Long-Term Fenofibrate Treatment Stimulates the Phenotypic Microevolution of Prostate Cancer Cells In Vitro
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
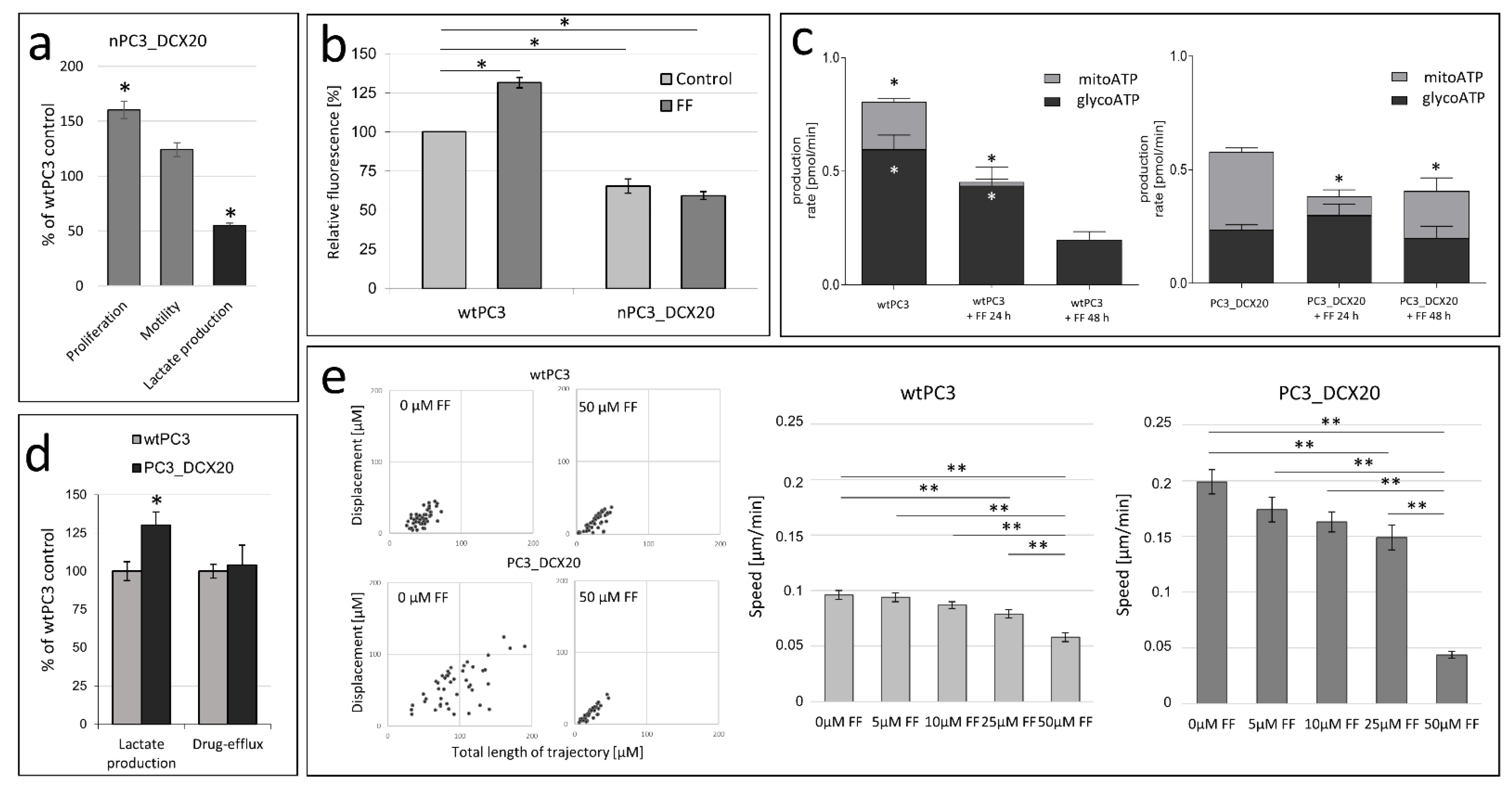
2.1. Drug Resistance of PC3 Cells Does Not Correlate with Their Sensitivity to Fenofibrate
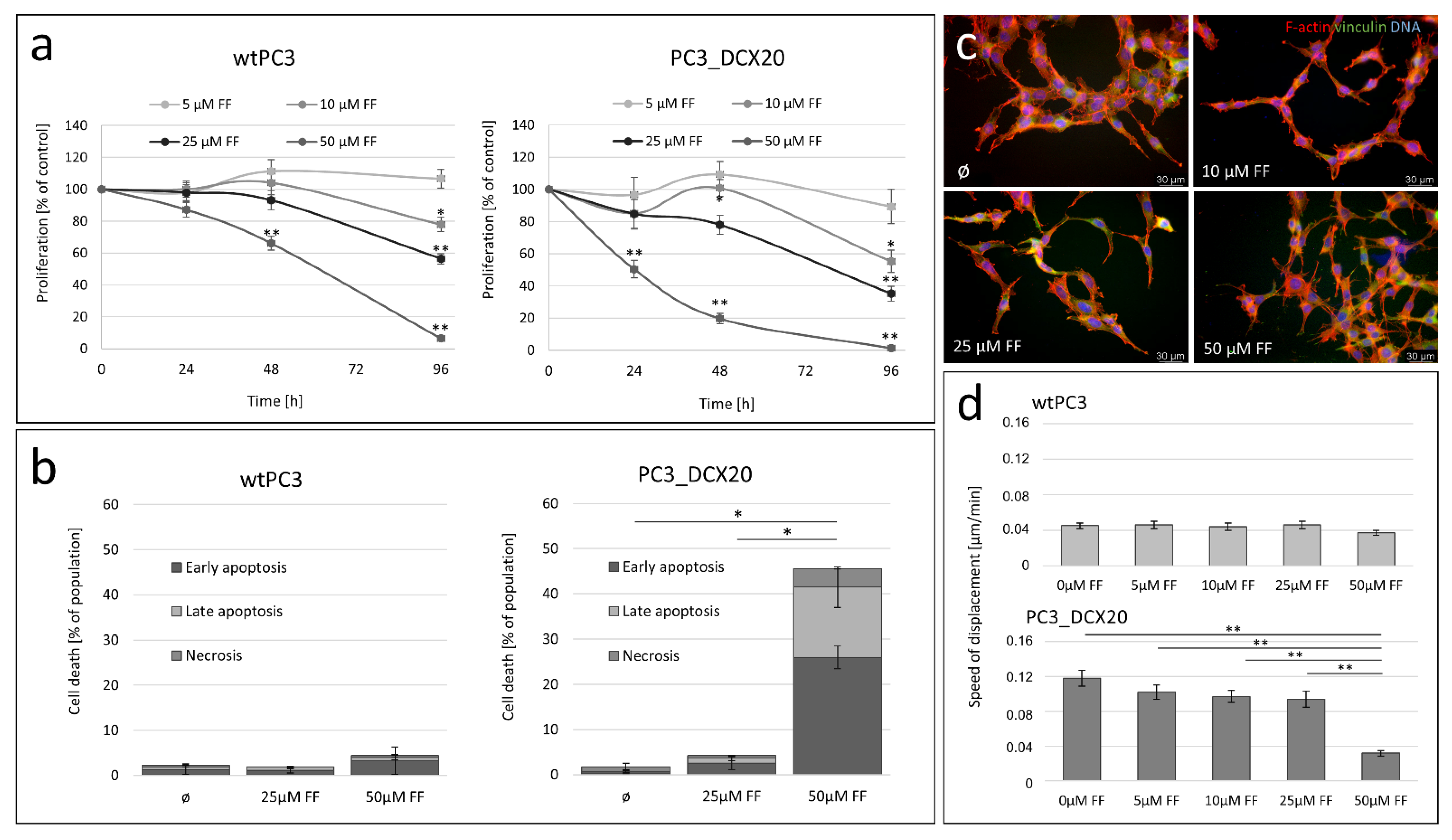
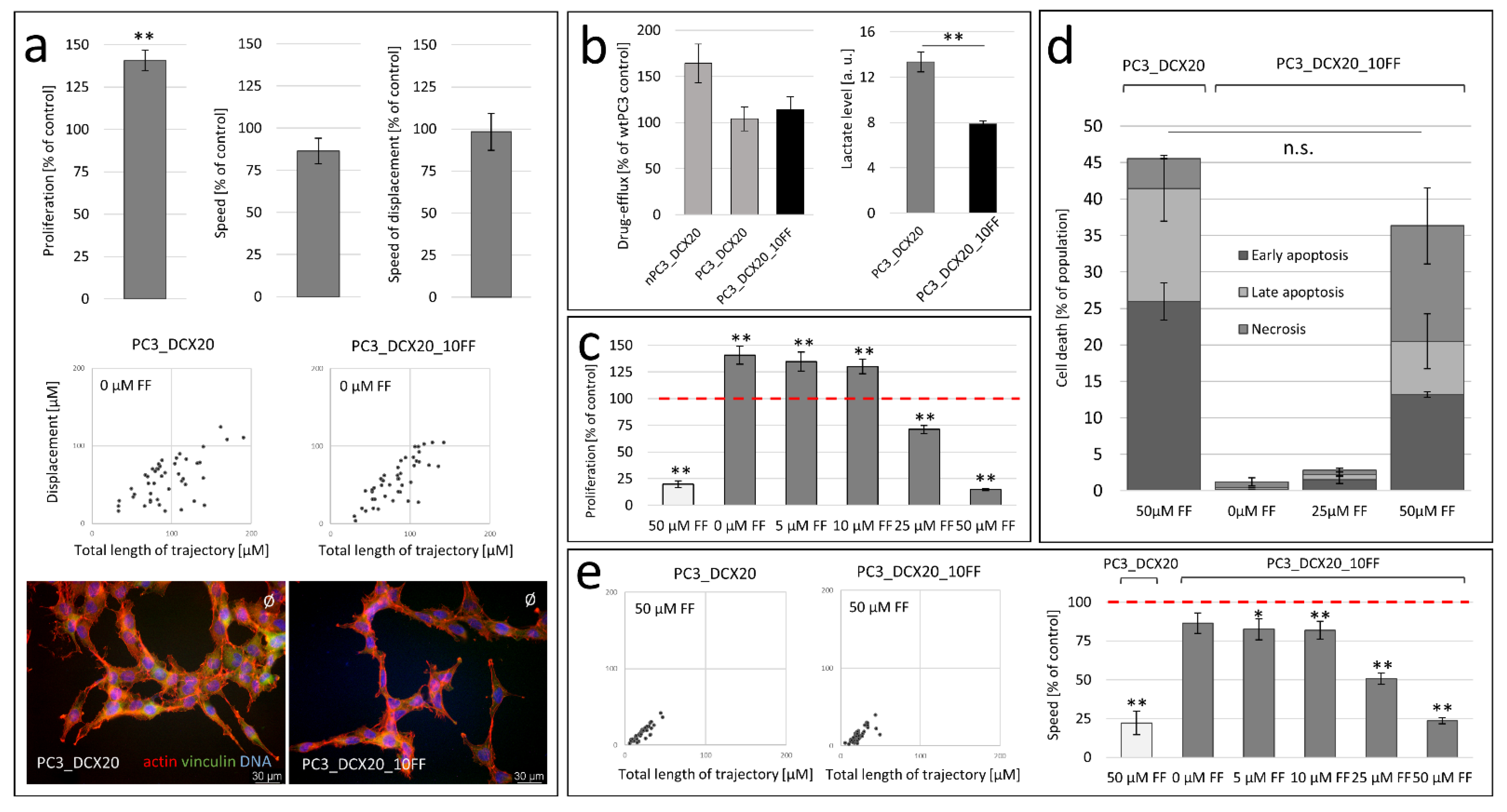
2.2. FF Sensitivity of PC3_DCX20 Cells
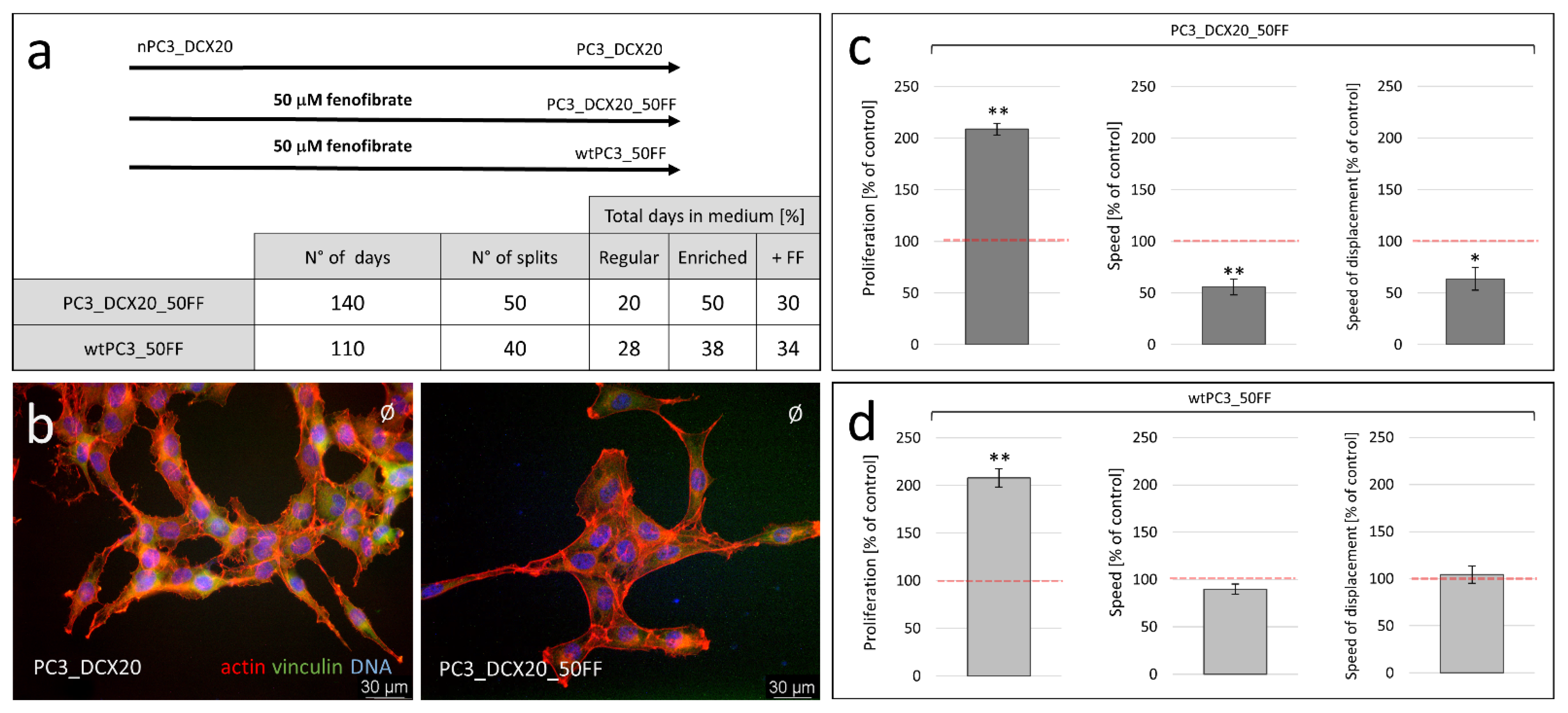
2.3. Long-Term Fenofibrate Treatment Induces Phenotypic Microevolution of PC3 Cells
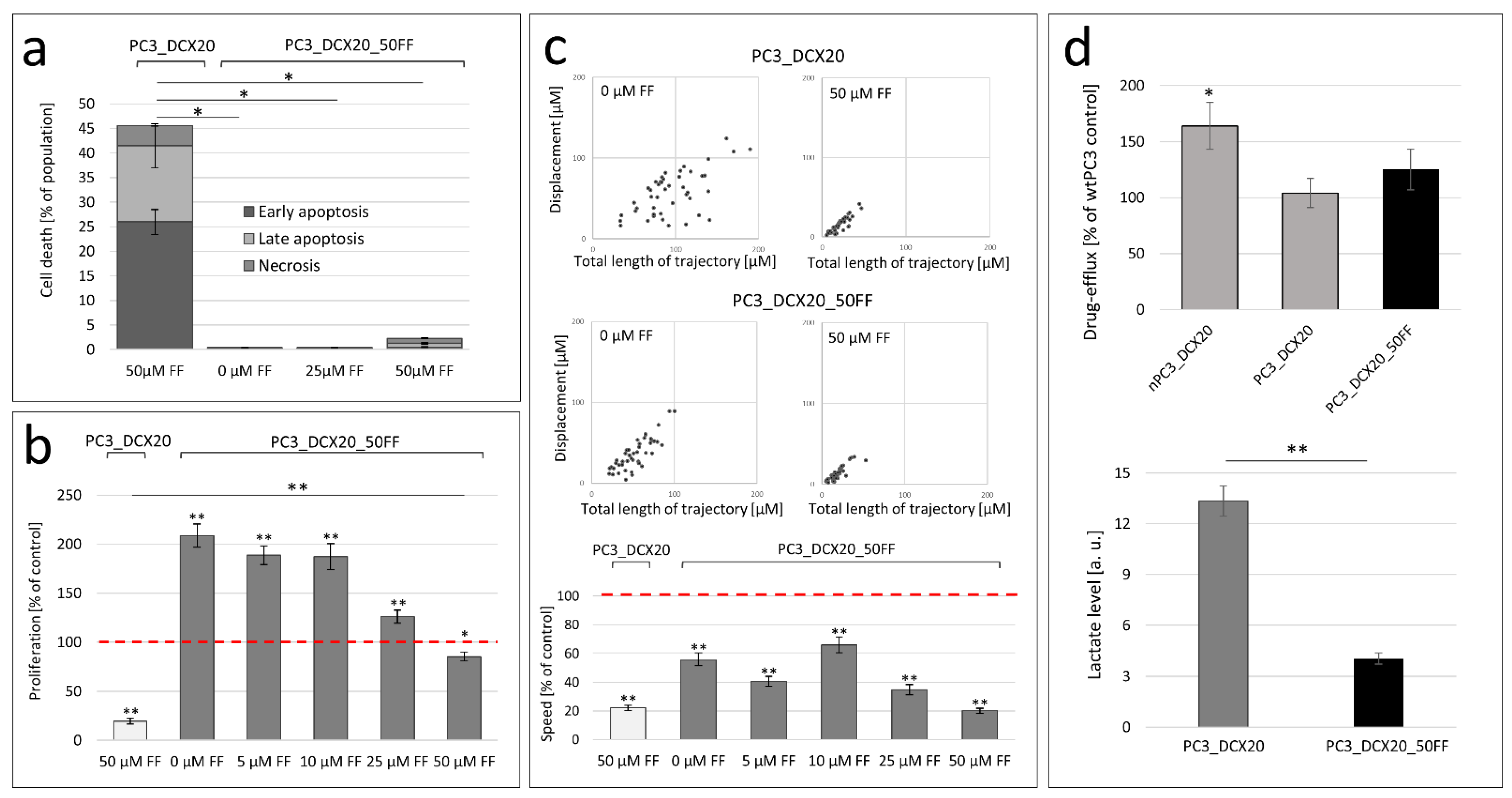
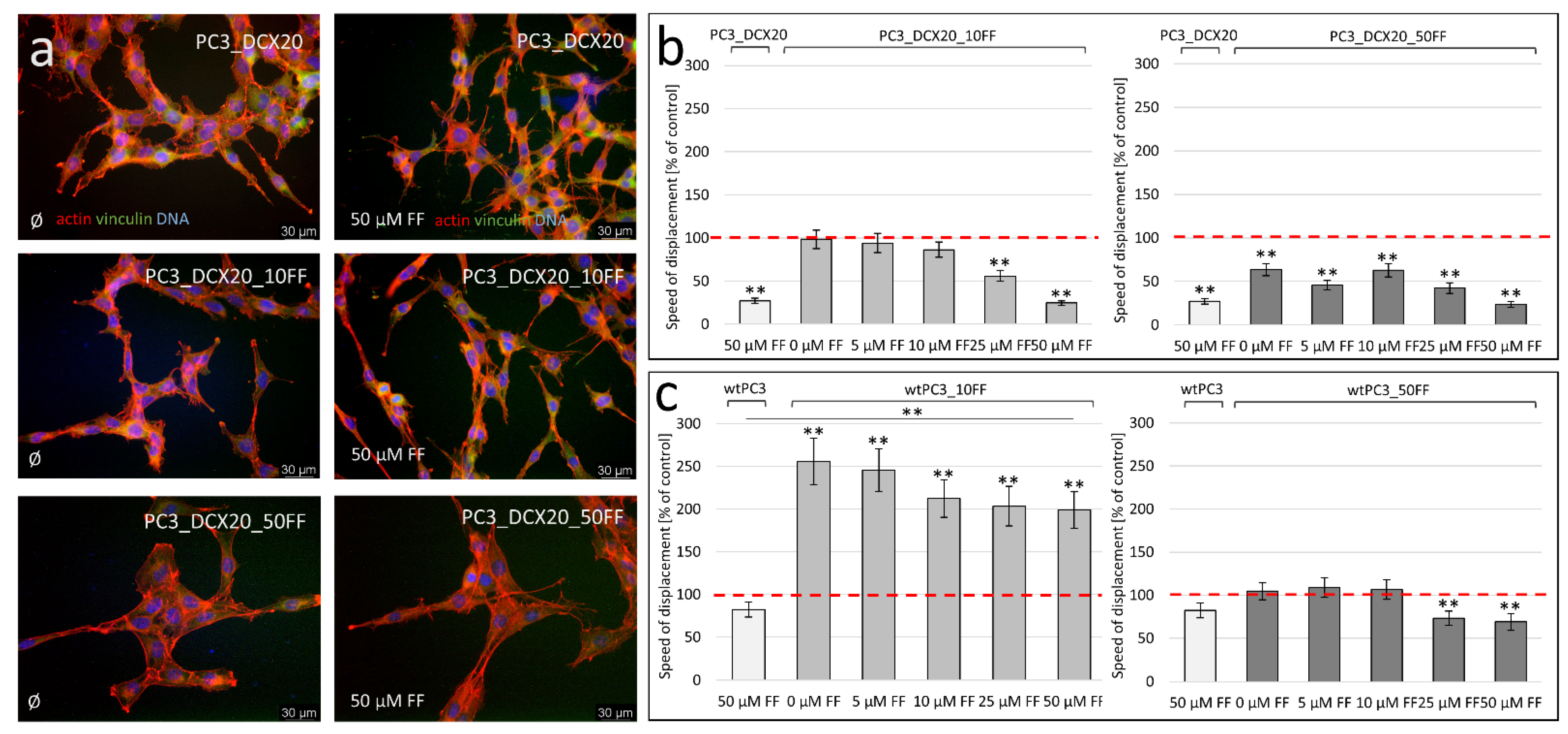
2.4. PC3_DCX20_50FF Cells Display the FF-Resistant Phenotype
2.5. Fenofibrate Bioavailability Affects PC3 Microevolution Pattern
2.6. Long-Term FF Treatment Does Not Prompt the Invasiveness of PC3 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Cultures
4.2. Proliferation and Apoptosis Assay
4.3. Cell Motility
4.4. Lactate Production Assay
4.5. Calcein Efflux Assay
4.6. Seahorse
4.7. Immunofluorescence
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Housman, G.; Byler, S.; Heerboth, S.; Lapinska, K.; Longacre, M.; Snyder, N.; Sarkar, S. Drug Resistance in Cancer: An Overview. Cancers 2014, 6, 1769–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Easwaran, H.; Tsai, H.C.; Baylin, S.B. Cancer Epigenetics: Tumor Heterogeneity, Plasticity of Stem-like States, and Drug Resistance. Mol. Cell 2014, 54, 716–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kochanowski, P.; Catapano, J.; Pudełek, M.; Wróbel, T.; Madeja, Z.; Ryszawy, D.; Czyż, J. Temozolomide Induces the Acquisition of Invasive Phenotype by O6-methylguanine-dna Methyltransferase (Mgmt)+ Glioblastoma Cells in a Snail-1/Cx43-dependent Manner. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Song, X.; Yang, Y.; Wan, X.; Alvarez, A.A.; Sastry, N.; Feng, H.; Hu, B.; Cheng, S.Y. Autophagy and Hallmarks of Cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncogen 2018, 23, 247–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, J.M.M.; Towers, C.G.; Thorburn, A. Targeting Autophagy in Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 528–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, M.; Mortezaee, K.; Majidpoor, J. Cancer Stem Cell (CSC) Resistance Drivers. Life Sci. 2019, 234, 116781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakir, B.; Chiarella, A.M.; Pitarresi, J.R.; Rustgi, A.K.; Rustgi, A.K. EMT, MET, Plasticity, and Tumor Metastasis Trends in Cell Biology. Trends Cell Biol. 2020, 30, 764–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoi, N.Y.L.; Eu, J.Q.; Hirpara, J.; Wang, L.; Lim, J.S.J.; Lee, S.C.; Lim, Y.C.; Pervaiz, S.; Goh, B.C.; Wong, A.L.A. Targeting Cell Metabolism as Cancer Therapy. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2020, 32, 285–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuvalov, O.; Daks, A.; Fedorova, O.; Petukhov, A.; Barlev, N. Linking Metabolic Reprogramming, Plasticity and Tumor Progression. Cancers 2021, 13, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, X.; Wang, G.; Zhou, H.; Zheng, Z.; Fu, Y.; Cai, L. Anticancer Properties of Fenofibrate: A Repurposing Use. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 1527–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeage, K.; Keating, G.M.; Bhatnagar, D.; Elam, M.B.; Farnier, M.; Mohiuddin, S.M. Fenofibrate: A Review of Its Use in Dyslipidaemia. Drugs 2011, 71, 1917–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botta, M.; Audano, M.; Sahebkar, A.; Sirtori, C.R.; Mitro, N.; Ruscica, M. PPAR Agonists and Metabolic Syndrome: An Established Role? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostapanos, M.S.; Kei, A.; Elisaf, M.S. Current Role of Fenofibrate in the Prevention and Management of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. World J. Hepatol. 