Abstract
Background: This study aimed to assess the effect of a fixed combination of Red Ginseng and Red Sage (RG–RS) on the gene expression of neuronal cells to evaluate the potential impacts on cellular functions and predict its relevance in the treatment of stress and aging-related diseases and disorders. Methods: Gene expression profiling was conducted by transcriptome-wide mRNA microarray analyses of murine HT22 hippocampal cell culture after treatment with RG–RS preparation. Ingenuity pathway analysis (IPA) was performed with datasets of significantly upregulated or downregulated genes and the expected effects on the physiological and cellular function and the diseases were identified. Results: RG–RS deregulates 1028 genes associated with cancer and 139 with metastasis, suggesting a predicted decrease in tumorigenesis, the proliferation of tumor cells, tumor growth, metastasis, and an increase in apoptosis and autophagy by their effects on the various signaling and metabolic pathways, including the inhibition of Warburg’s aerobic glycolysis, estrogen-mediated S-phase entry signaling, osteoarthritis signaling, and the super-pathway of cholesterol biosynthesis. Conclusion: The results of this study provide evidence of the potential efficacy of the fixed combination of Red Ginseng (Panax ginseng C.A. Mey.) and Red Sage/Danshen (Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge) in cancer. Further clinical and experimental studies are required to assess the efficacy and safety of RG–RS in preventing the progression of cancer, osteoarthritis, and other aging-related diseases.
1. Introduction
Various stresses/stressors of exogenous origin, such as environmental carcinogens, chemicals, and radiation, and others endogenously derived from the endoplasmic reticulum, such as hypoxia and oxidative stress, disrupt homeostasis and trigger the progression of many diseases, including cancer. With age, the accidence of cancer, cardiovascular, neurodegenerative, and some other diseases dramatically increases due to the systemic progression of aseptic chronic low-grade inflammation defined as inflammageing [1,2,3]. Inflammaging is neither harmful nor beneficial by itself and may be helpful in an adaptive manner or harmful in a maladaptive way, depending on environmental stressors and genetic background [1]. The human organism has developed a highly effective defense regulatory network, the neuroendocrine-immune complex, to adapt to these stresses. Adaptation to stress/stressors could finally lead to either beneficial or unfavorable consequences where the outcome may be aging-related diseases or healthy longevity [1].
Two well-known adaptogenic plants [4,5,6,7,8,9], Red Ginseng (Panax ginseng CA Mey) [10] and Red Sage/Danshen (Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge) [11], are used in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) as an effective treatment of diseases and conditions associated with inflammaging and aging-related diseases [4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17]. In Europe, Red Ginseng (RG) is approved as an herbal medicinal product to enhance cognitive functions and physical capacities in weakness, loss of concentration, exhaustion, tiredness, and convalescence [10]. According to ancient records, Red Ginseng enhances longevity with long-term intake [17]. The antitumor, cardioprotective, and neuroprotective effects of both plants were demonstrated in numerous in vivo and in vitro experimental studies [14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24], suggesting their usefulness in the treatment of aging-related disorders and diseases, including dysfunctions of the central nervous system (CNS), particularly those associated with Alzheimer’s disease, Huntington’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, traumatic brain injury, and ischemia. For example, ginsenosides modulate plentiful physiological and intracellular processes in the brain, including attenuation of oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, excitotoxicity, apoptosis, modulation of adaptive signaling pathways, maintenance of mitochondrial stability, and neurotransmitter homeostasis [21,22,23,24]. Regulations of these pathophysiological processes are associated with the beneficial effects of ginsenosides on cognitive function and stress-protective effects on the brain functions associated with neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases [4,5,21,22,23,24].
The results of clinical trials suggested the beneficial effects of Ginseng on stress and cognitive functions [25,26,27,28] of healthy subjects [29,30,31,32,33,34], and patients with mild cognitive impairments and neurological disorders [17,35,36,37,38,39]. Some clinical studies suggest that both plants are promising treatments for aging-related diseases, including neurodegenerative diseases, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and cancer [10,11]. That is in line with the traditional use of Red Korean Ginseng as a panacea for an extraordinary number of disease states normalizing body functions and strengthening body systems compromised by a wide variety of environmental assaults and emotional conditions, presumably due to the recovery of vital energy, alleviation of fatigue, tonic and overall protective effect on health [4,5,8,9].
The fixed combination of the extracts of Red Ginseng (RG) and Red Sage (RS), RG–RS, is known to have favorable cardiovascular effects and is adopted in TCM for treating cardiovascular disease [40,41]. RG–RS ameliorated the delayed onset of vascular stiffening resulting in a faster recovery of muscle soreness, and it prevented an increase in blood C-reactive protein and IL-6 induced by acute downhill running exercises of healthy subjects after supplementation for seven weeks in a daily dose corresponding to 1.75 g of each herbal substance (dry herb) [40]. However, at a lower dose (0.75 g of each herb), RG–RS supplementation for 12 weeks does not appear to modulate vascular and inflammatory adaptations to eccentric exercise training in middle-aged and older adults [41].
Several in vitro and in vivo [42,43,44,45] studies of the so-called “optimized” component formula” (OCF), composed of three active constituents of the extract, salvianolic acids, ginsenosides, and ginseng polysaccharides (5, 10, and 5 mg/L, respectively), in Lewis lung cancer cells (LLC) allografted in C57BL/6 mice and A549 xenografted in nude mice experiments suggested the potential efficacy in preventing cancer progression and tumor metastasis [42,43,44,45]. The OCF inhibited lung cancer cell proliferation and induced apoptosis without any cytotoxic effects on normal lung epithelial BEAS-2B cells. Furthermore, OCF inhibited lung cancer cell migration and invasion. OCF significantly promoted phosphatase and tensin homolog (p-PTEN) expression, which was followed by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway [43].
However, the results obtained in experiments with RG, RS, and OCF cannot be mechanistically extrapolated on RG–RS because that is a different substance with a different chemical composition consisting of 17 active constituents from RG and 53 active constituents from RS [46], which can interact synergistically and antagonistically in the target cells of the organism on transcriptomic and proteomic regulation levels of the cellular metabolism.
Therefore, we aimed in this study for the first time to uncover the mechanism of action (MOA) of RG–RS by assessing its effects on gene expression in isolated neuronal cells, followed by network pharmacology using Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) of significantly upregulated or downregulated genes, to disclose effects on cellular functions and diseases. That is important for understanding and predicting the potential risks and benefits of the therapeutic action of RG–RS.
