Physics-Informed Generative Adversarial Networks for Laser Speckle Noise Suppression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Method
2.1. Speckle Phenomenon Analysis
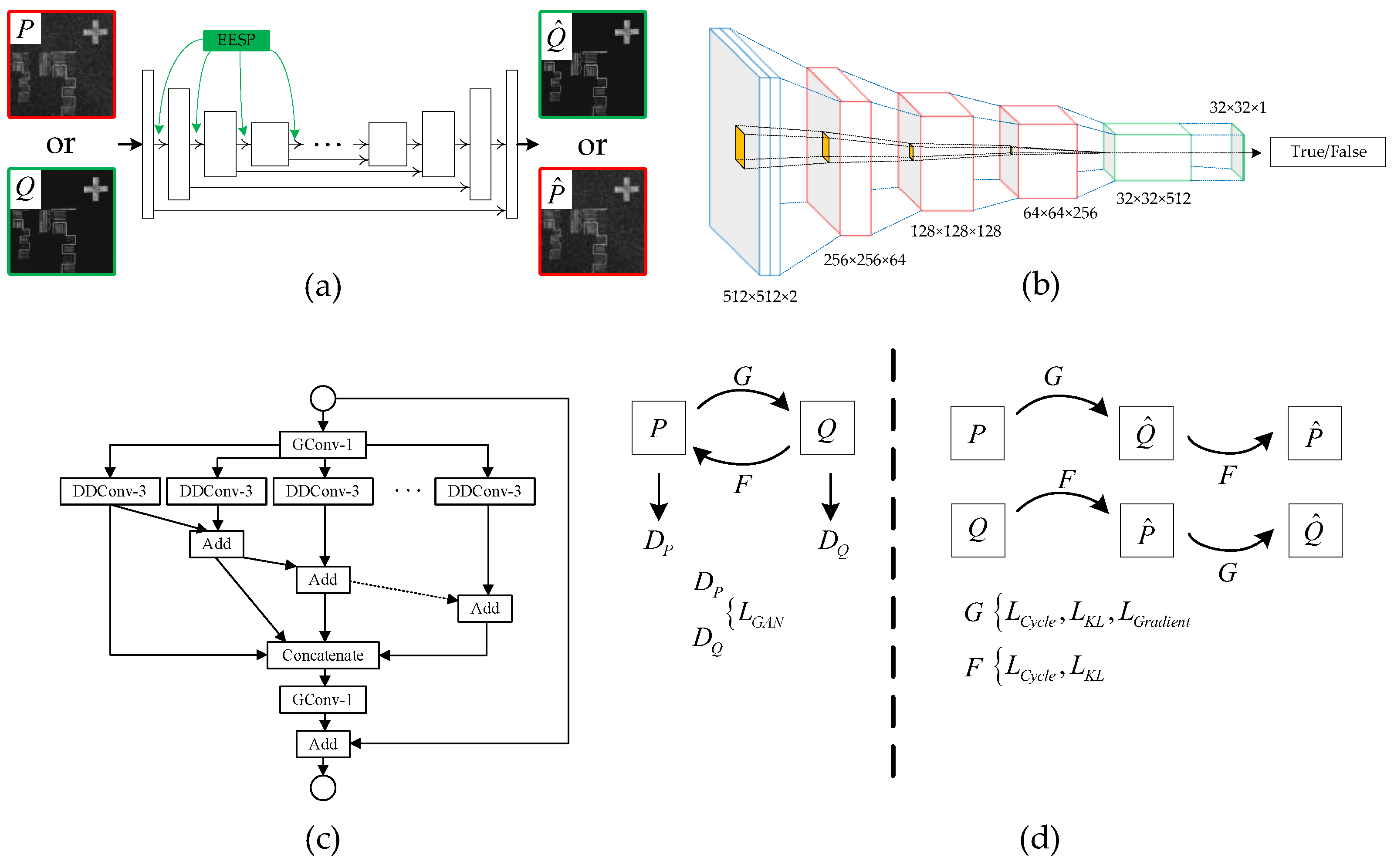
2.2. Network Architecture
2.3. Physics-Informed Loss Function
2.4. Dataset and Training Method
3. Experiments
3.1. Evaluation Metrics
