Combined Use of Non-Destructive Analysis Techniques to Investigate Ancient Bronze Statues
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The PT Mathematical Model
2.2. Experimental Setup
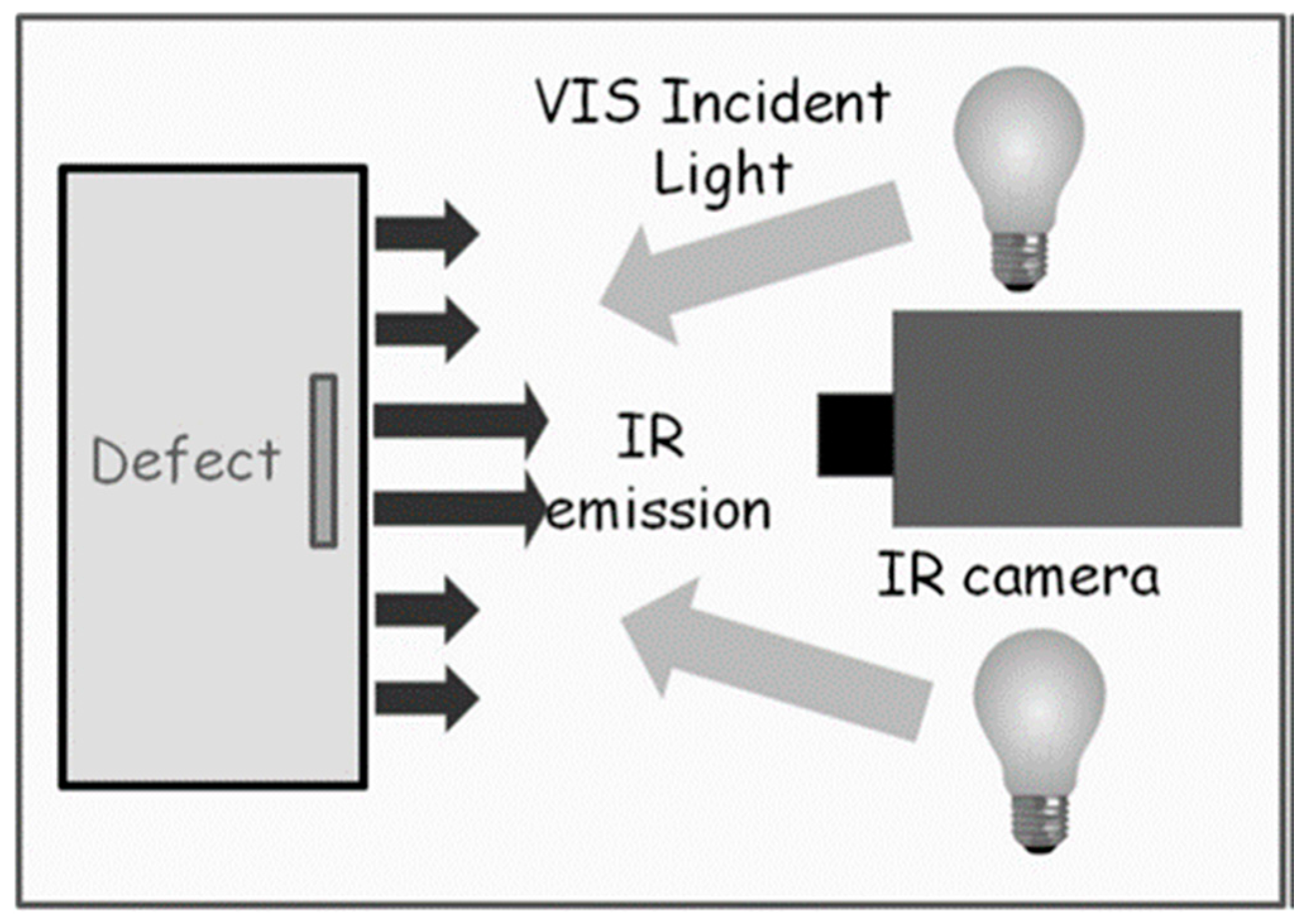
2.2.1. Pulsed Thermography
2.2.2. X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF)
- (a)
- The method of gilding (leaf or fire gilding);
- (b)
- The thickness;
- (c)
- The possible presence of a corrosion layer between the gilding and the substrate.