2013, 5, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, N.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, S.; Wang, Q.; Hu, W.; Zhou, S.; Zhao, L.; Xie, L.; Chen, J.; Wellstein, A.; et al. Fenofibrate Improves Vascular Endothelial Function and Contractility in Diabetic Mice. Redox Biol. 2019, 20, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esenboga, K.; Çiçek, Ö.F.; Oktay, A.A.; Ayral, P.A.; Gürlek, A. Effect of Fenofibrate on Serum Nitric Oxide Levels in Patients with Hypertriglyceridemia. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2019, 28, 931–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cheng, Y.; Gu, J.; Wang, S.; Zhou, S.; Wang, Y.; Tan, Y.; Feng, W.; Fu, Y.; Mellen, N.; et al. Fenofibrate Increases Cardiac Autophagy via FGF21/SIRT1 and Prevents Fibrosis and Inflammation in the Hearts of Type 1 Diabetic Mice. Clin. Sci. 2016, 130, 625–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Haggar, S.M.; Mostafa, T.M. Comparative Clinical Study between the Effect of Fenofibrate Alone and Its Combination with Pentoxifylline on Biochemical Parameters and Liver Stiffness in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Hepatol. Int. 2015, 9, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaribeygi, H.; Mohammadi, M.T.; Jamialahmadi, T.; Sahebkar, A. PPAR-alpha Agonist Fenofibrate Ameliorates Oxidative Stress in Testicular Tissue of Diabetic Rats. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 2020, 30, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enright, J.M.; Zhang, S.; Thebeau, C.; Siebert, E.; Jin, A.; Gadiraju, V.; Zhang, X.; Chen, S.; Semenkovich, C.F.; Rajagopal, R. Fenofibrate Reduces the Severity of Neuroretinopathy in a Type 2 Model of Diabetes without Inducing Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Alpha-Dependent Retinal Gene Expression. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilk, A.; Wyczechowska, D.; Zapata, A.; Dean, M.; Mullinax, J.; Marrero, L.; Parsons, C.; Peruzzi, F.; Culicchia, F.; Ochoa, A.; et al. Molecular Mechanisms of Fenofibrate-Induced Metabolic Catastrophe and Glioblastoma Cell Death. Mol. Cell Biol. 2015, 35, 182–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panigrahy, D.; Kaipainen, A.; Huang, S.; Butterfield, C.E.; Barnés, C.M.; Fannon, M.; Laforme, A.M.; Chaponis, D.M.; Folkman, J.; Kieran, M.W. PPARα Agonist Fenofibrate Suppresses Tumor Growth through Direct and Indirect Angiogenesis Inhibition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 985–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, T.; Zhao, F.; Xuan, Q.; Shen, Z.; Xiao, J.; Shen, Q. Fenofibrate Inhibits the Growth of Prostate Cancer through Regulating Autophagy and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 503, 2685–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, N.; Wagner, K.D. PPAR Beta/Delta and the Hallmarks of Cancer. Cells 2020, 9, 1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wybieralska, E.; Szpak, K.; Górecki, A.; Bonarek, P.; Miȩkus, K.; Drukała, J.; Majka, M.; Reiss, K.; Madeja, Z.; Czyz, J. Fenofibrate Attenuates Contact-Stimulated Cell Motility and Gap Junctional Coupling in DU-145 Human Prostate Cancer Cell Populations. Oncol. Rep. 2011, 26, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piwowarczyk, K.; Wybieralska, E.; Baran, J.; Borowczyk, J.; Rybak, P.; Kosińska, M.; Włodarczyk, A.J.; Michalik, M.; Siedlar, M.; Madeja, Z.; et al. Fenofibrate Enhances Barrier Function of Endothelial Continuum within the Metastatic Niche of Prostate Cancer Cells. Exp. Opin. Targets 2015, 19, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luty, M.; Piwowarczyk, K.; Łabędź-Masłowska, A.; Wróbel, T.; Szczygieł, M.; Catapano, J.; Drabik, G.; Ryszawy, D.; Kędracka-Krok, S.; Madeja, Z.; et