Dendritic Cells as Danger-Recognizing Biosensors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
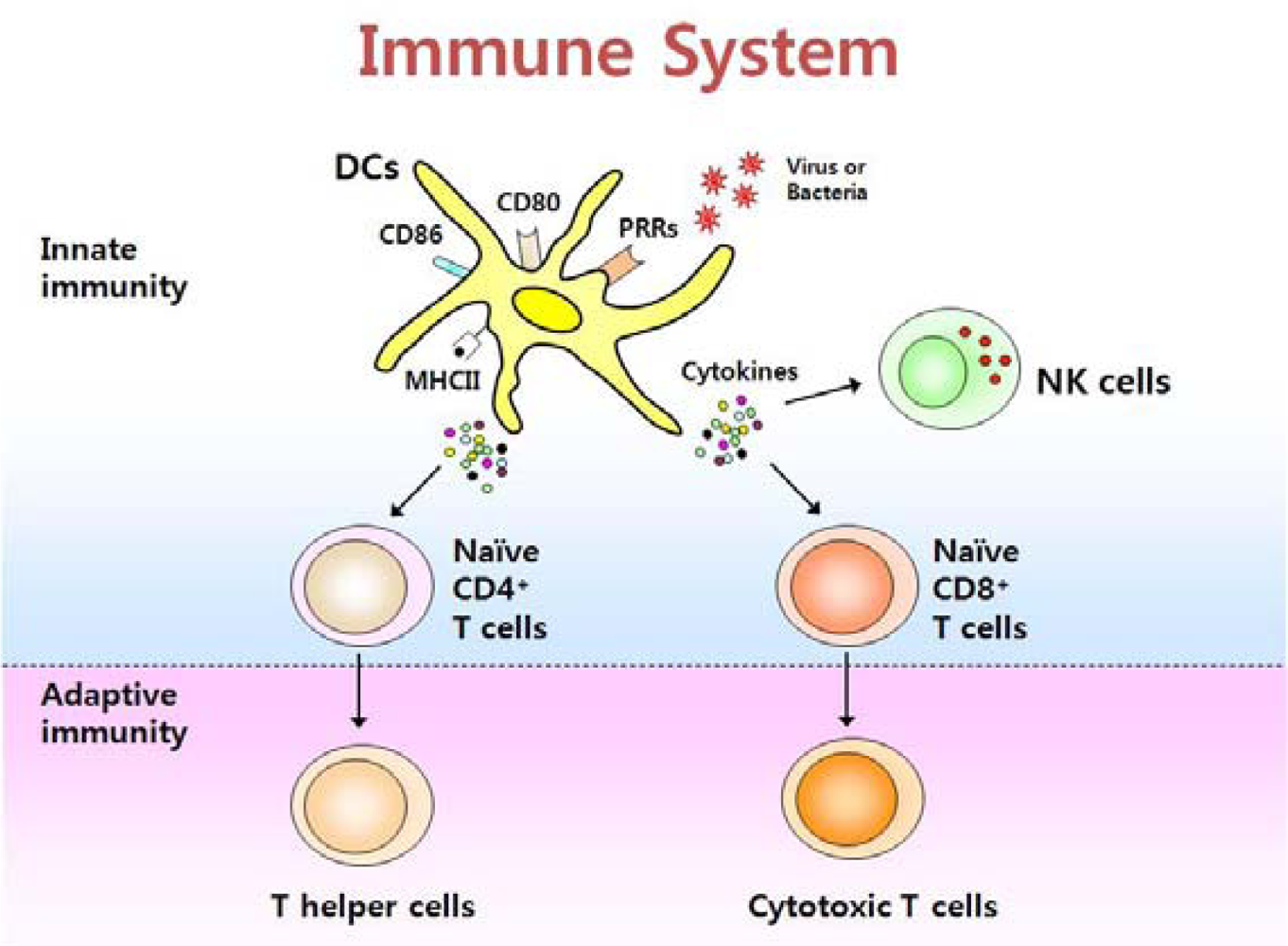
2. Dendritic Cells
2.1. DC Subsets
2.2. Recognition of Danger Signals by DCs
2.2.1. Pathogen Associated Molecular Patterns and Pattern Recognition Receptors
2.2.2. Alarmins and Their Receptors
2.3. Immunological Roles of DCs in Various Diseases
2.3.1. Infectious Diseases
2.3.2. Cancer
2.3.3. Autoimmune Diseases
2.3.4. Allergies
3. Research on DC Activation through Cytokine Reporter Mice
3.1. Cytokine Reporter Mouse Model
3.2. Cancer
3.3. Allergies
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References and Notes
- Hoebe, K.; Janssen, E.; Beutler, B. The interface between innate and adaptive immunity. Nat. Immunol 2004, 5, 971–974. [Google Scholar]
- Banchereau, J.; Paczesny, S.; Blanco, P.; Bennett, L.; Pascual, V.; Fay, J.; Palucka, A.K. Dendritic cells: controllers of the immune system and a new promise for immunotherapy. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci 2003, 987, 180–187. [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi, M.E. DAMPs, PAMPs and alarmins: all we need to know about danger. J. Leukoc. Biol 2007, 81, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, P.E. Recent advances in antigen processing and presentation. Nat. Immunol 2007, 8, 1041–1048. [Google Scholar]
- Vyas, J.M.; van der Veen, A.G.; Ploegh, H.L. The known unknowns of antigen processing and presentation. Nat. Rev. Immunol 2008, 8, 607–618. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, K.; Suematsu, A.; Okamoto, K.; Yamaguchi, A.; Morishita, Y.; Kadono, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Kodama, T.; Akira, S.; Iwakura, Y.; Cua, D.J.; Takayanagi, H. Th17 functions as an osteoclastogenic helper T cell subset that links T cell activation and bone destruction. J. Exp. Med 2006, 203, 2673–2682. [Google Scholar]
- Iwasaki, A.; Medzhitov, R. Toll-like receptor control of the adaptive immune responses. Nat. Immunol 2004, 5, 987–995. [Google Scholar]
- Toebak, M.J.; Gibbs, S.; Bruynzeel, D.P.; Scheper, R.J.; Rustemeyer, T. Dendritic cells: biology of the skin. Contact Dermatitis 2009, 60, 2–20. [Google Scholar]
- Hildner, K.; Edelson, B.T.; Purtha, W.E.; Diamond, M.; Matsushita, H.; Kohyama, M.; Calderon, B.; Schraml, B.U.; Unanue, E.R.; Diamond, M.S.; Schreiber, R.D.; Murphy, T.L.; Murphy, K.M. Batf3 deficiency reveals a critical role for CD8alpha+ dendritic cells in cytotoxic T cell immunity. Science 2008, 322, 1097–1100. [Google Scholar]
