1. Introduction
The rapid evolution of Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) has laid the foundation for pervasive data acquisition in large-scale environments. A typical WSN integrates a multitude of miniature sensing devices that possess sensing, computation, and communication capabilities. These nodes are cost-effective and capable of measuring diverse physical parameters such as temperature, humidity, and pressure, which makes them suitable for deployment in military, agricultural, industrial, and healthcare applications [
1,
2,
3,
4]. The convergence of such sensor-based networks with Internet connectivity has accelerated the formation of the Internet of Things (IoT), a paradigm that enables continuous monitoring and autonomous control of physical assets through distributed sensing and communication [
5,
6,
7]. Applications of IoT have become widespread and include smart infrastructure, intelligent transportation systems, and remote healthcare monitoring.
Building upon the foundation of IoT, industrial domains have increasingly integrated artificial intelligence (AI), edge computing, and big data analytics into their cyber-physical infrastructures [
8,
9,
10]. These technological advances have given rise to the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), where large-scale sensor networks and machine-to-machine communication enable automation, predictive maintenance, and real-time operational decision-making [
11,
12,
13]. As factories, warehouses, and logistics hubs continue to adopt IIoT solutions, ensuring dependable data acquisition has become essential for safe and efficient operations.
Among the various identification mechanisms used in IIoT, Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) has emerged as a critical technology for object tracking, material flow monitoring, and inventory automation [
14,
15]. RFID enables non-line-of-sight and high-speed identification, making it suitable for dense industrial deployments. However, large-scale RFID systems are highly susceptible to interference problems such as tag collision, reader-to-reader interference, and reader-to-tag interference, which severely degrade communication reliability and create coverage gaps [
16].
These interference problems are largely determined by the spatial arrangement of readers and the configuration of their interrogation ranges. When readers are placed too closely or operate with unnecessarily large interrogation radii, overlapping interrogation zones may create severe conflicts that result in missed readings, increased latency, and unpredictable system behavior. Consequently, designing a reader deployment strategy that simultaneously guarantees complete tag coverage and minimizes interference is crucial for dependable IIoT operation.
Although prior studies have proposed communication-level protocols or post-deployment optimization methods to alleviate interference, most rely on random or heuristic initialization strategies. These approaches may reduce redundant readers but cannot guarantee collision-free deployment or complete tag coverage, especially in dense or non-uniform environments.
Motivated by these challenges, this study proposes a deterministic reader-deployment framework designed to ensure collision-free coverage and dependable identification in RFID-enabled IIoT systems. Unlike traditional random or heuristic strategies, the proposed approach eliminates randomness in the decision-making process and provides stable and interference-resilient deployment outcomes. Such determinism is especially important in IIoT environments, where industrial automation requires consistent identification quality, minimal signal conflicts, and reliable system operation. To achieve this, the algorithm incorporates four key design principles.
Grid-based initialization: The monitored area is divided into uniform grid units to systematically enumerate all potential reader locations, avoiding suboptimal placements caused by random sampling.
Weighted tag assignment: Each virtual reader is assigned a coverage weight using a competitive nearest-distance rule, creating an importance-ordered list that prioritizes the most beneficial deployment positions.
Interference-aware selection: A candidate reader is activated only if it introduces no reader-to-tag or reader-to-reader conflict with previously deployed readers, ensuring reliable and interference-free operation.
Iterative range adjustment: After placement, each deployed reader refines its interrogation radius to the distance of its farthest assigned tag, minimizing redundant overlap and enabling additional non-conflicting deployment opportunities.
By integrating these principles, the proposed algorithm achieves complete tag coverage with fewer readers and effectively mitigates both reader-to-tag and reader-to-reader interference, thereby enhancing the overall reliability and efficiency of RFID-based IIoT environments. This article is a revised and expanded version of a paper entitled “An Enhanced Approach for RFID Reader Deployment in Industrial IoT Systems with Collision Avoidance and Optimized Coverage,” which was presented at the 10th IEEE International Conference on Dependable Systems and Their Applications (IEEE DSA 2023), Tokyo, Japan, 10–11 August 2023 [
17].
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows.
Section 2 reviews related research on RFID interference mitigation and reader deployment.
Section 3 presents the system model and formulates the deterministic deployment problem.
Section 4 describes the proposed RDA2R algorithm.
Section 5 analyzes computational complexity.
Section 6 evaluates performance, and
Section 7 concludes the study.
2. Related Work
In RFID systems, communication reliability is frequently hindered by two major types of interference: tag collisions and reader collisions. Before reviewing existing solutions,
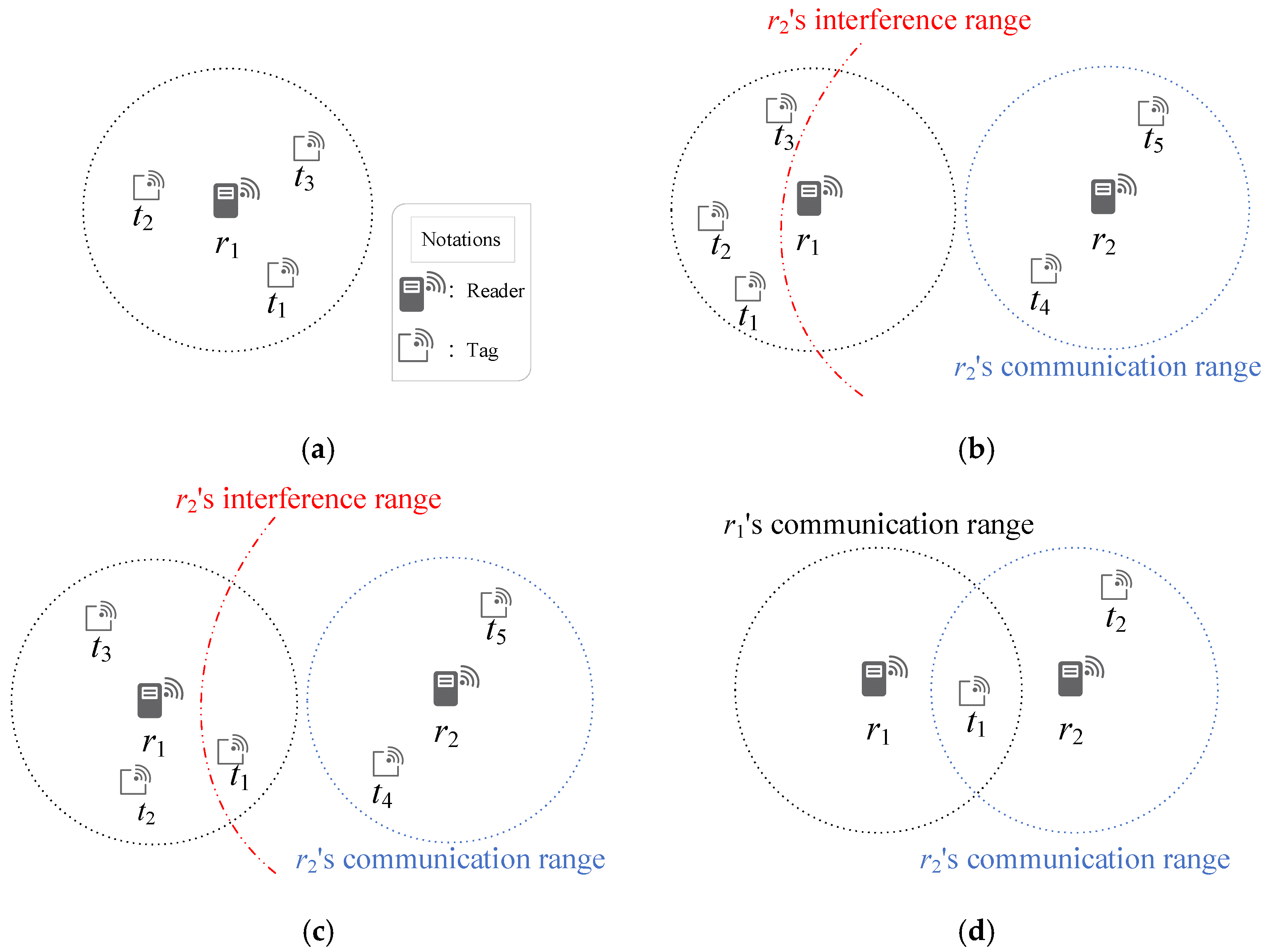
Figure 1 illustrates these interference scenarios and highlights their spatial complexity in large-scale IIoT deployments. In
Figure 1a, tag collisions occur when multiple tags attempt to communicate with the same reader simultaneously, leading to reception failure.
