hager, K.; Andreasen, N.; Scarpini, E.; Liu-Seifert, H.; et al. Trial of Solanezumab for Mild Dementia Due to Alzheimer’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 4, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.J. A preliminary investigation of Chinese medical evidence in patients with diabetes mellitus with mild cognitive impairment. J. Lingnan Univ. Chin. Med. 2012, 14, 209–210. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, E.; Luo, L. Alternative Therapies for Diabetes: A Comparison of Western and Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) Approaches. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2018, 14, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, N.; Chen, M.; Jin, H.; Nie, J.; Shi, J.; Jin, F. Procyanidin protects against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced dopaminergic neuron damage via the regulation of the PI3K/Akt signalling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 114, 108789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N. Effects of rhodiogenin on learning memory capacity and oxidative stress in rats with diabetes mellitus model. J. Chin. Med. 2017, 32, 1426–1429. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, S.Y.; Zhou, H.H.; Liu, Z.C. Serpentine attenuates inflammatory response in diabetic encephalopathy through inhibition of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Chin. J. Gerontol. 2015, 35, 4743–4746. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Zeng, Y.L. Preliminary pharmacodynamic analysis of intervention of different extracts of He Shou Wu in diabetic rats. J. Hubei Univ. Chin. Med. 2016, 18, 35–38. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.B.; Chen, W.Q.; Chen, Y.J.; Wang, N.Q.; Liu, Y. Study on the intervention of Yuan Zhi-Shi Calamus in serum methylglyoxal in diabetic cognitively impaired rats. Chin. J. Expl. Formula 2013, 19, 223–226. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Zhang, D.L. Effect of chuanxiongzine on the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in penicillin-induced epileptic rats. J. Math. Med. 2009, 22, 526–528. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Liu, D.M.; Wu, Q.S.; Yao, Y.Y.; LI, W.P. Effects of Astragalus membranaceus extract on the learning memory ability and expression of Bc1-2 and Bcl-xl in hippocampal neurons of Aβ25-35-induced Alzheimer’s disease model rats. J. Anhui Med. Univ. 2007, 42, 288–302. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, L.Y.; Wang, X. Exploring the mechanism of action of Huangjing-Liqi medicine in the treatment of diabetes mellitus combined with cognitive dysfunction based on network pharmacology and molecular docking technology. Chin. Med. Info. 2021, 38, 36–44. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; He, G.Z.; Huang, G. Effects of Eucommia polysaccharides on serum SOD, GSH-Px and MDA in mice with diabetes mellitus model. Jiangxi Trad. Chin. Med. 2016, 47, 34–36. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, P.P.; Liu, L.; Quan, Y.H. Meta-analysis of the efficacy of the method of tonifying the kidney and dispelling blood stasis in the treatment of cognitive dysfunction in diabetes mellitus. World J. Intg. Chin. West. Med. 2021, 16, 593–598, 606. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.H.; Cao, W.G.; Wang, W.P. Study on cognitive function and its correlation with glycated hemoglobin levels in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes. Chin. J. Gerontol. 2015, 15, 1170–1172. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.; Chen, M.J.; Shi, J. Correlation between lipid metabolism levels and cognitive function in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Chin. J. Gerontol. 2016, 36, 3713–3716. [Google Scholar]

| Author | Case (T/C) | Intervening Measure | Time (W) | Out Come | Random Method | Adverse Reaction | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | C | ||||||
| Li Quan 2022 [13] | 32/32 | Dihuang Yinzi Soup +C | Donepezil tablets | 12 | ①,②,③,④,⑥,⑦ | Random number table | T:2 cases of dizziness; C: 3 cases of Tinnitus occurred |
| Chen Weiming 2021 [14] | 37/37 | Naolin soup+C | Donepezil tablets | 24 | ①,②,③,④ | Random number table | None |
| Gan Panpan 2020 [15] | 26/26 | Bushen Qingnao Pobi soup+C | Donepezil tablets | 12 | ②,④,⑤,⑦ | Random number table | C:2 cases of diarrhea; 1 case of headache |
| Yan Xiaoyan 2019 [16] | 30/30 | Yizhi granule+C | Nimodipine | 24 | ②,③ | Only described as random | None |
| Yu Jinxin 2018 [17] | 26/25 | Xuefu Zhuyu Soup+C | Donepezil tablets | 8 | ②,⑥ | Random number table | None |
| Liu Zhonghua 2018 [18] | 46/46 | Yiben huoxue recipe+C | Nimodipine | 8 | ①,②,⑤,⑦ | Random number table | T:5 cases of constipation; C:3 cases of skin rash |
| Gu Qunshan 2018 [19] | 54/56 | Bushen Yinao granule+C | Donepezil tablets | 24 | ②,③,④ | Random number table | None |
| Hao Fengqing 2017 [20] | 60/60 | Zishen Huatan Qushi soup+C | Donepezil tablets | 24 | ①,③,④,⑥,⑦ | Only described as random | C:2 cases of dizziness |
| Fu Hong 2017 [21] | 38/38 | Bushen Huoxue granule+C | Nimodipine | 12 | ①,②,④,⑦ | Random number table | T:3 cases of constipation; C:13 cases of dizziness |
| Liu Runping 2017 [22] | 44/44 | Bushen Quyu Yizhi Soup+C | Nimodipine | 8 | ①,③ | Only described as random | None |
| Wang Xiaoyan 2017 [23] | 30/30 | Xingnao Yizhi soup+C | Nimodipine | 12 | ①,③ | Random number table | None |
| Wu Lijuan 2016 [24] | 24/22 | BuShen Huoxue Kaiqiao recipe+C | Nicergolin tablets | 24 | ①,③,④ | Random number table | None |
| Liu Yafen 2016 [25] | 35/35 | Yiqi Bushen Huoxue recipe+C | Nicergolin tablets | 12 | ①,③ | Only described as random | None |
| Zhao Lihua 2016 [26] | 30/30 | Buxu Quzhuo Tongluo soup+C | Donepezil tablets | 12 | ①,③,⑥ | Random number table | None |
| Wang Yu 2015 [27] | 57/57 | Bushen Huoxue soup+C | Nimodipine | 12 | ②,③ | Random number table | None |
| Zhao Huan 2014 [28] | 43/42 | Bushen Huoxue Kaiqiao granule+C | Nimodipine | 12 | ④,⑥,⑦ | Random number table | T:7 cases of dizziness C:7 cases of nausea and vomiting |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.; Guo, X. Adjuvant Chinese Medicine for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Combined with Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of a Randomised Controlled Trial. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1424. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15111424
Liu C, Guo X. Adjuvant Chinese Medicine for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Combined with Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of a Randomised Controlled Trial. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(11):1424. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15111424
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Changxing, and Xinyi Guo. 2022. "Adjuvant Chinese Medicine for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Combined with Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of a Randomised Controlled Trial" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 11: 1424. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15111424
APA StyleLiu, C., & Guo, X. (2022). Adjuvant Chinese Medicine for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Combined with Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of a Randomised Controlled Trial. Pharmaceuticals, 15(11), 1424. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15111424