Rethinking Infrared and Visible Image Fusion from a Heterogeneous Content Synergistic Perception Perspective
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose HCSPNet, the pioneering GAN-based framework for IVIF that utilizes heterogeneous dual discriminators. This design is specifically focused on maintaining the integrity of crucial information from source images, especially in challenging, degraded scenarios.
- The two discriminators, with our proposed ASID module, are optimized for their respective sensor modalities, allowing for the simultaneous targeted learning of thermal radiation regions and local details. This framework can serve as a plug-and-play framework for existing GAN-based methods.
- We have conducted extensive experiments on several public IVIF datasets, as well as on related tasks such as medical and biological image fusion. The results not only confirm the superior fusion quality of HCSPNet but also highlight its capability to improve performance in downstream high-level vision tasks and demonstrate the broad applicability of our proposed framework.
2. Related Works
2.1. Model-Based IVIF
2.2. Deep Learning-Based IVIF
2.3. GANs for IVIF
3. Methodology
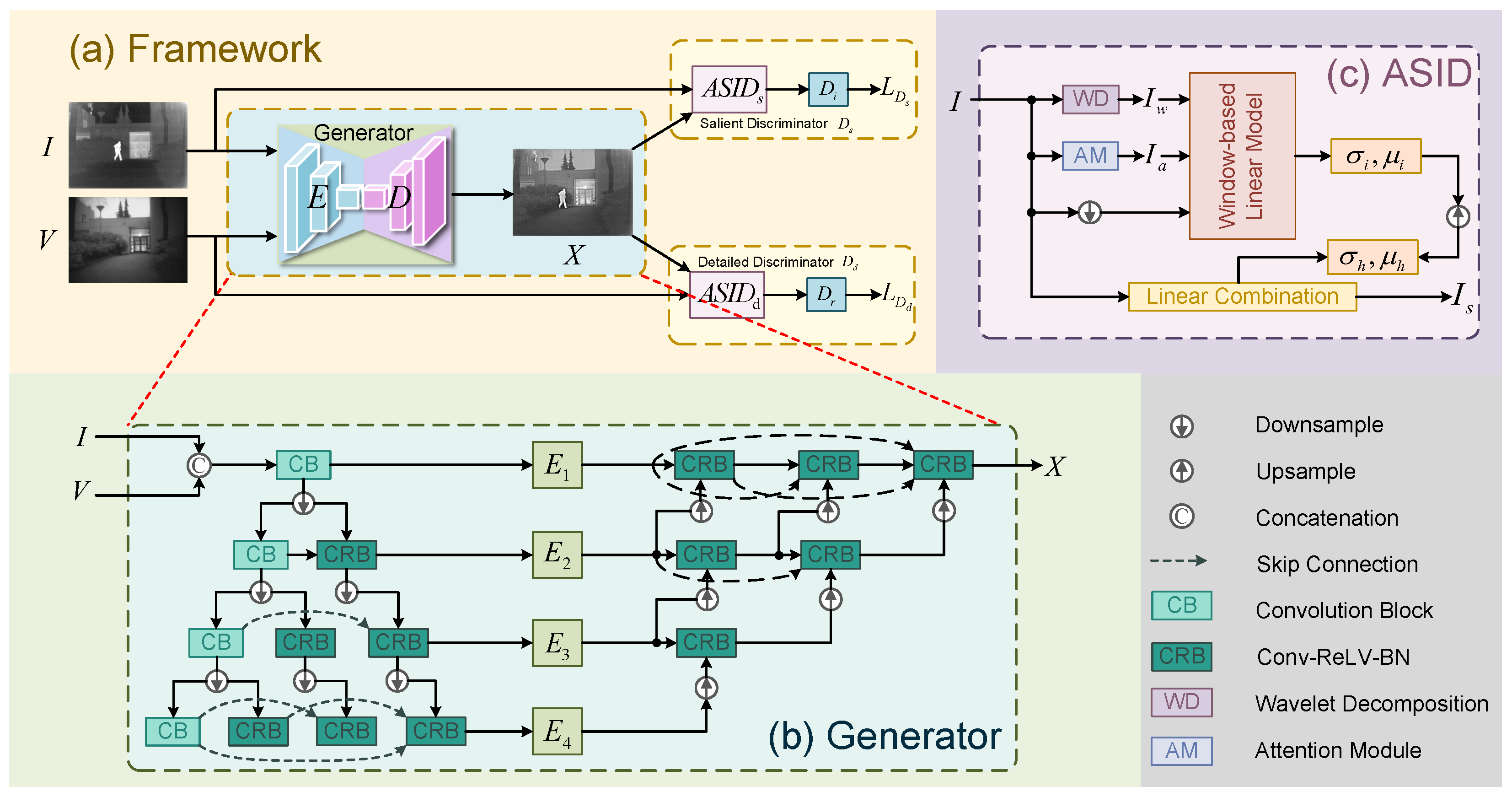
3.1. Overview
3.2. Generator
3.3. Heterogeneous Discriminators
Adaptive Salient Information Distillation Module
3.4. Optimization Strategy
- (1)
- Generator Loss: Our generator loss consists of the adversarial loss () and the basic loss (), generating a high-quality fused image as follows:where is the parameter used to balance the two terms. The adversarial loss is defined aswhere means expectation and is the distribution of X.The basic loss aims to constrain the preservation of important information from source images. Following [7], is defined aswherewhere is the trade-off parameter. and denote the Frobenius norm and norm.
- (2)
- Discriminator Loss: Discriminator loss is combined with the salient discriminator loss and the detailed discriminator loss .Given that the two heterogeneous discriminators may aggravate the imbalance conflict when the generator learns different features, we jointly train the two discriminators instead of calculating them separately [34,35]. The weight parameter is introduced to allow the model to adaptively adjust the optimization to solve the training imbalance arising from the difference of the discriminative structure as follows:wherewhere , . and denote the distributions of I and V.
4. Experiment
4.1. Implementation Details
- Datasets: Our empirical evaluation of HCSPNet was conducted on the following five publicly accessible IVIF datasets: TNO [36], INO [37], RoadScene [38], LLVIP [39], and [8]. For the TNO dataset (190 images), the latter 100 pairs were used for training and the rest for testing. From RoadScene (221 pairs), the initial 151 pairs formed the training set. For LLVIP (300 pairs selected as per DeRUN [7]) and (300 pairs), the first 100 pairs from each were allocated for training. To augment the training data, images were uniformly cropped into 128 × 128 pixel blocks, yielding a total of 14,503 training samples.
