The Status of Intelligent Control Technology for the Working Height of a Crop Harvesting Header
Abstract
1. Introduction
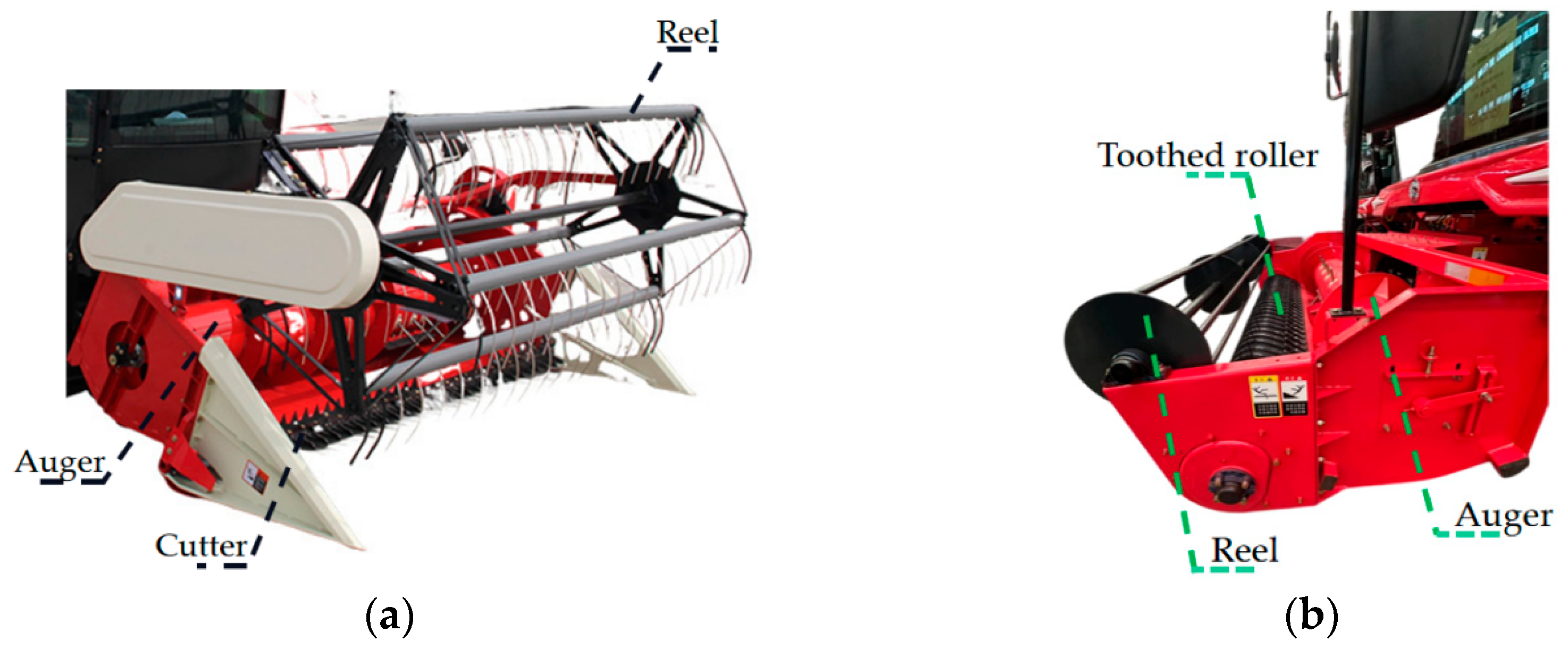
2. Structure and Principle of the Harvesting Header
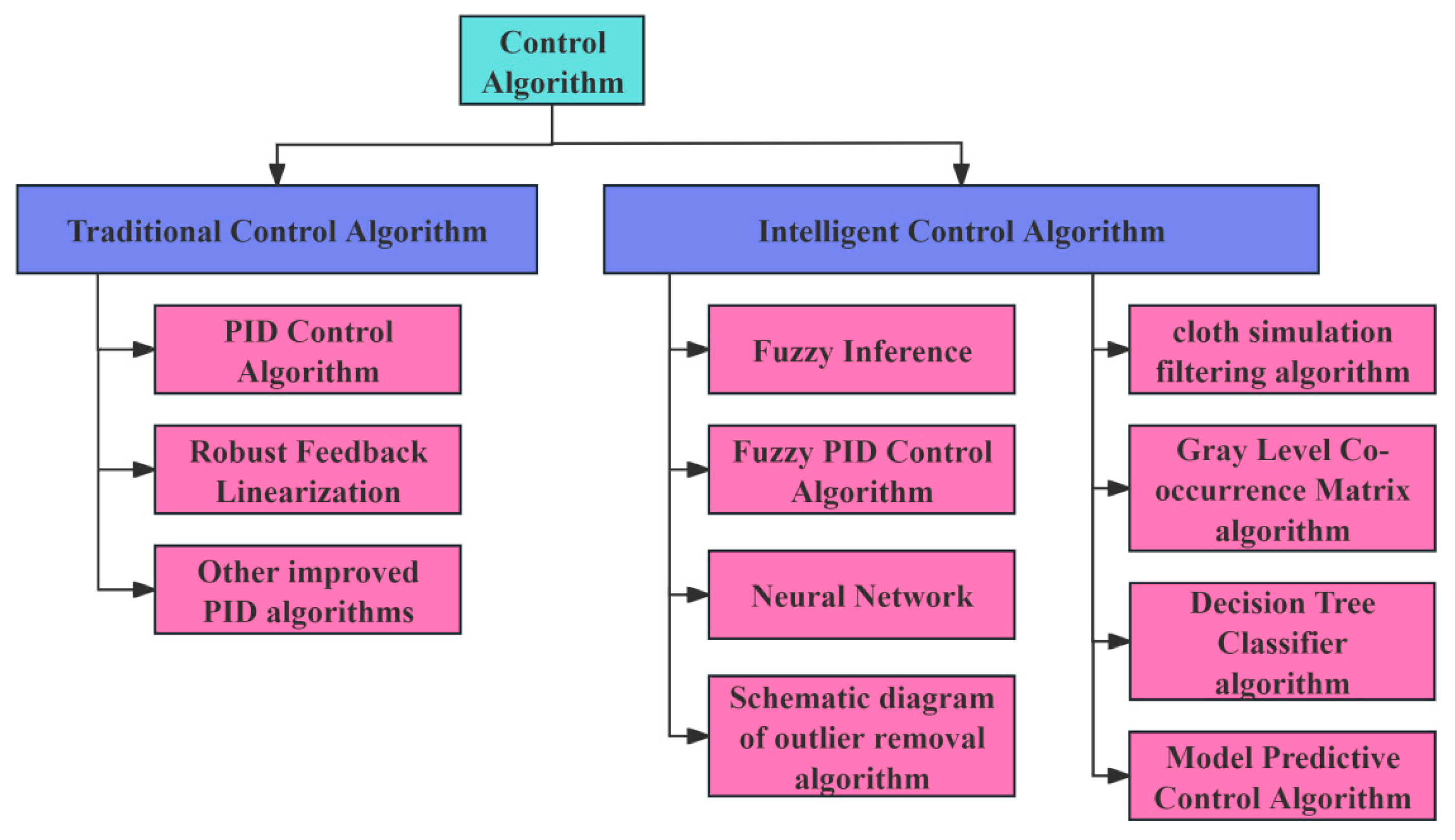
3. Classification of Intelligent Control Technology for the Working Height of a Crop Harvesting Header
3.1. Mechanical Profiling
