Bias-Reduced Localization for Drone Swarm Based on Sensor Selection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Problem Description
2.1. Drone Swarm Localization System Model
2.2. Analysis of the Performance Limits of Drone Swarm Localization
3. Sensor Selection Algorithm
3.1. Sensor Selection Model for Drone Swarm
3.2. Randomized SDP Algorithm Based on Drone Swarm
4. Bias Reduction Technology
4.1. Traditional CWLS Problem
4.2. BR-CWLS Algorithm
| Algorithm 1 BR-CWLS localization algorithm based on sensor selection. |
|
4.3. Analysis of Algorithm Complexity
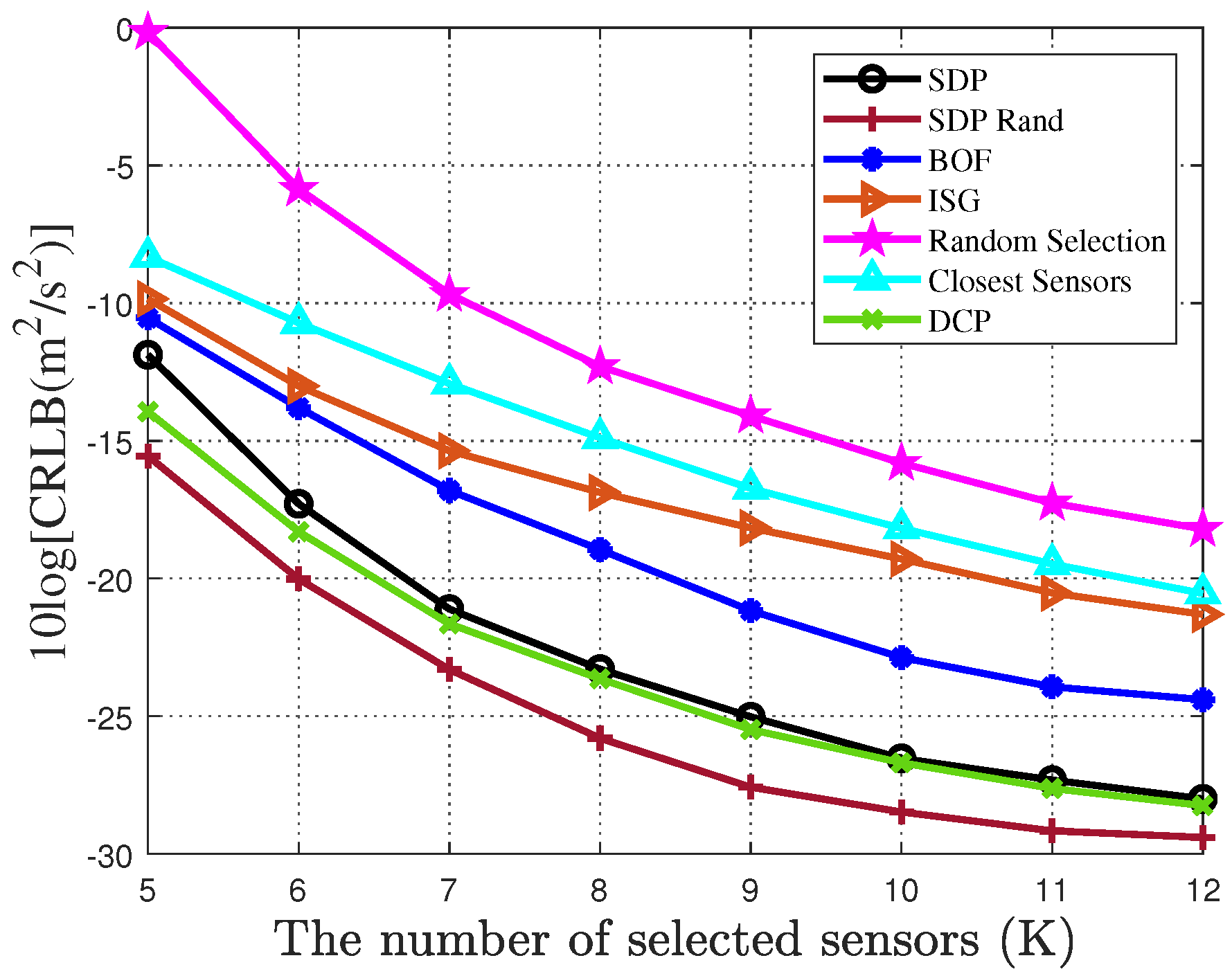
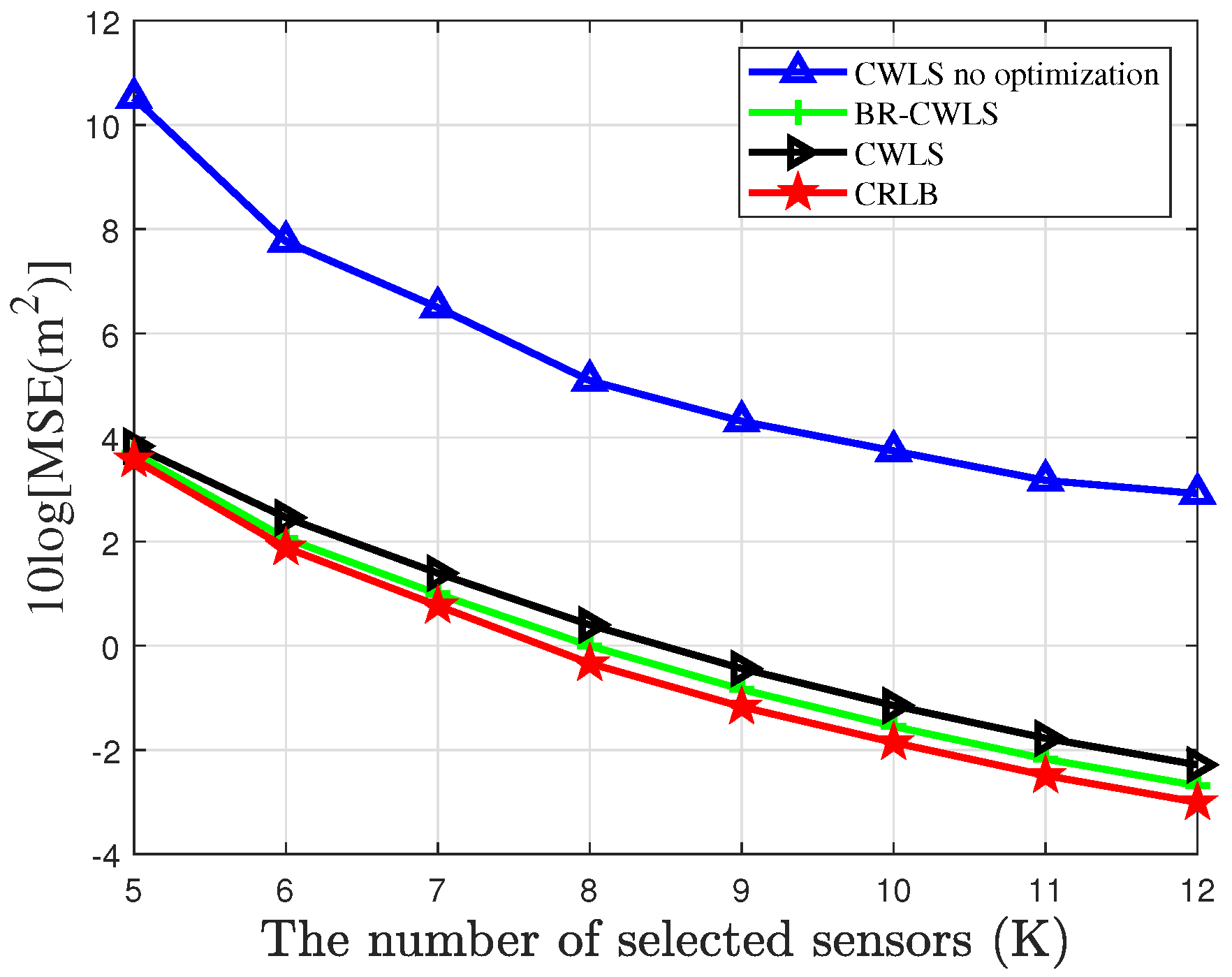
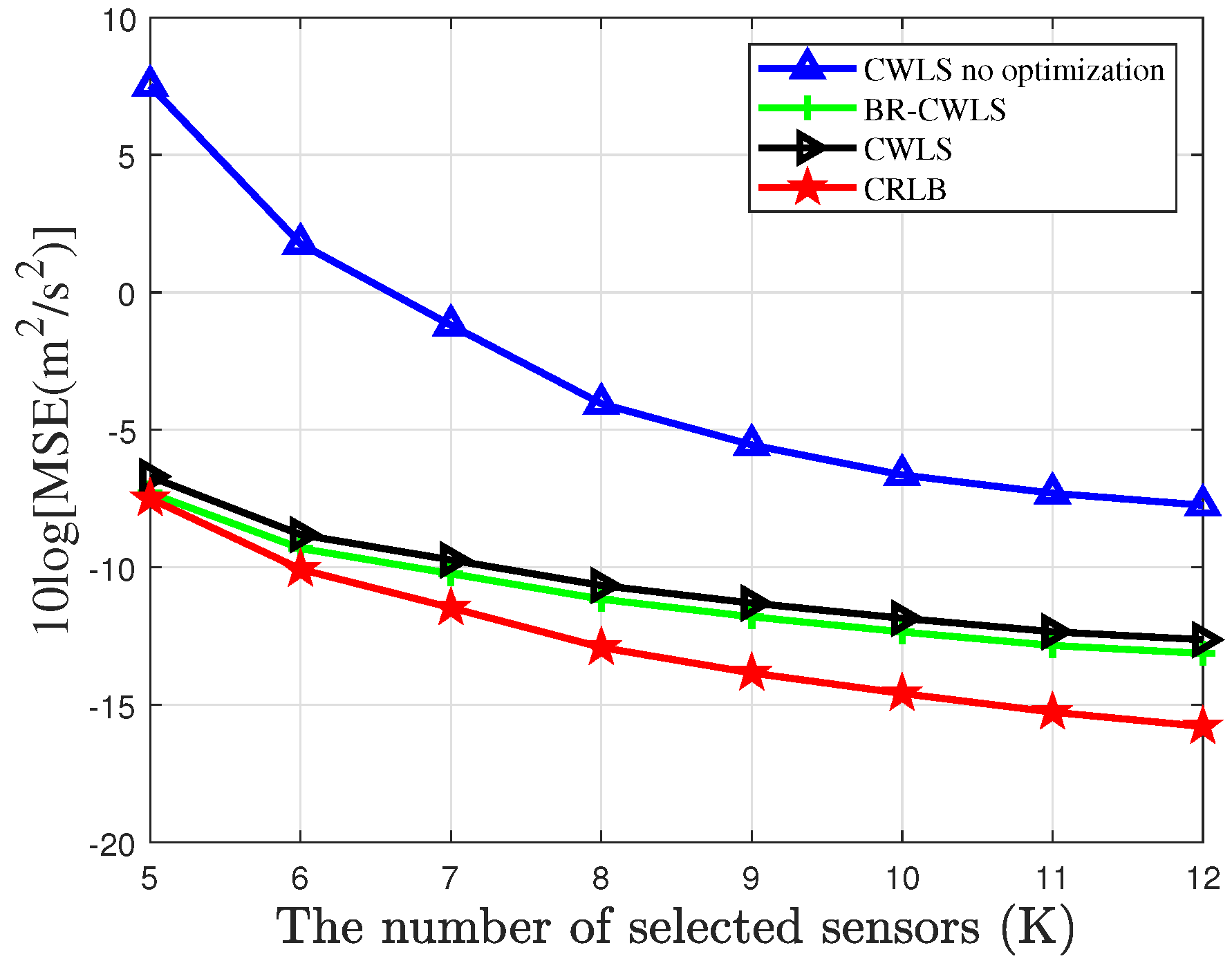
5. Simulation Result
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mukherjee, A.; De, D.; Dey, N.; Crespo, R.G.; Herrera-Viedma, E. DisastDrone: A Disaster Aware Consumer Internet of Drone Things System in Ultra-Low Latent 6G Network. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2023, 69, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Hwang, K.; Wu, D.; Hao, Y.; Chen, M. Drone Swarm Path Planning for Mobile Edge Computing in Industrial Internet of Things. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2023, 19, 6836–6848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaamoning, G.; Mendes, P.; Rosário, D.; Cerqueira, E. Drone Swarms as Networked Control Systems by Integration of Networking and Computing. Sensors 2021, 21, 2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidaliyeva, U.; Ilipbayeva, L.; Taissariyeva, K.; Smailov, N.; Matson, E.T. Advances and Challenges in Drone Detection and Classification Techniques: A State-of-the-Art Review. Sensors 2024, 24, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Duan, H.; Zeng, Z. Biological Eagle-Eye-Based Correlation Filter Learning for Fast UAV Tracking. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Meng, X.; Liu, J.; Guo, H.; Mao, B. Countering Large-Scale Drone Swarm Attack by Efficient Splitting. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2022, 71, 9967–9979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, M.-H.; Park, S.-O.; Choi, S.-H.; Choi, C.-T. Commercial Fixed-Wing Drone Redirection System Using GNSS Deception. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2023, 59, 5699–5713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasmine, G.; Maha, G.; Alaoui, A.E.H. Anti-drone systems: Current intelligent countermeasures from low to high risks. In Proceedings of the 7th IEEE Congress on Information Science and Technology (CiSt), Agadir–Essaouira, Morocco, 16–22 December 2023; pp. 317–322. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Ho, K.C. Unified near-field and far-field localization for AOA and hybrid AOA-TDOA positionings. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2018, 17, 1242–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Cai, S.; Li, Y.; Jin, M. Second-Order Cone Relaxation for TOA-Based Source Localization with Unknown Start Transmission Time. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2014, 63, 2973–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Fang, D.; Yang, Z.; Jiang, H.; Chen, X.; Wang, W.; Xing, T.; Cai, L. RSS Distribution-Based Passive Localization and Its Application in Sensor Networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2016, 15, 2883–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; So, A.M.-C.; Li, Y. Robust Convex Approximation Methods for TDOA-Based Localization Under NLOS Conditions. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2016, 64, 3281–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Li, Y.; Ansari, N. A Semidefinite Relaxation Method for Source Localization Using TDOA and FDOA Measurements. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2013, 62, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzi, A.; Slock, D.T.M.; Meilhac, L. On spatio-frequential smoothing for joint angles and times of arrival estimation of multipaths. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Shanghai, China, 20–25 March 2016; pp. 3311–3315. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, W.; Xu, C.; Pei, L.; Yu, W. Multidimensional scaling-based TDOA localization scheme using an auxiliary line. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2016, 23, 546–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anvaripour, M.; Saif, M.; Ahmadi, M. A Novel Approach to Reliable Sensor Selection and Target Tracking in Sensor Networks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2020, 16, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Zhong, Z.; Li, X.; Yue, Y. Node Selection and Path Optimization for Passive Target Localization via UAVs. Sensors 2025, 25, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savkin, A.V.; Huang, H. Navigation of a UAV Network for Optimal Surveillance of a Group of Ground Targets Moving Along a Road. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 9281–9285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, B.; You, C.; Yang, Z.; Gui, G. The Optimal Control Policy for RF-Powered Backscatter Communication Networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 67, 2804–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Han, B.; Schotten, H.D. Trustworthy UAV Cooperative Localization: Information Analysis of Performance and Security. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arafat, M.Y.; Moh, S. A Survey on Cluster-Based Routing Protocols for Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Networks. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 498–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, G.; Dai, L. Frequency-Invariant Sensor Selection for MVDR Beamforming in Wireless Acoustic Sensor Networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2022, 21, 10648–10661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, T.; Yamada, K.; Nakai, K.; Saito, Y.; Nonomura, T. Randomized Group-Greedy Method for Large-Scale Sensor Selection Problems. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 9536–9548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ding, J.; Li, B. Sparse Learning Method with Feature Selection for Sensor Placement and Response Prediction. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2024, 60, 8022–8033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, N.; Choi, S.; Masazade, E.; Varshney, P.K. Sensor Selection for Target Tracking in Wireless Sensor Networks with Uncertainty. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2016, 64, 5191–5204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Ho, D.K.C.; Xiong, W.; So, H.C.; Chun, Y.J. Cramér–Rao Lower Bound Analysis for Elliptic Localization with Random Sensor Placements. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2024, 60, 5587–5595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.; Chepuri, S.P.; Leus, G. Greedy sensor selection for non-linear models. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Workshop on Computational Advances in Multi-Sensor Adaptive Processing, Cancun, Mexico, 13–16 December 2015; pp. 241–244. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, S.; Boyd, S. Sensor selection via convex optimization. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2009, 57, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chepuri, S.P.; Leus, G. Continuous Sensor Placement. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2015, 22, 544–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Dang, X.; Cheng, Q.; Zhu, H. Sensor Selection Based on Sparse Sensing in the Presence of Sensor Position Error. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2023, 59, 8915–8930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, Z.; Hao, B.; Shi, J. Sensor Selection for TDOA-Based Localization in Wireless Sensor Networks with Non-Line-of-Sight Condition. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 9935–9950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Liu, H.; Ho, K.C.; Yang, Z.; Gao, S. Optimal Sensor Placement and Velocity Configuration for TDOA-FDOA Localization and Tracking of a Moving Source. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, B.; Li, Z.; Ren, Y.; Yin, W. On the Cramer-Rao bound of multiple sources localization using RDOAs and GROAs in the presence of sensor location uncertainties. In Proceedings of the IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), Paris, France, 1–4 April 2012; pp. 1937–1942. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, M.S.; Hosseinalipour, S.; Kim, T.; Love, D.J.; Krogmeier, J.V.; Brinton, C.G. Dynamic and Robust Sensor Selection Strategies for Wireless Positioning with TOA/RSS Measurement. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2023, 72, 14656–14672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foy, W.H. Position-location solutions by Taylor-series estimation. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1976, 12, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Liu, H. Semidefinite Programming Methods for Alleviating Clock Synchronization Bias and Sensor Position Errors in TDOA Localization. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2020, 27, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.C.; Sun, M. Passive Source Localization Using Time Differences of Arrival and Gain Ratios of Arrival. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2008, 56, 464–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, Y. An efficient semidefinite relaxation algorithm for moving source localization using TDOA and FDOA measurements. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2017, 21, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, Z.; Hong, S.; Chang, S. A Semidefinite Relaxation Approach for Mobile Target Localization Based on TOA and Doppler Frequency Shift Measurements. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 16051–16057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.C. Bias reduction for an explicit solution of source localization using TDOA. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2012, 60, 2101–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Q.; Li, Y.; Guo, Q. A semidefinite relaxation solution for time delay and Doppler shift localization considering sensor location errors and its bias reduction scheme. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 24890–24902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Wang, G.; Ho, K.C.; Huang, L. Reducing bias for multistatic localization of a moving object by transmitter at unknown position. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2023, 59, 5324–5341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Yang, S.; Pei, J.; Ho, K.C. Bias-Reduced SDR Method for Locating a Noncooperative Moving Source Using TOAs and FOAs. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2024, 60, 6146–6162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

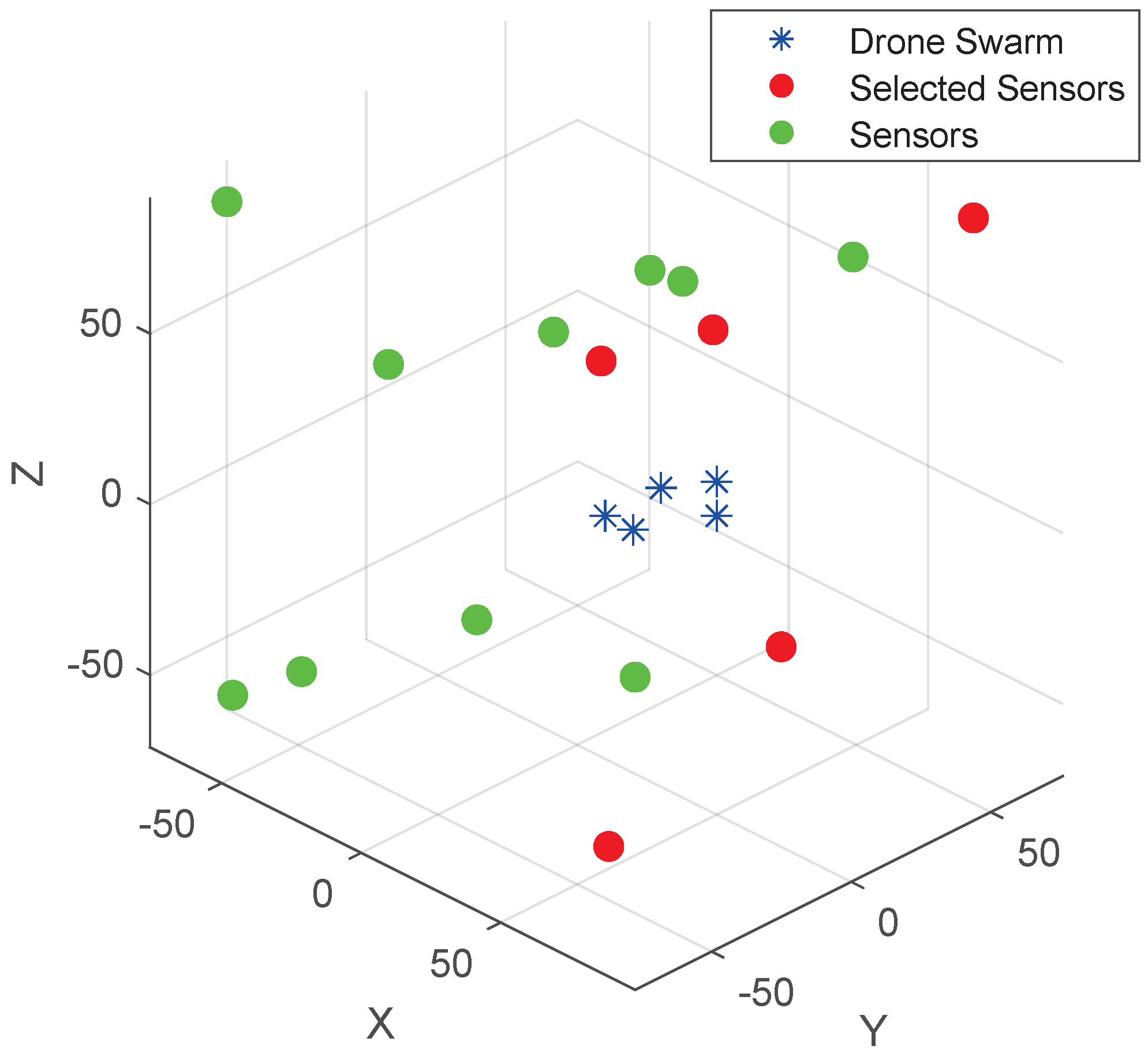
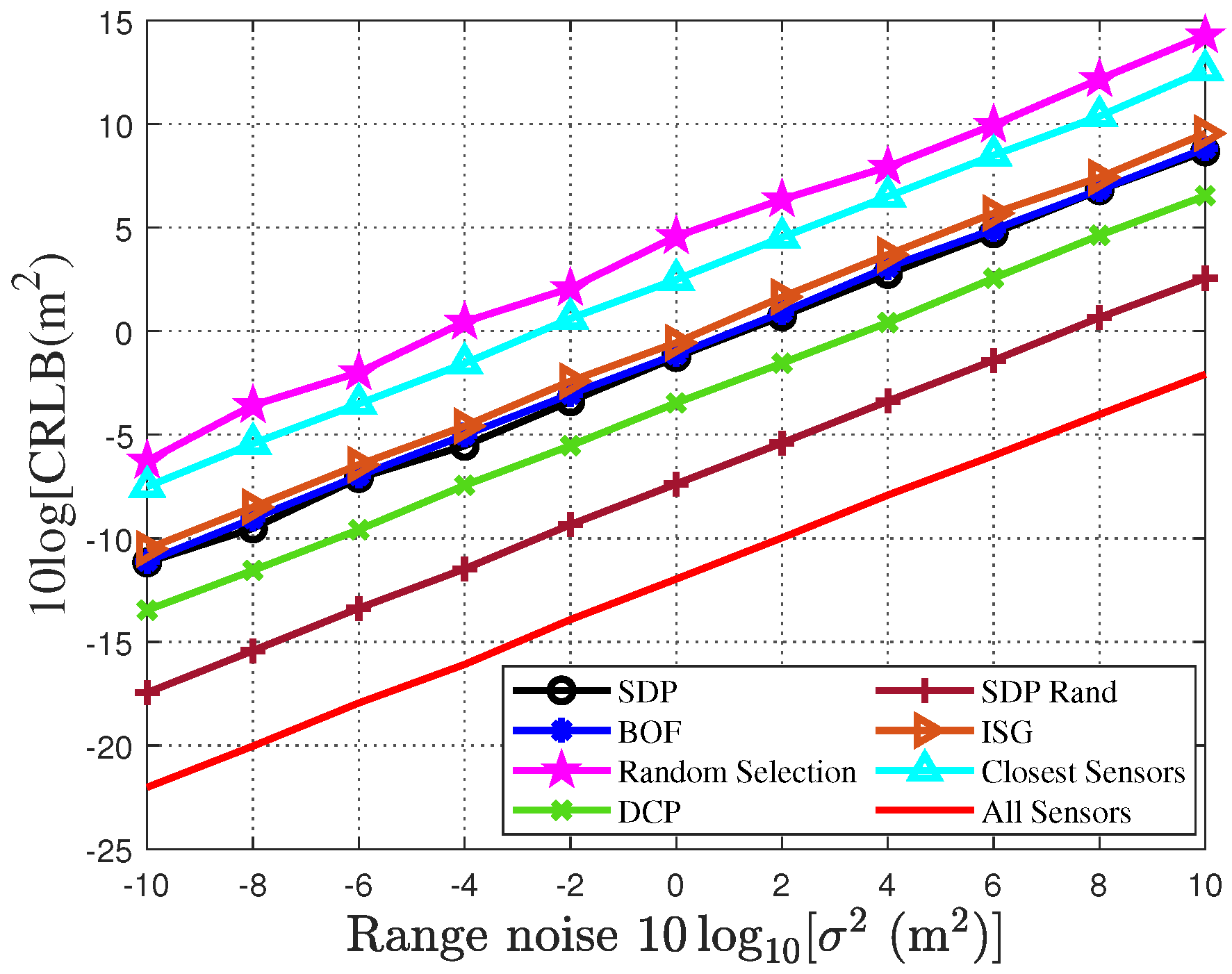

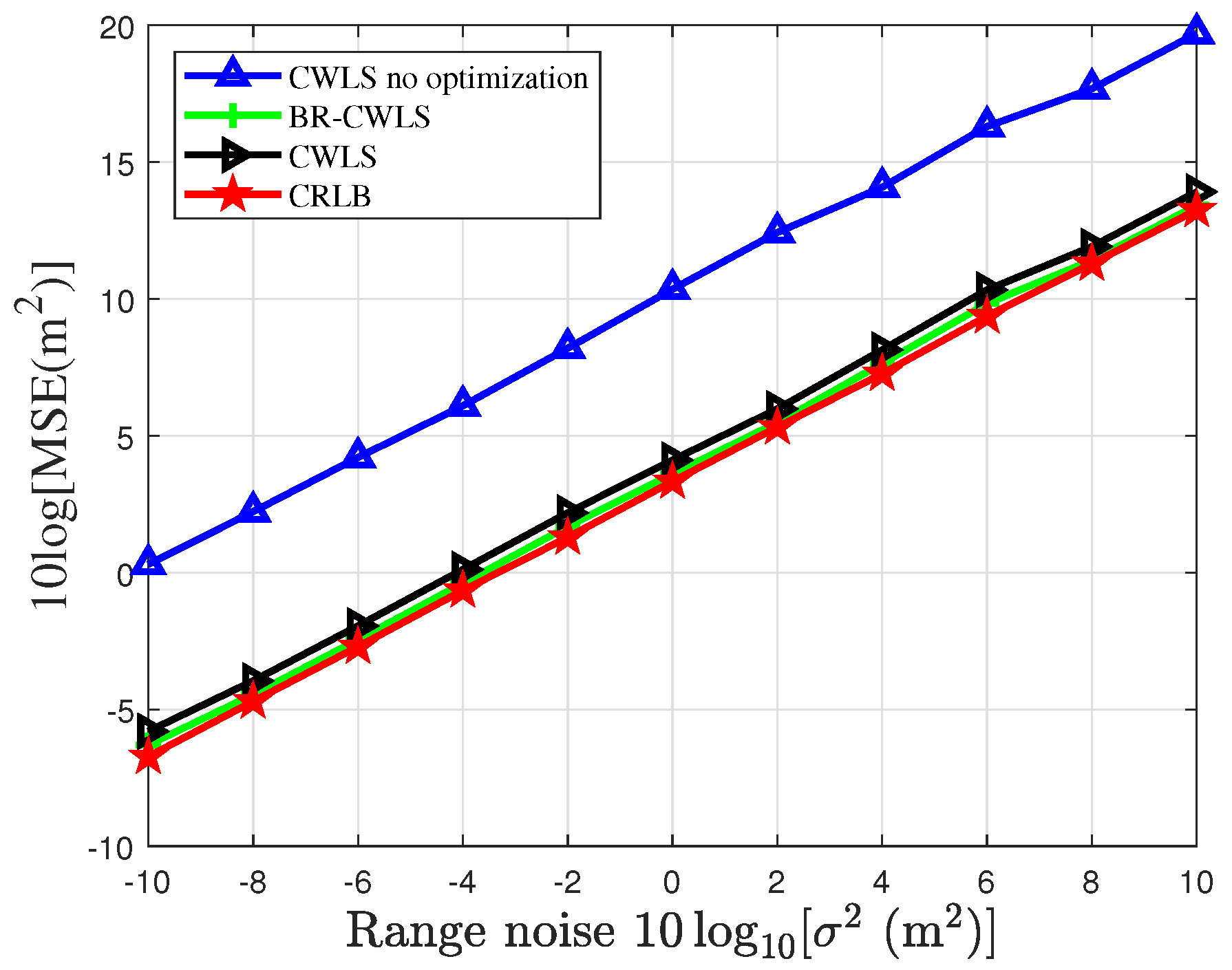
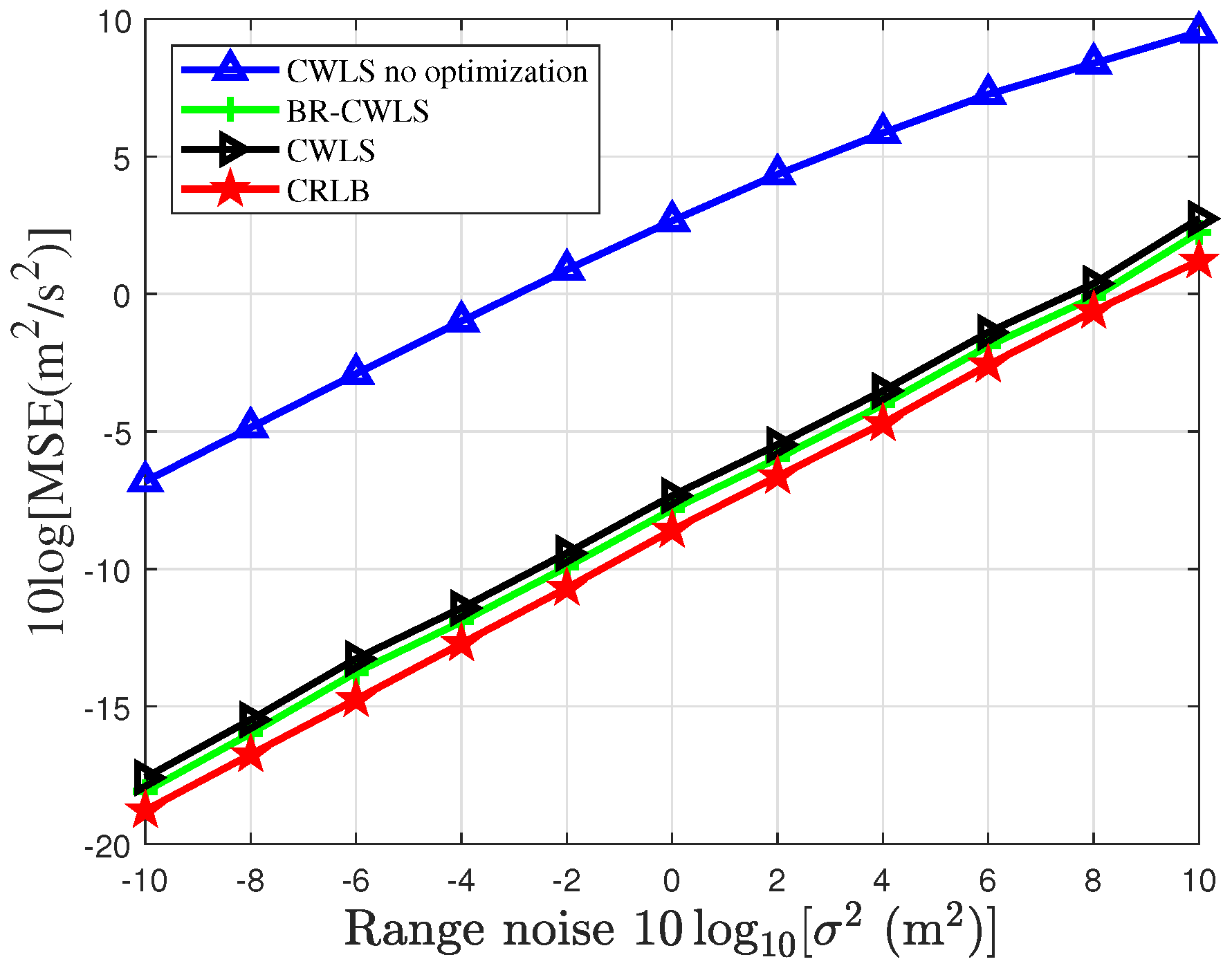

| Sensor | Source | Source Number | Localization Method | Sensor Selection Method | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| This Paper | Moving | Moving | Multiple | BR-CWLS | Randomized SDP |
| Reference [31] | Stationary | Stationary | Single | \ | SDP |
| Reference [34] | Stationary | Stationary/Moving | Single | \ | DMO |
| Reference [41] | Stationary | Moving | Single | BR-SDR | \ |
| Reference [42] | Moving | Stationary | Single | BR-CWLS | \ |
| Symbol | Description |
|---|---|
| , | Location and velocity of the nth drone swarm |
| , | Sensor location and velocity in 3D coordinates |
| , | Estimated value of the nth drone parameter |
| , | TDOA and FDOA measurements |
| Covariance matrix of TDOA and FDOA measurements | |
| , | Two boolean vectors |
| , | Sensor node selection matrix |
| Measurement noise covariance matrix for selected sensors | |
| M, K | Total number of sensors and number of sensors selected |
| Error vector ignoring second-order noise terms | |
