Secukinumab Loss of Efficacy Is Perfectly Counteracted by the Introduction of Combination Therapy (Rescue Therapy): Data from a Multicenter Real-Life Study in a Cohort of Italian Psoriatic Patients That Avoided Secukinumab Switching
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Clinical Characteristics
2.2. Therapeutic Outcomes
- -
- Apremilast and MTX was prescribed for the entire period of the study, according to in-label dose. The combination therapy with apremilast was reserved to patients that failed a TNF-alpha inhibitor and at least an another inhibitor of the IL-17/23 pathway due to the high pharmaco-economical impact and was approved by the Healthcare Commission of the Institute as compassionate use;
- -
- cyclosporin (dose: 3.5 mg/kg/die) was administered for 3 months, stopped for 1 months and then re-administered for 3 months
- -
- NB-UVB sessions were delivered in 3 cycles of 12 sessions each, starting form a minimum of 0,20 Joule and then increasing up to 1,50 J for each session, according to phototype
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design
4.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
4.3. Clinical Evaluation
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yan, B.X.; Chen, X.Y.; Ye, L.R.; Chen, J.Q.; Zheng, M.; Man, X.Y. Cutaneous and Systemic Psoriasis: Classifications and Classification for the Distinction. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 649408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyedmirzaei, H.; Rezaei, N. Cytokine alterations in psoriasis: An updated review. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2021, 17, 1323–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campanati, A.; Marani, A.; Martina, E.; Diotallevi, F.; Radi, G.; Offidani, A. Psoriasis as an Immune-Mediated and Inflammatory Systemic Disease: From Pathophysiology to Novel Therapeutic Approaches. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damiani, G.; Pacifico, A.; Rizzi, M.; Santus, P.; Bridgewood, C.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Adawi, M.; Watad, A. Patients with psoriatic arthritis have higher levels of FeNO than those with only psoriasis, which may reflect a higher prevalence of a subclinical respiratory involvement. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 39, 2981–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, B.G.; Wang, Y.; Ambati, S.; Ma, P.; Meagher, R.B. Airways therapy of obstructive sleep apnea dramatically improves aberrant levels of soluble cytokines involved in autoimmune disease. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 221, 108601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Östling, J.; van Geest, M.; Schofield, J.P.R.; Jevnikar, Z.; Wilson, S.; Ward, J.; Lutter, R.; Shaw, D.E.; Bakke, P.S.; Caruso, M.; et al. IL-17-high asthma with features of a psoriasis immunophenotype. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 144, 1198–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yip, K.H.; Papadopoulos, M.; Pant, H.; Tumes, D.J. The role of invariant T cells in inflammation of the skin and airways. Semin. Immunopathol. 2019, 41, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, A.; Al-Harbi, N.O.; Ansari, M.A.; Al-Harbi, M.M.; El-Sherbeeny, A.M.; Zoheir, K.M.A.; Attia, S.M.; Hafez, M.M.; Al-Shabanah, O.A.; Ahmad, S.F. Psoriatic inflammation enhances allergic airway inflammation through IL-23/STAT3 signaling in a murine model. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 124, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conic, R.R.; Damiani, G.; Schrom, K.P.; Ramser, A.E.; Zheng, C.; Xu, R.; McCormick, T.S.; Cooper, K.D. Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis Cardiovascular Disease Endotypes Identified by Red Blood Cell Distribution Width and Mean Platelet Volume. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groenendyk, J.W.; Rivera, A.S.; Sinha, A.; Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Feinstein, M.J. Changes in proportionate cardiovascular mortality in patients with chronic infectious and inflammatory conditions in the United States, 1999–2018. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Cui, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Shi, Y. Cardiometabolic Comorbidities in Patients with Psoriasis: Focusing on Risk, Biological Therapy, and Pathogenesis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 774808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, H.; Wang, X.; Kvist-Hansen, A.; Krakauer, M.; Gørtz, P.M.; McCauley, B.D.; Skov, L.; Becker, C.; Hansen, P.R. Biomarkers of subclinical atherosclerosis in patients with psoriasis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, C.N.; Neville, S.J.; Sayyouh, M.; Elder, J.T.; Nair, R.P.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; Ma, T.; Kazerooni, E.A.; Rubenfire, M.; Agarwal, P.P. Epicardial adipose tissue volume is greater in men with severe psoriasis, implying an increased cardiovascular disease risk: A cross-sectional study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2021. Available online: http://www.pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34678237/ (accessed on 12 January 2012). [CrossRef]
- Damiani, G.; Franchi, C.; Pigatto, P.; Altomare, A.; Pacifico, A.; Petrou, S.; Leone, S.; Pace, M.C.; Fiore, M. Outcomes assessment of hepatitis C virus-positive psoriatic patients treated using pegylated interferon in combination with ribavirin compared to new Direct-Acting Antiviral agents. World J. Hepatol. 2018, 10, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balak, D.M.W.; Piaserico, S.; Kasujee, I. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) in Patients with Psoriasis: A Review of the Hepatic Effects of Systemic Therapies. Psoriasis 2021, 11, 151–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.R.; Ker, A.; Kao, P.E.; Wei, J.C. Risk of inflammatory bowel disease in patients with psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis initiating interleukin 17 inhibitors. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34463055/ (accessed on 12 January 2012). [CrossRef]
- Letarouilly, J.G.; Pham, T.; Pierache, A.; Acquacalda, É.; Banneville, B.; Barbarot, S.; Baudart, P.; Bauer, É.; Claudepierre, P.; Constantin, A.; et al. New-Onset Inflammatory Bowel Diseases Among IL-17 inhibitors-Treated Patients: Results from The Case-Control MISSIL Study. Rheumatology 2021, keab819. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34730790/ (accessed on 12 January 2012). [CrossRef]
- Enos, C.W.; O’Connell, K.A.; Harrison, R.W.; McLean, R.R.; Dube, B.; Van Voorhees, A.S. Psoriasis Severity, Comorbidities, and Treatment Response Differ among Geographic Regions in the United States. JID Innov. 2021, 1, 100025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiani, G.; Conic, R.R.Z.; Pigatto, P.D.M.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Pacifico, A.; Malagoli, P. Young Dermatologists Italian Network. From randomized clinical trials to real life data. An Italian clinical experience with ixekizumab and its management. Dermatol. Ther. 2019, 32, e12886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiani, G.; Conic, R.R.Z.; de Vita, V.; Costanzo, A.; Regazzini, R.; Pigatto, P.D.M.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Pacifico, A.; Malagoli, P. When IL-17 inhibitors fail: Real-life evidence to switch from secukinumab to adalimumab or ustekinumab. Dermatol. Ther. 2019, 32, e12793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, A.; Damiani, G.; Ruggeri, R.; Odorici, G.; Farnetani, F.; Pigatto, P.D.M.; Pellacani, G. Switching infliximab in psoriatic patients during COVID-19 pandemics: A real-life retrospective study comparing intra-versus interclass switching strategies. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 34, e15088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, C.; Beauchet, A.; Reguiai, Z.; Severino-Freire, M.; Mazereeuw-Hautier, J.; Bursztejn, A.C.; Barbarot, S.; Hadj-Rabia, S.; Girard, C.; Phan, A.; et al. Switching biologics in children with psoriasis: Results from the BiPe cohort. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2021. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34888920/ (accessed on 7 January 2022). [CrossRef]
- Schmitt-Egenolf, M.; Freilich, J.; Stelmaszuk-Zadykowicz, N.M.; Apol, E.; Hansen, J.B.; Levin, L.Å. Drug Persistence of Biologic Treatments in Psoriasis: A Swedish National Population Study. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 11, 2107–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardona, R.; Pelet Del Toro, N.M.; Michelen-Gómez, E.; Arias-Berrios, G.E.; Martín-García, R.F. Failure of Biologic Therapy in Psoriasis. P. R. Health Sci. J. 2021, 40, 63–67. [Google Scholar]
- Akdogan, N.; Dogan, S.; Bostan, E.; Gulseren, D.; Yalici-Armagan, B.; Elcin, G.; Evans, S.E.; Karaduman, A.; Atakan, N. Age and psoriatic arthritis are important predictors of biologic agent switch in psoriasis. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 1–7. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34519227/ (accessed on 7 January 2022). [CrossRef]
- Gisondi, P.; Altomare, G.; Ayala, F.; Bardazzi, F.; Bianchi, L.; Chiricozzi, A.; Costanzo, A.; Conti, A.; Dapavo, P.; De Simone, C.; et al. Italian guidelines on the systemic treatments of moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2017, 31, 774–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Schoot, L.S.; van der Reek, J.M.P.A. Data-driven prediction of biologic treatment responses in psoriasis: Steps towards precision medicine. Br. J. Dermatol. 2021, 185, 698–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadon, D.R.; Stober, C.; Pennington, S.R.; FitzGerald, O. Applying precision medicine to unmet clinical needs in psoriatic disease. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2020, 16, 609–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, C.; Cordingley, L.; Warren, R.B.; Griffiths, C.E.M. Progress to Date in Advancing Stratified Medicine in Psoriasis. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2020, 21, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corazza, M.; Odorici, G.; Conti, A.; Di Lernia, V.; Motolese, A.; Bardazzi, F.; Di Nuzzo, S.; Monti, A.; Arginelli, F.; Filippi, F.; et al. Dimethyl fumarate treatment for psoriasis in a real-life setting: A multicentric retrospective study. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 34, e15066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timis, T.L.; Florian, I.A.; Vesa, S.C.; Mitrea, D.R.; Orasan, R.I. An updated guide in the management of psoriasis for every practitioner. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2021, 75, e14290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagel, J.; Butler, B.; Nelson, E.; Hetzel, A. A Retrospective Review of Patients’ Response to Biologic Therapy for Psoriasis. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2021, 20, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piaserico, S.; Conti, A.; Messina, F.; Meneguzzo, A.; Odorici, G.; Bellinato, F.; Gisondi, P. Cross-Switch from Etanercept Originator to Biosimilar SB4 and to GP2015 in Patients with Chronic Plaque Psoriasis. BioDrugs 2021, 35, 469–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldman, S.R.; Tian, H.; Wang, X.; Germino, R. Health Care Utilization and Cost Associated with Biologic Treatment Patterns Among Patients with Moderate to Severe Psoriasis: Analyses from a Large U.S. Claims Database. J. Manag. Care Spec. Pharm. 