- Dudziak, D.; Kamphorst, A.O.; Heidkamp, G.F.; Buchholz, V.R.; Trumpfheller, C.; Yamazaki, S.; Cheong, C.; Liu, K.; Lee, H.W.; Park, C.G.; Steinman, R.M.; Nussenzweig, M.C. Differential antigen processing by dendritic cell subsets in vivo. Science 2007, 315, 107–111. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, J.; Avalos, A.M.; Mao, S.Y.; Chen, B.; Senthil, K.; Wu, H.; Parroche, P.; Drabic, S.; Golenbock, D.; Sirois, C.; Hua, J.; An, L.L.; Audoly, L.; La Rosa, G.; Bierhaus, A.; Naworth, P.; Marshak-Rothstein, A.; Crow, M.K.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; Latz, E.; Kiener, P.A.; Coyle, A.J. Toll-like receptor 9-dependent activation by DNA-containing immune complexes is mediated by HMGB1 and RAGE. Nat. Immunol 2007, 8, 487–496. [Google Scholar]
- Naik, S.H.; Proietto, A.I.; Wilson, N.S.; Dakic, A.; Schnorrer, P.; Fuchsberger, M.; Lahoud, M.H.; O'Keeffe, M.; Shao, Q.X.; Chen, W.F.; Villadangos, J.A.; Shortman, K.; Wu, L. Cutting edge: generation of splenic CD8+ and CD8− dendritic cell equivalents in Fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 ligand bone marrow cultures. J. Immunol 2005, 174, 6592–6597. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, C.W.; Housseau, F. The ‘kiss of death’ by dendritic cells to cancer cells. Cell Death Differ 2008, 15, 58–69. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhry, U.I.; Katz, S.C.; Kingham, T.P.; Pillarisetty, V.G.; Raab, J.R.; Shah, A.B.; DeMatteo, R.P. In vivo overexpression of Flt3 ligand expands and activates murine spleen natural killer dendritic cells. FASEB J 2006, 20, 982–984. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhry, U.I.; Plitas, G.; Burt, B.M.; Kingham, T.P.; Raab, J.R.; DeMatteo, R.P. NK dendritic cells expanded in IL-15 exhibit antitumor responses in vivo. J. Immunol 2007, 179, 4654–4660. [Google Scholar]
- Hardy, A.W.; Graham, D.R.; Shearer, G.M.; Herbeuval, J.P. HIV turns plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDC) into TRAIL-expressing killer pDC and down-regulates HIV coreceptors by Toll-like receptor 7-induced IFN-alpha. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 17453–17458. [Google Scholar]
- Kono, H.; Rock, K.L. How dying cells alert the immune system to danger. Nat. Rev. Immunol 2008, 8, 279–289. [Google Scholar]
- Janeway, C.A., Jr.; Medzhitov, R. Innate immune recognition. Annu. Rev. Immunol 2002, 20, 197–216. [Google Scholar]
- Takeda, K.; Kaisho, T.; Akira, S. Toll-like receptors. Annu. Rev. Immunol 2003, 21, 335–376. [Google Scholar]
- Lund, J.; Sato, A.; Akira, S.; Medzhitov, R.; Iwasaki, A. Toll-like receptor 9-mediated recognition of Herpes simplex virus-2 by plasmacytoid dendritic cells. J. Exp. Med 2003, 198, 513–520. [Google Scholar]