al. Fenofibrate Augments the Sensitivity of Drug-Resistant Prostate Cancer Cells to Docetaxel. Cancers 2019, 11, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hönigova, K.; Navratil, J.; Peltanova, B.; Polanska, H.H.; Raudenska, M.; Masarik, M. Metabolic Tricks of Cancer Cells. Biochim Biophys. Acta-Rev. Cancer 2022, 1877, 188705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirpara, J.; Eu, J.Q.; Tan, J.K.M.; Wong, A.L.; Clement, M.V.; Kong, L.R.; Ohi, N.; Tsunoda, T.; Qu, J.; Goh, B.C.; et al. Metabolic Reprogramming of Oncogene-Addicted Cancer Cells to OXPHOS as a Mechanism of Drug Resistance. Redox Biol. 2019, 25, 101076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ippolito, L.; Marini, A.; Cavallini, L.; Morandi, A.; Pietrovito, L.; Pintus, G.; Giannoni, E.; Schrader, T.; Puhr, M.; Chiarugi, P.; et al. Metabolic Shift toward Oxidative Phosphorylation in Docetaxel Resistant Prostate Cancer Cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 61890–61904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wróbel, T.; Luty, M.; Catapano, J.; Karnas, E.; Szczygieł, M.; Piwowarczyk, K.; Ryszawy, D.; Drabik, G.; Zuba-Surma, E.; Siedlar, M.; et al. CD44+ Cells Determine Fenofibrate-Induced Microevolution of Drug-Resistance in Prostate Cancer Cell Populations. Stem Cells 2020, 38, 1544–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, N.W.; Tsai, M.H.; Lin, C.; Hsu, H.T.; Chu, P.Y.; Yeh, C.M.; Chiu, C.F.; Yeh, K.T. Fenofibrate Exhibits a High Potential to Suppress the Formation of Squamous Cell Carcinoma in an Oral-Specific 4-Nitroquinoline 1-Oxide/Arecoline Mouse Model. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2011, 1812, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbanska, K.; Pannizzo, P.; Grabacka, M.; Croul, S.; del Valle, L.; Khalili, K.; Reiss, K. Activation of PPARα Inhibits IGF-I-Mediated Growth and Survival. Responses in Medulloblastoma Cell Lines. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 123, 1015–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabacka, M.; Placha, W.; Plonka, P.M.; Pajak, S.; Urbanska, K.; Laidler, P.; Slominski, A. Inhibition of Melanoma Metastases by Fenofibrate. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2004, 296, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piwowarczyk, K.; Kwiecień, E.; Sośniak, J.; Zimoląg, E.; Guzik, E.; Sroka, J.; Madeja, Z.; Czyż, J. Fenofibrate Interferes with the Diapedesis of Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells through the Interference with Cx43/EGF-Dependent Intercellular Signaling. Cancers 2018, 10, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, C.C.; Gilan, O. Principles and Mechanisms of Non-Genetic Resistance in Cancer. Brit. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalano, A.; Iacopetta, D.; Ceramella, J.; Scumaci, D.; Giuzio, F.; Saturnino, C.; Aquaro, S.; Rosano, C.; Sinicropi, M.S. Multidrug Resistance (MDR): A Widespread Phenomenon in Pharmacological Therapies. Molecules 2022, 27, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vendramin, R.; Litchfield, K.; Swanton, C. Cancer Evolution: Darwin and Beyond. EMBO J. 2021, 40, e108389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, A.; De, S. Drivers of Dynamic Intratumor Heterogeneity and Phenotypic Plasticity. Am. J. Phys. Cell Phys. 2021, 320, C750–C760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, B.; Zhao, K. The Epigenetic Basis of Cellular Heterogeneity. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2021, 22, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staels, B.; Auwerx, J. Regulation of Apo A-I Gene Expression by Fibrates. Atherosclerosis 1998, 137, S19–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, J.C.; Pruimboom-Brees, I.; Francone, O.L.; Amacher, D.E.; Boldt, S.E.; Kerlin, R.L.; Ballinger, W.E. The PPARα Agonists Fenofibrate and CP-778875 Cause Increased β-Oxidation, Leading to Oxidative Injury in Skeletal and Cardiac Muscle in the Rat. Toxicol. Pathol. 