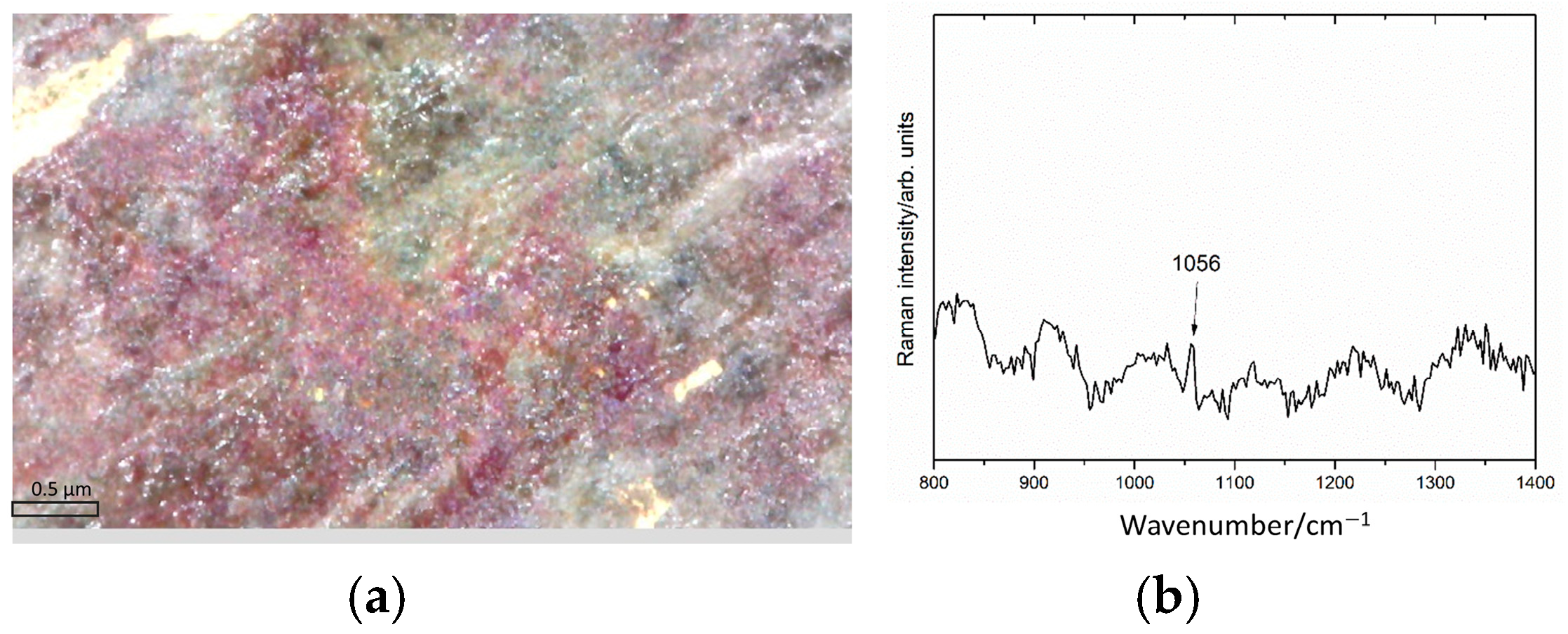
2.2.3. Raman Spectroscopy
3. Results and Discussion
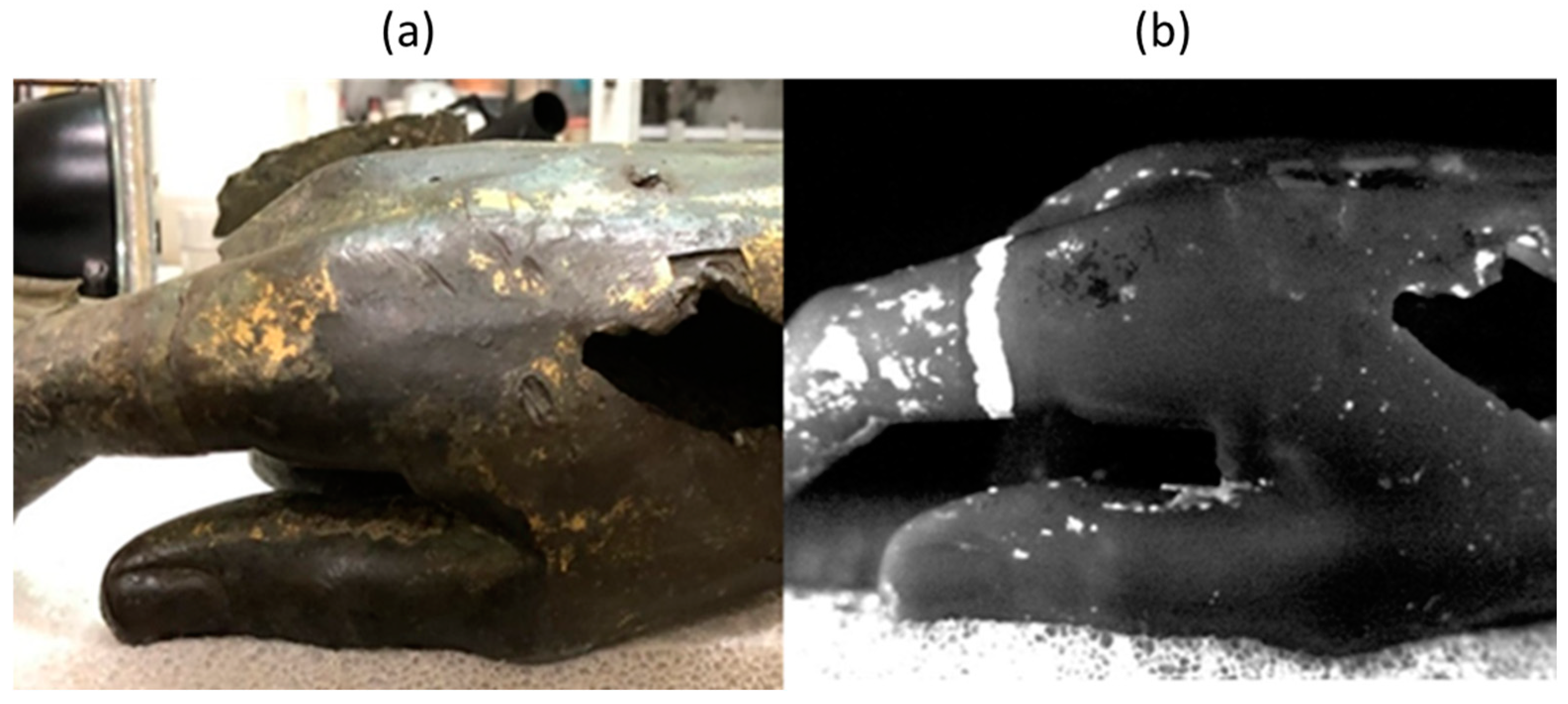
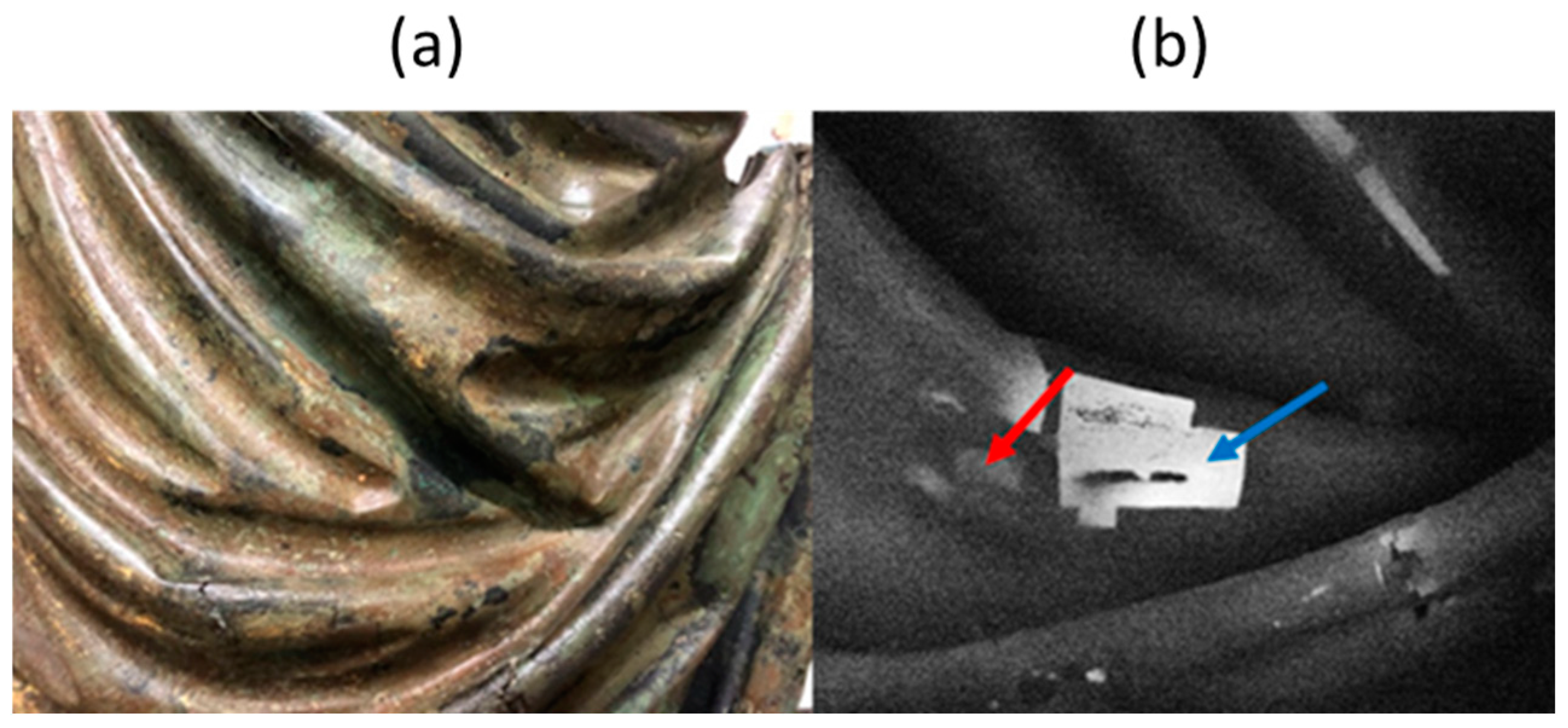
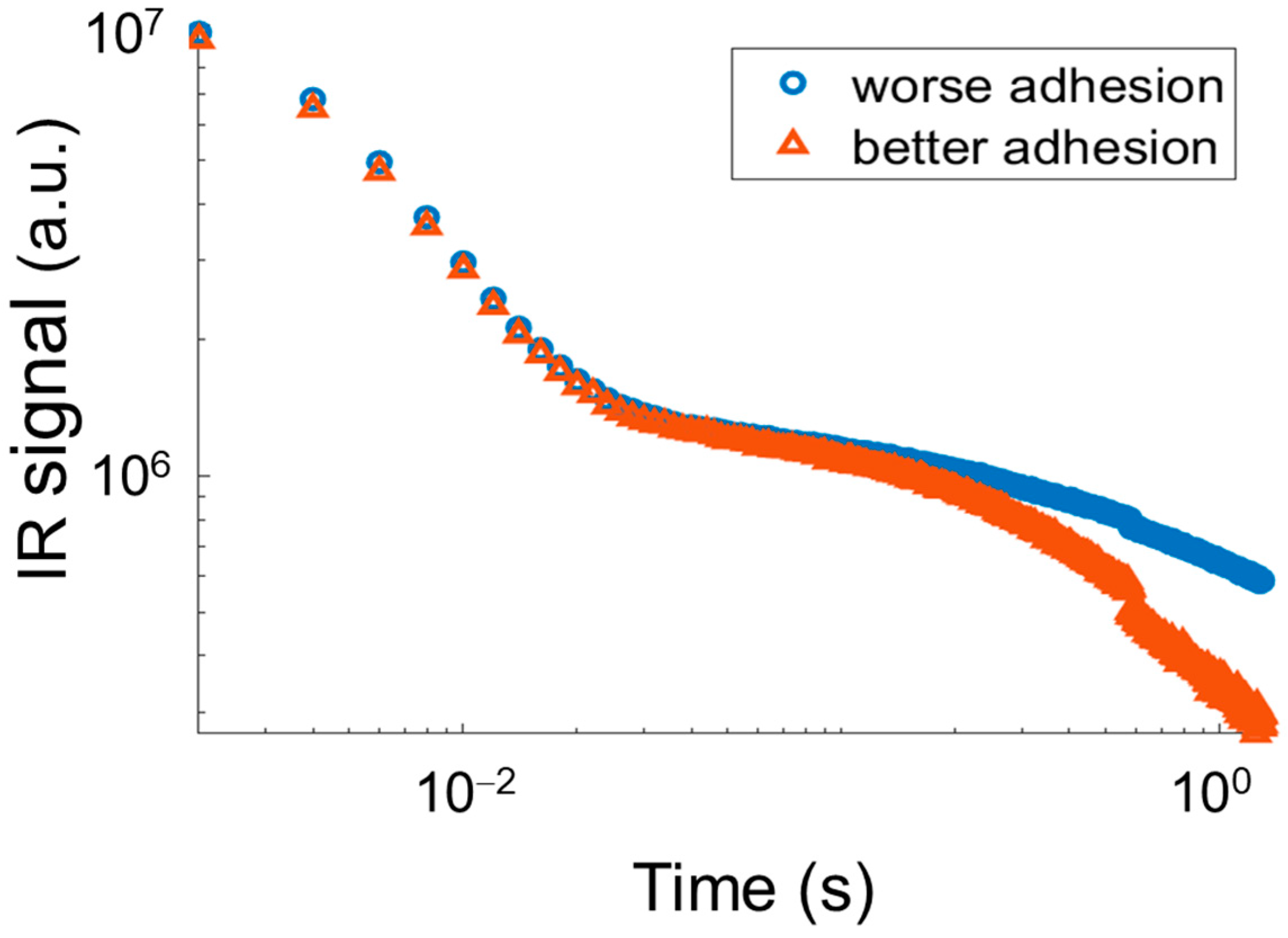
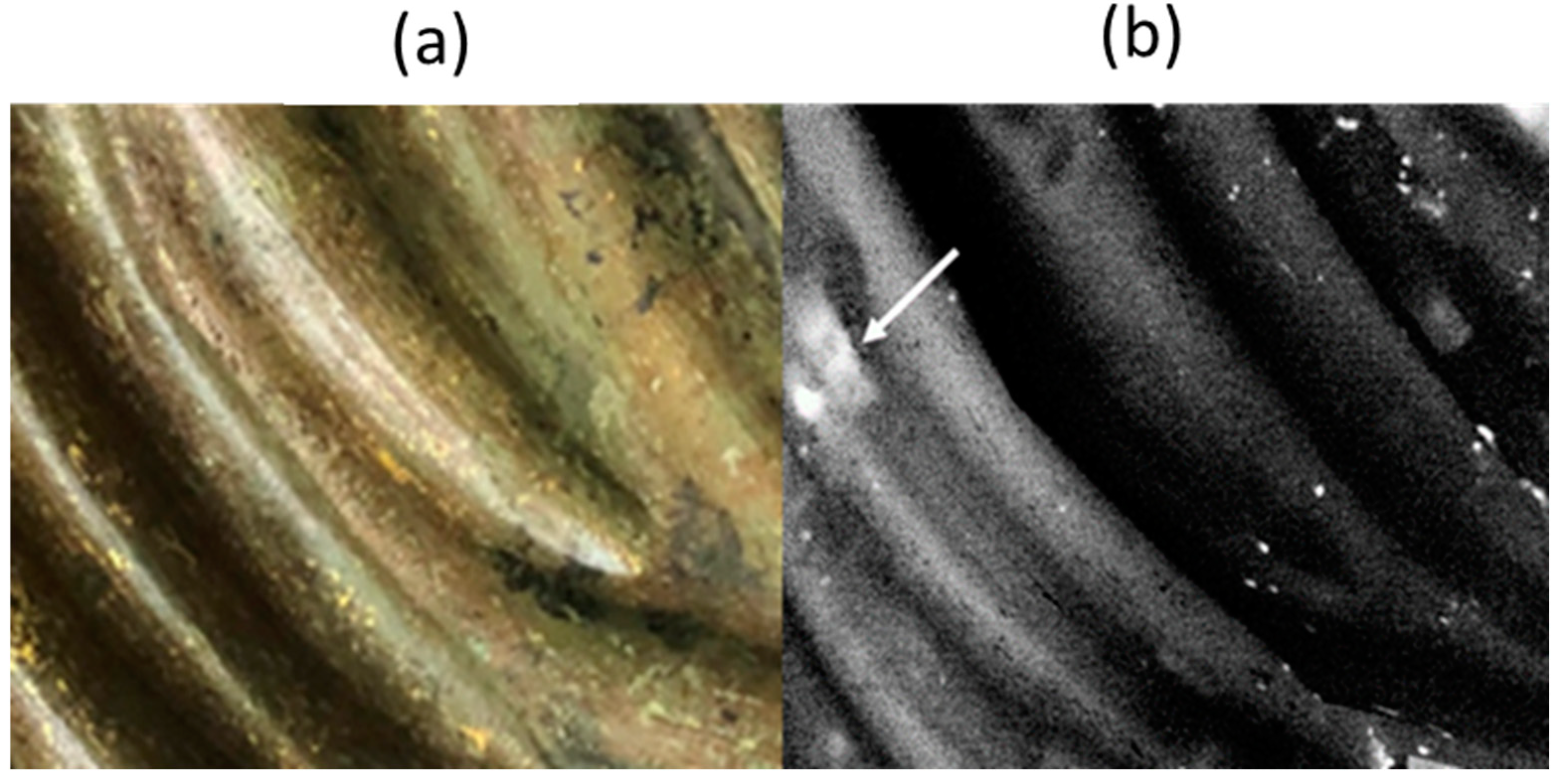
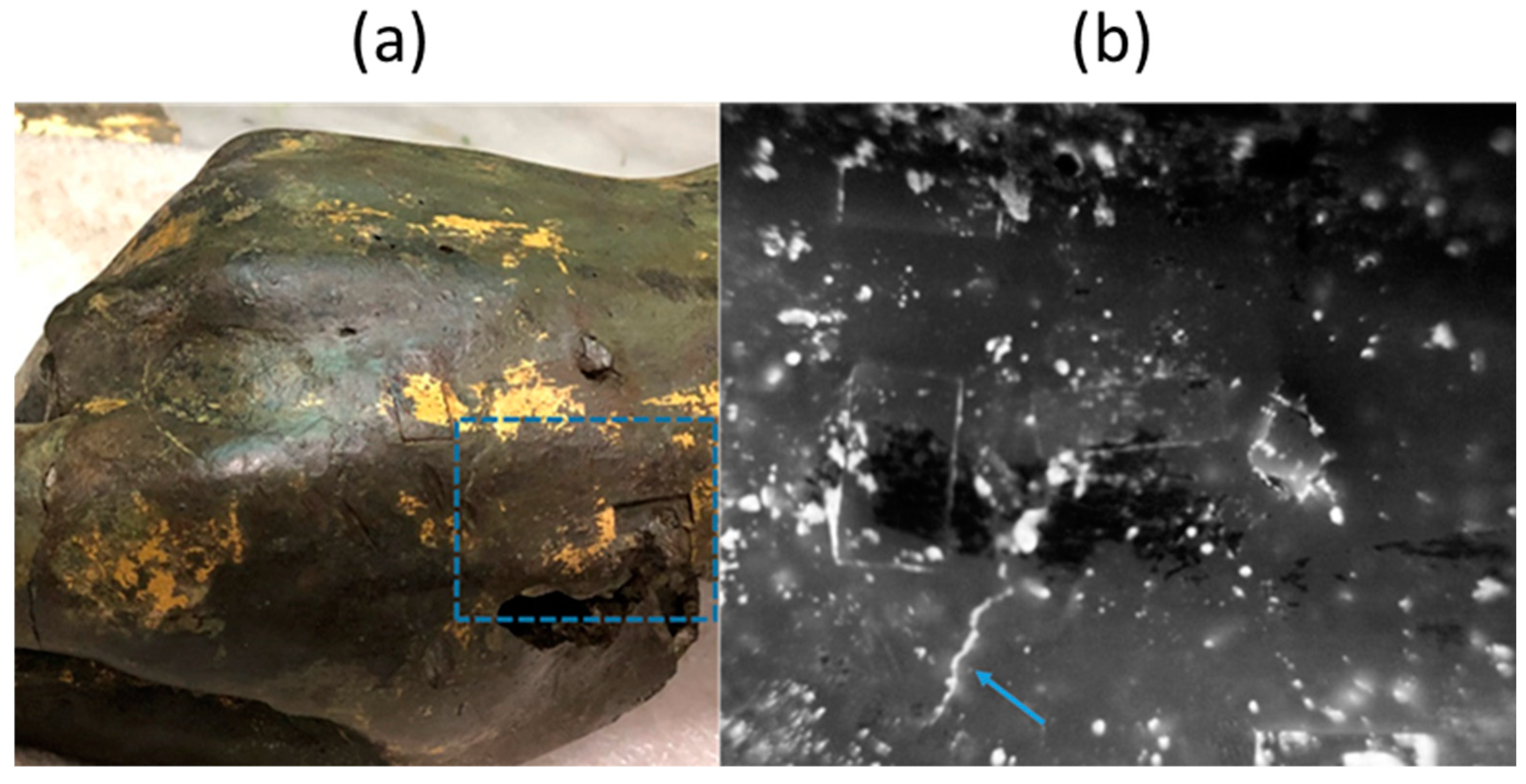
3.1. Pulsed Thermography
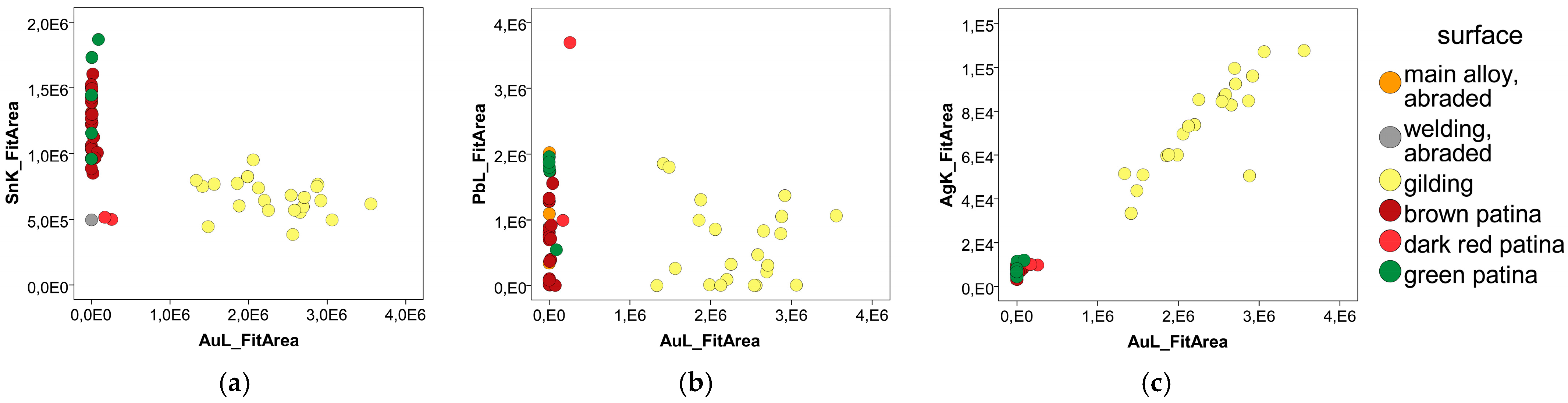
3.2. XRF and Raman Spectroscopy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ibarra-Castanedo, C.; Khodayar, F.; Klein, M.; Sfarra, S.; Maldague, X.; Helal, H.; Tayoubi, M.; Marini, B.; Barré, J.C. Infrared vision for artwork and cultural heritage NDE studies: Principles and case studies. Insight Non-Destr. Test. Cond. Monit. 2017, 59, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blessley, K.; Young, C.; Nunn, J.; Coddington, J.; Shepard, S. The feasibility of flash thermography for the examination and conservation of works of art. Stud. Conserv. 2010, 55, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfarra, S.; Regi, M.; Tortora, M.; Casieri, C.; Perilli, S.; Paoletti, D. A multi-technique nondestructive approach for characterizing the state of conservation of ancient bookbindings. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2018, 132, 1367–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfarra, S.; Ibarra-Castanedo, C.; Ambrosini, D.; Paoletti, D.; Bendada, A.; Maldague, X. Integrated approach between pulsed thermography, near-infrared reflectography and sandwich holography for wooden panel paintings advanced monitoring. Russ. J. Nondestruct. Test. 2011, 47, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosini, D.; Daffara, C.; Di Biase, R.; Paoletti, D.; Pezzati, L.; Bellucci, R.; Bettini, F. Integrated reflectography and thermography for wooden paintings diagnostics. J. Cult. Herit. 2010, 11, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfarra, S.; Regi, M. Wavelet analysis applied to thermographic data for the detection of sub-superficial flaws in mosaics. Eur. Phys. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 73, 31001. [Google Scholar]