- Krug, A.; Luker, G.D.; Barchet, W.; Leib, D.A.; Akira, S.; Colonna, M. Herpes simplex virus type 1 activates murine natural interferon-producing cells through toll-like receptor 9. Blood 2004, 103, 1433–1437. [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri, G. Interleukin-12 and the regulation of innate resistance and adaptive immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol 2003, 3, 133–146. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, T.; Amakawa, R.; Kaisho, T.; Hemmi, H.; Tajima, K.; Uehira, K.; Ozaki, Y.; Tomizawa, H.; Akira, S.; Fukuhara, S. Interferon-alpha and interleukin-12 are induced differentially by Toll-like receptor 7 ligands in human blood dendritic cell subsets. J. Exp. Med 2002, 195, 1507–1512. [Google Scholar]
- Redecke, V.; Hacker, H.; Datta, S.K.; Fermin, A.; Pitha, P.M.; Broide, D.H.; Raz, E. Cutting edge: activation of Toll-like receptor 2 induces a Th2 immune response and promotes experimental asthma. J. Immunol 2004, 172, 2739–2743. [Google Scholar]
- Aranami, T.; Yamamura, T. Th17 Cells and autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE/MS). Allergol. Int 2008, 57, 115–120. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, X.; Tarbell, K.V.; Yang, H.; Pothoven, K.; Bailey, S.L.; Ding, R.; Steinman, R.M.; Suthanthiran, M. Dendritic cells with TGF-beta1 differentiate naive CD4+CD25− T cells into islet-protective Foxp3+ regulatory T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 2007, 104, 2821–2826. [Google Scholar]
- Akbari, O.; DeKruyff, R.H.; Umetsu, D.T. Pulmonary dendritic cells producing IL-10 mediate tolerance induced by respiratory exposure to antigen. Nat. Immunol 2001, 2, 725–731. [Google Scholar]
- Jonuleit, H.; Schmitt, E.; Schuler, G.; Knop, J.; Enk, A.H. Induction of interleukin 10-producing, nonproliferating CD4(+) T cells with regulatory properties by repetitive stimulation with allogeneic immature human dendritic cells. J. Exp. Med 2000, 192, 1213–1222. [Google Scholar]
- Meylan, E.; Tschopp, J.; Karin, M. Intracellular pattern recognition receptors in the host response. Nature 2006, 442, 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Girardin, S.E.; Boneca, I.G.; Viala, J.; Chamaillard, M.; Labigne, A.; Thomas, G.; Philpott, D.J.; Sansonetti, P.J. Nod2 is a general sensor of peptidoglycan through muramyl dipeptide (MDP) detection. J. Biol. Chem 2003, 278, 8869–8872. [Google Scholar]
