Polydatin, a Glycoside of Resveratrol, Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits Metastasis Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells In Vitro
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
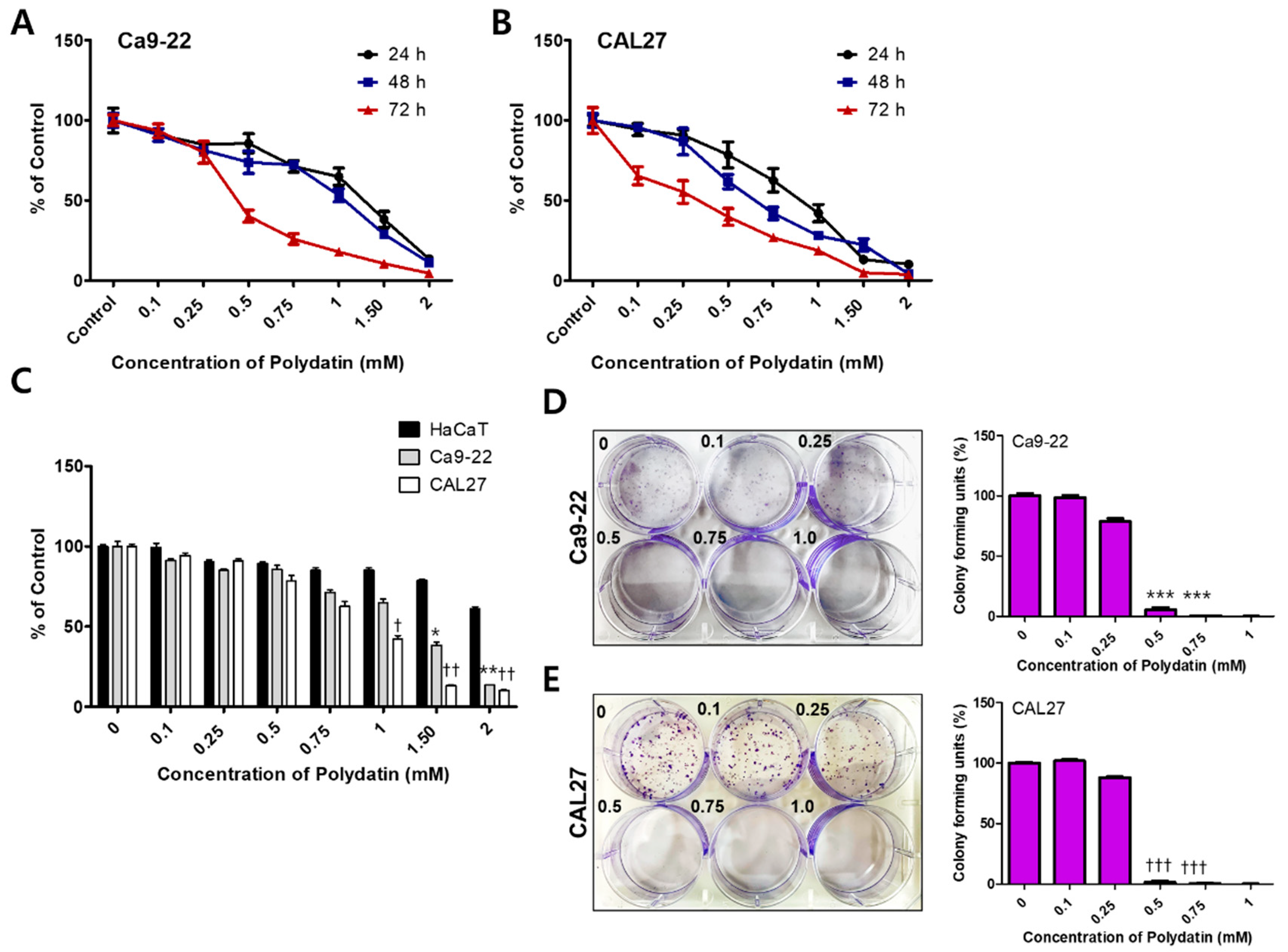
2.1. Polydatin Inhibits the Viability and Proliferation of OSCC Cells
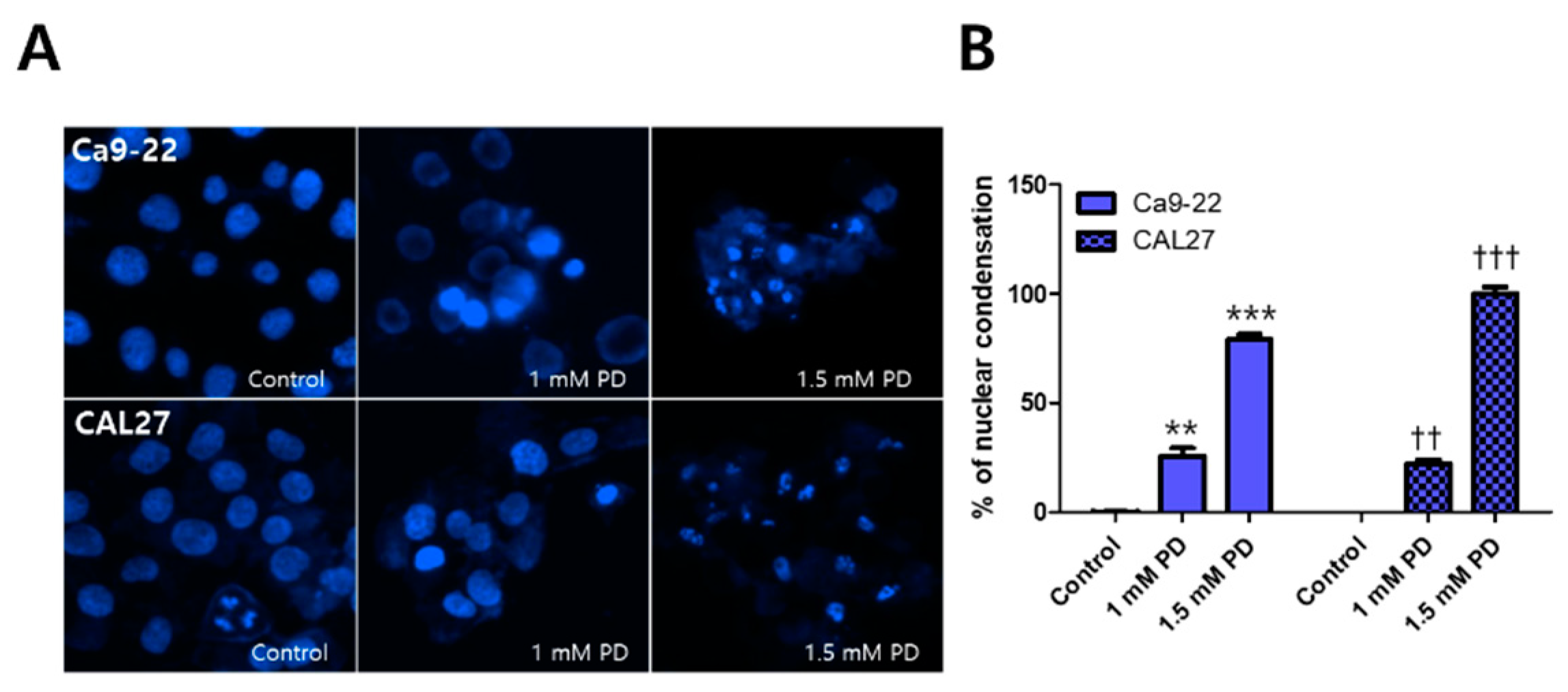
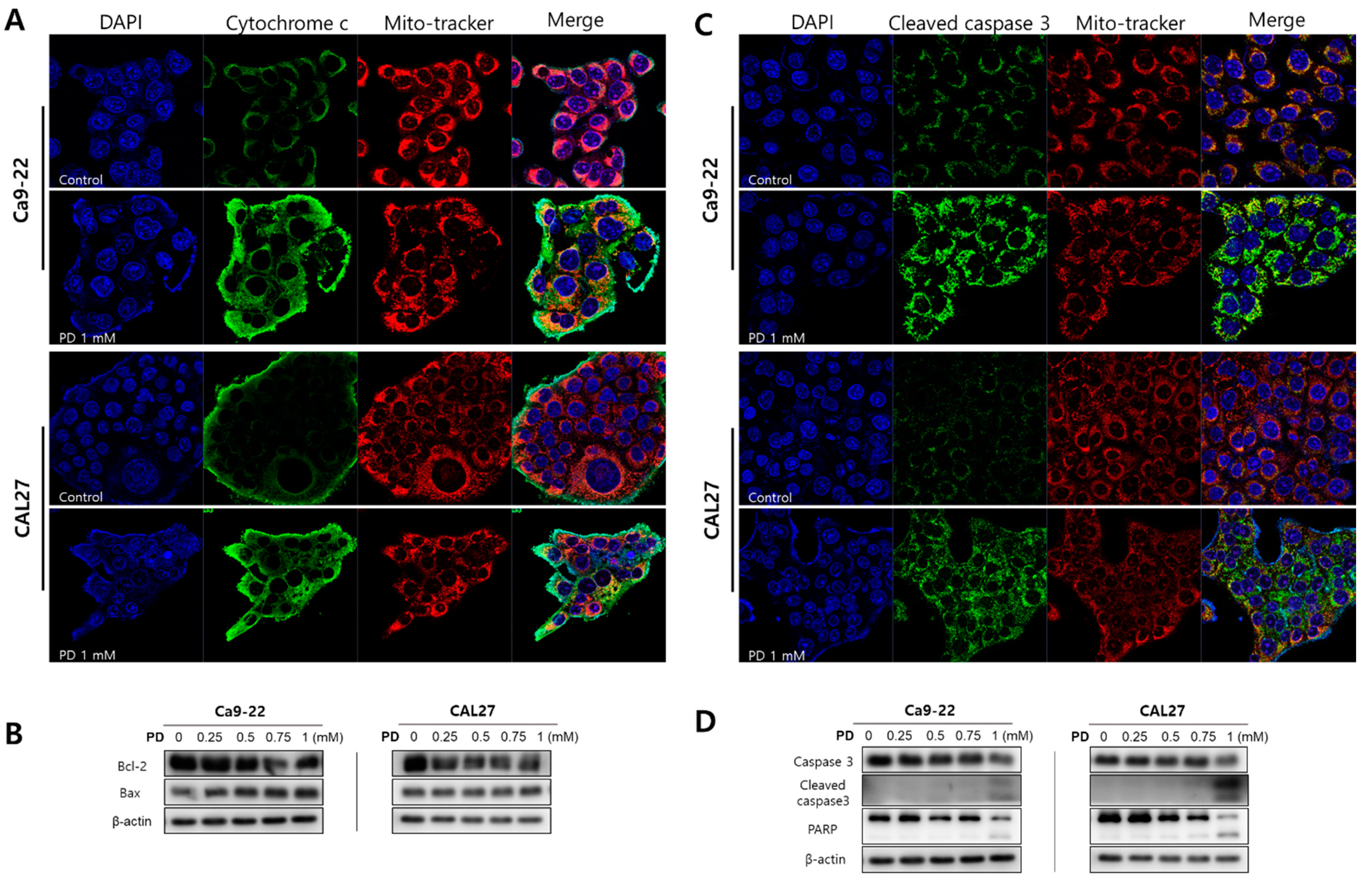
2.2. Polydatin Induces Apoptosis of OSCC Cells through the Mitochondrial Intrinsic Pathway
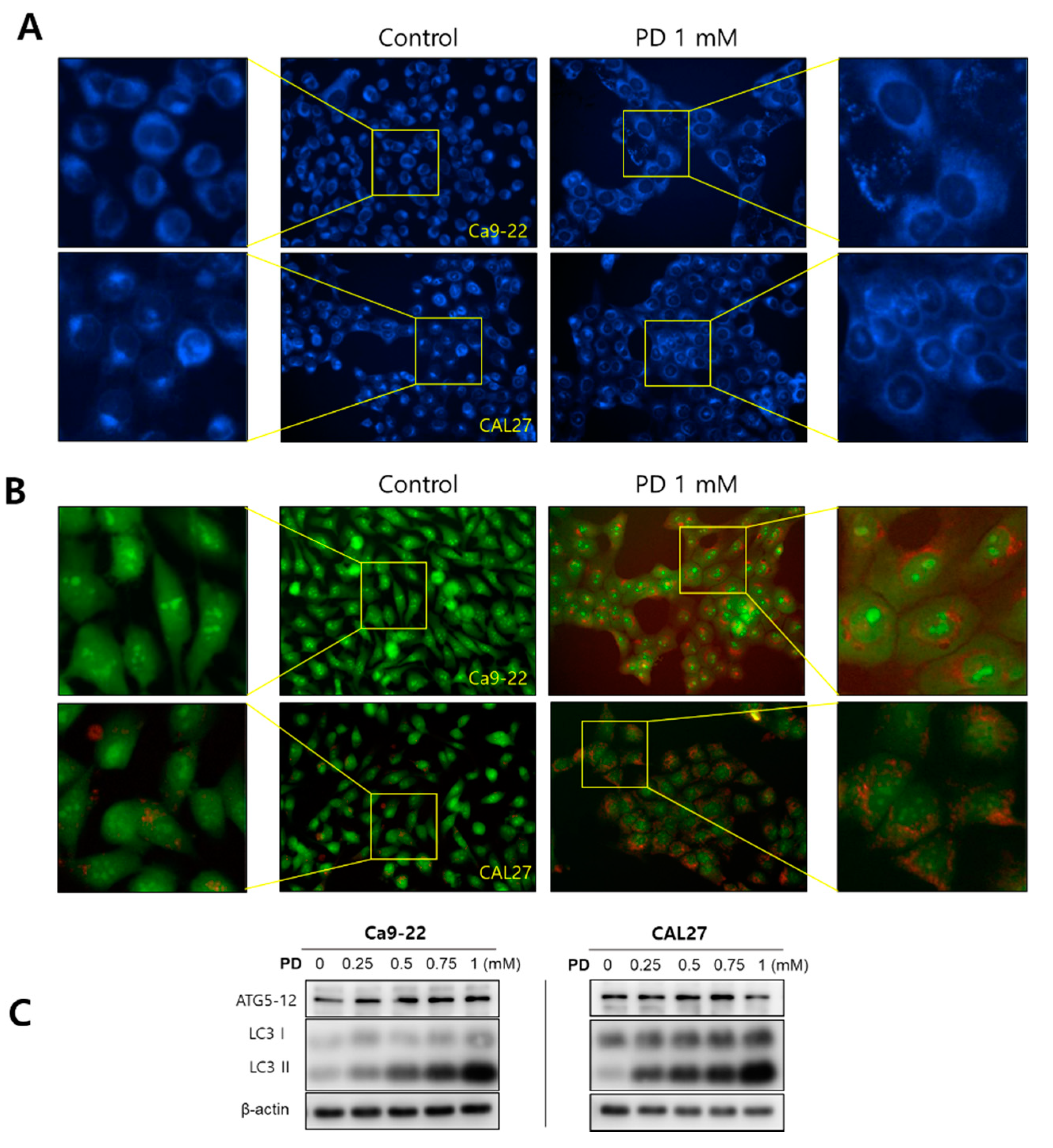
2.3. Polydatin Induces Autophagy in OSCC Cells
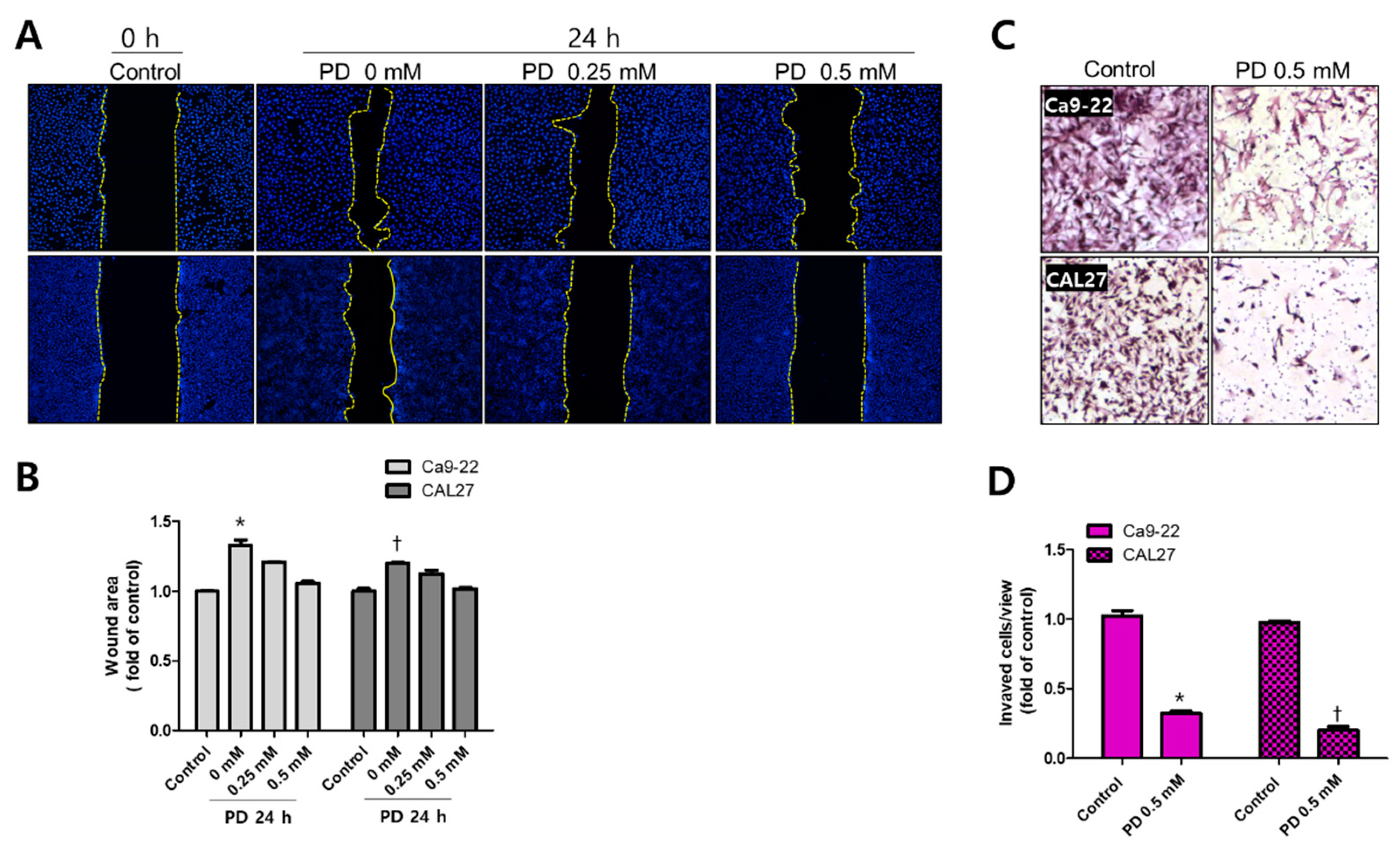
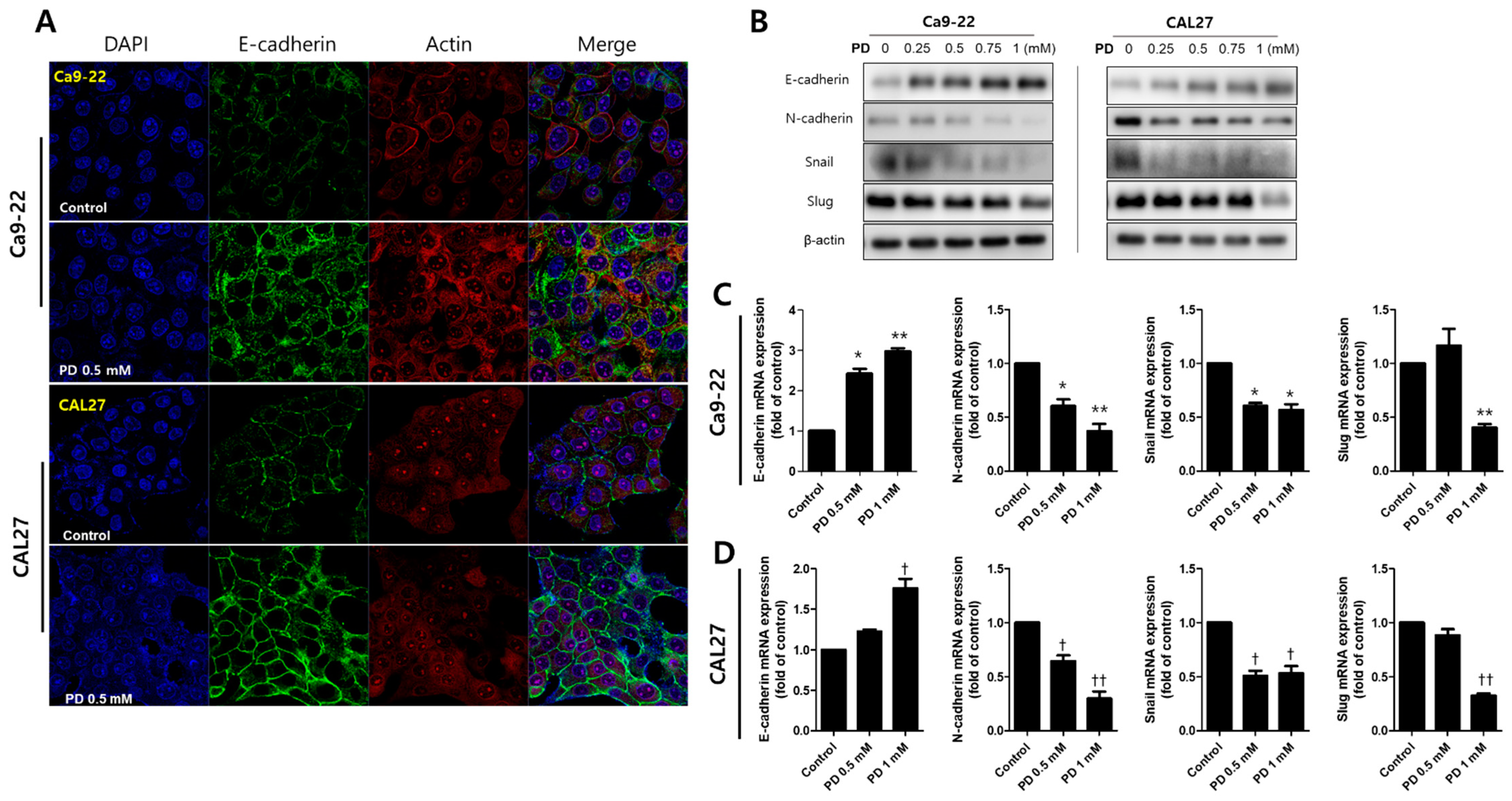
2.4. Polydatin Prevents EMT in OSCC Cells
3. Discussion
3.1. Toxicity of Polydatin for Cancers
3.2. Induction of Apoptosis by Polydatin
3.3. Inhibiton of EMT by Polydatin
3.4. Proposal of a Therapeutic Approach Using Polydatin in OSCC
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Polydatin Treatment
4.2. MTT Assay
4.3. Colony Formation Assay
4.4. Hoechst 33342 Staining
4.5. Immunofluorescence Staining
4.6. Arcridin Orange (AO) and Monodansylcadaverine (MDC) Staining
4.7. Wound-Healing Assay
4.8. Cell Invasion Assay
4.9. Western Blot Assay
4.10. RNA Isolation and RT-qPCR
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hassanpour, S.H.; Dehghani, M. Review of cancer from perspective of molecular. J. Cancer Res. Pract. 