Multi-Object Tracking with Confidence-Based Trajectory Prediction Scheme
Abstract
1. Introduction
- 1.
- In the data association stage, confidence scores are integrated into the cost matrix to improve matching accuracy and achieve more reliable assignment results.
- 2.
- In the trajectory prediction stage, a confidence-based trajectory prediction scheme has been proposed based on KF, which achieves more accurate prediction performance by controlling the measurement noise in KF.
- 3.
- In the trajectory management stage, a trajectory deletion scheme has been proposed to determine the duration of trajectories and delete less reliable trajectories to avoid possible incorrect matches.
2. Related Works
2.1. Motion Models
2.2. Cost Matrix
2.3. Trajectories Management
3. Method
3.1. Confidence-Based Adaptive KF
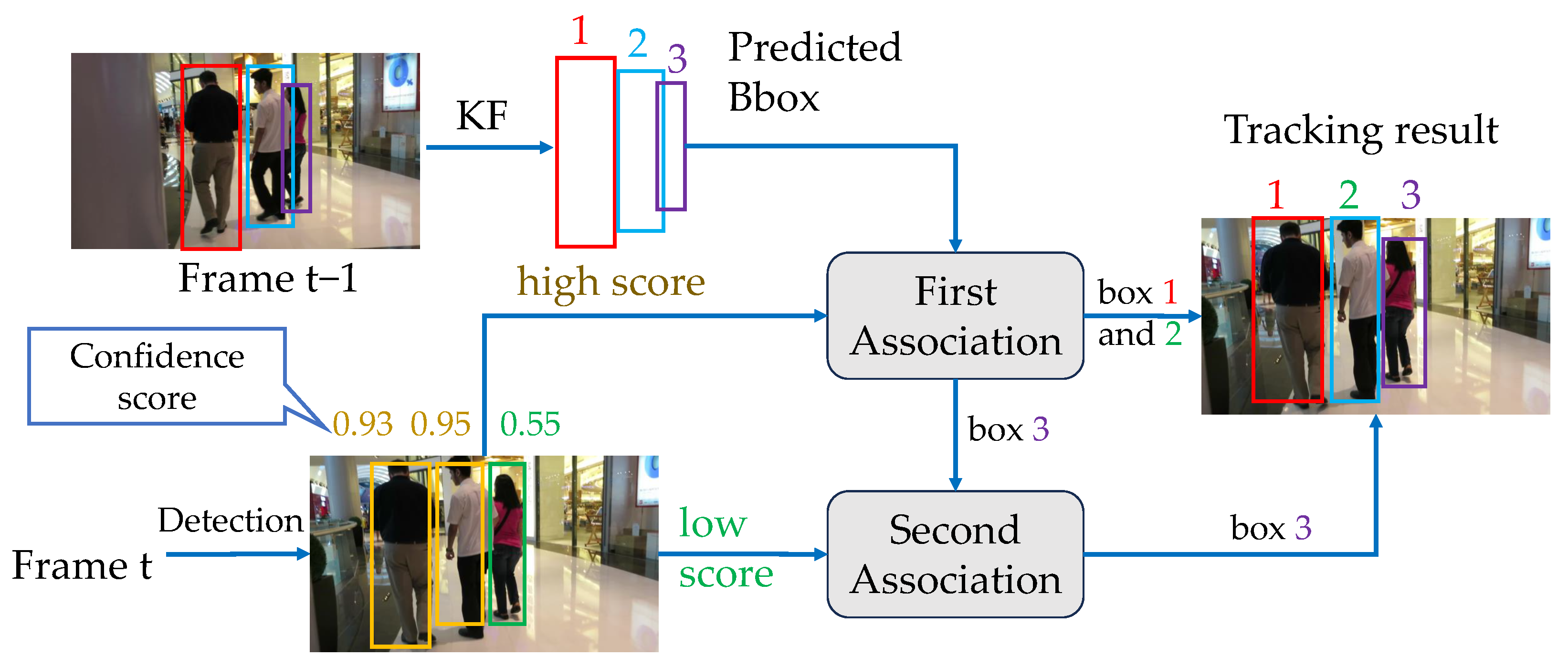
3.2. Data Association
3.3. Deletion Strategy
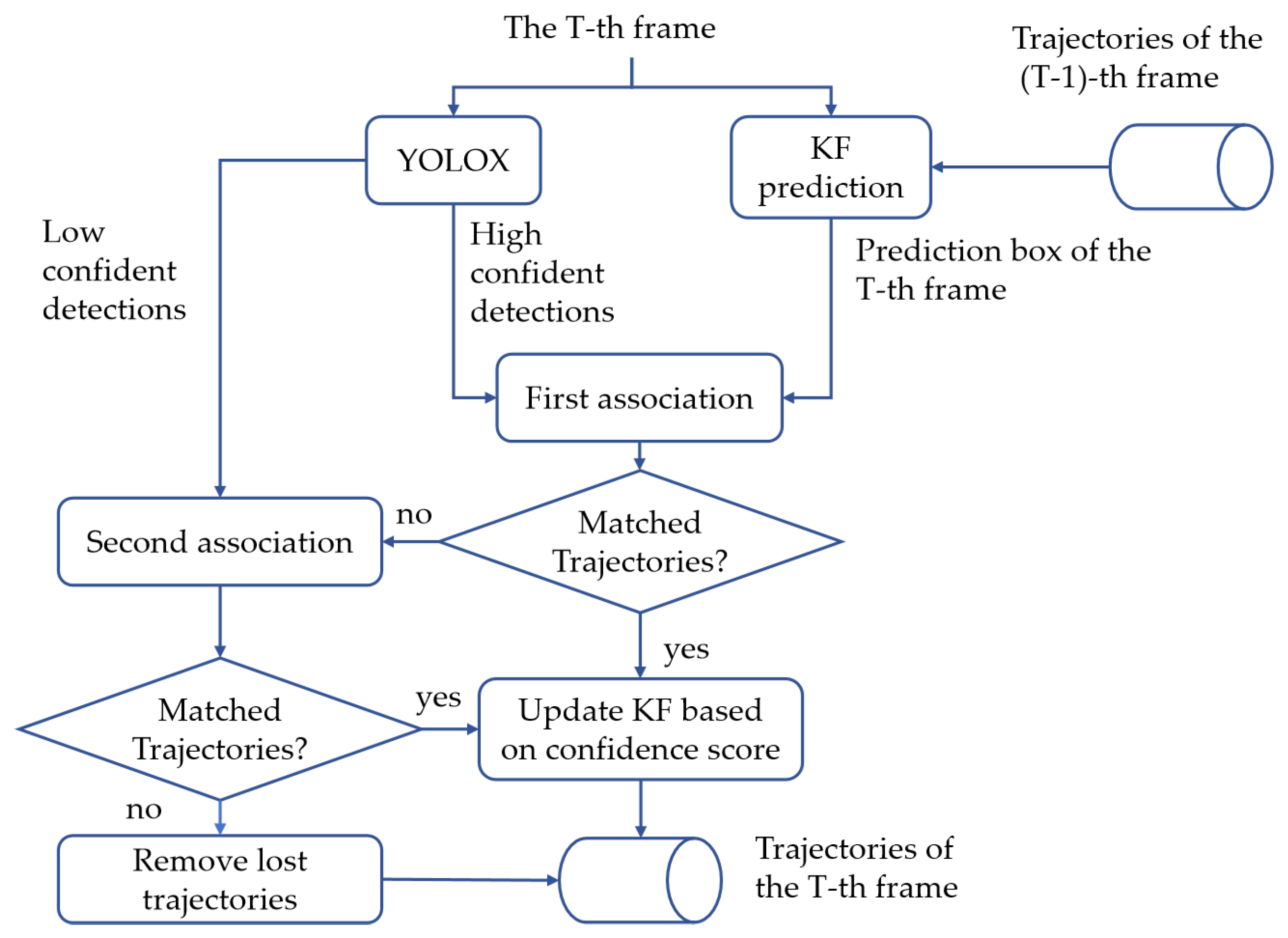
3.4. Tracking Procedure
| Algorithm 1: Pseudo-code of tracking |
 |
4. Experiment
4.1. Datasets
4.2. Metrics
4.3. Implementation Details
4.4. Experimental Results
4.4.1. Results on MOT17
4.4.2. Results on MOT20
4.4.3. Comprehensive Analysis
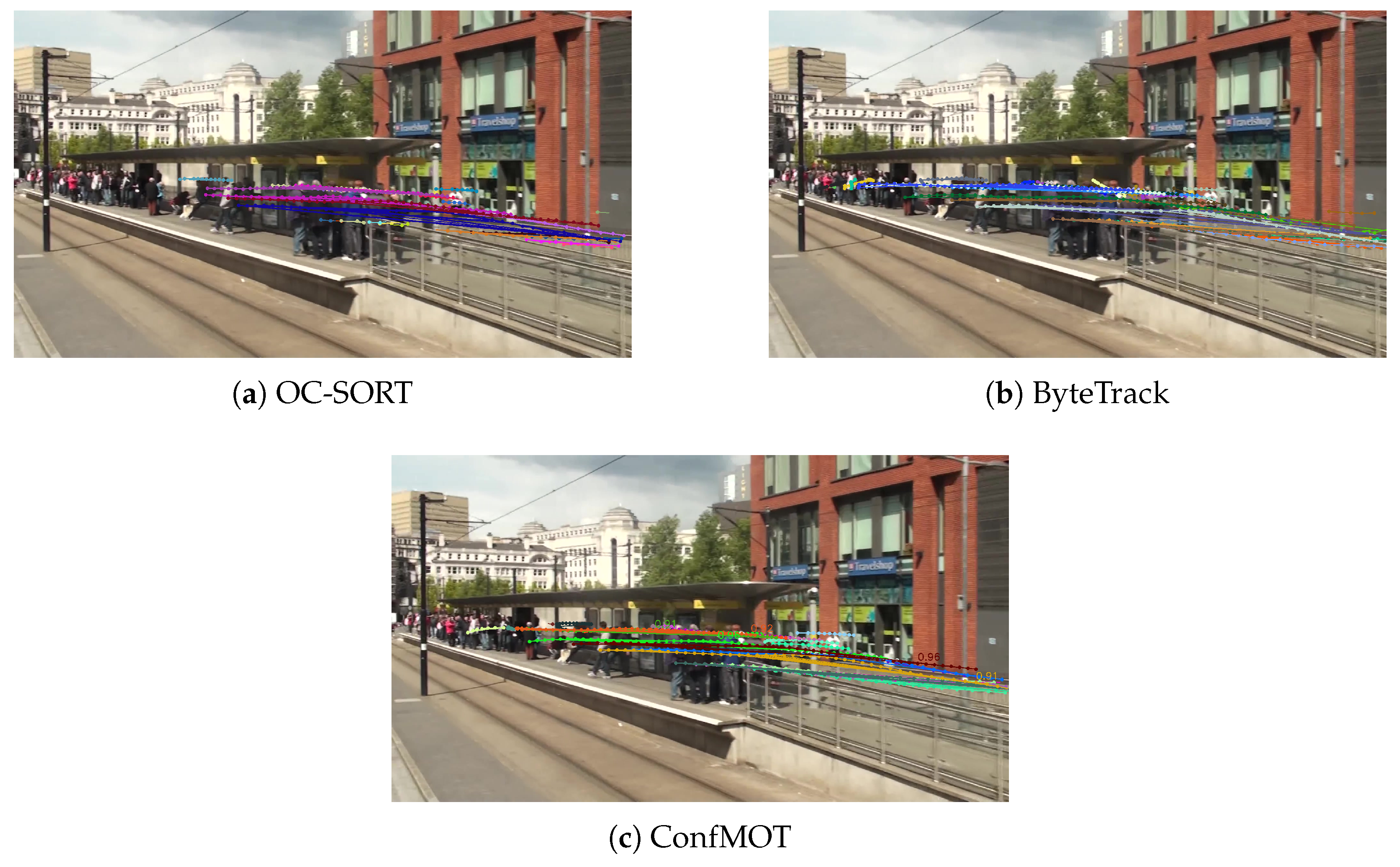
4.4.4. Visualization of Trajectories
4.5. Ablation Studies
4.5.1. KF Based on the Confidence Score
4.5.2. Deletion Strategy Based on the Confidence Score
4.5.3. Cost Matrix Based on the Confidence Score
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wojke, N.; Bewley, A.; Paulus, D. Simple online and realtime tracking with a deep association metric. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Beijing, China, 17–20 September 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 3645–3649. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, P.; Jiang, Y.; Yu, D.; Weng, F.; Yuan, Z.; Luo, P.; Liu, W.; Wang, X. Bytetrack: Multi-object tracking by associating every detection box. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2022: 17th European Conference, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Proceedings, Part XXII. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhang, X. Motrv2: Bootstrapping end-to-end multi-object tracking by pretrained object detectors. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 22056–22065. [Google Scholar]