- Chamaillard, M.; Hashimoto, M.; Horie, Y.; Masumoto, J.; Qiu, S.; Saab, L.; Ogura, Y.; Kawasaki, A.; Fukase, K.; Kusumoto, S.; Valvano, M.A.; Foster, S.J.; Mak, T.W.; Nunez, G.; Inohara, N. An essential role for NOD1 in host recognition of bacterial peptidoglycan containing diaminopimelic acid. Nat. Immunol 2003, 4, 702–707. [Google Scholar]
- Yoneyama, M.; Kikuchi, M.; Natsukawa, T.; Shinobu, N.; Imaizumi, T.; Miyagishi, M.; Taira, K.; Akira, S.; Fujita, T. The RNA helicase RIG-I has an essential function in double-stranded RNA-induced innate antiviral responses. Nat. Immunol 2004, 5, 730–737. [Google Scholar]
- Bierhaus, A.; Humpert, P.M.; Morcos, M.; Wendt, T.; Chavakis, T.; Arnold, B.; Stern, D.M.; Nawroth, P.P. Understanding RAGE, the receptor for advanced glycation end products. J. Mol. Med 2005, 83, 876–886. [Google Scholar]
- Rovere-Querini, P.; Capobianco, A.; Scaffidi, P.; Valentinis, B.; Catalanotti, F.; Giazzon, M.; Dumitriu, I.E.; Muller, S.; Iannacone, M.; Traversari, C.; Bianchi, M.E.; Manfredi, A.A. HMGB1 is an endogenous immune adjuvant released by necrotic cells. EMBO Rep 2004, 5, 825–830. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.J.; Tian, D.Y.; Xu, D.; Yang, D.F.; Zhu, H.F.; Liang, Z.H.; Zhang, Z.G. Uric acid enhances T cell immune responses to hepatitis B surface antigen-pulsed-dendritic cells in mice. World J. Gastroenterol 2007, 13, 1060–1066. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Ochani, M.; Li, J.; Qiang, X.; Tanovic, M.; Harris, H.E.; Susarla, S.M.; Ulloa, L.; Wang, H.; DiRaimo, R.; Czura, C.J.; Roth, J.; Warren, H.S.; Fink, M.P.; Fenton, M.J.; Andersson, U.; Tracey, K.J. Reversing established sepsis with antagonists of endogenous high-mobility group box 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 2004, 101, 296–301. [Google Scholar]
- Kokkola, R.; Li, J.; Sundberg, E.; Aveberger, A.C.; Palmblad, K.; Yang, H.; Tracey, K.J.; Andersson, U.; Harris, H.E. Successful treatment of collagen-induced arthritis in mice and rats by targeting extracellular high mobility group box chromosomal protein 1 activity. Arthritis Rheum 2003, 48, 2052–2058. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, K.; Kawahara, K.; Biswas, K.K.; Ando, K.; Mitsudo, K.; Nobuyoshi, M.; Maruyama, I. HMGB1 expression by activated vascular smooth muscle cells in advanced human atherosclerosis plaques. Cardiovasc. Pathol 2007, 16, 136–143. [Google Scholar]
- Popovic, K.; Ek, M.; Espinosa, A.; Padyukov, L.; Harris, H.E.; Wahren-Herlenius, M.; Nyberg, F. Increased expression of the novel proinflammatory cytokine high mobility group box chromosomal protein 1 in skin lesions of patients with lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 2005, 52, 3639–3645. [Google Scholar]