- Comparative Methods: We compare our proposed method, HCSPNet, with nine state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods, including U2Fusion [38], FusionGAN [30], DDcGAN [31], GANMcC [40], GAN-FM [32], TarDAL [8], DeRUN [7], GAN-HA [41], DSFD [42], and ReFusion [43]. The selection emphasizes GAN-based techniques to provide a direct comparison for our novel discriminative framework, supplemented by U2Fusion [38] and DeRUN [7] for broader context. All comparisons utilized publicly available code and their originally parameter settings.
- Evaluation Metric: Following the approaches outlined in [7,17], we utilize six commonly used metrics to evaluate the performance of IVIF methods from multiple perspectives. These metrics include entropy (EN) [44], average gradient (AG) [45], spatial frequency (SF) [46], feature mutual information (FMI) [47], visual information fidelity (VIF) [48], and the universal image quality index (UIQI). EN measures information richness; AG reflects texture detail via gradients; SF indicates the overall activity level and edge information; FMI quantifies shared information between fused and source images; VIF assesses perceptual similarity to source images; and UIQI evaluates structural similarity, luminance, and contrast. Higher values for all these metrics signify better fusion quality.
- Training Details: The proposed HCSPNet is implemented by PyTorch on two RTX4090 GPUs and is optimized by an Adam optimizer with momentum terms (0.9, 0.999). Our epoch is set as 160 with a batch size of 8. The learning rates are initialized as and for the generator and the heterogeneous discriminators, respectively. Furthermore, the hyperparameters , , and in Equations (7), (9), and (11) are set to 10, 1, and 1, respectively.
4.2. Results on the IVIF Task
- Quantitative Comparisons: The average scores for the six evaluation metrics across the five datasets are presented in Table 1. HCSPNet consistently achieved the highest scores for nearly all metrics across all datasets. This demonstrates its superior capability in preserving gradients, textures, enhancing visual quality, and maximizing information content. Notably, HCSPNet often showed substantial improvements over the cutting-edge methods, ReFusion an DSFD, underscoring the efficacy of the heterogeneous content synergistic perception framework.
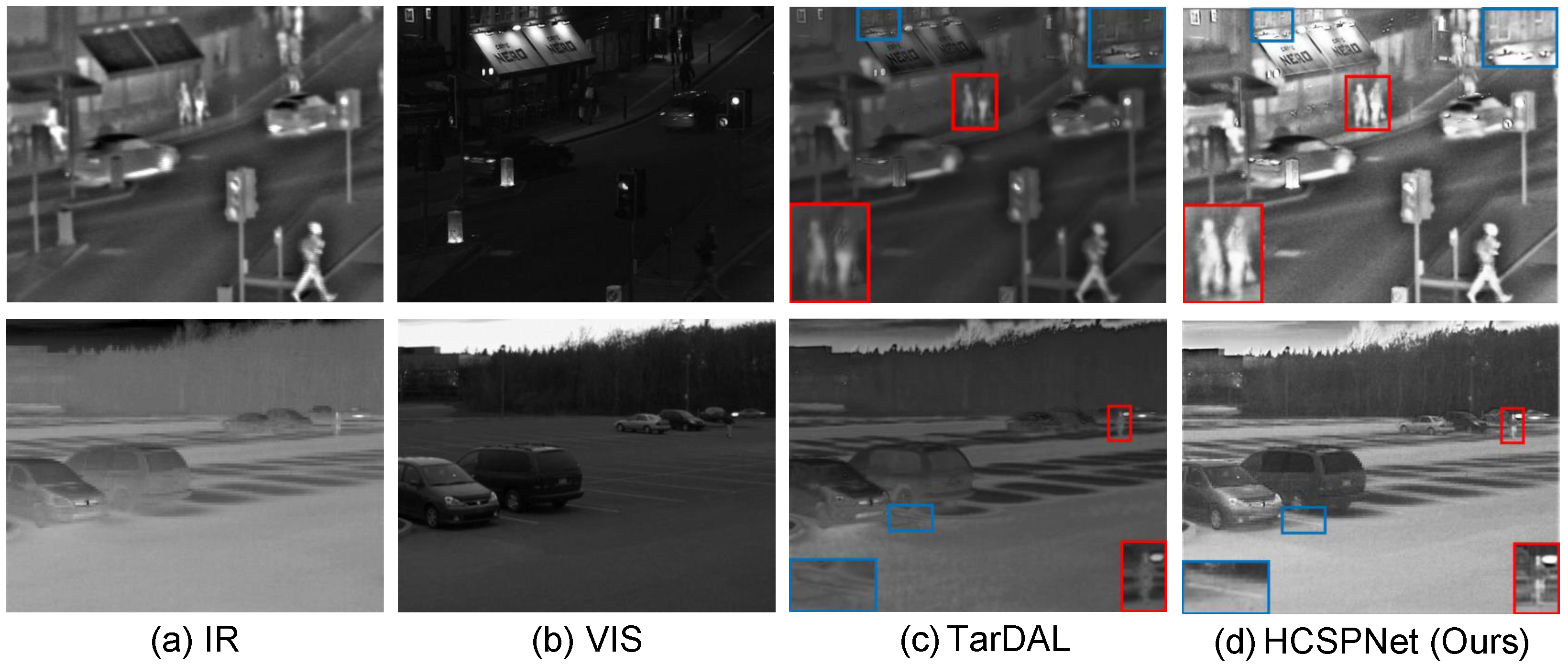
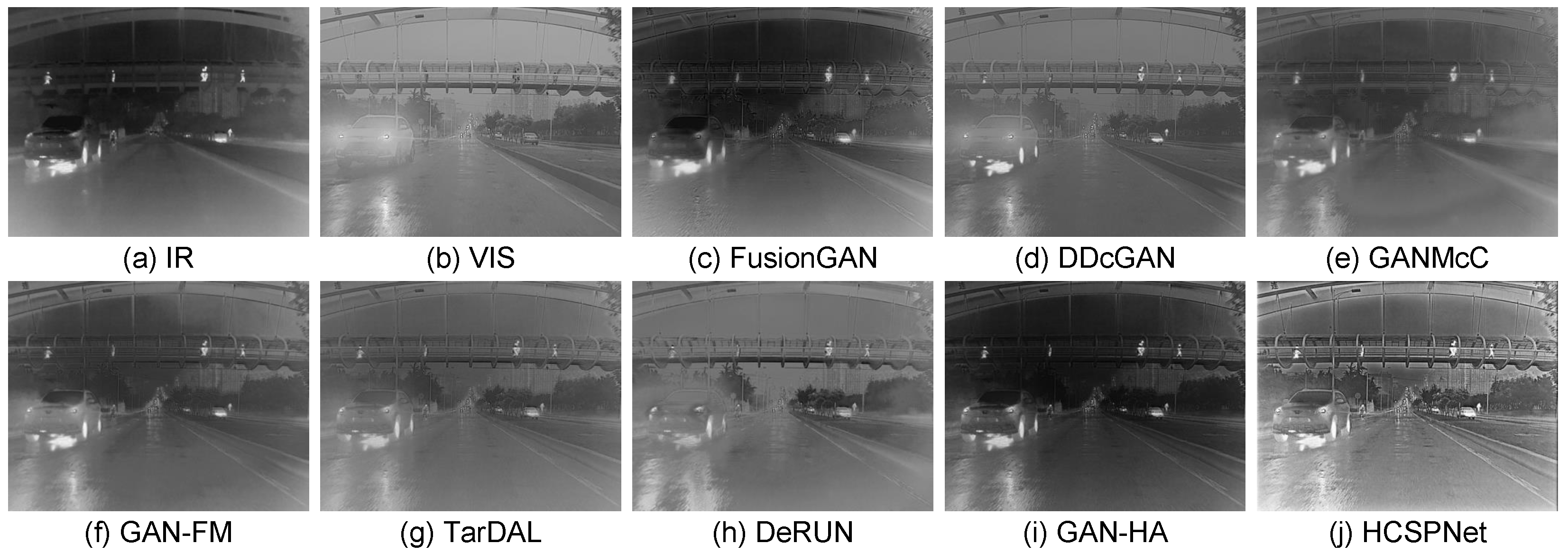
- Qualitative Comparisons: To demonstrate the superiority of our model, we qualitatively assess three representative image pairs from the test set and compare the results with the nine state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods. The fusion outcomes of HCSPNet and the comparative algorithms are illustrated in Figure 4 and Figure 5. The evaluation focuses on salient thermal information, represented by bright human body regions, and texture details, such as lane lines, license plates, and bushes.
4.3. Ablation Study
- Effect of our discriminators: We employ dual heterogeneous discriminators, namely, the salient discriminator () and the detailed discriminator (), to approach the IVIF problem from a heterogeneous content synergistic perception perspective. As demonstrated in Table 2, our method achieves the highest performance when both and are utilized, underscoring the effectiveness and superiority of our dual-discriminator framework.
- Generalization of our discriminators: Our dual heterogeneous discriminators, equipped with ASID modules, enhance the extraction of salient information from the fused images, directing the discriminators to concentrate on key components when determining whether the fused images effectively preserve crucial information from the source images. Consequently, our dual-discriminator framework ensures that the generator retains essential content from the source images. In this subsection, we further integrate our dual-discriminator structure into existing GAN-based methods. As shown in Table 3, we observe significant performance improvements when incorporating our framework into other methods, further validating the superiority of our approach.
