Experimental Study of Smart Steel Cables with Tubular Spot-Welded Grating Sensors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Fiber Bragg Grating Basic Principles and Tubular Spot-Welded Grating Sensor
3. Shear Test for a Metal Substrate with Spot-Welded Steel Wires
4. Experimental Study on the Mechanical Performance of Smart Cables with Tubular Spot-Welded Grating Sensors
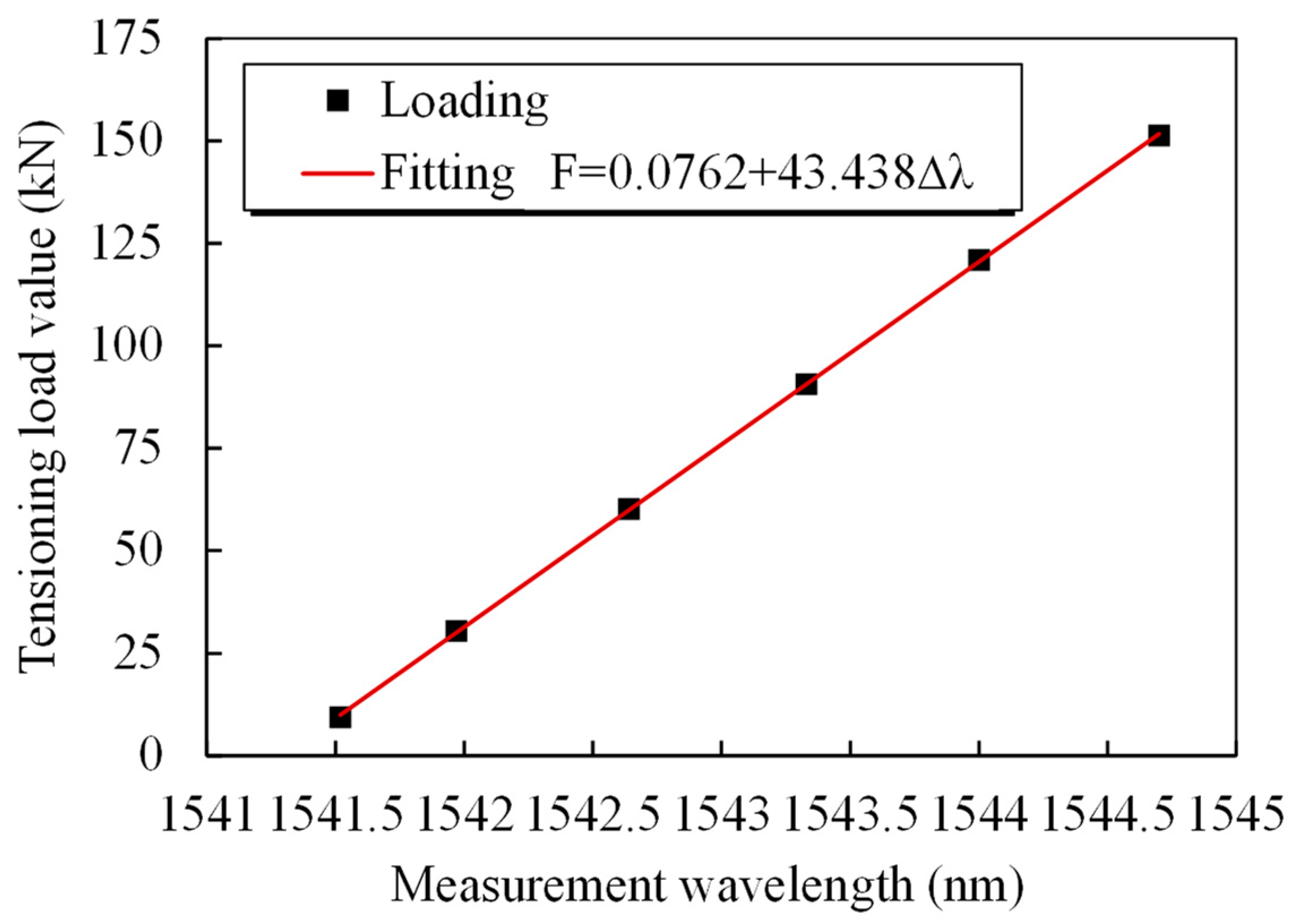
4.1. Force Sensing Performance of the Smart Steel Strand Wire
4.2. Temperature Test for Steel Cables and Compensation Method
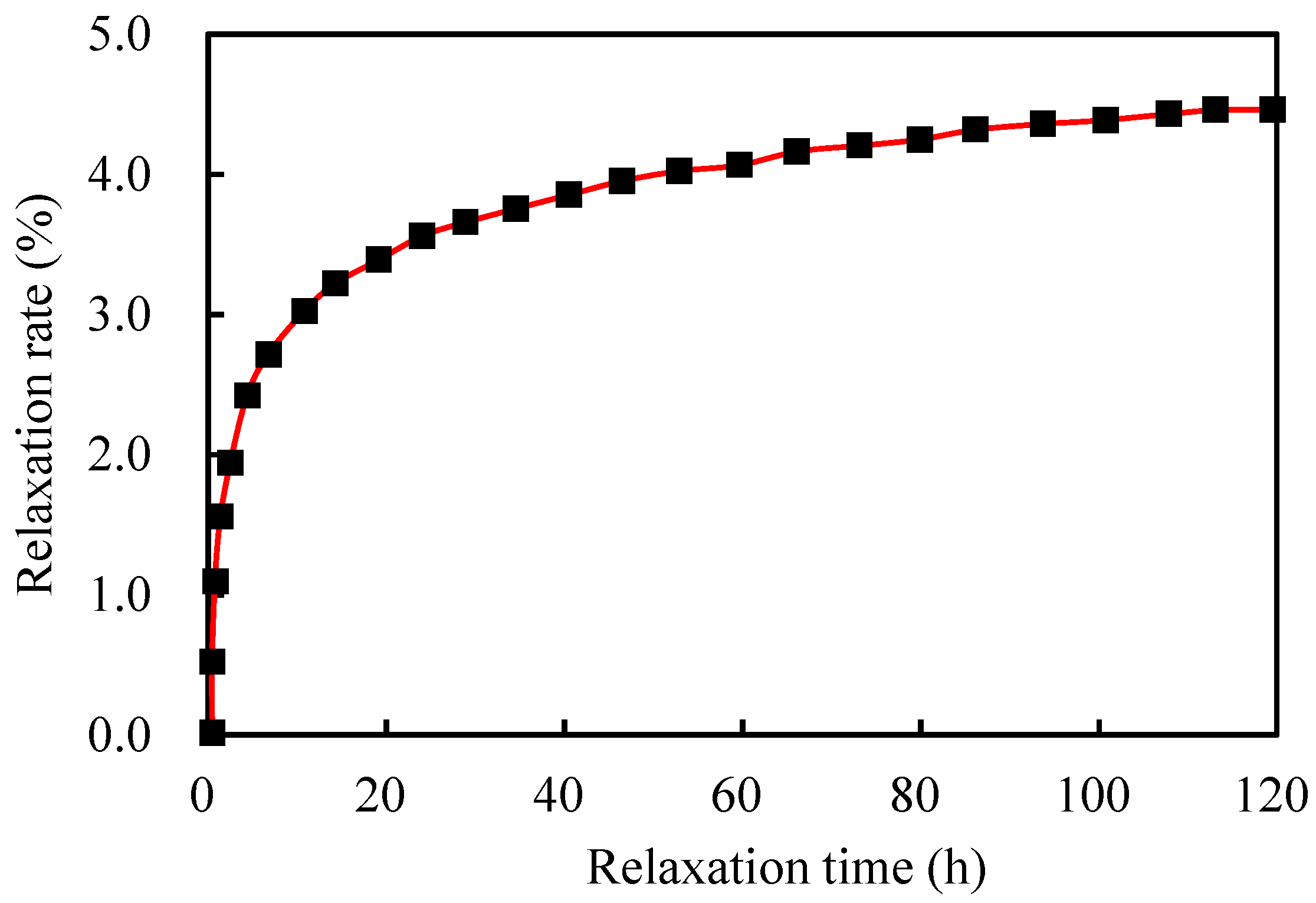
4.3. Tests on the Stress Relaxation of the Steel Strands
4.4. Smart Steel Strand Cable Performance Test
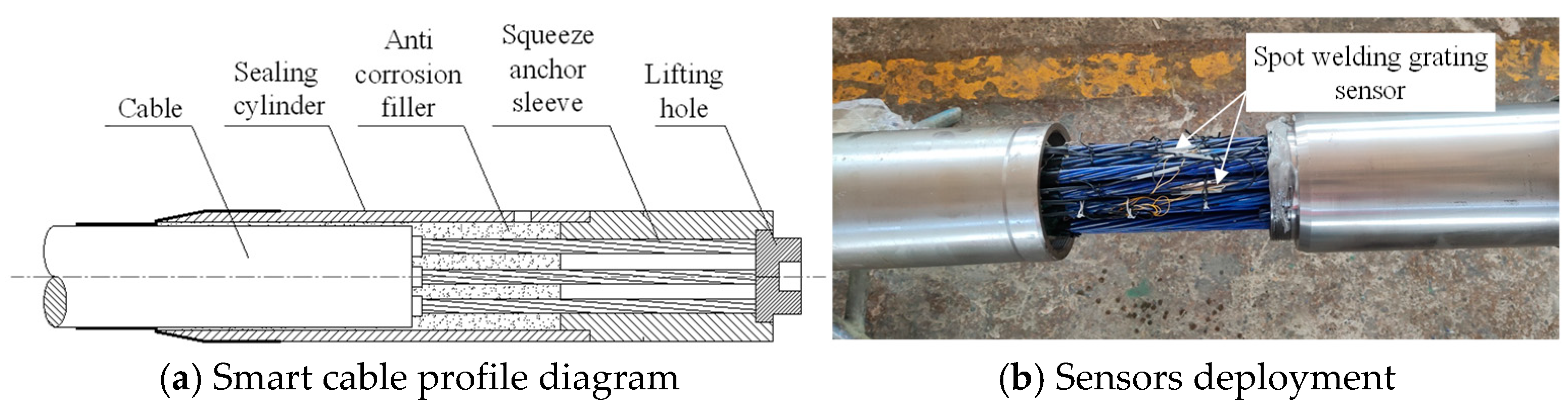
4.5. Engineering Applications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wei, C.; Hu, D.-X. Selection of Cable-stay System for Cable-stayed Bridge Based on Full Life Design Theory. J. Shijiazhuang Tiedao Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2011, 25, 11–14. [Google Scholar]
- Calvi, G.M.; Moratti, M.; O’Reilly, G.J. Once upon a time in Italy: The tale of the Morandi bridge. Struct. Eng. Int. 2018, 29, 198–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Ou, J.-P. Development of FBG sensors for Structural Health Monitoring in civil infrastructures. In Proceeding of the North American Euro-Pacific Workshop “Sensing Issues in Civil Structural Health Monitoring”, Oahu, HI, USA, 10–13 November 2004; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, T.H.T.; Yu, L.; Tam, H.Y. Fiber Bragg grating sensors for structural health monitoring of Tsing Ma bridge: Background and experimental observation. Eng. Struct. 2006, 28, 648–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floris, I.; Sangiorgio, V.; Adam, J.M.; Uva, G.; Rapido, M.; Calderón, P.A.; Madrigal, J. Effects of bonding on the performance of optical fiber strain sensors. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2021, 28, e2782. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.-S. Damage Monitoring and Health Diagnosis for Arch Bridge Suspender; Harbin Institute of Technology: Harbin, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.-G.; Liu, G.-W.; Fu, S.-G.; Xing, F. Recent Progress of Fiber-Optic Sensors for the Structural Health Monitoring of Civil Infrastructure. Sensors 2020, 20, 4517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.-S.; Zhou, Z.; Ou, J.-P. Development and sensing properties study of FRP-FBG smart stay cable for bridge health monitoring applications. Measurement 2011, 44, 722–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, N.-C.; Qian, X.-P.; Sun, L.-M.; Long, Y. Research on Bridge Cable Force Measurement Technology Based on GFRP-OFBG Reinforcement. J. Shijiazhuang Tiedao Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2010, 23, 81–87. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.-P.; Zhou, Z.; Ou, J.-P. Optic fiber sensor-based smart bridge cable with functionality of self-sensing. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2013, 35, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-Z. Study on FBG Sensing Technology-Based Fiber Reinforced Polymer Smart Stayed Cable Wire; Beijing Jiaotong University: Beijing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.-P. Full-Scale Distributed Monitoring Technology of Optical Fiber Brillouin and Its Applications in Civil Engineering; Harbin Institute of Technology: Harbin, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, H.-Y.; Zhang, H.-L.; Zhu, W.-X. Calibration Experiment of Large Range Smart Steel Strand with FBG Sensor Pre-pressed and Embedded in Groove. Railw. Stand. Des. 2018, 62, 76–81. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, H.