2018, 1–11. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30556761/ (accessed on 7 January 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Körber, A.; Thaçi, D.; von Kiedrowski, R.; Bachhuber, T.; Melzer, N.; Kasparek, T.; Kraehn-Senftleben, G.; Amon, U.; Augustin, M. Secukinumab treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in routine clinical care: Real-life data of prior and concomitant use of psoriasis treatments from the PROSPECT study. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2018, 32, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notario, J.; Deza, G.; Vilarrasa, E.; Valentí, F.; Muñoz, C.; Mollet, J.; Rocamora, V.; Carrascosa, J.M.; Del Alcázar, E.; Alsina, M.; et al. Treatment of patients with plaque psoriasis with secukinumab in a real-life setting: A 52-week, multicenter, retrospective study in Spain. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2018, 30, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwensen, J.F.; Clemmensen, A.; Sand, C.; Gniadecki, R.; Skov, L.; Zachariae, C.; Iversen, L.; Rasmussen, M.; Thomsen, S.F. Effectiveness and safety of secukinumab in 69 patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: A retrospective multicenter study. Dermatol. Ther. 2017, 30, e12550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothstein, B.E.; McQuade, B.; Greb, J.E.; Goldminz, A.M.; Gottlieb, A.B. Apremilast and Secukinumab Combined Therapy in a Patient With Recalcitrant Plaque Psoriasis. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2016, 15, 648–649. [Google Scholar]
- Deodhar, A.; Mease, P.J.; McInnes, I.B.; Baraliakos, X.; Reich, K.; Blauvelt, A.; Leonardi, C.; Porter, B.; Das Gupta, A.; Widmer, A.; et al. Long-term safety of secukinumab in patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis: Integrated pooled clinical trial and post-marketing surveillance data. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2019, 21, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiricozzi, A.; Guttman-Yassky, E.; Suárez-Fariñas, M.; Nograles, K.E.; Tian, S.; Cardinale, I.; Chimenti, S.; Krueger, J.G. Integrative responses to IL-17 and TNF-α in human keratinocytes account for key inflammatory pathogenic circuits in psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibezim, A.; Onah, E.; Dim, E.N.; Ntie-Kang, F. A computational multi-targeting approach for drug repositioning for psoriasis treatment. BMC Complement Med. Ther. 2021, 21, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnano, M.; Loi, C.; Patrizi, A.; Sgubbi, P.; Balestri, R.; Rech, G.; Tasin, L.; Girardelli, C.R.; Conti, A.; Odorici, G.; et al. Secukinumab in multi-failure psoriatic patients: The last hope? J. Dermatol. Treat. 2018, 29, 583–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, A.; Torres, T. The successful treatment with ixekizumab in a multi-failure psoriasis patient. Dermatol. Online J. 2018, 24, 13030/qt2qn1p4bz. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30677837/ (accessed on 7 January 2022). [CrossRef]
- García-Beloso, N.; Altabás-González, I.; Samartín-Ucha, M.; Gayoso-Rey, M.; De Castro-Parga, M.L.; Salgado-Barreira, Á.; Cibeira-Badia, A.; Piñeiro-Corrales, M.G.; González-Vilas, D.; Pego-Reigosa, J.M.; et al. Switching between reference adalimumab and biosimilars in chronic immune-mediated inflammatory diseases: A systematic literature review. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34622969/ (accessed on 7 January 2022). [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Chen, Z.; Bi, X. An Update Review of Biosimilars of Adalimumab in Psoriasis—Bioequivalence and Interchangeability. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2021, 15, 2987–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaba, L.C.; Cardinale, I.; Gilleaudeau, P.; Sullivan-Whalen, M.; Suárez-Fariñas, M.; Fuentes-Duculan, J.; Novitskaya, I.; Khatcherian, A.; Bluth, M.J.; Lowes, M.A.; et al. Amelioration of epidermal hyperplasia by TNF inhibition is associated with reduced Th17 responses. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 3183–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dand, N.; Duckworth, M.; Baudry, D.; Russell, A.; Curtis, C.J.; Lee, S.H.; Evans, I.; Mason, K.J.; Alsharqi, A.; Becher, G.; et al. HLA-C*06:02 genotype is a predictive biomarker of biologic treatment response in psoriasis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 2120–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardazzi, F.; Bigi, L.; Campanati, A.; Conti, A.; Di Lernia, V.; Di Nuzzo, S.; Kaleci, S.; Lasagni, C.; Offidani, A.M.; Giacchetti, A.; et al. Outcome following a short period of adalimumab dose escalation as rescue therapy in psoriatic patients. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2020, 30, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nast, A.; Gisondi, P.; Ormerod, A.D.; Saiag, P.; Smith, C.; Spuls, P.I.; Arenberger, P.; Bachelez, H.; Barker, J.; Dauden, E.; et al. European S3-Guidelines on the systemic treatment of psoriasis vulgaris—Update 2015—Short version—EDF in cooperation with EADV and IPC. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2015, 29, 2277–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.W.; Kim, B.R.; Ohn, J.; Youn, S.W. The Advantage of Cyclosporine A and Methotrexate Rotational Therapy in Long-Term Systemic Treatment for Chronic Plaque Psoriasis in a Real World Practice. Ann. Dermatol. 2017, 29, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissonnette, R.; Luger, T.; Thaci, D.; Toth, D.; Lacombe, A.; Xia, S.; Mazur, R.; Patekar, M.; Charef, P.; Milutinovic, M.; et al. Secukinumab demonstrates high sustained efficacy and a favourable safety profile in patients with moderate-to-severe psoriasis through 5 years of treatment (SCULPTURE Extension Study). J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2018, 32, 1507–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galluzzo, M.; D’Adamio, S.; Silvaggio, D.; Lombardo, P.; Bianchi, L.; Talamonti, M. In which patients the best efficacy of secukinumab? Update of a real-life analysis after 136 weeks of treatment with secukinumab in moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2020, 20, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, A.; Bartelstein, M.K.; Fujiwara, T.; Antonescu, C.R.; Healey, J.H.; Vaynrub, M. Anti-IL17 antibody Secukinumab therapy is associated with ossification in giant cell tumor of bone: A case report of pathologic similarities and therapeutic potential similar to Denosumab. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocic, H.; Damiani, G.; Stamenkovic, B.; Tirant, M.; Jovic, A.; Tiodorovic, D.; Peris, K. Dietary compounds as potential modulators of microRNA expression in psoriasis. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2019, 10, 2040622319864805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhinsa, H.; Wu, N.; Gibbons, M.; Chaudhry, S.B.; Wu, C.; Eyek, P.T.; Powers, J.G. Diet and nutritional behaviors in patients with psoriasis: A cross-sectional study. JAAD Int. 2021, 5, 76–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingkapairoj, K.; Chularojanamontri, L.; Chaiyabutr, C.; Silpa-Archa, N.; Wongpraparut, C.; Bunyaratavej, S. Dietary habits and perceptions of psoriatic patients: Mediterranean versus Asian diets. J. Dermatolog. Treat. 2021, 1–7. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34289800/ (accessed on 7 January 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.; Wu, X.; Santos Rocha, C.; Rolston, M.; Garcia-Melchor, E.; Huynh, M.; Nguyen, M.; Law, T.; Haas, K.N.; Yamada, D.; et al. Short-Term Western Diet Intake Promotes IL-23-Mediated Skin and Joint Inflammation Accompanied by Changes to the Gut Microbiota in Mice. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 141, 1780–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blauvelt, A.; Shi, N.; Burge, R.; Malatestinic, W.N.; Lin, C.Y.; Lew, C.R.; Zimmerman, N.M.; Goldblum, O.M.; Zhu, B.; Murage, M.J. Comparison of real-world treatment patterns among patients with psoriasis prescribed ixekizumab or secukinumab. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 82, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb, A.B.; Wu, J.J.; Grriffiths, C.E.M.; Marfo, K.; Muscianisi, E.; Meng, X.; Frueh, J.; Lebwohl, M. Clinical efficacy and safety of secukinumab in patients with psoriasis and comorbidities: Pooled analysis of 4 phase 3 clinical trials. J. Dermatolog. Treat. 2020, 1–9. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33023357/ (accessed on 7 January 2022). [CrossRef]
- Kostaki, D.; Aquila, E.; Macaluso, L.; Mattozzi, C.; Richetta, A.G. Optimizing Secukinumab Treatment in Psoriasis with Concomitant Methotrexate Administration: Minireview and A Case Report. Case Rep. Dermatol. 2019, 11, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrowietz, U.; de Jong, E.M.; Kragballe, K.; Langley, R.; Nast, A.; Puig, L.; Reich, K.; Schmitt, J.; Warren, R.B. Consensus report on appropriate treatment optimization and transitioning in the management of moderate—Severe plaque psoriasis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2014, 28, 438–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, A.; Lebwohl, M. Secukinumab and apremilast combination therapy for recalcitrant psoriasis. J. Psoriasis Psoriatic Arthritis 2017, 2, 59–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisar, M.K. Combining secukinumab and apremilast to successfully treat refractory psoriatic skin and joint disease: A novel approach. Eur. J. Rheumatol. 2018, 19, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacchelli, L.; Patrizi, A.; Loi, C.; Bardazzi, F. Combination therapy of apremilast and secukinumab in patients with moderate-to-severe, recalcitrant plaque psoriasis. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2019, 44, e243–e244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragazzi, N.L.; Riccò, M.; Pacifico, A.; Malagoli, P.; Kridin, K.; Pigatto, P.; Damiani, G. COVID-19 knowledge prevents biologics discontinuation: Data from an Italian multicenter survey during RED-ZONE declaration. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 33, e13508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byerly, M.J.; Nakonezny, P.A.; Rush, A.J. The Brief Adherence Rating Scale (BARS) validated against electronic monitoring in assessing the antipsychotic medication adherence of outpatients with schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder. Schizophr. Res. 2008, 100, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiani, G.; Pacifico, A.; Russo, F.; Pigatto, P.D.M.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Bonifati, C.; Morrone, A.; Watad, A.; Adawi, M. Use of Secukinumab in a Cohort of Erythrodermic Psoriatic Patients: A Pilot Study. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svanström, C.; Lonne-Rahm, S.B.; Nordlind, K. Psoriasis and alcohol. Psoriasis 2019, 9, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montolio Chiva, L.; Martínez Ferrer, À.; Mateu Puchades, A.; Campos Fernández, C.; Narváez Garcia, J.; Alegre Sancho, J.J. Psoriasis induced by biological therapy. Reumatol. Clin. (Engl. Ed.) 2021, 17, 437–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Yoon, H.Y.; Yee, J.; Kim, M.G.; Gwak, H.S. Antihypertensive drug use and psoriasis: A systematic review, meta- and network meta-analysis. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34611920/ (accessed on 7 January 2022). [CrossRef]