Figure 1b,c present two forms of reader-to-reader interference: in
Figure 1b, overlapping interference ranges of two readers disrupt one another’s signals, whereas in
Figure 1c, one reader’s interference range overlaps with the communication path between another reader and a tag, causing data loss. In addition,
Figure 1d depicts reader-to-tag interference, where a tag located within the overlapping interrogation zones of multiple readers undergoes simultaneous interrogation and thus communication failure. These examples underscore the diverse interference patterns that arise in dense RFID deployments. Accordingly, the following section reviews representative approaches proposed to mitigate these two major categories of interference in practical RFID systems.
2.1. Tag Collision
A considerable body of research has focused on minimizing tag collisions by regulating the active response time of tags. Among the most prominent approaches is the Dynamic Framed Slotted ALOHA (DFSA [
18]). The DFSA [
18] protocol dynamically adjusts the frame length according to the estimated number of tags within the interrogation field. By observing the number of collision slots, the system estimates tag population and tunes the frame size accordingly to improve identification efficiency.
Subsequent studies have refined this idea to enhance responsiveness. For example, the Improved Linearized Combinatorial Model (ILCM [
19]) emphasized the need for a faster estimation of the number of responding tags to further reduce idle and collision slots. The authors of ILCM [
19] proposed an adaptive frame adjustment mechanism that improves DFSA [
18] efficiency. However, they also observed that conventional tag estimation methods are computationally intensive, leading to latency during estimation. To address this, ILCM [
19] enables more efficient tag estimation while maintaining low computational cost.
2.2. Reader Collision
Reader collision is typically divided into two categories: reader-to-reader interference and reader-to-tag interference. The following subsections summarize research efforts addressing each category.
2.2.1. Reader-to-Reader Interference
Reader-to-reader interference occurs when the transmission signals of multiple readers overlap in frequency or time, resulting in degraded signal quality and packet loss. To mitigate this issue, several distributed power control and coordination mechanisms have been proposed. DPC [
20] introduces a power-control–based conflict avoidance scheme that dynamically adjusts the transmission power of readers to minimize the overlap between their interrogation ranges. Similarly, CSMA [
21] has been explored as a coordination mechanism, allowing readers to sense channel activity and schedule interrogation timing to reduce mutual interference.
2.2.2. Reader-to-Tag Interference
Reader-to-tag interference represents a more intricate problem, as it involves multiple readers simultaneously attempting to communicate with the same tag. Existing studies have approached this challenge through two main strategies: redundant reader elimination and deterministic deployment planning.
The first strategy aims to reduce the number of active readers while maintaining adequate coverage. Neighboring Coverage Density (NCD [
22]) allows each reader to assign weights to nearby tags according to their spatial density, and redundant readers are then deactivated based on these weights to reduce interference. An enhanced version, Neighboring Coverage Density Movement Detection (NCDMD [
22]), further incorporates motion detection to minimize unnecessary tag write operations in dynamic environments.
Threshold Selection Algorithm (TSA [
23]) determines the activation of readers according to a descending order of coverage thresholds. To accommodate tag mobility, the TSAMD (Threshold Selection with Movement Detection) [
23] extension dynamically re-evaluates threshold values when tag positions change. Similarly, the Dynamic Range-Based Algorithm (DRBA [
24]) iteratively selects readers maximizing tag coverage and adjusts their reading ranges in a recursive manner until full coverage is achieved or no further readers can be activated.
Although redundant-reader–elimination methods can reduce interference and lower reader density, they often depend on randomly initialized deployments and cannot ensure full tag coverage. Deterministic deployment approaches, on the other hand, are more suitable when complete coverage and stable communication performance are required. A representative method is the Minimum-Cost RFID Reader Deployment algorithm (MR2D [
25]), which formulates reader placement as a deterministic optimization problem using known tag coordinates and a predefined set of allowable reading ranges. By clustering spatially close tags and assigning readers accordingly, MR2D [
25] identifies deployment positions that achieve full coverage while minimizing cost and preventing reader-to-tag interference.
To clarify the strengths and limitations of representative methods,
Table 1 summarizes seven approaches: DFSA [
18], ILCM [
19], DPC [
20], CSMA [
21], NCD [
22], NCDMD [
22], TSA [
23], DRBA [
24], and MR2D [
25]. DFSA [
18] and ILCM [
19] reduce tag collisions through dynamic frame adjustment and improved tag-population estimation, respectively, but neither addresses interference between readers. DPC [
20] adapts transmission power to manage reader interference, and CSMA [
21] relies on carrier sensing, although both operate only after deployment and cannot ensure collision-free coverage in dense environments. NCD [
22], NCDMD [
22], TSA [
23], and DRBA [
24] also function exclusively in the post-deployment stage; they adjust reader activation or interrogation ranges but remain constrained by the initial random placement and by fixed-range assumptions. MR2D [
25] applies a deterministic placement strategy with adjustable discrete ranges, but its candidate reader positions are limited to locations within each cluster, which may result in deploying more readers than necessary. Taken together, these comparisons highlight the need for a deterministic deployment framework that can provide predictable coverage and interference-aware performance in large-scale IIoT RFID systems.
In summary, previous research on RFID interference mitigation has primarily emphasized communication-level coordination or post-deployment optimization to reduce redundant readers and minimize interference. Although these methods can improve system performance under certain conditions, they generally rely on stochastic deployment or reactive adjustment, which may lead to incomplete coverage or unpredictable interference zones. Motivated by these limitations, the next section presents the system model and formulates the deterministic reader deployment problem addressed in this study.
3. System Model and Problem Formulation
Consider a set of RFID tags denoted by T = {t1, t2, t3, …, tn}. The tags are assumed to be randomly distributed over a two-dimensional plane of size w × l. The positions of all tags are known in advance, which can be obtained through localization techniques or Global Positioning System (GPS) data. The goal is to determine the optimal placement of RFID readers that can fully cover these tags while minimizing interference and the total number of readers required.
A deterministic deployment strategy is adopted for reader placement. Each reader ri ∈ R = {ri|1 ≤ i ≤ m, m = |R|} possesses an adjustable interrogation range denoted as di ∈ D = {di|1 ≤ i ≤ k, k = |D|}, where D represents the set of available reading ranges. For each reader, the appropriate reading range is selected according to the proposed algorithm in order to achieve efficient coverage and avoid interference. A tag ti is considered covered when at least one reader can successfully interrogate it; this condition is represented by a binary function F(ti), where F(ti) = 1 if ti is covered and F(ti) = 0 otherwise. The set of tags covered by reader ri is represented as C(ri).