- Sensitivity analysis of hyperparameters: In our framework, the final loss function is balanced by three key hyperparameters: , , and . To analyze their impact on model performance, we conduct a sensitivity analysis by varying each parameter while keeping the others at their default values (). The quantitative results of this analysis on the RoadScene dataset are presented in Table 4. As shown, our chosen set of parameters consistently yields the best or nearly the best results across all six evaluation metrics (EN, AG, SF, FMI, VIF, and UIQI), while performance varies with different hyperparameter values, the model demonstrates robust performance across a reasonable range, indicating that it is not overly sensitive to the precise choice of these parameters. This analysis confirms the rationale behind our selected hyperparameters, which effectively balance the contributions of the adversarial loss, the content loss, and the dual-discriminator losses to achieve optimal fusion quality.
4.4. Subsequent Application Verification
- Object detection: Object detection is a widely used machine vision technique [49] for identifying specific objects, such as people, vehicles, and other important entities, within images. Fused images with enhanced quality of salient information are expected to yield better downstream performance compared to individual images. Furthermore, algorithms that effectively preserve salient information from heterogeneous source images tend to outperform others in object detection tasks. Following the methodology in [7,50], we employ the general-purpose detector YOLOv5 for object detection experiments on the LLVIP and datasets. The results for these two datasets are presented in Table 5 and Figure 6. In this context, Precision indicates the probability of correctly detecting true positives among all detected objects, with higher precision implying more accurate identification of real samples. Recall measures the probability of correctly recognizing all positive samples, with higher recall indicating fewer missed targets. The mean average precision (mAP) serves as a comprehensive metric that balances Precision and Recall to assess model performance. The mAP score ranges from 0 to 1, with values closer to 1 representing better performance. The mAP@.5 and mAP@.95 correspond to the mAP values at confidence thresholds of 0.5 and 0.95, respectively. The results clearly demonstrate that HCSPNet achieves superior performance across these metrics.
- Visual tracking: Visual tracking, which aims to localize the position of specific objects in video sequences, is a crucial task in computer vision. Following the methodology in [51], we apply our algorithm to the VOT-RGBT sub-challenge, which focuses on short-term tracking as part of VOT2020, to comparatively assess the impact of the fusion approach on tracking performance. The VOT-RGBT benchmark, as outlined in [33,52], consists of 60 video sequences with aligned infrared and visible image pairs. For evaluation, we employ the following two trackers: the learning adaptive discriminative correlation filter (LADCF) [53] and the group feature selection and discriminative filter (GFSDCF) [54]. LADCF demonstrated top performance in the VOT-ST2018 sub-challenge, while GFSDCF further refines LADCF by eliminating redundant information using a group feature selection strategy. Both trackers’ codes are publicly available. For quantitative analysis, we use the following three metrics to evaluate tracking performance: Accuracy, Failure, and Expected Average Overlap (EAO). Accuracy measures the average overlap between the predicted bounding boxes and the ground truth, while Failure assesses tracker robustness. EAO evaluates the expected average overlap between the tracker’s output and the ground truth over time. For both Accuracy and EAO, higher values indicate better performance, while lower Failure values signify better robustness. The results are shown in Table 6 and Figure 7. HCSPNet demonstrates superior performance in enhancing visual tracking compared to other fusion methods.