-Y.; Zhang, H.-L.; Tang, H. The Stress Analysis of Different Spiral Groove Steel Wire Based on ANSYS. J. Shenyang Jianzhu Univ. 2017, 33, 86–93. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.-X.; Shen, Q.-X.; Qin, H.-Y. Monitoring of prestress and bond stress of self-sensing FBG steel strand. Measurement 2021, 177, 109246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-J. The Thin Rod Fiber Bragg Grating Vibration Sensor and Its Application in Cable Force Monitoring; Guilin University of Technology: Guilin, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.-H.; Zhao, X.; Li, S. Smart bridge cable integrated with fiber Bragg grating sensors. J. Highw. Transp. Res. Dev. 2010, 30, 234–237. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, L.-H.; Ji, J.-B. Reliability research on smart bridge cable with built-in fiber Bragg grating sensors. Piezoelectr. Acoustooptics 2013, 35, 33–37. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, R.; Liu, L.; Zhao, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, C.; Hua, X. Investigation of measurability and reliability of adhesive-bonded built-in fiber Bragg grating sensors on steel wire for bridge cable force monitoring. Measurement 2018, 129, 349–357. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 17107-2008; Hot-Dip Galvanized Steel Wires For Bridge Cables. Standardization Admin: Beijing, China, 2008.
- GB/T 5223-2014; Steel Wire for Prestressing of Concrete. AQSIQ: Beijing, China, 2014.
- GB/T5224; Steel Strand for Prestressed Concrete. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2014.
