Minimization of Resource Consumption with URLLC Constraints for Relay-Assisted IIoT
Abstract
1. Introduction
- 1.
- Unlike the recent studies that mainly focus on PEP minimization, this work aims to minimize resource consumption, which is the total blocklength of the two hops, by optimizing the PEPs of each hop and the blocklength allocation between the source and relay nodes. Latency, reliability, and coding rate constraints are taken into account. This is equivalent to maximizing resource utilization, which is meaningful in resource-limited IIoT scenarios.
- 2.
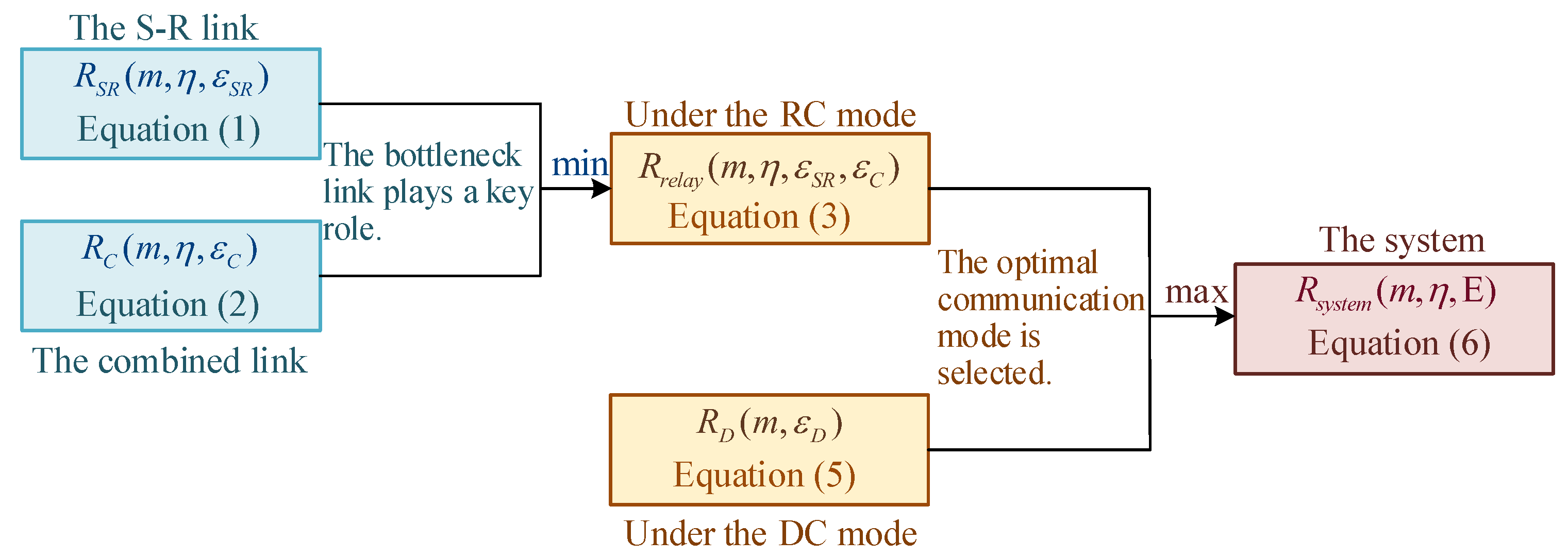
- The original problem of resource consumption minimization is reformulated as two equivalent subproblems. In the first subproblem, for a given total blocklength, we consider the joint optimization of PEP and blocklength allocation for achievable rate maximization (JPB-ARM). The expressions of the objective function and constraints of the first subproblem vary under different communication modes. Therefore, an optimal solution is found for each mode, and the mode with the higher achievable rate is selected. Under the RC mode, through theoretical analysis, a near-optimal solution for the PEPs of each hop is first obtained. Then, the first subproblem is reformulated as a quartic equation, and the closed-form solution for optimal blocklength allocation is derived using Ferrari’s method. Under the DC mode, the maximum achievable rate of the system is derived through a simple proof. In the second subproblem, the resource consumption minimization (RCM) is considered, which is solved by integrating the solution of the first subproblem with the bisection search method.
