A Sensorless Rotor Position Detection Method for Permanent Synchronous Motors Based on High-Frequency Square Wave Voltage Signal Injection
Highlights
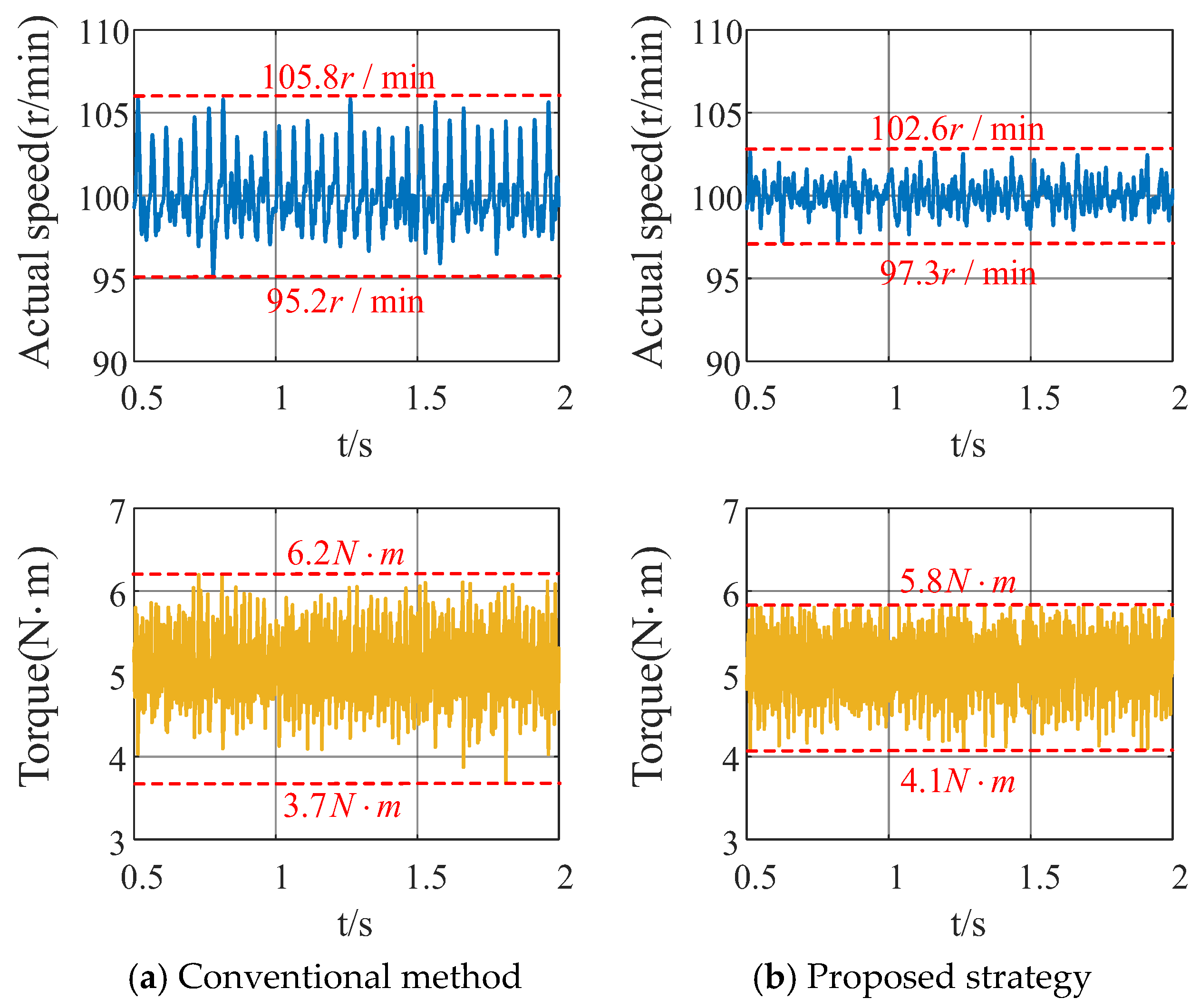
- A sensorless control strategy for permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSM) based on high-frequency square-wave injection with multi-coordinate transformation voltage harmonic suppression using a sixth-order quasi-proportional resonant (QPR) controller is proposed, which exhibits superior harmonic interference rejection performance and significantly reduced speed and torque fluctuations.
- The multi-coordinate transformation architecture can effectively extract the AC components of stator current harmonics by converting them into DC components.
- The establishment of the voltage compensation mathematical model facilitates the compensation of harmonic currents and enables real-time tracking of harmonic components.
