MCAF-Net: Multi-Channel Temporal Cross-Attention Network with Dynamic Gating for Sleep Stage Classification
Abstract
1. Introduction
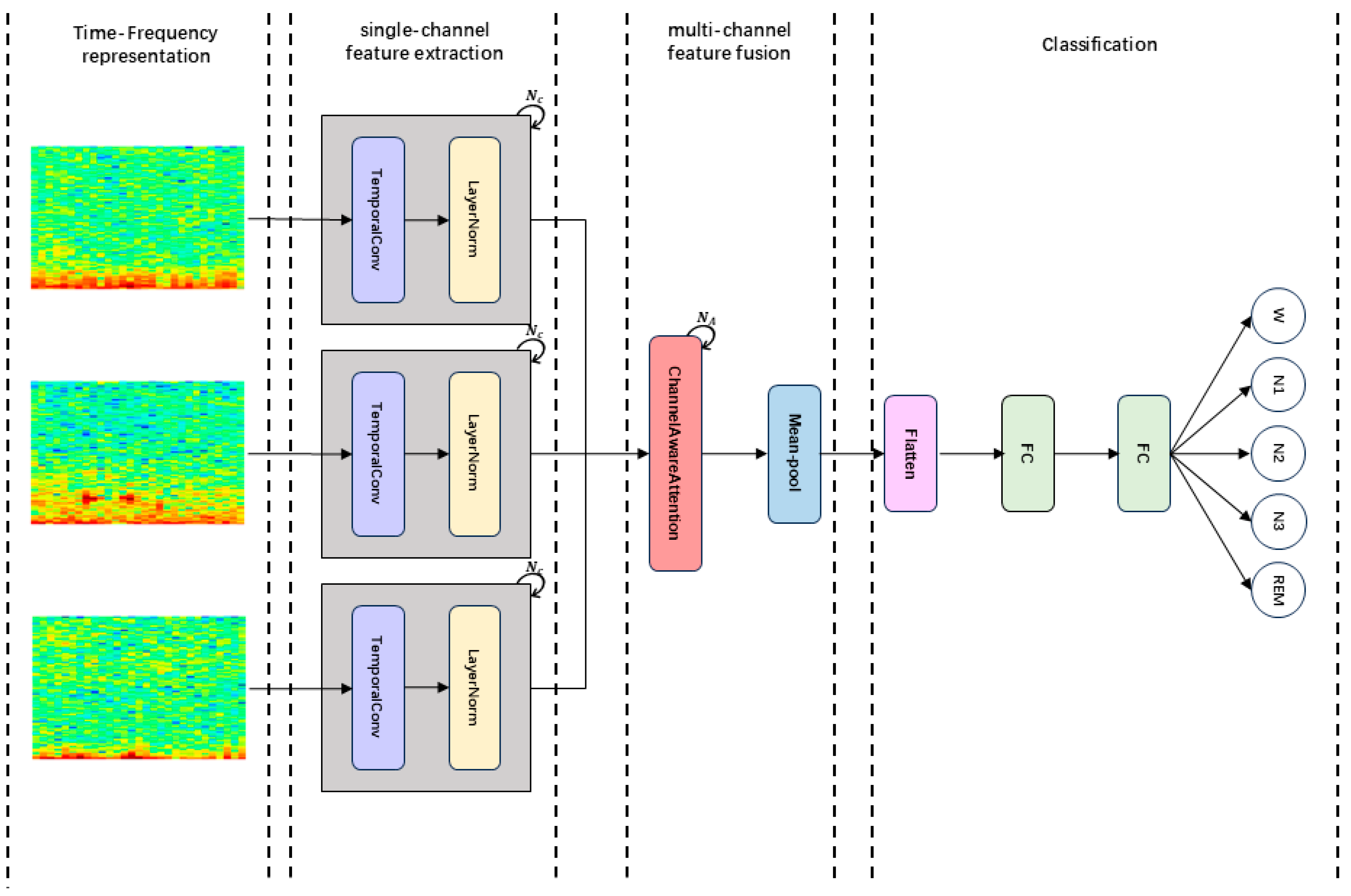
2. Methodology
2.1. Time-Frequency Representation
