Knowledge Distillation with Geometry-Consistent Feature Alignment for Robust Low-Light Apple Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset Construction and Noise Modelling
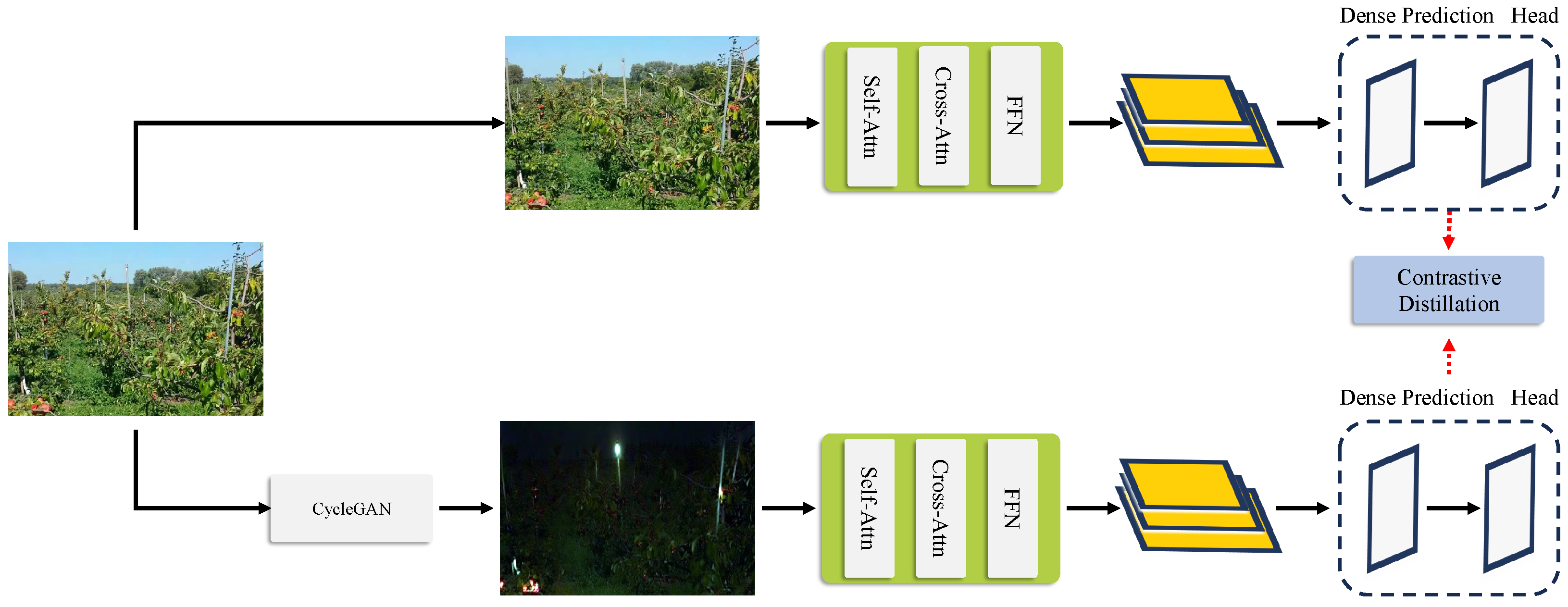
2.2. Knowledge Distillation and Feature Alignment (KDFA) Model
2.2.1. Model Architecture Overview
2.2.2. Backbone Network Architecture
2.2.3. Contrastive Knowledge Distillation (CKD)
2.2.4. Total Loss Function
2.3. Training Procedure
3. Results
3.1. Dataset and Evaluation Metrics
3.2. Experimental Setup
3.3. Quantitative Results
3.3.1. Benchmark Accuracy Comparison
3.3.2. Computational Efficiency Analysis
| Method | Params (M) | Memory @FP16 (MB) | GFLOPs () | FPS NVIDIA Jetson Orin | FPS RTXA6000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RetinexNet+Faster R-CNN | 83 | 421 | 157 | 12 | 98 |
| Grounding DINO | 79 | 390 | 145 | 15 | 122 |
| YOLOv8 | 68 | 256 | 92 | 22 | 180 |
| Dark-YOLO | 69 | 260 | 95 | 21 | 175 |
| Deformable DETR | 64 | 285 | 110 | 18 | 140 |
| KDFA-OED(ours) | 11 | 48 | 6.3 | 30 | 210 |
3.4. Image Enhancement Quality
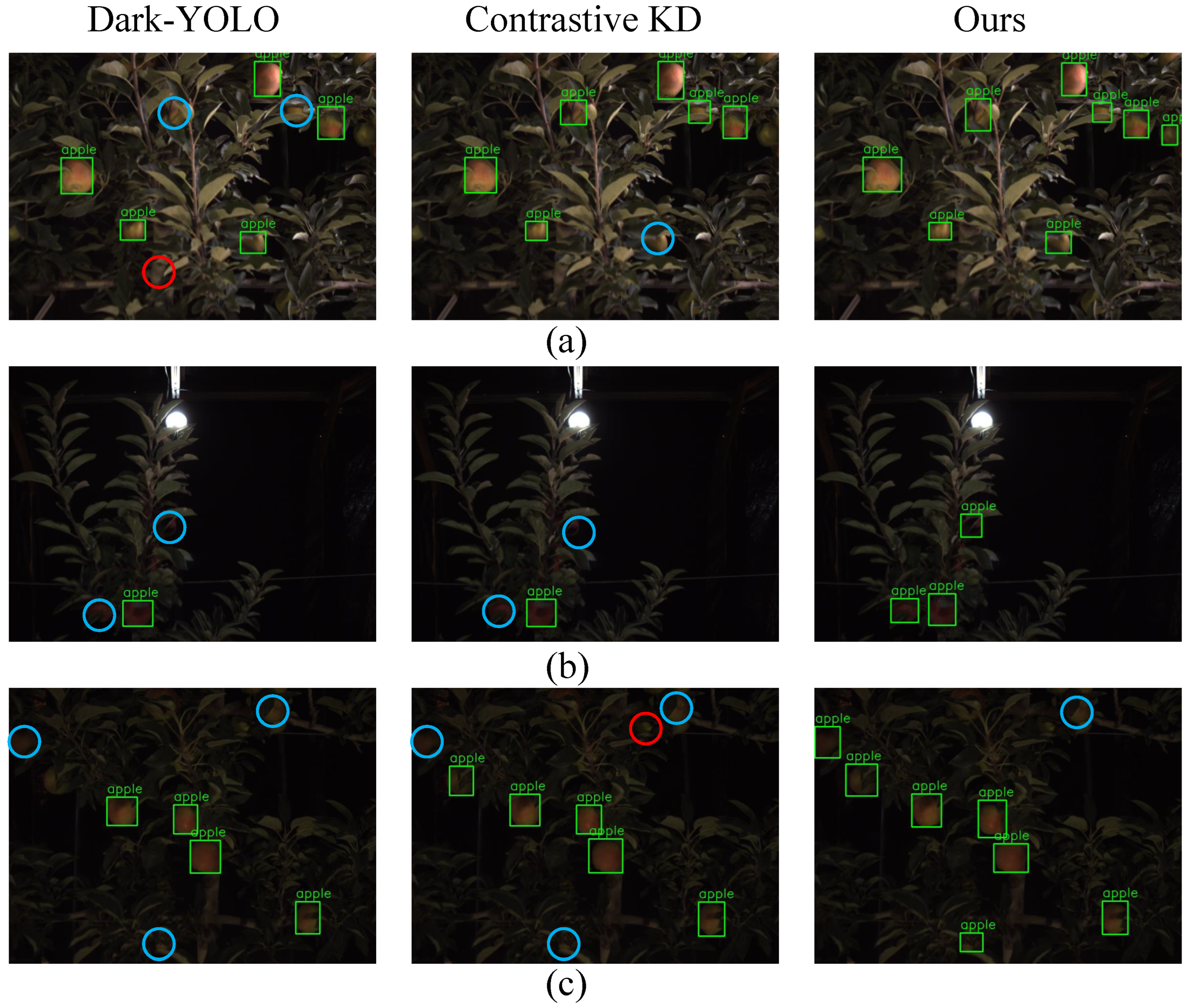
3.5. Qualitative Results
3.5.1. Detection Robustness Across Night-Time Illumination Regimes
3.5.2. Generalisation to Synthetic Low-Illumination Augmentation
3.6. Ablation Studies
3.6.1. Component Contribution Analysis
| Components Added | AP@[0.5:0.95] | AP |
|---|---|---|
| Baseline Detector | 36.8 | - |
| +Image Enhancement Decoder | 40.1 | +3.3 |
| +Feature Imitation Loss () | 44.2 | +7.4 |
| +Contrastive KD () | 49.3 | +12.5 |
| +Occlusion Handling Mechanism | 53.0 | +16.2 |
| Ours (All Components) | 56.1 | +19.3 |
3.6.2. Influence of Dynamic Loss-Weight Balancing
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2014: 13th European Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Proceedings, Part V 13. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar]
- Darcet, T.; Oquab, M.; Mairal, J.; Bojanowski, P. Vision transformers need registers. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.16588. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R. Fast r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 13–16 December 2015; pp. 1440–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.Y.; Berg, A.C. Ssd: Single shot multibox detector. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Proceedings, Part I 14. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Carion, N.; Massa, F.; Synnaeve, G.; Usunier, N.; Kirillov, A.; Zagoruyko, S. End-to-end object detection with transformers. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 213–229. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Zeng, Z.; Ren, T.; Li, F.; Zhang, H.; Yang, J.; Li, C.; Yang, J.; Su, H.; Zhu, J.; et al. Grounding dino: Marrying dino with grounded pre-training for open-set object detection. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 38–55. [Google Scholar]
- Denninger, M.; Sundermeyer, M.; Winkelbauer, D.; Zidan, Y.; Olefir, D.; Elbadrawy, M.; Lodhi, A.; Katam, H. Blenderproc. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.01911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, J.; Goel, S.; Deng, K.; Luthra, A.; Xu, L.; Gundogdu, E.; Zhang, X.; Vicente, T.F.Y.; Dideriksen, T.; Arora, H.; et al. Abo: Dataset and benchmarks for real-world 3d object understanding. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 21126–21136. [Google Scholar]
- Oord, A.v.d.; Li, Y.; Vinyals, O. Representation learning with contrastive predictive coding. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.03748. [Google Scholar]
- Bulat, A.; Guerrero, R.; Martinez, B.; Tzimiropoulos, G. Fs-detr: Few-shot detection transformer with prompting and without re-training. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 11793–11802. [Google Scholar]
- Doumanoglou, A.; Kouskouridas, R.; Malassiotis, S.; Kim, T.K. Recovering 6D object pose and predicting next-best-view in the crowd. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 3583–3592. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, B.; Yang, G.; Zuo, W.; Zhang, L. Consept: Continual semantic segmentation via adapter-based vision transformer. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.16674. [Google Scholar]
- McVitie, D.G.; Wilson, L.B. The stable marriage problem. Commun. ACM 1971, 14, 486–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, A.; Han, Y.; Zhu, L.; Yang, Y. Universal-prototype enhancing for few-shot object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 9567–9576. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, P.; Geng, S.; Zhang, R.; Ma, T.; Fang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Qiao, Y. Clip-adapter: Better vision-language models with feature adapters. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2024, 132, 581–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caron, M.; Touvron, H.; Misra, I.; Jégou, H.; Mairal, J.; Bojanowski, P.; Joulin, A. Emerging properties in self-supervised vision transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 9650–9660. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Jiang, A.; Ye, J.; Wang, M.W. Making of night vision: Object detection under low-illumination. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 123075–123086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, B.; Zhang, H.; Ma, B.; Tao, Z. Enhancing real-time low-light object detection via multi-scale edge and illumination-guided features in YOLOv8: B. J. Supercomput. 2025, 81, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xiang, J.; Duan, J. A low illumination target detection method based on a dynamic gradient gain allocation strategy. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 29058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hnewa, M.; Rahimpour, A.; Miller, J.; Upadhyay, D.; Radha, H. Cross modality knowledge distillation for robust pedestrian detection in low light and adverse weather conditions. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2023-2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Rhodes Island, Greece, 4–10 June 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Guo, H.; Chakraborty, C.; Khosravi, M.R.; Berretti, S.; Wan, S. Edge computing driven low-light image dynamic enhancement for object detection. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 3086–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Wang, W.; Yang, W.; Liu, J. Deep retinex decomposition for low-light enhancement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1808.04560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Guo, C.; Loy, C.C. Learning to enhance low-light image via zero-reference deep curve estimation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 44, 4225–4238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wan, R.; Yang, W.; Li, H.; Chau, L.P.; Kot, A. Low-light image enhancement with normalizing flow. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Virtual, 22 February–1 March 2022; Volume 36, pp. 2604–2612. [Google Scholar]