2. System Model and Problem Formulation
2.1. System Model
2.2. Achievable Rate Under the RC Mode in the FBL Regime
2.3. Achievable Rate Under the DC Mode in the FBL Regime
2.4. The System’s Achievable Rate in the FBL Regime
2.5. The Problem of Minimizing Resource Consumption
3. The Solution of Problem
3.1. An Equivalent Formulation of Problem
3.2. Analysis of Problem and
- 1.
- Under the DC mode, with , and according to Proposition 2. The value of , or denoted simply as , is determined, because and are known.
- 2.
- Under the RC mode, . Based on Proposition 2, Constraint is transformed into . In addition, Constraint is transformed into . In fact, the feasible range of can be relaxed to under the RC mode. This does not affect the final outcome of Problem , which is demonstrated in Appendix C. When is known, the optimization of , , and is required to obtain the maximum value of , which is formulated as:The optimal value of in Problem is denoted as .
3.3. Find the Optimal Solution to Problem
- 1.
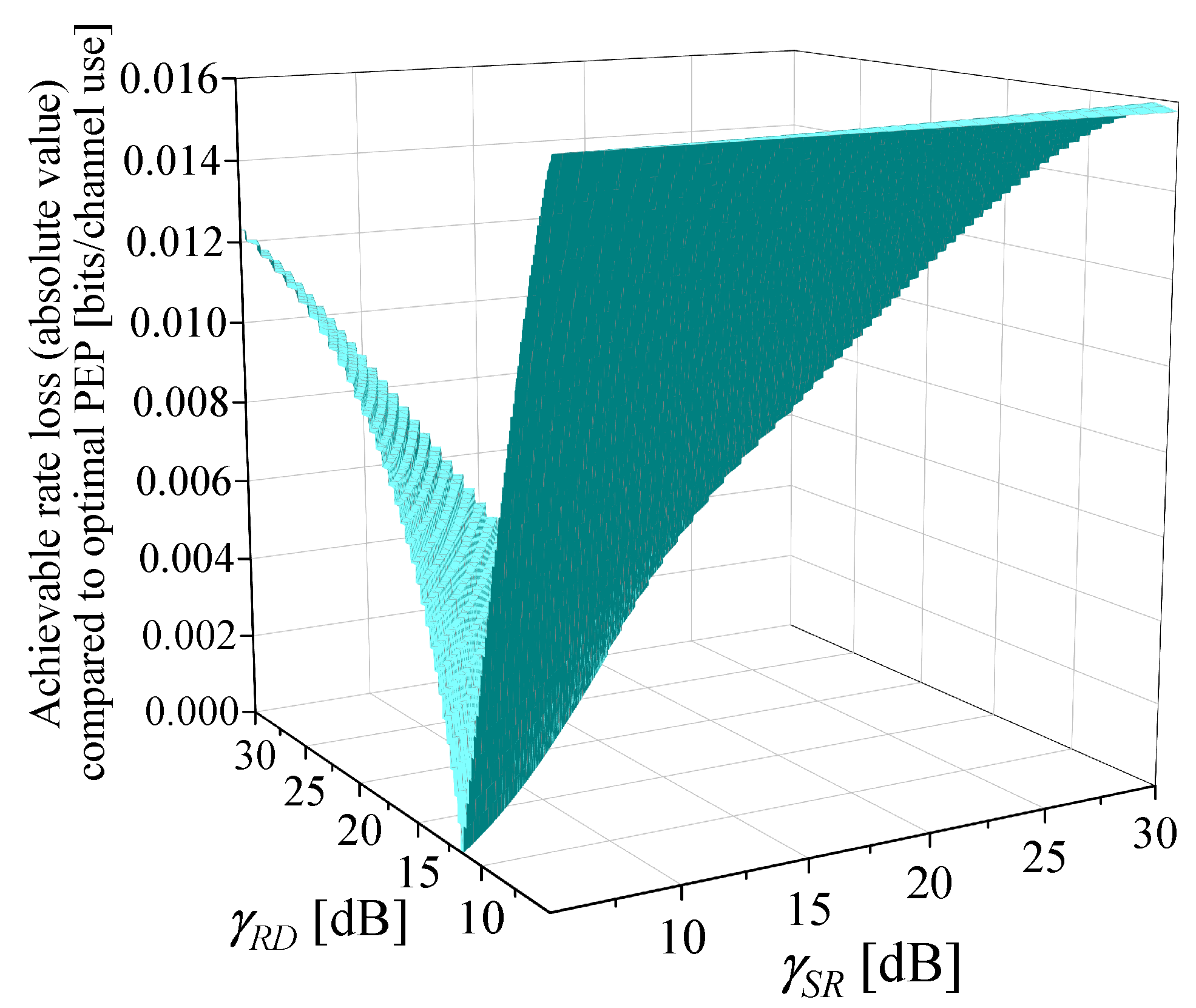
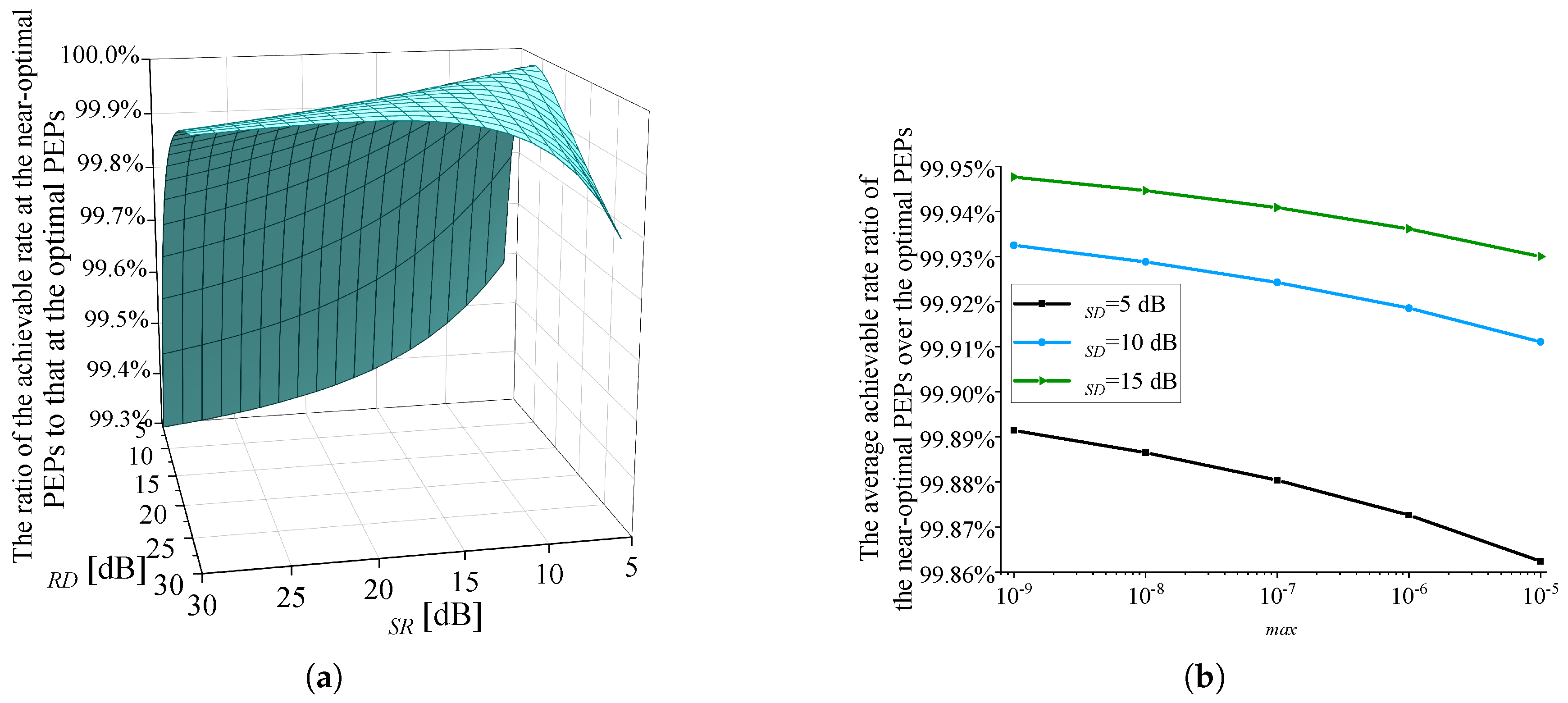
- The optimization of : In existing studies, such as [8,16], near-optimal setting of PEPs, , is adopted. The effect of this setting is demonstrated in Figure 3 through the observation of a case. The following parameters are used in Figure 3: dB, dB, dB, and . Given , by setting the variable to , Figure 3 illustrates the variation of , , and with respect to . Based on the definition of given in (3), holds for any . In Figure 3, is also indicated. As approaches , the maximum value of is obtained, which is also the optimal value of by comparing with . At (point A), the corresponding deviates from the optimal by just around 0.5%, indicating near-optimal performance. This can be further validated through a mathematical proof, which is shown in Appendix D.