- GB/T21839-2019; Test Methods for Steel Strands for Prestressed Concrete. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Wu, L.-Y.; Guo, W.-B.; Wu, T.-J. Research on portable spot welding machine for lithium battery. Electron. Des. Eng. 2022, 30, 158–161. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.-L.; Sun, B.-C.; Zhang, G.-L. Smart Materials and Structural Health Monitoring. Huazhong University of Science and Technology Press: Wuhan, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Carlos, R.; Carlos, F.; Armindo, L. Development of a long-term monitoring system based on FBG sensors applied to concrete bridges. Eng. Struct. 2010, 32, 1993–2002. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.-H. Key Technology of Metallic Package for Surface-Mounted Fiber Bragg Grating Strain Sensors. Chongqing University: Chongqing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, K.-Y.; Sun, Q.-H.; Ou, Y.-H. Fiber grating tube packaging and its sensing characteristics. Opt. Commun. Tech. 2021, 45, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.-H. Fiber Bragg Grating Capillary Spot Welding Packaging and lts Temperature Sensing Characteristics; Nanchang University: Nanchang, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, H.; Jiang, L.; Xiang, P. Improving the durability of the optical fiber sensor based on strain transfer analysis. Opt. Fiber. Technol. 2018, 42, 97–104. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L. Analysis of Application Problems in Fiber Bragg Grating Sensing; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2011; pp. 101–102. [Google Scholar]


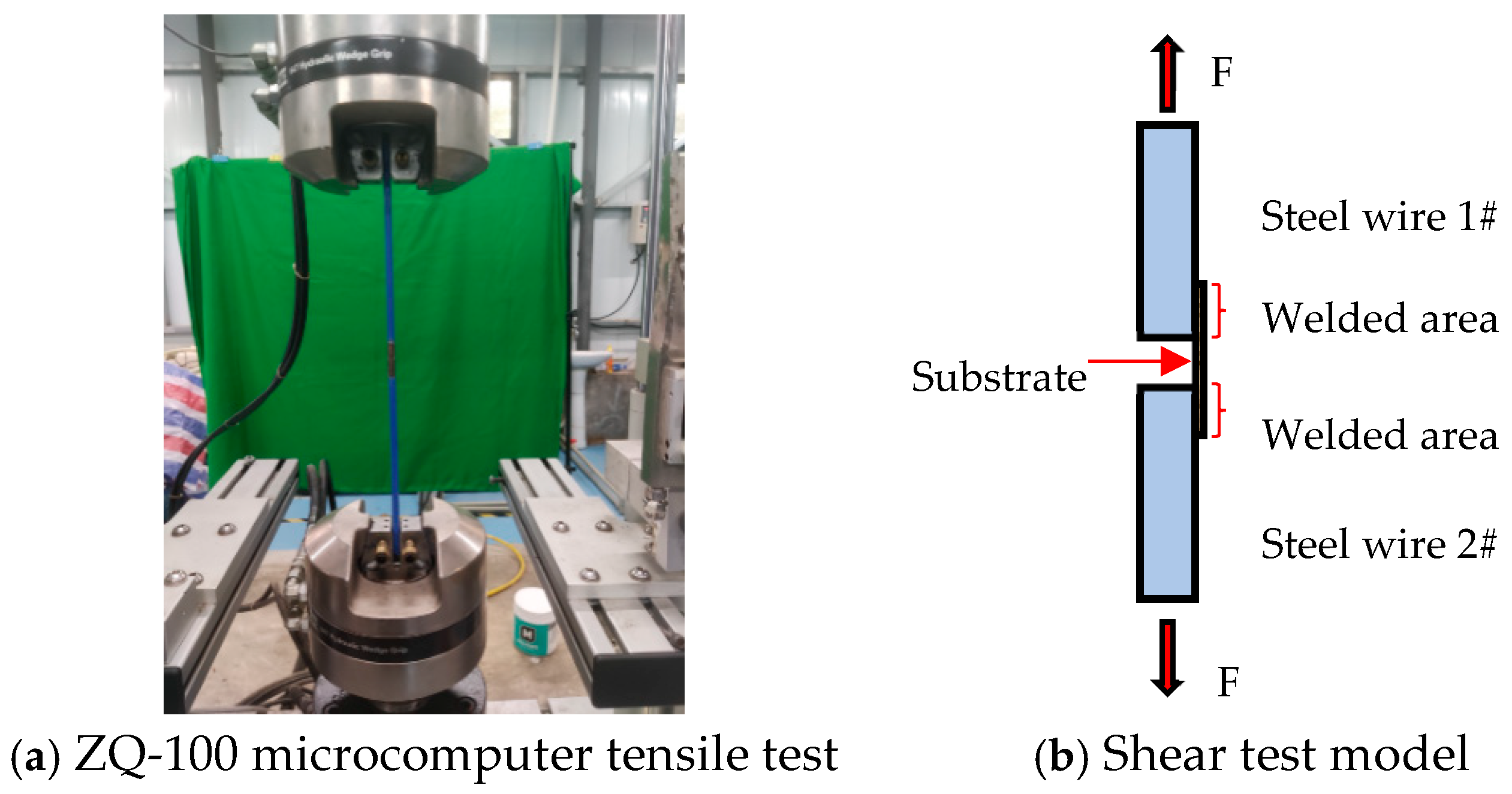











| Test | Spot Welding Quantity/n | Tension/N | Shear Stress/MPa |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 54.7 | 35.5 |
| 2 | 4 | 118.2 | 38.4 |
| 3 | 6 | 174.2 | 37.7 |
| Average | — | — | 37.2 |
| Standard Force/kN | 9.5 | 30 | 60 | 90 | 120 | 150 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st wavelength/nm | 1541.522 | 1541.983 | 1542.686 | 1543.376 | 1544.065 | 1544.752 |
| Calculated force/kN | 9.6 | 29.6 | 60.1 | 90.1 | 120 | 149.9 |