3.2. Ablation Experiment
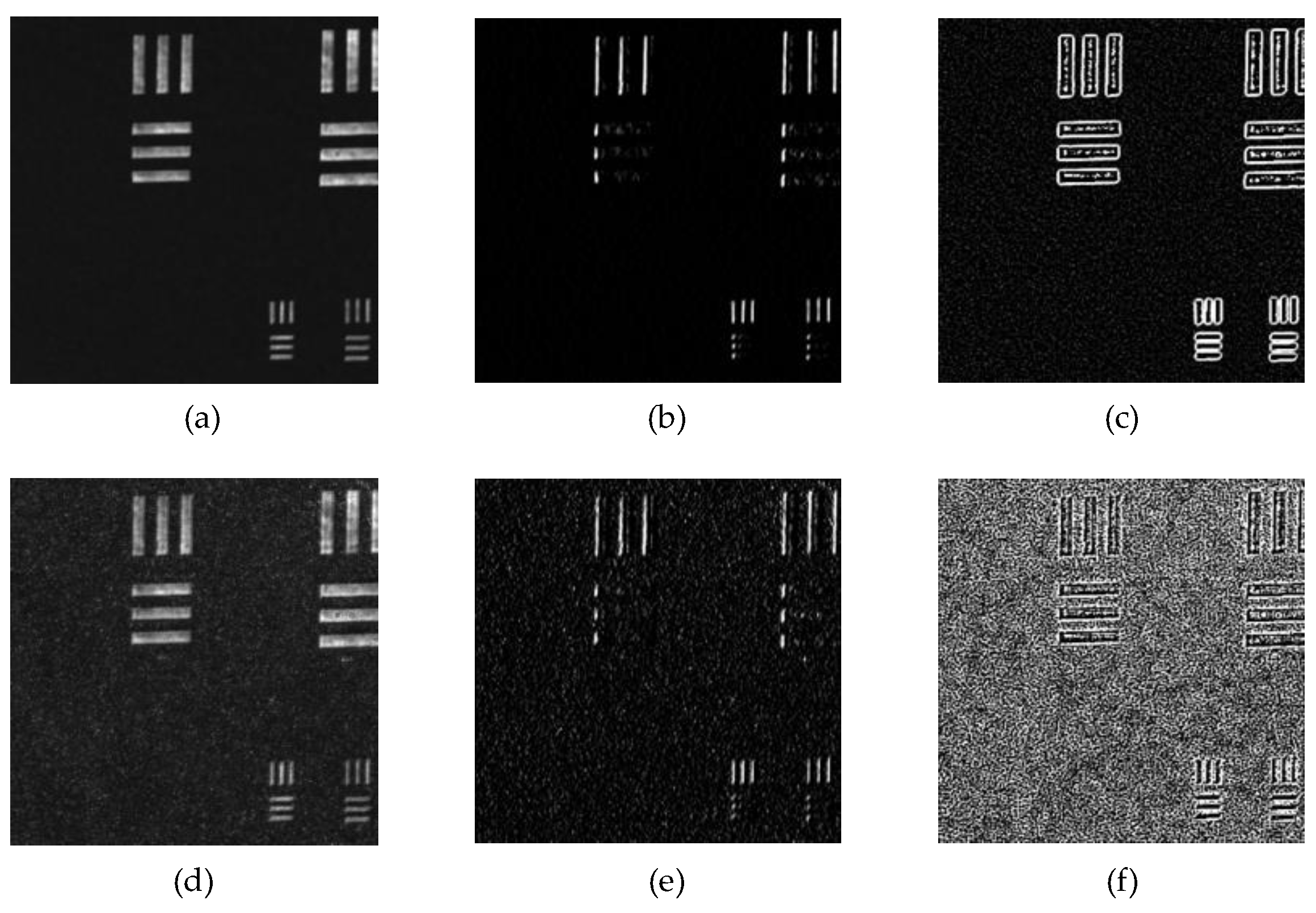
3.2.1. Network Structure
- Simple encoder–decoder structure;
- Standard U-Net network structure;
- U-Net structure with additional EESP blocks (U-Net + EESP). The discriminator and network training strategy were kept consistent to avoid the influence of other factors on the results.