- 2.
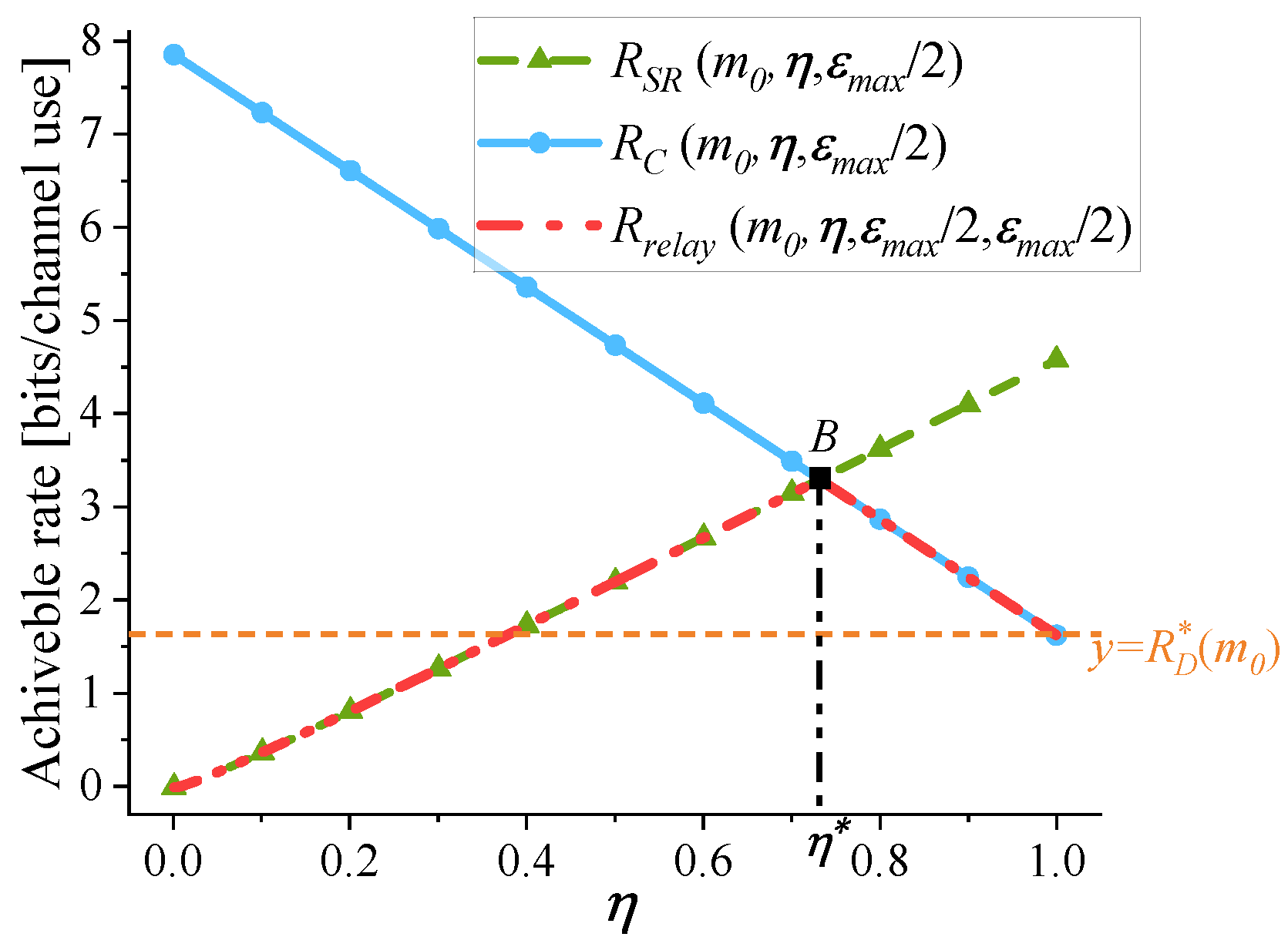
- The optimization of : Figure 4 illustrates the variation of , , and with respect to . Figure 4 adopts the same parameter settings as Figure 3. Given , near-optimal setting of PEPs is adopted: . As shown in Figure 4, when changes, varies significantly. reaches its maximum at . When , the S-R link is the bottleneck link and . When , . Besides, the optimal value of in Problem is also reached at , because the achievable rate under the RC mode is higher than that under the DC mode.