The choice of murine neuronal HT22 cells as an in vitro model is based on many publications where a neuroprotective effect of Red Ginseng extracts [47,48,49], Ginsenosides Rg5, Rb2, Rg1, Re [50,51,52,53], Compound K [54,55] and tanshinons I and II [56,57] in various experiments with murine hippocampal HT22 cells was demonstrated. Furthermore, Red Ginseng root preparation HRG80TM (RG, used in this study) modulates ionotropic glutamate NMDA, and kainate receptors mediated transmission in ex vivo experiments of the excitability of hippocampal pyramidal cells of rats [58]. Finally, it was effective in preventing and mitigating the stress-induced deterioration of cognitive functions in healthy subjects [29] and elderly patients with mild cognitive disorders, substantially affecting various brain regions depending on the mental load during relaxation and cognitive tasks associated with memory, attention, and mental performance, suggesting an improvement in mood and calming effects associated with GABA-ergic neurotransmission [39].
2. Results
2.1. Effect of RG–RS on the Gene Expression Profile in the Hippocampal Neuronal Cell Line HT22
Table 1 shows the number of genes deregulated (>20-fold compared to control) by RG–SG, RG, and ginsenosides Rb1, Rg3, Rg5, and Rk1 in the hippocampal neuronal cell line HT22; for details, see Supplemental Tables S1–S3 and Table 1.

Table 1.
Final concentrations of RG–SG, RG, and their active constituents, ginsenosides Rb1, Rg3, Rg5, and Rk1 in the hippocampal neuronal cell line HT22, and of the number of deregulated genes (>20 fold compared to control).
The combination RG–RS has a more substantial impact than RG on gene expression in hippocampal neurons, deregulating almost three-fold (1151/394) more genes, Figure 1.
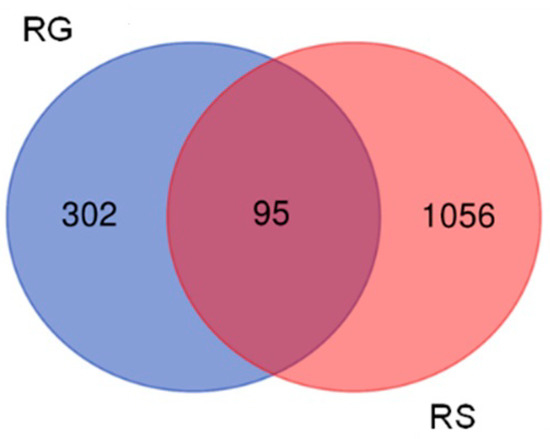
Figure 1.
Venn diagrams the number of genes deregulated by RG and RG–RS in the hippocampal neuronal cell line HT22.
The profiles (signatures) of deregulated genes by RG–RS and RS are quite different; only 24% of the genes (95 of 397) deregulated by RG were deregulated by the combination RG– RS Figure 1 and Supplemental Tables S1–S3).
These observations also show that the gene expression profile of hippocampal neurons is specific for the combination RG–RS and quite different from RG extract.
2.2. Effects of RG–RS on Signaling Canonical Pathways
Figure 2 and Supplementary Figure S1, and Supplementary Table S4 show the predicted effects (−log p-value > 1.3, z-score > 2) of RG–RS on the canonical signaling pathways, including:
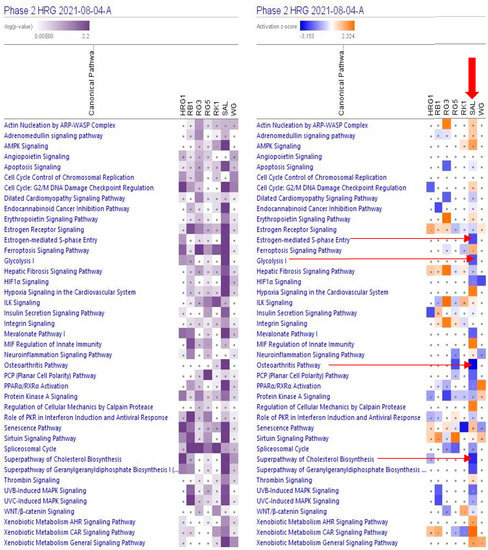
Figure 2.
Effects of RG–RS (SAL) at concentrations of 20 μg/mL, RG at concentrations of 10 μg/mL (HRG1), white ginseng (WG), and ginsenosides Rb1, Rg3, Rg5, Rk1 at the concentration of 0.1 μM on selected canonical pathways. The violet color shows the p-value (calculated using a Right-Tailed Fisher’s Exact Test), indicating the statistical significance of the overlap of analyzed dataset genes within the pathway; the intensity of color corresponds to the log p-value in a scale from 0 to 2.2 (upper panel). The brown color shows the predicted activation, and the blue color shows the predicted inhibition of signaling pathways; the intensity of the color corresponds to the activation zone on a scale from −3.153 to +2.324 (upper panel). symbol · shows that the activation z-score was < 2 and the −log p-value <1.3 = p < 0.05. An absolute z-score ≥2 is considered significant activation (+) or inhibition (-). The activation z-score predicts the activation state of the canonical pathway using the gene expression patterns of the genes within the pathway.
- Inhibition of glycolysis, estrogen-mediated S-phase entry, PCP (planar cell polarity), mevalonate, osteoarthritis pathways, cholesterol, and geranylgeranyl diphosphate biosynthesis super-pathways, and
- Activation of MIF regulation of innate immunity, regulation of cellular mechanics by calpain protease, hypoxia signaling in the cardiovascular system, and xenobiotic metabolism CAR signaling pathways.
A large part (about 89%) of deregulated genes consist of networks significantly associated with cancer (Table 1, Figure 3 and Supplementary Tables S5 and S6). The IPA analysis shows the predicted (activation score z > [±2], −log p-value > 1.3) inhibition of diseases, Figure 4 and Supplementary Table S6.