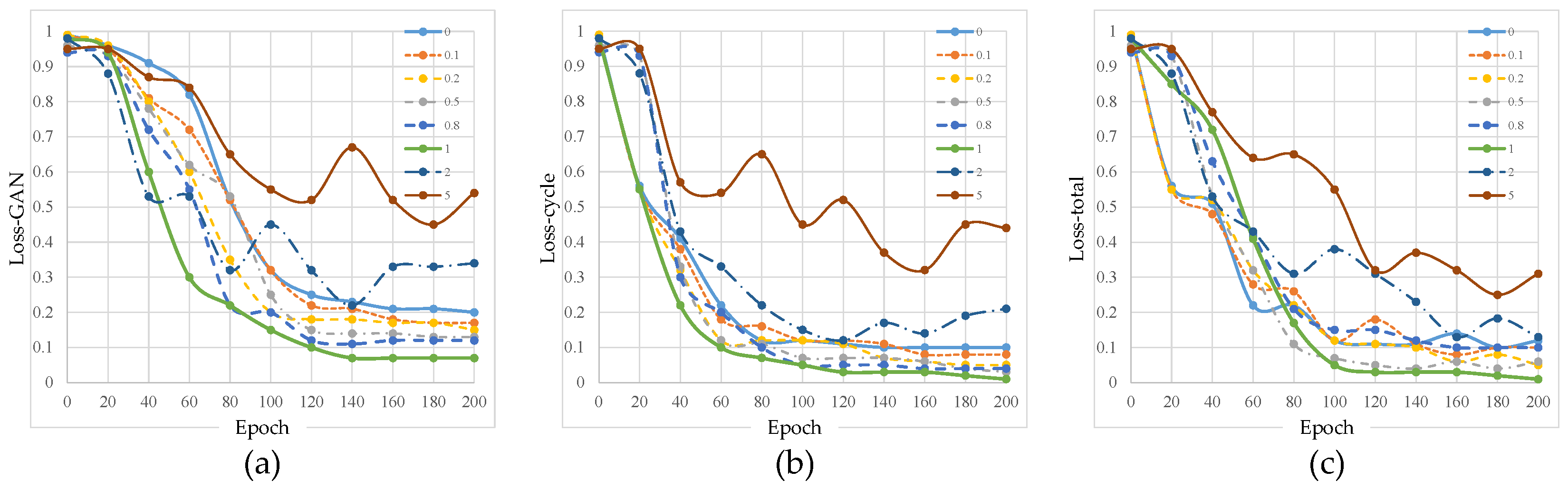
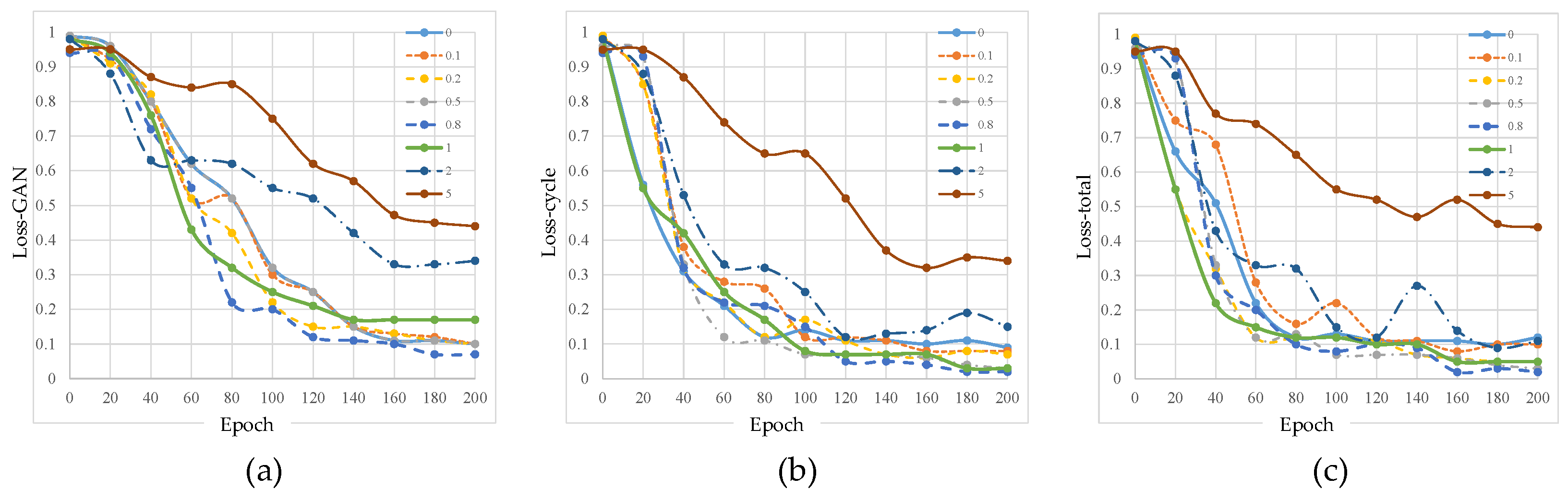
3.2.2. Loss Function
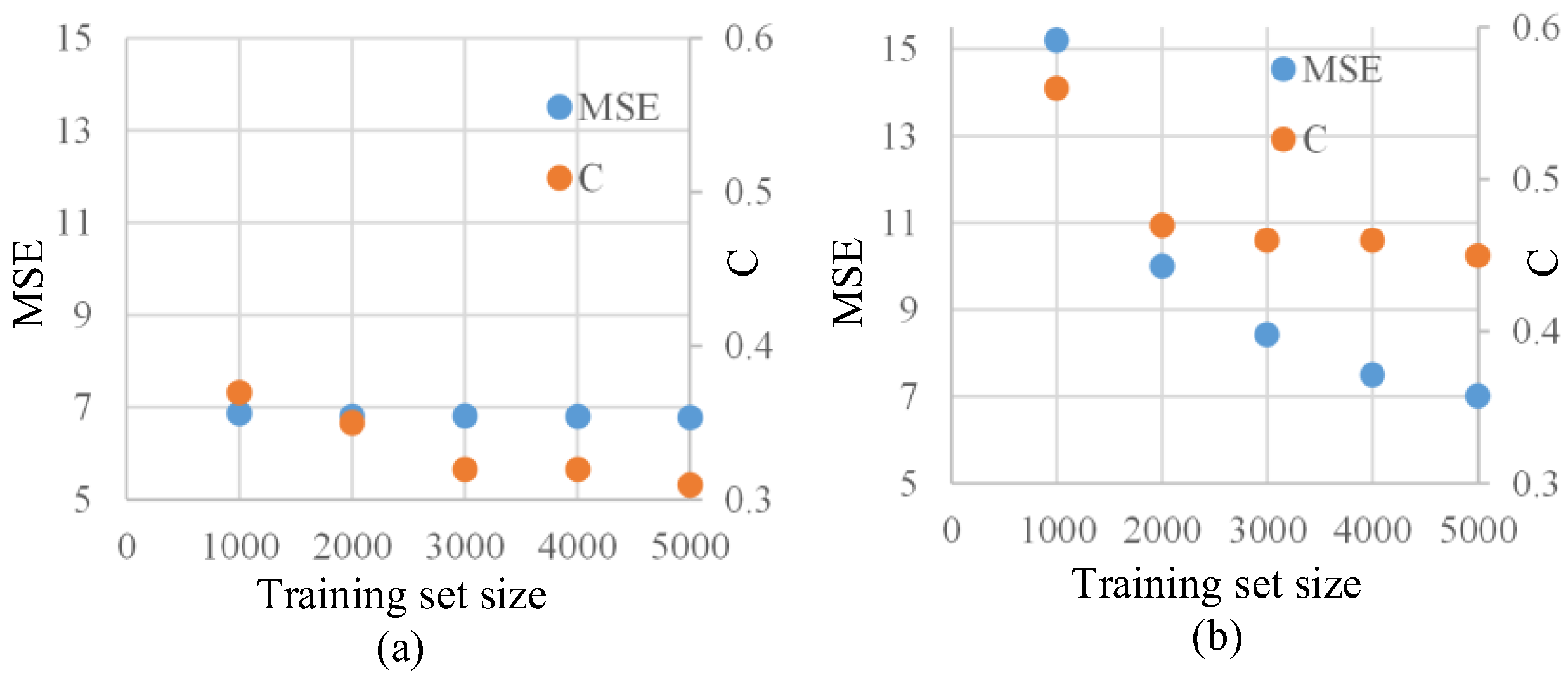
3.3. Dataset Scale Experiment
3.4. Comparison Experiment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goldfarb, D.L.; Broadbent, W.; Wylie, M.; Felix, N.; Corliss, D. Through-pellicle defect inspection of EUV masks using an ArF-based inspection tool. In Proceedings of the Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) Lithography VII, San Jose, CA, USA, 22–24 March 2016; pp. 418–424. [Google Scholar]
- Broadbent, W.H.; Alles, D.S.; Giusti, M.T.; Kvamme, D.F.; Shi, R.-F.; Sousa, W.L.; Walsh, R.; Xiong, Y. Results from a new 193 nm die-to-database reticle inspection platform. In Proceedings of the Photomask and Next-Generation Lithography Mask Technology XVII, Yokohama, Japan, 13–15 April 2010; pp. 684–692. [Google Scholar]
- Sibole, S.C.; Moo, E.K.; Federico, S.; Herzog, W. Dynamic deformation calculation of articular cartilage and cells using resonance-driven laser scanning microscopy. J. Biomech. Eng. 2023, 145, 021005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimura, M.; Marcelino, K.; Romero, R.; Zhao, J.; Kim, K.; Nessaee, A.; Kim, Y.; Stratton, D.; Curiel-Lewandrowski, C.; Garfinkel, J. Speckle Noise Reduction in Portable Confocal Microscopy for in vivo Human Skin Imaging. In Proceedings of the Microscopy Histopathology and Analytics, Fort Lauderdale, FL, USA, 7–10 April 2024; p. MM1A.6. [Google Scholar]
- Bianco, V.; Memmolo, P.; Leo, M.; Montresor, S.; Distante, C.; Paturzo, M.; Picart, P.; Javidi, B.; Ferraro, P. Strategies for reducing speckle noise in digital holography. Light Sci. Appl. 2018, 7, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevkunov, I.; Katkovnik, V.; Claus, D.; Pedrini, G.; Petrov, N.V.; Egiazarian, K. Spectral object recognition in hyperspectral holography with complex-domain denoising. Sensors 2019, 19, 5188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanninen, A. Vibrational imaging of metabolites for improved microbial cell strains. J. Biomed. Opt. 2024, 29, S22711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González Olmos, A.; Zilpelwar, S.; Sunil, S.; Boas, D.A.; Postnov, D.D. Optimizing the precision of laser speckle contrast imaging. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 17970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.; Zheng, Y.; Ke, W.; Feng, T.; Zhang, H.; Fan, R.; Cao, Y.; Li, L. Fast and high-resolution multimode fiber speckle imaging via optical coherence control. Opt. Express 2025, 33, 8476–8489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, K.; Min, D.; Hong, J.; Park, J.