KPMapNet: Keypoint Representation Learning for Online Vectorized High-Definition Map Construction
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A keypoint fine-tuning strategy is proposed that optimizes the preservation of original ground truth shape features, establishing a novel method for ground truth representation in this field.
- A novel framework, KPMapNet, is introduced that integrates map mask feature fusion with an innovative point-to-line hybrid matching loss, thereby enabling the precise modeling of map elements.
- KPMapNet achieves 75.1 mAP on the NuScenes dataset and 74.2 mAP on the Argoverse2 dataset. Moreover, the visualization results demonstrate the framework’s improved predictive performance for instances exhibiting complex shapes.
2. Related Works
2.1. Online HD Map Construction
2.2. Map Instance Modeling
2.3. Map Mask for Segmentations
3. The Proposed Method
3.1. Model Pipeline
3.2. Ground Truth Representation
3.3. Architecture Detail
3.4. Training Loss
4. Experiments
4.1. Datasets
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
4.3. Implementation Details
4.4. Main Results
4.5. Ablation Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liang, M.; Yang, B.; Hu, R.; Chen, Y.; Liao, R.; Feng, S.; Urtasun, R. Learning lane graph representations for motion forecasting. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Proceedings, Part II 16. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 541–556. [Google Scholar]
- Song, H.; Luan, D.; Ding, W.; Wang, M.Y.; Chen, Q. Learning to predict vehicle trajectories with model-based planning. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning, PMLR, Auckland, New Zealand, 14–18 December 2022; pp. 1035–1045. [Google Scholar]
- Deo, N.; Wolff, E.; Beijbom, O. Multimodal trajectory prediction conditioned on lane-graph traversals. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning, PMLR, Auckland, New Zealand, 14–18 December 2022; pp. 203–212. [Google Scholar]
- Da, F.; Zhang, Y. Path-aware graph attention for hd maps in motion prediction. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 23–27 May 2022; pp. 6430–6436. [Google Scholar]
- Espinoza, J.L.V.; Liniger, A.; Schwarting, W.; Rus, D.; Van Gool, L. Deep interactive motion prediction and planning: Playing games with motion prediction models. In Proceedings of the Learning for Dynamics and Control Conference. PMLR, Stanford, CA, USA, 23–24 June 2022; pp. 1006–1019. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Huang, X.; Cui, J.; Liu, C.; Xiao, W. Modified adaptive ant colony optimization algorithm and its application for solving path planning of mobile robot. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 215, 119410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levinson, J.; Montemerlo, M.; Thrun, S. Map-based precision vehicle localization in urban environments. In Proceedings of the Robotics: Science and Systems, Atlanta, GA, USA, 27–30 June 2007; Volume 4, pp. 121–128. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Yang, J.; Chen, L.; Li, K.; Sima, C.; Zhu, X.; Chai, S.; Du, S.; Lin, T.; Wang, W.; et al. Planning-oriented autonomous driving. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 17853–17862. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, J. Machine learning assisted high-definition map creation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 42nd Annual Computer Software and Applications Conference (COMPSAC), Tokyo, Japan, 23–27 July 2018; Volume 1, pp. 367–373. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.; Van De Molengraft, M.J.G.; Dubbelman, G. Monocular semantic occupancy grid mapping with convolutional variational encoder–decoder networks. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2019, 4, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Sun, J.; Leung, H.Y.T.; Andonian, A.; Zhou, B. Cross-view semantic segmentation for sensing surroundings. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 4867–4873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, H. Hdmapnet: An online hd map construction and evaluation framework. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 23–27 May 2022; pp. 4628–4634. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, B.; Chen, S.; Wang, X.; Cheng, T.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, W.; Huang, C. MapTR: Structured Modeling and Learning for Online Vectorized HD Map Construction. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Kigali, Rwanda, 1–5 May 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Roddick, T.; Cipolla, R. Predicting semantic map representations from images using pyramid occupancy networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11138–11147. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Zheng, W.; Huang, J.; Huang, G.; Zhou, J.; Lu, J. Beverse: Unified perception and prediction in birds-eye-view for vision-centric autonomous driving. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.09743. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Yuan, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, H. Vectormapnet: End-to-end vectorized hd map learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Honolulu, HI, USA, 23–29 July 2023; pp. 22352–22369. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, B.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, W.; Huang, C.; Wang, X. Maptrv2: An end-to-end framework for online vectorized hd map construction. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2025, 133, 1352–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caesar, H.; Bankiti, V.; Lang, A.H.; Vora, S.; Liong, V.E.; Xu, Q.; Krishnan, A.; Pan, Y.; Baldan, G.; Beijbom, O. nuScenes: A multimodal dataset for autonomous driving. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1903.11027. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, B.; Qi, W.; Agarwal, T.; Lambert, J.; Singh, J.; Khandelwal, S.; Pan, B.; Kumar, R.; Hartnett, A.; Pontes, J.K.; et al. Argoverse 2: Next Generation Datasets for Self-driving Perception and Forecasting. In Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing Systems Track on Datasets and Benchmarks (NeurIPS Datasets and Benchmarks 2021), Virtual, 4–6 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, T.; Englot, B. Lego-loam: Lightweight and ground-optimized lidar odometry and mapping on variable terrain. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Madrid, Spain, 1–5 October 2018; pp. 4758–4765. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, T.; Bai, X.; Yang, H.; Hou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Yang, R.; Manocha, D.; Zhu, X. Vision-centric bev perception: A survey. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2208.02797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Sima, C.; Dai, J.; Wang, W.; Lu, L.; Wang, H.; Zeng, J.; Li, Z.; Yang, J.; Deng, H.; et al. Delving into the devils of bird’s-eye-view perception: A review, evaluation and recipe. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 46, 2151–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Tang, H.; Amini, A.; Yang, X.; Mao, H.; Rus, D.L.; Han, S. Bevfusion: Multi-task multi-sensor fusion with unified bird’s-eye view representation. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), London, UK, 29 May–2 June 2023; pp. 2774–2781. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, L.; Ding, W.; Qiu, X.; Zhang, C. End-to-end vectorized hd-map construction with piecewise bezier curve. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 13218–13228. [Google Scholar]
- Philion, J.; Fidler, S. Lift, splat, shoot: Encoding images from arbitrary camera rigs by implicitly unprojecting to 3d. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Proceedings, Part XIV 16. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 194–210. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, T.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, H. StreamMapNet: Streaming Mapping Network for Vectorized Online HD Map Construction. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2024; pp. 7356–7365. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, W.; Qiao, L.; Qiu, X.; Zhang, C. Pivotnet: Vectorized pivot learning for end-to-end hd map construction. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 3672–3682. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, T.; Wang, X.; Chen, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, W. Sparse instance activation for real-time instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–22 June 2022; pp. 4433–4442. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.; Homayounfar, N.; Ma, W.C.; Xiong, Y.; Hu, R.; Urtasun, R. Polytransform: Deep polygon transformer for instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 9131–9140. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, J.; Xue, N.; Xia, G.S.; Schiele, B.; Dai, D. Hgformer: Hierarchical grouping transformer for domain generalized semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 15413–15423. [Google Scholar]