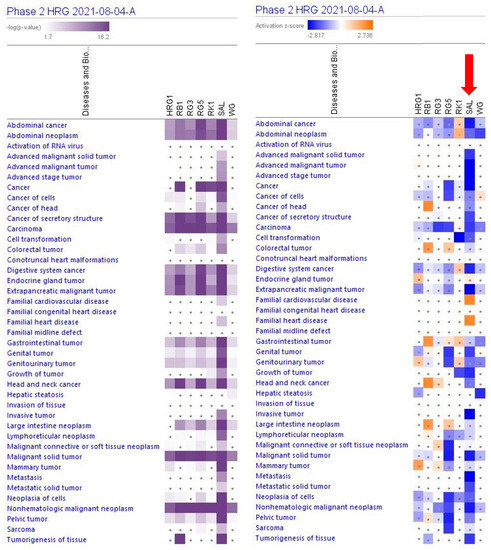
Figure 3.
Predicted effects of RG–RS (SAL) at concentrations of 20 μg/mL, RG at concentrations of 10 μg/mL (HRG1), white ginseng (WG), and ginsenosides Rb1, Rg3, Rg5, Rk1 at a concentration of 0.1 μM. The violet color shows the p-value (calculated using a Right-Tailed Fisher’s Exact Test), indicating the statistical significance of the overlap of analyzed dataset genes within the diseases; the intensity of color corresponds to the log p-value in a scale from 1.7 to 16.2 (upper panel). Disease scores are shown using a gradient from dark blue to brown for predicted activation and light to dark blue for predicted inhibition of diseases on a scale from −2.817 to +2.736 (upper panel); symbol · shows that the activation z-score was < 2, and the −log p-value <1.3 = p < 0.05. An absolute z-score ≥ 2 is considered significant activation (+) or inhibition (-).
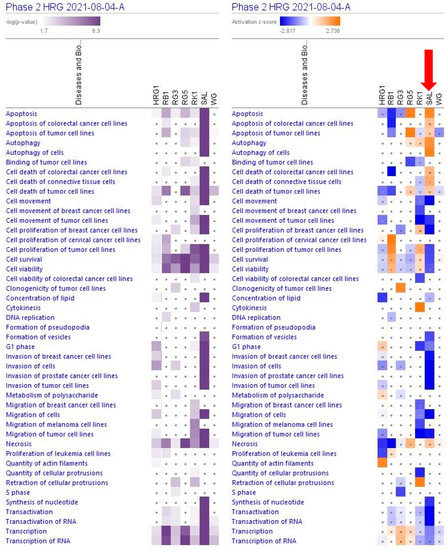
Figure 4.
Predicted effects of RG–RS (SAL) at a concentration of 20 μg/mL, RG at a concentration of 10 μg/mL (HRG1), white ginseng (WG), and ginsenosides Rb1, Rg3, Rg5, Rk1 at a concentration of 0.1 μM on cellular and physiological functions. The violet color shows the p-value (calculated using a Right-Tailed Fisher’s Exact Test), indicating the statistical significance of the overlap of analyzed dataset genes within the functions; the intensity of color corresponds to the log p-value in a scale from 1.7 to 6.3 (upper panel). The function scores are shown using a gradient from dark blue to brown for predicted activation and light to dark blue for predicted inhibition of diseases; the intensity of color corresponds to the activation zone on a scale from −2.817 to +2.736 (upper panel). symbol · shows that the activation z-score was < 2 and the −log p-value <1.3 = p < 0.05. An absolute z-score ≥2 is considered significant activation (+) or inhibition (-). The activation z-score predicts the activation state of the function using the gene expression patterns.
The largest part of deregulated genes (1011 genes, about 88%) consist of networks significantly associated with decreased tumorigenesis (Figure 4 and Supplementary Tables S7 and S8), 139 genes (12%) with reduced metastasis, 81 (7%) with increased autophagy, and 312 (27%) with increased apoptosis (Figure 5 and Supplementary Tables S7 and S9).
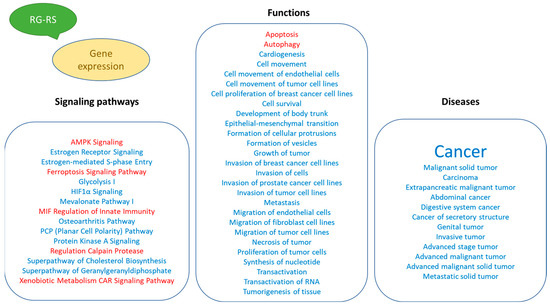
Figure 5.
Potential effects of RG–RS on diseases and disorders, biological processes, cellular and physiological function, and detected impact on intracellular signaling and metabolic pathways.
3. Discussion
This study’s primary aim was to employ transcriptomics of neuronal cells to uncover the mechanisms of action (MOA) and potential pharmacological activities of a fixed combination RG–RS, consisting of two adaptogenic plants traditionally used in aging-related diseases and disorders. The MOA of both plants and many of their active constituents have been described in numerous publications. However, they might be quite different if both plants are combined in one formulation due to various synergistic and antagonistic interactions within the organism. Consequently, pharmacological and toxicological profiles might be considerably diverse in purified constituents. The present study confirms this common rule, as evident from Figure 1 and Table 1; e.g., RG–RS has to impact the expression of 302 genes specifically deregulated by RG. Furthermore, the gene expression profiles activated or inhibited the signaling pathways and predicted that the pharmacological effects are different (see Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4 and Supplementary Tables S1–S3).
To our best knowledge, only two clinical studies have been conducted with the RG–RS combination [40,41], suggesting its efficacy in the recovery of muscle soreness and preventing an increase in proinflammatory protein in exercising healthy subjects. Several in vitro and in vivo [42,43,44,45] studies conducted with a combination of purified active constituents of the plant extracts, i.e., salvianolic acids, ginsenosides, and ginseng polysaccharides, suggest the potential efficacy in preventing cancer progression and tumor metastasis [42,43,44,45], which are presumably associated with an inhibition of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway [43]. From the chemical point of view, the substance RG–RS studied in our experiments differs from the substance used in any other study of RG, RS, and their constituents, except for two clinical studies in athletes. RG consists of nearly 300 compounds (more than 200 have been isolated from Red Ginseng and more than 100 from Red Sage), while OCF [42,43,44,45] has only 3 constituents—salvianolic acids, ginsenosides, and ginseng polysaccharides. Consequently, it is not surprising that the pharmacological profile of the combination RG–RS is unique and different from other substances observed in other studies. It is noteworthy that, in our study, we have observed an effect on the transcriptomic level of regulation of cellular response in vitro model; our experiments did not cover many other effects on the proteomic level of regulation, including effects on the enzymatic activity of proteins, interactions with receptors, and other functions of proteins.
