Identification of Loading Location and Amplitude in Conductive Composite Materials via Deep Learning Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
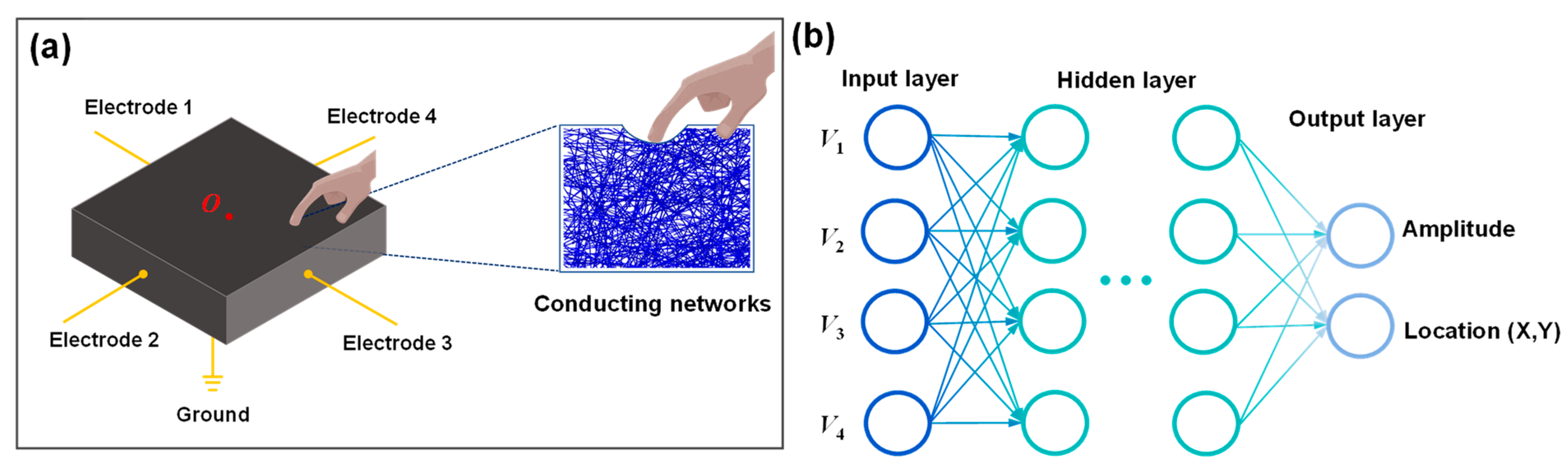
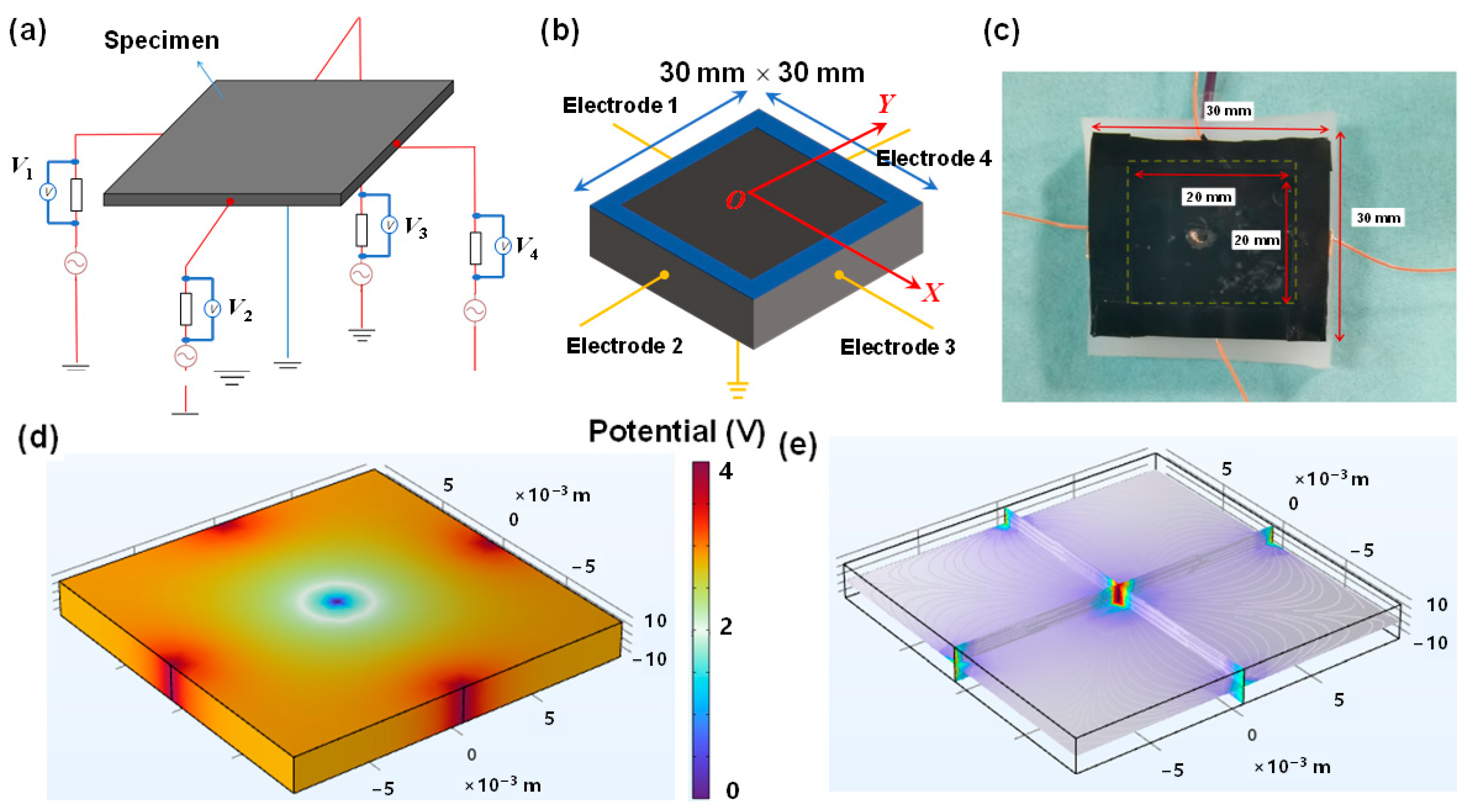
2.1. Design Principle
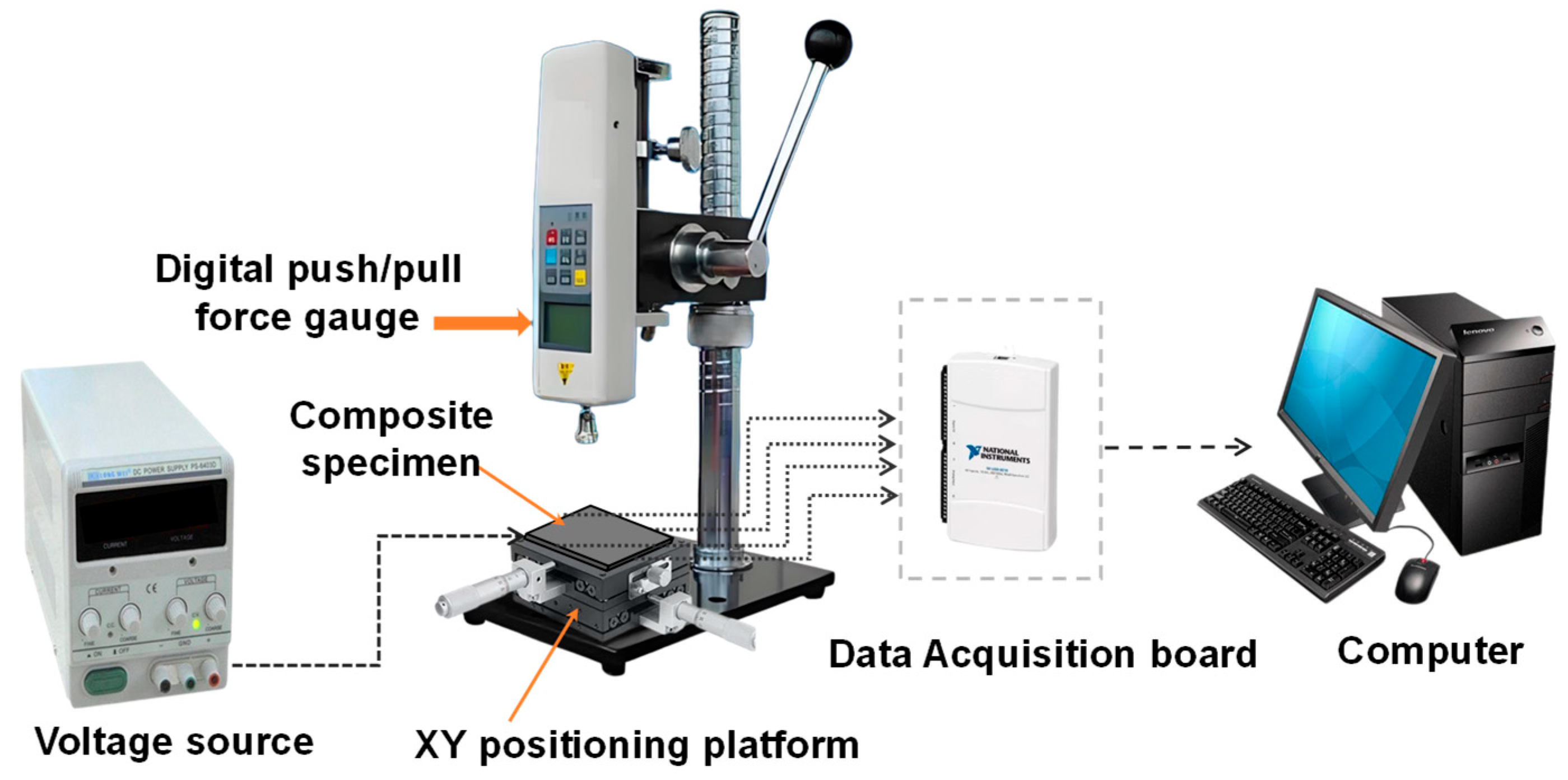
2.2. Materials and Characterizations
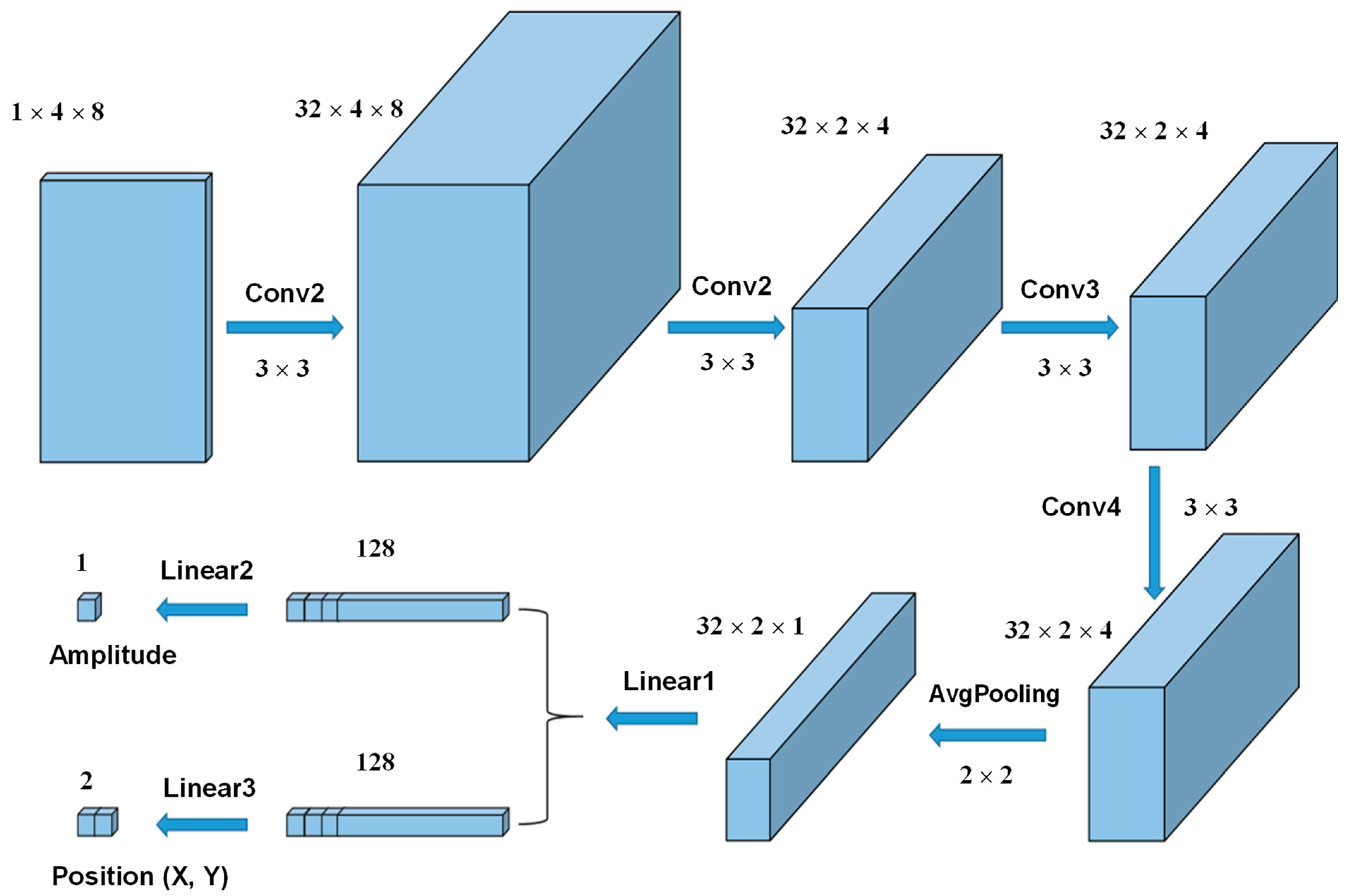
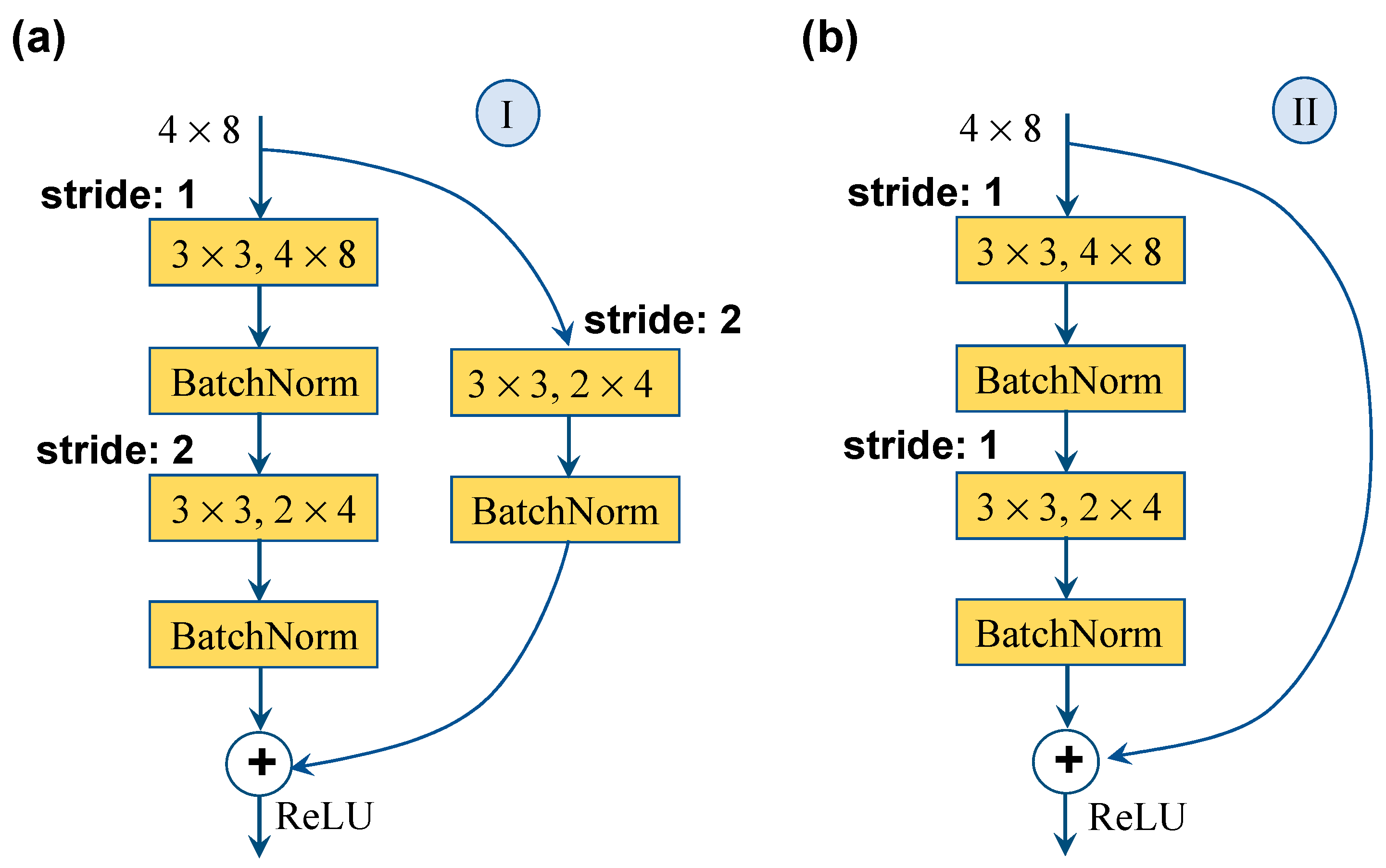
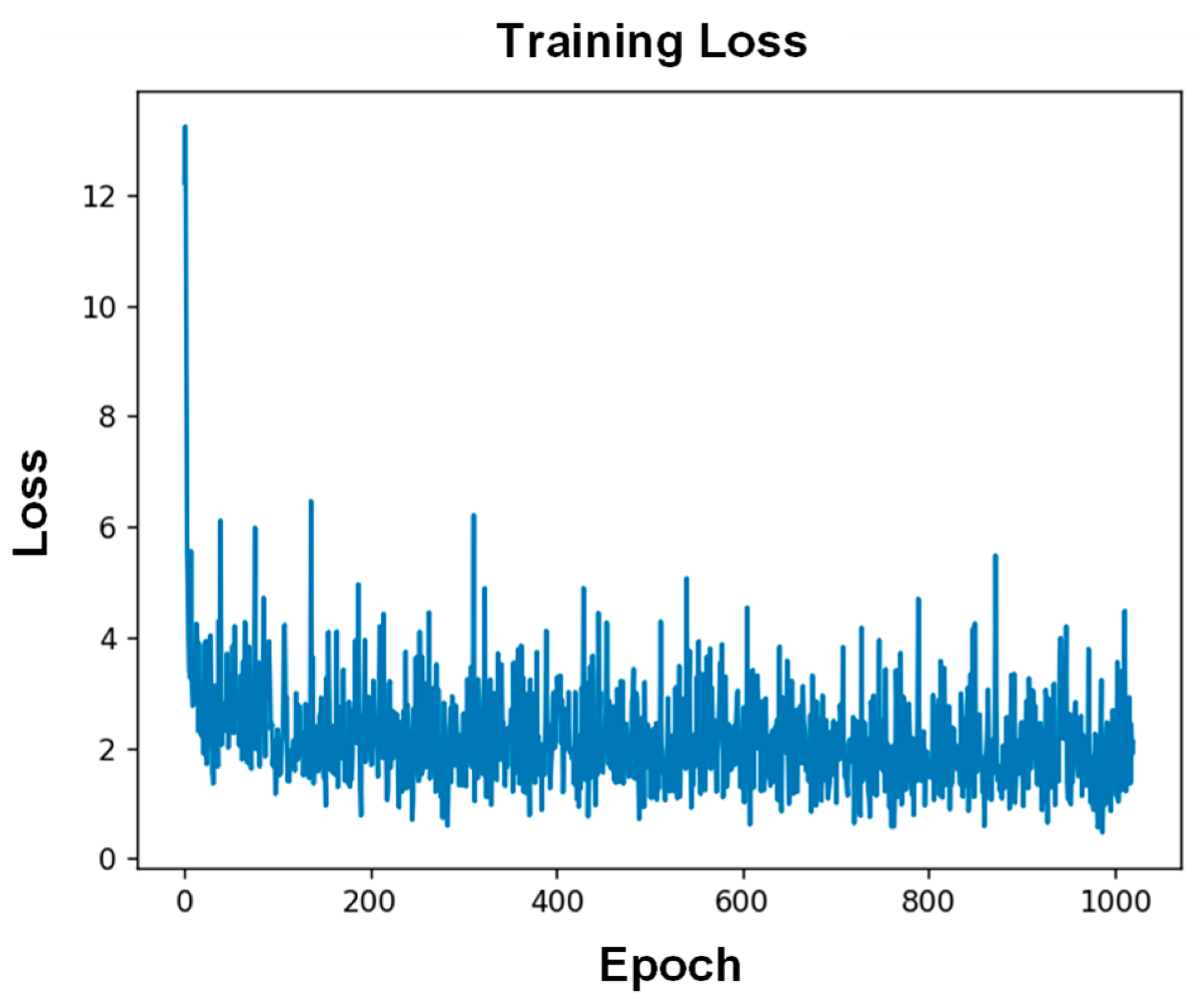
2.3. CNN Model
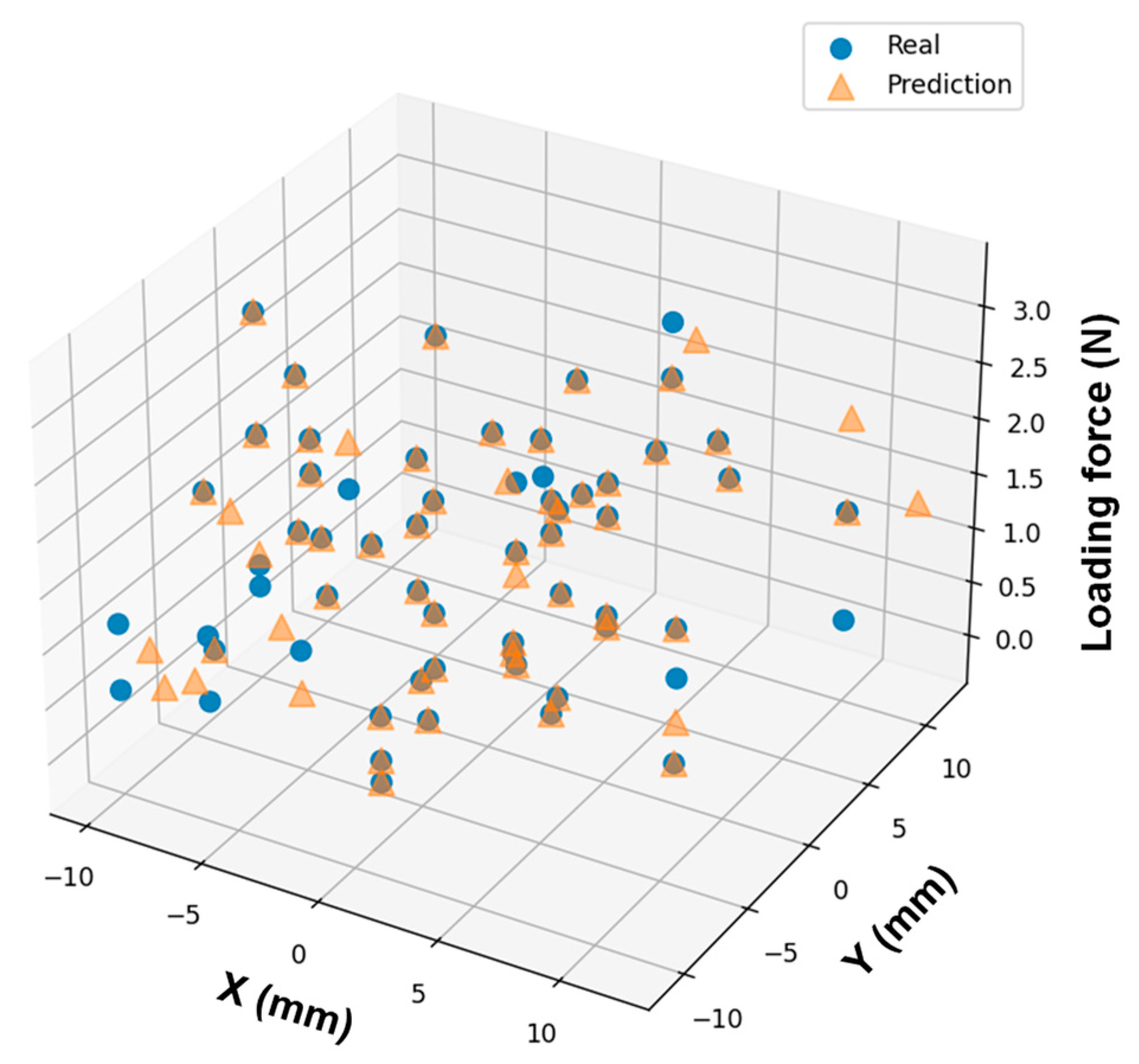
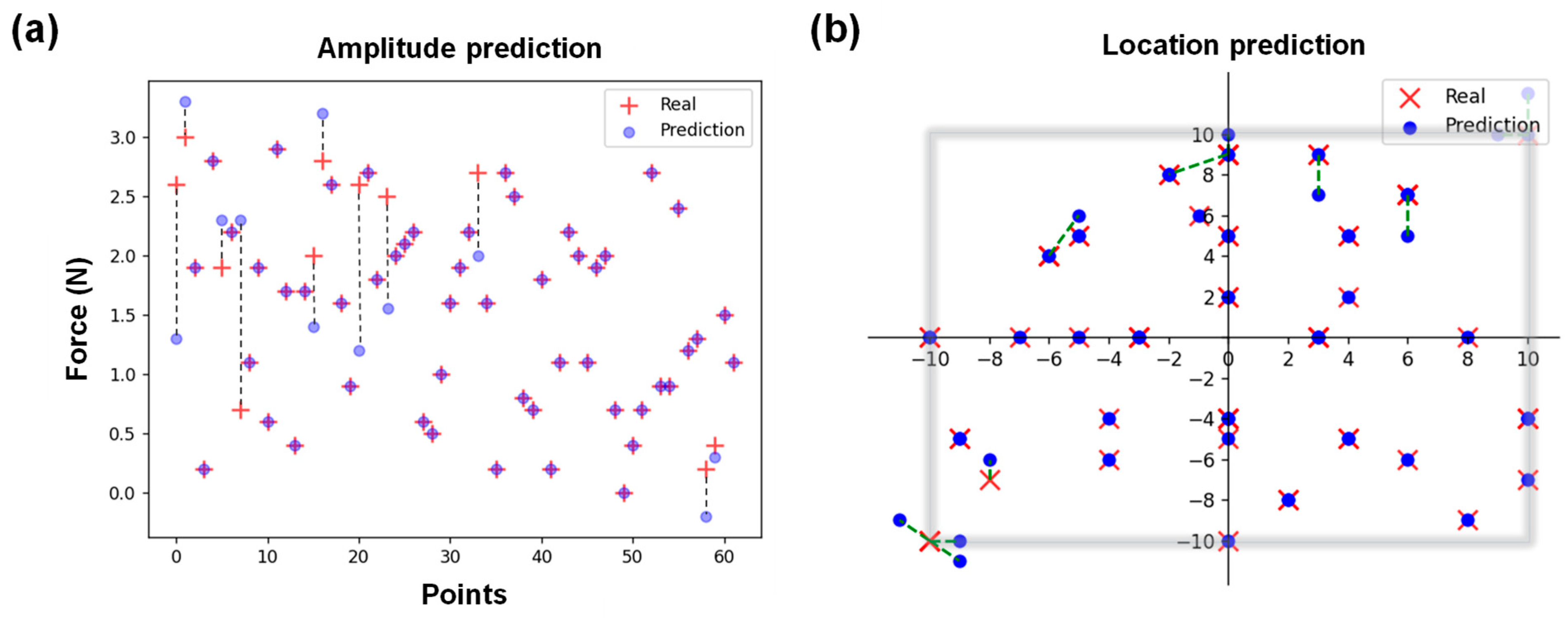
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CNT | Carbon Nanotube |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| EIT | Electrical Impedance Tomography |
| CFRP | Carbon Fiber-reinforced Polymer |
| MAE | Mean Absolute Error |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
References
- Forintos, N.; Czigany, T. Multifunctional application of carbon fiber reinforced polymer composites: Electrical properties of the reinforcing carbon fibers—A short review. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 162, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lin, G.; Vaidya, U.; Wang, H. Past, present and future prospective of global carbon fibre composite developments and applications. Compos. Part B Eng. 2023, 250, 110463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kormanikova, E.; Zmindak, M.; Novak, P.; Sabol, P. Tensile properties of carbon fiber reinforced polymer matrix composites: Application for the strengthening of reinforced concrete structure. Compos. Struct. 