2012, 40, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, R.A.K. Fenofibrate Ameliorates Diabetic and Dyslipidemic Profiles in KKAy Mice Partly via Down-Regulation of 11β-HSD1, PEPCK and DGAT2. Eur. J. Pharm. 2009, 607, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drukala, J.; Urbanska, K.; Wilk, A.; Grabacka, M.; Wybieralska, E.; del Valle, L.; Madeja, Z.; Reiss, K. ROS Accumulation and IGF-IR Inhibition Contribute to Fenofibrate/PPARα -Mediated Inhibition of Glioma Cell Motility in Vitro. Mol. Cancer 2010, 9, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamasaki, D.; Kawabe, N.; Nakamura, H.; Tachibana, K.; Ishimoto, K.; Tanaka, T.; Aburatani, H.; Sakai, J.; Hamakubo, T.; Kodama, T.; et al. Fenofibrate Suppresses Growth of the Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell via PPARα-Independent Mechanisms. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 90, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabacka, M.M.; Wilk, A.; Antonczyk, A.; Banks, P.; Walczyk-Tytko, E.; Dean, M.; Pierzchalska, M.; Reiss, K. Fenofibrate Induces Ketone Body Production in Melanoma and Glioblastoma Cells. Front. Endocrinol. 2016, 7, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokil, A.; Sancho, P. Mitochondrial Determinants of Chemoresistance. Cancer Drug Resist. 2019, 2, 634–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Erenpreisa, J.; Sikora, E. Polyploid Giant Cancer Cells: An Emerging New Field of Cancer Biology. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 81, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorolskaya, V.G.; Gureev, A.P.; Shaforostova, E.A.; Laver, D.A.; Popov, V.N. The Fenofibrate Effect on Genotoxicity in Brain and Liver and on the Expression of Genes Regulating Fatty Acids Metabolism of Mice. Biochem. Mosc. Suppl. B Biomed. Chem. 2020, 14, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornu-chagnon, M.C.; Dupont, H.; Edgar, A. Fenofibrate: Metabolism and Species Differences for Peroxisome Proliferation in Cultured Hepatocytes. Toxicol. Sci. 1995, 26, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sroka, J.; Antosik, A.; Czyż, J.; Nalvarte, I.; Olsson, J.M.; Spyrou, G.; Madeja, Z. Overexpression of Thioredoxin Reductase 1 Inhibits Migration of HEK-293 Cells. Biol. Cell 2007, 99, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Warzecha, K.W.; Pudełek, M.; Catapano, J.; Madeja, Z.; Czyż, J. Long-Term Fenofibrate Treatment Stimulates the Phenotypic Microevolution of Prostate Cancer Cells In Vitro. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1320. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15111320
Warzecha KW, Pudełek M, Catapano J, Madeja Z, Czyż J. Long-Term Fenofibrate Treatment Stimulates the Phenotypic Microevolution of Prostate Cancer Cells In Vitro. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(11):1320. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15111320
Chicago/Turabian StyleWarzecha, Karolina W., Maciej Pudełek, Jessica Catapano, Zbigniew Madeja, and Jarosław Czyż. 2022. "Long-Term Fenofibrate Treatment Stimulates the Phenotypic Microevolution of Prostate Cancer Cells In Vitro" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 11: 1320. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15111320
APA StyleWarzecha, K. W., Pudełek, M., Catapano, J., Madeja, Z., & Czyż, J. (2022). Long-Term Fenofibrate Treatment Stimulates the Phenotypic Microevolution of Prostate Cancer Cells In Vitro. Pharmaceuticals, 15(11), 1320. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15111320