The proposed system model is well suited for industrial and logistics IIoT environments, including smart factory production lines and warehouse management systems. In such settings, RFID tags are typically attached to products, pallets, or equipment, and the proposed algorithm provides the backend planning mechanism that determines optimal reader locations and corresponding interrogation ranges. This enables reliable full coverage, minimizes reader interference, and supports stable data acquisition for higher-level IIoT functions such as inventory tracking, automated material handling, and real-time monitoring.
The objective of this study is to minimize the total number of deployed readers while maintaining complete tag coverage and avoiding overlap among reader interrogation zones. The mathematical formulation of the proposed problem is defined through three core equations. Equation (1) expresses the objective of minimizing the total number of deployed readers required to achieve complete coverage of all tags within the monitored region. This objective reflects the efficiency of the deployment strategy in reducing both hardware costs and potential interference among readers. Equation (2) enforces the coverage constraint, ensuring that every tag in the set
T is covered by at least one reader. This condition guarantees full accessibility of tag information across the monitored field and prevents coverage gaps that may lead to incomplete data collection. Equation (3) defines the interference avoidance constraint, which restricts overlapping tag coverage between any two active readers
ri and
rj. This constraint is designed to prevent reader-to-tag interference, thereby maintaining reliable communication and reducing redundant interrogation of the same tag. Together, these three equations constitute a constrained optimization problem that seeks to achieve complete tag coverage with the minimum number of readers while preserving collision-free communication.
4. The Concept and Approach
This section presents the design concept and operational procedure of the proposed Reader Deployment Algorithm with Adjustable Reader range (RDA2R). The algorithm aims to determine optimal reader positions and corresponding interrogation ranges based on the known spatial distribution of RFID tags. By integrating deterministic placement with adaptive range adjustment, the proposed framework effectively mitigates reader-to-tag interference and minimizes the number of deployed readers required for complete tag coverage.
4.1. Virtual Reader Initialization
To evaluate potential reader deployment locations, the monitored area is divided into a uniform grid structure. Each intersection point within this grid represents a candidate position for a virtual reader. For a two-dimensional field with dimensions w × l and a grid interval of one unit, the total number of virtual readers is (w − 1) × (l − 1). This grid-based initialization provides an evenly distributed set of reference points across the monitored region. These virtual readers serve as reference points for subsequent weight evaluation and actual reader deployment.
4.2. Evaluation of Tag Coverage Weights
Based on the initialized grid, each virtual reader is assigned a coverage weight according to the number of tags located within its maximum reading range. The weight reflects the potential contribution of that position to overall tag coverage. To prevent tag interference, a competitive assignment strategy is applied: each tag is temporarily associated with the nearest virtual reader based on Euclidean distance, ensuring that each tag contributes to only one reader’s weight. If a tag lies within the coverage of multiple readers, it is assigned to the reader with the smallest index. Tags outside all readers’ maximum ranges are excluded. This step establishes a weighted coverage map that will guide the subsequent reader selection process.
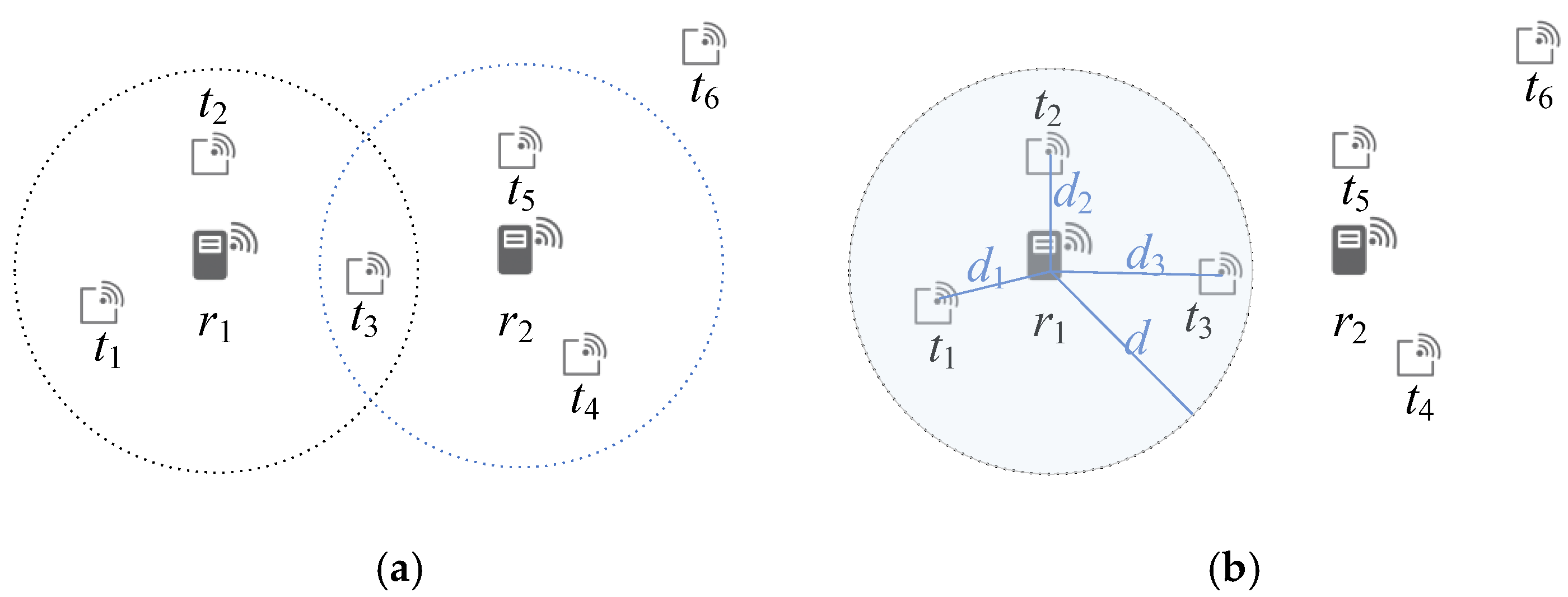
As illustrated in
Figure 2a, each tag temporarily selects the nearest reader as its potential connection. For example, tag
t2 is closer to reader
r1 than to
r2, and thus contributes to
r1’s weight. When multiple readers have equal distance to a tag, the one with the smaller index is prioritized. Tags located beyond the maximum reading range of all readers are excluded from the weight calculation. This weighting process establishes a preliminary estimation of each reader’s coverage effectiveness.
4.3. Reader Selection and Interference Handling
According to the computed coverage weights, virtual readers are ranked in descending order. The algorithm sequentially activates readers starting from the highest-weight candidate. For each candidate reader ri, it verifies whether its coverage overlaps with that of any already-activated reader. If no overlapping tags are detected, ri is deployed as an active reader. Otherwise, ri is skipped to avoid reader-to-tag interference, and the algorithm proceeds to the next candidate.
Figure 2b illustrates the weighted selection process. Reader
r1 covers tags {
t1,
t2,
t3} with a weight of three, while reader
r2 covers tags {
t4,
t5} with a weight of two. Since
r1 yields the highest weight and has no overlapping tags with other active readers, it is deployed first. In the following iteration,
r2 is evaluated but rejected due to overlap with
r1’s interrogation area. This iterative selection continues until no further readers can be deployed without interference.