2021, 275, 114448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Jia, M.; He, M.; Liu, Q.; Lin, Y.; Yi, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, X.; Tang, Y.; Gu, J. Fabrication, applications, and prospects for poly (p-phenylene benzobisoxazole) nanofibers. SusMat 2024, 4, e245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehrani, M.; Boroujeni, A.; Hartman, T.; Haugh, T.; Case, S.; Al-Haik, M. Mechanical characterization and impact damage assessment of a woven carbon fiber reinforced carbon nanotube–epoxy composite. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2013, 75, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Ma, J.; Sun, W.; Yin, B.; Liew, K. Low-velocity impact and compression-after-impact behaviors of twill woven carbon fiber/glass fiber hybrid composite laminates with flame retardant epoxy resin. Compos. Struct. 2023, 321, 117253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panopoulou, A.; Loutas, T.; Roulias, D.; Fransen, S.; Kostopoulos, V. Dynamic fiber Bragg gratings based health monitoring system of composite aerospace structures. Acta Astronaut. 2011, 69, 445–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Palardy, G. Damage monitoring methods for fiber-reinforced polymer joints: A review. Compos. Struct. 2022, 299, 116043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCrory, J.P.; Al-Jumaili, S.K.; Crivelli, D.; Pearson, M.R.; Eaton, M.J.; Featherston, C.A.; Guagliano, M.; Holford, K.M.; Pullin, R. Damage classification in carbon fibre composites using acoustic emission: A comparison of three techniques. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 68, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamath, G.; Sundaram, R.; Gupta, N.; Rao, M.S. Damage studies in composite structures for structural health monitoring using strain sensors. Struct. Health Monit. 2010, 9, 497–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Sante, R. Fibre optic sensors for structural health monitoring of aircraft composite structures: Recent advances and applications. Sensors 2015, 15, 18666–18713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giurgiutiu, V.; Santoni-Bottai, G. Structural health monitoring of composite structures with piezoelectric-wafer active sensors. AIAA J. 2011, 49, 565–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swait, T.; Jones, F.; Hayes, S. A practical structural health monitoring system for carbon fibre reinforced composite based on electrical resistance. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2012, 72, 1515–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Wang, X.; Qiu, L.; Ni, Y.; Dong, X.; Cui, Y.; Ashour, A.; Han, B.; Ou, J. Self-sensing cementitious composites with hierarchical carbon fiber-carbon nanotube composite fillers for crack development monitoring of a maglev girder. Small 2023, 19, 2206258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, L. Development