- Bewley, A.; Ge, Z.; Ott, L.; Ramos, F.; Upcroft, B. Simple online and realtime tracking. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Phoenix, AZ, USA, 25–28 September 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 3464–3468. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Zhang, J.; Gao, D.; Fan, B.; Fu, Z. Occlusion-aware visual object tracking based on multi-template updating Siamese network. Digit. Signal Process. 2024, 148, 104440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Liang, X.; Yuan, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, G.; Tamura, S. Multi-object tracking via deep feature fusion and association analysis. Eng. Artif. Intell. 2023, 124, 106527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Ban, Y.; Delorme, G.; Gan, C.; Rus, D.; Alameda-Pineda, X. Transcenter: Transformers with dense representations for multiple-object tracking. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 45, 7820–7835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Huang, X.; Sun, J.; Zhang, X. AMtrack: Anti-occlusion multi-object tracking algorithm. Signal Image Video Process. 2024, 18, 9305–9318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.; Wang, X.; Yu, H.; Niu, K.; Li, B.; Xue, X. Denoising-mot: Towards multiple object tracking with severe occlusions. In Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 29 October–3 November 2023; pp. 2734–2743. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zheng, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, S. Towards real-time multi-object tracking. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Proceedings, Part XI 16. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 107–122. [Google Scholar]
- Milan, A.; Leal-Taixé, L.; Reid, I.; Roth, S.; Schindler, K. Mot16: A benchmark for multi-object tracking. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1603.00831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dendorfer, P.; Rezatofighi, H.; Milan, A.; Shi, J.; Cremers, D.; Reid, I.; Roth, S.; Schindler, K.; Leal-Taixé, L. Mot20: A benchmark for multi object tracking in crowded scenes. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.09003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, F.; Li, Z.; Sun, J. Yolox: Exceeding yolo series in 2021. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.08430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Pang, J.; Weng, X.; Khirodkar, R.; Kitani, K. Observation-centric sort: Rethinking sort for robust multi-object tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 9686–9696. [Google Scholar]