- A sixth-order quasi-proportional resonant (QPR) controller, operating in parallel with the proportional-integral (PI) controller, can further suppress additional harmonics of the relevant order introduced during the compensation process.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Rotor Position Extraction Based on High-Frequency Square-Wave Voltage Injection
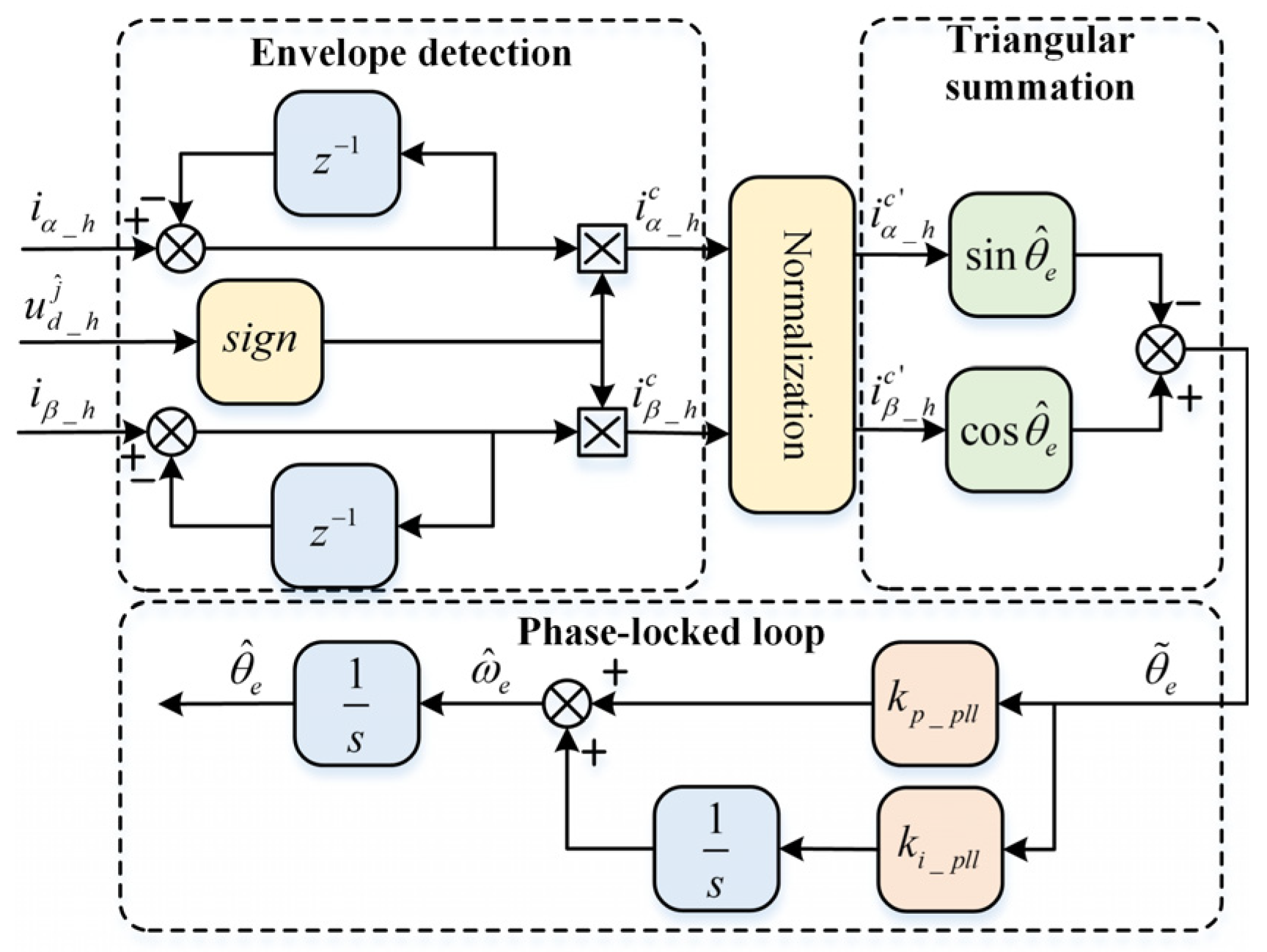
2.1. Square-Wave Injection Position Estimation Without Filter
2.2. Rotor Position Signal Extraction
3. Analysis of Predictive Current Harmonic Suppression Based on Multiple Coordinate Systems
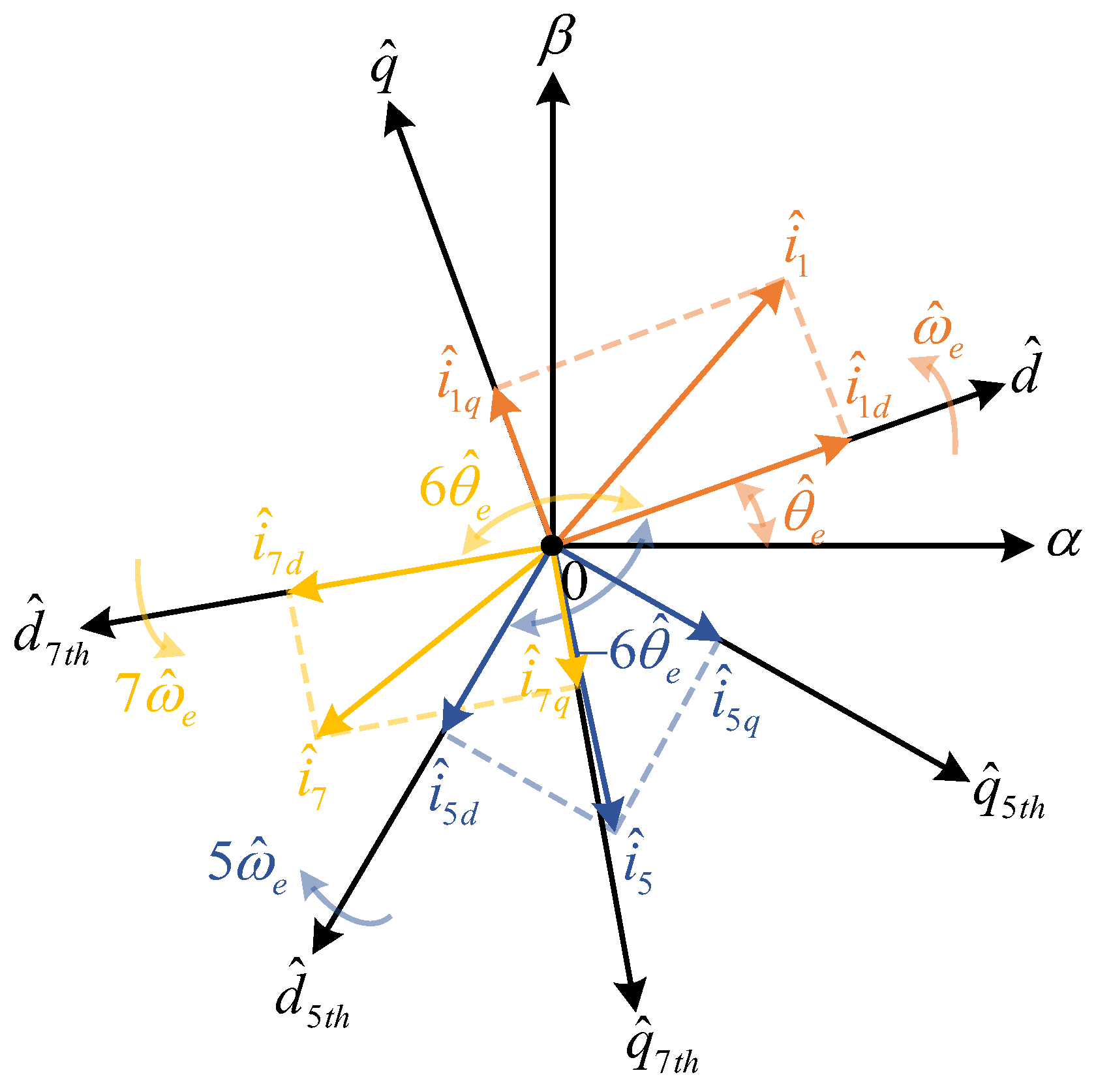
3.1. Stator Current Harmonic Analysis
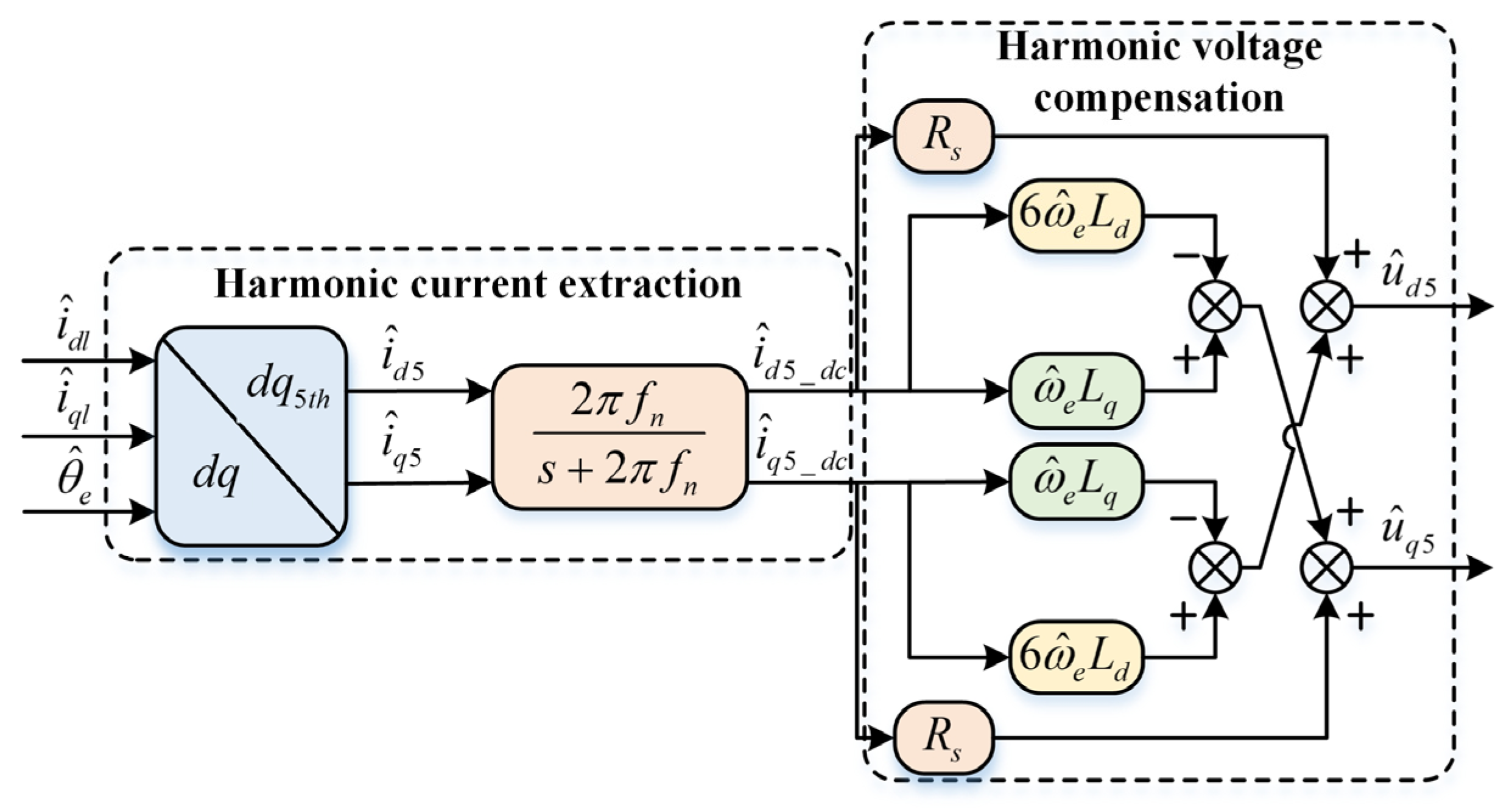
3.2. Current Harmonic Extraction
3.3. Voltage Compensation Based on Multi-Coordinate System Current Harmonic Extraction
4. Multi-Coordinate-System Predictive Current Harmonic Voltage Compensation Strategy Based on Sixth-Order Quasi-Proportional Resonant Control
4.1. Current Loop Control Based on Sixth-Order Quasi-Proportional Resonant Control
4.2. Parameter Tuning Analysis of the Quasi-Proportional Resonant Controller
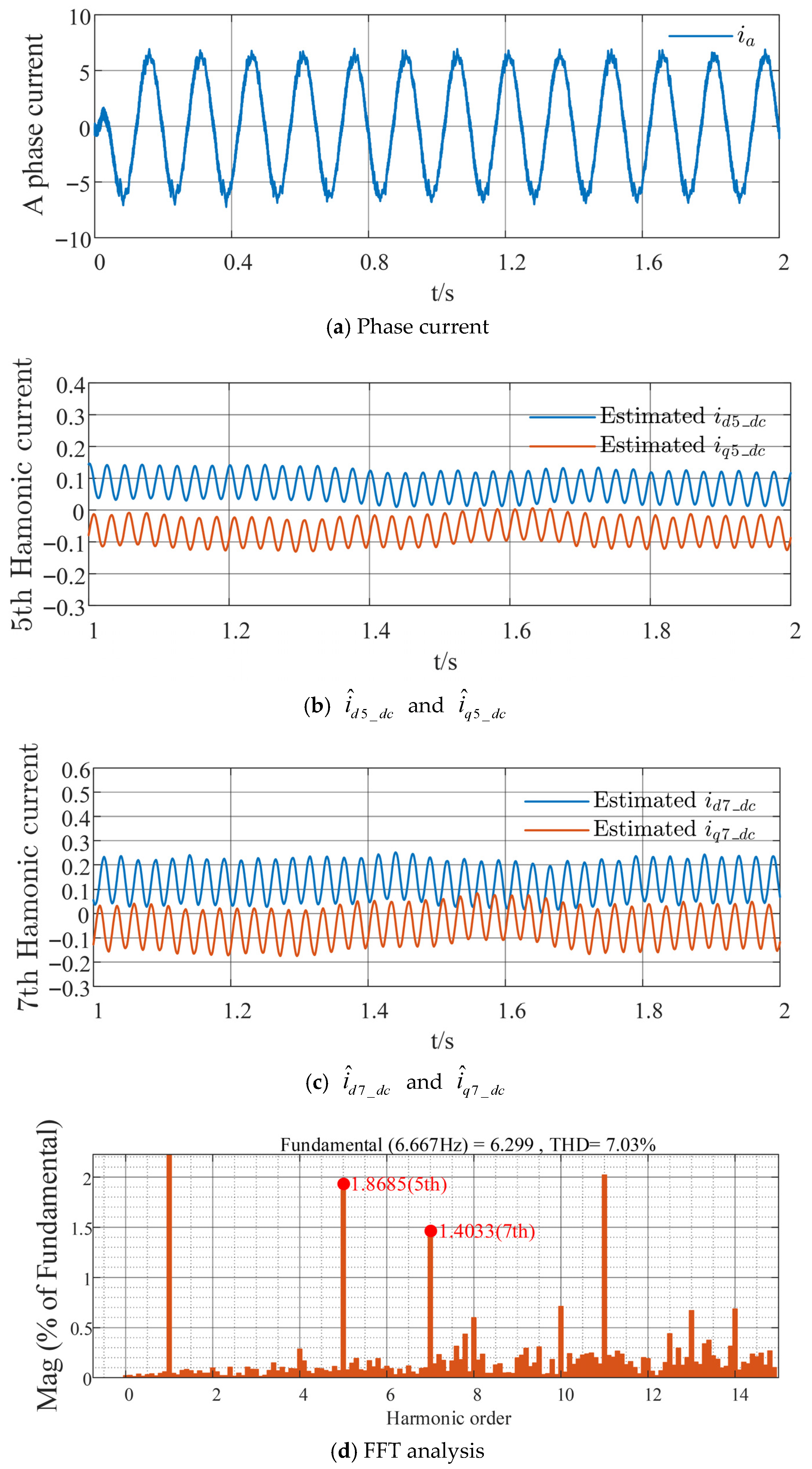
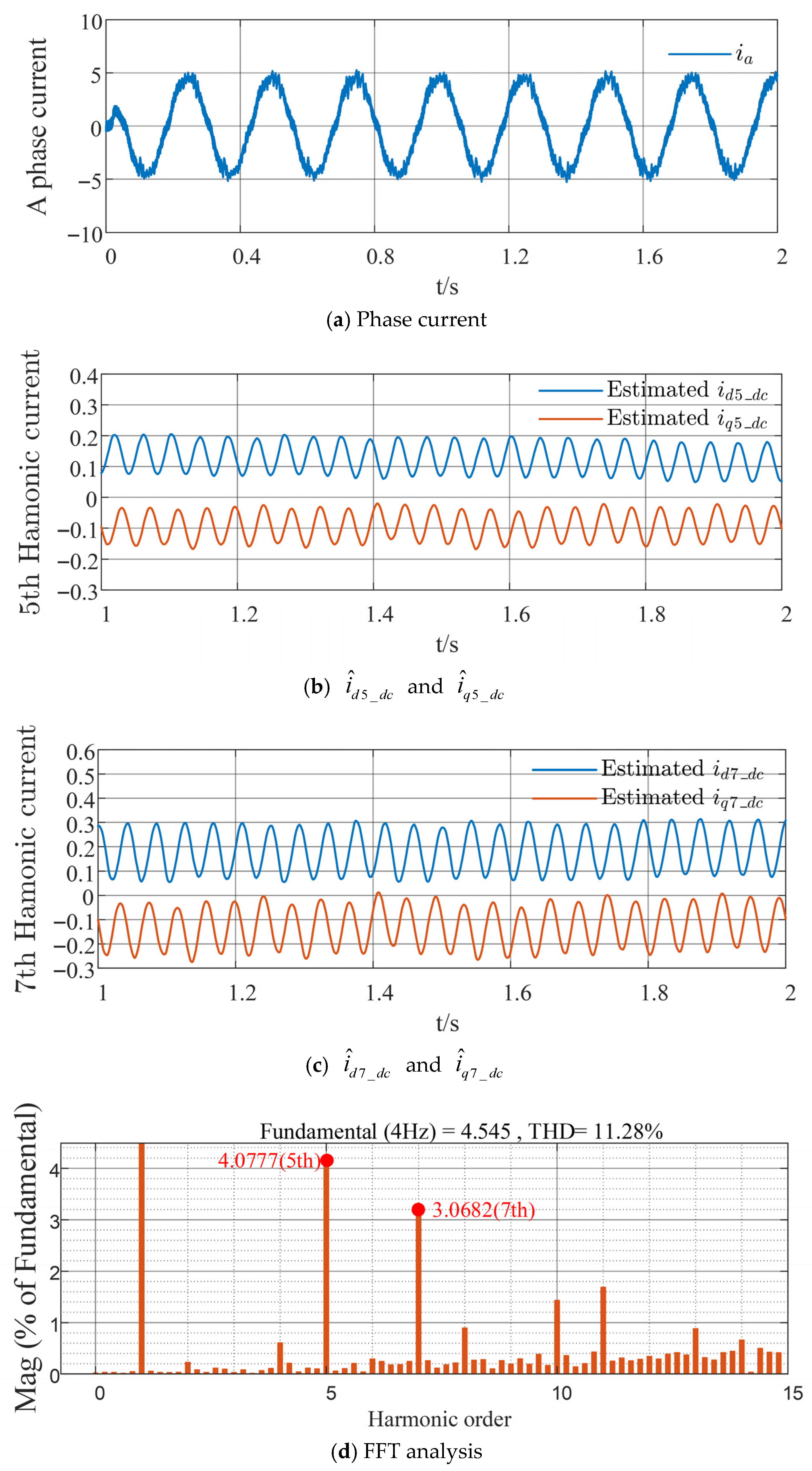
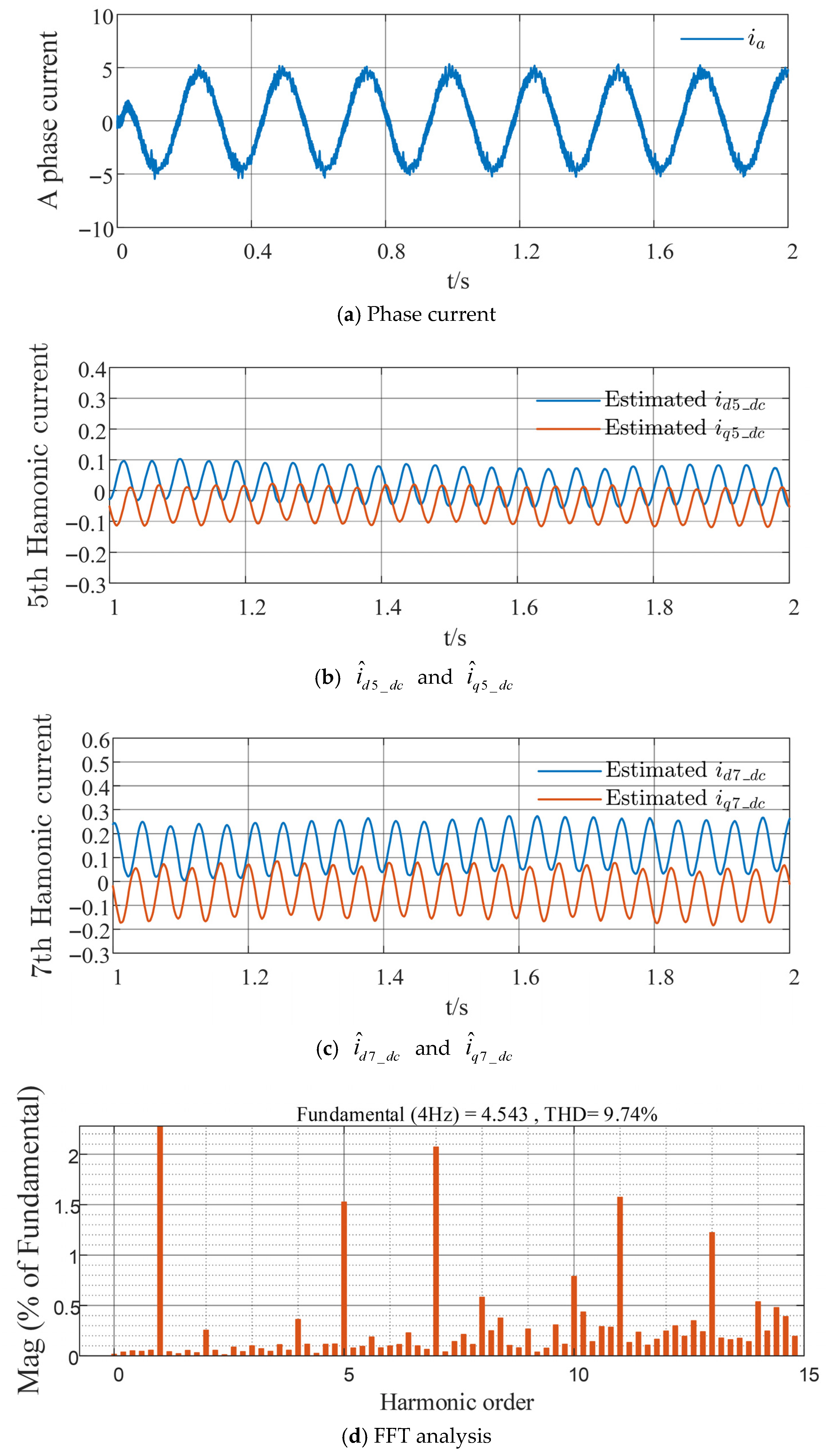
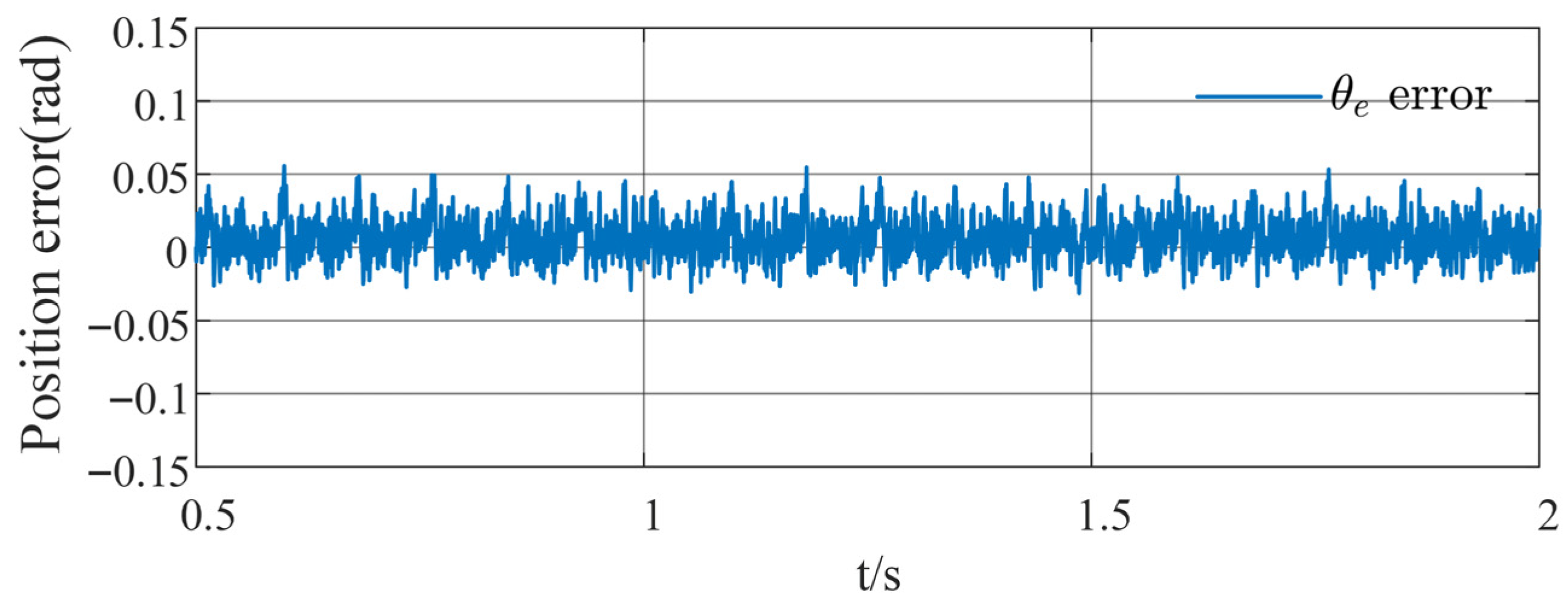