of self-sensing cementitious composite incorporating hybrid graphene nanoplates and carbon nanotubes for structural health monitoring. Sens. Actuators A 2022, 336, 113367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexopoulos, N.; Bartholome, C.; Poulin, P.; Marioli-Riga, Z. Structural health monitoring of glass fiber reinforced composites using embedded carbon nanotube (CNT) fibers. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2010, 70, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, M.; Khan, T.; Hussain, T.; Liao, K.; Umer, R. Carbon coated piezoresistive fiber sensors: From process monitoring to structural health monitoring of composites–A review. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2021, 141, 106236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, J.; Schehl, N.; Bouchard, M.; Li, L.; Lagounov, A.; Lafdi, K. Health monitoring of structural composites with embedded carbon nanotube coated glass fiber sensors. Carbon 2014, 66, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Liu, J.; Zheng, K.; Wu, Z.; Shi, L.; Hu, X. Monitoring of damage evolution in carbon fiber reinforced polymer composites by electrical impedance tomography. NDT E Int. 2024, 148, 103239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallman, T.N.; Smyl, D.J. Structural health and condition monitoring via electrical impedance tomography in self-sensing materials: A review. Smart Mater. Struct. 2020, 29, 123001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonn, S.; Schagerl, M.; Zhao, Y.; Gschossmann, S.; Kralovec, C. Application of electrical impedance tomography to an anisotropic carbon fiber-reinforced polymer composite laminate for damage localization. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 160, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, H.; Fernandes, C.; Ferreira, N.; Lafont, U.; Nunes, J.P. Damage localization on CFRP composites by electrical impedance tomography. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 32, 104164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.; Nicholls, G.; Fox, C. Imaging convex quadrilateral inclusions in uniform conductors from electrical boundary measurements. Stat. Comput. 2009, 19, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Liew, J.; Liew, K. Data-driven machine learning approach for exploring and assessing mechanical properties of carbon nanotube-reinforced cement composites. Compos. Struct. 2021, 267, 113917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepasdar, R.; Karpatne, A.; Shakiba, M. A data-driven approach to full-field nonlinear stress distribution and failure pattern prediction in composites using deep learning. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2022, 397, 115126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.-H.; Kim, H.-S. Deep-learning based damage sensing of carbon fiber/polypropylene composite via addressable conducting network. Compos Struct. 