Robust Estimation of Earthquake Magnitude in Indonesia Using PGD Scaling Law from Regional High-Rate GNSS Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. High-Rate GNSS Data Collection and Processing
2.2. PGD Scaling Law
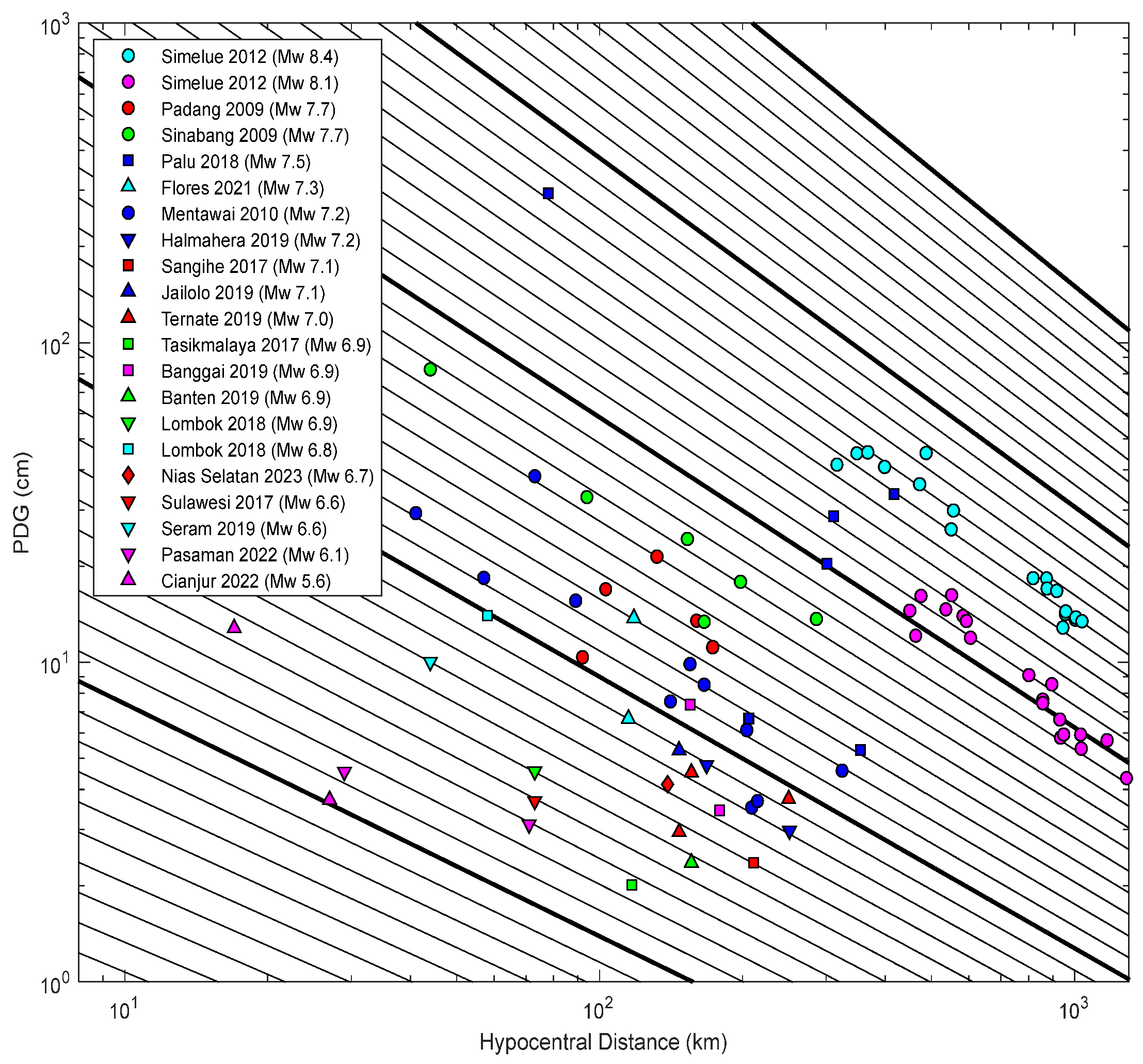
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hutchings, S.J.; Mooney, W.D. The Seismicity of Indonesia and Tectonic Implications. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2021, 22, e2021GC009812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newcomb, K.R.; McCann, W.R. Seismic history and seismotectonics of the Sunda arc. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1987, 92, 421–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, Y.; Prawirodirdjo, L.; Genrich, J.F.; Stevens, C.W.; McCaffrey, R.; Subarya, C.; Puntodewo, S.S.O.; Calais, E. Crustal motion in Indonesia from Global Positioning System measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlton, T.R. Tertiary evolution of the Eastern Indonesia Collision Complex. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2000, 18, 603–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syamsidik; Nugroho, A.; Oktari, R.S.; Fahmi, M. Aceh Pasca 15 Tahun Tsunami: Kilas Balik dan Proses Pemulihan; Tsunami and Disaster Research Center (TDMRC): Banda Aceh, Indonesia, 2019; pp. I.5–II.4. [Google Scholar]
- Kerr, R.A. Failure to Gauge the Quake Crippled the Warning Effort. Science 2005, 307, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, S.; Okal, E. Speed and size of the Sumatra earthquake. Nature 2005, 434, 581–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blewitt, G.; Kreemer, C.; Hammond, W.C.; Plag, H.-P.; Stein, S.; Okal, E. Rapid determination of earthquake magnitude using GPS for tsunami warning systems. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L11309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, T.J.; Houlié, N.; Hildyard, M.; Iwabuchi, T. Real-time, reliable magnitudes for large earthquakes from 1 Hz GPS precise point positioning: The 2011 Tohoku-Oki (Japan) earthquake. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L12302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Tsushima, H.; Miura, S.; Hino, R.; Takasu, T.; Fujimoto, H.; Iinuma, T.; Tachibana, K.; Demachi, T.; et al. Quasi real-time fault model estimation for near-field tsunami forecasting based on RTK-GPS analysis: Application to the 2011 Tohoku-Oki earthquake (Mw 9.0). J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, B02311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilich, A.; Cassidy, J.F.; Larson, K.M. GPS seismology: Application to the 2002 Mw 7.9 Denali fault earthquake. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2008, 98, 593–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowell, B.W.; Melgar, D.; Bock, Y.; Haase, J.S.; Geng, J. Earthquake magnitude scaling using seismogeodetic data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 6089–6094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melgar, D.; Crowell, B.W.; Geng, J.; Allen, R.M.; Bock, Y.; Riquelme, S.; Hill, E.M.; Protti, M.; Ganas, A. Earthquake magnitude calculation without saturation from the scaling of peak ground displacement. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 5197–5205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowell, B.W.; Schmidt, D.A.; Bodin, P.; Vidale, J.E.; Gomberg, J.; Hartog, J.R.; Kress, V.C.; Melbourne, T.I.; Santillan, M.; Minson, S.E.; et al. Demonstration of the Cascadia G-FAST Geodetic Earthquake Early Warning System for the Nisqually, Washington, earthquake. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2016, 87, 930–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhl, C.J.; Melgar, D.; Geng, J.; Goldberg, D.E.; Crowell, B.W.; Allen, R.M.; Bock, Y.; Barrientos, S.; Riquelme, S.; Baez, J.C.; et al. A global database of strong-motion displacement GNSS recordings and an example application to PGD scaling. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2019, 90, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Li, Y.; Shan, X.; Zhu, C. Earthquake Magnitude Estimation from High-Rate GNSS Data: A Case Study of the 2021 Mw7.3 Maduo Earthquake. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhl, C.J.; Melgar, D.; Grapenthin, R.; Allen, R.M. The value of real-time GNSS to earthquake early warning. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 8311–8319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, J.; Xu, C.; Li, X. Scaling earthquake magnitude in real time with high-rate GNSS peak ground displacement from variometric approach. GPS Solut. 2020, 24, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melgar, D.; Hayes, G.P. Characterizing large earthquakes before rupture is complete. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaav2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melgar, D.; Melbourne, T.I.; Crowell, B.W.; Geng, J.; Szeliga, W.; Scrivner, C.; Santillan, M.; Goldberg, D.E. Real-time high-rate GNSS displacements: Performance demonstration during the 2019 Ridgecrest, California, Earthquakes. Seismol Res. Lett. 2020, 91, 1943–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, C.; Liang, H.; Li, Y.; Zhan, W. Earthquake Source Parameters Estimated from High-Rate Multi-GNSS Data: A Case Study of the 2022 M6.9 Menyuan Earthquake. Acta Geophys. 2023, 71, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solak, H.İ.; Şentürk, M.D.; Çakanşimşek, E.B.; Yaşar, Ş.Ş.; Eyübagil, E.E.; Erdoğan, A.O.; Aktuğ, B.; Yiğit, C.Ö.; Tiryakioğlu, İ. Earthquake Magnitude Estimation Based on Peak Ground Displacements Recorded by High-Rate GNSS for February 6, 2023, Earthquake Sequence in Turkiye. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2024, 139, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundakir, I.A.; Mukti, F.Z.; Mauradhia, A.; Fitri, W.; Wibowo, S.T. Ina-CORS Growth Story. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2024, 1418, 012027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- InaTEWS Earthquake Repository. Available online: https://repogempa.bmkg.go.id/ (accessed on 17 December 2024).
- Feng, L.; Hill, E.M.; Banerjee, P.; Hermawan, I.; Tsang, L.L.H.; Natawidjaja, D.H.; Suwargadi, B.W.; Sieh, K. A Unified GPS-Based Earthquake Catalog for the Sumatran Plate Boundary between 2002 and 2013. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2015, 120, 3566–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global CMT Catalog Search. Available online:https://www.globalcmt.org/CMTsearch.html (accessed on 17 December 2024).
- Geng, J.; Teferle, F.N.; Shi, C.; Meng, X.; Dodson, A.H.; Liu, J. Ambiguity Resolution in Precise Point Positioning with Hourly Data. GPS Solut. 2009, 13, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Meng, X.; Dodson, A.H.; Teferle, F.N. Integer Ambiguity Resolution in Precise Point Positioning: Method Comparison. J. Geod. 2010, 84, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Shi, C. Rapid Initialization of Real-Time PPP by Resolving Undifferenced GPS and GLONASS Ambiguities Simultaneously. J. Geod. 2017, 91, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Chen, X.; Pan, Y.; Mao, S.; Li, C.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, K. PRIDE PPP-AR: An Open-Source Software for GPS PPP Ambiguity Resolution. GPS Solut. 2019, 23, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saastamoinen, J. Contributions to the Theory of Atmospheric Refraction. Bull. Géod. 1973, 47, 13–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, J.; Niell, A.; Tregoning, P.; Schuh, H. Global Mapping Function (GMF): A New Empirical Mapping Function Based on Numerical Weather Model Data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L07304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melbourne, W.G. The Case for Ranging in GPS-Based Geodetic Systems. In Proceedings of the 1st International Symposium on Precise Positioning with the Global Positioning System, Rockville, MD, USA, 15–19 April 1985; pp. 373–386. [Google Scholar]
- Wübbena, G. Software Developments for Geodetic Positioning with GPS Using TI-4100 Code and Carrier Measurements. In Proceedings of the 1st International Symposium on Precise Positioning with the Global Positioning System, Rockville, MD, USA, 15–19 April 1985; pp. 403–412. [Google Scholar]
- Petit, G.; Luzum, B. IERS Conventions (2010); IERS Technical Note No. 36; Verlag des Bundesamtes für Kartographie und Geodäsie: Frankfurt am Main, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Rothacher, M.; Schmid, R. ANTEX: The Antenna Exchange Format; Version 1.4; IGS Central Bureau: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Teunissen, P.J.G. The Least-Squares Ambiguity Decorrelation Adjustment: A Method for Fast GPS Integer Ambiguity Estimation. J. Geod. 1995, 70, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Yao, M.; Tang, S.; Liu, H.; Xing, P.; Zhang, Y. Data Quality Check and Visual Analysis of CORS Station Based on Anubis Software. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2020, 42, 1295–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kautsar, M.A. (Geospatial Information Agency of Indonesia, BIG, Cibinong). Personal Communication. 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, H.; Ampuero, J.P.; Meng, L.; Fielding, E.J.; Liang, C.; Milliner, C.W.D.; Feng, T.; Huang, H. Early and persistent supershear rupture of the 2018 magnitude 7.5 Palu earthquake. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socquet, A.; Hollingsworth, J.; Pathier, E.; Bouchon, M. Evidence of supershear during the 2018 magnitude 7.5 Palu earthquake from space geodesy. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Xu, C.; Wen, Y.; Wang, S.; Xu, G.; Zhao, Y.; Yi, L. The 2018 Mw 7.5 Palu Earthquake: A Supershear Rupture Event Constrained by InSAR and Broadband Regional Seismograms. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, W.; Broerse, T.; Kleptsova, O.; Nijholt, N.; Pietrzak, J.; Naeije, M.; Lhermitte, S.; Visser, P.; Riva, R.; Shen, L.; et al. A Tsunami Generated by a Strike-Slip Event: Constraints from GPS and SAR Data on the 2018 Palu Earthquake. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2022, 127, e2022JB024191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, R.; Zheng, J.; Geng, J.; Shu, Y.; Shi, C.; Liu, J. Earthquake Magnitude Scaling Using Peak Ground Velocity Derived from High-Rate GNSS Observations. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2021, 92, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riquelme, S.; Bravo, F.; Melgar, D.; Benavente, R.; Geng, J.; Barrientos, S.; Campos, J. W-phase Source Inversion Using High-Rate Regional GPS Data for Large Earthquakes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 3178–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Bock, Y.; Melgar, D.; Crowell, B.W.; Haase, J.S. A New Seismogeodetic Approach Applied to GPS and Accelerometer Observations of the 2012 Brawley Seismic Swarm: Implications for Earthquake Early Warning. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2013, 14, 2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Direktorat Gempabumi dan Tsunami, Badan Meteorologi Klimatologi dan Geofisika (BMKG). Standar Operasional Prosedur (SOP) Gempabumi National Tsunami Warning Center (NTWC); BMKG: Jakarta, Indonesia,, 2025; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Gutenberg, B. Amplitude of surface waves and magnitudes of shallow earthquakes. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1945, 35, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessel, P.; Smith, W.H.F.; Scharroo, R.; Luis, J.; Wobbe, F. Generic Mapping Tools: Improved version released. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2013, 94, 409–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Item | Strategies |
|---|---|
| PPP mode | Ionospheric-free (IF) combination PPP |
| Observation | GPS/GLONASS/Galileo pseudorange and phase observation |
| Sampling rate | 1 Hz |
| Signal frequency | GPS(LI/L2), GLONASS(L1/L2), Galileo(E1/E5a) |
| Satellite orbit, clock, and ERP | WUM Rapid product |
| Cutoff elevation | 7° |
| Estimation method | Least-squares principle of the parameter elimination–recovery method |
| Coordinate reference system | IGS14 |
| Antenna phase center correction | Corrected using IGS14.atx in ANTEX format |
| Tropospheric delay | Corrected by the Saastamoinen model; combined with GMF projection |
| Ionospheric delay | Eliminated by the IF combination |
| Tide correction | IERS 2010 convention |
| Cycle slip detection | GF + MW |
| Ambiguity resolution | LAMBDA for narrow lane and rounding for wide lane |
| No | Event Name | Origin Time (UTC) | Longitude (°) | Latitude (°) | Depth (km) | Mechanism | Mw | MPGD | Number of GNSS Station |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Padang, West Sumatra | 30 September 2009 10:16:10 | 99.88 | −0.80 | 81 | Reverse | 7.6 | 7.35 ± 0.39 | 5 |
| 2 | Sinabang, North Sumatra | 6 April 2010 22:15:03 | 97.11 | 2.24 | 29 | Thrust | 7.7 | 7.68 ± 0.11 | 6 |
| 3 | Mentawai, West Sumatra | 25 October 2010 14:42:20 | 100.16 | −3.41 | 10 | Reverse | 7.1 | 7.15 ± 0.21 | 11 |
| 4 | Simelue, Aceh | 11 April 2012 08:38:34 | 93.03 | 2.31 | 10 | Strike slip | 8.4 | 8.53 ± 0.15 | 18 |
| 5 | Simelue, Aceh | 11 April 2012 10:43:11 | 92.41 | 0.73 | 26 | Strike slip | 8.1 | 8.03 ± 0.12 | 19 |
| 6 | Sangihe, North Sulawesi | 28 April 2017 20:23:18 | 125.00 | 5.45 | 10 | Reverse | 7.1 | 6.59 ± 0.51 | 1 |
| 7 | Palu, Central Sulawesi | 29 May 2017 14:35:23 | 120.44 | −1.29 | 11 | Normal | 6.6 | 6.38 ± 0.22 | 1 |
| 8 | Tasikmalaya, West Java | 15 December 2017 16:47:58 | 108.11 | −7.75 | 107 | Strike slip | 7.2 | 6.25 ± 0.65 | 1 |
| 9 | Lombok, West Nusa Tenggara | 5 August 2018 11:46:37 | 116.47 | −8.35 | 32 | Reverse | 6.8 | 6.98 ± 0.18 | 1 |
| 10 | Lombok, West Nusa Tenggara | 19 August 2018 14:56:27 | 116.7 | −8.37 | 18 | Reverse | 6.9 | 6.50 ± 0.40 | 1 |
| 11 | Palu-Donggala, Central Sulawesi | 28 September 2018 10:02:44 | 119.85 | −0.22 | 10 | Strike slip | 7.5 | 7.98 ± 0.74 | 6 |
| 12 | Banggai Island, Central Sulawesi | 12 April 2019 11:40:50 | 122.59 | −1.89 | 23 | Strike slip | 6.8 | 6.91 ± 0.18 | 2 |
| 13 | Ternate, North Maluku | 7 July 2019 15:08:42 | 126.16 | 0.51 | 47 | Reverse | 7.0 | 6.77 ± 0.28 | 3 |
| 14 | Halmahera, North Maluku | 14 July-2019 09:10:51 | 128.1 | −0.54 | 17 | Strike slip | 7.1 | 6.84 ± 0.36 | 2 |
| 15 | Sumur, Banten | 2 August 2019 12:03:27 | 104.79 | −7.27 | 55 | Reverse | 6.9 | 6.46 ± 0.44 | 1 |
| 16 | Ambon, Maluku | 25 September -2019 23:46:45 | 128.45 | −3.42 | 10 | Strike slip | 6.6 | 6.69 ± 0.09 | 1 |
| 17 | Jailolo, North Maluku | 14 November 2019 16:17:43 | 126.37 | 1.66 | 62 | Reverse | 7.1 | 6.88 ± 0.22 | 1 |
| 18 | Flores, East Nusa Tenggara | 14 December 2021 03:20:23 | 122.23 | −7.59 | 10 | Strike slip | 7.3 | 7.09 ± 0.29 | 2 |
| 19 | Pasaman, West Sumatra | 25 February 2022 01:39:29 | 99.93 | 0.14 | 10 | Strike slip | 6.1 | 6.21 ± 0.13 | 2 |
| 20 | Nias Selatan, West Sumatra | 13 March 2022 21:09:22 | 98.5 | −0.71 | 25 | Reverse | 6.7 | 6.72 ± 0.02 | 1 |
| 21 | Cianjur, West Java | 21 November 2022 06:21:10 | 107.03 | −6.85 | 11 | Strike slip | 5.6 | 6.22 ± 0.66 | 2 |
| A | B | C | HR GNSS Data | Origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −4.434 | 1.047 | −0.138 | Global, 10 earthquakes, 1321 HR GNSS Data | Melgar et al. (2015) [13] |
| −6.687 | 1.500 | −0.214 | Global, 3 earthquakes, 112 HR GNSS Data | Crowell et al. (2016) [14] |
| −5.919 | 1.009 | −0.145 | Global, 29 earthquakes, 3433 HR GNSS Data | Ruhl et al. (2019) [15] |
| −4.729 | 1.005 | −0.121 | Regional (Indonesia), 21 earthquakes, 87 HR GNSS Data | This study |
| No | Earthquake | PGD Scaling Law (MPGD ± Std.Dev) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Melgar (2015) [13] | Crowell (2016) [14] | Ruhl (2019) [15] | This Study | ||
| 1 | Tehuepec Mw 8.2 2017, Mexico | 8.38 ± 0.35 | 8.60 ± 0.49 | 8.32 ± 0.36 | 8.13 ± 0.28 |
| 2 | Kaikoura Mw 7.8, 2016, New Zealand | 7.91 ± 0.21 | 8.06 ± 0.28 | 7.80 ± 0.20 | 7.77 ± 0.15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hardy, T.; Meilano, I.; Abidin, H.Z.; Susilo; Sudrajat, A.; Rohadi, S.; Kambali, R.A.P.; Rahman, A.; Samapta, B.T.; Al Kautsar, M.; et al. Robust Estimation of Earthquake Magnitude in Indonesia Using PGD Scaling Law from Regional High-Rate GNSS Data. Sensors 2025, 25, 4113. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25134113
Hardy T, Meilano I, Abidin HZ, Susilo, Sudrajat A, Rohadi S, Kambali RAP, Rahman A, Samapta BT, Al Kautsar M, et al. Robust Estimation of Earthquake Magnitude in Indonesia Using PGD Scaling Law from Regional High-Rate GNSS Data. Sensors. 2025; 25(13):4113. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25134113
Chicago/Turabian StyleHardy, Thomas, Irwan Meilano, Hasanuddin Z. Abidin, Susilo, Ajat Sudrajat, Supriyanto Rohadi, Retno Agung P. Kambali, Aditya Rahman, Brilian Tatag Samapta, Muhammad Al Kautsar, and et al. 2025. "Robust Estimation of Earthquake Magnitude in Indonesia Using PGD Scaling Law from Regional High-Rate GNSS Data" Sensors 25, no. 13: 4113. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25134113
APA StyleHardy, T., Meilano, I., Abidin, H. Z., Susilo, Sudrajat, A., Rohadi, S., Kambali, R. A. P., Rahman, A., Samapta, B. T., Al Kautsar, M., Manurung, A. S., & Widyadharma, P. H. (2025). Robust Estimation of Earthquake Magnitude in Indonesia Using PGD Scaling Law from Regional High-Rate GNSS Data. Sensors, 25(13), 4113. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25134113







