Inhibition of Intercellular Cytosolic Traffic via Gap Junctions Reinforces Lomustine-Induced Toxicity in Glioblastoma Independent of MGMT Promoter Methylation Status
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
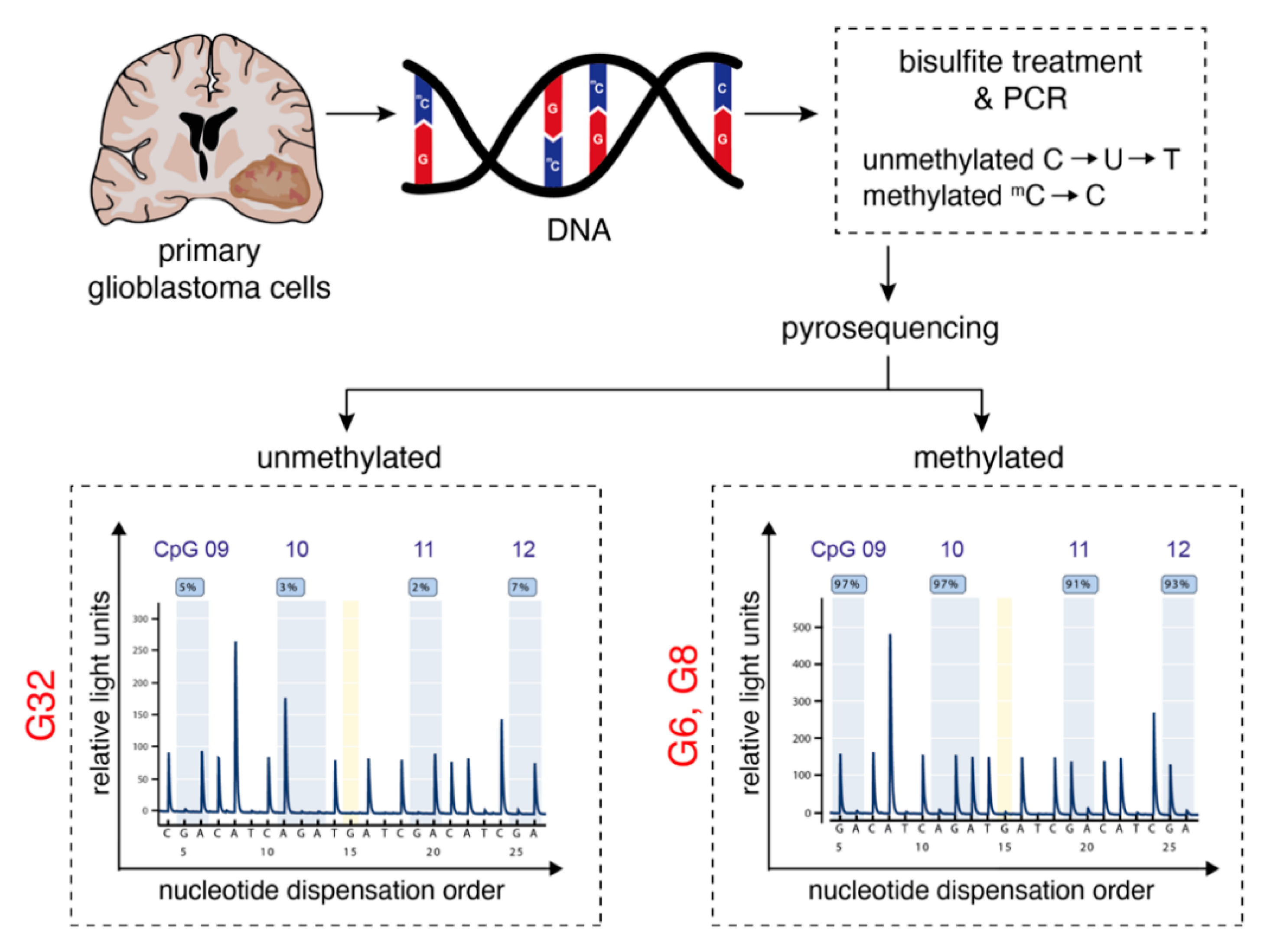
2.1. Characterization of Primary Human Glioblastoma Cell Populations
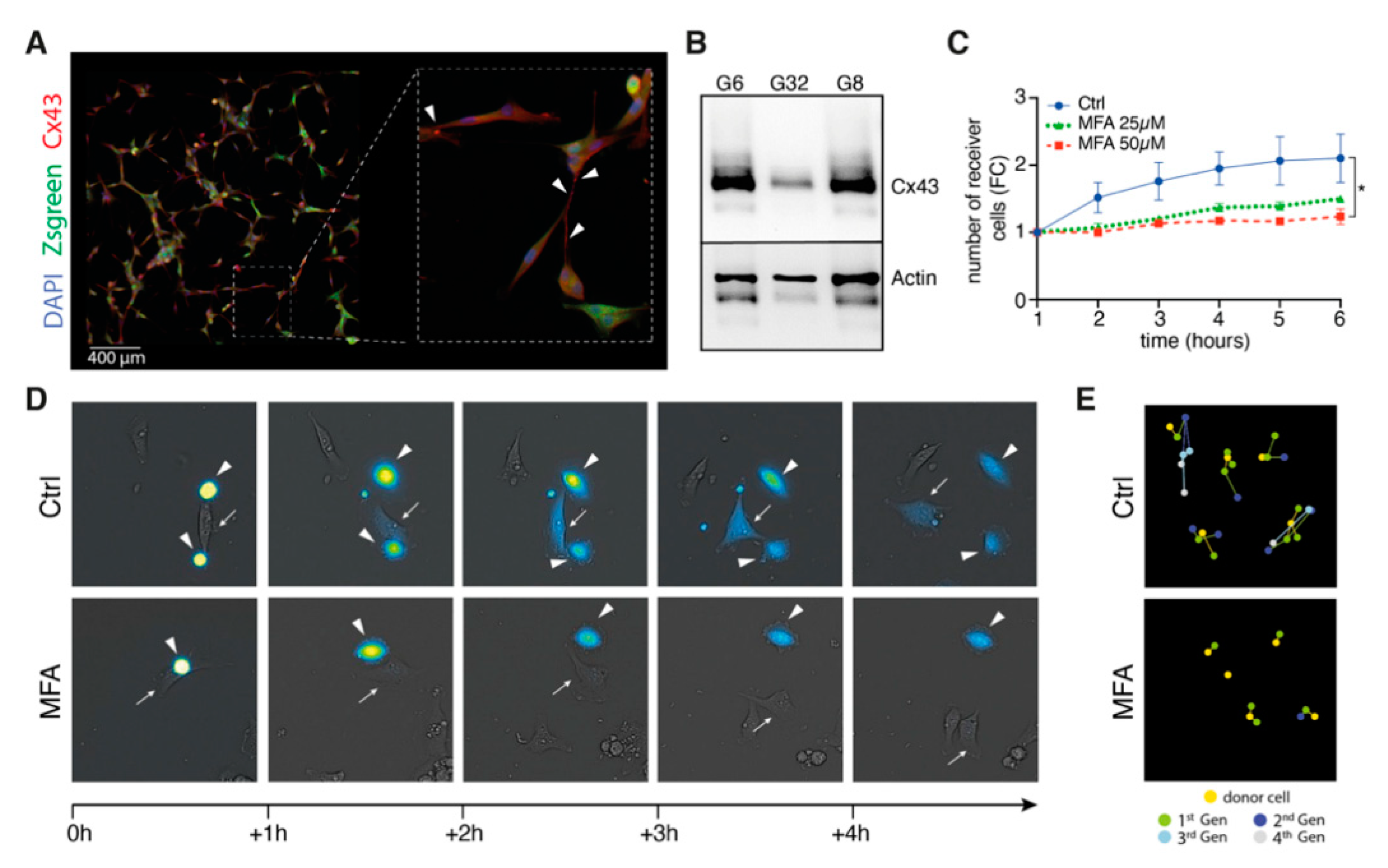
2.2. Meclofenamate Blocks Gap Junction-Mediated Intercellular Cytosolic Traffic
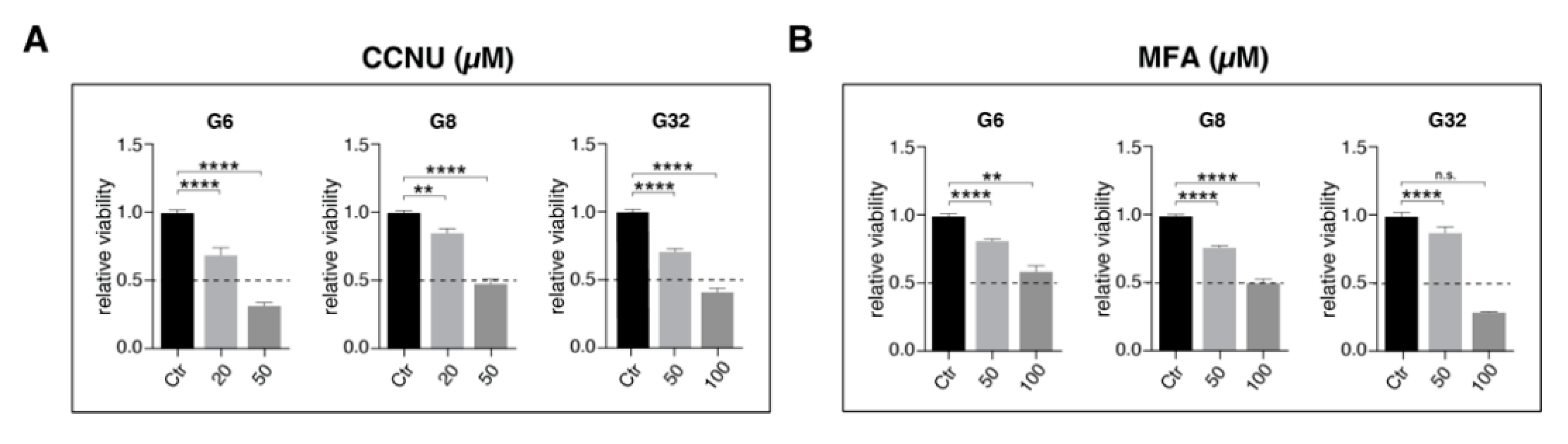
2.3. Reduced Intercellular Connectivity via Gap Junctions Synergizes to Lomustine-Mediated Antitumoral Effects
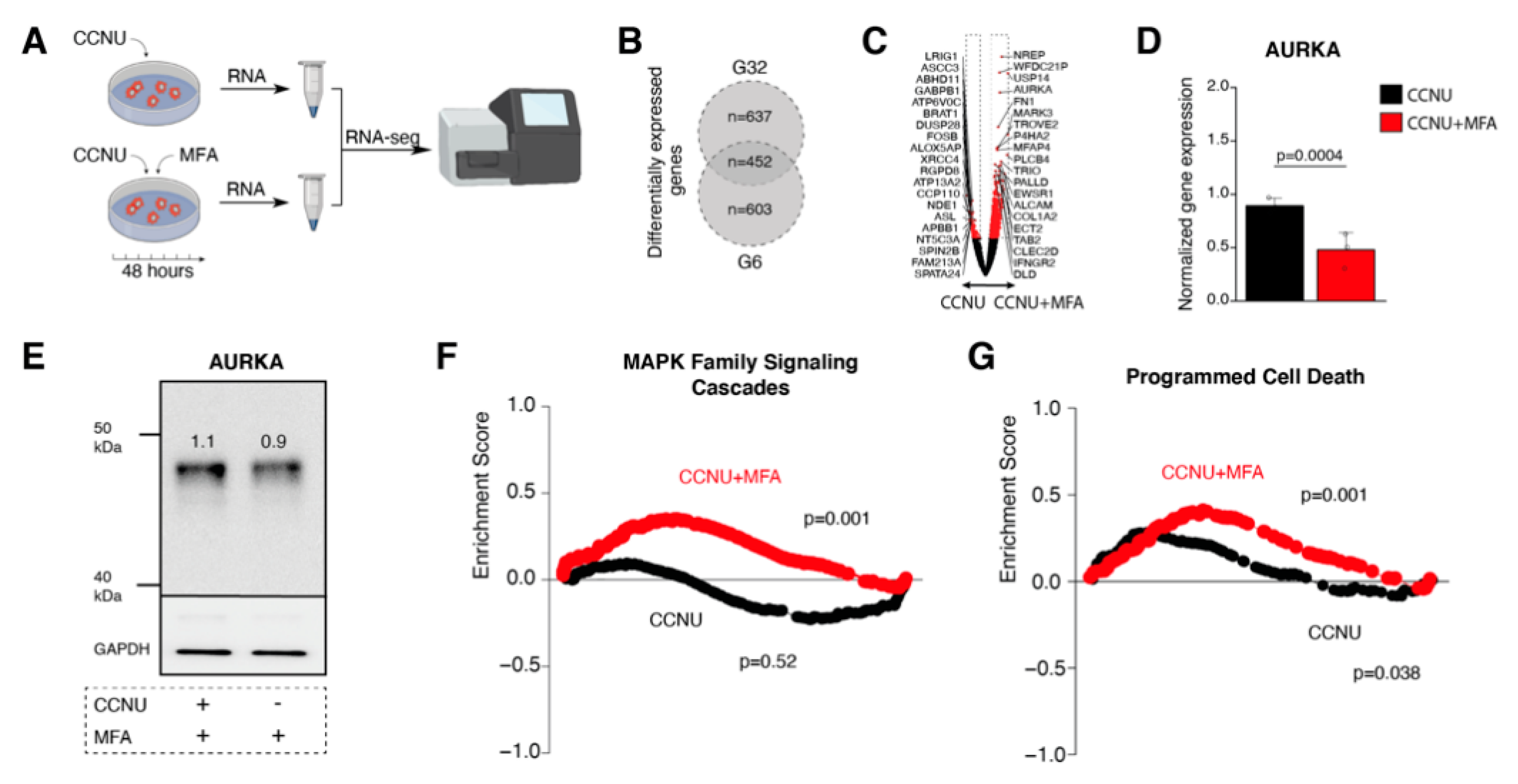
2.4. Meclofenamate-Mediated Sensitizing Effects are Accompanied by Reduced Aurora Kinase A Expression and Reveal Elevated Programmed Cell Death Pathway Signaling
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Growth Conditions
4.2. Characterization of Glioblastoma Cell Populations
4.3. Viral Transduction
4.4. Reagents
4.5. Immunofluorescence
4.6. Protein Immunoblotting
4.7. Calcein Dye Transfer
4.8. MTT
4.9. Proliferation Measurement
4.10. Flow Cytometric Analysis of Cell Death
4.11. Bliss Independence Analysis
4.12. RNA Sequencing
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jung, E.; Alfonso, J.; Monyer, H.; Wick, W.; Winkler, F. Neuronal Signatures in Cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 147, 3281–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osswald, M.; Jung, E.; Sahm, F.; Solecki, G.; Venkataramani, V.; Blaes, J.; Weil, S.; Horstmann, H.; Wiestler, B.; Syed, M.; et al. Brain Tumour Cells Interconnect to a Functional and Resistant Network. Nature 2015, 528, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weil, S.; Osswald, M.; Solecki, G.; Grosch, J.; Jung, E.; Lemke, D.; Ratliff, M.; Hanggi, D.; Wick, W.; Winkler, F. Tumor Microtubes Convey Resistance to Surgical Lesions and Chemotherapy in Gliomas. Neuro. Oncol. 