- Carlomagno, G.M.; Di Maio, R.; Meola, C.; Roberti, N. Infrared thermography and geophysical techniques in cultural heritage conservation. Quant. InfraRed Thermogr. J. 2005, 2, 5–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colacicchi Alessandri, O.; Caruso, G.; Orazi, N.; Ferretti, M. A technical Examination of the Great Bronzes of the Museo Nazionale Romano. Stud. Conserv. 2021, 68, 326–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orazi, N.; Paoloni, S.; Zammit, U.; Cicero, C.; Ferretti, M.; Caruso, G.; Colacicchi Alessandri, O.; Paris, R.; Mercuri, F. Thermographic Investigation of Bronze Artefacts: Characterization of Structure Elements and Casting Faults in Masterpieces of the Bronze Statuary of Rome. Int. J. Thermophys. 2018, 39, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accardo, G.; Bottoni, M.; Fabretti, G.; Santin, V. Esame delle disomogeneità strutturali in manufatti metallici mediante termografia. In Proceedings of the 9dtinternational Conference on NDT in Conservation of Works of Art, Rome, Italy, 27–29 October 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Bottoni, M.; Fabretti, G. Model for the analysis of sun radiation structuresexposed to open air: Consideration of its validity and usefulness based onits experimentation in situ. In Proceedings of the Volume 4360, Thermosense XXIII, Orlando, FL, USA, 16–20 April 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Cagnetti, V.; Diana, M.; Ferretti, M.; Moioli, P. The Chimera of Arezzo: Study of some metallurgical and structural aspects by means of X-ray fluorescence and high-resolution thermography. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference NDT, Microanalytical Methods and Environment Evaluation for Study and Conservation of Work of Art, Brescia, Italy, 1992; pp. 215–228. [Google Scholar]