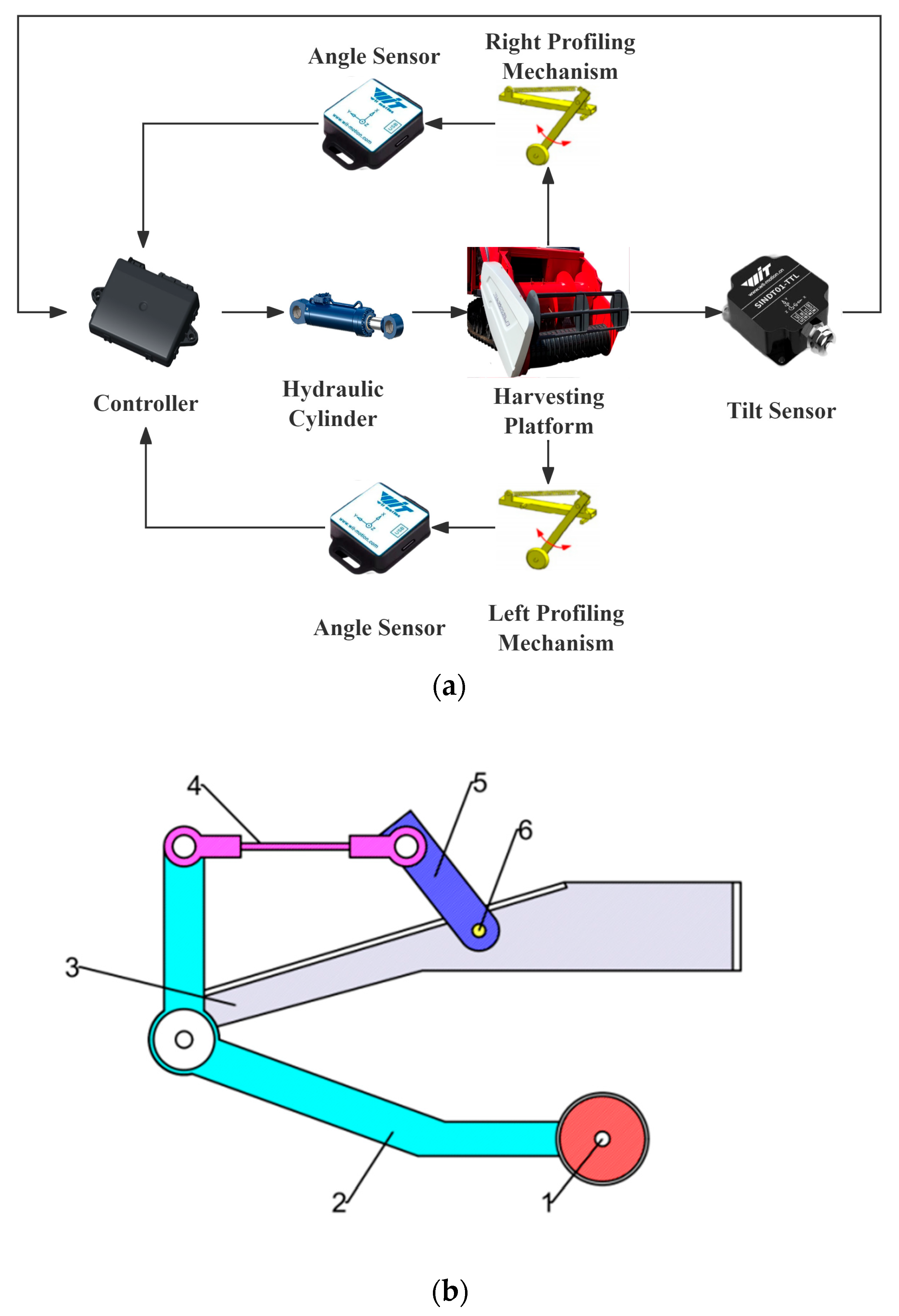
3.2. Electro-Hydraulic Profiling
4. Measurement Methods and Control Algorithms of the Working Height of a Crop Harvesting Header
4.1. Measurement Methods of the Working Height of a Crop Harvesting Header
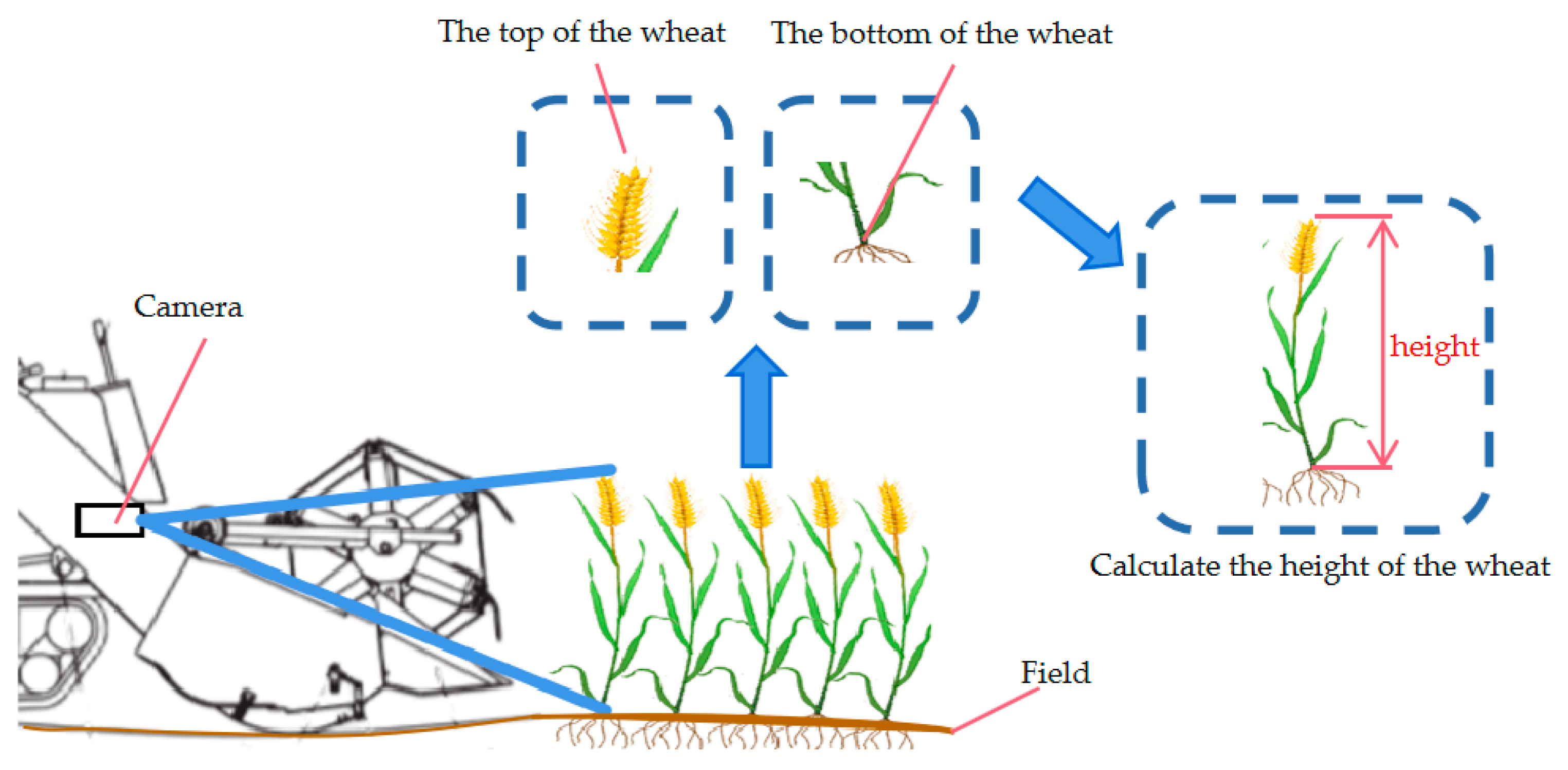
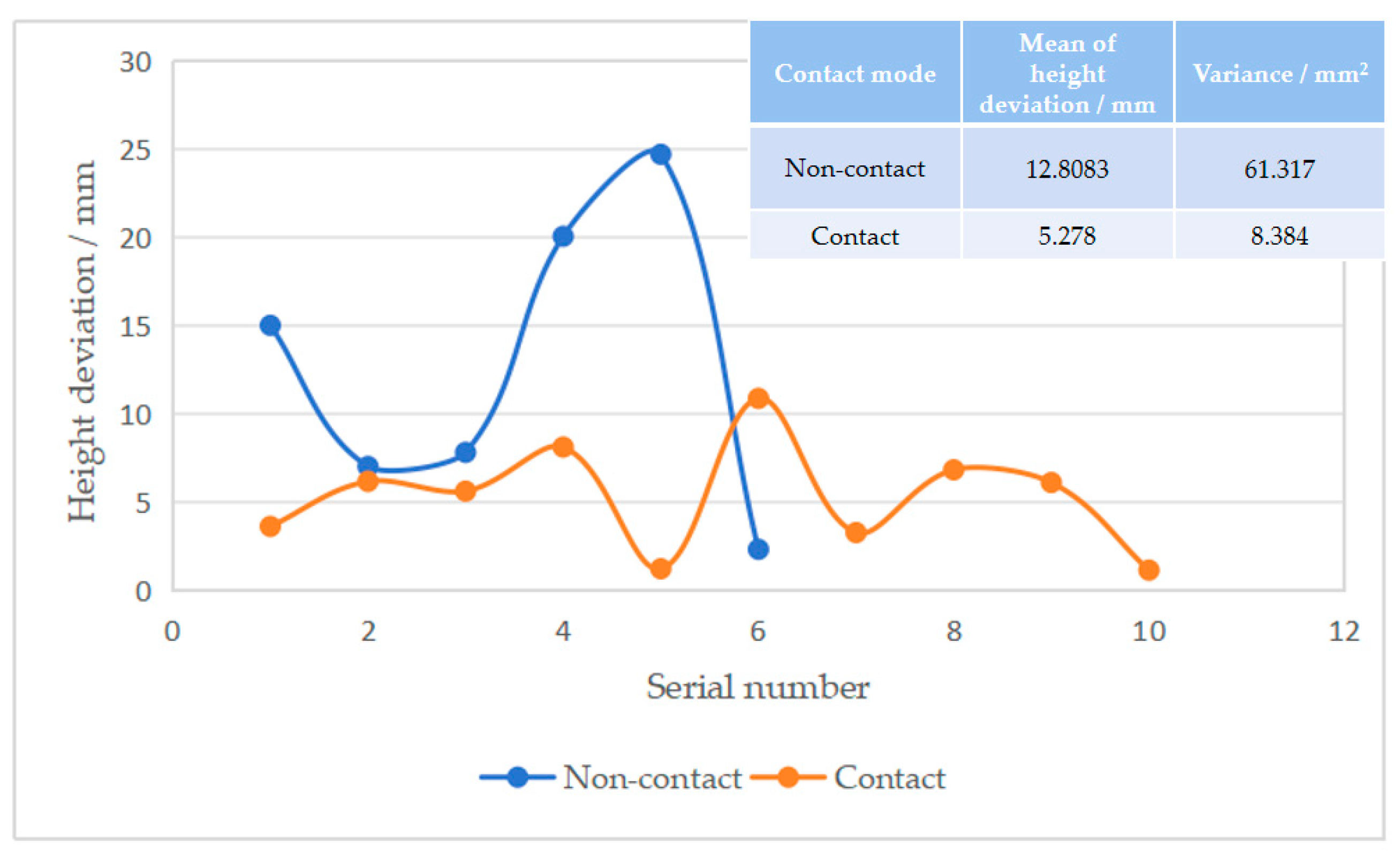
4.1.1. Non-Contact Measurement
- Structure and principle
- 2.