4.4. Adaptive Range Adjustment
Initially, all readers are assumed to operate at the maximum allowable reading range. After the initial deployment, each active reader’s range is refined according to the farthest tag within its coverage. The interrogation radius is reduced to exactly reach that tag, thus minimizing redundant overlap while ensuring complete tag coverage. As illustrated in
Figure 2b, reader
r1 initially covers three tags {
t1,
t2,
t3} with distances
d1,
d2, and
d3, respectively. Since
d3 is the largest, the reader’s final interrogation radius is set to
d3.
After the initial range adjustment, the algorithm performs an iterative refinement in which the maximum allowable reading radius is reduced by one unit at each step. This unit decrement matches the spatial resolution of the discretized grid used for tag locations and candidate reader positions, ensuring that all feasible configurations are examined. For each reduced radius, the algorithm returns to Step 2 and executes Steps 2–4 to identify additional reader positions that satisfy the updated interference constraints. As the maximum radius becomes smaller, candidate readers are less likely to produce overlapping coverage, which helps suppress reader–tag interference. Larger radii may allow a single reader to cover more tags but often generate excessive overlap with neighboring readers. Smaller radii confine each reader’s coverage region and may expose feasible placements that were previously blocked by interference. By evaluating radii from the initial upper bound down to the minimum value of one unit, the algorithm ensures that all tags are covered in at least one iteration while progressively reducing redundant coverage and interference. This iterative reduction process produces a final deployment that achieves complete coverage with minimal overlap.
By integrating grid-based initialization, weighted tag assignment, interference-aware selection, and iterative range adjustment, the proposed RDA2R algorithm achieves efficient, interference-minimized RFID reader deployment while ensuring full tag coverage in IIoT environments.
4.5. Pseudocode of the Proposed RDA2R
The complete procedure of the proposed RDA2R algorithm is summarized in Algorithm 1. This pseudocode consolidates the individual components described in
Section 4.1,
Section 4.2,
Section 4.3 and
Section 4.4, including grid-based initialization, weighted tag assignment, interference-aware activation, and adaptive radius refinement.
| Algorithm 1: Reader Deployment Algorithm with Adjustable Reader range (RDA2R) |
Input:
T: set of tags, each tag t ∈ T has coordinates (xt, yt)
W, L: width and length of the monitored field
dmin: minimum allowable reading radius (one unit distance)
dmax: maximum allowable reading radius
Δ: grid interval (one unit distance)
Output:
Ract: set of deployed readers with positions and final radii |
// Step 1: Grid-based initialization
1: Generate all virtual reader positions Rvirt on a Δ-grid.
2: Ract ← ∅
3: dcur ← dmax
4: while dcur ≥ dmin do
// Step 2: Weighted Tag Assignment
5: For each reader r ∈ Rvirt, rest its temporary coverage set and weight.
6: For each tag t ∈ T do
7: Find all readers within distance dcur of t.
8: Assign t to the nearest reader that covers it.
9: end for
10: Compute coverage weight for each reader (number of assigned tags).
// Step 3: Interference-Aware Activation
11: Sort readers in descending order of weight.
12: For each reader r in sorted order do
13: If r does not conflict with any activated reader then
// Step 4: Adaptive Range Adjustment
14: Determine r’s final radius as the distance to its farthest assigned tag.
15: Add r to Ract.
16: end if
17: end for
// Iterative Reduction of Maximum Radius
18: dcur ← dcur − 1
19: end while
20: return Ract |
4.6. Conceptual and Algorithmic Differences from MR2D [25] and DRBA [24]
The proposed RDA2R algorithm differs substantially from DRBA [
24] and MR2D [
25] in both conceptual design and deployment objectives. DRBA [
24] is formulated as a post-deployment collision-avoidance mechanism in which all reader positions are fixed in advance. Its primary goal is to prevent reader–tag interference by selecting interrogation radii from a discrete candidate set. This objective can be expressed as:
DRBA [
24] operates exclusively after deployment, adjusts only the interrogation ranges, and its performance is therefore constrained by the initial random placement and the discrete nature of its radius options.
In contrast, MR2D [
25] formulates deployment as a deterministic optimization problem. It clusters spatially close tags into groups and uses the cluster centers as candidate reader locations. The placement objective can be written as:
However, MR2D [
25] restricts reader placement to cluster centers and relies on a fixed set of discrete interrogation radii, which limits spatial flexibility and may lead to unnecessary readers when tag distributions are irregular or highly nonuniform.
RDA2R addresses these limitations by integrating grid-based deterministic placement, interference-aware reader activation, and adaptive range refinement. Unlike DRBA [
24] and MR2D [
25], RDA2R evaluates all feasible grid points as candidate reader locations rather than restricting them to precomputed cluster centers or an initial deployment. Each activated reader’s interrogation radius is adaptively set to the farthest assigned tag instead of being selected from a discrete set, enabling fine-grained range control. This integrated design ensures complete tag coverage while preventing reader-to-tag interference and minimizing the number of active readers. Consequently, RDA2R offers more spatial flexibility and provides a more effective deployment strategy than DRBA [
24] and MR2D [
25].
Table 2 summarizes these conceptual and algorithmic differences, including deployment assumptions, optimization goals, and range-design strategies.
5. Complexity Analysis
In this section, it is established that the problem discussed in this paper falls under the category of NP-hard. Furthermore, an analysis of the time complexity of the proposed algorithm is conducted.
5.1. NP-Hard Problem
To show the reader deployment problem discussed in this paper is NP-hard, the problem can be reduced to the set covering problem, which is an existing NP-hard problem [
26,
27]. The set covering problem is illustrated as follows.
Next, the process of transforming the reader deployment problem into a set covering problem will be illustrated. Firstly, the set formed by the tags is defined as U, and for each virtual reader ri, the set of tags it can cover is defined as si, where S = s1 ∪ s2 ∪ … ∪ sn, with n being the number of virtual readers in the target field, and S = U. In the process of selecting virtual readers, it is determined whether to deploy actual readers at those locations based on the magnitude of the weights assigned to si. These weights are calculated based on the tags covered by the virtual reader. In other words, in addressing the reader deployment problem, the goal is also to find the minimum subset from the subsets of S whose union equals U (i.e., finding the minimum collection of subsets C, such that each element belongs to at least one subset in C). The distinction lies in the calculation and ordering of weight values, which can be accomplished in polynomial time. Since the reader deployment problem can be transformed into a set covering problem in polynomial time, the reader deployment problem is also NP-hard.
5.2. Complexity Analysis
To analyze the computational complexity of the proposed RDA2R algorithm, the notation used in this section is introduced as follows. Let nt denote the number of RFID tags in the monitored region. Let nr = (l − 1) × (w − 1) represent the number of virtual readers generated by a grid-based discretization of the field, where the grid interval is set to 1. During the execution of the algorithm, a subset of these virtual readers is activated; let nq denote the number of activated readers in a given iteration, where nq ≤ nr. For each activated reader, the number of tags temporarily assigned for determining its refined interrogation radius is denoted as nw, where nw ≤ nt. The algorithm evaluates every feasible interrogation radius between dmax and dmin, resulting in z = dmax − dmin + 1 iterations.