4.5. Extension of the Proposed HCSPNet
- (1)
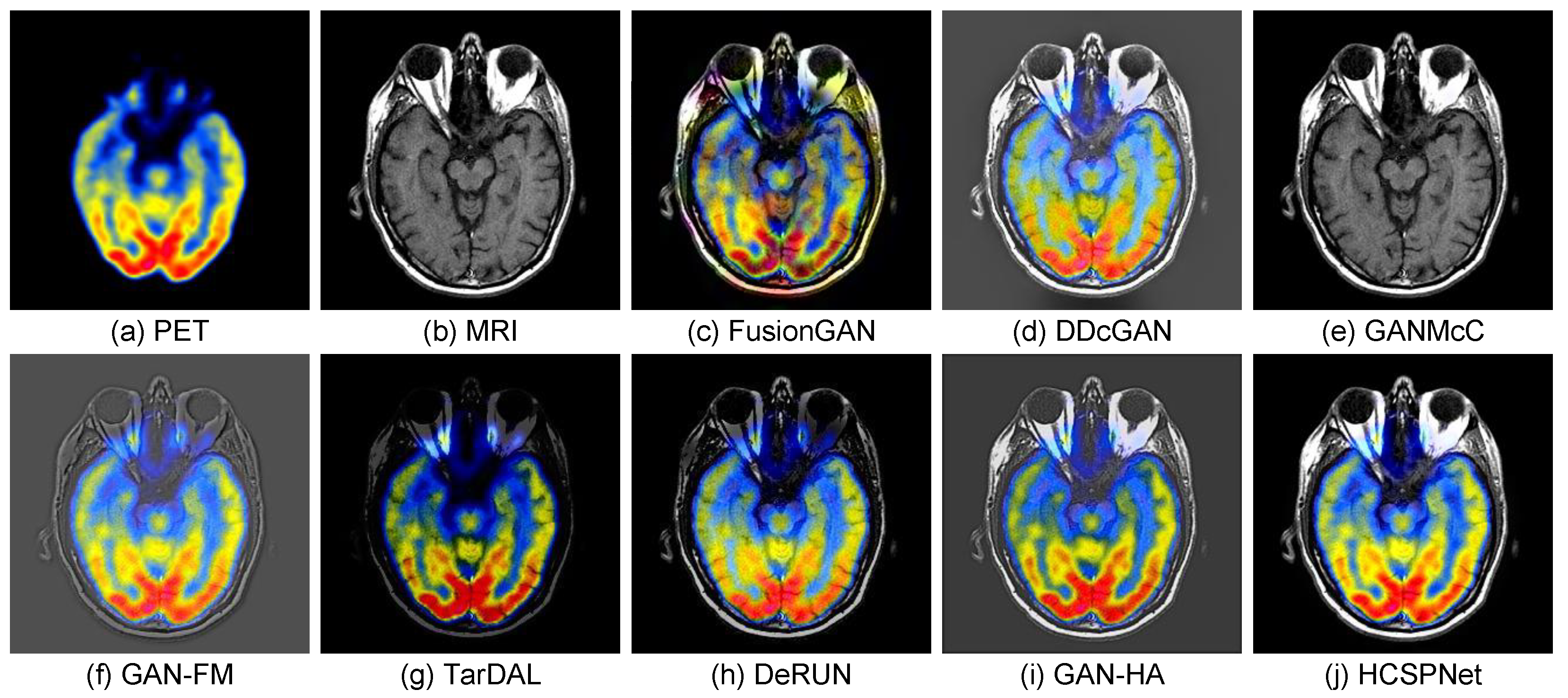
- Medical Image Fusion: For the medical image fusion task, we conduct experiments on PET and MRI image fusion using the HWBA dataset [55], which consists of 144 image pairs for training. We utilize the same evaluation metrics and comparison methods as applied in the IVIF task. The results, as shown in Table 7, indicate that our method achieves superior performance across all metrics, significantly surpassing existing methods. This enhanced performance is primarily due to our proposed heterogeneous content synergistic perception framework and the specifically designed attention module. Visual results of the medical image fusion are presented in Figure 8. These figures illustrate that HCSPNet provides better fusion outcomes with improved salient information compared to other methods, which may suffer from issues related to detail distortion and color component preservation.
- (2)
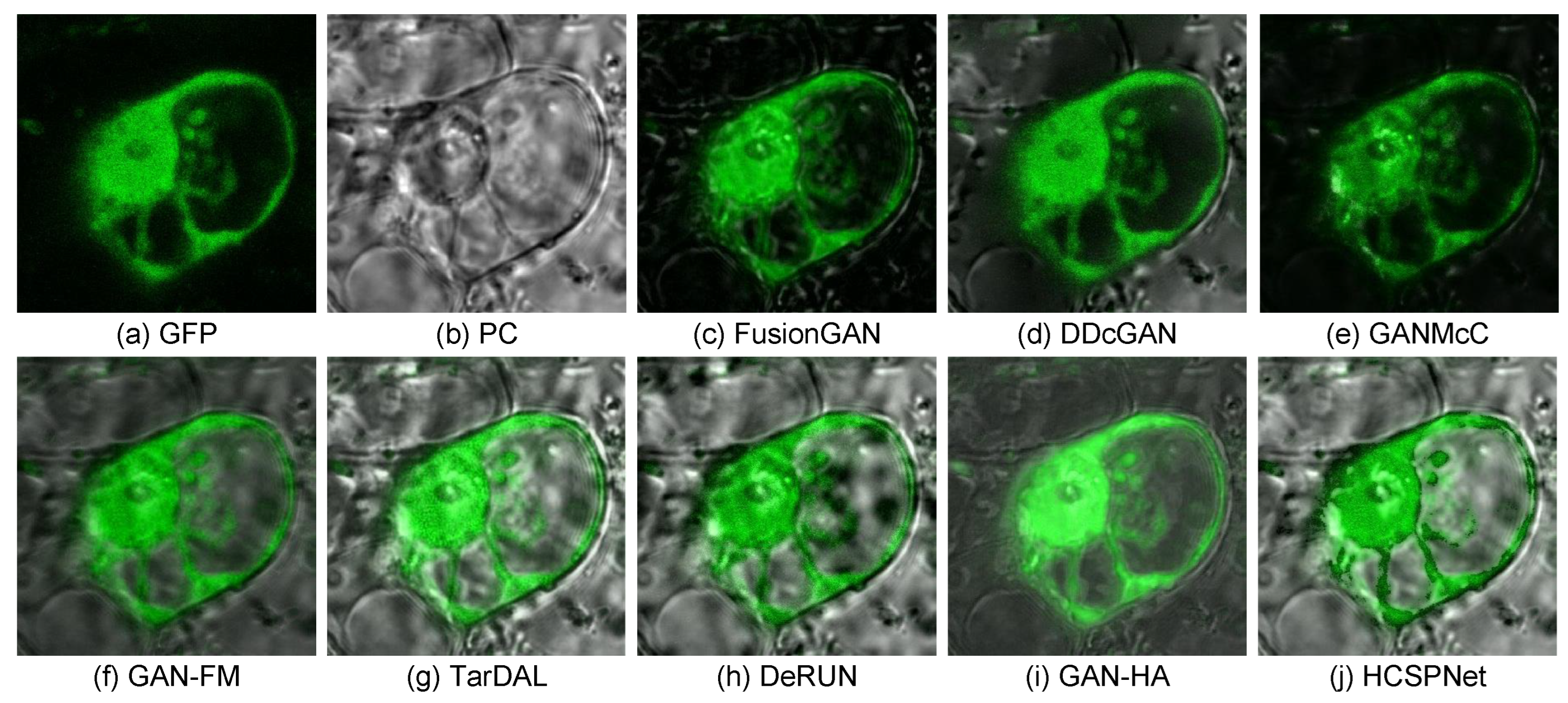
- Biological Image Fusion: In the biological image fusion task, we use the ATC dataset [56] for network training, focusing on the green fluorescent protein (GFP) and phase contrast (PC) image fusion (GFP) task. The training set consists of 60 image pairs. Quantitative results are reported in Table 8. As depicted in Table 8, our method achieves the best performance across all metrics. Additionally, visual comparisons are provided in Figure 9. These figures demonstrate that our approach effectively preserves salient information from GFP and PC images while mitigating phase noise issues from PC images.
5. Discussion
6. Future Work
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ju, M.; Yu, X. Semantic-Aware Low-Light Image Enhancement Network for Recognizing Semantics in Intelligent Transportation Systems. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2025; early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Shen, Y.; Fang, C.; Xiao, F.; Tang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zuo, W.; Guo, Z.; Li, X. Diffusion Models in Low-Level Vision: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2024, 47, 4630–4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Wu, H.; He, D.; Lan, R.; Liu, Z.; Pan, X. AcFusion: Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Based on Self-Attention and Convolution With Enhanced Information Extraction. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2023, 70, 4155–4167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Fu, Y. FCDFusion: A fast, low color deviation method for fusing visible and infrared image pairs. Comput. Vis. Media 2025, 11, 195–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, Z.; Shao, R.; Zhang, T.; Fu, Y. Noise Calibration and Spatial-Frequency Interactive Network for STEM Image Enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Conference, Nashville, TN, USA, 11–15 June 2025; pp. 21287–21296. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, M.; Xie, S.; Li, F. Improving skip connection in u-net through fusion perspective with mamba for image dehazing. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2024, 70, 7505–7514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Li, K.; Xu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, R.; Guo, Z.; Li, X. Degradation-Resistant Unfolding Network for Heterogeneous Image Fusion. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 12611–12621. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Fan, X.; Huang, Z.; Wu, G.; Liu, R.; Zhong, W.; Luo, Z. Target-aware dual adversarial learning and a multi-scenario multi-modality benchmark to fuse infrared and visible for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 5802–5811. [Google Scholar]
- Burt, P.J.; Adelson, E.H. The Laplacian pyramid as a compact image code. In Readings in Computer Vision; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1987; pp. 671–679. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, M.; Ding, C.; Guo, Y.J.; Zhang, D. IDGCP: Image dehazing based on gamma correction prior. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 29, 3104–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, J.J.; O’Callaghan, R.J.; Nikolov, S.G.; Bull, D.R.; Canagarajah, N. Pixel-and region-based image fusion with complex wavelets. Inf. Fusion 2007, 8, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Xu, G.; Yan, J.; Tang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, X. Hqg-net: Unpaired medical image enhancement with high-quality guidance. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2023, 35, 18404–18418. [Google Scholar]