- Application status
- (1)
- Ultrasonic sensor
- (2)
- LIDAR sensor
- (3)
- Multi-sensor fusion
- (4)
- Machine vision
4.1.2. Contact Measurement
- Structure and principle
- 2.
- Application status
- (1)
- Profiling rod (plate)
- (2)
- Single and dual profiling wheels
4.2. Control Algorithms of the Working Height of a Crop Harvesting Header
4.2.1. Traditional Control Algorithms
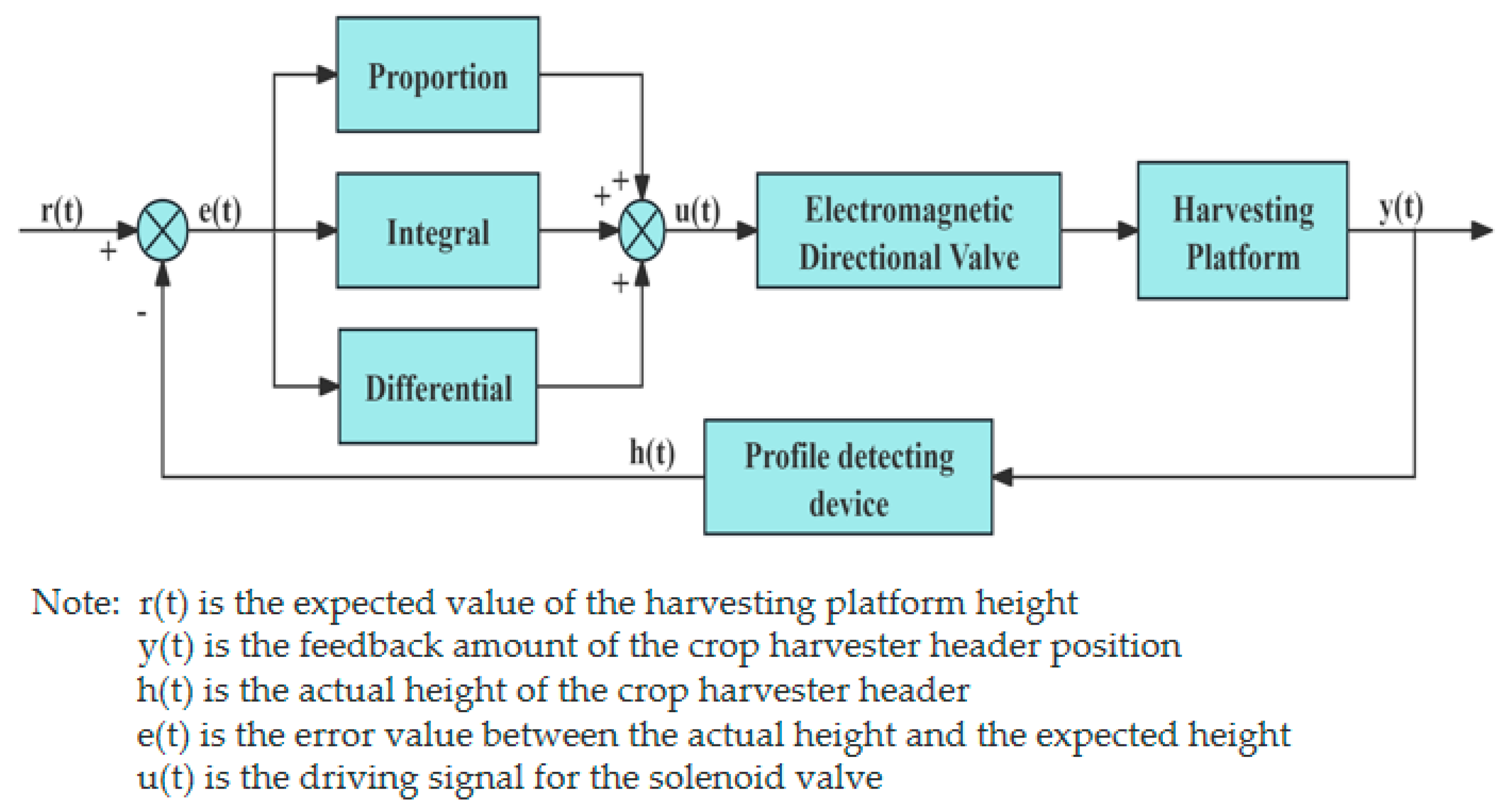
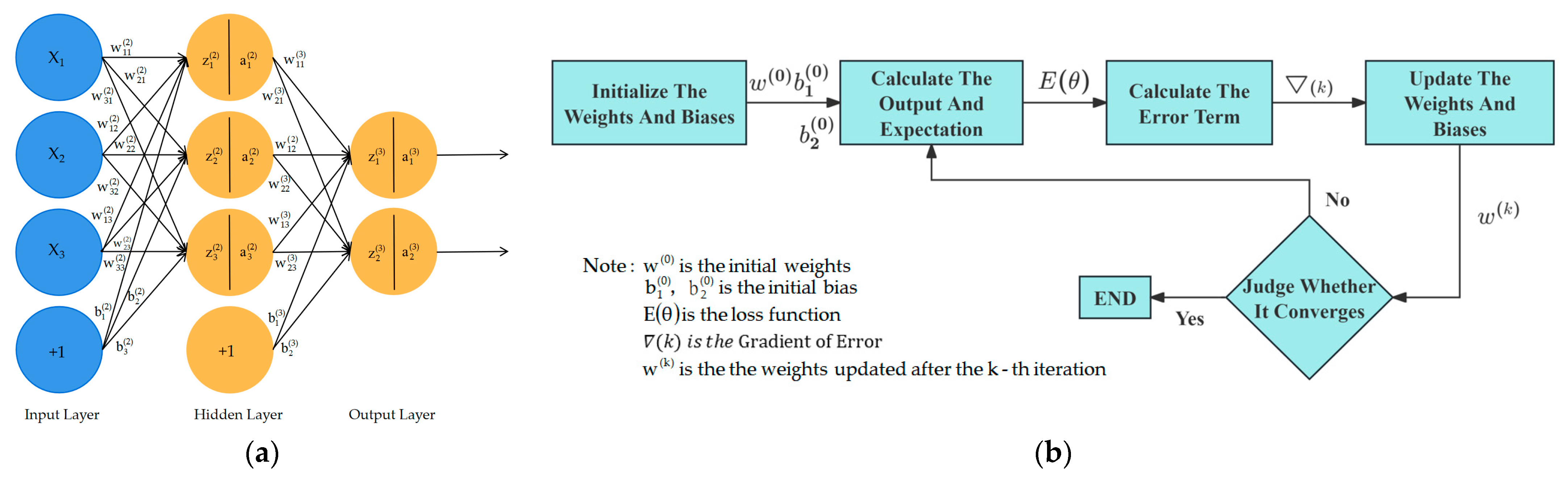
- Traditional PID control algorithms and their improved algorithms
- 2.