2.2. Single-Channel Feature Extraction
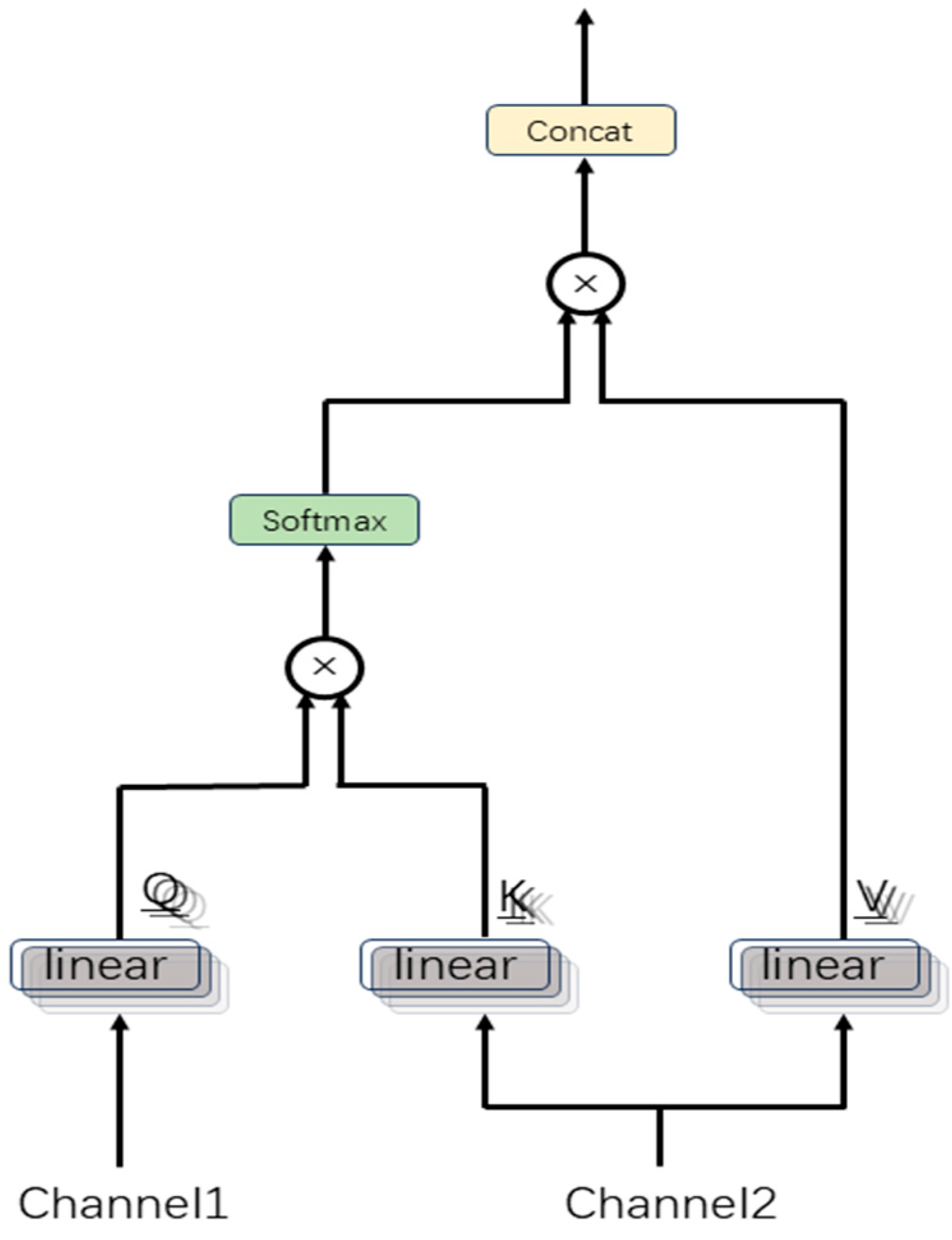
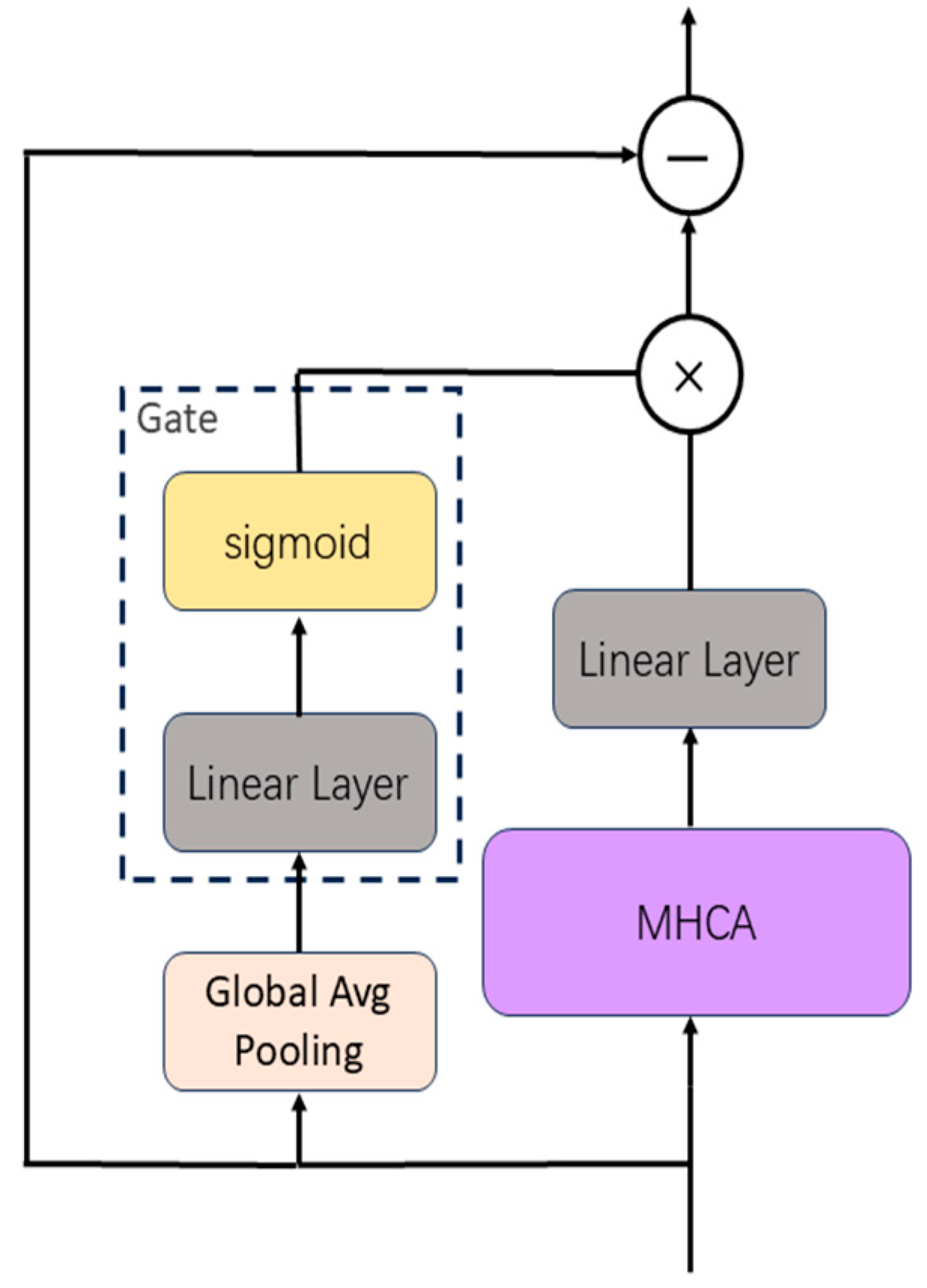
2.3. Multi-Channel Feature Fusion
2.4. Classification
2.5. Experiments
2.5.1. Dataset
2.5.2. Parameter
3. Experimental Results
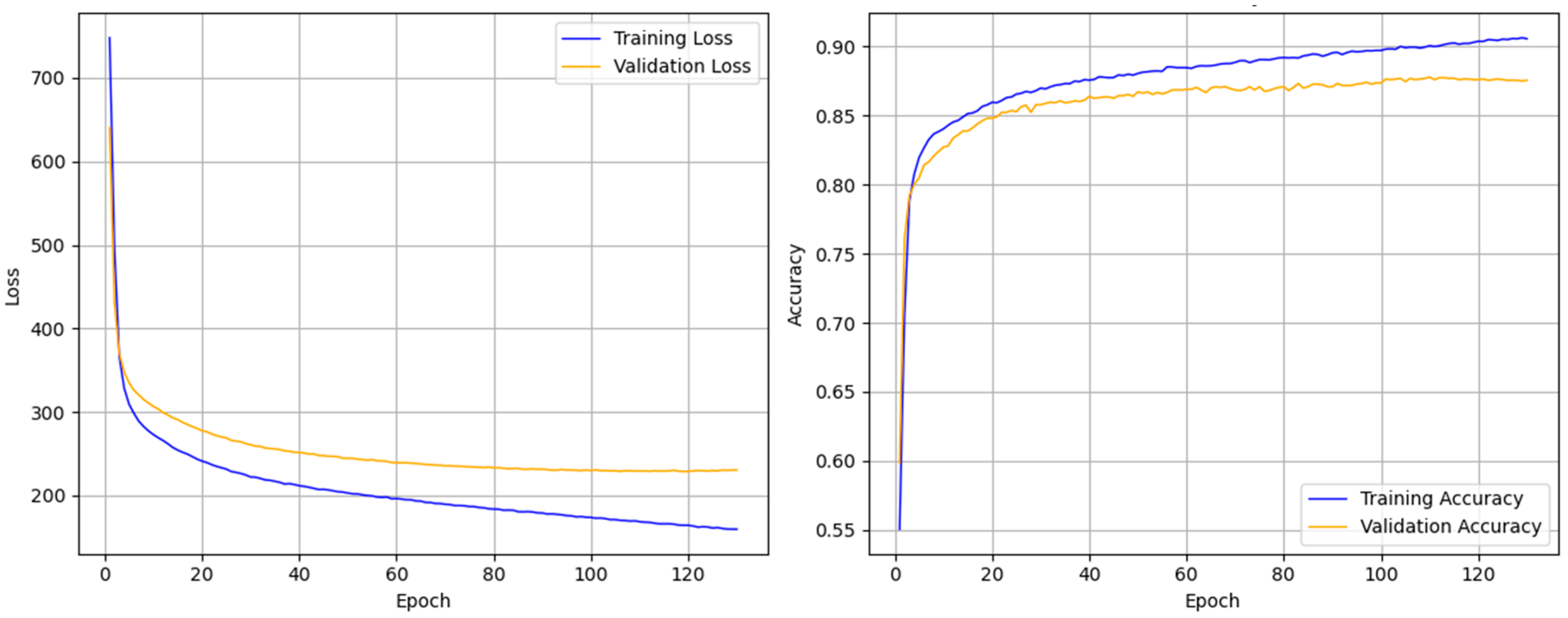
3.1. Sleep Staging Performance
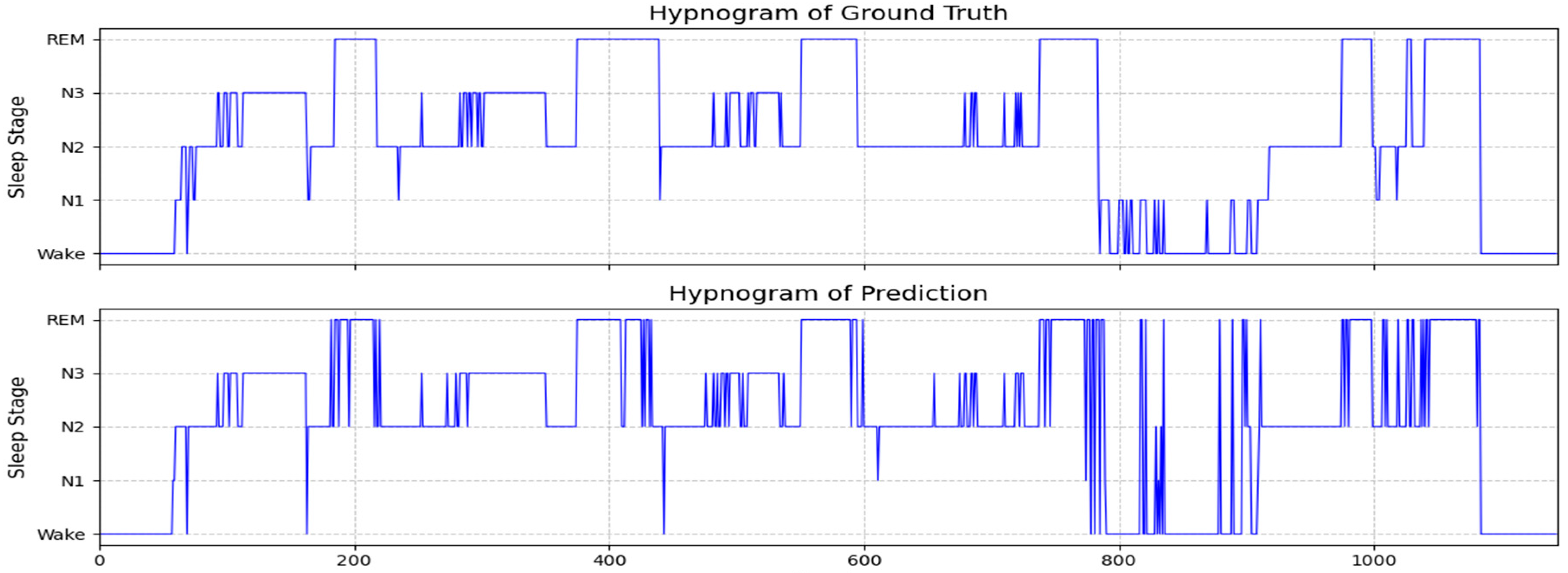
3.2. Hypnogram
3.3. Performance Comparison
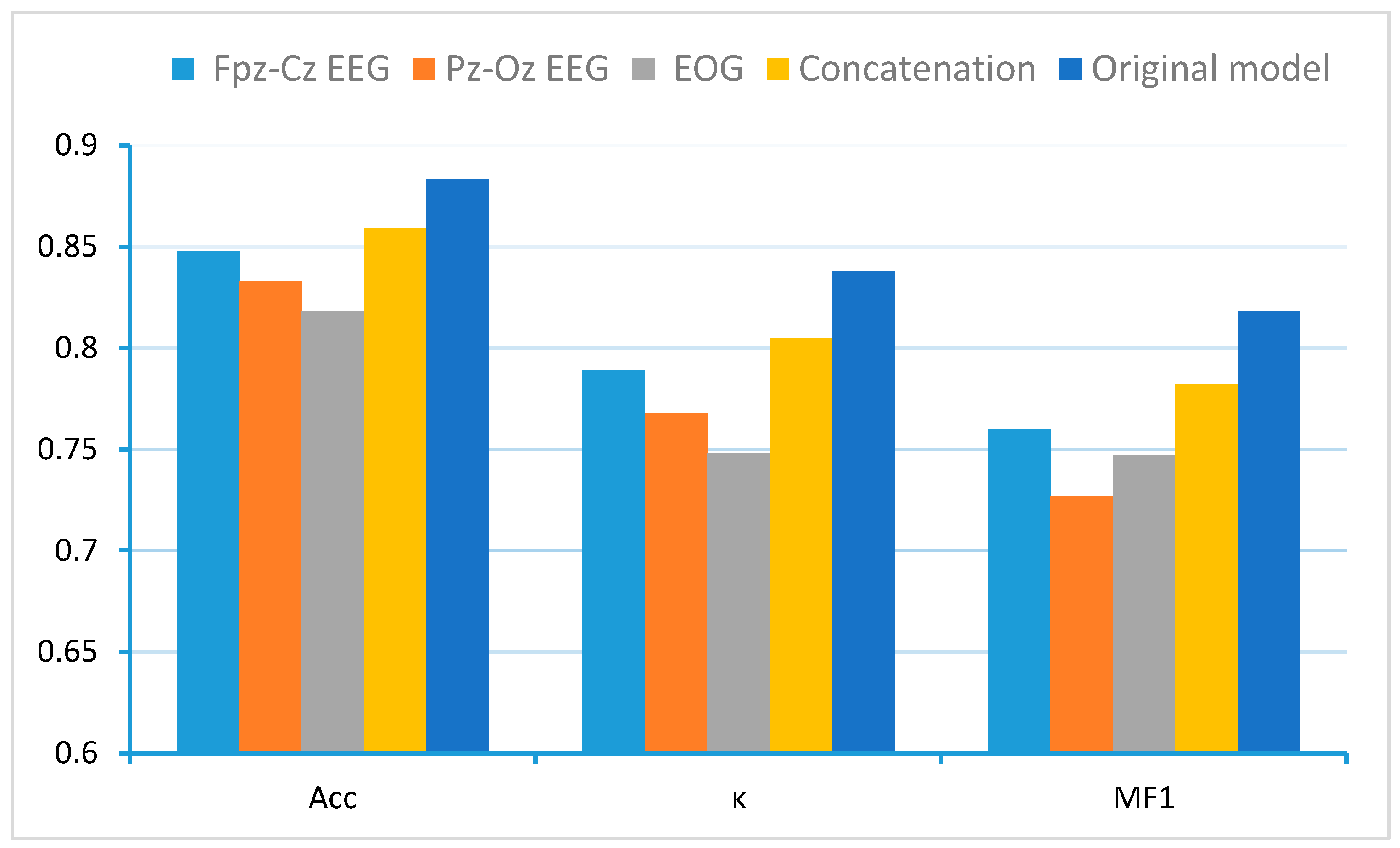
3.4. Ablation Study on Multi-Channel Fusion
- Fpz-Cz EEG: A single-channel feature extraction block processing only the Fpz-Cz EEG channel.
- Pz-Oz EEG: A single-channel feature extraction block processing only the Pz-Oz EEG channel.
- EOG: A single-channel feature extraction block processing only the EOG channel.
- Concatenation: The three channels were concatenated at the input stage without employing any multi-channel feature fusion block.
3.5. Ablation Study on TemporalConv and Channel-Aware Attention
3.6. Analysis of Channel-Wise Attention Weights in MCAF-Net
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goldstein, A.N.; Walker, M.P. The role of sleep in emotional brain function. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2014, 10, 679–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chattu, V.K.; Manzar, M.D.; Kumary, S.; Burman, D.; Spence, D.W.; Pandi-Perumal, S.R. The global problem of insufficient sleep and its serious public health implications. Healthcare 2018, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, F.; Dan, Y. Circuit-based interrogation of sleep control. Nature 2016, 538, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenan, S.A. An overview of polysomnography. Handb. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2005, 6, 33–50. [Google Scholar]
- Iber, C. The AASM manual for the scoring of sleep and associated events. In Rules, Terminology and Technical Specifications, 1st ed.; American Academy of Sleep Medicine: Westchester, IL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Berry, R.B.; Brooks, R.; Gamaldo, C.; Harding, S.M.; Lloyd, R.M.; Quan, S.F.; Troester, M.T.; Vaughn, B.V. AASM scoring manual updates for 2017 (version 2.4). J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2017, 13, 665–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, A.; Younes, M.; Kuna, S.T.; Benca, R.; Kushida, C.A.; Walsh, J.; Hanlon, A.; Staley, B.; Pack, A.I.; Pien, G.W. Performance of an automated polysomnography scoring system versus computer-assisted manual scoring. Sleep 2013, 36, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunes, S.; Polat, K.; Yosunkaya, S. Efficient sleep stage recognition system based on EEG signal using k-means clustering based feature weighting. Expert Syst. Appl. 2010, 37, 7922–7928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koley, B.; Dey, D. An ensemble system for automatic sleep stage classification using single channel EEG signal. Comput. Biol. Med. 2012, 42, 1186–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alickovic, E.; Subasi, A. Ensemble SVM method for automatic sleep stage classification. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2018, 67, 1258–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cui, L.; Tao, S.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, G.Q. HyCLASSS: A hybrid classifier for automatic sleep stage scoring. IEEE J. Biomed.Health Inform. 2018, 22, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memar, P.; Faradji, F. A novel multi-class EEG-based sleep stage classification system. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2018, 26, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadhav, P.; Mukhopadhyay, S. Automated sleep stage scoring using time-frequency spectra convolution neural network. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 2510309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sors, A.; Bonnet, S.; Mirek, S.; Vercueil, L.; Payen, J.F. A convolutional neural network for sleep stage scoring from raw single-channel EEG. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2018, 42, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, H.; Andreotti, F.; Cooray, N.; Chen, O.Y.; de Vos, M. SeqSleepNet: End-to-end hierarchical recurrent neural network for sequence-to-sequence automatic sleep staging. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2019, 27, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supratak, A.; Dong, H.; Wu, C.; Guo, Y. DeepSleepNet: A model for automatic sleep stage scoring based on raw single-channel EEG. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2017, 25, 1998–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.; Afghah, F.; Acharya, U.R. SleepEEGNet: Automated sleep stage scoring with sequence to sequence deep learning approach. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkalainen, H.; Aakko, J.; Nikkonen, S.; Kainulainen, S.; Leino, A.; Duce, B.; Afarem, I.O.; Myllymaa, S.; Töyräs, J.; Leppänen, T. Accurat deep learning-based sleep staging in a clinical population with suspected obstructive sleep apnea. IEEE J.Biomed. Health Inform. 2020, 24, 2073–2081. [Google Scholar]
- Eldele, E.; Chen, Z.; Liu, C.; Wu, M.; Kwoh, C.K.; Li, X.; Guan, C. An attention-based deep learning approach for sleep stage classification with single-channel EEG. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2021, 29, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, H.; Mikkelsen, K.; Chen, O.Y.; Koch, P.; Mertins, A.; Vos, M.D. SleepTransformer: Automatic sleep staging with interpretability and uncertainty quantification. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 69, 2456–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Cai, X.; Jiao, Z. Multi-modal physiological signals based squeeze-and-excitation network with domain adversarial learning for sleep staging. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 3464–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Li, X.; Liang, S.; Wang, L.; Duan, Q.; Yang, H.; Zhang, C.; Li, L.; Li, X.; Liao, X. MultiChannelSleepNet: A Transformer-Based Model for Automatic Sleep Stage Classification With PSG. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2023, 27, 4204–4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loshchilov, I.; Hutter, F. Decoupled Weight Decay Regularization. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1711.05101. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Kemp, B.; Zwinderman, A.H.; Tuk, B.; Kamphuisen, H.A.C.; Oberye, J.J.L. Analysis of a sleep-dependent neuronal feedback loop: The slowwave microcontinuity of the EEG. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2000, 47, 1185–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberger, A.L.; Amaral, L.A.; Glass, L.; Hausdorff, J.M.; Ivanov, P.C.; Mark, R.G.; Mietus, J.E.; Moody, G.B.; Peng, C.-K.; Stanley, H.E. Physiobank, physiotoolkit, and physionet-Components of a new research resource for complex physiologic signals. Circulation 2000, 101, E215–E220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rechtschaffen, A.; Kales, A. A Manual of Standardized Terminology, Techniques and Scoring System for Sleep Stages of Human Subjects; U.S. National Institute of Neurological Diseases and Blindness, NIH: Bethesda, MD, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Yan, R.; Mahini, R.; Wei, L.; Wang, Z.; Mathiak, K.; Liu, R.; Cong, F. End-to-end sleep staging using convolutional neural network in raw single-channel EEG. Biomed. Signal Process Control 2021, 63, 102203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. A coefficient of agreement for nominal scales. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1960, 20, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, D.D.; Schapire, R.E.; Callan, J.P.; Papka, R. Training algorithms for linear text classifiers. In Proceedings of the 19th Annual International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Zurich, Switzerland, 18–22 August 1996; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 1996; pp. 298–306. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, W.; Wang, Z.; Hong, H.; Chi, Z.; Feng, D.D.; Grunstein, R.; Gordon, C. A residual based attention model for EEG based sleep staging. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2020, 24, 2833–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Li, J.; Guo, Y. Sleepcontextnet: A temporal context network for automatic sleep staging based single-channel EEG. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2022, 220, 106806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michielli, N.; Acharya, U.R.; Molinari, F. Cascaded LSTM recurrent neural network for automated sleep stage classification using singlechannel EEG signals. Comput. Biol. Med. 2019, 106, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tautan, A.-M.; Rossi, A.C.; Francisco, R.D.; Ionescu, B. Automatic sleep stage detection: A study on the influence of various PSG input signals. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. Annu. Int. Conf. 2020, 2020, 5330–5334. [Google Scholar]
- Piryatinska, A.; Woyczynski, W.A.; Scher, M.S.; Loparo, K.A. Optimal channel selection for analysis of EEG-sleep patterns of neonates. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2012, 106, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Dateset | Subjects | W | N1 | N2 | N3 | REM | Total Sample |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SleepEDF-20 | 20 | 9118 | 2804 | 17,799 | 5703 | 77,177 | 43,141 |
| 21.10% | 6.50% | 41.30% | 13.20% | 17.90% | |||
| SleepEDF-78 | 79 | 66,822 | 21,522 | 69,132 | 13,039 | 25,835 | 196,350 |
| 14.30% | 3.20% | 43.70% | 18.50% | 20.30% |
| Predicted | MCAF-Net | MultiChannelNet [22] | AttnSleep [19] | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W | N1 | N2 | N3 | REM | PR | RE | F1 | PR | RE | F1 | PR | RE | F1 | |
| W | 8652 | 224 | 98 | 15 | 150 | 92.8 | 94.7 | 93.7 | 93.4 | 92.1 | 92.8 | 89.6 | 89.7 | 89.7 |
| N1 | 454 | 1096 | 657 | 5 | 610 | 65.2 | 38.8 | 48.7 | 55.0 | 44.4 | 49.1 | 47.1 | 39.1 | 42.8 |
| N2 | 106 | 206 | 16,525 | 411 | 673 | 89.6 | 92.2 | 90.9 | 89.5 | 90.3 | 90.0 | 89.1 | 88.6 | 88.8 |
| N3 | 17 | 0 | 646 | 4768 | 4 | 91.7 | 87.7 | 89.6 | 89.1 | 89.5 | 89.3 | 80.7 | 89.8 | 90.2 |
| REM | 91 | 154 | 512 | 3 | 6955 | 82.9 | 90.1 | 86.4 | 82.3 | 87.5 | 84.8 | 76.1 | 82.2 | 79.0 |
| Predicted | MCAF-Net | MultiChannelNet [22] | AttnSleep [19] | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W | N1 | N2 | N3 | REM | PR | RE | F1 | PR | RE | F1 | PR | RE | F1 | |
| W | 57,878 | 2121 | 346 | 32 | 370 | 94.0 | 95.3 | 94.6 | 95.0 | 93.1 | 94.0 | 92.3 | 91.8 | 92.0 |
| N1 | 2902 | 9061 | 5713 | 36 | 1854 | 59.7 | 46.3 | 52.1 | 58.1 | 48.7 | 53.0 | 45.3 | 39.2 | 42.1 |
| N2 | 412 | 2682 | 56,410 | 1265 | 2078 | 84.7 | 89.8 | 87.2 | 84.0 | 90.0 | 86.9 | 83.5 | 86.5 | 85 |
| N3 | 44 | 11 | 2326 | 9457 | 16 | 87.6 | 79.8 | 83.5 | 83.1 | 80.7 | 81.8 | 82.3 | 82.0 | 82.1 |
| REM | 343 | 1312 | 1805 | 5 | 20,021 | 82.3 | 85.2 | 83.7 | 82.0 | 83.1 | 82.6 | 73.1 | 75.3 | 74.2 |
| Overall Metrics | Per-Class F1_Score | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dataset | System | Acc | κ | MF1 | W | N1 | N2 | N3 | REM |
| SleepEDF-20 | MCAF-Net | 88.3 | 0.84 | 81.8 | 93.7 | 48.7 | 90.9 | 89.6 | 86.4 |
| MultiChannelSleepNet [22] | 87.2 | 0.82 | 81.2 | 92.8 | 49.1 | 90.0 | 89.3 | 84.8 | |
| SeqSleepNet [15] | 86.0 | 0.81 | 79.7 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| AttnSleep [19] | 84.4 | 0.79 | 78.1 | 89.7 | 42.8 | 88.8 | 90.2 | 79.0 | |
| DeepSleepNet [16] | 82.0 | 0.76 | 76.9 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| SleepEEGNet [17] | 84.3 | 0.79 | 79.7 | 89.2 | 52.2 | 89.8 | 85.1 | 85.0 | |
| SleepEDF-78 | MCAF-Net | 85.6 | 80.0 | 80.1 | 94.6 | 52.1 | 87.2 | 83.5 | 83.7 |
| MultiChannelSleepNet [22] | 85.0 | 0.79 | 79.6 | 94.0 | 53.0 | 86.9 | 81.8 | 82.6 | |
| SeqSleepNet [15] | 83.8 | 0.78 | 78.2 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| AttnSleep [19] | 81.3 | 0.74 | 75.3 | 92.0 | 42.1 | 85.0 | 82.1 | 74.2 | |
| SleepTransformer [20] | 81.4 | 0.74 | 74.3 | 91.7 | 40.4 | 84.3 | 77.9 | 77.2 | |
| SleepEEGNet [17] | 80.0 | 0.73 | 73.6 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Model Configuration | ACC | κ | MF1 | Sens | Spec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TemporalConv | 87.4 | 0.83 | 81.0 | 0.80 | 0.96 |
| Channel-Aware Attention | 86.0 | 0.80 | 78.6 | 0.77 | 0.96 |
| TemporalConv + Channel-Aware Attention | 88.3 | 0.84 | 81.8 | 0.81 | 0.97 |
| Input Channel | Overall Metrics | Per-Class F1-Score | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acc | κ | MF1 | W | N1 | N2 | N3 | REM | |
| Fpz-cz | 80.7 | 0.73 | 72.4 | 91.6 | 37.3 | 83.7 | 78.7 | 70.6 |
| Fpz-cz + Pz-Oz | 84.9 | 0.79 | 78.7 | 94.8 | 47.1 | 87.0 | 83.6 | 80.9 |
| Fpz-cz + EOG | 85.0 | 0.79 | 78.9 | 94.0 | 47.0 | 86.8 | 83.1 | 83.7 |
| Fpz-cz + Pz-Oz + EOG | 85.6 | 80.0 | 80.1 | 94.6 | 52.1 | 87.2 | 83.5 | 83.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y. MCAF-Net: Multi-Channel Temporal Cross-Attention Network with Dynamic Gating for Sleep Stage Classification. Sensors 2025, 25, 4251. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25144251
Xu X, Wang Q, Wang C, Zhang Y. MCAF-Net: Multi-Channel Temporal Cross-Attention Network with Dynamic Gating for Sleep Stage Classification. Sensors. 2025; 25(14):4251. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25144251
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Xuegang, Quan Wang, Changyuan Wang, and Yaxin Zhang. 2025. "MCAF-Net: Multi-Channel Temporal Cross-Attention Network with Dynamic Gating for Sleep Stage Classification" Sensors 25, no. 14: 4251. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25144251
APA StyleXu, X., Wang, Q., Wang, C., & Zhang, Y. (2025). MCAF-Net: Multi-Channel Temporal Cross-Attention Network with Dynamic Gating for Sleep Stage Classification. Sensors, 25(14), 4251. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25144251