3.4. Find the Optimal Solution to Problem
| Algorithm 1 JPB-ARM using Ferrari’s Method (Algorithm for Problem ) |
Input: Channel conditions: , , , maximum latency: , total blocklength:
Output: Optimal solution to Problem : , , the optimal objective value of Problem : |
3.5. Find the Optimal Solution to Problem
- 1.
- Single variable: Problem involves only one variable, m.
- 2.
- Monotonicity of : Based on Proposition 1, it is easy to prove that the information bits that can be transmitted, , are monotonically increasing with respect to m.
- 3.
- Existence of a solution: Proposition 1 establishes the condition ensuring solution existence. Due to the monotonicity of , the existence of a solution implies its uniqueness.
- 4.
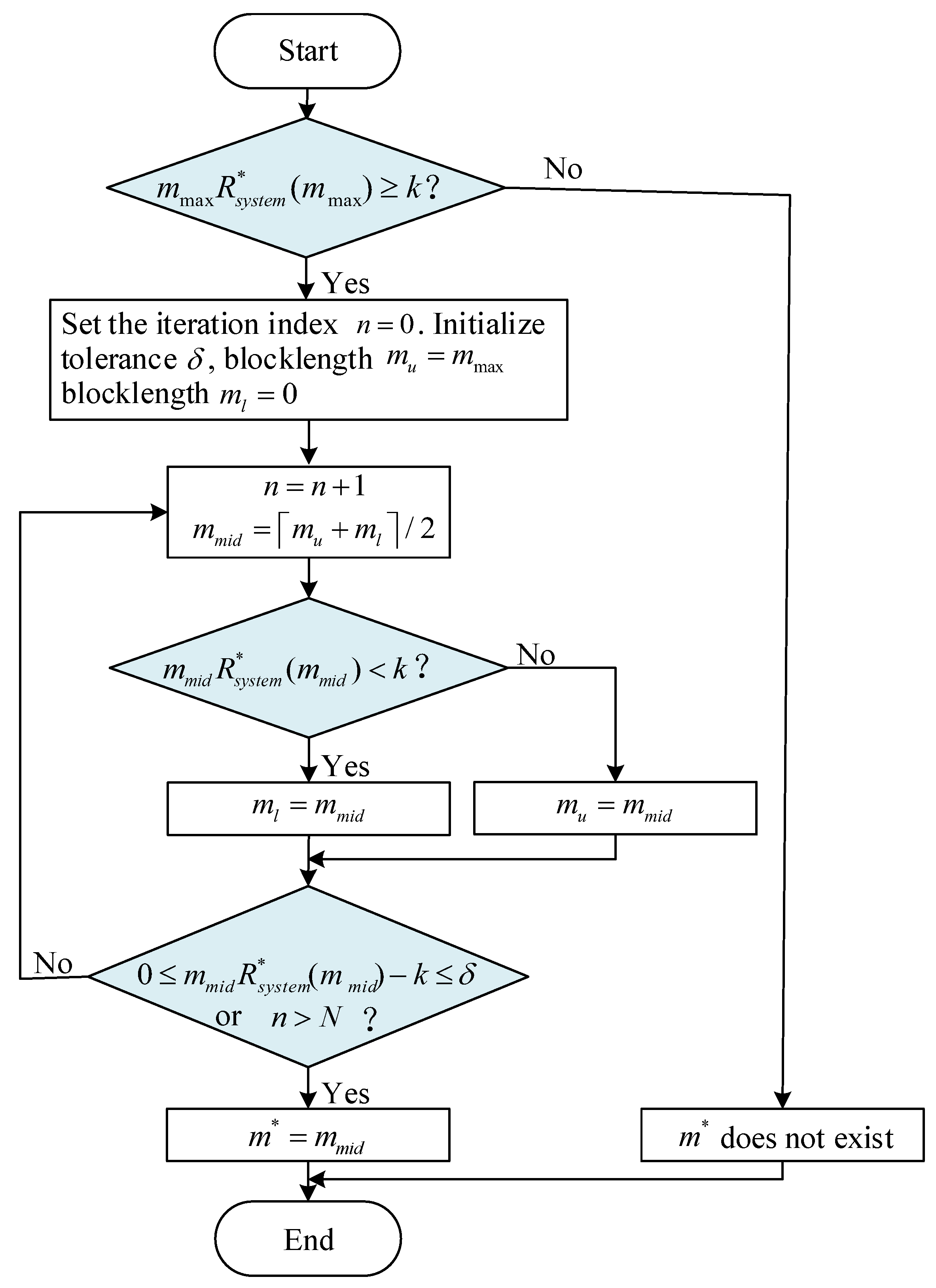
- Applicability of the bisection algorithm: Let . because it is impossible to transmit any data when the blocklength is zero. Thus, . If the solution exists, let . Also, satisfies . Due to the monotonicity of , is located in the range . By iteratively narrowing the interval , convergence to is achieved. This aligns with the way the bisection algorithm works.