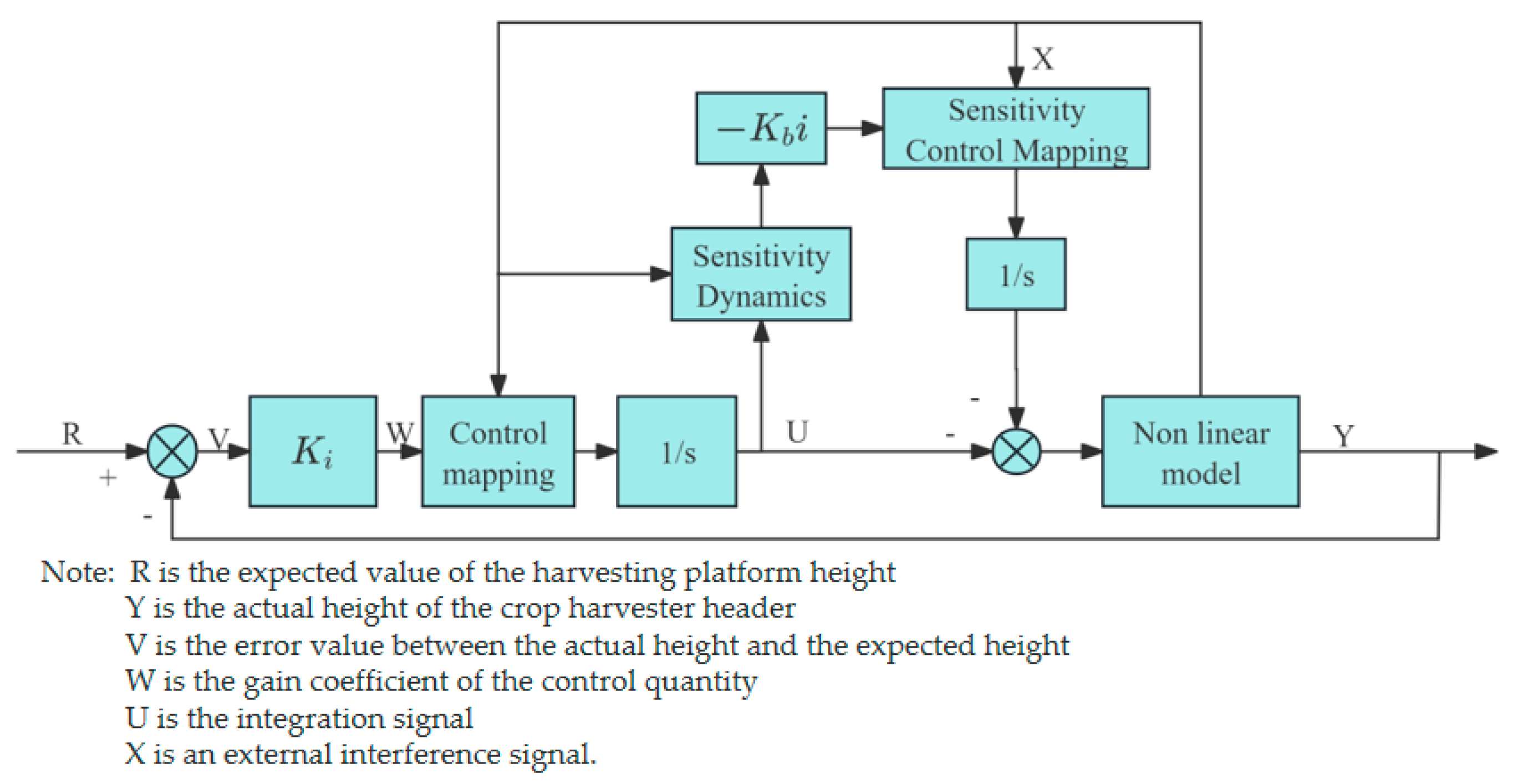
- Robust feedback linearization control algorithm
4.2.2. Intelligent Control Algorithm
- Fuzzy inference control algorithm
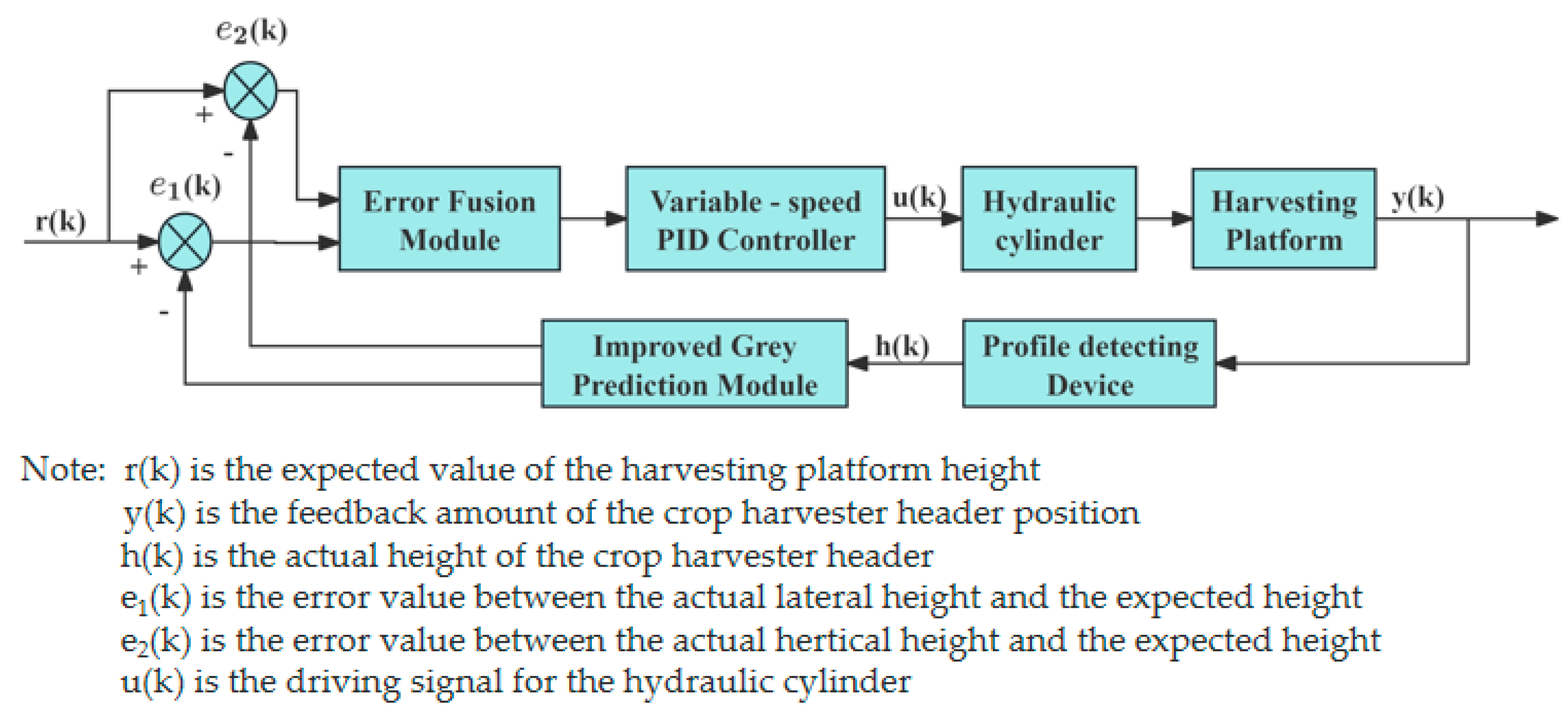
- 2.
- Fuzzy PID control algorithm
- 3.
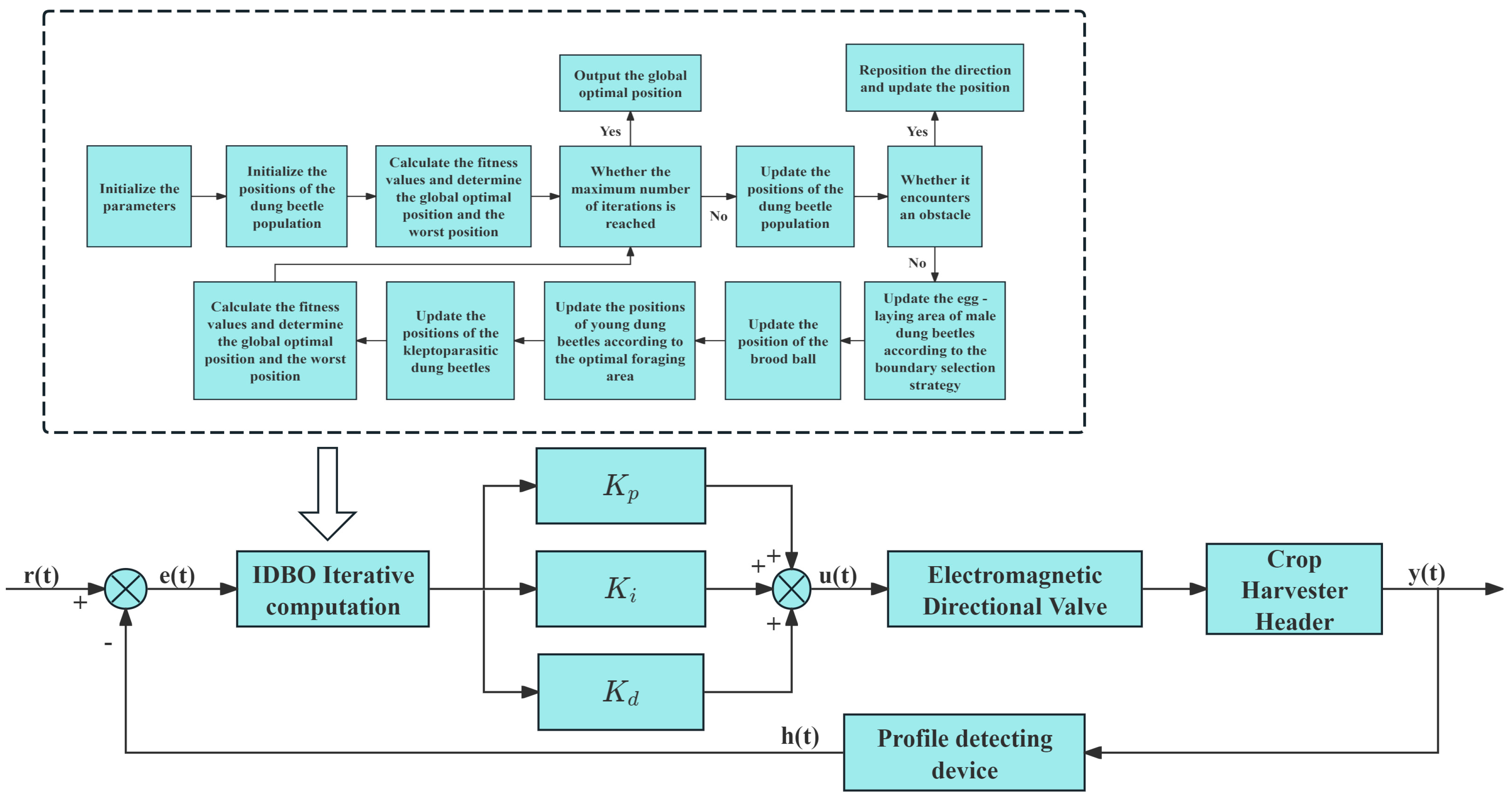
- IDBO-PID control algorithm
- 4.