| Unknown vector for the nth drone | |
| Weighting matrices in the presence of error | |
| Measurement matrices in the presence of error |
| Algorithm | Total Number of Operations | Time Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| BOF | ||
| ISG | ||
| DCP | – | |
| SDP | – | |
| Randomized SDP | – | |
| Exhaustive Search |
| x | 3 m | 6 m | 9 m | 3 m | 9 m |
| y | 0 m | 0 m | 6 m | 6 m | 6 m |
| z | 0 m | 0 m | 0 m | 0 m | 3 m |
| Parameters | Size and Scope |
|---|---|
| Drone swarm velocity | 50 m/s |
| Distance scope per two drones | 3–6 m |
| Number scope of sensors M | 20–40 |
| Selection of the number scope of sensors K | 5–12 |
| Sensor velocity scope | 0–20 m/s |
| Measurement noise scope | −10–10 dB |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, B.; Shen, B.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, Z. Bias-Reduced Localization for Drone Swarm Based on Sensor Selection. Sensors 2025, 25, 4034. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25134034
Wu B, Shen B, Zhang Y, Yang L, Wang Z. Bias-Reduced Localization for Drone Swarm Based on Sensor Selection. Sensors. 2025; 25(13):4034. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25134034
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Bo, Bazhong Shen, Yonggan Zhang, Li Yang, and Zhiguo Wang. 2025. "Bias-Reduced Localization for Drone Swarm Based on Sensor Selection" Sensors 25, no. 13: 4034. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25134034
APA StyleWu, B., Shen, B., Zhang, Y., Yang, L., & Wang, Z. (2025). Bias-Reduced Localization for Drone Swarm Based on Sensor Selection. Sensors, 25(13), 4034. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25134034