| Algorithm 2 RCM Using Bisection Search (Algorithm for ) |
Input: Channel conditions: , , , maximum latency: , packet size in bits: k, maximum blocklength: , the maximum iteration count: N
Output: Optimal solution to Problem : |
4. Simulation Results and Analysis
- 1.
- Algorithm A-EA-MRC [5]. It assumes the direct link is available (A), and the blocklength is evenly allocated (EA) for each hop. The receiver applies MRC method to merge the data.
- 2.
- Algorithm A-EA-MIC [6]. It differs from Algorithm A-EA-MRC by employing the MI combining (MIC) method to merge the data at the receiver.
- 3.
- Algorithm NA-OA [10]. It assumes the direct link is not available (NA), and the blocklength is optimally allocated (OA).
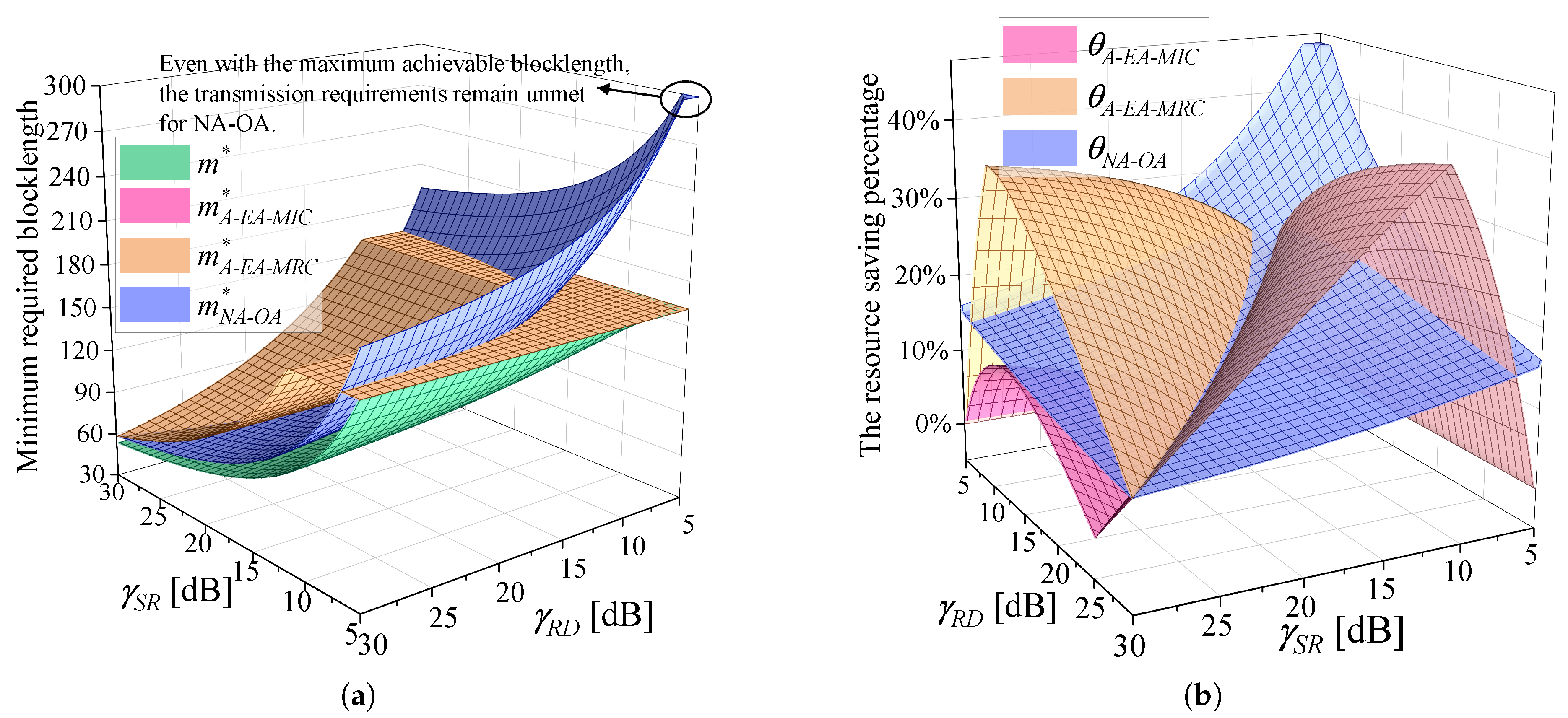
4.1. Performance Evaluation of Algorithm 1
4.2. Performance Evaluation of Algorithm 2
4.3. Application Insights and Discussions
- Multi-user scenarios: The scheme introduced in this paper is applicable to multi-user systems, as it allows the decomposition of multi-user transmissions into multiple transmitter–relay–receiver pairs shown in Figure 1, permitting distributed optimization of resource allocation per pair.
- Variable packet sizes, dynamic traffic: The packet size serves as an input parameter to the proposed algorithms. Therefore, the proposed algorithms are capable of operating under various packet sizes and producing the corresponding optimized two-hop blocklength allocation and PEP results. This adaptability enables the algorithms to handle varying traffic conditions in practical IIoT scenarios.
- Interference scenarios: When interference exists, the calculation for channel dispersion changes. The dispersion derived for non-Gaussian noise can be found in [18]. However, the analysis process remains unchanged.
- Dynamic industrial environments (e.g., with mobility): This scenario requires accurate prediction or real-time feedback of channel and network conditions to ensure timely and effective adaptation of resource allocation strategies. Since the proposed scheme can handle PEP and blocklength allocation under arbitrary channel conditions, its performance largely depends on the accuracy of real-time channel condition prediction or feedback. This research direction will be a focus of our future work.
- Multi-relay scenarios: In multi-relay systems, one of the key challenges is how to select the optimal relay. Building on the current research, it is possible to evaluate and predict the communication performance of various relay choices. This can offer valuable guidance for relay selection, which is a meaningful direction for future work.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Proof of Proposition 1
Appendix B. Proof of Proposition 2
Appendix C
Appendix D
Appendix E. Proof of Proposition 3
Appendix F. Proof of Proposition 4
References
- ITU-R Recommendation M.2083-0. IMT Vision—Framework and Overall Objectives of the Future Development of IMT for 2020 and Beyond. 2015, pp. 1–19. Available online: https://www.itu.int/dms_pubrec/itu-r/rec/m/r-rec-m.2083-0-201509-i!!pdf-e.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2025).[Green Version]
- 3GPP Technical Report 38.913. Study on Scenarios and Requirements for Next Generation Access Technologies. 2022, pp. 1–40. Available online: https://portal.3gpp.org/desktopmodules/Specifications/SpecificationDetails.aspx?specificationId=2996 (accessed on 20 June 2025).[Green Version]
- ITU-R Report M.2516-0. Future Technology Trends of Terrestrial International Mobile Telecommunications Systems Towards 2030 and Beyond. 2022, pp. 1–47. Available online: https://www.itu.int/dms_pub/itu-r/opb/rep/R-REP-M.2516-2022-PDF-E.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2025).[Green Version]
- Hu, Y.; Gursoy, M.C.; Schmeink, A. Relaying-Enabled Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communications in 5G. IEEE Netw. 2018, 32, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.; Guo, X.; Liu, C.; Wu, J.; Jiang, B. Channel State Information-Aware Incremental Selection Hybrid Decode-Amplify-Forward by Unified Destination Scheduling. IEEE Sensors J. 2023, 23, 29458–29470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Shikh-Bahaei, M. An Efficient Relay Selection Scheme for Relay-assisted HARQ. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Rhodes Island, Greece, 4–10 June 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Singh, K.; Ku, M.-L.; Flanagan, M.F. Resource Allocation in Energy-Efficient URLLC Multi-user Multicarrier AF Relay Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Dublin, Ireland, 7–11 June 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Cheng, J.; Shen, C. Relay-Assisted Uplink Transmission Design of URLLC Packets. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 18839–18853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurma, S.; Sharma, P.K.; Dhok, S.; Singh, K.; Li, C.-P. Adaptive AF/DF Two-Way Relaying in FD Multiuser URLLC System with User Mobility. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2022, 21, 10224–10241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, H.; Zhu, X.; Liu, Z.; Tu, X. Joint Blocklength and Trajectory Optimizations for URLLC-Enabled UAV Relay System. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2024, 28, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Schnelling, C.; Gursoy, M.C.; Schmeink, A. Multi-Relay-Assisted Low-Latency High-Reliability Communications with Best Single Relay Selection. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 7630–7642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Pan, C.; Deng, Y.; Elkashlan, M.; Nallanathan, A. Joint Power and Blocklength Optimization for URLLC in a Factory Automation Scenario. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2020, 19, 1786–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Guo, Y.; Peng, T. A Simplified Link-granularity Framework of Interference Identification and Performance Prediction for UDN Uplink. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CIC International Conference on Communications in China (ICCC), China, Sanshui, Foshan, China, 11–13 August 2022; pp. 979–984. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Polyanskiy, Y.; Poor, H.V.; Verdu, S. Channel Coding Rate in the Finite Blocklength Regime. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory. 2010, 56, 2307–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-H.; Park, D.