- Damiani, G.; Cazzaniga, S.; Conic, R.R.Z.; Naldi, L.; Psocare Registry Network. Pruritus Characteristics in a Large Italian Cohort of Psoriatic Patients. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2019, 33, 1316–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purzycka-Bohdan, D.; Gleñ, J.; Zabłotna, M.; Nedoszytko, B.; Szczerkowska-Dobosz, A.; Sokołowska-Wojdyło, M.; Rêbała, K.; Nowicki, R.J. Significance of interleukin-31 (IL-31) gene polymorphisms and IL-31 serum level in psoriasis in correlation with pruritus. Postepy Dermatol. Alergol. 2021, 38, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hölsken, S.; Krefting, F.; Schedlowski, M.; Sondermann, W. Expectation-induced enhancement of pain, itch and quality of life in psoriasis patients: Study protocol of a randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e047099. [Google Scholar]
- Fredriksson, T.; Pettersson, U. Severe psoriasis—Oral therapy with a new retinoid. Dermatologica 1978, 157, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, G.H.; Buch, M.H.; Lawson, C.; Waxman, R.; Helliwell, P.S. Evaluation of an existing screening tool for psoriatic arthritis in people with psoriasis and the development of a new instrument: The Psoriasis Epidemiology Screening Tool (PEST) questionnaire. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2009, 27, 469–474. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen, C.B.; McHorney, C.A.; Larsen, L.S.; Lophaven, K.W.; Moeller, A.H.; Reaney, M. Reliability and validity of the Psoriasis Itch Visual Analog Scale in psoriasis vulgaris. J. Dermatolog. Treat. 2017, 28, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlay, A.Y.; Khan, G.K. Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI): A simple practical measure for routine clinical use. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 1994, 19, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odorici, G.; Di Nuzzo, S.; Corazza, M.; Bardazzi, F.; Cortelazzi, C.; Sacchelli, L.; Conti, A. Phototherapy: The patients’ point of view. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2021, 37, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, F.; Vispi, M.; Sirna, R.; Mancini, V.; Bagnoni, G.; Bartoli, L.; Bellini, M.; Brandini, L.; Caproni, M.; Castelli, A.; et al. Tuscan consensus on the use of UVBnb phototherapy in the treatment of psoriasis. G. Ital. Dermatol. Venereol. 2019, 154, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacifico, A.; Conic, R.R.Z.; Cristaudo, A.; Garbarino, S.; Ardigò, M.; Morrone, A.; Iacovelli, P.; di Gregorio, S.; Pigatto, P.D.M.; Grada, A.; et al. Diet-Related Phototoxic Reactions in Psoriatic Patients Undergoing Phototherapy: Results from a Multicenter Prospective Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacifico, A.; Damiani, G.; Iacovelli, P.; Conic, R.R.Z.; Scarabello, A.; Filoni, A.; Malagoli, P.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Pigatto, P.D.M.; Morrone, A. Photoadaptation to ultraviolet B TL01 in psoriatic patients. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34, 1750–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Secukinumab + Apremilast (n = 7) | Secukinumab + Cyclosporin (n = 11) | Secukinumab + Methotrexate (n = 15) | Secukinumab + NB-UVB (n = 7) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (median [IQR], years old) | 42.0 [37.0–47.5] | 42.0 [33.5–51.5] | 48.0 [38.5–50.0] | 49.0 [41.0–53,5] |
| Gender, M/F (n) | 5/2 | 7/4 | 9/6 | 3/4 |
| Family history of psoriasis (n (%)) | 4 (57.1) | 7 (63.6) | 6 (40.0) | 3 (42.9) |