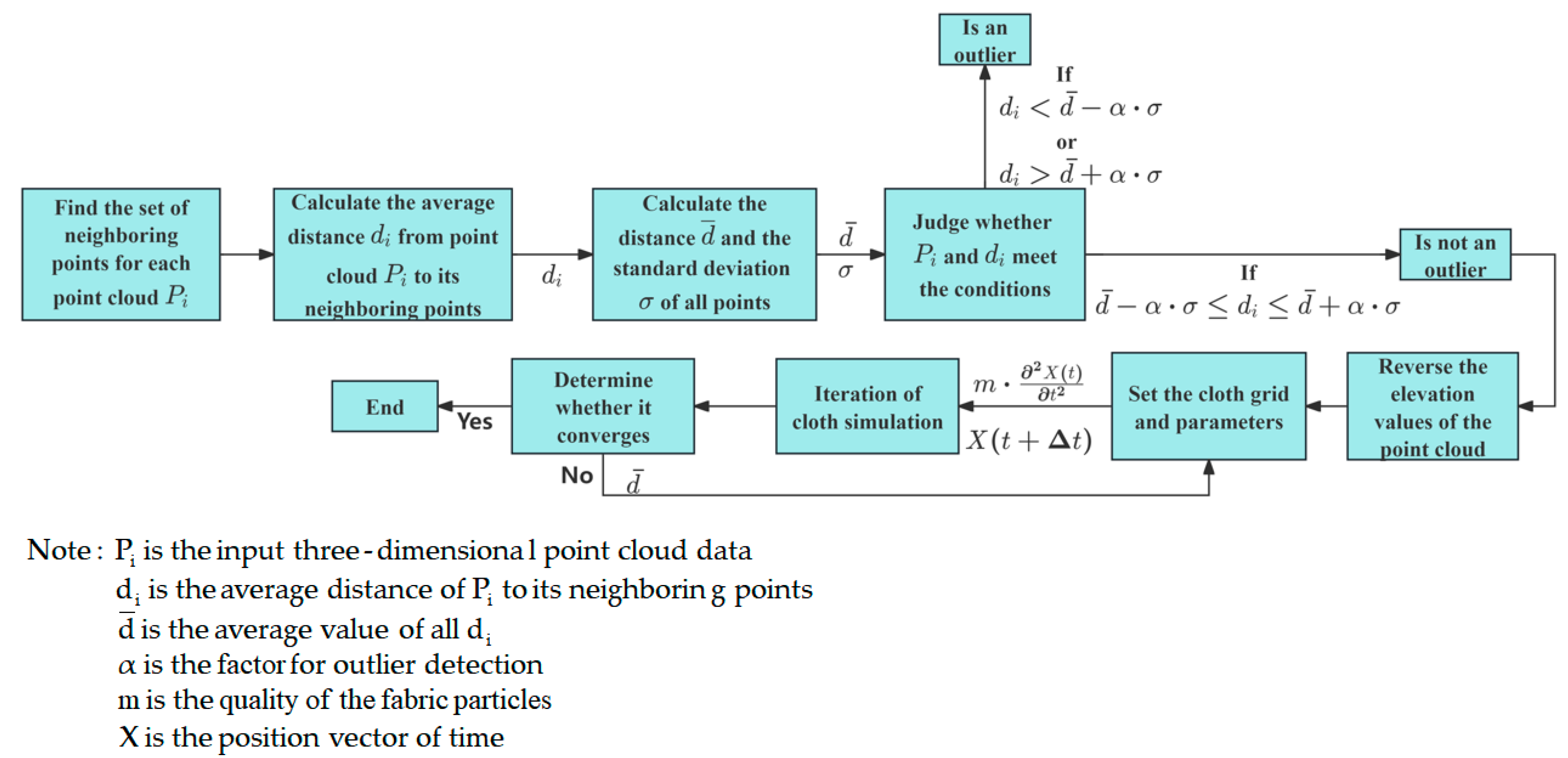
- Outlier removal algorithm and cloth simulation filter algorithm
- 5.
- Grayscale coexistence matrix algorithm and decision tree classifier algorithm
- 6.
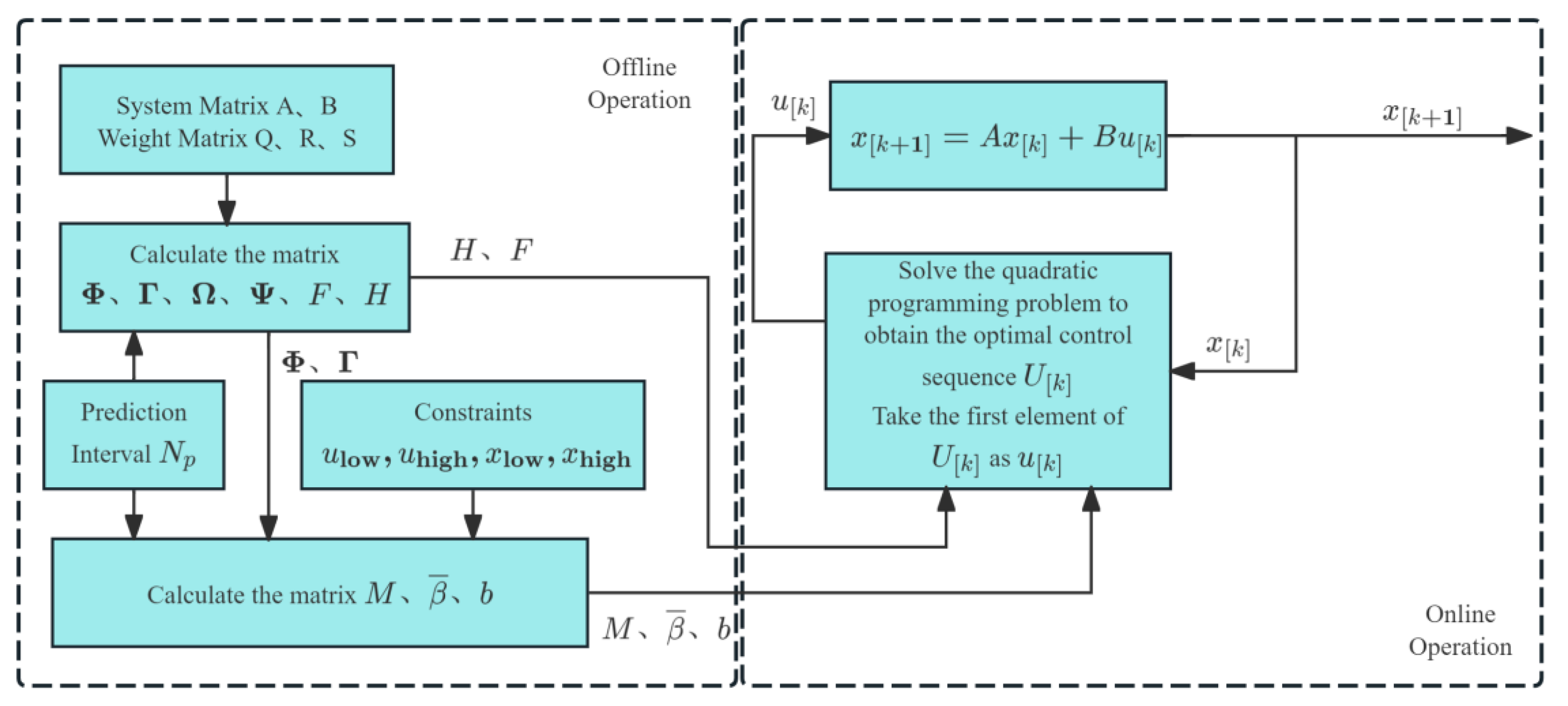
- Model predictive control algorithm
5. Conclusions and Prospects
5.1. Conclusions
5.2. Prospects
- Insufficient measurement accuracy of working height in complex terrain. Soil conditions and planting patterns vary significantly across different regions. Traditional profiling devices are typically rigid structures, which struggle to fully conform to the ground when operating in terrain with significant undulations, steep slopes, or soft ground. Under such extreme conditions, sensors may exhibit sluggish responses and significantly increased errors. It is necessary to optimize the manufacturing materials of profiling devices, replacing existing materials with shape memory alloys such as nickel-titanium alloys. By leveraging their self-responsive properties (e.g., force feedback), these materials can rapidly and reversibly transition between “soft” and “rigid” states, When encountering a trench, the profiling device is subjected to upward force, inducing stress-induced martensite transformation that softens the entire structure, causing the device to actively sink and adhere to the ground. Upon encountering an elevated object, external force is released, instantly restoring the austenitic state. The profiling device then rebounds, maintaining ground contact pressure.