- You, S.; Yao, H.; Xu, C. Multi-object tracking with spatial-temporal topology-based detector. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2021, 32, 3023–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Wan, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, B.; Tong, Z.; Dong, J. Giaotracker: A comprehensive framework for mcmot with global information and optimizing strategies in visdrone 2021. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 2809–2819. [Google Scholar]
- Khurana, T.; Dave, A.; Ramanan, D. Detecting invisible people. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 3174–3184. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Gu, R.; Liu, Z.; Hu, W.; Song, M.; Hwang, J.-N. Track without appearance: Learn box and tracklet embedding with local and global motion patterns for vehicle tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 9876–9886. [Google Scholar]
- Bergmann, P.; Meinhardt, T.; Leal-Taixe, L. Tracking without bells and whistles. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 941–951. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Ai, H.; Zhuang, Z.; Shang, C. Real-time multiple people tracking with deeply learned candidate selection and person re-identification. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), San Diego, CA, USA, 23-27 July 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Zeng, W.; Liu, W. Fairmot: On the fairness of detection and re-identification in multiple object tracking. Int. Comput. Vis. 2021, 129, 3069–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Zhao, Z.; Li, B.; Xiao, T.; Yu, G.; Zhang, X.; Sun, J. Crowdhuman: A benchmark for detecting human in a crowd. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.00123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Benenson, R.; Schiele, B. Citypersons: A diverse dataset for pedestrian detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 3213–3221. [Google Scholar]
- Ess, A.; Leibe, B.; Schindler, K.; Gool, L.V. A mobile vision system for robust multi-person tracking. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Anchorage, AK, USA, 23–28 June 2008; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2014: 13th European Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Proceedings, Part V 13. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Qin, S.; Li, S.; Gao, Y.; Wu, Y. Synergistic-aware cascaded association and trajectory refinement for multi-object tracking. Image Vis. Comput. 2025, 162, 105695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psalta, A.; Tsironis, V.; Karantzalos, K. Transformer-based assignment decision network for multiple object tracking. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2024, 241, 103957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-F.; Ji, H.-B.; Zhang, W.-B.; Lai, Y.-K. Learning discriminative motion models for multiple object tracking. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2024, 26, 11372–11385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Cao, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Xie, E.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, C.; Luo, P. Transtrack: Multiple object tracking with transformer. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2012.15460. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, J.; Xu, M.; Li, W.; Xiong, Y.; Xia, W.; Tu, Z.; Soatto, S. Memot: Multi-object tracking with memory. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 8090–8100. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, R.; Wang, L. Memotr: Long-term memory-augmented transformer for multi-object tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 4–6 October 2023; pp. 9901–9910. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, R.; Song, Z.; Ma, L.; Wei, J.; Yang, W.; Yang, M. Diffusiontrack: Diffusion model for multi-object tracking. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 26–27 February 2024; Volume 38, pp. 3991–3999. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, M.; Zhu, X.; Wang, H.; Cao, S.; Liu, C.; Song, Q. Stdformer: Spatial-temporal motion transformer for multiple object tracking. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2023, 33, 6571–6594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, E.; Li, Z.; Han, S.; Wang, H. Relationtrack: Relation-aware multiple object tracking with decoupled representation. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2022, 25, 2686–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Jiang, M.; Kong, J. Bgtracker: Cross-task bidirectional guidance strategy for multiple object tracking. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2023, 25, 8132–8144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, J.; Fu, Y. Collaborative tracking learning for frame-rate-insensitive multi-object tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 4–6 October 2023; pp. 9964–9973. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Shen, H.; Shen, Y. Jdt-nas: Designing efficient multi-object tracking architectures for non-gpu computers. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2023, 33, 7541–7553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, K.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Z.; Hu, W.; Li, B.; Lu, F. Jointing recurrent across-channel and spatial attention for multi-object tracking with block-erasing data augmentation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2023, 33, 4054–4069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.; Mo, E.; Jiang, M.; Liu, T. Motfr: Multiple object tracking based on feature recoding. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2022, 32, 7746–7757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Pan, P.; Xu, Y. Multiple object tracking with correlation learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 3876–3886. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, P.; Wang, J.; You, Q.; Ling, H.; Liu, Z. Transmot: Spatial-temporal graph transformer for multiple object tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 2–7 January 2023; pp. 4870–4880. [Google Scholar]
- Stadler, D.; Beyerer, J. Modelling ambiguous assignments for multi-person tracking in crowds. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2022; pp. 133–142. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, W.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, D. One-shot multiple object tracking with robust id preservation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2023, 34, 4473–4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidenschwarz, J.; Brasó, G.; Serrano, V.C.; Elezi, I.; Leal-Taixé, L. Simple cues lead to a strong multi-object tracker. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 13813–13823. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, S.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yang, F.; Lu, W.; Li, D. GGSTrack: Geometric graph with spatio-temporal convolution for multi-object tracking. Neurocomputing 2025, 653, 131234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Yang, G.; Li, Y.; Lu, M.; Sun, H. Multi-object tracking using score-driven hierarchical association strategy between predicted tracklets and objects. Image Vis. Comput. 2024, 152, 105303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, V.; Jung, G.; Lee, S.-W. AM-SORT: Adaptable motion predictor with historical trajectory embedding for multi-object tracking. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, Jeju Island, Republic of Korea, 18–21 June 2024; pp. 92–107. [Google Scholar]