- Nencini, F.; Garzelli, A.; Baronti, S.; Alparone, L. Remote sensing image fusion using the curvelet transform. Inf. Fusion 2007, 8, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, M.; Ding, C.; Guo, C.A.; Ren, W.; Tao, D. IDRLP: Image dehazing using region line prior. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 9043–9057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, M.; Ding, C.; Ren, W.; Yang, Y. IDBP: Image dehazing using blended priors including non-local, local, and global priors. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2021, 32, 4867–4871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Li, K.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Li, X. Camouflaged object detection with feature decomposition and edge reconstruction. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 22046–22055. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, M.; Ding, C.; Ren, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Guo, Y.J. IDE: Image dehazing and exposure using an enhanced atmospheric scattering model. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 2180–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Zhang, X.; Hu, Q.; Han, H. RepVGGFuse: An approach for infrared and visible image fusion network based on RepVGG architecture. In Proceedings of the 2023 4th International Conference on Computing, Networks and Internet of Things, Xiamen, China, 26–28 May 2023; pp. 375–379. [Google Scholar]
- He, C.; Li, K.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Tang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, L.; Farsiu, S. Segment concealed object with incomplete supervision. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2025; early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Essock, E.A.; Hansen, B.C. An advanced image fusion algorithm based on wavelet transform: Incorporation with PCA and morphological processing. In Proceedings of the Image Processing: Algorithms and Systems III, San Jose, CA, USA, 18–22 January 2004; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2004; Volume 5298, pp. 177–187. [Google Scholar]
- Cvejic, N.; Bull, D.; Canagarajah, N. Region-based multimodal image fusion using ICA bases. IEEE Sens. J. 2007, 7, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z. A general framework for image fusion based on multi-scale transform and sparse representation. Inf. Fusion 2015, 24, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Li, K.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, G.; Tang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Li, X. Weakly-Supervised Concealed Object Segmentation with SAM-based Pseudo Labeling and Multi-scale Feature Grouping. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2023, 36, 30726–30737. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Peng, H.; Wang, Z. Multi-focus image fusion with a deep convolutional neural network. Inf. Fusion 2017, 36, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, X.-j.; Durrani, T.S. Infrared and visible image fusion with ResNet and zero-phase component analysis. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2019, 102, 103039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, P.; Yan, H.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, L. IFCNN: A general image fusion framework based on convolutional neural network. Inf. Fusion 2020, 54, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, X.J. DenseFuse: A fusion approach to infrared and visible images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 28, 2614–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Wu, X.J.; Durrani, T. NestFuse: An infrared and visible image fusion architecture based on nest connection and spatial/channel attention models. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 9645–9656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, X. UNFusion: A unified multi-scale densely connected network for infrared and visible image fusion. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2021, 32, 3360–3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Yu, W.; Liang, P.; Li, C.; Jiang, J. FusionGAN: A generative adversarial network for infrared and visible image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2019, 48, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Xu, H.; Jiang, J.; Mei, X.; Zhang, X.P. DDcGAN: A dual-discriminator conditional generative adversarial network for multi-resolution image fusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 4980–4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yuan, J.; Tian, X.; Ma, J. GAN-FM: Infrared and visible image fusion using GAN with full-scale skip connection and dual Markovian discriminators. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 2021, 7, 1134–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Zhang, R.; Xiao, F.; Fang, C.; Tang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, L.; Fan, D.P.; Li, K.; Farsiu, S. RUN: Reversible Unfolding Network for Concealed Object Segmentation. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2501.18783. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhong, B.; Liang, Q.; Mo, Z.; Zhang, S.; Li, X. Odtrack: Online dense temporal token learning for visual tracking. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 26–27 February 2024; Volume 38, pp. 7588–7596. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhong, B.; Liang, Q.; Li, G.; Ji, R.; Li, X. Toward unified token learning for vision-language tracking. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2023, 34, 2125–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toet, A. The TNO multiband image data collection. Data Brief 2017, 15, 249–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Chen, C.; Li, C.; Huang, J. Infrared and visible image fusion via gradient transfer and total variation minimization. Inf. Fusion 2016, 31, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Ma, J.; Jiang, J.; Guo, X.; Ling, H. U2Fusion: A unified unsupervised image fusion network. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 44, 502–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Zhu, C.; Li, M.; Tang, W.; Zhou, W. LLVIP: A visible-infrared paired dataset for low-light vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 3496–3504. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Zhang, H.; Shao, Z.; Liang, P.; Xu, H. GANMcC: A generative adversarial network with multiclassification constraints for infrared and visible image fusion. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 70, 5005014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Fang, Z.; Tian, J.; Huang, H.; Xu, Y.; Han, Z.; Kang, Y.; Feng, C.; Zhao, Z. GAN-HA: A generative adversarial network with a novel heterogeneous dual-discriminator network and a new attention-based fusion strategy for infrared and visible image fusion. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2024, 142, 105548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Nan, X.; Zhou, X.; Shen, Y.; Zhou, Q. A dual-stream feature decomposition network with weight transformation for multi-modality image fusion. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 7467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Y.; Deng, L.; Cui, Y.; Jiang, B.; Xu, S. Refusion: Learning image fusion from reconstruction with learnable loss via meta-learning. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2025, 133, 2547–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Liu, Y.; Kong, A.W.K. Tf-icon: Diffusion-based training-free cross-domain image composition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 2294–2305. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, S.; Wang, Z.; Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Kong, A.W.K. Mace: Mass concept erasure in diffusion models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 6430–6440. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, S.; Zhou, Z.; Lu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Kong, A.W.K. Robust watermarking using generative priors against image editing: From benchmarking to advances. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.18775. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhong, B.; Liang, Q.; Tang, Z.; Ji, R.; Li, X. Leveraging local and global cues for visual tracking via parallel interaction network. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2022, 33, 1671–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhong, B.; Liang, Q.; Li, N.; Song, S. Decoupled Spatio-Temporal Consistency Learning for Self-Supervised Tracking. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 25 February–4 March 2025; Volume 39, pp. 10635–10643. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Ouyang, W.; Wang, X.; Fieguth, P.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Pietikäinen, M. Deep learning for generic object detection: A survey. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2020, 128, 261–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, M.; He, C.; Ding, C.; Ren, W.; Zhang, L.; Ma, K.K. All-inclusive image enhancement for degraded images exhibiting low-frequency corruption. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2024, 35, 838–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, X.J.; Kittler, J. MDLatLRR: A novel decomposition method for infrared and visible image fusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 4733–4746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristan, M.; Matas, J.; Leonardis, A.; Felsberg, M.; Pflugfelder, R.; Kamarainen, J.K.; Cehovin Zajc, L.; Drbohlav, O.; Lukezic, A.; Berg, A.; et al. The seventh visual object tracking VOT2019 challenge results. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27–28 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, T.; Feng, Z.H.; Wu, X.J.; Kittler, J. Learning adaptive discriminative correlation filters via temporal consistency preserving spatial feature selection for robust visual object tracking. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 28, 5596–5609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Feng, Z.H.; Wu, X.J.; Kittler, J. Joint group feature selection and discriminative filter learning for robust visual object tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27–28 October 2019; pp. 7950–7960. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, K.A.; Becker, J.A. The Whole Brain Atlas. 1997. Available online: https://www.med.harvard.edu/aanlib/ (accessed on 19 May 2025).