The results of this study, for the first time, describe the effect of RG–RS on the gene expression profile of isolated neurons, the potential impacts of RG–RS on diseases and disorders, biological processes, cellular and physiological function, and implications on intracellular signaling and metabolic pathways (Figure 5).
In this study, we, for the first time, demonstrate the inhibitory effect of RG–RS on gene expression regulating glycolysis metabolic enzymes (Figure 6 and Supplementary Figures S2 and S3), which is crucial in cancer.
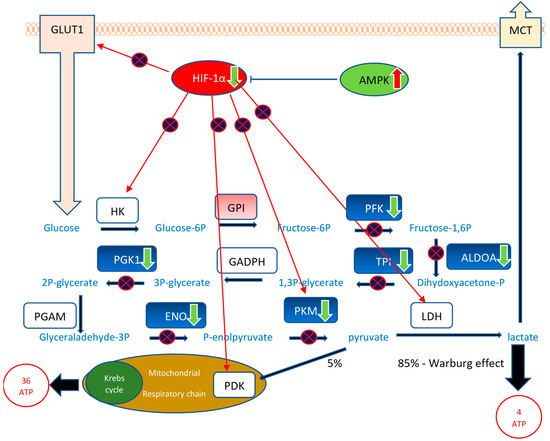
Figure 6.
The effect of RG–RS on glycolysis: RG–RS strongly downregulates the expression of 8 genes encoding eight enzymes of the glucose metabolic pathway, significantly inhibits the HIF-1α signaling pathway, a master regulator of glycolysis, and activates antitumor monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) suggesting substantial inhibition of the conversion of glucose into lactate (Warburg effect) in cancer that is crucial for proliferation and survival of tumor cells. Downregulated genes are shown in the green color, corresponding enzymes in the blue color: the neuron-specific enolase (NSE) ENO1 gene (−2562-fold change), phosphoglycerate kinase 1 PGK1 gene (−1426-fold change), the pyruvate kinase PKM gene (−1094-fold change), the aldolase ALDOA gene (−855-fold change), the triose phosphate isomerase TPI gene (−810-fold change), phosphofructokinase, encoded by the PFK gene (−730-fold change). HKs—hexokinases HK1, HK2, HK3, HK4, which are encoded by the HK1, HK2, HK3, and HK4 genes; GPI—glucose-6-phosphate isomerase encoded by the GPI gene (+372-fold change); GAPDH: glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase, encoded by the GAPDH gene; PGAM—phosphoglycerate mutase, encoded by the PGAM gene; LDH—lactate dehydrogenases; which are encoded by LDHA and LDHB genes; GLUT1—glucose transporting proteins encoded by the SLC2 gene; MCTs: lactate transporters encoded by the SLC16 gene. Tumor suppressors are shown in green, and oncogenes are in red. RG–RS inhibits (p > 1.3; z 1.5, Supplement Table S6) the oncogenic Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1α) and activates (p > 1.3; z—1.7, Supplement Table S6) tumor suppressor adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) signaling pathways.
Most cancer cells are characterized by a high rate of aerobic glycolysis for the energy supply of proliferation, tumor growth, and survival, even with sufficient oxygen supply [59,60,61,62]. Highly proliferating cancer cells undergo the Warburg effect, i.e., a metabolic switch from oxidative phosphorylation providing 36 molecules of energy molecules (ATP) to an abnormal and ineffective energy supply metabolic pathway, aerobic glycolysis, providing only 4 ATP molecules and mostly lactate instead of pyruvate (Figure 6). The glucose metabolic pathway is activated by several tumor-promoting (P3IK/AKT, HIF-1α, mTOR, K-Ras, c-Myc, miRNAs,) and inhibited by tumor-suppressing (AMPK, p53) signaling pathways in highly proliferative cancer cells [60,62].
Several transcription factors and signaling molecules, such as HIF-1α, c-Myc, Akt, and mTOR, and other upstream regulators, including oncogene K-Ras, tumor suppressor p53, energy sensor adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK), non-coding RNAs, and sirtuin family proteins and deacetylation, are also involved in this process [59,60,61,62]. Decreased glycolytic flux in response to AMPK or p53 may be an adaptive response to shut off proliferative metabolism during periods of oxidative stress or low energy availability [59].
Figure 6 and Supplementary Table S10 show that RG–RS strongly downregulates the expression of five genes upregulated in cancer cells: 2562-fold downregulated neuron-specific enolase (NSE) ENO1 gene, 1426-fold downregulated phosphoglycerate kinase 1 PGK1 gene, 1094-fold downregulated pyruvate kinase PKM gene, 855-fold downregulated aldolase ALDOA gene, and 810-fold downregulated triose phosphate isomerase TPI gene. Moreover, RG–RS significantly inhibits the HIF-1α signaling pathway, a master regulator of glycolysis, and activates antitumor monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK), suggesting the substantial inhibition of the conversion of glucose into lactate (Warburg effect) in cancer, which is crucial for the proliferation and survival of tumor cells.
Figure 6 shows that RG–RS targets 10 (!) disease-specific molecules (5 directly and 5 indirectly via upstream regulators HIF-1α and AMPK) in the tumor’s energy supply source.
Overall, RG–RS targets 1028 targets associated with cancer and 139 with metastasis, Table 1 and Supplementary Tables S8 and S9. In silico IPA analysis of the effects of RG–RS on gene expression in isolated neurons predicts the antitumor activity of RG–RS, which is in line with other studies [42,43,44,45].
Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4 show the potential effects of RG–RS on the canonical signaling pathways, cellular and physiological functions, and aging-related diseases, particularly the inhibition of the osteoarthritis signaling pathway where the probability of prediction is significant (−log p-value 1.7, z-score -3.2; Supplementary Table S6 and Supplementary Figure S1). That is in line with other studies of RG and RS where the potential health effect of Reg Ginseng [63,64,65,66,67] and Red Sage [68,69,70,71,72] in osteoarthritis was demonstrated.
A limitation in this study is related to the lack of scientific literature about the direction (negative or positive) of correlations between gene expression and physiological function or disease for predicting the effects of some experimental data used in silico analysis.