5. Simulation Results and Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IPMSM | interior permanent magnet synchronous motor |
| HFSWI | high-frequency square-wave injection |
| QPR | quasi-proportional resonant |
| HF | high-frequency |
| EMF | electromotive force |
| HPF | high-pass filter |
| LPF | low-pass filter |
| PWM | pulse width modulation |
| DC | direct current |
| AC | alternating current |
| PI | proportional-integral |
| MTPA | maximum torque per ampere |
| FFT | fast Fourier transform |
| THD | total harmonic distortion |
References
- Yan, H.; Wang, W.; Xu, Y.; Zou, J. Position Sensorless Control for PMSM Drives with Single Current Sensor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 70, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Lai, C.; Galkina, A.; Großbichler, M.; Iyer, L.V. Adaptive Current Observer Design for Single Current Sensor Control in PMSM Drives. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2024, 10, 6928–6939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpato Filho, C.J.; Fang, G.; Scalcon, F.P.; Vieira, R.P.; Nahid-Mobarakeh, B. Study on QEMF Model and Adaptive Full-Order Observer Design for Universal Sensorless Control of IPMSMs. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2024, 10, 1335–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.; Kim, H.-S.; Sul, S.-K. MTPA Tracking Control of Sensorless IPMSM Based on Square-Wave Voltage Signal Injection. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 12525–12537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Zhang, Z.; Li, H.; Li, Z.; Xing, Q.; Liu, X.; Wang, F.; Rodriguez, J. A Robust Encoderless Control for PMSM Drives: A Revised Hybrid Active Flux-Based Technique. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 14438–14449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-W.; Lee, J.; Biswas, M.; Park, J.-W. New Acoustic Noise Reduction Method for Signal-Injection-Based IPMSM Sensorless Drive. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 3180–3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Gan, C. High-Frequency Voltage Injection Sensorless Control Technique for IPMSMs Fed by a Three-Phase Four-Switch Inverter With a Single Current Sensor. IEEE ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2018, 23, 758–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, J.; Wu, Y.; Cheng, M. An Improved High-Frequency Voltage Injection Method for Interturn Short-Circuit Fault Detection in PMSMs. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2023, 9, 3228–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tap, A.; Akgul, K.; Ergenc, A.F.; Yilmaz, M.; Ergene, L.T. A Lean Approach to Zero and Low-Speed Sensorless Control of PMaSynRMs. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 35406–135422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Xu, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, X.; Nie, J.; Wang, X. Sensorless Control Impact on Electromagnetic Vibrations and Acoustic Noises in Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2025, 11, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Gao, C.; Gu, M.; Cheng, M. A Novel Vector Magnetic Circuit Based Position Observer for IPMSM Drives Using High-Frequency Signal Injection. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2024, 39, 1333–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Tang, Q.; Shen, A.; Zhang, Q. PMSM Sensorless Control by Injecting HF Pulsating Carrier Signal Into Estimated Fixed-Frequency Rotating Reference Frame. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 2294–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Tang, X.; Li, J.; Liu, G. Time delay compensation strategy for PMSM sensorless control based on high-frequency square-wave signal injection. Electr. Eng. 2025, 107, 11949–11958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.L.; Zhu, Z.Q. Novel Square-Wave Signal Injection Method Using Zero-Sequence Voltage for Sensorless Control of PMSM Drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 7444–7454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, I.; Kwon, Y.-C.; Sul, S.-K. Enhanced Dynamic Operation of Heavily Saturated IPMSM in Signal-Injection Sensorless Control With Ancillary Reference Frame. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 5726–5741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yin, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhang, R.; Sun, X. IPMSM Sensorless Control Using High-Frequency Voltage Injection Method With Random Switching Frequency for Audible Noise Improvement. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 6019–6030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhou, H.; Zhao, N.; Li, C.; Xu, D. Sensorless Control of IPMSM Drives Using a Pseudo-Random Phase-Switching Fixed-Frequency Signal Injection Scheme. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 7660–7671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Xiao, D.; Zhang, G.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Xu, D. Sensorless Control Scheme of IPMSMs Using HF Orthogonal Square-Wave Voltage Injection Into a Stationary Reference Frame. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 2573–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kwon, Y.-C.; Sul, S.-K.; Kim, J.-H.; Yu, R.