- Douglas, D.H.; Peucker, T.K. Algorithms for the reduction of the number of points required to represent a digitized line or its caricature. Cartogr. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Geovisualization 1973, 10, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visvalingam, M.; Whyatt, J. Line generalisation by repeated elimination of points. Cartogr. J. 1993, 30, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q. Efficientnet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; pp. 6105–6114. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.; Hwang, J.w.; Lee, S.; Bae, Y.; Park, J. An Energy and GPU-Computation Efficient Backbone Network for Real-Time Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Huang, G.; Zhu, Z.; Ye, Y.; Du, D. Bevdet: High-performance multi-camera 3d object detection in bird-eye-view. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.11790. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Ge, Z.; Yu, G.; Yang, J.; Wang, Z.; Shi, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, Z. Bevdepth: Acquisition of reliable depth for multi-view 3d object detection. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Montréal, QC, Canada, 8–10 August 2023; Volume 37, pp. 1477–1485. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Huang, G. Bevpoolv2: A cutting-edge implementation of bevdet toward deployment. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2211.17111. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Cheng, T.; Wang, X.; Meng, W.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, W. Efficient and robust 2d-to-bev representation learning via geometry-guided kernel transformer. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.04584. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Su, W.; Lu, L.; Li, B.; Wang, X.; Dai, J. Deformable detr: Deformable transformers for end-to-end object detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.04159. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Wang, W.; Li, H.; Xie, E.; Sima, C.; Lu, T.; Qiao, Y.; Dai, J. Bevformer: Learning bird’s-eye-view representation from multi-camera images via spatiotemporal transformers. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Loshchilov, I.; Hutter, F. Fixing Weight Decay Regularization in Adam. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1711.05101. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Lin, J.; Wu, S.; Luo, Z.; Xue, Y.; Lu, S.; Wang, Z. Online map vectorization for autonomous driving: A rasterization perspective. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 36, 31865–31877. [Google Scholar]
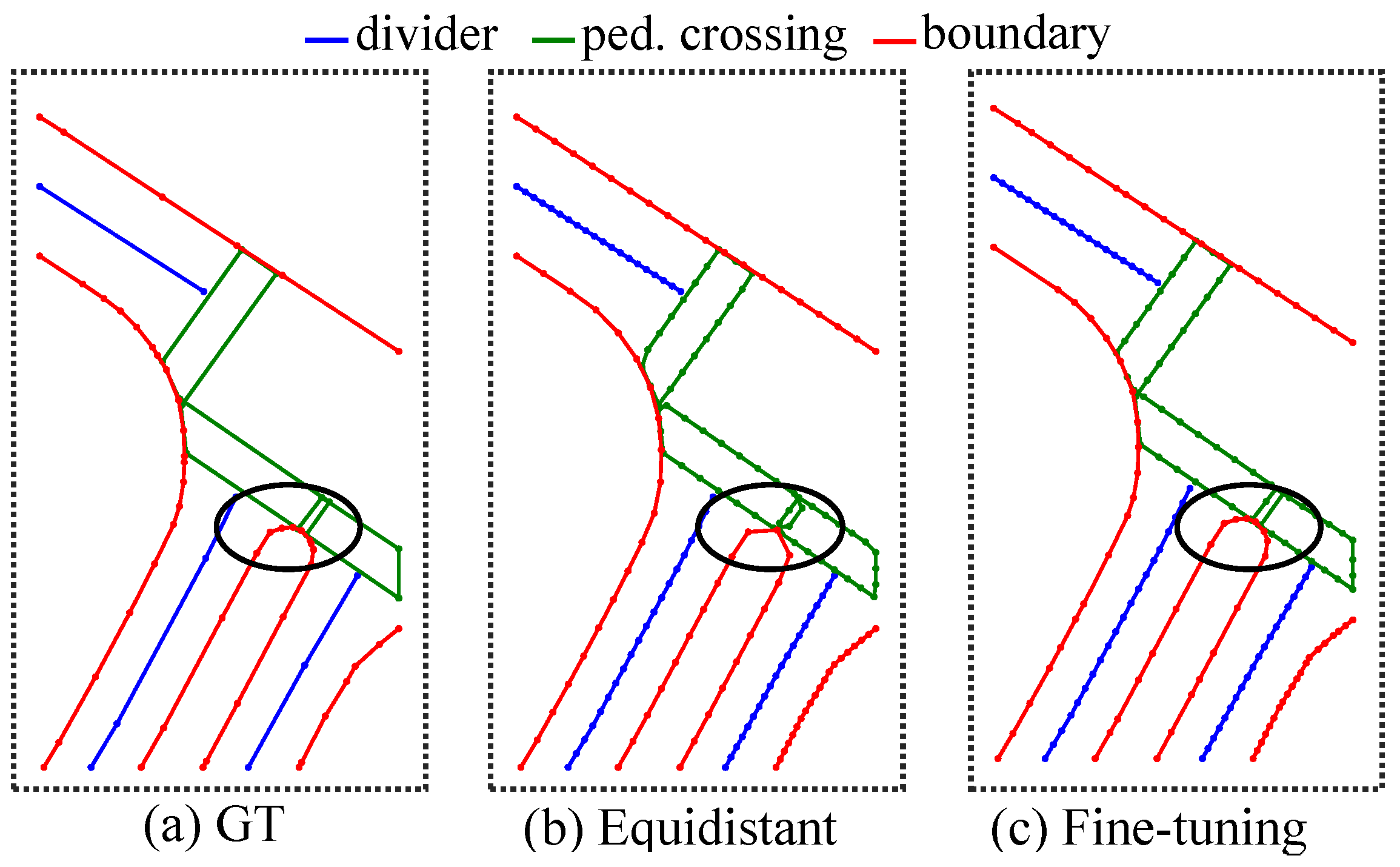


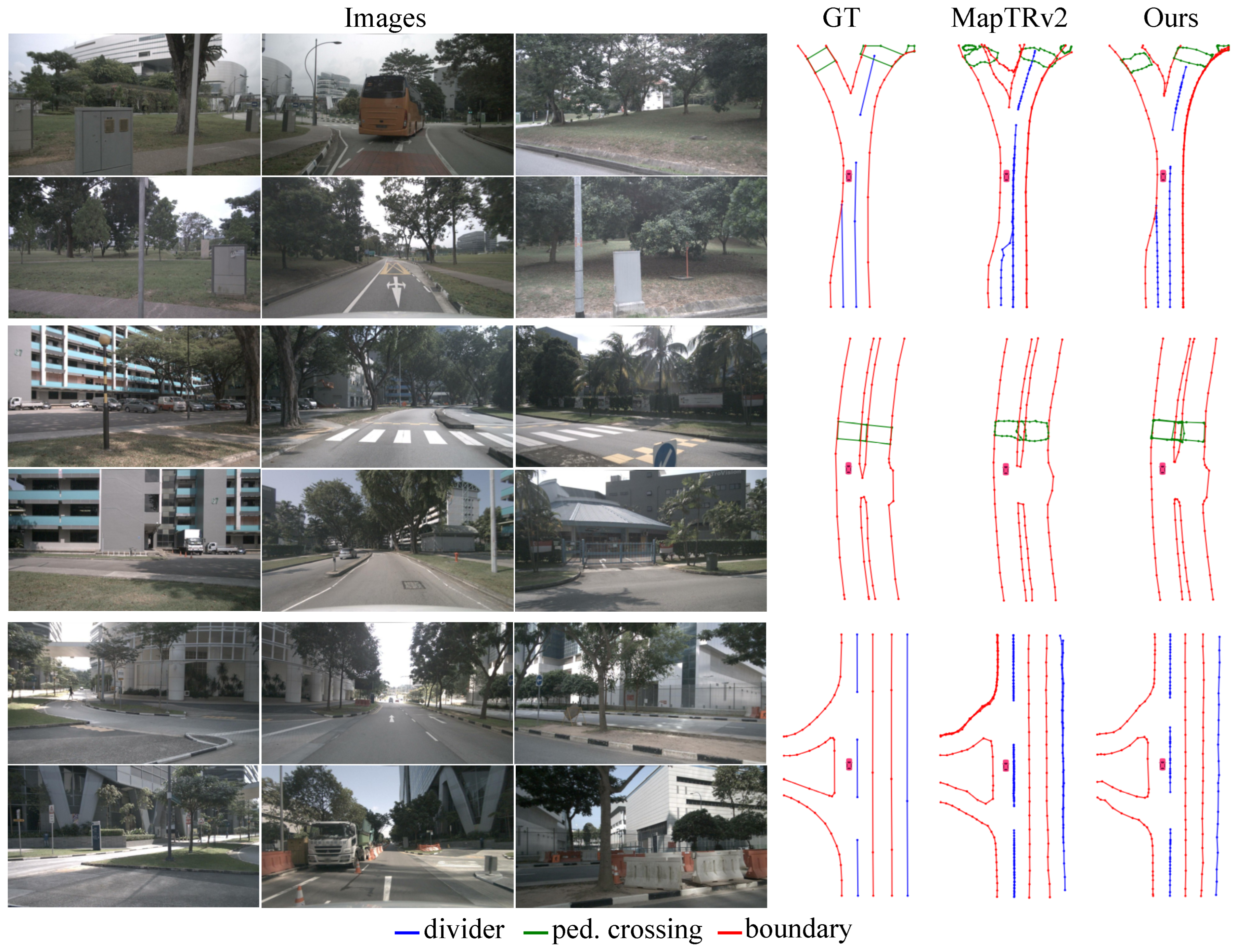
| Method | Backbone | Epoch | APdiv. | APped. | APbou. | mAP | APdiv. | APped. | APbou. | mAP | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDMapNet [12] | EB0 | 30 | 23.6 | 24.1 | 43.5 | 31.4 | 17.7 | 13.6 | 32.7 | 21.3 | 0.8 |
| KpMapNet (Ours) | EB0 | 30 | 26.2 | 33.5 | 45.3 | 35.0 | 14.5 | 15.8 | 25.0 | 18.4 | 14.1 |
| VectorMapNet [16] | R50 | 110 | 47.3 | 36.1 | 39.3 | 40.9 | 27.2 | 18.2 | 18.4 | 21.3 | 2.2 |
| MapTR [13] | R50 | 24 | 51.5 | 46.3 | 53.1 | 50.3 | 30.7 | 23.2 | 28.2 | 27.3 | 15.1 |
| MapVR [44] | R50 | 24 | 54.4 | 47.7 | 51.4 | 51.2 | - | - | - | - | 15.1 |
| PivotNet [27] | R50 | 24 | 56.5 | 56.2 | 60.1 | 57.6 | 41.4 | 34.3 | 39.8 | 38.5 | 10.4 |
| MapTRv2 [17] | R50 | 24 | 62.4 | 59.8 | 62.4 | 61.5 | 40.0 | 35.4 | 36.3 | 37.2 | 14.1 |