- Slow response and large delay of working height hydraulic control system. Hydraulic systems exhibit slow response times, low energy efficiency, and complex system structures. Typical hydraulic systems achieve transmission efficiencies of around 70%, with response times exceeding 50 ms. Additionally, hydraulic systems require numerous auxiliary components such as reservoirs, filters, coolers, accumulators, and intricate piping networks. Maintenance complexity is high, necessitating regular replacement of hydraulic fluid and filter elements, along with leak inspections. In contrast, electric drive systems achieve over 90% efficiency, a 28% improvement. with response times under 10 ms, an 80% reduction. They require far fewer components than hydraulic systems, ensuring significantly lower failure rates.
- Incompatibility between working height control models and strategies. Simple kinematic models are only applicable under low-speed conditions, while designing dynamic models results in increased computational complexity. Developing an accurate and easily controllable control model is the future direction of research. Current research primarily focuses on low-speed operation, and existing control strategies poor robustness at high speeds. In practical applications, a single control strategy may have certain drawbacks. In the future, algorithms such as PID control and model predictive control can be integrated. By tuning the weighting coefficients of the MPC control algorithm through PID tuning, the system can both account for past errors and predict future height. Leveraging their complementary advantages will enhance system stability.
- The height measurement method is limited to a single approach. Non-contact height measurement is susceptible to environmental factors such as lighting and dust; contact-based height measurement is affected by protrusions like hard soil clumps, leading to increased errors. In the future, integrating both measurement methods through techniques like complementary filtering and adjusting the confidence level for each scenario could effectively mitigate their respective drawbacks and reduce measurement errors.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lian, X.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Y. Research status analysis of key technology and loss of soybean harvester header. J. Chin. Agric. Mech. 2024, 45, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Hamam, H. Rethinking Intelligence: From Human Cognition to Artificial Futures. Vokasi Unesa Bull. Eng. Technol. Appl. Sci. (VUBETA) 2025, 2, 531–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Shi, B.; Wang, C.; Liao, Q.; Wu, A.; Ou, Y. Development status and trend of mechanization of rapeseed and wheat sowing in hilly and mountainous region of southern China. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2025, 41, 12–26. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Y.; Li, R.; Liu, W.; Rong, K.; Hong, H.; Zhang, G. Development and Testing of the Adaptive Control System for Profiling Grain Header. Agriculture 2025, 15, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Yang, H.; Yu, Z.; Shen, H.; Gu, M.; Luo, W.; Wu, F.; Gu, F.; Ren, G.; Hu, Z. Development and Test of a Self-Propelled Peanut Combine Harvester for Hilly and Mountainous Regions. Agriculture 2025, 15, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Li, H.; Sun, W.; Li, H. Investigation of the Traveling Performance of the Tracked Chassis of a Potato Combine Harvester in Hilly and Mountainous Areas. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wu, F.; Gu, F.; Cao, M.; Yang, H.; Shi, L.; Wang, B.; Wang, B. Recent Research Progress on Key Technologies and Equipment for Mechanized Potato Harvesting. Agriculture 2025, 15, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Sun, W.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Simionescu, P.A. Study on the Process of Soil Clod Removal and Potato Damage in the Front Harvesting Device of Potato Combine Harvester. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamadneh, T.; Batiha, B.; Alsayyed, O.; Aribowo, W.; Montazeri, Z.; Dehghani, M.; Werner, F.; Ali, H.; Jawad, R.K.; Ibraheem, I.K.; et al. Barber Optimization Algorithm: A New Human-Based Approach for Solving Optimization Problems. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2025, 83, 2678–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abilzhanuly, T.; Abilzhanov, D.; Khamitov, N.; Seipataliyev, O.; Karaivanov, D.; Kosherbay, D. The Development of a Forage Harvester Ensuring Two-Level Mowing of Tall Stalk Forage. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Jin, C.; Chen, M.; Yang, T.; Xu, J. Online detection method of detecting crushing rate of soybean harvesters based on DeepLabV3+ network. J. Chin. Agric. Mech. 2023, 44, 170–175. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.; Wang, X.; Huang, X.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J. Adaptive control system of header for cabbage combine harvester based on IPSO-fuzzy PID controller. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2025, 232, 110044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y. On farm harvest and storage losses of oil crops and the impact on resources and environment in china. Chin. J. Oil Crop Sci. 2022, 44, 249–256. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Hu, Z.; Yao, L.; Peng, B.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y. Simulation and parameter optimisation of pickup device for full-feed peanut combine harvester. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 192, 106602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Jin, C.; Wang, T.; Zhou, L.; Liu, Z. Design and experiments of the 4LZ-1.5 soybean combine harvester. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2022, 38, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, C.; Qi, Y.; Liu, G.; Yang, T.; Ni, Y. Mechanism analysis and parameter optimization of soybean combine harvester reel. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2023, 54, 104–113. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, X.; Cao, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Hou, X. YOLOv8-DBW: An Improved YOLOv8-Based Algorithm for Maize Leaf Diseases and Pests Detection. Sensors 2025, 25, 4529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Su, G.; Meng, P.; Han, M.; Jin, C.; Li, Z. Design and experiments of the potato combine harvester with elastic rubbing technology. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2023, 39, 60–69. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.; Miao, Z.; Huang, W.; Han, W.; Guo, Z.; Li, T. SGW-YOLOv8n: An Improved YOLOv8n-Based Model for Apple Detection and Segmentation in Complex Orchard Environments. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Liu, C.; Wang, B.; Shi, H.; Sun, H.; Li, Y.; Hu, J. Research on the Operational Parameters and Performance of Key Components of an Industrial Hemp Harvester and Drier. Agriculture 2025, 15, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, D.; Lu, Z.; Xie, B.; Wang, Z. Design and Test of a No power Input Sweet Potato Harvester. J. Agric. Mech. Res. 2025, 47, 107–111. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S. Research on Key Technologies and Equipment for Peanut Pickup Combine Harvesting. Doctoral Thesis, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Wu, N.; Cheng, G.; Wu, F.; Gu, F.; Shi, L.; Wang, B. Design and Optimization of a Lightweight and Simple Self-Propelled Crawler Potato Combine Harvester. Agronomy 2025, 15, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Wang, W.; Morigenbilige; Liu, W.; Li, L.; Cui, H. Experimental on Performance of Spring-finger Cylinder Pickup Collector. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2017, 48, 106–112. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, P.; Cao, M.; Gu, F.; Wu, F.; Hu, Z. Design and Experiment of Pneumatic Conveying Device for Seedlings of Peanut Harvester. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2022, 53, 126–137. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q. Development and Experimental Research of Teeth Belt Buckwheat Pickup Test Platform. Master’s Thesis, Northwest A&F University, Xianyang, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, T.; Liang, S.; Jin, M.; Tang, Q.; Wu, C. Comparative Experimental Study on Operation Performance of Tooth-belt Pickup Header and Spring-finger Cylinder Pickup Header. J. Agric. Mech. Res. 2018, 40, 171–175. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, D.; Yan, L.; Chen, X.; Mo, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wu, T. Improved Design and Test of Longitudinal Nail-tooth-chain Plastic Film Pickup Device. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2025, 56, 267–281. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Yang, D.; Liu, M.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Cheng, Z. Parameter Optimization and Experiment of Picking Device of Selfpropelled Potato Collecting Machine. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2023, 54, 20–29. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, S.; Li, K.; Hu, Y.; Pan, B.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, X.; Cui, Q.; Tang, Z. Design and Experimentation of the Millet Combine Harvester Header. Machines 2024, 12, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhang, S.; Hu, G.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, J.; Chen, Y.; Chen, J.; Gao, S.; Chen, Y.; Shi, T. Parameter Optimization of the Harvest Method in the Standardized Hedge Cultivation Mode of Lycium barbarum Using Response Surface Methodology. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chegini, G.R. Determine of Optimum Operating Conditions of Combine Harvester with Stripper-Header. World Appl. Sci. J. 2013, 23, 1399–1407. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, C.; Xing, Y.; Yan, C.; Tan, H.; Ma, S.; Xu, L. Simulation and experiment of shovel-screen type farmland stone picking and collecting machine. J. China Agric. Univ. 2022, 27, 221–233. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Ni, Y.; Yang, T.; Qi, Y.; Jin, C. Design and experiment of header height automatic control System for soybean harvester. J. Chin. Agric. Mech. 2023, 44, 155–160. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, W.; Wang, X.; Han, D.; Ohiemi, I.E. Analysis of the Resistance to Teeth During the Picking Process Based on DEM-MBD Coupling Simulation. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Xie, J.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wu, S. Design and Operating Parameters Optimization of the Hook-and Tooth Chain Rail Type Residual Film Picking Device. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hu, Z.; Gu, F.; Wang, B.; Fan, J.; Yang, H.; Wu, F. DEM-MBD Coupling Simulation and Analysis of the Working Process of Soil and Tuber Separation of a Potato Combine Harvester. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Jin, C.; Liang, S.; Ni, Y. The Research of Soybean Harvested by Machine. J. Agric. Mech. Res. 2017, 39, 1–9, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, M.; Shen, H.; Ling, J.; Yu, Z.; Luo, W.; Wu, F.; Gu, F.; Hu, Z. Online detection of broken and impurity rates in half-feed peanut combine harvesters based on improved YOLOv8-Seg. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2025, 237, 110494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Jin, C.; Feng, Y.; Yuan, W. Current status of soya bean harvest mechanization. J. Chin. Agric. Mech. 2021, 42, 228–236. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, Y.; Jin, C.; Chen, M.; Wang, T.; Li, Z.; Yuan, W. Research progress on mechanized production technology and equipment of soybean in China. J. Chin. Agric. Mech. 2019, 40, 17–25. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Jin, C.; Yuan, W.; Feng, Y.; Yuan, J. Design Optimization and Experiment of Spring-tooth Drum Type Picking Device for Vegetable Soybean Harvester. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2022, 53, 171–180. [Google Scholar]
- Shearer, B.R. Header with Flexible Crop Cutting Knife Mounted on Flex Blades. U.S. Patent 10,791,671, 6 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, S. A Flexible Header. Chinese Patent CN211580707U, 29 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Xing, L. Soybean Flexible Cutter Device. Chinese Patent CN101347072A, 21 January 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, J.; Luo, H.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Q.; Qiu, Q.; Zhang, L. Design and Test of a Low-Loss Soybean Header Based on Synchronous Profiling. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Liu, G.; Ni, Y.; Yang, T.; Wang, T.; Qi, Y. Design and experiment of header profiling mechanism for combine harvester based on MBD-DEM coupling. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2022, 38, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Salem, A.; Liu, Y.; Sun, B.; Shi, G.; He, X.; Wang, D.; Chang, Z. Design and Experiment of a Dual-Disc Potato Pickup and Harvesting Device. AgriEngineering 2025, 7, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gou, F.; Qian, Z.; Ni, Y.; Jin, C. A Review of Intelligent Header Technology for Grain Combine Harvester. INMATEH Agric. Eng. 2024, 73, 731–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, G.T.; Magalh Es, P.S.G.; Nóbrega, E.G.O. AE–Automation and Engineering Technologies: Optimal Header Height Control System for Combine Harvesters. Biosyst. Eng. 2002, 81, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Wang, F.; Li, Z.; Jin, C. Design and Experiment of Crawler Self-propelled Sorting Type Potato Harvester. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2023, 54, 95–106. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, W.; Sun, W.; Liu, X.; Shi, R.; Zhang, H.; Chen, P.; Gao, K. The Design and Experimentation of a Wheeled-Chassis Potato Combine Harvester with Integrated Bagging and Ton Bag-Lifting Systems. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Ni, Y.; Jin, C.; Xu, J.; Zhang, G. Online Monitoring Method of Mechanized Soybean Harvest Quality Based on Machine Visio. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2021, 52, 91–98. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, Y.; Jin, C.; Chen, M.; Yuan, W.; Qian, Z.; Yang, T.; Cai, Z. Computational model and adjustment system of header height of soybean harvesters based on soil-machine system. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 183, 105907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Dogra, R.; Dogra, B.; Singh, D.; Arora, R. Ultrasonic bund detection system for header of combine harvester. Curr. Sci. 2024, 127, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y. Full-Time Master Degree Dissertation. Master’s Thesis, Shanxi Agricultural University, Jinzhong, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.; Zhang, C. Design and Simulation Analysis of Header Height Control System of Corn Harvester Based on Fuzzy PID Algorithm. J. Anhui Sci. Technol. Univ. 2021, 35, 160. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Z.; Li, H.; Su, G.; Sun, C.; Liu, W.; Li, X. Design and Experiment of Potato Combined Harvester Based on Multi-stage Separation Technology. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2019, 50, 140–152. [Google Scholar]
- Karim, M.R.; Reza, M.N.; Ahmed, S.; Lee, K.; Sung, J.; Chung, S. Proximal LiDAR Sensing for Monitoring of Vegetative Growth in Rice at Different Growing Stages. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, Q.; Ye, S.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, D. Header Height Detection and Terrain-Adaptive Control Strategy Using Area Array LiDAR. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Wang, J.; Song, Z.; Zhang, R. Design and Parameter Optimization of a Reciprocating In-Soil Cutting Device in a Green Leafy Vegetable Orderly Harvester. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 7326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Qian, Z.; Jin, C.; Yang, T. Research Progress on Control Algorithms for Grain Combine Harvesters. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, S.; Lv, D.; Ekhlo, G. Multi-Sensor Signal Acquisition and Data Processing Analysis Ofcombine Harvester. INMATEH Agric. Eng. 2021, 61, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wu, F.; Gu, F.; Gu, M.; Ni, J.; Luo, W.; Pei, J.; Cao, M.; Wang, B. Design and Parameter Optimization of Drum Pick-Up Machine Based on Archimedean Curve. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Z.H.; Xiang, Y.; Li, Y.J.; Hu, Z.F.; Liu, A.W.; Dai, X.F. Adaptive adjustment system of header height based on inclination sensor. J. China Agric. Univ. 2021, 26, 200–208. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, M.; Li, Y.; Pan, Y.; Lu, L.; Wei, J. Design of an Adaptive Height Control System for Sugarcane Harvester Header. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y. Research on Intelligent Control System of Leaf Vegetable Harvester Based on Multi Sensor Fusion. Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang Agriculture and Forestry University, Hangzhou, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Yao, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Yao, L. Contour Control System of Leaf Vegetable Harvester Based on Machine Learning. J. Agric. Mech. Res. 2025, 47, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, X.; Gu, X.; Hu, L.; Zhao, R.; Yue, M.; He, J.; Huang, P.; Wang, P. Research Status and Outlook of Farmland Boundary Recognition Technology in Large-scale Unmanned Smart Farms. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2025, 56, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Zhao, Y.; Du, Z. Advances in Multi-modal Fusion Techniques and Applications in Agricultural Field. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2025, 56, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, G.; Ke, Y.; Su, J.; Zhao, Z. Crop Height Measurement System Based on Laser Vision. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2018, 49, 22–27. [Google Scholar]
- Haydar, Z.; Esau, T.J.; Farooque, A.A.; Zaman, Q.U.; Hennessy, P.J.; Singh, K.; Abbas, F. Deep learning supported machine vision system to precisely automate the wild blueberry harvester header. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 10198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Chai, X.; Xu, L.; Quan, L.; Yuan, C.; Weng, S.; Cao, G.; Jiang, W. Research on predictive control of a novel electric cleaning system for combine harvester based on data-driven. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2025, 232, 110075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Gu, Y.; Li, P.; Feng, W.; Zhang, X.; Cao, Z.; Zhou, X.; Li, Y.; Li, G. Design and Experiment of Soybean Cutting Table Height Control System Under Multi-level Regulation. J. Agric. Mech. Res. 2025, 47, 77–83. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Lao, L.; Zhang, H.; Tang, Z.; Qian, P.; He, Q. Structural Fault Detection and Diagnosis for Combine Harvesters: A Critical Review. Sensors 2025, 25, 3851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Wei, X.; Liu, C.; Ge, J.; Cui, X.; Wang, F.; Wang, A.; Chen, W. Adaptive path tracking and control system for unmanned crawler harvesters in paddy fields. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2025, 230, 109878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Shang, S.; Zhang, N.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Xu, N. Design and Experimentation of a Low-Damage Combined Full-Feeding Peanut Picking Device. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, R.; Chen, D.; Wang, J.; Li, X. Design of Header Profiling Height Control System Based on PID Regulation. J. Agric. Mech. Res. 2024, 46, 97–102. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Meng, Z.; Qin, W.; Wang, F.