| Error/%F.S. | −0.1 | 0.3 | −0.1 | −0.1 | 0 | 0.1 |
| 2nd wavelength/nm | 1541.526 | 1541.97 | 1542.659 | 1543.342 | 1544.023 | 1544.717 |
| Calculated force/kN | 9.6 | 28.9 | 58.8 | 88.6 | 118.1 | 148.2 |
| Error/%F.S. | −0.1 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 1.3 | 1.2 |
| 3rd wavelength/nm | 1541.528 | 1541.962 | 1542.645 | 1543.324 | 1543.989 | 1544.699 |
| Calculated force/kN | 9.6 | 28.4 | 58.1 | 87.6 | 116.5 | 147.3 |
| Error/%F.S. | −0.1 | 1.1 | 1.3 | 1.6 | 2.3 | 1.8 |
| Load/kN | Wavelength/nm | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −20 °C | −10 °C | 0 °C | 10 °C | 20 °C | 30 °C | 40 °C | 50 °C | |
| 9.5 | 1540.54 | 1540.788 | 1541.028 | 1541.276 | 1541.523 | 1541.771 | 1542.112 | 1542.412 |
| 30 | 1541.001 | 1541.249 | 1541.489 | 1541.737 | 1541.984 | 1542.232 | 1542.573 | 1542.874 |
| 60 | 1541.702 | 1541.95 | 1542.19 | 1542.438 | 1542.685 | 1542.933 | 1543.273 | 1543.574 |
| 90 | 1542.393 | 1542.641 | 1542.881 | 1543.129 | 1543.376 | 1543.624 | 1543.965 | 1544.265 |
| 120 | 1543.083 | 1543.331 | 1543.571 | 1543.819 | 1544.066 | 1544.314 | 1544.655 | 1544.956 |
| 150 | 1543.768 | 1544.016 | 1544.256 | 1544.504 | 1544.751 | 1544.999 | 1545.34 | 1545.641 |
| Standard Load | 9.5 | 30 | 60 | 90 | 120 | 107.3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −20 °C Calculated uncompensated force | −32.9 | −12.8 | 17.5 | 47.6 | 77.6 | 153.3 |
| −20 °C Calculated compensated force | 13.0 | 33.0 | 63.5 | 93.5 | 123.5 | 118.1 |
| −10 °C Calculated uncompensated force | −22.1 | −2.1 | 28.4 | 58.4 | 88.4 | 152.6 |
| −10 °C Calculated compensated force | 12.3 | 32.3 | 62.8 | 92.8 | 122.8 | 128.5 |
| 0 °C Calculated uncompensated force | −11.7 | 8.3 | 38.8 | 68.8 | 98.8 | 151.5 |
| 0 °C Calculated compensated force | 11.2 | 31.3 | 61.7 | 91.7 | 121.7 | 139.3 |