| MapTRv2 † [17] | R50 | 24 | 56.0 † | 57.3 † | 62.0 † | 58.4 † | 37.2 † | 31.9 † | 37.0 † | 35.4 † | 14.1 |
| KpMapNet (Ours) | R50 | 24 | 62.4 | 63.7 | 66.1 | 64.1 | 42.7 | 37.9 | 43.5 | 41.4 | 13.9 |
| MapTRv2 [17] | V2-99 | 24 | 67.1 | 63.6 | 69.2 | 66.6 | - | - | - | - | 9.9 |
| MapTRv2 [17] | V2-99 | 110 | 73.7 | 71.4 | 75.0 | 73.4 | - | - | - | - | 9.9 |
| KpMapNet (Ours) | V2-99 | 24 | 65.9 | 63.7 | 71.2 | 66.9 | 45.9 | 37.2 | 48.5 | 43.9 | 9.3 |
| KpMapNet (Ours) | V2-99 | 110 | 74.2 | 73.4 | 77.6 | 75.1 | 56.3 | 47.1 | 56.1 | 53.2 | 9.3 |
| Method | Backbone | Epoch | APdiv. | APped. | APbou. | mAP | APdiv. | APped. | APbou. | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VectorMapNet [16] | R50 | - | 36.1 | 38.3 | 39.2 | 37.9 | - | - | - | - |
| MapTR [13] | R50 | 6 | 58.1 | 54.7 | 56.7 | 56.5 | 42.2 | 28.3 | 33.7 | 34.8 |
| MapVR [44] | R50 | - | 60.0 | 54.6 | 58.0 | 57.5 | - | - | - | - |
| PivotNet [27] | R50 | 6 | - | - | - | - | 47.5 | 31.3 | 43.4 | 40.7 |
| MapTRv2 [17] | R50 | 6 | 72.1 | 62.9 | 67.1 | 67.4 | 52.5 | 34.8 | 40.6 | 42.6 |
| KpMapNet (Ours) | R50 | 6 | 69.4 | 74.7 | 78.5 | 74.2 | 53.3 | 45.7 | 56.1 | 51.7 |
| Fine-Tuning | Point-Line | Fusion | Hybrid | APdiv. | APped. | APbou. | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | 61.2 | 58.9 | 61.5 | 60.5 |
| ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | 55.7 | 57.5 | 61.5 | 58.2 |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | 57.6 | 59.9 | 63.3 | 60.3 |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | 61.2 | 63.1 | 65.2 | 63.2 |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | 59.3 | 60.5 | 64.5 | 61.8 |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 62.4 | 63.7 | 66.1 | 64.1 |
| Loss Weight | APdiv. | APped. | APbou. | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 61.0 | 63.0 | 66.6 | 63.5 |
| 5 | 61.3 | 64.5 | 65.9 | 63.9 |
| 6 | 62.4 | 63.7 | 66.1 | 64.1 |
| 7 | 61.3 | 61.6 | 65.7 | 62.9 |
| APdiv. | APped. | APbou. | mAP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ✗ | 59.3 | 63.0 | 64.9 | 62.4 |
| ✓ | 62.4 | 63.7 | 66.1 | 64.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, B.; Hao, W.; Qiu, W.; Pang, S. KPMapNet: Keypoint Representation Learning for Online Vectorized High-Definition Map Construction. Sensors 2025, 25, 1897. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061897
Jin B, Hao W, Qiu W, Pang S. KPMapNet: Keypoint Representation Learning for Online Vectorized High-Definition Map Construction. Sensors. 2025; 25(6):1897. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061897
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Bicheng, Wenyu Hao, Wenzhao Qiu, and Shanmin Pang. 2025. "KPMapNet: Keypoint Representation Learning for Online Vectorized High-Definition Map Construction" Sensors 25, no. 6: 1897. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061897
APA StyleJin, B., Hao, W., Qiu, W., & Pang, S. (2025). KPMapNet: Keypoint Representation Learning for Online Vectorized High-Definition Map Construction. Sensors, 25(6), 1897. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061897