2017, 19, 1316–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potthoff, A.L.; Heiland, D.H.; Evert, B.O.; Almeida, F.R.; Behringer, S.P.; Dolf, A.; Güresir, Á.; Güresir, E.; Joseph, K.; Pietsch, T.; et al. Inhibition of Gap Junctions Sensitizes Primary Glioblastoma Cells for Temozolomide. Cancers 2019, 11, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westhoff, M.A.; Zhou, S.; Bachem, M.G.; Debatin, K.M.; Fulda, S. Identification of a Novel Switch in the Dominant Forms of Cell Adhesion-Mediated Drug Resistance in Glioblastoma Cells. Oncogene 2008, 27, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yulyana, Y.; Endaya, B.B.; Ng, W.H.; Guo, C.M.; Hui, K.M.; Lam, P.Y.; Ho, I.A. Carbenoxolone Enhances Trail-Induced Apoptosis through the Upregulation of Death Receptor 5 and Inhibition of Gap Junction Intercellular Communication in Human Glioma. Stem Cells Dev. 2013, 22, 1870–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, S.F.; Varghese, R.T.; Lamouille, S.; Guo, S.; Pridham, K.J.; Kanabur, P.; Osimani, A.M.; Sharma, S.; Jourdan, J.; Rodgers, C.M.; et al. Connexin 43 Inhibition Sensitizes Chemoresistant Glioblastoma Cells to Temozolomide. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Stevens, M.F.; Bradshaw, T.D. Temozolomide: Mechanisms of Action, Repair and Resistance. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2012, 5, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wick, W.; Gorlia, T.; Bendszus, M.; Taphoorn, M.; Sahm, F.; Harting, I.; Brandes, A.A.; Taal, W.; Domont, J.; Idbaih, A.; et al. Lomustine and Bevacizumab in Progressive Glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1954–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weller, M.; Le Rhun, E. How Did Lomustine Become Standard of Care in Recurrent Glioblastoma? Cancer Treat Rev. 2020, 87, 102029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrlinger, U.; Tzaridis, T.; Mack, F.; Steinbach, J.P.; Schlegel, U.; Sabel, M.; Hau, P.; Kortmann, R.D.; Krex, D.; Grauer, O.; et al. Lomustine-Temozolomide Combination Therapy Versus Standard Temozolomide Therapy in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma with Methylated Mgmt Promoter (Ceteg/Noa-09): A Randomised, Open-Label, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet 2019, 393, 678–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjarrez-Marmolejo, J.; Franco-Perez, J. Gap Junction Blockers: An Overview of Their Effects on Induced Seizures in Animal Models. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2016, 14, 759–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, N.; Wen, Y.; Li, Y.; Li., J. Meclofenamic Acid Blocks the Gap Junction Communication between the Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2013, 32, 1164–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naus, C.C.; Laird, D.W. Implications and Challenges of Connexin Connections to Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bacco, F.; D’Ambrosio, A.; Casanova, E.; Orzan, F.; Neggia, R.; Albano, R.; Verginelli, F.; Cominelli, M.; Poliani, P.L.; Luraghi, P.; et al. Met Inhibition Overcomes Radiation Resistance of Glioblastoma Stem-Like Cells. EMBO Mol. Med. 2016, 8, 550–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzaridis, T.; Schäfer, N.; Weller, J.; Steinbach, J.P.; Schlegel, U.; Seidel, S.; Sabel, M.; Hau, P.; Seidel, C.; Krex, D.; et al. Mgmt Promoter Methylation Analysis for Allocating Combined Ccnu/Tmz Chemotherapy: Lessons Learned from the Ceteg/Noa-09 Trial. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 148, 1695–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohn, K.W. Interstrand Cross-Linking of DNA by 1,3-Bis(2-Chloroethyl)-1-Nitrosourea and Other 1-(2-Haloethyl)-1-Nitrosoureas. Cancer Res. 1977, 37, 1450–1454. [Google Scholar]
- Fisusi, F.A.; Siew, A.; Chooi, K.W.; Okubanjo, O.; Garrett, N.; Lalatsa, K.; Serrano, D.; Summers, I.; Moger, J.; Stapleton, P.; et al. Lomustine Nanoparticles Enable Both Bone Marrow Sparing and High Brain Drug Levels—A Strategy for Brain Cancer Treatments. Pharm. Res. 2016, 33, 1289–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Boire, A.; Jin, X.; Valiente, M.; Er, E.E.; Lopez-Soto, A.; Jacob, L.; Patwa, R.; Shah, H.; Xu, K.; et