| 10 °C Calculated uncompensated force | −0.9 | 19.1 | 49.5 | 79.6 | 109.5 | 150.8 |
| 10 °C Calculated compensated force | 10.5 | 30.6 | 61.0 | 91.0 | 121.0 | 150.0 |
| 20 °C Calculated uncompensated force | 9.8 | 29.8 | 60.3 | 90.3 | 120.3 | 150.0 |
| 20 °C Calculated compensated force | 9.8 | 29.8 | 60.3 | 90.3 | 120.3 | 160.8 |
| 30 °C Calculated uncompensated force | 20.5 | 40.6 | 71.1 | 101.1 | 131.1 | 149.3 |
| 30 °C Calculated compensated force | 9.1 | 29.1 | 59.6 | 89.6 | 119.6 | 175.7 |
| 40 °C Calculated uncompensated force | 35.4 | 55.4 | 85.8 | 115.9 | 145.9 | 152.7 |
| 40 °C Calculated compensated force | 12.4 | 32.4 | 62.8 | 92.9 | 122.9 | 188.7 |
| 50 °C Calculated uncompensated force | 48.4 | 68.5 | 98.9 | 128.9 | 159.0 | 154.3 |
| 50 °C Calculated compensated force | 13.9 | 34.0 | 64.4 | 94.5 | 124.5 | 107.3 |
| Test Time | Relaxation Force (kN) | Relaxation Rate/% | Test Time | Relaxation Force (kN) | Relaxation Rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 min | 0.200 | 0.11 | 1 h | 3.000 | 1.67 |
| 2 min | 0.400 | 0.22 | 2 h | 3.600 | 2.00 |
| 3 min | 0.500 | 0.28 | 4 h | 4.500 | 2.50 |
| 4 min | 0.600 | 0.33 | 8 h | 5.200 | 2.89 |
| 5 min | 0.700 | 0.39 | 16 h | 5.900 | 3.28 |
| 8 min | 0.900 | 0.50 | 24 h | 6.400 | 3.56 |
| 10 min | 1.800 | 1.00 | 48 h | 7.100 | 3.94 |
| 15 min | 1.800 | 1.00 | 72 h | 7.500 | 4.17 |
| 30 min | 2.300 | 1.28 | 96 h | 7.800 | 4.33 |
| 45 min | 2.600 | 1.44 | 120 h | 8.000 | 4.44 |
| Time | Standard Load (kN) | Wavelength (nm) | Wavelength Variation (nm) | Actual Relaxation Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before loading | 0 | 1537.111 | - | 0.044 |
| 1 min | 180.2 | 1541.071 | 3.960 | |
| 120 h | 172.1 | 1540.884 | 3.773 |
| Standard Load (kN) | Wavelength 1# (nm) | Wavelength 2# (nm) | Average Wavelength Change (nm) | Calculated Cable Tension (kN) | Error/%F.S. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1562.571 | 1554.408 | 0 | −10.2 | −0.3 |