2021, 267, 113871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Qiao, L. Convolutional neural network method for damage detection of CFRP in electrical impedance tomography. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2022, 34, 025401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikdar, S.; Liu, D.; Kundu, A. Acoustic emission data based deep learning approach for classification and detection of damage-sources in a composite panel. Compos. Part B Eng. 2022, 228, 109450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Escobar, J.; Díaz-Montiel, P.; Venkataraman, S.; Díaz-Ramírez, A. Classification and characterization of damage in composite laminates using electrical resistance tomography and supervised machine learning. Control. Health Monit. 2023, 1, 1675867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; Liu, L. High deformation/damage localization accuracy of fibrous composites through deep-learning of single channel data from carbon nanotube sensors. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2024, 187, 108512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böger, L.; Wichmann, M.H.G.; Meyer, L.O.; Schulte, K. Load and health monitoring in glass fibre reinforced composites with an electrically conductive nanocomposite epoxy matrix. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2008, 68, 1886–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Aranda, C.; Rivero-Ayala, M.; Falla, C.; Gamboa, F.; Avilés, F. Electrical monitoring of structural health of laminated composite panels under compressive loading using carbon nanotube yarns. Compos. Commun. 2025, 59, 102565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.-H.; Li, Y.-Q.; Huang, P.; Wang, H.; Hu, N.; Fu, S.-Y. Comprehensive evaluation of the piezoresistive behavior of carbon nanotube-based composite strain sensors. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2021, 208, 108761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabian, I.; Fu, H.; Sharif Khodaei, Z. A convolutional neural network for impact detection and characterization of complex composite structures. Sensors 2019, 19, 4933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Guo, S.; He, S.; Li, W.; Yang, D. Structure health monitoring of a composite wing based on flight load and strain data using deep learning method. Compos. Struct. 2022, 286, 115305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Yang, B.; Tan, J.; Jin, Y.; Xiao, B.; Xian, G.; Xue, X.; Li, Y. Impact damage localization and mode identifcation of CFRPs panels using an electric resistance change method. Compos. Struct. 2021, 276, 114587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.Y.; Jang, J.; Park, Y.-B. Advanced structural health monitoring in carbon fiber-reinforced plastic using real-time self-sensing data and convolutional neural network architectures. Mater. Des. 2022, 224, 111348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Authors | Methods | Objectives | Number of Electrodes | Localization Errors (mm) | Amplitude Errors (Force/N) | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lin et al. | CNN | Damage Detection | N/A | 1800 | N/A | [35] |