4. Materials and Methods
All the materials and methods used in this study have been recently described in detail in our recent publication [24], which was conducted by the same experimental protocol [24]. They include mRNA microarray hybridization conducted by the same experimental protocol, Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA), and Statistical Analysis [24].
4.1. Test Samples and Their Concentrations in Murine Hippocampal Neuronal HT22 Cells Culture
Panax ginseng C.A. Mey. (Korean Ginseng), radix and Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge (Danshen/Red Sage), radix et rhizome were hydroponically cultivated in controlled conditions at Botalys S. A. (Ath, Belgium). Korean Ginseng was steamed to Red Ginseng, which was dried, powdered, and standardized for the content of ginsenosides Rk1 and Rg5 to obtain Red Ginseng HRG80TM preparation containing 7.6% of total ginsenosides. HRG80TM preparation was exhaustively extracted by 70% methanol and evaporated to dryness to obtain HRG extract (DER 4: 1) containing 1.9% Rg5 and 1.0% Rk1; the content of total ginsenosides in the HRG extract was 30.32%.
Red Sage radix et rhizomatic were extracted by 70% methanol to obtain salvianolic acid-free extract (RS) containing 0.883% cryptotanshinones, 0.673% tetrahydrotanshinone, 0.094% dihydrotanshinones, and 0.029% tanshinone IIA; total tanshinons content—1.72%.
Murine hippocampal neuronal HT22 cells were incubated with test samples at final concentrations of 10 μg/mL of RG and 10 μg/mL RS in RG–RS, 10 μg/mL of RG, 0.1 µM of ginsenosides Rb1, Rg3, Rg5, and Rk1 (Table 1) or DMSO as solvent control (0.5%) for 24 h.
Purified reference standards of ginsenosides were purchased from Merck KGaA (Darmstadt, Germany) and Extrasynthese (Genay, France).
HPLC conditions. Analytical samples were analyzed by Waters LC system using reverse phase HPLC column ACE C18 5 μm (250 × 4.6 mm) and the solvent system containing gradually increasing concentration (from 21 to 90% in eight steps) of acetonitrile in water solution of 0.1% ortho-phosphoric acid at 30 °C, flow rate-1.2 mL/min.; diode array detection at 203 nm. The content of analytical markers in the analytes was quantified by reference standards used to generate calibration curves. The analytical method was validated for selectivity, precision, and accuracy (RSD < 5%).
4.2. mRNA Microarray Hybridization
Murine hippocampal neuronal HT22 cells were seeded and attached for 24 h before drug treatment. Cells were then treated for 24 h at final concentrations of 10 μg/mL of RG and 10 μg/mL RS in RG–RS, 10 μg/mL of RG, 0.1 µM of ginsenosides Rb1, Rg3, Rg5, and Rk1 (Table 1) or DMSO as solvent control (0.5%). The total RNA Nanochip assay was applied on an Agilent 2100 bioanalyzer (Agilent Technologies GmbH) for quality control of RNA. An RNA index value > 8.5 served as a threshold for further processing of RNA samples. Every two independent experiments have been performed. The mRNA microarray hybridization has been performed at the Genomics and Proteomics Core Facility, German Cancer Research Center (Heidelberg, Germany), using Affymetrix GeneChips® with mouse Clariom S assays. A quantile normalization algorithm has normalized the measurements without background subtraction. The standard deviation differences were calculated in one-by-one comparisons to identify differentially regulated genes. The Chipster software (The Finnish IT Center for Science CSC) was used for further evaluation of the results.
4.3. Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA)
The interpretation of microarray data and gene expression changes was performed using Ingenuity Pathways Analysis (IPA) software, summer release 2021 (QIAGEN Bio-informatics, Aarhus C, Denmark), which relies on the Ingenuity Knowledge Base, a continuously updated database gathering observations with more than 8.1 million findings manually curated from the biomedical literature or integrated from 45 third-party databases. The IPA network contains 40,000 nodes representing mammalian genes, molecules, and biological functions, linked by 1,480,000 edges representing experimentally observed cause–effect relationships (either activating or inhibiting) related to gene expression, transcription, activation, molecular metabolism, and binding. Network edges are also associated with a direction (either activating or inhibiting) of the causal effect [73].
Using the IPA Core Analysis tool for all tested transcriptomic datasets, we performed predictive analyses of the impact of test samples on canonical signaling and metabolic pathways, which displayed the molecules of interest within well-established pathways; and diseases, disorders, molecular and cellular functions that are activated or inhibited downstream and upstream of the genes, whose expression has been altered.
4.4. Statistical Analysis
Two statistical methods of analysis of gene expression datasets were used in the IPA: (i) the gene-set-enrichment method, where differentially expressed genes are intersected with sets of genes that are associated with a particular biological function or pathway providing an “enrichment” score (Fisher’s exact test p-value) that measures the overlap of the observed and predicted regulated gene sets [74,75], (ii) the method based on cause–effect relationships related to the direction of effects reported in the literature [76,77] that provides the so-called z-score measuring the match of observed and predicted up/down-regulation [73]. The predicted effects are based on gene expression changes in the experimental samples relative to the control; z-score > 2, −log p-value > 1.3.
5. Conclusions
The results of this study present evidence of the potential efficacy of the fixed combination of Red Ginseng (Panax ginseng C.A. Mey.) and Red Sage/Danshen (Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge) in cancer. Further preclinical and clinical studies are warranted to assess the efficacy and safety of RG–RS in preventing the progression of cancer and other aging-related diseases.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ph15111345/s1; Supplementary Tables S1–S9 and Figures S1–S3. Table S1.All genes fold changes; Table S2. RG-RS deregulated genes; Table S3 Venn diagrams; Table S5. Functions; Table S6. Signaling pathways; Table S7. Cancer predicted inhibition; Table S8. Tumorigenesis predicted inhibition; Table S9. Metastasis predicted inhibition. Figure S1. Signaling pathways. Figure S2. Glycolysis metabolic pathway RG-RS deregulated genes fold changes; Figure S3. Glycolysis metabolic pathway RG and RG-RS deregulated genes heatmap.
Author Contributions
S.A. contributed to the execution of experiments, data management, and manuscript preparation. T.E. contributed to the overall management of the study and manuscript preparation. A.P. contributed to the study conception, design and evaluation, data analysis, interpretation of the results, and drafting and preparation of the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by Europharma USA (Green Bay, WI, USA) and Botalys SA (Ath, Belgium). The research sponsors were Terrence Lemerond, Europharma USA Inc., USA; Pierre-Antoine Mariage and Paul-Evence Coppee, Botalys SA, Belgium (grant number 2019-03).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article and supplementary material.