-H. Speckle reduction for single sideband-encoded computer-generated holograms by using an optimized carrier wave. Opt. Express 2024, 32, 13508–13526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Wang, J.; Zheng, L.; Chen, S.; An, H.; Li, L.; Long, Y. Method of generating speckle patterns for digital image correlation based on modified Conway’s Game of Life. Optics Express 2024, 32, 11654–11664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Dubey, A.K.; Gupta, M.; Singh, V.; Butola, A.; Mehta, D.S. Speckle noise reduction strategies in laser-based projection imaging, fluorescence microscopy, and digital holography with uniform illumination, improved image sharpness, and resolution. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 141, 107079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Ren, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Ali, Z.; Cui, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J. Semi-supervised dual generative adversarial network for low-dose CT artifact suppression. Optics Express 2025, 33, 9715–9732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H. Speckle attenuation for optical coherence tomography images using the generalized low rank approximations of matrices. Optics Express 2023, 31, 11745–11759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrokhi, H.; Rohith, T.M.; Boonruangkan, J.; Han, S.; Kim, H.; Kim, S.-W.; Kim, Y.-J. High-brightness laser imaging with tunable speckle reduction enabled by electroactive micro-optic diffusers. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Jo, Y.; Nam, S.-W.; Chae, M.; Chun, C.; Kim, Y.; Jeong, Y.; Lee, B. Speckle reduced holographic display system with a jointly optimized rotating phase mask. Optics Express 2024, 49, 5659–5662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fridman, L.; Yelin, D. Pinhole shifting for reducing speckle contrast in reflectance confocal microscopy. Opt. Lett. 2022, 47, 5735–5738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zhu, J.; Xu, M.; Pu, M.; Wang, S. Continuous-wave degenerate cavity laser for optical imaging in scattering media. Optics Express 2024, 49, 4350–4353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memmolo, P.; Bianco, V.; Paturzo, M.; Ferraro, P. Numerical manipulation of digital holograms for 3-D imaging and display: An overview. Proc. IEEE 