| Methods | MOT17 | MOT20 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HOTA↑ | MOTA↑ | IDF1↑ | IDS↓ | FPS↑ | HOTA↑ | MOTA↑ | IDF1↑ | IDS↓ | FPS↑ | |
| TADN [27] | - | 69.0% | 60.8% | - | - | - | 68.7% | 61.0% | - | - |
| DMMTracker [28] | 52.1% | 67.1% | 64.3% | 3135 | 16.1 | 48.7% | 62.5% | 60.5% | 2043 | 9.7 |
| TransTrack [29] | 54.1% | 75.2% | 63.5% | 3603 | 10.0 | 48.5% | 65.0% | 59.4% | 3608 | 7.2 |
| TransCenter [7] | 54.5% | 73.2% | 62.2% | 4614 | 1.0 | 43.5% | 61.9% | 50.4% | 4653 | 1.0 |
| MeMOT [30] | 56.9% | 72.5% | 69.0% | 2724 | - | 54.1% | 63.7% | 66.1% | 1938 | - |
| AMtrack [8] | 58.6% | 74.4% | 71.5% | 4740 | - | 56.8% | 73.2% | 69.2% | 1870 | - |
| DNMOT [9] | 58.0% | 75.6% | 68.1% | 2529 | - | 58.6% | 70.5% | 73.2% | 987 | - |
| MeMOTR [31] | 58.8% | 72.8% | 71.5% | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| FairMOT [21] | 59.3% | 73.7% | 72.3% | 3303 | 25.9 | 54.6% | 61.8% | 67.3% | 5243 | 13.2 |
| DiffusionTrack [32] | 60.8% | 77.9% | 73.8% | 3819 | - | 55.3% | 72.8% | 66.3% | 4117 | - |
| STDFormer-LMPH [33] | 60.9% | 78.4% | 73.1% | 5091 | - | 60.2% | 76.2% | 72.1% | 5245 | - |
| RelationTrack [34] | 61.0% | 73.8% | 74.4% | 1374 | 7.4 | 56.5% | 67.2% | 70.5% | 4243 | 2.7 |
| BGTracker [35] | 61.0% | 75.6% | 73.8% | 3735 | 20.7 | 57.5% | 71.6% | 71.8% | 2471 | 12.8 |
| ColTrack [36] | 61.0% | 78.8% | 73.9% | 1881 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| JDT-NAS-T1 [37] | - | 74.3% | 72.0% | 2818 | 13.3 | - | - | - | - | - |
| DcMOT [38] | 61.3% | 74.5% | 75.2% | 2682 | 20.4 | 53.8% | 59.7% | 67.4% | 5636 | 10.6 |
| MOTFR [39] | 61.8% | 74.4% | 76.3% | 2652 | 22.2 | 57.2% | 69.0% | 71.7% | 3648 | 13.3 |
| CorrTracker [40] | - | 76.5% | 73.6% | 3369 | 14.8 | - | 65.2% | 69.1% | 5183 | 8.5 |
| TransMOT [41] | - | 76.7% | 75.1% | 2346 | - | - | 77.5% | 75.2% | 1615 | - |
| MAA [42] | 62.0% | 79.4% | 75.9% | 1452 | 189.1 | 57.3% | 73.9% | 71.2% | 1331 | 14.7 |
| MOTRv2 [3] | 62.0% | 78.6% | 75.0% | - | - | 61.0% | 76.2% | 73.1% | - | - |
| PID-MOT [43] | 62.1% | 74.7% | 76.3% | 1563 | 19.7 | 57.0% | 67.5% | 71.3% | 1015 | 8.7 |