- Koroleva, O.A.; Tomlinson, M.L.; Leader, D.; Shaw, P.; Doonan, J.H. High-throughput protein localization in Arabidopsis using Agrobacterium-mediated transient expression of GFP-ORF fusions. Plant J. 2005, 41, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Ke, Q.; Peng, J.; Cao, X.; Zhao, Z. Pan-Denoising: Guided Hyperspectral Image Denoising via Weighted Represent Coefficient Total Variation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5528714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Data | Metrics | U2Fusion | FusionGAN | DDcGAN | GANMcC | GAN-FM | TarDAL | DeRUN | GAN-HA | DSFD * | ReFusion | HCSPNet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TNO | EN ↑ | 6.612 | 6.828 | 6.619 | 6.758 | 6.384 | 6.567 | 6.841 | 6.265 | — | 6.675 | 6.974 |
| AG ↑ | 4.016 | 3.759 | 3.953 | 2.666 | 2.296 | 2.493 | 4.151 | 4.032 | — | 4.208 | 4.369 | |
| SF ↑ | 10.677 | 8.888 | 11.051 | 10.674 | 11.874 | 12.162 | 12.825 | 11.767 | — | 11.186 | 13.720 | |
| FMI ↑ | 0.878 | 0.868 | 0.875 | 0.868 | 0.875 | 0.882 | 0.872 | 0.853 | — | 0.879 | 0.895 | |
| VIF ↑ | 0.571 | 0.643 | 0.645 | 0.446 | 0.286 | 0.456 | 0.495 | 0.472 | — | 0.577 | 0.646 | |
| UIQI ↑ | 0.771 | 0.846 | 0.582 | 0.426 | 0.712 | 0.752 | 0.713 | 0.736 | — | 0.863 | 0.868 | |
| INO | EN ↑ | 7.096 | 7.152 | 7.263 | 7.035 | 6.805 | 6.985 | 7.203 | 7.066 | — | 7.038 | 7.429 |
| AG ↑ | 3.696 | 3.007 | 3.637 | 2.585 | 2.377 | 2.370 | 3.155 | 3.705 | — | 3.816 | 3.882 | |
| SF ↑ | 10.151 | 7.429 | 9.734 | 6.481 | 5.970 | 5.990 | 7.869 | 8.855 | — | 10.758 | 11.931 | |
| FMI ↑ | 0.896 | 0.898 | 0.896 | 0.865 | 0.858 | 0.892 | 0.893 | 0.896 | — | 0.896 | 0.899 | |
| VIF ↑ | 0.465 | 0.558 | 0.655 | 0.464 | 0.268 | 0.457 | 0.461 | 0.502 | — | 0.670 | 0.738 | |
| UIQI ↑ | 0.766 | 0.850 | 0.623 | 0.520 | 0.841 | 0.776 | 0.654 | 0.705 | — | 0.719 | 0.843 | |
| RoadScene | EN ↑ | 7.192 | 7.472 | 7.111 | 7.048 | 7.209 | 7.431 | 7.293 | 7.293 | — | 7.283 | 7.499 |
| AG ↑ | 3.529 | 5.102 | 5.002 | 3.550 | 3.409 | 3.818 | 4.801 | 5.173 | — | 5.232 | 5.263 | |
| SF ↑ | 9.904 | 12.883 | 13.646 | 8.608 | 8.833 | 9.122 | 12.560 | 14.035 | 8.089 | 14.206 | 14.067 | |
| FMI ↑ | 0.858 | 0.848 | 0.839 | 0.847 | 0.850 | 0.861 | 0.854 | 0.862 | — | 0.866 | 0.868 | |
| VIF ↑ | 0.229 | 0.442 | 0.463 | 0.337 | 0.274 | 0.427 | 0.420 | 0.453 | 0.844 | 0.459 | 0.465 | |
| UIQI ↑ | 0.844 | 0.807 | 0.699 | 0.434 | 0.720 | 0.731 | 0.769 | 0.832 | — | 0.863 | 0.868 | |
| LLVIP | EN ↑ | 7.126 | 6.924 | 5.263 | 6.861 | 6.365 | 6.708 | 7.338 | 7.108 | — | 7.502 | 7.695 |
| AG ↑ | 3.748 | 2.903 | 2.365 | 2.041 | 2.044 | 2.276 | 3.082 | 3.352 | — | 4.315 | 4.676 | |
| SF ↑ | 13.737 | 9.259 | 10.847 | 5.728 | 7.308 | 7.432 | 10.348 | 15.325 | — | 15.023 | 15.577 | |
| FMI ↑ | 0.904 | 0.902 | 0.903 | 0.899 | 0.901 | 0.901 | 0.903 | 0.900 | — | 0.906 | 0.914 | |
| VIF ↑ | 0.405 | 0.431 | 0.283 | 0.362 | 0.206 | 0.364 | 0.470 | 1.001 | — | 0.973 | 1.053 | |
| UIQI ↑ | 0.785 | 0.275 | 0.436 | 0.769 | 0.824 | 0.533 | 0.694 | 0.703 | — | 0.823 | 0.848 | |
| EN ↑ | 6.428 | 6.728 | 6.843 | 6.428 | 6.639 | 6.780 | 7.085 | 7.536 | — | 7.712 | 7.803 | |
| AG ↑ | 4.239 | 3.640 | 4.240 | 2.411 | 2.769 | 2.719 | 3.671 | 4.237 | — | 5.020 | 5.483 | |
| SF ↑ | 12.822 | 10.072 | 12.881 | 6.458 | 8.355 | 7.654 | 10.768 | 12.308 | 14.764 | 15.362 | 16.226 | |
| FMI ↑ | 0.887 | 0.881 | 0.871 | 0.866 | 0.878 | 0.874 | 0.878 | 0.883 | — | 0.888 | 0.891 | |
| VIF ↑ | 0.349 | 0.445 | 0.603 | 0.302 | 0.211 | 0.381 | 0.378 | 0.857 | 0.844 | 0.875 | 0.892 | |
| UIQI ↑ | 0.721 | 0.609 | 0.432 | 0.806 | 0.809 | 0.626 | 0.814 | 0.823 | — | 0.883 | 0.886 |
| Methods | RoadScene | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EN ↑ | AG ↑ | SF ↑ | FMI ↑ | VIF ↑ | UIQI ↑ | |
| w/o | 4.536 | 3.361 | 8.024 | 0.779 | 0.332 | 0.833 |
| w/ | 5.148 | 4.904 | 12.604 | 0.843 | 0.368 | 0.850 |
| w/ | 5.137 | 3.883 | 10.500 | 0.847 | 0.258 | 0.842 |
| Ours | 7.499 | 5.263 | 14.067 | 0.868 | 0.465 | 0.868 |
| Methods | RoadScene | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EN ↑ | AG ↑ | SF ↑ | FMI ↑ | VIF ↑ | UIQI ↑ | |
| GANMcC | 7.048 | 3.550 | 8.608 | 0.847 | 0.337 | 0.434 |
| GANMcC+ | 7.135 | 3.676 | 8.623 | 0.850 | 0.341 | 0.439 |
| GAM-FM | 7.209 | 3.409 | 8.833 | 0.850 | 0.274 | 0.720 |
| GAM-FM+ | 7.404 | 3.886 | 10.017 | 0.860 | 0.360 | 0.735 |
| TarDAL | 7.431 | 3.818 | 9.122 | 0.861 | 0.427 | 0.731 |
| TarDAL+ | 7.616 | 4.253 | 11.705 | 0.870 | 0.467 | 0.778 |
| GAN-HA | 7.293 | 5.173 | 14.035 | 0.862 | 0.453 | 0.832 |
| GAN-HA+ | 7.306 | 5.186 | 14.336 | 0.875 | 0.463 | 0.837 |
| Metrics | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 1 | 10 (Ours) | 100 | 0.1 | 1 (Ours) | 10 | 100 | 0.1 | 1 (Ours) | 10 | 100 | |
| EN ↑ | 7.069 | 7.167 | 7.499 | 7.273 | 7.196 | 7.499 | 7.203 | 6.949 | 7.185 | 7.499 | 7.207 | 6.975 |
| AG ↑ | 4.415 | 5.037 | 5.263 | 4.386 | 5.076 | 5.263 | 5.217 | 5.027 | 4.778 | 5.263 | 5.015 | 4.615 |
| SF ↑ | 11.326 | 13.308 | 14.067 | 12.219 | 13.318 | 14.067 | 14.003 | 12.893 | 13.014 | 14.067 | 13.716 | 13.805 |
| FMI ↑ | 0.861 | 0.860 | 0.868 | 0.855 | 0.865 | 0.868 | 0.866 | 0.866 | 0.863 | 0.868 | 0.862 | 0.860 |
| VIF ↑ | 0.366 | 0.427 | 0.465 | 0.437 | 0.453 | 0.465 | 0.450 | 0.438 | 0.447 | 0.465 | 0.452 | 0.426 |
| UIQI ↑ | 0.849 | 0.861 | 0.868 | 0.858 | 0.856 | 0.868 | 0.853 | 0.862 | 0.857 | 0.868 | 0.860 | 0.852 |
| Datasets | LLVIP | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metrics | Precision ↑ | Recall ↑ | mAP@.5 ↑ | mAP@.95 ↑ | Precision ↑ | Recall ↑ | mAP@.5 ↑ | mAP@.95 ↑ |
| Infrared | 0.929 | 0.849 | 0.905 | 0.472 | 0.793 | 0.547 | 0.603 | 0.359 |
| Visible | 0.931 | 0.880 | 0.933 | 0.521 | 0.796 | 0.585 | 0.645 | 0.385 |
| GAN-FM | 0.928 | 0.847 | 0.915 | 0.467 | 0.765 | 0.528 | 0.579 | 0.362 |
| TarDAL | 0.939 | 0.882 | 0.923 | 0.489 | 0.766 | 0.570 | 0.618 | 0.355 |
| DeRUN | 0.936 | 0.885 | 0.937 | 0.520 | 0.736 | 0.585 | 0.631 | 0.368 |
| GAN-HA | 0.954 | 0.880 | 0.935 | 0.533 | 0.813 | 0.592 | 0.663 | 0.373 |
| HCSPNet | 0.958 | 0.885 | 0.947 | 0.566 | 0.825 | 0.603 | 0.668 | 0.406 |
| Tracker | LADCF | GFSDCF | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metrics | Accuracy ↑ | Failure ↓ | EAO ↑ | Accuracy ↑ | Failure ↓ | EAO ↑ |
| Infrared | 0.472 | 73.48 | 0.209 | 0.585 | 45.71 | 0.239 |
| Visible | 0.407 | 68.23 | 0.160 | 0.438 | 60.05 | 0.183 |
| GAN-FM | 0.519 | 41.22 | 0.195 | 0.586 | 38.35 | 0.262 |
| TarDAL | 0.469 | 48.57 | 0.178 | 0.493 | 46.22 | 0.203 |
| DeRUN | 0.417 | 36.82 | 0.173 | 0.457 | 60.37 | 0.178 |
| GAN-HA | 0.572 | 38.47 | 0.226 | 0.618 | 31.45 | 0.228 |
| HCSPNet | 0.596 | 37.32 | 0.231 | 0.630 | 29.43 | 0.267 |
| Metrics | U2Fusion | FusionGAN | DDcGAN | GANMcC | GAN-FM | TarDAL | DeRUN | GAN-HA | HCSPNet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EN ↑ | 4.085 | 4.223 | 4.275 | 3.443 | 4.271 | 3.109 | 3.953 | 4.813 | 4.935 |
| AG ↑ | 5.878 | 5.916 | 5.935 | 4.988 | 5.367 | 2.972 | 3.655 | 5.537 | 6.083 |
| VIF ↑ | 0.506 | 0.457 | 0.473 | 0.298 | 0.383 | 0.306 | 0.517 | 0.553 | 0.675 |
| UIQI ↑ | 0.933 | 0.857 | 0.773 | 0.518 | 0.556 | 0.483 | 0.645 | 0.682 | 0.933 |
| Metrics | U2Fusion | FusionGAN | DDcGAN | GANMcC | GAN-FM | TarDAL | DeRUN | GAN-HA | HCSPNet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EN ↑ | 6.572 | 6.581 | 6.672 | 4.864 | 6.682 | 4.857 | 5.687 | 6.678 | 6.935 |
| AG ↑ | 3.769 | 3.853 | 4.738 | 3.652 | 4.657 | 5.384 | 3.768 | 5.083 | 5.169 |
| VIF ↑ | 0.364 | 0.513 | 0.625 | 0.438 | 0.702 | 0.656 | 0.347 | 0.567 | 0.772 |
| UIQI ↑ | 0.769 | 0.853 | 0.862 | 0.418 | 0.836 | 0.398 | 0.716 | 0.883 | 0.903 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, M.; Huang, G.; Ju, M.; Ma, K.-K. Rethinking Infrared and Visible Image Fusion from a Heterogeneous Content Synergistic Perception Perspective. Sensors 2025, 25, 4658. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25154658
Shen M, Huang G, Ju M, Ma K-K. Rethinking Infrared and Visible Image Fusion from a Heterogeneous Content Synergistic Perception Perspective. Sensors. 2025; 25(15):4658. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25154658
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Minxian, Gongrui Huang, Mingye Ju, and Kai-Kuang Ma. 2025. "Rethinking Infrared and Visible Image Fusion from a Heterogeneous Content Synergistic Perception Perspective" Sensors 25, no. 15: 4658. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25154658
APA StyleShen, M., Huang, G., Ju, M., & Ma, K.-K. (2025). Rethinking Infrared and Visible Image Fusion from a Heterogeneous Content Synergistic Perception Perspective. Sensors, 25(15), 4658. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25154658