| Nonn and Rocha et al. | EIT | Damage localization | 16 | 2–5 | N/A | [21,22] |
| Yang et al. | EIT | Damage localization | 16 | 6 | N/A | [36] |
| Lee et al. | CNN | Damage localization | 4 | 20–180 | N/A | [37] |
| Jiang et al. | CNN | Damage localization | 2 | 5.5 | N/A | [30] |
| Tang et al. | CNN | Load localization | 4 | 0.91 | 0.13 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Tang, Z.-H.; Hu, D.-S.; Pan, J.-R.; Li, Y.-Q.; Fu, S.-Y. Identification of Loading Location and Amplitude in Conductive Composite Materials via Deep Learning Method. Sensors 2026, 26, 779. https://doi.org/10.3390/s26030779
Tang Z-H, Hu D-S, Pan J-R, Li Y-Q, Fu S-Y. Identification of Loading Location and Amplitude in Conductive Composite Materials via Deep Learning Method. Sensors. 2026; 26(3):779. https://doi.org/10.3390/s26030779
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Zhen-Hua, Di-Sen Hu, Jun-Rong Pan, Yuan-Qing Li, and Shao-Yun Fu. 2026. "Identification of Loading Location and Amplitude in Conductive Composite Materials via Deep Learning Method" Sensors 26, no. 3: 779. https://doi.org/10.3390/s26030779
APA StyleTang, Z.-H., Hu, D.-S., Pan, J.-R., Li, Y.-Q., & Fu, S.-Y. (2026). Identification of Loading Location and Amplitude in Conductive Composite Materials via Deep Learning Method. Sensors, 26(3), 779. https://doi.org/10.3390/s26030779