| Psoriatic Arthritis (n (%)) | 7 (100.0) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (13.3) | 0 (0.0) |
| Comorbidities (n, (%)) | ||||
| - Hypertension | 2 (28.6) | 0 (0.0) | 4 (26.7) | 6 (85.7) |
| - COPD | 0 (0.0) | 2 (18.2) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (42.9) |
| - Diabetes | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (13.3) | 1 (14.3) |
| - Uveitis | 0 (0.0) | 1 (9.1) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Biologics naive (n (%)) | 3 (42.9) | 5 (45.5) | 7 (46.7) | 4 (57.1) |
| Secukinumab monotherapy longevity (months, median [IQR]) | 9 [8.5–10.5] | 9 [7.5–11.0] | 11 [9.5–13.0] | 12 [10.0–13.0] |
| Combination therapy duration, (months, median [IQR]) | 12 months | 3+ 3 months | 12 months | 3 cycles of 12 phototherapy sessions each |
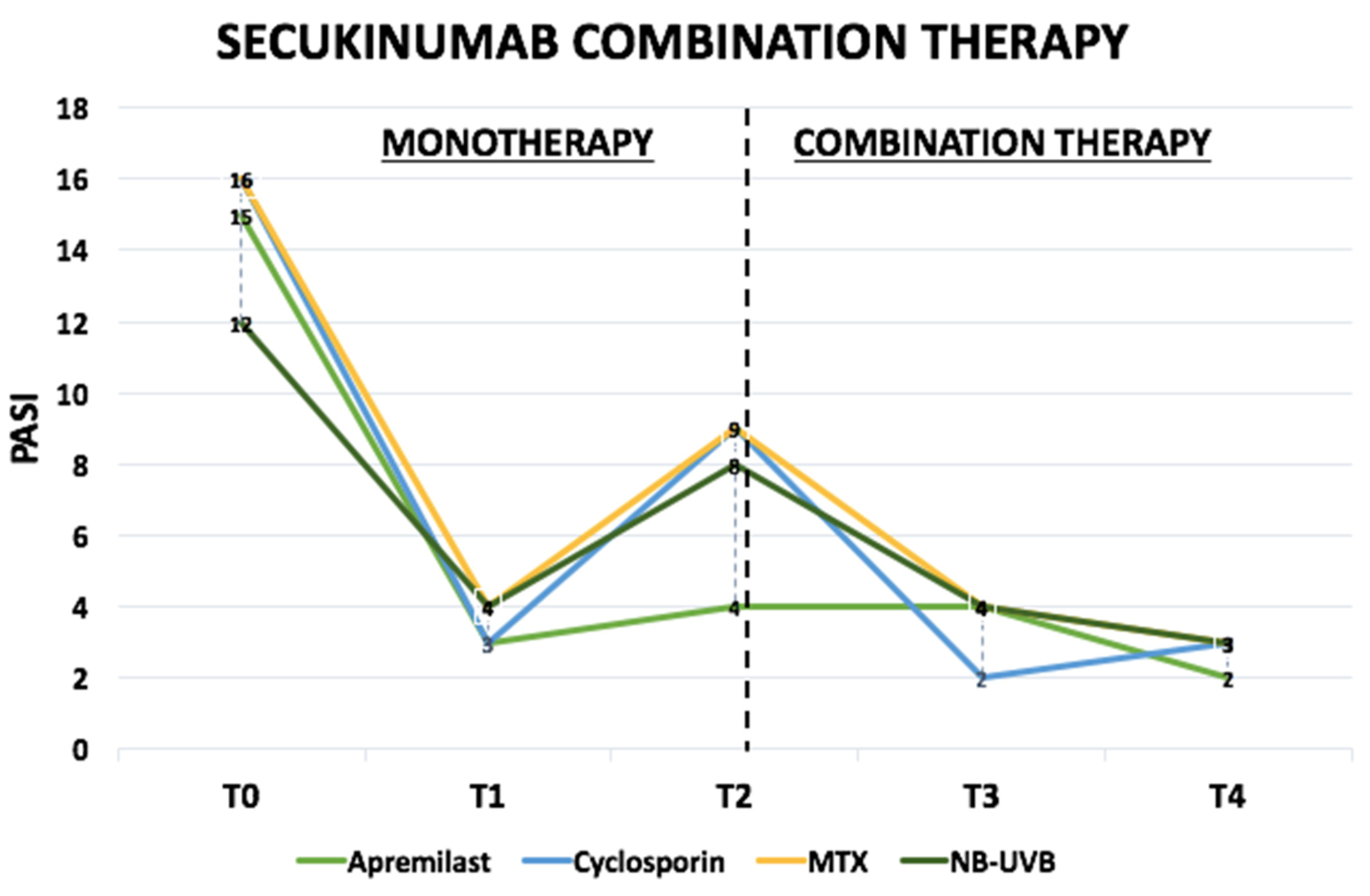
| PASI (median [IQR]) | ||||
| ➣ T0 | 15 [14.0–17.0] | 16 [15.0–20.5] | 16 [13.5–18.0] | 12 [12.0–13.5] |
| ➣ T1 | 3 [2.0–4.0] | 3 [3.0–4.0] | 4 [3.0–5.0] | 4 [3.0–4.5] |
| ➣ T2 | 4 [2.5–5.0] | 9 [8.0–9.5] | 9 [8.0–10.0] | 8 [7.5–9.0] |
| ➣ T3 | 4 [2.5–4.0] | 2 [2.0–3.0] | 4 [3.0–5.0] | 4 [3.0–4.0] |
| ➣ T4 | 2 [0.5–2.0] | 3 [2.0–3.5] | 3 [3.0–3.5] | 3 [2.0–4.0] |
| DLQI (median [IQR]) | ||||
| ➣ T2 | 16 [14.0–17.0] | 14 [13.0–15.0] | 12 [11.5–13.5] | 12 [10.5–12.5] |
| ➣ T4 | 2 [2.0–3.0] | 2 [1.5–3.0] | 3 [2.0–3.5] | 3 [2.5–4.5] |
| PASI 75 (n, (%)) | ||||
| ➣ T3 | 5 (71.4) | 8 (72.7) | 8 (53.3) | 3 (42.9) |
| ➣ T4 | 4 (57.1) | 9 (81.8) | 13 (86.7) | 4 (57.1) |
| PASI 90 (n, (%)) | ||||
| ➣ T3 | 1 (14.3) | 2 (18.2) | 1 (6.7) | 0 (0.0) |
| ➣ T4 | 1 (14.3) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| PASI 100 (n, (%)) | ||||
| ➣ T3 | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| ➣ T4 | 2 (28.6) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Side-effects (n, (%)) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Damiani, G.; Odorici, G.; Pacifico, A.; Morrone, A.; Conic, R.R.Z.; Davidson, T.; Watad, A.; Pigatto, P.D.M.; Colombo, D.; Malagoli, P.; et al. Secukinumab Loss of Efficacy Is Perfectly Counteracted by the Introduction of Combination Therapy (Rescue Therapy): Data from a Multicenter Real-Life Study in a Cohort of Italian Psoriatic Patients That Avoided Secukinumab Switching. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15010095
Damiani G, Odorici G, Pacifico A, Morrone A, Conic RRZ, Davidson T, Watad A, Pigatto PDM, Colombo D, Malagoli P, et al. Secukinumab Loss of Efficacy Is Perfectly Counteracted by the Introduction of Combination Therapy (Rescue Therapy): Data from a Multicenter Real-Life Study in a Cohort of Italian Psoriatic Patients That Avoided Secukinumab Switching. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(1):95. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15010095
Chicago/Turabian StyleDamiani, Giovanni, Giulia Odorici, Alessia Pacifico, Aldo Morrone, Rosalynn R. Z. Conic, Tima Davidson, Abdulla Watad, Paolo D. M. Pigatto, Delia Colombo, Piergiorgio Malagoli, and et al. 2022. "Secukinumab Loss of Efficacy Is Perfectly Counteracted by the Introduction of Combination Therapy (Rescue Therapy): Data from a Multicenter Real-Life Study in a Cohort of Italian Psoriatic Patients That Avoided Secukinumab Switching" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 1: 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15010095
APA StyleDamiani, G., Odorici, G., Pacifico, A., Morrone, A., Conic, R. R. Z., Davidson, T., Watad, A., Pigatto, P. D. M., Colombo, D., Malagoli, P., & Fiore, M. (2022). Secukinumab Loss of Efficacy Is Perfectly Counteracted by the Introduction of Combination Therapy (Rescue Therapy): Data from a Multicenter Real-Life Study in a Cohort of Italian Psoriatic Patients That Avoided Secukinumab Switching. Pharmaceuticals, 15(1), 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15010095