Acknowledgments
The author acknowledges the support of Botalys SA for the supply of investigational products and their characterization. Quality control was performed by Pierre-Antoine Mariage and Sylvie Defrère, Botalys SA, Belgium. We thank the Microarray Unit of the Genomics and Proteomics Core Facility, German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ), for providing excellent Expression Profiling services. The authors are grateful to Reiner Kunze (Institute of Physiology and Pathophysiology, Department of Medicine, Heidelberg University) for the generous gift of the murine neuronal cell line HT-22.
Conflicts of Interest
AP has an independent-contractor agreement with EuroPharmaUSA Inc. All other authors declare no competing interests. The funders had no role in the study’s design, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Fulop, T.; Larbi, A.; Pawelec, G.; Khalil, A.; Cohen, A.A.; Hirokawa, K.; Witkowski, J.M.; Franceschi, C. Immunology of Aging: The Birth of Inflammaging. Allergy Immunol. 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fülöp, T.; Larbi, A.; Witkowski, J.M. Human Inflammaging. Gerontology 2019, 65, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teissier, T.; Boulanger, E.; Cox, L.S. Interconnections between Inflammageing and Immunosenescence during Ageing. Cells 2022, 11, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panossian, A.G.; Efferth, T.; Shikov, A.N.; Pozharitskaya, O.N.; Kuchta, K.; Mukherjee, P.K.; Banerjee, S.; Heinrich, M.; Wu, W.; Guo, D.; et al. Evolution of the adaptogenic concept from traditional use to medical systems: Pharmacology of stress- and aging-related diseases. Med. Res. Rev. 2021, 41, 630–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panossian, A.G.; Efferth, T. Network Pharmacology of Adaptogens in the Assessment of Their Pleiotropic Therapeutic Activity. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, L.Y.; He, Y.F.; Li, L.; Meng, H.; Dong, Y.M.; Yi, F.; Xiao, P.G. A preliminary review of studies on adaptogens: Comparison of heir bioactivity in TCM with that of ginseng-like herbs used worldwide. Chin. Med. 2018, 13, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.Y.; Ming, Q.L.; Rahman, K.; Han, T.; Qin, L.P. Salvia miltiorrhiza: Traditional medicinal uses, chemistry, and pharmacology. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2015, 13, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flagg, A.J. Traditional and current use of Ginseng. Nurs. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 56, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.M.; Bae, B.S.; Park, H.W.; Ahn, N.G.; Cho, B.G.; Cho, Y.L.; Kwak, Y.S. Characterization of Korean Red Ginseng (Panax ginseng Meyer): History, preparation method, and chemical composition. J. Ginseng Res. 2015, 39, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EMA/HMPC/321232/2012; Assessment Report on Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer, Radix. Committee on Herbal Medicinal Products (HMPC): London, UK, 2014; pp. 1–124. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/herbal-report/final-assessment-report-panax-ginseng-ca-meyer-radix_en.pdf (accessed on 27 October 2022).
- EMA/HMPC/509932/2019; Assessment Report on Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge, Radix et Rhizome. Committee on Herbal Medicinal Products (HMPC): London, UK, 30 March 2022; pp. 1–34. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/herbal-report/draft-assessment-report-salvia-miltiorrhiza-bunge-radix-et-rhizoma-first-version_en.pdf (accessed on 27 October 2022).
- Xu, J.; Wei, K.; Zhang, G.; Lei, L.; Yang, D.; Wang, W.; Han, Q.; Xia, Y.; Bi, Y.; Yang, M.; et al. Ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry, and pharmacology of Chinese Salvia species: A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 225, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Zanuso, B.; de Oliveira Dos Santos, A.R.; Miola, V.; Guissoni Campos, L.M.; Spilla, C.; Barbalho, S.M. Panax ginseng and aging related disorders: A systematic review. Exp. Gerontol. 2022, 161, 111731. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nocerino, E.; Amato, M.; Izzo, A.A. The aphrodisiac and adaptogenic properties of Ginseng. Fitoterapia 2000, 71 (Suppl. S1), S1–S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MEIm, X.D.; Cao, Y.F.; Che, Y.Y.; Li, J.; Shang, Z.P.; Zhao, W.J.; Qiao, Y.J.; Zhang, J.Y. Danshen: A phytochemical and pharmacological overview. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2019, 17, 59–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zuo, Z.; Chow, M.S. Danshen: An overview of its chemistry, pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, and clinical use. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2005, 45, 1345–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Jung, S.W.; Kim, S.Y.; Cho, I.H.; Kim, H.C.; Rhim, H.; Kim, M.; Nah, S.Y. Panax ginseng as an adjuvant treatment for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, I.; Kim, H.; Moon, S.; Lee, H.; Kim, B. Overview of Salvia miltiorrhiza as a Potential Therapeutic Agent for Various Diseases: An Update on Efficacy and Mechanisms of Action. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Chang, Y.C.; Hu, W.L.; Hung, Y.C. Oxidative Stress and Salvia miltiorrhiza in Aging-Associated Cardiovascular Diseases. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 4797102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Ma, R.; Liu, C.; Liu, H.; Zhu, R.; Guo, S.; Tang, M.; Li, Y.; Niu, J.; Fu, M.; et al. Salvia miltiorrhiza: A Potential Red Light to the Development of Cardiovascular Diseases. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 1077–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T.; Raza, S.H.; Maryam, A.; Setzer, W.N.; Braidy, N.; Nabavi, S.F.; de Oliveira, M.R.; Nabavi, S.M. Ginsenoside Rb1 as a neuroprotective agent: A review. Brain Res. Bull. 2016, 125, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Sur, B.; Oh, S. Neuroprotective effect of Korean Red Ginseng against single prolonged stress-induced memory impairments and inflammation in the rat brain associated with BDNF expression. J. Ginseng Res. 2022, 46, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panossian, A.; Abdelfatah, S.; Efferth, T. Network Pharmacology of Red Ginseng (Part I): Effects of Ginsenoside Rg5 at Physiological and Sub-Physiological Concentrations. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panossian, A.; Abdelfatah, S.; Efferth, T. Network Pharmacology of Ginseng (Part II): The Differential Effects of Red Ginseng and Ginsenoside Rg5 in Cancer and Heart Diseases as Determined by Transcriptomics. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, J.; Dong, J.; Ni, H.; Lee, M.S.; Wu, T.; Jiang, K.; Wang, G.; Zhou, A.L.; Malouf, R. Ginseng for cognition. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2010, 12, CD007769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.S.; Yang, E.J.; Kim, J.I.; Ernst, E. Ginseng for cognitive function in Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review. J. Alzheimer Dis. 2009, 18, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Kim, T.