| GHOST [44] | 62.8% | 78.7% | 77.1% | 2325 | - | 61.2% | 73.7% | 75.2% | 1264 | - |
| GGSTrack [45] | 62.8% | 80.2% | - | 1689 | 58.0 | 61.8% | 75.1% | - | 1498 | 15.3 |
| ScoreMOT [46] | 63.0% | 79.8% | 76.7% | 4007 | 25.6 | 62.3% | 77.7% | 75.6% | 1440 | 16.2 |
| ByteTrack [2] | 63.1% | 80.3% | 77.3% | 2196 | 29.6 | 61.3% | 77.8% | 75.2% | 1223 | 17.5 |
| OC-SORT [14] | 63.2% | 78.0% | 77.5% | 1950 | 29.0 | 62.1% | 75.5% | 75.9% | 913 | 18.7 |
| AM-SORT [47] | 63.3% | 78.0% | 77.8% | - | - | 62.0% | 75.5% | 76.1% | - | - |
| SCTrack [26] | 63.5% | 79.4% | 77.7% | 2022 | - | 61.4% | 75.6% | 76.1% | 837 | - |
| ConfMOT | 64.5% | 80.5% | 79.3% | 1980 | 26.1 | 62.9% | 78.3% | 76.1% | 1359 | 15.2 |
| Tracker | AssA (%)↑ | AssPr (%)↑ | AssRe (%)↑ | DetA (%)↑ | LocA (%)↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ByteTrack [2] | 62.0 | 76.0 | 68.2 | 64.5 | 83.0 |
| OC-SORT [14] | 63.4 | 80.8 | 67.5 | 63.2 | 83.4 |
| ConfMOT (Ours) | 63.8 | 77.9 | 70.0 | 64.9 | 83.4 |
| Tracker | ↑ | AssPr↑ | AssRe↑ | DetA↑ | LocA↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ByteTrack [2] | 59.6% | 74.6% | 66.2% | 63.4% | 83.6% |
| OC-SORT [14] | 60.5% | 75.1% | 67.1% | 64.2% | 83.9% |
| ConfMOT | 61.4% | 77.1% | 67.8% | 64.6% | 84.7% |
| KF | DS | CM+CS | HOTA↑ | MOTA↑ | IDF1↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 67.8% | 77.9% | 79.6% | |||
| ✔ | 68.1% | 77.9% | 79.8% | ||
| ✔ | ✔ | 68.3% | 78.0% | 80.2% | |
| ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | 68.7% | 78.4% | 80.5% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yi, K.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y. Multi-Object Tracking with Confidence-Based Trajectory Prediction Scheme. Sensors 2025, 25, 7221. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25237221
Yi K, Li J, Zhang Y. Multi-Object Tracking with Confidence-Based Trajectory Prediction Scheme. Sensors. 2025; 25(23):7221. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25237221
Chicago/Turabian StyleYi, Kai, Jiarong Li, and Yi Zhang. 2025. "Multi-Object Tracking with Confidence-Based Trajectory Prediction Scheme" Sensors 25, no. 23: 7221. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25237221
APA StyleYi, K., Li, J., & Zhang, Y. (2025). Multi-Object Tracking with Confidence-Based Trajectory Prediction Scheme. Sensors, 25(23), 7221. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25237221