- Taguchi, A.; Blood, D.C.; del Toro, G.; Canet, A.; Lee, D.C.; Qu, W.; Tanji, N.; Lu, Y.; Lalla, E.; Fu, C.; Hofmann, M.A.; Kislinger, T.; Ingram, M.; Lu, A.; Tanaka, H.; Hori, O.; Ogawa, S.; Stern, D.M.; Schmidt, A.M. Blockade of RAGE-amphoterin signalling suppresses tumour growth and metastases. Nature 2000, 405, 354–360. [Google Scholar]
- Sitia, G.; Iannacone, M.; Muller, S.; Bianchi, M.E.; Guidotti, L.G. Treatment with HMGB1 inhibitors diminishes CTL-induced liver disease in HBV transgenic mice. J. Leukoc. Biol 2007, 81, 100–107. [Google Scholar]
- Blander, J.M.; Medzhitov, R. Regulation of phagosome maturation by signals from toll-like receptors. Science 2004, 304, 1014–1018. [Google Scholar]
- Hacker, H.; Redecke, V.; Blagoev, B.; Kratchmarova, I.; Hsu, L.C.; Wang, G.G.; Kamps, M.P.; Raz, E.; Wagner, H.; Hacker, G.; Mann, M.; Karin, M. Specificity in Toll-like receptor signalling through distinct effector functions of TRAF3 and TRAF6. Nature 2006, 439, 204–207. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.J.; Chen, W.; Carrigan, S.O.; Chen, W.M.; Roth, K.; Akiyama, T.; Inoue, J.; Marshall, J.S.; Berman, J.N.; Lin, T.J. TRAF6 specifically contributes to FcepsilonRI-mediated cytokine production but not mast cell degranulation. J. Biol. Chem 2008, 283, 32110–32118. [Google Scholar]
- Lapenta, C.; Santini, S.M.; Logozzi, M.; Spada, M.; Andreotti, M.; Di Pucchio, T.; Parlato, S.; Belardelli, F. Potent immune response against HIV-1 and protection from virus challenge in hu-PBL-SCID mice immunized with inactivated virus-pulsed dendritic cells generated in the presence of IFN-alpha. J. Exp. Med 2003, 198, 361–367. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, W.; Arraes, L.C.; Ferreira, W.T.; Andrieu, J.M. Therapeutic dendritic-cell vaccine for chronic HIV-1 infection. Nat. Med 2004, 10, 1359–1365. [Google Scholar]
- Probst, H.C.; van den Broek, M. Priming of CTLs by lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus depends on dendritic cells. J. Immunol 2005, 174, 3920–3924. [Google Scholar]
- Berberich, C.; Ramirez-Pineda, J.R.; Hambrecht, C.; Alber, G.; Skeiky, Y.A.; Moll, H. Dendritic cell (DC)-based protection against an intracellular pathogen is dependent upon DC-derived IL-12 and can be induced by molecularly defined antigens. J. Immunol 2003, 170, 3171–3179. [Google Scholar]
- Wozniak, K.L.; Vyas, J.M.; Levitz, S.M. In vivo role of dendritic cells in a murine model of pulmonary cryptococcosis. Infect. Immun 2006, 74, 3817–3824. [Google Scholar]