-H.; Choi, T.-Y.; Lee, M.S. Ginseng for Health Care: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials Literature. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, W.-Y.; Farooqui, T.; Koh, H.-L.; Farooqui, A.A.; Ling, E.-A. Protective effects of Ginseng on neurological disorders. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2015, 7, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariage, P.-A.; Hovhannisyan, A.; Panossian, A.G. Efficacy of Panax ginseng Meyer Herbal Preparation HRG80 in Preventing and Mitigating Stress-Induced Failure of Cognitive Functions in Healthy Subjects: A Pilot, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Crossover Trial. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reay, J.L.; Kennedy, D.O.; Scholey, A.B. Effects of Panax ginseng, consumed with and without glucose, on blood glucose levels and cognitive performance during sustained ‘mentally demanding’ tasks. J. Psychopharmacol. 2006, 20, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, D.O.; Scholey, A.B.; Wesnes, K.A. Dose dependent changes in cognitive performance and mood following acute administration of Ginseng to healthy young volunteers. Nutr. Neurosci. 2001, 4, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, D.O.; Reay, J.L.; Scholey, A.B. Effects of 8 weeks administration of Korean Panax ginseng extract on the mood and cognitive performance of healthy individuals. J. Ginseng Res. 2007, 31, 34–43. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, D.; Scholey, A. Ginseng: Potential for the enhancement of cognitive performance and mood. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2003, 75, 687–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, H.-B.; Yoon, H.-K.; Lee, H.-J.; Kang, S.-G.; Jung, K.-Y.; Kim, L. Effects of Korean Red Ginseng on Cognitive and Motor Function: A Double-blind, Randomized, Placebo-controlled Trial. J. Ginseng Res. 2012, 36, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.; Jin, H.; Rhee, H.Y.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.E.; Kim, Y.O.; Kim, G.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Yim, S.V.; Choi, Y.C. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial of Korean Ginseng as a functional food in mild cognitive impairment. Alzheimer Dement. 2013, 9, P804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-T.; Chu, K.; Sim, J.-Y.; Heo, J.-H.; Kim, M. Panax Ginseng Enhances Cognitive Performance in Alzheimer Disease. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2008, 22, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, J.H.; Lee, S.T.; Chu, K.; Oh, M.J.; Park, H.J.; Shim, J.Y.; Kim, M. An open-label trial of Korean red Ginseng as an adjuvant treatment for cognitive impairment in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Neurol. 2008, 15, 865–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, J.H.; Lee, S.T.; Oh, M.J.; Park, H.J.; Shim, J.Y.; Chu, K.; Kim, M. Improvement of cognitive deficit in Alzheimer’s disease patients by long term treatment with Korean red Ginseng. J. Ginseng Res. 2011, 35, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimpfel, W.; Mariage, P.-A.; Panossian, A. Effects of Red and White Ginseng Preparations on Electrical Activity of the Brain in Elderly Subjects: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Three-Armed Cross-Over Study. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.F.; Chou, C.C.; Chao, H.H.; Tanaka, H. Panax ginseng and Salvia miltiorrhiza supplementation during eccentric resistance training in middle-aged and older adults: A double-blind randomized control trial. Complement. Ther. Med. 2016, 29, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.F.; Tung, K.; Chou, C.C.; Lin, C.C.; Lin, J.G.; Tanaka, H. Panax ginseng and Salvia miltiorrhiza supplementation abolishes eccentric exercise-induced vascular stiffening: A double-blind randomized control trial. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, L.; Yan, X.; Yang, Y.; Qian, L.; Tian, Y.; Mao, J.H.; Chen, W. The component formula of Salvia miltiorrhiza and Panax Ginseng induces apoptosis and inhibits cell invasion and migration through targeting PTEN in lung cancer cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 101599–101613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Qiu, S.; Qian, L.; Tian, Y.; Chen, Y.; Bi, L.; Chen, W. OCF can repress tumor metastasis by inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition involved in PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway in lung cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Q.; Lu, Q.; Wang, G.; Zhu, W.; Teng, L.; Chen, W.; Bi, L. Optimizing component formula suppresses lung cancer by blocking DTL-mediated PDCD4 ubiquitination to regulate the MAPK/JNK pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 299, 115546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.J.; Yang, Y.; Bi, L.; Chen, S.S.; Zhu, J.J.; Chen, W.P. Effects of component formula of Salviae Miltiorrhizae Radix et Rhizoma and Ginseng Radix et Rhizoma on cell proliferation, apoptosis and skeleton in lung cancer A549 cells. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2014, 39, 4436–4441. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xin, G.J.; Zhao, Y.W.; Li, L.M.; Jia, F.F.; Han, X.; Li, L.; Guo, H.; Meng, H.X.; Fu, J.H.; Liu, J.X. Mechanism of ‘Invigorating Qi and Promoting Blood Circulation’ Drug Pair Ginseng-Danshen on Treatment of Ischemic Heart Disease Based on Network Pharmacology. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2021, 27, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.J.; Jeon, S.G.; Kim, J.-I.; Jeong, Y.-O.; Kim, S.; Park, Y.H.; Lee, S.-K.; Park, H.H.; Hong, S.B.; Oh, S.; et al. Red Ginseng Attenuates Aβ-Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Aβ-mediated Pathology in an Animal Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, S.; Seo, J.Y.; Lee, S.K.; Oh, J.; Kim, J.S. Oral administration of hydrolyzed red ginseng extract improves learning and memory capability of scopolamine-treated C57BL/6J mice via upregulation of Nrf2-mediated antioxidant mechanism. J. Ginseng Res. 2021, 45, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.J.; Nam, Y.; Park, Y.H.; Kim, M.-J.; Lee, E.; Jeon, S.G.; Bae, B.-S.; Seo, J.; Shim, S.-L.; Kim, J.-S.; et al. Therapeutic effects of non-saponin fraction with rich polysaccharide from Korean red Ginseng on aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 164, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-Y.; Kim, K.-J.; Song, J.-H.; Lee, B.-Y. Ginsenoside Rg5 prevents apoptosis by modulating heme-oxygenase-1/nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 signaling and alters the expression of cognitive impairment-associated genes in thermal stress-exposed HT22 cells. J. Ginseng Res. 2017, 42, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Kim, D.W.; Jung, B.H.