2017, 4, 127–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabadi, H.; Hosseini, O.; Damavandi Kamali, K.; Jazayeri Shoushtari, F.; Rashedi, M.; Haghi-Aminjan, H.; Saravanan, M. Emerging theranostic silver nanomaterials to combat lung cancer: A systematic review. J. Clust. Sci. 2020, 31, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.W.; Chin, H.K.; Lee, S.L.; Chiu, C.F.; Chung, J.G.; Lin, Z.Y.; Wu, C.Y.; Liu, Y.C.; Hsiao, Y.T.; Feng, C.H. Ursolic acid induces apoptosis and autophagy in oral cancer cells. Environ. Toxicol. 2019, 34, 983–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzistefanou, I.; Lubek, J.; Markou, K.; Ord, R.A. The role of perineural invasion in treatment decisions for oral cancer patients: A review of the literature. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 45, 821–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilleron, S.; Sarfati, D.; Janssen-Heijnen, M.; Vignat, J.; Ferlay, J.; Bray, F.; Soerjomataram, I. Global cancer incidence in older adults, 2012 and 2035: A population-based study. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, J.; Abbasi, B.A.; Mahmood, T.; Kanwal, S.; Ali, B.; Shah, S.A.; Khalil, A.T. Plant-derived anticancer agents: A green anticancer approach. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2017, 7, 1129–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zeng, Y.-N.; Zhang, K.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Y.-Y.; Li, G.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Zhang, M.; Lai, F.; Wang, J.-B.; et al. Polydatin increases radiosensitivity by inducing apoptosis of stem cells in colorectal cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 15, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Tao, J.; Zhong, F.; Jiao, Y.; Xu, J.; Shen, Q.; Wang, H.; Fan, S.; Zhang, Y. Polydatin down-regulates the phosphorylation level of Creb and induces apoptosis in human breast cancer cell. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Arcy, M.S. Cell death: A review of the major forms of apoptosis, necrosis and autophagy. Cell Biol. Int. 2019, 43, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sas, K.; Szabó, E.; Vécsei, L. Mitochondria, oxidative stress and the kynurenine system, with a focus on ageing and neuroprotection. Molecules 2018, 23, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kepp, O.; Galluzzi, L.; Lipinski, M.; Yuan, J.; Kroemer, G. Cell death assays for drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 10, 221–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.N.; Bhowmick, N.A. Role of EMT in metastasis and therapy resistance. J. Clin. Med. 2016, 5, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Micalizzi, D.S.; Farabaugh, S.M.; Ford, H.L. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer: Parallels between normal development and tumor progression. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia 2010, 15, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dissanayaka, W.L.; Pitiyage, G.; Kumarasiri, P.V.R.; Liyanage, R.L.P.R.; Dias, K.D.; Tilakaratne, W.M. Clinical and histopathologic parameters in survival of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2012, 113, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cory, S.; Adams, J.M. Killing cancer cells by flipping the Bcl-2/Bax switch. Cancer Cell 2005, 8, 5–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarah, P.; David, M. Mechanisms of anticancer drugs. In Scott-Brown’s Otorhinolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery; CRC Press: London, UK, 2018; pp. 39–50. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, D.; Kodera, Y. Intraperitoneal chemotherapy for gastric cancer with peritoneal metastasis. Gastric Cancer 2017, 20, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weng, C.-J.; Yen, G.-C. Chemopreventive effects of dietary phytochemicals against cancer invasion and metastasis: Phenolic acids, monophenol, polyphenol, and their derivatives. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2012, 38, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buyel, J.F. Plants as sources of natural and recombinant anti-cancer agents. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 506–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritz, H.; Seely, D.; Kennedy, D.A.; Fernandes, R.; Cooley, K.; Fergusson, D. Green tea and lung cancer: A systematic review. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X. Polydatin suppresses proliferation and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer cells by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation via NF-κB pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 108, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Zhan, X.; Zhang, B.; Chen, Y.; Liu, C.; Yu, L. Polydatin Exerts an Antitumor Effect Through Regulating the miR-382/PD-L1 Axis in Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2020, 35, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhu, X.; Wu, H.; Jiang, K.; Zhao, G.; Shaukat, A.; Deng, G.; Qiu, C. Targeting the ROS/PI3K/AKT/HIF-1α/HK2 axis of breast cancer cells: Combined administration of Polydatin and 2-Deoxy-d-glucose. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 3711–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Du, D. Polydatin inhibits cell proliferation, invasion and migration, and induces cell apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Braz. J. Med Biol. Res. 2018, 51, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.-q.; Ma, L.-l.; Lv, Z.-d.; Feng, F.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Z.-D. Polydatin induces apoptosis and autophagy via STAT3 signaling in human osteosarcoma MG-63 cells. J. Nat. Med. 2020, 74, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martano, M.; Stiuso, P.; Facchiano, A.; De Maria, S.; Vanacore, D.; Restucci, B.; Rubini, C.; Caraglia, M.; Ravagnan, G.; Lo Muzio, L. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor, a tumor grade-associated marker of oral cancer, is directly downregulated by polydatin: A pilot study. Oncol Rep 2018, 40, 1435–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mele, L.; Paino, F.; Papaccio, F.; Regad, T.; Boocock, D.; Stiuso, P.; Lombardi, A.; Liccardo, D.; Aquino, G.; Barbieri, A. A new inhibitor of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase blocks pentose phosphate pathway and suppresses malignant proliferation and metastasis in vivo. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nikoletopoulou, V.; Markaki, M.; Palikaras, K.; Tavernarakis, N. Crosstalk between apoptosis, necrosis and autophagy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Res. 2013, 1833, 3448–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghobrial, I.M.; Witzig, T.E.; Adjei, A.A. Targeting apoptosis pathways in cancer therapy. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2005, 55, 178–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portt, L.; Norman, G.; Clapp, C.; Greenwood, M.; Greenwood, M.T. Anti-apoptosis and cell survival: A review. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Res. 2011, 1813, 238–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Gu, W. miR-338 suppresses the growth and metastasis of OSCC cells by targeting NRP1. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 398, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerboth, S.; Housman, G.; Leary, M.; Longacre, M.; Byler, S.; Lapinska, K.; Willbanks, A.; Sarkar, S. EMT and tumor metastasis. Clin. Transl. Med. 2015, 4, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamouille, S.; Xu, J.; Derynck, R. Molecular mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 178–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loh, C.-Y.; Chai, J.; Tang, T.; Wong, W.; Sethi, G.; Shanmugam, M.; Chong, P.; Looi, C. The E-Cadherin and N-Cadherin Switch in Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition: Signaling, Therapeutic Implications, and Challenges. Cells 2019, 8, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hodorogea, A.; Calinescu, A.; Antohe, M.; Balaban, M.; Nedelcu, R.I.; Turcu, G.; Ion, D.A.; Badarau, I.A.; Popescu, C.M.; Popescu, R. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in skin cancers: A review. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2019, 2019, 3851576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.-W.; Lee, S.-A.; Shin, J.-M.; Park, I.-H.; Lee, H.-M. Glucocorticoids ameliorate TGF-β1-mediated epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of airway epithelium through MAPK and Snail/Slug signaling pathways. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saravanan, M.; Barabadi, H.; Vahidi, H.; Webster, T.J.; Medina-Cruz, D.; Mostafavi, E.; Vernet-Crua, A.; Cholula-Diaz, J.L.; Periakaruppan, P. Chapter 19—Emerging theranostic silver and gold nanobiomaterials for breast cancer: Present status and future prospects. In Handbook on Nanobiomaterials for Therapeutics and Diagnostic Applications; Anand, K., Saravanan, M., Chandrasekaran, B., Kanchi, S., Jeeva Panchu, S., Chen, Q., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 439–456. [Google Scholar]
- Barabadi, H.; Vahidi, H.; Kamali, K.D.; Rashedi, M.; Saravanan, M. Antineoplastic biogenic silver nanomaterials to combat cervical cancer: A novel approach in cancer therapeutics. J. Clust. Sci. 2020, 31, 659–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayalakshmi, S.; Mariadoss, A.V.A.; Ramachandran, V.; Shalini, V.; Agilan, B.; Sangeetha, C.C.; Balu, P.; Kotakadi, V.S.; Karthikkumar, V.; Ernest, D. Polydatin Encapsulated Poly [Lactic-co-glycolic acid] Nanoformulation Counteract the 7,12-Dimethylbenz[a] Anthracene Mediated Experimental Carcinogenesis through the Inhibition of Cell Proliferation. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, J.-M.; Park, B.-S.; Shin, S.-H.; Kim, I.-R. Low-level laser irradiation stimulates RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis via the MAPK pathway in RAW 264.7 cells. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derveaux, S.; Vandesompele, J.; Hellemans, J. How to do successful gene expression analysis using real-time PCR. Methods 2010, 50, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bang, T.-H.; Park, B.-S.; Kang, H.-M.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, I.-R. Polydatin, a Glycoside of Resveratrol, Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits Metastasis Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells In Vitro. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14090902
Bang T-H, Park B-S, Kang H-M, Kim J-H, Kim I-R. Polydatin, a Glycoside of Resveratrol, Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits Metastasis Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells In Vitro. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(9):902. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14090902
Chicago/Turabian StyleBang, Tae-Hyun, Bong-Soo Park, Hae-Mi Kang, Jung-Han Kim, and In-Ryoung Kim. 2021. "Polydatin, a Glycoside of Resveratrol, Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits Metastasis Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells In Vitro" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 9: 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14090902
APA StyleBang, T.-H., Park, B.-S., Kang, H.-M., Kim, J.-H., & Kim, I.-R. (2021). Polydatin, a Glycoside of Resveratrol, Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits Metastasis Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells In Vitro. Pharmaceuticals, 14(9), 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14090902