The major computational effort arises in Steps 2 through 4 of Algorithm 1. In Step 2, each virtual reader evaluates its coverage with respect to all tags, which leads to a time complexity of
O(
nrnt). Step 3 sorts the virtual readers according to their weights, requiring
O(
nrlog
nr). After sorting, each candidate reader is checked for potential interference with the activated readers. The worst-case cost of this process is
O(
nq2), and this value is bounded above by
O(
nr2) since
nq never exceeds
nr. Following activation, Step 4 refines the interrogation radius of each activated reader by examining the distances to its assigned tags. This refinement process requires
O(
nqnw) time and is therefore bounded above by
O(
nrnt), because
nq ≤
nr and
nw ≤
nt. By combining these components, the computational cost of one radius iteration can be expressed as
which simplifies to
Since the same procedure is repeated for each of the
z considered interrogation radii, the total time complexity of the RDA2R algorithm becomes
When the monitored field size and the grid interval remain unchanged, the value of
nr = (
l − 1)(
w − 1) does not scale with the number of tags. Under such conditions, nr can be regarded as a constant, and the above expression simplifies to
The simplified form applies only when the grid configuration remains fixed. In the general case, the complete expression O(z(nrnt + nrlognr + nr2)) describes the computational complexity of the RDA2R algorithm.
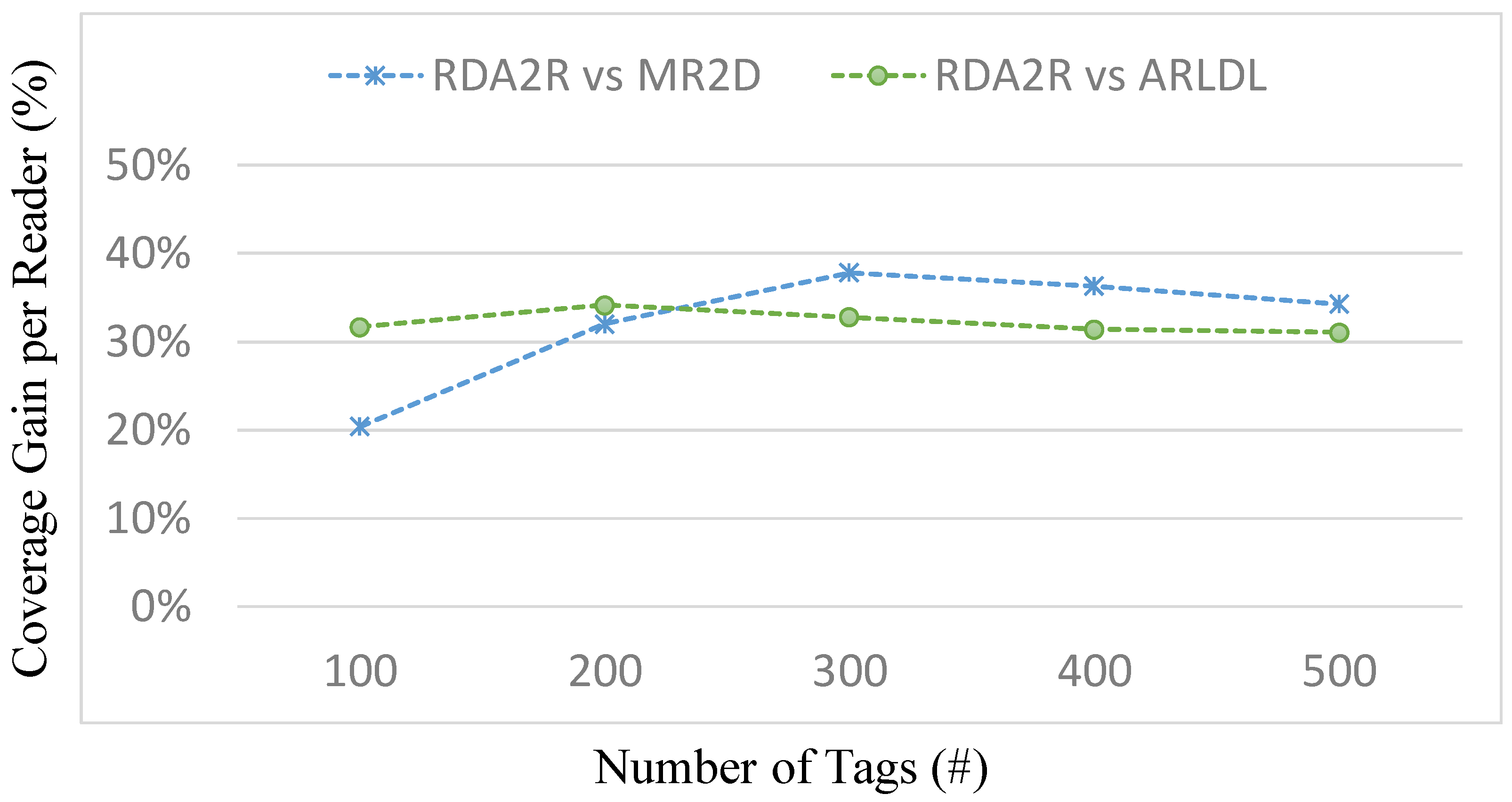
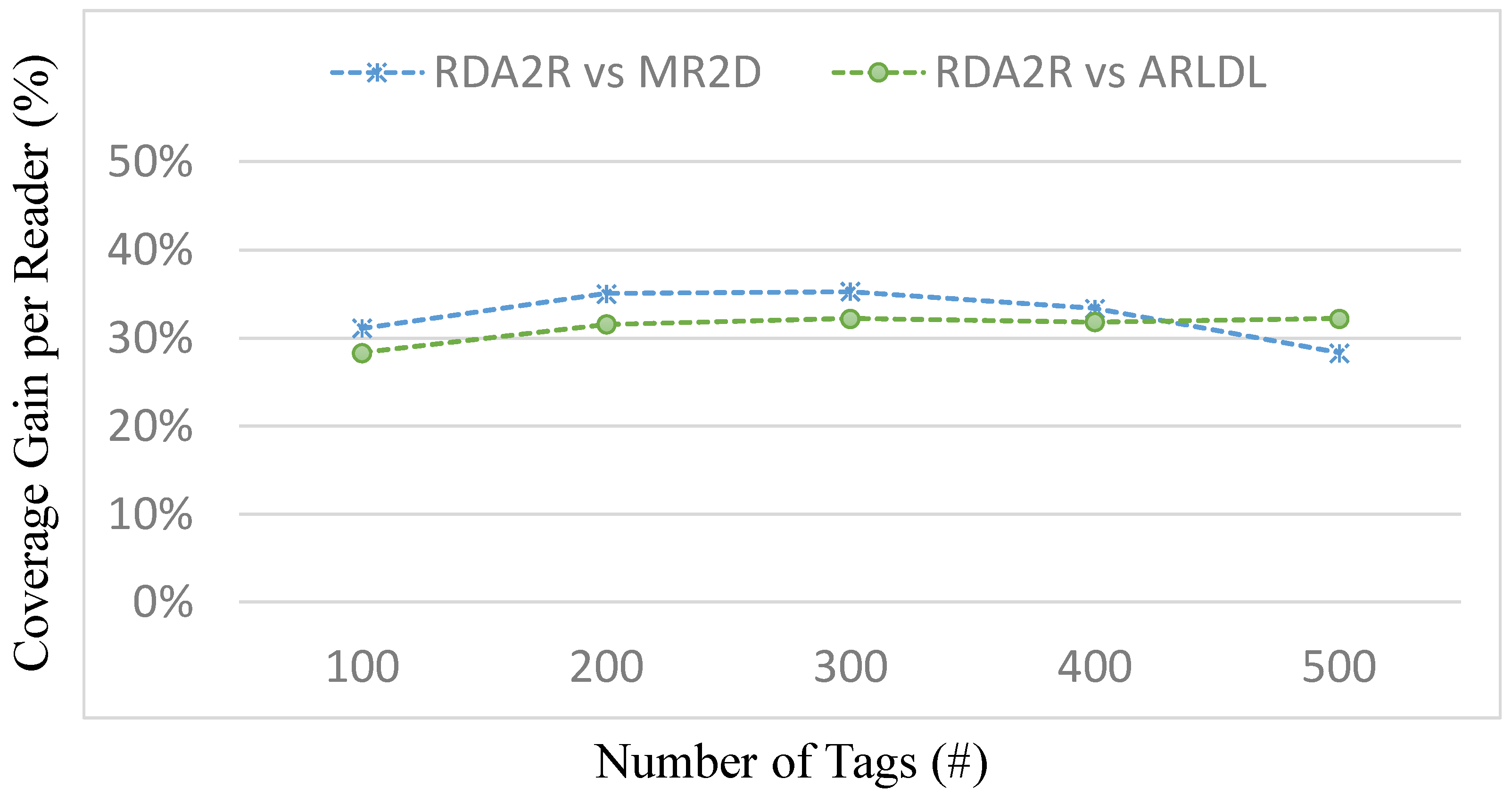
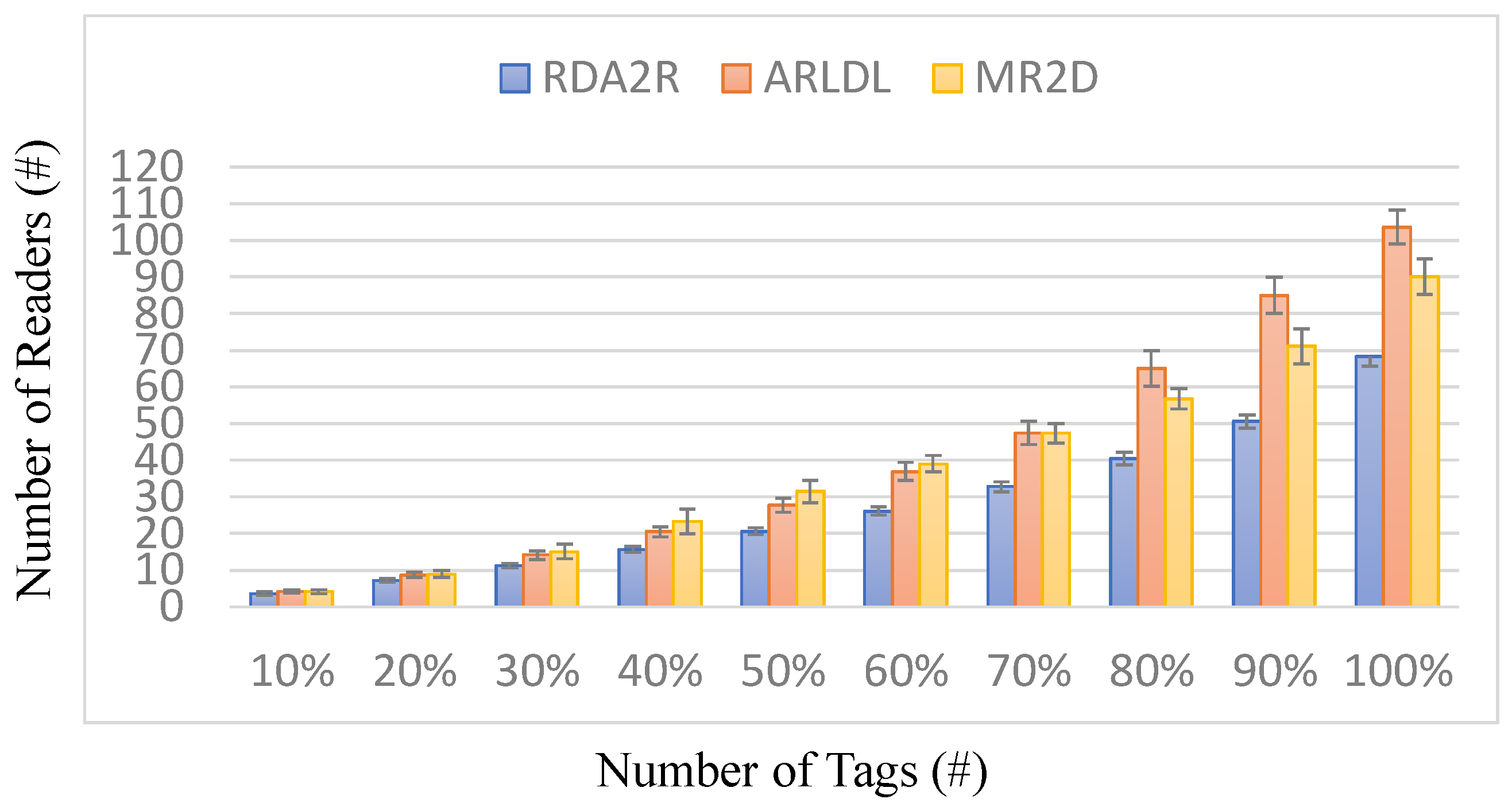
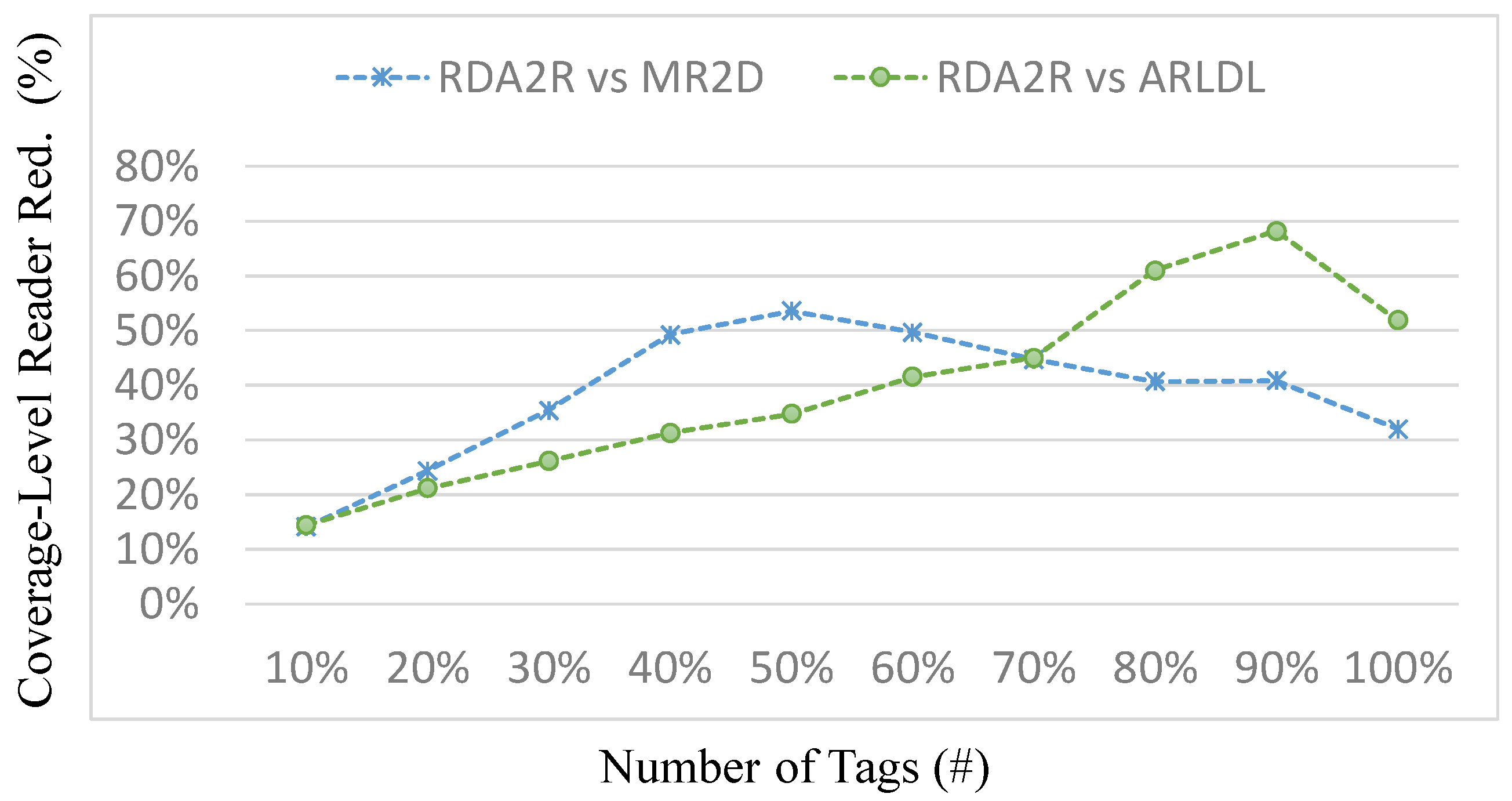
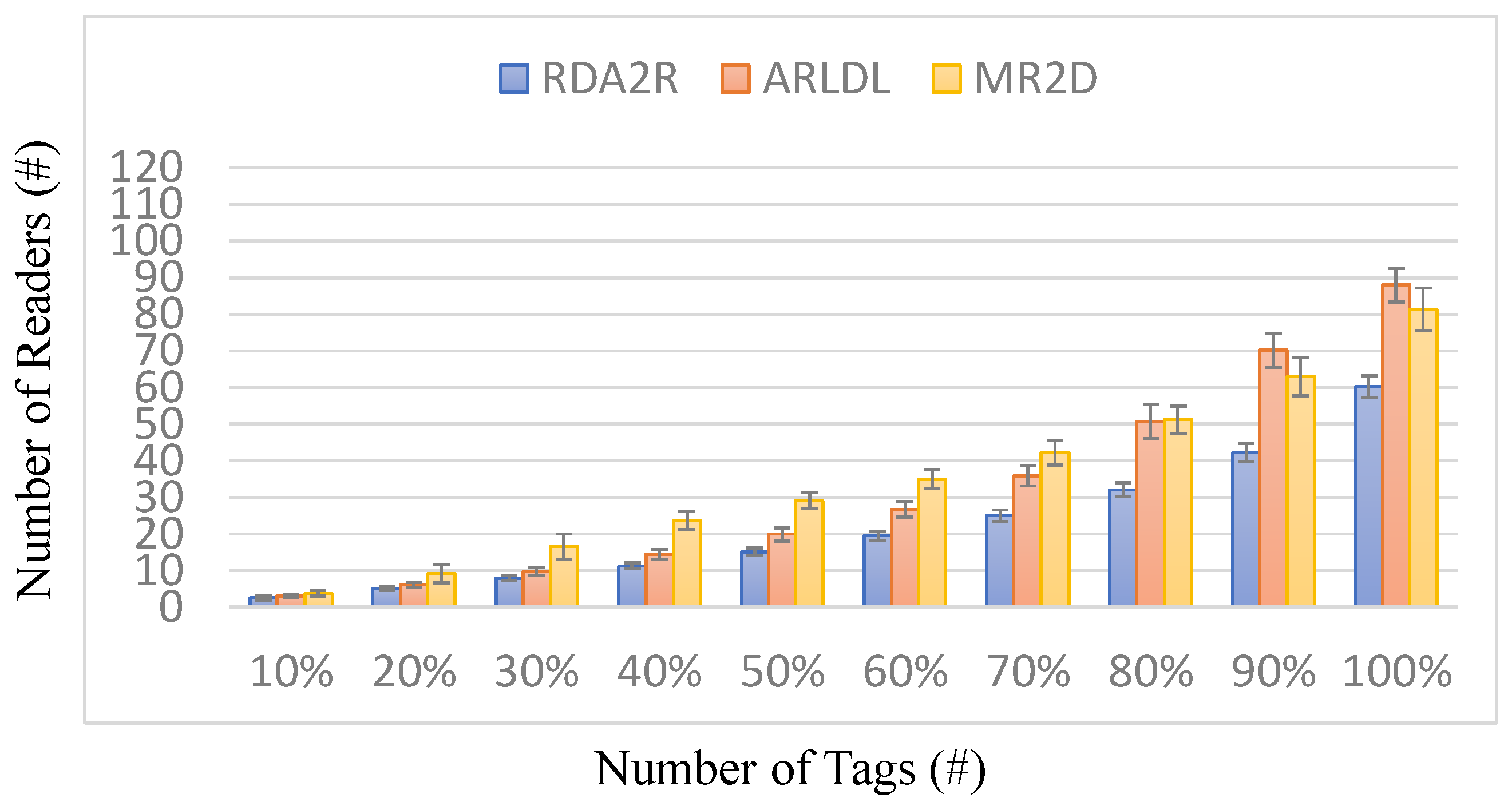
7. Conclusions
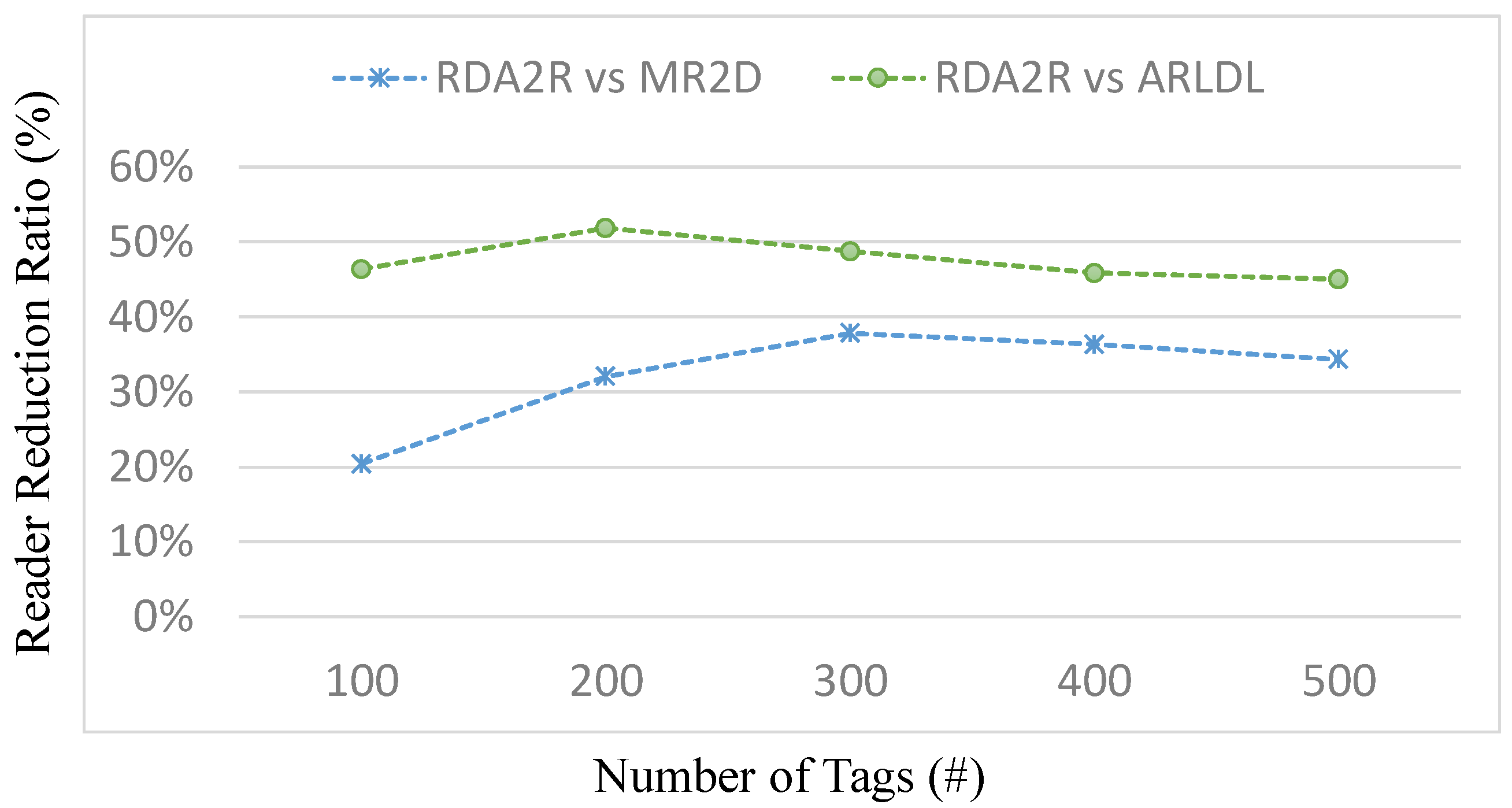
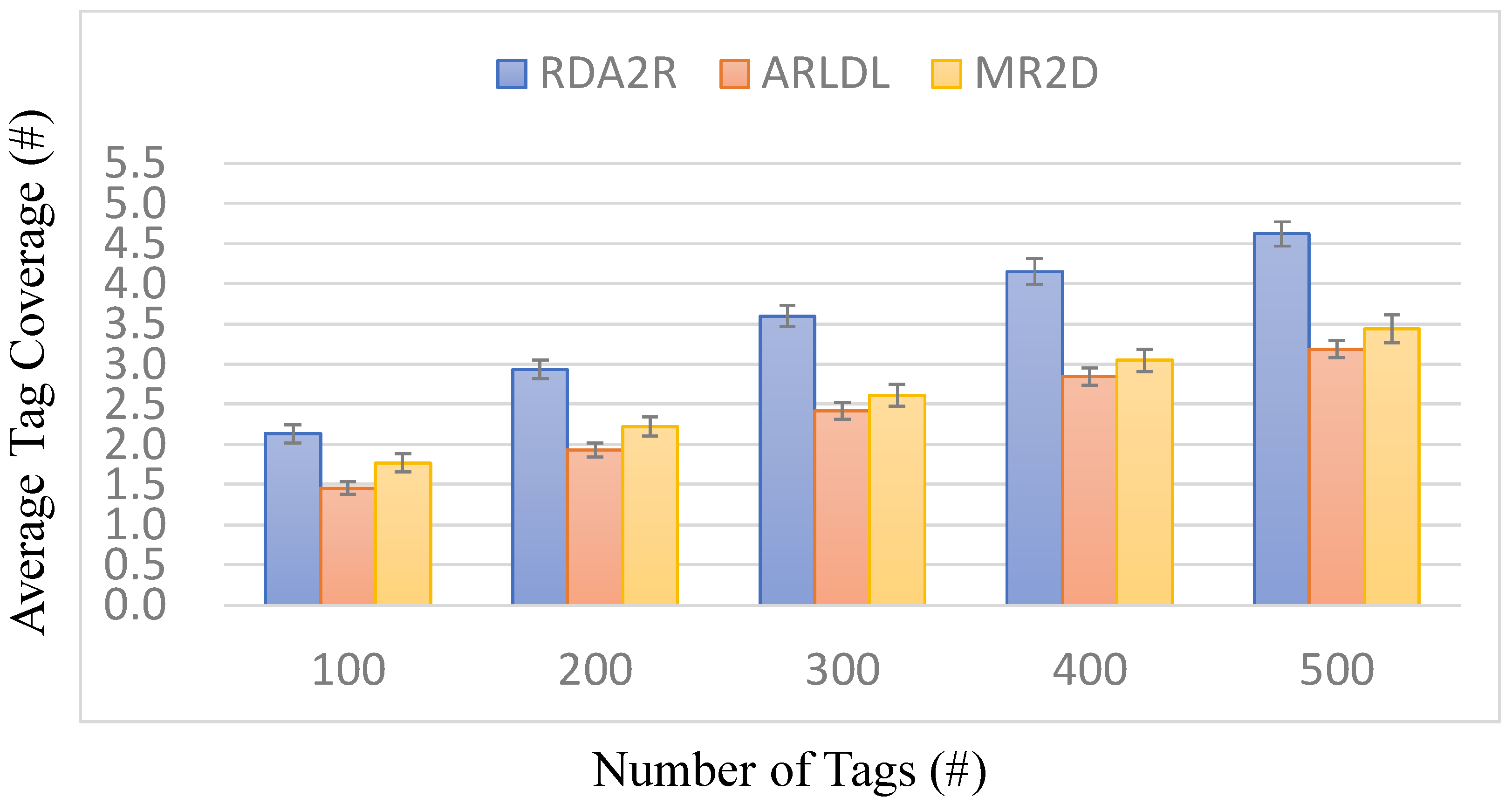
This paper presented RDA2R, a deterministic and interference-aware reader deployment framework for RFID-enabled IIoT environments. The proposed method integrates grid-based initialization, competitive tag-to-reader association, interference-aware reader activation, and