- Coutanceau, E.; Decalf, J.; Martino, A.; Babon, A.; Winter, N.; Cole, S.T.; Albert, M.L.; Demangel, C. Selective suppression of dendritic cell functions by Mycobacterium ulcerans toxin mycolactone. J. Exp. Med 2007, 204, 1395–1403. [Google Scholar]
- Serra, A.; Nuti, S.; Tavarini, S.; Sammicheli, C.; Rosa, D.; Saletti, G.; Soldaini, E.; Abrignani, S.; Wack, A. Coligation of the hepatitis C virus receptor CD81 with CD28 primes naive T lymphocytes to acquire type 2 effector function. J. Immunol 2008, 181, 174–185. [Google Scholar]
- Kortylewski, M.; Yu, H. Role of Stat3 in suppressing anti-tumor immunity. Curr. Opin. Immunol 2008, 20, 228–233. [Google Scholar]
- Blaskovich, M.A.; Sun, J.; Cantor, A.; Turkson, J.; Jove, R.; Sebti, S.M. Discovery of JSI-124 (cucurbitacin I), a selective Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 signaling pathway inhibitor with potent antitumor activity against human and murine cancer cells in mice. Cancer. Res 2003, 63, 1270–1279. [Google Scholar]
- Apetoh, L.; Ghiringhelli, F.; Tesniere, A.; Criollo, A.; Ortiz, C.; Lidereau, R.; Mariette, C.; Chaput, N.; Mira, J.P.; Delaloge, S.; Andre, F.; Tursz, T.; Kroemer, G.; Zitvogel, L. The interaction between HMGB1 and TLR4 dictates the outcome of anticancer chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Immunol. Rev 2007, 220, 47–59. [Google Scholar]
- Jasani, B.; Navabi, H.; Adams, M. Ampligen: A potential toll-like 3 receptor adjuvant for immunotherapy of cancer. Vaccine 2009, 27, 3401–3404. [Google Scholar]
- Gilboa, E. DC-based cancer vaccines. J. Clin. Invest 2007, 117, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar]
- Lowes, M.A.; Chamian, F.; Abello, M.V.; Fuentes-Duculan, J.; Lin, S.L.; Nussbaum, R.; Novitskaya, I.; Carbonaro, H.; Cardinale, I.; Kikuchi, T.; Gilleaudeau, P.; Sullivan-Whalen, M.; Wittkowski, K.M.; Papp, K.; Garovoy, M.; Dummer, W.; Steinman, R.M.; Krueger, J.G. Increase in TNF-alpha and inducible nitric oxide synthase-expressing dendritic cells in psoriasis and reduction with efalizumab (anti-CD11a). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 19057–19062. [Google Scholar]
- Mangini, A.J.; Lafyatis, R.; Van Seventer, J.M. Type I interferons inhibition of inflammatory T helper cell responses in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci 2007, 1108, 11–23. [Google Scholar]
- Pascual, V.; Banchereau, J.; Palucka, A.K. The central role of dendritic cells and interferon-alpha in SLE. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol 2003, 15, 548–556. [Google Scholar]