al. Carcinoma-Astrocyte Gap Junctions Promote Brain Metastasis by Cgamp Transfer. Nature 2016, 533, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida Magalhaes, T.; de Sousa, G.R.; Cruzeiro, G.A.V.; Tone, L.G.; Valera, E.T.; Borges, K.S. The Therapeutic Potential of Aurora Kinases Targeting in Glioblastoma: From Preclinical Research to Translational Oncology. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 98, 495–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, Y.C.; Kao, C.Y.; Chung, Y.F.; Lee, D.C.; Liu, J.W.; Chiu, I.M. Activation of Aurora a Kinase through the Fgf1/Fgfr Signaling Axis Sustains the Stem Cell Characteristics of Glioblastoma Cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2016, 344, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannino, M.; Gomez-Roman, N.; Hochegger, H.; Chalmers, A.J. Differential Sensitivity of Glioma Stem Cells to Aurora Kinase a Inhibitors: Implications for Stem Cell Mitosis and Centrosome Dynamics. Stem Cell Res. 2014, 13, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogiso, M.; Qi, L.; Braun, F.K.; Injac, S.G.; Zhang, L.; Du, Y.; Zhang, H.; Lin, F.Y.; Zhao, S.; Lindsay, H.; et al. Concurrent Inhibition of Neurosphere and Monolayer Cells of Pediatric Glioblastoma by Aurora a Inhibitor Mln8237 Predicted Survival Extension in Pdox Models. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 2159–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, B.A.; Tetzlaff, W.; Weiss, S. A Multipotent Egf-Responsive Striatal Embryonic Progenitor Cell Produces Neurons and Astrocytes. J. Neurosci. 1992, 12, 4565–4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Wu, B.; Dong, X.; Han, Y.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Luo, S.X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, H.; et al. Identification of Driver Genes and Key Pathways of Glioblastoma Shows Jnj-7706621 as a Novel Antiglioblastoma Drug. World Neurosurg 2018, 109, e329–e342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aasen, T.; Mesnil, M.; Naus, C.C.; Lampe, P.D.; Laird, D.W. Gap Junctions and Cancer: Communicating for 50 Years. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 775–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallenstein, M.C.; Mauss, E.A. Effect of Prostaglandin Synthetase Inhibitors on Experimentally Induced Convulsions in Rats. Pharmacology 1984, 29, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koup, J.R.; Tucker, E.; Thomas, D.J.; Kinkel, A.W.; Sedman, A.J.; Dyer, R.; Sharoky, M. A Single and Multiple Dose Pharmacokinetic and Metabolism Study of Meclofenamate Sodium. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 1990, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.; Ströbele, S.; Nonnenmacher, L.; Siegelin, M.D.; Tepper, M.; Stroh, S.; Hasslacher, S.; Enzenmüller, S.; Strauss, G.; Baumann, B.; et al. A Paired Comparison between Glioblastoma “Stem Cells” and Differentiated Cells. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 138, 1709–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikeska, T.; Bock, C.; El-Maarri, O.; Hubner, A.; Ehrentraut, D.; Schramm, J.; Felsberg, J.; Kahl, P.; Buttner, R.; Pietsch, T.; et al. Optimization of Quantitative Mgmt Promoter Methylation Analysis Using Pyrosequencing and Combined Bisulfite Restriction Analysis. J. Mol. Diagn. 2007, 9, 368–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evert, B.O.; Wullner, U.; Schulz, J.B.; Weller, M.; Groscurth, P.; Trottier, Y.; Brice, A.; Klockgether, T. High Level Expression of Expanded Full-Length Ataxin-3 in Vitro Causes Cell Death and Formation of Intranuclear Inclusions in Neuronal Cells. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1999, 8, 1169–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- McQuin, C.; Goodman, A.; Chernyshev, V.; Kamentsky, L.; Cimini, B.A.; Karhohs, K.W.; Doan, M.; Ding, L.; Rafelski, S.M.; Thirstrup, D.; et al. Cellprofiler 3.0: Next-Generation Image Processing for Biology. PLoS Biol. 2018, 16, e2005970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riccardi, C.; Nicoletti, I. Analysis of Apoptosis by Propidium Iodide Staining and Flow Cytometry. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 1458–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schneider, M.; Potthoff, A.-L.; Evert, B.O.; Dicks, M.; Ehrentraut, D.; Dolf, A.; Schmidt, E.N.C.; Schäfer, N.; Borger, V.; Pietsch, T.; et al. Inhibition of Intercellular Cytosolic Traffic via Gap Junctions Reinforces Lomustine-Induced Toxicity in Glioblastoma Independent of MGMT Promoter Methylation Status. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14030195
Schneider M, Potthoff A-L, Evert BO, Dicks M, Ehrentraut D, Dolf A, Schmidt ENC, Schäfer N, Borger V, Pietsch T, et al. Inhibition of Intercellular Cytosolic Traffic via Gap Junctions Reinforces Lomustine-Induced Toxicity in Glioblastoma Independent of MGMT Promoter Methylation Status. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(3):195. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14030195
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchneider, Matthias, Anna-Laura Potthoff, Bernd O. Evert, Marius Dicks, Denise Ehrentraut, Andreas Dolf, Elena N. C. Schmidt, Niklas Schäfer, Valeri Borger, Torsten Pietsch, and et al. 2021. "Inhibition of Intercellular Cytosolic Traffic via Gap Junctions Reinforces Lomustine-Induced Toxicity in Glioblastoma Independent of MGMT Promoter Methylation Status" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 3: 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14030195
APA StyleSchneider, M., Potthoff, A.-L., Evert, B. O., Dicks, M., Ehrentraut, D., Dolf, A., Schmidt, E. N. C., Schäfer, N., Borger, V., Pietsch, T., Westhoff, M.-A., Güresir, E., Waha, A., Vatter, H., Heiland, D. H., Schuss, P., & Herrlinger, U. (2021). Inhibition of Intercellular Cytosolic Traffic via Gap Junctions Reinforces Lomustine-Induced Toxicity in Glioblastoma Independent of MGMT Promoter Methylation Status. Pharmaceuticals, 14(3), 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14030195