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, Q.; Wen, C.; Yin, Y. A fuzzy decision-making algorithm-based header height measurement system for combine harvester. Measurement 2025, 249, 116918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Che, Y.; Wang, F.; Li, W. Design and Experiment of the Ground Profiling Control System of Combine Header. J. Agric. Mech. Res. 2017, 39, 150–154. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Xu, L.; Xu, X.; Lei, X.; Chai, X. Design and Simulation of Mechanical-hydraulic Combined Soybean Header Profiling Device. J. Agric. Mech. Res. 2024, 5, 60–65. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M. Research on Intelligent Control System of Corn Harvester Header. Master’s Thesis, Shandong Agricultural University, Taian, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Li, B.; Chen, S.; Tang, Z.; Zhou, W.; Guo, X. Design and Performance Test of Soybean Profiling Header Suitable for Harvesting Bottom Pods on Film. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Wang, G.; Zhou, S.; Jia, H.; Qu, M.; Xiang, M.; Gao, X.; Zhou, Z.; Li, H.; Zou, Z. Design and Experiment of Header Height Adaptive Adjustment System for Maize (Zea mays L.) Harvester. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Liao, Z.; Shi, S.; Dai, J.; Yuan, K.; Zhao, J.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Z. Design and Testing of a 2-DOF Adaptive Profiling Header for Forage Harvesters. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, R. Adaptive Control System for Cutting Table Height of Regenerated Rice Harvester Design and Performance Test. Master’s Thesis, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y. Design and Test of Adaptive Adjustment System for Combine Harvesting header Height. Master’s Thesis, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, R.; Liu, L.; Mu, X.; Wang, W. Control Method of Self Balance Test Device for Forage Harvester Header. J. Agric. Mech. Res. 2022, 44, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Pinglu, C.; Zhipeng, X.; Jing, X.; Muhua, L. Simulation and parameter optimization of high moisture rice drying on combine harvester before threshing. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 215, 108451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.; Shen, H.; Ling, J.; Yu, Z.; Luo, W.; Wu, F.; Gu, F.; Hu, Z. Current Status and Development Strategies of the Research on Half-Feed Peanut Combine Harvester. Sustainability 2025, 17, 1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Lang, X. Design of Conveying Control System for Sugarcane Harvester Based on Machine Vision. Agriengineering 2025, 7, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhou, D.; He, F.; Deng, G.; Cui, Z.; Wang, X.; Chen, Z. Control system of sugarcane harvester cutter based on fuzzy PID optimized by genetic algorithm. J. Huazhong Agric. Univ. 2023, 42, 243–250. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, A.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, A.; Zheng, J. Design and Experiment of Automatic Control System for Corn Header Height. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach 2020, 51, 118–125. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Fu, L.; Zhou, T.; Zhou, Z.; Ren, Z. Design and Testing of the Longitudinal Height and Lateral Tilt Synergistic Profiling System for the Header of a Combine Harvester. China Mech. Eng. 2025, 41, 1119–1123. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, R.; Wang, Z.; Shang, S.; Zhang, J.; Qing, Y.; Zha, X. The Design and Experimentation of EVPIVS-PID Harvesters, Header Height Control System Based on Sensor Ground Profiling Monitoring. Agriculture 2022, 12, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y. Cutting table control system of combine harvester based on IDBO-PID. Agric. Eng. 2024, 14, 21–28. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, X.; Li, Y. Header Height Control Strategy of Harvester Based on Robust Feedback Linearization. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach 2020, 51, 123–130. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, N.; Hu, Y.; Miao, Y. Research on Fuzzy Control of Harvester Header Height. Mechatronics 2018, 24, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Luo, X.; Zeng, S.; Zeng, L. Performance test and analysis of the self-adaptive profiling header for ratooning rice based on fuzzy PID control. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2022, 38, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, J. Research on Automatic Adjustment System of Intelligent Wheat Harvester’s Cutting Platform. Master’s Thesis, Anhui Polytechnic University, Wuhu, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C. Development of Intelligent Control System for Rape Combine Harvester. Master’s Thesis, Southeast University, Nanjing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, B.; Wang, J.; Jiang, H.; Zhao, S.; Liu, J.; Jin, Y.; Li, Y. Multi-feature detection of in-field grain lodging for adaptive low-loss control of combine harvesters. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 208, 107772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Reibman, A.R.; Ault, A.C.; Krogmeier, J.V. Video-Based Prediction for Header-Height Control of a Combine Harvester. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Conference on Multimedia Information Processing and Retrieval (MIPR), San Jose, CA, USA, 1 March 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Meng, Z.; Wen, C.; Qin, W.; Wang, F.; Zhang, A.; Zhao, C.; Yin, Y. Grain combine harvester header profiling control system development and testing. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 223, 109082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Crop | Height Measurement Sensor | Performance | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Buckwheat | Ultrasonic sensor | The average error in the height of the harvesting header above the ground is 15 mm | [56] |
| Corn | The average error in the height of the harvesting header above the ground is 7 mm | [57] | |
| Rice | Tilt sensor | The average error in the height of the harvesting header above the ground is 7.8 mm | [65] |
| Sugarcane | LIDAR sensor Displacement sensor | The average error in the height of the harvesting header above the ground is 20 mm | [66] |
| Leafy vegetables | LIDAR sensor | The average error in the height of the harvesting header above the ground is 24.7 mm | [67,68] |
| Blueberries | Camera module | The average error in the height of the harvesting header above the ground is 2.3 mm | [72] |
| Crop | Type of Profiling Device | Performance | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rice | Profiling rod | The average error in the height of the harvesting header above the ground is 3.6 mm | [79] |
| Rice | The average error in the height of the harvesting header above the ground is 6.15 mm | [80] | |
| Soybeans | Profiling plate | The average error in the height of the harvesting header above the ground is 5.6 mm | [81] |
| Corn | The average error in the height of the harvesting header above the ground is 8.1 mm | [82] | |
| Soybeans | profiling wheel | The average error in the height of the harvesting header above the ground is 1.2 mm | [83] |
| Corn | The average error in the height of the harvesting header above the ground is 10.86 mm | [84] | |
| Grass | The average error in the height of the harvesting header above the ground is 3.25 mm | [85] | |
| Rice | The average error in the height of the harvesting header above the ground is 6.81 mm | [86] | |
| Rice | The average error in the height of the harvesting header above the ground is 6.09 mm | [87] | |
| Grass | The average error in the height of the harvesting header above the ground is 1.12 mm | [88] |
| Arithmetic | Response Time/s | Average Error /mm | Applicable Scenarios | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PID | / | 8.25 | Simple linear control system | [93] |
| Grey prediction speed change PID | 2 | 8.68 | Slow time-varying, small lag system | [94] |
| EVPIVS-PID | / | 2.95 | Systems subject to significant external interference and integration saturation | [95] |
| Robust feedback linearization | / | 4.65 | Nonlinear systems with model uncertainty and external disturbances | [96] |
| Fuzzy PID | 1.68 | 6.75 | Nonlinear systems with certain requirements for response speed | [98] |
| IDBO-PID | 1.11 | 5.4 | Complex multivariable, strongly coupled systems | [101] |
| Outlier removal | / | 2.5 | A system with high data quality requirements, large data scale, and complex abnormal situations and dynamic simulation of fabric effects in virtual scenes | [102] |
| Cloth simulation filter | ||||
| Model predictive control | 0.625 | 4.25 | A system with multiple variables, nonlinearity, and high requirements for control accuracy and real-time performance | [104] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, C.; Wu, F.; Gu, F.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, P.; Pei, J.; Yang, H. The Status of Intelligent Control Technology for the Working Height of a Crop Harvesting Header. Sensors 2025, 25, 6367. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25206367
Zhao C, Wu F, Gu F, Zhou X, Zhang Y, Chen P, Pei J, Yang H. The Status of Intelligent Control Technology for the Working Height of a Crop Harvesting Header. Sensors. 2025; 25(20):6367. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25206367
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Chenxu, Feng Wu, Fengwei Gu, Xinsheng Zhou, Yanqin Zhang, Peng Chen, Jiayong Pei, and Hongguang Yang. 2025. "The Status of Intelligent Control Technology for the Working Height of a Crop Harvesting Header" Sensors 25, no. 20: 6367. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25206367
APA StyleZhao, C., Wu, F., Gu, F., Zhou, X., Zhang, Y., Chen, P., Pei, J., & Yang, H. (2025). The Status of Intelligent Control Technology for the Working Height of a Crop Harvesting Header. Sensors, 25(20), 6367. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25206367