- Asselin-Paturel, C.; Trinchieri, G. Production of type I interferons: plasmacytoid dendritic cells and beyond. J. Exp. Med 2005, 202, 461–465. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.J.; Soumelis, V.; Watanabe, N.; Ito, T.; Wang, Y.H.; Malefyt Rde, W.; Omori, M.; Zhou, B.; Ziegler, S.F. TSLP: an epithelial cell cytokine that regulates T cell differentiation by conditioning dendritic cell maturation. Annu. Rev. Immunol 2007, 25, 193–219. [Google Scholar]
- Hammad, H.; Lambrecht, B.N. Dendritic cells and epithelial cells: linking innate and adaptive immunity in asthma. Nat. Rev. Immunol 2008, 8, 193–204. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, A.M.; Khader, S.A. IL-12p40: an inherently agonistic cytokine. Trends Immunol 2007, 28, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
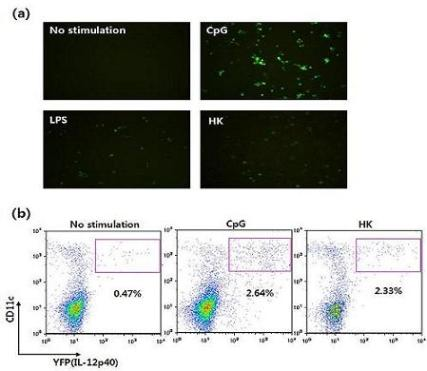
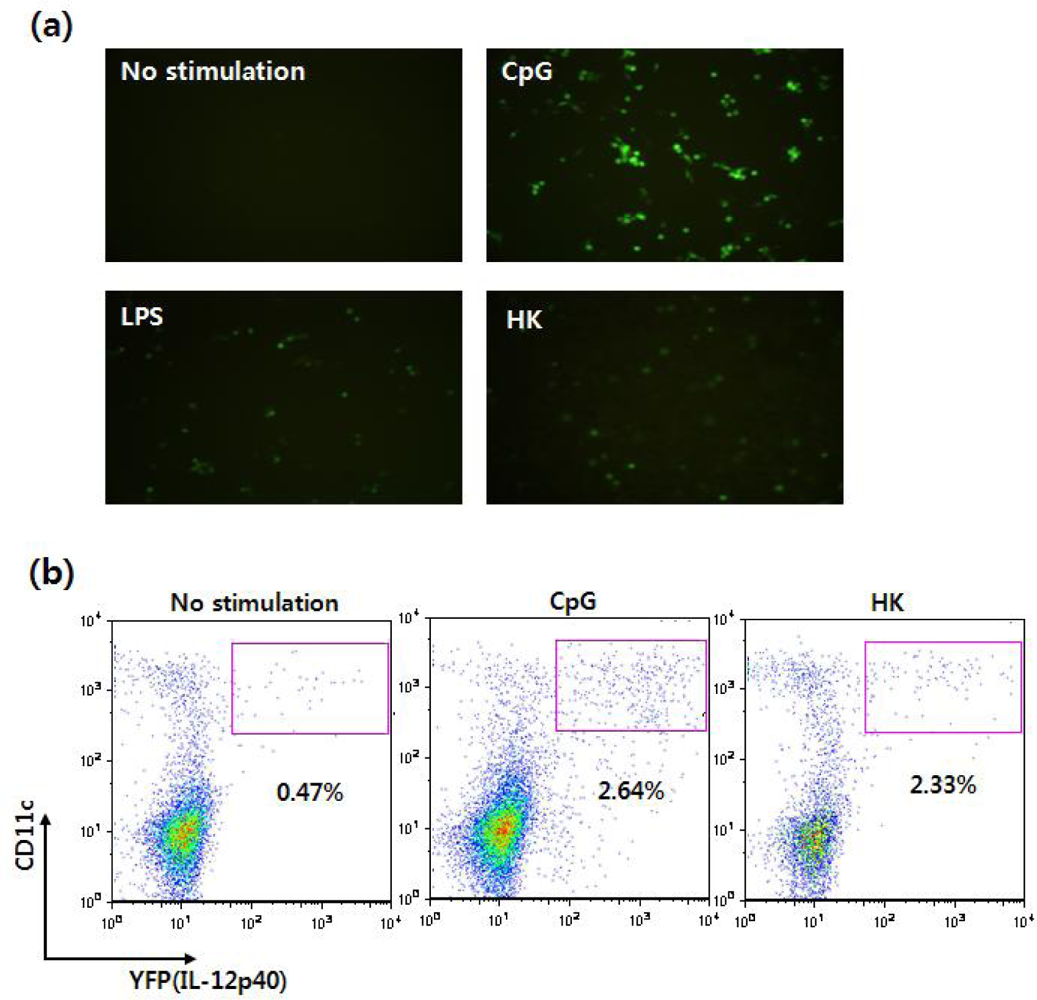
- Im, W.; Kim, H.; Yun, D.; Seo, S.Y.; Park, S.H.; Locksley, R.M.; Hong, S. Cytokine reporter mouse system for screening novel IL12/23 p40-inducing compounds. Mol. Cells 2005, 20, 288–296. [Google Scholar]
- Reinhardt, R.L.; Hong, S.; Kang, S.J.; Wang, Z.E.; Locksley, R.M. Visualization of IL-12/23p40 in vivo reveals immunostimulatory dendritic cell migrants that promote Th1 differentiation. J. Immunol 2006, 177, 1618–1627. [Google Scholar]
- Khader, S.A.; Partida-Sanchez, S.; Bell, G.; Jelley-Gibbs, D.M.; Swain, S.; Pearl, J.E.; Ghilardi, N.; Desauvage, F.J.; Lund, F.E.; Cooper, A.M. Interleukin 12p40 is required for dendritic cell migration and T cell priming after Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. J. Exp. Med 2006, 203, 1805–1815. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Yang, J.Y.; Lee, K.; Oh, K.H.; Gi, M.; Kim, J.M.; Paik, D.J.; Hong, S.; Youn, J. Bacillus subtilis-specific poly-gamma-glutamic acid regulates development pathways of naive CD4(+) T cells through antigen-presenting cell-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Int. Immunol 2009, 21, 977–990. [Google Scholar]
- Strome, S.E.; Voss, S.; Wilcox, R.; Wakefield, T.L.; Tamada, K.; Flies, D.; Chapoval, A.; Lu, J.; Kasperbauer, J.L.; Padley, D.; Vile, R.; Gastineau, D.; Wettstein, P.; Chen, L. Strategies for antigen loading of dendritic cells to enhance the antitumor immune response. Cancer Res 2002, 62, 1884–1889. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, T.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, H.; Hong, C.; Lee, H.; Lee, C.K.; Lee, K.H.; Hong, S.; Park, S.H. Anti-tumor immunostimulatory effect of heat-killed tumor cells. Exp. Mol. Med 2008, 40, 130–144. [Google Scholar]