- Scudieri, F.; Mercuri, F.; Volterri, R. Non-invasive analysis of artistic heritageand archaeological findings by time resolved IR thermography. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2001, 66, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldague, X. Applications of infrared thermography in non-destructive evalu-ation. In Trends in Optical Nondestructive Testing; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2000; pp. 591–609. [Google Scholar]
- Casali, F. X-Ray and Neutron Digital radiography and Computed Tomography for Cultural Heritage. In Physical Techniques in the Study of Art, Archaeology and Cultural Heritage; Bradley, D., Creagh, D., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; Volume 1, pp. 41–123. [Google Scholar]
- Visser, D. Neutron Radiography and Tomography: A New Technique for the Scientific Study of Bronzes. In From Vulcan’s Forge: Bronzes from the Rijksmuseum; Scholten, F., Verber, M., Eds.; Daniel Katz: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 1450–1800, Daniel Katz: London, UK, 2005; pp. 150–154. [Google Scholar]
- AA. VV. Archeologia a Roma: La Materia e la Tecnica Nell’arte Antica; De Luca Edizioni d’arte: Rome, Italy, 1990; pp. 107–108. [Google Scholar]
- Usai, C. Un metodo di ricomposizione di una statua bronzea in frammenti. In Materiali e Strutture: Problemi di Conservazione I, 1; L’Erma di Bretschneider: Rome, Italy, 1991; pp. 27–31. [Google Scholar]
- Maldague, X. Theory and Practice of Infrared Technology for Nondestructive Testing; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Caruso, G.; Paoloni, S.; Orazi, N.; Cicero, C.; Zammit, U.; Mercuri, F. Quantitative evaluations by infrared thermography in optically semi-transparent paper-based artefacts. Measurements 2019, 143, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, H.G.M.; Vandenabeele, P.; Colomban, P. Raman Spectroscopy in Cultural Heritage Preservation; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hayez, V.; Costa, V.; Guillaume, J.; Terryn, H.; Hubin, A. Micro