-J. A New Power Allocation Method for Parallel AWGN Channels in the Finite Block Length Regime. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2012, 16, 1392–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; She, C.; Yang, C.; Quek, T.Q.S.; Li, Y.; Vucetic, B. Optimizing Resource Allocation in the Short Blocklength Regime for Ultra-Reliable and Low-Latency Communications. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2019, 18, 402–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 3GPP Technical Report 36.814. Further Advancements for E-UTRA Physical Layer Aspects. 2017, pp. 1–105. Available online: https://portal.3gpp.org/desktopmodules/Specifications/SpecificationDetails.aspx?specificationId=2493 (accessed on 20 June 2025).[Green Version]
- Scarlett, J.; Tan, V.Y.F.; Durisi, G. The Dispersion of Nearest-Neighbor Decoding for Additive Non-Gaussian Channels. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory. 2017, 63, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Jindal, N. Coding versus ARQ in Fading Channels: How Reliable Should the PHY Be? IEEE Trans. Commun. 2011, 59, 3363–3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardano, G.; Witmer, T.R.; Ore, O. The Rules of Algebra: Ars Magna; Courier Corporation: Mineola, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar][Green Version]





| Variable | Meaning |
|---|---|
| SNR of each link | |
| PEP of the corresponding link | |
| The set of PEPs | |
| Blocklength occupied by the source node | |
| Blocklength occupied by the relay node | |
| or | The achievable rate of the S-R link |
| or | The achievable rate of the combined link |
| or | The achievable rate under the RC mode |
| or | The achievable rate under the DC mode |
| or | The system’s achievable rate under the best communication mode |
| Maximum achievable rate under the RC mode at | |
| Maximum achievable rate under the DC mode at | |
| The minimum required total blocklength |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| The maximum blocklength | 300 channel uses |
| PEP limit | |
| Packet size | 32 bytes |
| White noise power density | −174 dBm/Hz |
| Path loss model | |
| Tolerance | 0.01 |
| The maximum iteration count N | 100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Peng, T.; Guo, Y.; Niu, Y.; Wang, W. Minimization of Resource Consumption with URLLC Constraints for Relay-Assisted IIoT. Sensors 2025, 25, 4846. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25154846
Zhao Y, Peng T, Guo Y, Niu Y, Wang W. Minimization of Resource Consumption with URLLC Constraints for Relay-Assisted IIoT. Sensors. 2025; 25(15):4846. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25154846
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yujie, Tao Peng, Yichen Guo, Yijing Niu, and Wenbo Wang. 2025. "Minimization of Resource Consumption with URLLC Constraints for Relay-Assisted IIoT" Sensors 25, no. 15: 4846. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25154846
APA StyleZhao, Y., Peng, T., Guo, Y., Niu, Y., & Wang, W. (2025). Minimization of Resource Consumption with URLLC Constraints for Relay-Assisted IIoT. Sensors, 25(15), 4846. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25154846