| Method | AP@[0.5:0.95] | AP@0.5 | AP@0.75 | APS | APM | ARS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RetinexNet + Faster R-CNN | 0.338 | 0.600 | 0.350 | 0.120 | 0.330 | 0.18 |
| Grounding DINO (Transformer) | 0.450 | 0.700 | 0.500 | 0.250 | 0.500 | 0.37 |
| YOLOv8 (One-stage CNN) | 0.427 | 0.683 | 0.460 | 0.200 | 0.450 | 0.30 |
| Dark-YOLO (Low-light CNN) | 0.442 | 0.713 | 0.520 | 0.220 | 0.470 | 0.32 |
| Deformable DETR (Transformer) | 0.416 | 0.650 | 0.440 | 0.180 | 0.420 | 0.27 |
| Contrastive KD | 0.450 | 0.700 | 0.480 | 0.250 | 0.470 | 0.38 |
| Feature Alignment KD | 0.460 | 0.720 | 0.500 | 0.260 | 0.480 | 0.40 |
| KDFA-OED (ours) | 0.480 | 0.760 | 0.550 | 0.300 | 0.500 | 0.45 |
| Method | PSNR (dB) | SSIM |
|---|---|---|
| RetinexNet [26] | 17.7 | 0.658 |
| Zero-DCE++ [27] | 18.9 | 0.646 |
| LLFlow [28] | 21.4 | 0.830 |
| Ours | 25.6 | 0.87 |
| Weighting Strategy | AP@[0.5:0.95] | PSNR (dB) | SSIM | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No balancing (detection only) | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.427 | 22.0 | 0.810 |
| Uniform static weights | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.445 | 23.1 | 0.842 |
| Heuristic static (0.7/0.1/0.2) | 0.70 | 0.10 | 0.20 | 0.462 | 23.8 | 0.848 |
| GradNor m dynamic dynamic (ours) | learned | learned | learned | 0.480 | 25.6 | 0.870 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, Y.; Ma, Y.; Geng, L.; Chu, L.; Li, B.; Li, W. Knowledge Distillation with Geometry-Consistent Feature Alignment for Robust Low-Light Apple Detection. Sensors 2025, 25, 4871. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25154871
Shi Y, Ma Y, Geng L, Chu L, Li B, Li W. Knowledge Distillation with Geometry-Consistent Feature Alignment for Robust Low-Light Apple Detection. Sensors. 2025; 25(15):4871. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25154871
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Yuanping, Yanheng Ma, Liang Geng, Lina Chu, Bingxuan Li, and Wei Li. 2025. "Knowledge Distillation with Geometry-Consistent Feature Alignment for Robust Low-Light Apple Detection" Sensors 25, no. 15: 4871. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25154871
APA StyleShi, Y., Ma, Y., Geng, L., Chu, L., Li, B., & Li, W. (2025). Knowledge Distillation with Geometry-Consistent Feature Alignment for Robust Low-Light Apple Detection. Sensors, 25(15), 4871. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25154871