Raman spectroscopy used for the study of corrosion products on copper alloys: Study of the chemical composition of artificial patinas used for restoration purposes. Analyst 2005, 130, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferretti, M. The investigation of ancient metal artefacts by portable X-Ray fluorescence devices. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2014, 29, 1753–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solé, V.A.; Papillon, E.; Cotte, M.; Walter, P.; Susini, J. A Multiplatform Code for the Analysis of Energy-Dispersive X-Ray Fluorescence Spectra. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2007, 62, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbiola, L.; Blengino, J.M.; Fiaud, C. Morphology and mechanisms of formation of natural patinas on archaeological Cu–Sn alloy. Corros. Sci. 1998, 40, 2083–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongiorno, V.; Campodonico, S.; Caffara, R.; Piccardo, P.; Carnasciali, M.M. Micro-Raman spectroscopy for the characterization of artistic patinas produced on copper-based alloys. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2012, 43, 1617–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanova Municchia, A.; Bellatreccia, F.; D’ercoli, G.; Lo Mastro, S.; Reho, I.; Ricci, M.A.; Sodo, A. Characterisation of artificial patinas on bronze sculptures of the Carlo Bilotti Museum (Rome). Appl. Phys. A 2016, 122, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Privitera, A.; Corbascio, A.; Calcani, G.; Della Ventura, G.; Ricci, M.A.; Sodo, A. Raman approach to the forensic study of bronze patinas. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2021, 39, 103115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercuri, F.; Caruso, G.; Orazi, N.; Zammit, U.; Cicero, C.; Colacicchi Alessandri, O.; Ferretti, M.; Paoloni, S. Interface thermal conductance characterization by infrared thermography: A tool for the study of insertions in bronze ancient statuary. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2018, 90, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zienkiewics, O.C.; Taylor, R.L.; Zhu, J.Z. The Finite Element Method; Its Basis and Fundamentals; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Balageas, D.L. Defense and illustration of time-resolved pulsed thermography for NDE. Quant. InfraRed Thermogr. J. 2012, 9, 3–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiti, M.; Donghia, R.; Esposito, A.; Ferretti, M.; Gorghinian, A.; Porcinai, S. Comparison of the analytical performances of X-ray Fluorescence devices. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2204, 012025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heginbotham, A.; Bassett, J.; Bourgarit, D.; Eveleigh, C.; Glinsman, L.; Hook, D.; Smith, D.; Speakman, R.J.; Shugar, A.; Van Langh, R. The copper CHARM Set: A new set of certified reference materials for the standardization of quantitative X-Ray fluorescence analysis of heritage copper alloys. Archaeometry 2015, 57, 856–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oddy, A. Gilding through the ages. Gold Bull 1981, 14, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercuri, F.; Zammit, U.; Paoloni, S.; Caruso, G.; Ferretti, M.; Porcinai, S.; Orazi, N. Infrared thermography for the thermal diffusivity evaluation in Sn-Pb bronze alloys: A tool for the investigation of ancient statuary. Measurement 2022, 201, 111731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiara, G.; Maniquet, C.; Carnasciali, M.; Piccardo, P. A morphological and chemical classification of bronze corrosion features from an Iron Age hoard (Tintignac, France): The effect of metallurgical factors. Acta Imeko 2022, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oddy, W.A. A History of gilding with particular reference to statuary. In Gilded Metals. History, Technology and Conservation; Drayman-Weisser, T., Ed.; Archetype Publications: London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Darque-Ceretti, E.; Felder, E.; Aucouturier, M. Foil and leaf gilding on cultural artifacts: Forming and adhesion. Matéria 2011, 16, 540–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, M.; Cesareo, R.; Marabelli, M.; Guida, G. The Analysis of Bronze Alloys from the Equestrian Statue of Marco Aurelio by Means of a Thin Sample XRF Technique. Nucl. Instrum. Methods 1989, B36, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Anode | W |
| Voltage (kV) | 70 |
| Current (µA) | 55 |
| Filter | Cu 72 µm |
| Collimator | 2 mm |
| Measurement time | 100 s |
| Dead time | 20% |
| H [mm] | ρ [kg/m3] | c [J/(kg K)] | k [W/(m K)] | I [W/m2] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | 8800 | 380 | 56.85 | 1000 |
| Mn% | Fe% | Co% | Ni% | Cu% | Zn% | As% | Ag% | Sn% | Sb% | Pb% | Bi% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alloy | 0.156 | 1.43 | 0.007 | 0.017 | 60.0 | 0.057 | 0.176 | 0.077 | 15.0 | 0.226 | 22.8 | 0.099 |
| Welding | 0.036 | 0.966 | 0 | 0 | 69.6 | 0 | 0.167 | 0.038 | 7.33 | 0.115 | 21.7 | 0.013 |
| ID | Gilding Composition (%) | Gilding Thickness (µm) | Corrosion Layer Composition (%) | Corrosion Layer Thickness (µm) | Substrate Composition | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Au% | Ag% | Cu% | Cu Oxide % | Pb Carbonate % | Fe% | Cu% | Sn% | Pb% | |||
| Tog004 | 86.26 | 3.82 | 9.92 | 3.0 | 52 | 48 | 18 | 1.44 | 60.47 | 15.13 | 22.96 |
| Tog015 | 86.37 | 3.70 | 9.93 | 2.4 | 71 | 29 | 12.3 | ||||
| Tog016 | 86.2 | 3.9 | 9.9 | 1.65 | 64 | 36 | 11 | ||||
| Tog017 | 86.2 | 3.9 | 9.9 | 2.7 | 69 | 31 | 18 | ||||
| Tog018 | 87.16 | 4.75 | 8.09 | 1.45 | 47 | 53 | 6 | ||||
| Tog002 | 88.26 | 3.55 | 8.19 | 3.3 | 27 | 73 | 23 | ||||
| Tog003 | 88.26 | 3.55 | 8.19 | 2.5 | 35 | 65 | 20 | ||||
| Tog019 | 88.08 | 3.75 | 8.17 | 2.2 | 60 | 40 | 29 | ||||
| Tog020 | 88.03 | 3.8 | 8.17 | 2.0 | 27 | 73 | 25 | ||||
| Tog021 | 88.03 | 3.8 | 8.17 | 2.15 | 55 | 45 | 20 | ||||