| 332 | 1562.804 | 1554.623 | 0.223 | 319.9 | −0.4 |
| 630 | 1563.039 | 1554.821 | 0.44 | 641.0 | 0.4 |
| 1122 | 1563.385 | 1555.138 | 0.771 | 1130.9 | 0.3 |
| 1631 | 1563.742 | 1555.476 | 1.119 | 1646.0 | 0.5 |
| 2122 | 1564.075 | 1555.785 | 1.44 | 2121.2 | 0 |
| 2620 | 1564.428 | 1556.107 | 1.777 | 2620.0 | 0 |
| 3123 | 1564.773 | 1556.425 | 2.109 | 3111.4 | −0.4 |
| Cable Index | Cable Force Fitting | Fg/kN | Fa/kN | Error/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| s#1 | F = 2456.23Δλ − 10.18 | 388 | 393 | −1.3 |
| x#1 | F = 1527.70Δλ + 14.30 | 403 | 409 | −1.5 |
| s#2 | F = 2458.75Δλ − 1.66 | 368 | 370 | −0.1 |
| x#2 | F = 2927.28Δλ − 17.07 | 379 | 383 | −1.0 |
| s#3 | F = 1583.77Δλ + 56.17 | 363 | 365 | −0.1 |
| x#3 | F = 1495.78Δλ − 9.57 | 369 | 371 | −0.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, N.; Han, Z.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Z. Experimental Study of Smart Steel Cables with Tubular Spot-Welded Grating Sensors. Sensors 2025, 25, 2148. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072148
Deng N, Han Z, Chen Z, Chen Z. Experimental Study of Smart Steel Cables with Tubular Spot-Welded Grating Sensors. Sensors. 2025; 25(7):2148. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072148
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Nianchun, Zhongqing Han, Zhiqian Chen, and Zhaotao Chen. 2025. "Experimental Study of Smart Steel Cables with Tubular Spot-Welded Grating Sensors" Sensors 25, no. 7: 2148. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072148
APA StyleDeng, N., Han, Z., Chen, Z., & Chen, Z. (2025). Experimental Study of Smart Steel Cables with Tubular Spot-Welded Grating Sensors. Sensors, 25(7), 2148. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072148