2016, 105, 892–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggioni, M.; Katkovnik, V.; Egiazarian, K.; Foi, A. Nonlocal transform-domain filter for volumetric data denoising and reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2012, 22, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katkovnik, V.; Egiazarian, K. Sparse phase imaging based on complex domain nonlocal BM3D techniques. Digit. Signal Process. 2017, 63, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevkunov, I.; Katkovnik, V.; Claus, D.; Pedrini, G.; Petrov, N.V.; Egiazarian, K. Hyperspectral phase imaging based on denoising in complex-valued eigensubspace. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2020, 127, 105973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielyan, A.; Katkovnik, V.; Egiazarian, K. BM3D frames and variational image deblurring. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2011, 21, 1715–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katkovnik, V.; Shevkunov, I.; Egiazarian, K. Hyperspectral complex domain denoising. In Proceedings of the 2019 27th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), A Coruna, Spain, 2–6 September 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Haouat, M.; Garcia-Sucerquia, J.; Kellou, A.; Picart, P. Reduction of speckle noise in holographic images using spatial jittering in numerical reconstructions. Optics Express 2017, 42, 1047–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katkovnik, V.; Bioucas-Dias, J. Wavefront reconstruction in phase-shifting interferometry via sparse coding of amplitude and absolute phase. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2014, 31, 1801–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Chen, L.; Xiao, J.; Li, J.; Hu, Y.; Wen, K. Speckle reduction in digital holography with non-local means filter based on the Pearson correlation coefficient and Butterworth filter. Opt. Lett. 2022, 47, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donoho, D.L.; Johnstone, I.M. Ideal spatial adaptation by wavelet shrinkage. Biometrika 1994, 81, 425–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudin, L.I.; Osher, S.; Fatemi, E. Nonlinear total variation based noise removal algorithms. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 1992, 60, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perona, P.; Malik, J. Scale-space and edge detection using anisotropic diffusion. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2002, 12, 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, W.; Jeong, W.; Son, K.; Yang, H. Speckle noise reduction for digital holographic images using multi-scale convolutional neural networks. Opt. Lett. 2018, 43, 4240–4243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liao, H.; Kong, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhuang, S. Speckle denoising based on Swin-UNet in digital holographic interferometry. Optics Express 2024, 32, 33465–33482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, G.; Xu, Y.; Cai, R.; Zhao, H.; Wu, J.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, S. Compact speckle spectrometer based on CNN-LSTM denoising. Opt. Lett. 2024, 49, 6521–6524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krull, A.; Buchholz, T.-O.; Jug, F. Noise2void-learning denoising from single noisy images. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 2129–2137. [Google Scholar]
- Batson, J.; Royer, L. Noise2self: Blind denoising by self-supervision. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; pp. 524–533. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Fan, Y.; Liao, H. Self-supervised speckle noise reduction of optical coherence tomography without clean data. Biomed. Opt. Express 2022, 13, 6357–6372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isola, P.; Zhu, J.-Y.; Zhou, T.; Efros, A.A. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1125–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Raissi, M.; Perdikaris, P.; Karniadakis, G.E. Physics informed deep learning (part i): Data-driven solutions of nonlinear partial differential equations. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.10561v1. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Bentivegna, E.; Zhou, W.; Klein, L.; Elmegreen, B. Physics-informed neural network super resolution for advection-diffusion models. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2011.02519. [Google Scholar]
- Xypakis, E.; De Turris, V.; Gala, F.; Ruocco, G.; Leonetti, M. Physics-informed deep neural network for image denoising. Optics Express 2023, 31, 43838–43849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, J.W. Speckle Phenomena in Optics: Theory and Applications; Roberts and Company Publishers: Greenwood Village, CO, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ohtsubo, J.; Asakura, T. Statistical properties of speckle patterns produced by coherent light at the image and defocus planes. Optik 1976, 45, 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.-Y.; