LKD-YOLOv8: A Lightweight Knowledge Distillation-Based Method for Infrared Object Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose an innovative framework for infrared object detection, LKD-YOLOv8, which leverages knowledge distillation to improve detection accuracy while maintaining a lightweight network suitable for real-time processing.
- LKD-YOLOv8 incorporates LDConv and CA. LDConv enhances spatial feature extraction by dynamically adjusting kernel offsets. CA improves feature alignment through channel-wise interaction, thereby enhancing the perception ability of small or blurred infrared targets.
- By distilling a lightweight student model (YOLOv8n) with a larger teacher model (YOLOv8s), our method effectively transfers knowledge and achieves a balance between model effectiveness and resource expense. The experimental results demonstrate that LKD-YOLOv8 outperforms baseline methods, improving mAP@0.5:0.95 by 1.18% while reducing parameter size by 7.9%.
2. Related Work
2.1. Model Compression and Acceleration
- Model pruning, which simplifies the model by discarding redundant weights and network links, thereby streamlining the model architecture without compromising performance.
- Knowledge distillation, which leverages a high-capacity teacher model to guide the training of a more compact student model, effectively transferring knowledge and facilitating the improvement of lightweight models.
- Tensor decomposition, which decomposes tensors to reduce the dimensionality of the model, thus decreasing storage requirements and enhancing computational efficiency.
2.2. Attention Mechanisms
3. Proposed Method
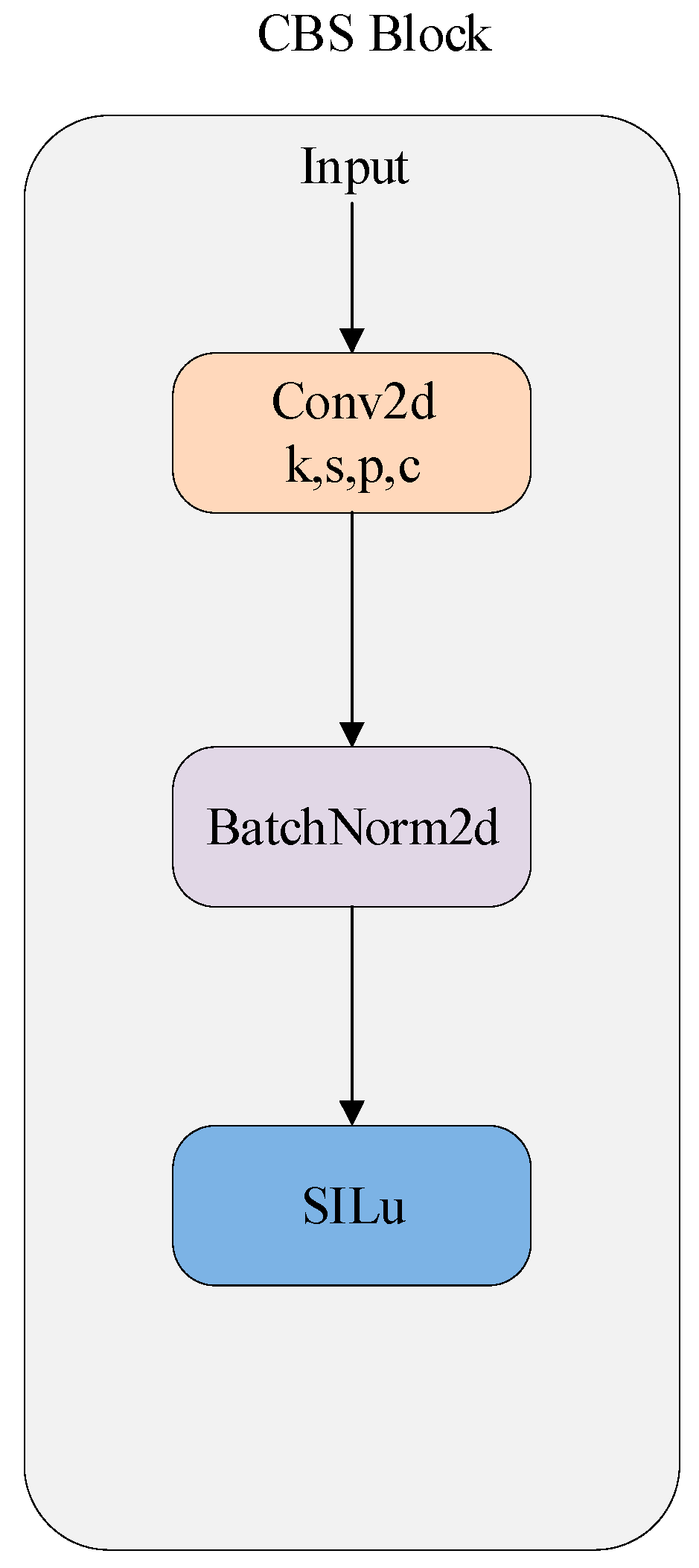
3.1. Network Design
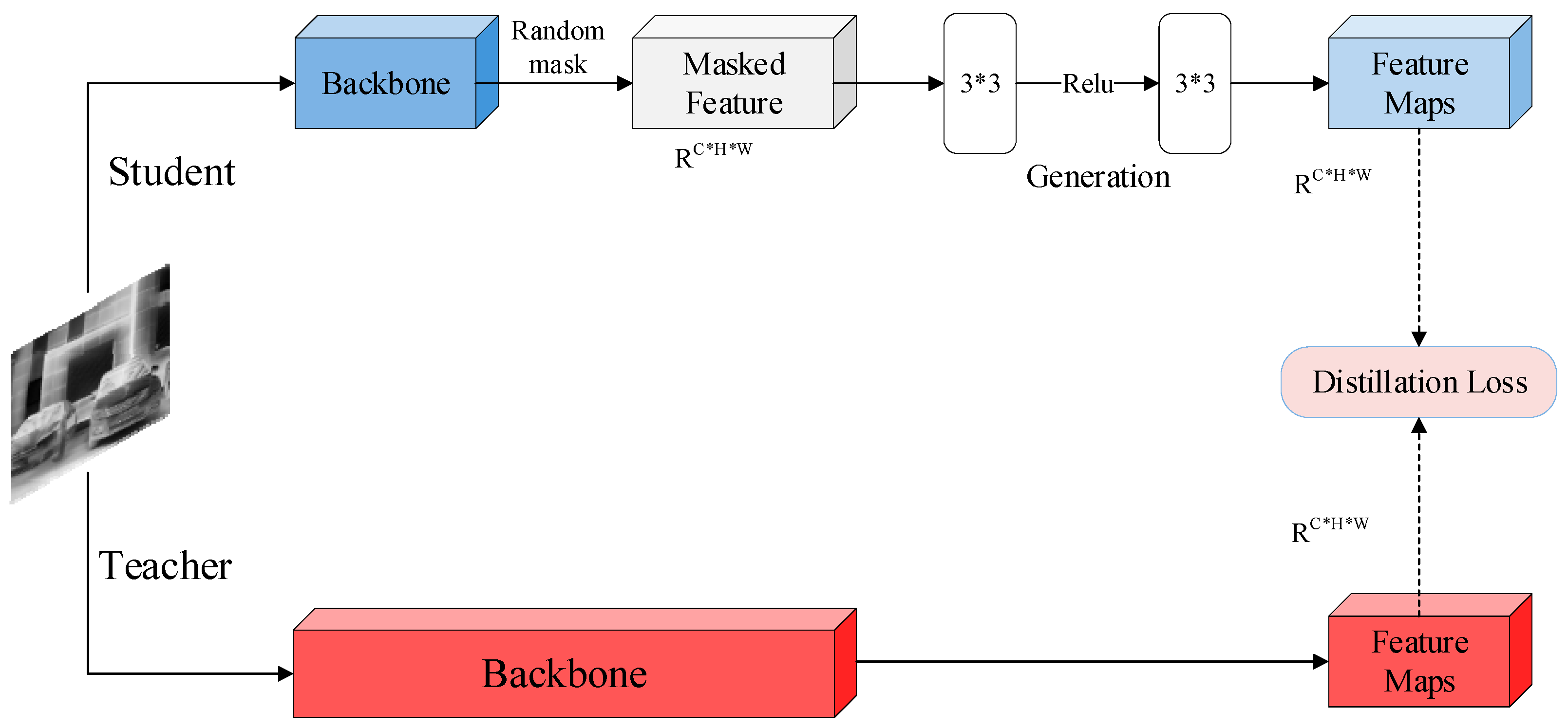
3.2. Masked Generative Distillation
3.3. Coordinate Attention
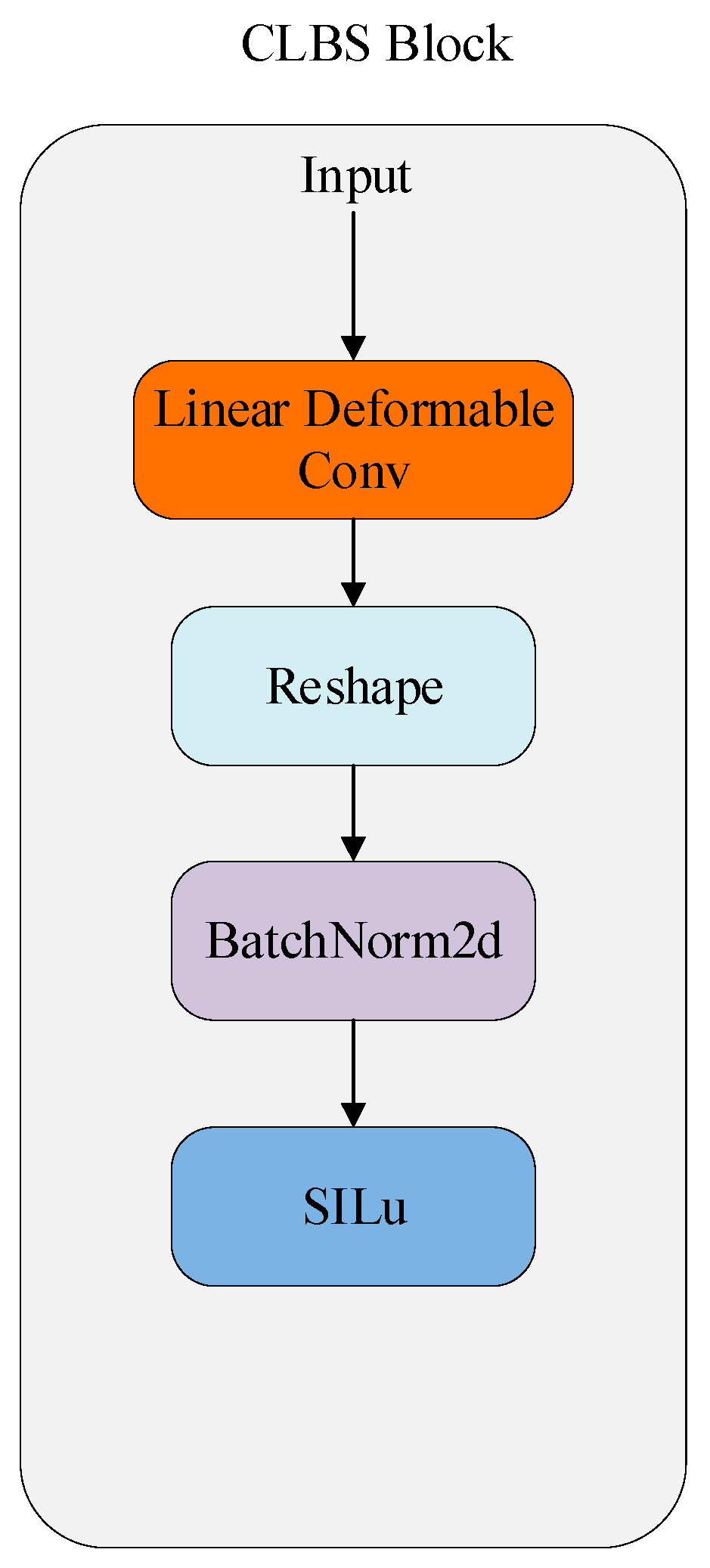
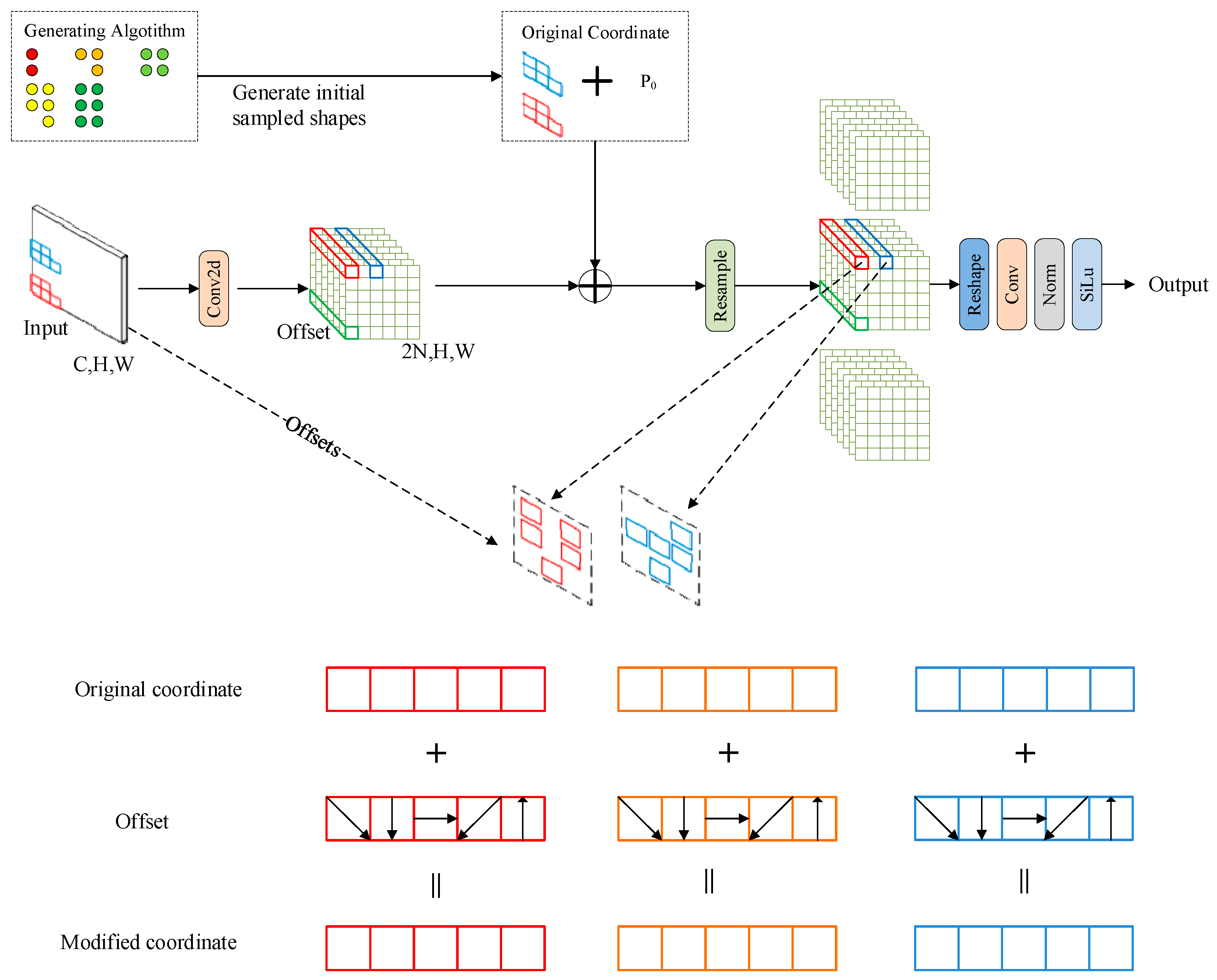
3.4. Linear Deformable Convolution
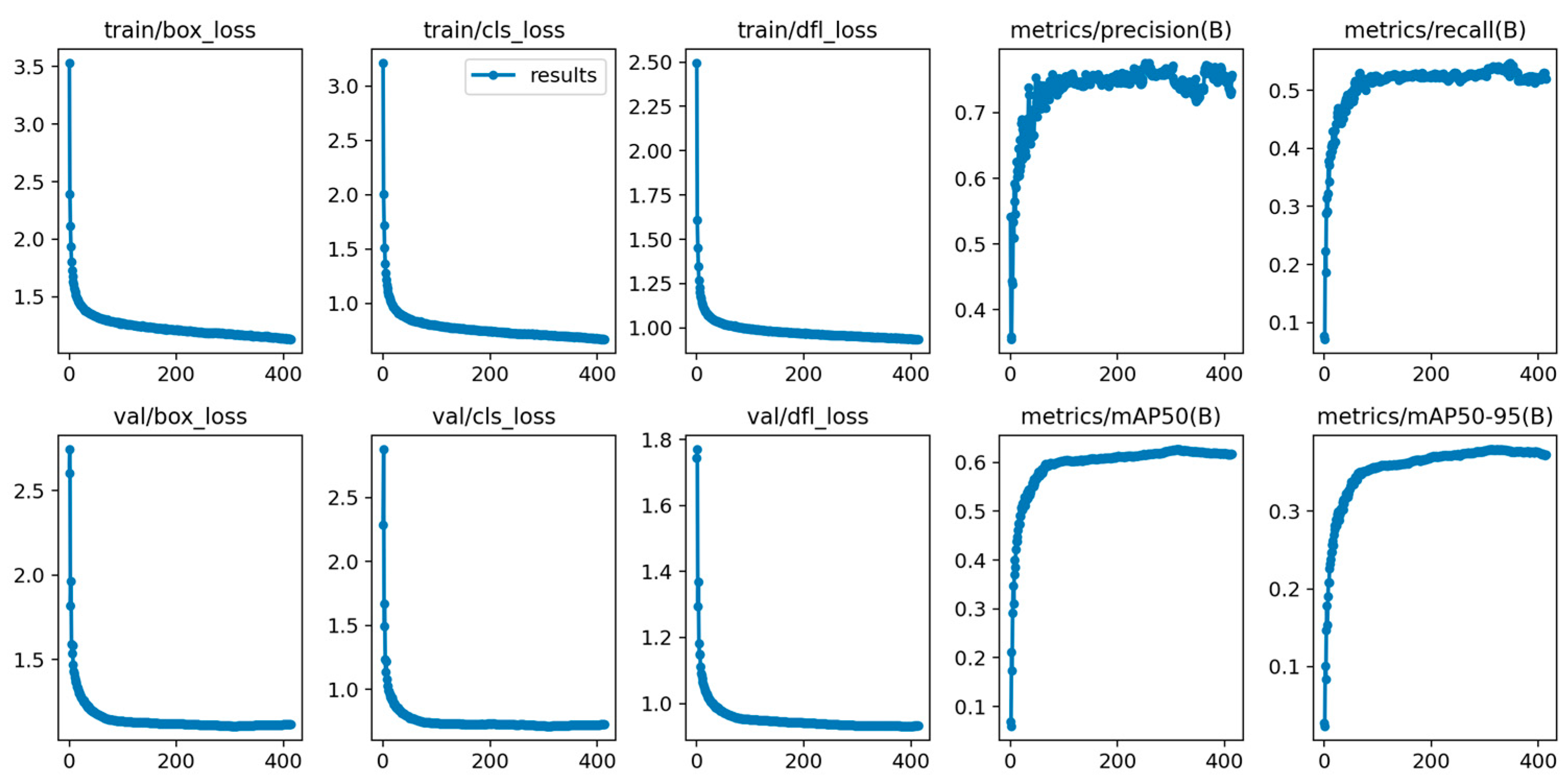
4. Experimental Analysis
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Experimental Settings
4.3. Evaluation Metrics
4.4. Ablation Experiments
4.5. Comparison with SOTAs
4.5.1. Quantitative Experiments
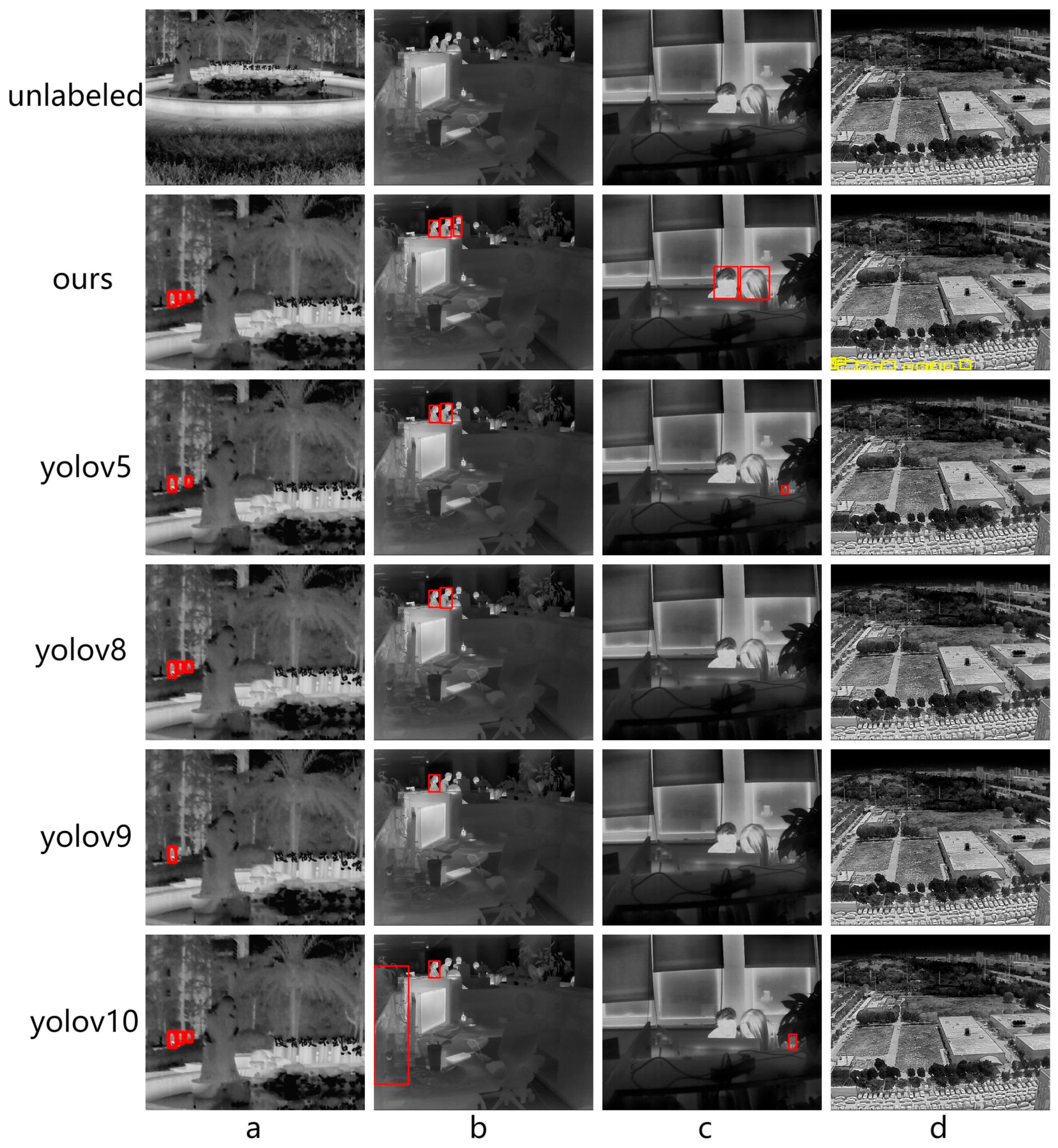
4.5.2. Qualitative Experiments
4.6. Experiments Evaluation Results
4.7. Compare with Logit-Based Distillation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, T.-Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R. Fast r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1440–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Malik, J. Region-based convolutional networks for accurate object detection and segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 38, 142–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2015, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terven, J.; Córdova-Esparza, D.-M.; Romero-González, J.-A. A comprehensive review of yolo architectures in computer vision: From yolov1 to yolov8 and yolo-nas. Mach. Learn. Knowl. Extr. 2023, 5, 1680–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Chen, H.; Liu, L.; Chen, K.; Lin, Z.; Han, J.; Ding, G. Yolov10: Real-time end-to-end object detection. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.14458. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Yeh, I.-H.; Mark Liao, H.-Y. Yolov9: Learning what you want to learn using programmable gradient information. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Milan, Italy, 29 September–4 October 2024; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Hinton, G.; Vinyals, O.; Dean, J. Distilling the knowledge in a neural network. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1503.02531. [Google Scholar]
- Mansourian, A.M.; Ahmadi, R.; Ghafouri, M.; Babaei, A.M.; Golezani, E.B.; Ghamchi, Z.Y.; Ramezanian, V.; Taherian, A.; Dinashi, K.; Miri, A. A Comprehensive Survey on Knowledge Distillation. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2503.12067. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Z.; Gong, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Lin, C.; Dong, A.; Jiao, J.; Lu, J.; Jiang, D.; Majumder, R. Prod: Progressive distillation for dense retrieval. In Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2023, New York, NY, USA, 30 April–4 May 2023; pp. 3299–3308. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, C.-Y.; Li, C.-L.; Yeh, C.-K.; Nakhost, H.; Fujii, Y.; Ratner, A.; Krishna, R.; Lee, C.-Y.; Pfister, T. Distilling step-by-step! outperforming larger language models with less training data and smaller model sizes. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.02301. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Krishnan, D.; Isola, P. Contrastive representation distillation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.10699. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, J.; Yang, H.; Li, P. Wasserstein distance rivals kullback-leibler divergence for knowledge distillation. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 37, 65445–65475. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Li, Z.; Shao, M.; Shi, D.; Yuan, Z.; Yuan, C. Masked generative distillation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23 October 2022; pp. 53–69. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Song, Y.; Song, T.; Yang, D.; Ye, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, L. LDConv: Linear deformable convolution for improving convolutional neural networks. Image Vis. Comput. 2024, 149, 105190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Zhou, D.; Feng, J. Coordinate attention for efficient mobile network design. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 13713–13722. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Li, J.; Shen, Z.; Huang, G.; Yan, S.; Zhang, C. Learning efficient convolutional networks through network slimming. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2736–2744. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.; Chen, S.; Pan, S. Learning to prune deep neural networks via layer-wise optimal brain surgeon. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Shopkhoev, D.; Ali, A.; Zhussip, M.; Malykh, V.; Lefkimmiatis, S.; Komodakis, N.; Zagoruyko, S. ReplaceMe: Network Simplification via Layer Pruning and Linear Transformations. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2505.02819. [Google Scholar]
- Zniyed, Y.; Nguyen, T.P. Efficient tensor decomposition-based filter pruning. Neural Netw. 2024, 178, 106393. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.-D.; Park, E.; Yoo, S.; Choi, T.; Yang, L.; Shin, D. Compression of deep convolutional neural networks for fast and low power mobile applications. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.06530. [Google Scholar]
- Gusak, J.; Kholiavchenko, M.; Ponomarev, E.; Markeeva, L.; Blagoveschensky, P.; Cichocki, A.; Oseledets, I. Automated multi-stage compression of neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27–28 October 2019; pp. 2501–2508. [Google Scholar]
- Saragadam, V.; Balestriero, R.; Veeraraghavan, A.; Baraniuk, R.G. DeepTensor: Low-rank tensor decomposition with deep network priors. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2024, 46, 10337–10348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.; Hu, S.X.; Damianou, A.; Lawrence, N.D.; Dai, Z. Variational information distillation for knowledge transfer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2019; pp. 9163–9171. [Google Scholar]
- Yim, J.; Joo, D.; Bae, J.; Kim, J. A gift from knowledge distillation: Fast optimization, network minimization and transfer learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4133–4141. [Google Scholar]
- Romero, A.; Ballas, N.; Kahou, S.E.; Chassang, A.; Gatta, C.; Bengio, Y. Fitnets: Hints for thin deep nets. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6550. [Google Scholar]
- Park, W.; Kim, D.; Lu, Y.; Cho, M. Relational knowledge distillation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 3967–3976. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.-H.; Yao, Y.; Hsu, C.-F.; Xie, H.; Shuai, H.-H.; Cheng, W.-H. Feature-based One-For-All: A Universal Framework for Heterogeneous Knowledge Distillation. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2501.08885. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Ye, R.; Wang, P.; Ren, D.; Zuo, W.; Hou, Q.; Cheng, M.-M. Localization distillation for dense object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 9407–9416. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, B.; Cui, Q.; Song, R.; Qiu, Y.; Liang, J. Decoupled knowledge distillation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 11953–11962. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Li, Z.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, T.; Lao, S.; Yuan, C.; Li, Y. Rethinking knowledge distillation via cross-entropy. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2208.10139. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.; Ren, W.; Li, J.; Wang, R.; Cao, X. Logit standardization in knowledge distillation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 15731–15740. [Google Scholar]
- Gou, J.; Yu, B.; Maybank, S.J.; Tao, D. Knowledge distillation: A survey. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2021, 129, 1789–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, J.; Nie, L.; Shao, J.; Liu, W.; Chua, T.-S. Sca-cnn: Spatial and channel-wise attention in convolutional networks for image captioning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 5659–5667. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Han, L.; Huang, Z.; Zheng, N. MCA: Moment channel attention networks. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, Canada, 26–27 February 2024; pp. 2579–2588. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Byeon, W.; Xu, J.; Gu, J.; Cheung, K.C.; Wang, X.; Han, K.; Kautz, J.; Liu, S. Parallel Sequence Modeling via Generalized Spatial Propagation Network. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2501.12381. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Liao, H.-Y.M.; Wu, Y.-H.; Chen, P.-Y.; Hsieh, J.-W.; Yeh, I.-H. CSPNet: A new backbone that can enhance learning capability of CNN. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 390–391. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Xu, J.; Lin, S.; Wei, F.; Hu, H. Gcnet: Non-local networks meet squeeze-excitation networks and beyond. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27–28 October 2019; pp. 1971–1980. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Mnih, V.; Heess, N.; Graves, A.; Kavukcuoglu, K. Recurrent models of visual attention. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2014, 27, 2204–2212. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.; Qi, H.; Xiong, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y. Deformable convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 764–773. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Hu, H.; Lin, S.; Dai, J. Deformable convnets v2: More deformable, better results. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 9308–9316. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Malik, J. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 580–587. [Google Scholar]
- Henderson, P.; Ferrari, V. End-to-end training of object class detectors for mean average precision. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ACCV 2016: 13th Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Taipei, Taiwan, 20–24 November 2016; Revised Selected Papers, Part V 13, 2017. pp. 198–213. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, D.; Fang, J.; Song, X.; Guan, C.; Yin, J.; Dai, Y.; Yang, R. Iou loss for 2d/3d object detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Québec City, QC, Canada, 16–19 September 2019; pp. 85–94. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Xu, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, Q.; Yoo, B.; Han, J.-J. Learning generalized intersection over union for dense pixelwise prediction. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, 8–24 July 2021; pp. 12198–12207. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, C.; Liu, Y.; Gao, J.; Yan, Z.; Shen, C. Channel-wise knowledge distillation for dense prediction. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 5311–5320. [Google Scholar]




| Group | LDConv | CA | Parameter (million) | FLOPs (G) | FPS | Map@0.5:0.95 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | × | × | 3.01 | 8.2 | 196 | 0.3756 |
| 2 | √ | × | 2.65 | 7.51 | 217 | 0.3748 |
| 3 | × | √ | 3.02 | 8.2 | 192 | 0.3892 |
| 4 | √ | √ | 2.78 | 7.66 | 202 | 0.3824 |
| Group | Teacher | MGD | LDConv | CA | Parameter (million) | FLOPs (G) | FPS | Map@0.5:0.95 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | × | × | × | × | 3.01 | 8.2 | 196 | 0.3756 |
| 2 | LKD-YOLOv8s | √ | × | × | 3.01 | 8.2 | 196 | 0.3889 |
| 3 | LKD-YOLOv8s | √ | × | √ | 3.01 | 8.1 | 175 | 0.3972 |
| 4 | LKD-YOLOv8s | √ | √ | √ | 2.77 | 7.6 | 181 | 0.3874 |
| Group | Method | Parameter (million) | FLOPs (G) | mAP@0.5:0.95 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | YOLOv8n | 3.01 | 8.2 | 0.3756 |
| 2 | YOLOv5n | 1.77 | 4.2 | 0.3121 |
| 3 | YOLOv9t | 2.0 | 7.7 | 0.3612 |
| 4 | YOLOv10n | 2.69 | 8.2 | 0.3663 |
| 5 | PP-YOLOE-S | 7.96 | 17.36 | 0.3931 |
| 6 | YOLO-NAS | 12.88 | 17.52 | 0.3942 |
| 7 | LKD-YOLOv8n (ours) | 2.77 | 7.6 | 0.3874 |
| Group | Method | Map@0.5:0.95 (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | MGD | 0.3874 |
| 2 | CWD | 0.3796 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, H. LKD-YOLOv8: A Lightweight Knowledge Distillation-Based Method for Infrared Object Detection. Sensors 2025, 25, 4054. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25134054
Cao X, Hu Y, Zhang H. LKD-YOLOv8: A Lightweight Knowledge Distillation-Based Method for Infrared Object Detection. Sensors. 2025; 25(13):4054. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25134054
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Xiancheng, Yueli Hu, and Haikun Zhang. 2025. "LKD-YOLOv8: A Lightweight Knowledge Distillation-Based Method for Infrared Object Detection" Sensors 25, no. 13: 4054. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25134054
APA StyleCao, X., Hu, Y., & Zhang, H. (2025). LKD-YOLOv8: A Lightweight Knowledge Distillation-Based Method for Infrared Object Detection. Sensors, 25(13), 4054. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25134054