- Stetson, D.B.; Mohrs, M.; Reinhardt, R.L.; Baron, J.L.; Wang, Z.E.; Gapin, L.; Kronenberg, M.; Locksley, R.M. Constitutive cytokine mRNAs mark natural killer (NK) and NK T cells poised for rapid effector function. J. Exp. Med 2003, 198, 1069–1076. [Google Scholar]
- Leung, D.Y.; Boguniewicz, M.; Howell, M.D.; Nomura, I.; Hamid, Q.A. New insights into atopic dermatitis. J. Clin. Invest 2004, 113, 651–657. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda, H.; Watanabe, N.; Geba, G.P.; Sperl, J.; Tsudzuki, M.; Hiroi, J.; Matsumoto, M.; Ushio, H.; Saito, S.; Askenase, P.W.; Ra, C. Development of atopic dermatitis-like skin lesion with IgE hyperproduction in NC/Nga mice. Int. Immunol 1997, 9, 461–466. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto, M.; Itakura, A.; Tanaka, A.; Fujisawa, C.; Matsuda, H. Inability of IL-12 to down-regulate IgE synthesis due to defective production of IFN-gamma in atopic NC/Nga mice. J. Immunol 2001, 167, 5955–5962. [Google Scholar]








| DC subsets | Features | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site | Function | Phenotype | TLR expression | ||
| cDC | CD8α+ | Lymphoid organ (T cell zone) | Cross presentation | CD11b−CD11c+ | TLR1, 2, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9 |
| CD8α− | Lymphoid organ (Marginal zone) | APC | CD11bhiCD4+/−CD11c+ | TLR1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 9 | |
| pDC | Mast organs | APC | CD11b−B220+CD11c+ | TLR1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 | |
| Langerhans cell | Skin | APC | CD11b+CD8α−CD4+/−CD11c+ | TLR1, 3, 6, 7 | |
| Interstitial DC | Peripheral organ | APC | CD11b+CD8α−CD4−CD11c+ | TLR1-8 | |
| NKDC | Lymphoid organ | Cytotoxicity/APC | NK1.1+B220+CD11c+ | TLR9 | |
| TLRs | Ligands |
|---|---|
| TLR1/TLR2 | Triacylated lipopeptides |
| TLR2/TLR6 | Diacylated lipopeptides |
| TLR3 | Viral dsRNA |
| TLR4 | Lipopolysaccharide |
| TLR5 | Flagellin |
| TLR7 | Viral ssRNA |
| TLR8 | Viral ssRNA |
| TLR9 | Bacterial or viral CpG DNA |
| TLR11 | Profilin |
| TLR10, 12, 13 | Unknown |
© 2009 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Gi, M.; Im, W.; Hong, S. Dendritic Cells as Danger-Recognizing Biosensors. Sensors 2009, 9, 6730-6751. https://doi.org/10.3390/s90906730
Gi M, Im W, Hong S. Dendritic Cells as Danger-Recognizing Biosensors. Sensors. 2009; 9(9):6730-6751. https://doi.org/10.3390/s90906730
Chicago/Turabian StyleGi, Mia, Wooseok Im, and Seokmann Hong. 2009. "Dendritic Cells as Danger-Recognizing Biosensors" Sensors 9, no. 9: 6730-6751. https://doi.org/10.3390/s90906730
APA StyleGi, M., Im, W., & Hong, S. (2009). Dendritic Cells as Danger-Recognizing Biosensors. Sensors, 9(9), 6730-6751. https://doi.org/10.3390/s90906730