adaptive range adjustment to achieve complete tag coverage with the minimum number of readers while suppressing redundant overlap and communication interference. Extensive simulations under random and congregation tag distributions confirm the robustness and scalability of RDA2R across different tag densities ranging from 100 to 500. Under the random tag distribution, RDA2R demonstrates stable scalability and balanced deployment efficiency as tag density increases. For full coverage, RDA2R reduces the number of deployed readers by approximately 46% compared with ARLDL and 32% compared with MR2D [
25]. It also enhances tag-to-reader utilization by about 31–33%, indicating that each reader contributes more effectively to overall coverage while maintaining interference-free operation. Under the congregation tag distribution, where tags are spatially clustered, RDA2R exhibits stronger performance gains. The number of required readers decreases by roughly 47% relative to ARLDL and 33% relative to MR2D [
25] at full coverage. When the partial coverage levels range from 10% to 100%, RDA2R consistently requires fewer readers than the benchmark methods. At an 80% coverage level, RDA2R achieves improvement ratios of approximately 58% over ARLDL and 60% over MR2D [
25], indicating that it requires about one-third fewer readers to reach the same coverage. Even at full coverage, RDA2R maintains reductions of approximately 46% compared with ARLDL and 35% compared with MR2D [
25], demonstrating its efficiency and scalability under clustered deployment conditions. Overall, RDA2R achieves reliable, scalable, and interference-minimized reader deployment for RFID-based IIoT applications. It ensures complete tag accessibility while significantly reducing hardware requirements and potential interference zones compared with benchmark algorithms. As this study is based on simulation, future work will include hardware validation using adjustable-range RFID readers to examine the practical deployment behavior of RDA2R in real IIoT environments.