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, H.; Hwang, G.S.; Kang, K.S.; Lee, J.W. Ginsenoside Rb2 suppresses the glutamate-mediated oxidative stress and neuronal cell death in HT22 cells. J. Ginseng Res. 2019, 43, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, L.; Zhang, D.; Li, L.; Dong, X.; Li, Y.; Qun, S.; Li, W. Ginsenoside Rg1 attenuates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury due to inhibition of NOX2-mediated calcium homeostasis dysregulation in mice. J. Ginseng Res. 2022, 46, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhi, I.; Kim, J.H.; Shin, J.E.; Kim, Y. Ginsenoside Re exhibits neuroprotective effects by inhibiting neuroinflammation via CAMK/MAPK/NF-κB signaling in microglia. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 24, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, J.Y.; Ju, S.H.; Oh, J.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, J.S. Neuroprotective and Cognition-Enhancing Effects of Compound K Isolated from Red Ginseng. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 2855–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Li, H.; Yang, Q.; Lan, X.; Wang, J.; Cao, Z.; Shi, X.; Li, J.; Kan, M.; Qu, X.; et al. Ginsenoside compound K ameliorates Alzheimer’s disease in HT22 cells by adjusting energy metabolism. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2019, 46, 5323–5332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Tang, Q.; Wang, G.; Han, R. Tanshinone IIA Protects Hippocampal Neuronal Cells from Reactive Oxygen Species Through Changes in Autophagy and Activation of Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase, Protein Kinas B, and Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin Pathways. Curr. Neurovasc. Res. 2017, 14, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, F.; Sheng, P.; Xia, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Yan, B.C. A network-based method for mechanistic investigation and neuroprotective effect on treatment of tanshinone Ⅰ against ischemic stroke in mouse. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 272, 113923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimpfel, W.; Schombert, L.; Panossian, A.G. Panax ginseng preparations enhance long term potentiation in rat hippocampal slices by glutamatergic NMDA and kainate receptor mediated transmission. J. Alternat. Complement. Integr. Med. 2020, 6, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vander Heiden, M.G.; Cantley, L.C.; Thompson, C.B. Understanding the Warburg effect: The metabolic requirements of cell proliferation. Science 2009, 324, 1029–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Chen, X.; Sun, X.; Wang, L.; Chen, S. The Glycolytic Switch in Tumors: How Many Players Are Involved? J. Cancer 2017, 8, 3430–3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, N.; Kulma, A.; Gutowicz, J. Up-regulation of Key Glycolysis Proteins in Cancer Development. Open Life Sci. 2008, 13, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Jin, Y.; Fan, Z. The Mechanism of Warburg Effect-Induced Chemoresistance in Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 698023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.S. Ameliorative effects of Ginseng and ginsenosides on rheumatic diseases. J. Ginseng Res. 2019, 43, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.I.; Chon, S.J.; Seon, K.E.; Seo, S.K.; Choi, Y.R. Clinical Effects of Korean Red Ginseng in Postmenopausal Women With Hand Osteoarthritis: A Double-Blind, Randomized Controlled Trial. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 745568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.A.; Alam, M.J.; Kim, B.; Kang, C.W.; Kim, J.H. Ginsenoside-Rb1 prevents bone cartilage destruction through down-regulation of p-Akt, p-P38, and p-P65 signaling in rabbit. Phytomedicine 2022, 100, 154039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, J.; Che, G.; Man, G.; Xiao, F. Ginsenoside Rb1 from Panax ginseng attenuates monoiodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis by inhibiting miR-21-5p/FGF18-mediated inflammation. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e14340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Lim, H.; Shehzad, O.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, H.P. Ginsenosides from Korean red Ginseng inhibit matrix metalloproteinase-13 expression in articular chondrocytes and prevent cartilage degradation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 724, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Li, Y.; Xue, L.; Severino, R.P.; Gao, S.; Niu, J.; Qin, L.P.; Zhang, D.; Brömme, D. Salvia miltiorrhiza: An ancient Chinese herbal medicine as a source for anti-osteoporotic drugs. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 155, 1401–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhou, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, F.; Ma, H.; Cao, L. Identification of the molecular mechanisms of Salvia miltiorrhiza relevant to the treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology. Discov. Med. 2020, 30, 83–95. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Lv, H.; Li, X.; Su, H.; Zhang, X.; Yang, J. Danshen attenuates cartilage injuries in osteoarthritis in vivo and in vitro by activating JAK2/STAT3 and AKT pathways. Exp. Anim. 2018, 67, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.; Li, Y. Danshen prevents articular cartilage degeneration via antioxidation in rabbits with osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2016, 24, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Lv, H.; Li, X.; Su, H.; Zhang, X.; Yang, J. Danshen attenuates osteoarthritis-related cartilage degeneration through inhibition of NF-κB signaling pathway in vivo and in vitro. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2017, 95, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krämer, A.; Green, J.; Pollard, J., Jr.; Tugendreich, S. Causal analysis approaches in Ingenuity Pathway Analysis. Bioinformatics. 2014, 30, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abatangelo, L.; Maglietta, R.; Distaso, A.; D’Addabbo, A.; Creanza, T.M.; Mukherjee, S.; Ancona, N. Comparative study of gene set enrichment methods. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihnatova, I.; Popovici, V.; Budinska, E. A critical comparison of topology-based pathway analysis methods. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakhry, C.T.; Choudhary, P.; Gutteridge, A.; Sidders, B.; Chen, P.; Ziemek, D.; Zarringhalam, K. Interpreting transcriptional changes using causal graphs: New methods and their practical utility on public networks. BMC Bioinform. 2016, 17, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chindelevitch, L.; Ziemek, D.; Enayetallah, A.; Randhawa, R.; Sidders, B.; Brockel, C.; Huang, E.S. Causal reasoning on biological networks: Interpreting transcriptional changes. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1114–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).