-S. Suppression of Injection Voltage Disturbance for High-Frequency Square-Wave Injection Sensorless Drive With Regulation of Induced High-Frequency Current Ripple. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 52, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, X.; Yuan, D.; Liu, J. Estimated position error suppression using novel PLL for IPMSM sensorless drives based on fullorder SMO. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 4463–4474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Huang, S.; Liu, K.; Lu, K.; Hu, Y.; Pan, W.; Peng, X. Enhanced position sensorless control using bilinear recursive least squares adaptive filter for interior permanent magnet synchronous motor. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 681–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yin, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, P. A Harmonic Suppression Strategy Based on Adaptive Synchronous Rotating Frame Transformation for Improving the Estimation Accuracy of Sensorless Drivers With Small Capacitors. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2024, 39, 3521–3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| IPMSM Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Rated speed/(r·min−1) | 1500 |
| Stator resistance/Ω | 0.958 |
| Moment of inertia/(kg·m2) | 0.003 |
| -axis inductance/mH | 5.25 |
| -axis inductance/mH | 12 |
| Permanent magnet flux linkage/Wb | 0.1827 |
| Number of pole pairs | 4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Song, A.; Feng, Z.; Huang, B.; Ning, B. A Sensorless Rotor Position Detection Method for Permanent Synchronous Motors Based on High-Frequency Square Wave Voltage Signal Injection. Sensors 2026, 26, 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/s26010028
Song A, Feng Z, Huang B, Ning B. A Sensorless Rotor Position Detection Method for Permanent Synchronous Motors Based on High-Frequency Square Wave Voltage Signal Injection. Sensors. 2026; 26(1):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/s26010028
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Anran, Zilong Feng, Bo Huang, and Bowen Ning. 2026. "A Sensorless Rotor Position Detection Method for Permanent Synchronous Motors Based on High-Frequency Square Wave Voltage Signal Injection" Sensors 26, no. 1: 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/s26010028
APA StyleSong, A., Feng, Z., Huang, B., & Ning, B. (2026). A Sensorless Rotor Position Detection Method for Permanent Synchronous Motors Based on High-Frequency Square Wave Voltage Signal Injection. Sensors, 26(1), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/s26010028