| Tog022 | 87.24 | 4.66 | 8.1 | 0.8 | 35 | 65 | 12 | ||||
| Tog023 | 87.24 | 4.66 | 8.1 | 1.15 | 63 | 37 | 18 | ||||
| Tog024 | 87.55 | 4.32 | 8.13 | 1.6 | 65 | 35 | 13 | ||||
| Tog025 | 87.64 | 4.22 | 8.14 | 1.95 | 40 | 60 | 15 | ||||
| Tog026 | 87.57 | 4.3 | 8.13 | 1.55 | 18 | 82 | 11 | ||||
| Tog037 | 87.57 | 4.3 | 8.13 | 2.2 | 16 | 84 | 17 | ||||
| Tog038 | 88.01 | 3.72 | 8.18 | 2.8 | 28 | 72 | 20 | ||||
| Tog039 | 88.1 | 3.94 | 8.18 | 2.0 | 21 | 79 | 18 | ||||
| Tog040 | 87.91 | 3.93 | 8.16 | 1.1 | 16 | 84 | 17 | ||||
| Tog041 | 88.29 | 3.51 | 8.2 | 3.2 | 22 | 78 | 20 | ||||
| Tog051 | 87.69 | 4.17 | 8.14 | 1.0 | 50 | 50 | 37 | ||||
| Tog052 | 87.69 | 4.17 | 8.14 | 1.3 | 58 | 42 | 30 | ||||
| Average Values | 88 | 4 | 8 | 2 | 43 | 57 | 19 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luvidi, L.; Casanova Municchia, A.; Konstantakopoulou, E.; Orazi, N.; Ferretti, M.; Caruso, G. Combined Use of Non-Destructive Analysis Techniques to Investigate Ancient Bronze Statues. Sensors 2025, 25, 1727. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061727
Luvidi L, Casanova Municchia A, Konstantakopoulou E, Orazi N, Ferretti M, Caruso G. Combined Use of Non-Destructive Analysis Techniques to Investigate Ancient Bronze Statues. Sensors. 2025; 25(6):1727. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061727
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuvidi, Loredana, Annalaura Casanova Municchia, Eleni Konstantakopoulou, Noemi Orazi, Marco Ferretti, and Giovanni Caruso. 2025. "Combined Use of Non-Destructive Analysis Techniques to Investigate Ancient Bronze Statues" Sensors 25, no. 6: 1727. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061727
APA StyleLuvidi, L., Casanova Municchia, A., Konstantakopoulou, E., Orazi, N., Ferretti, M., & Caruso, G. (2025). Combined Use of Non-Destructive Analysis Techniques to Investigate Ancient Bronze Statues. Sensors, 25(6), 1727. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061727








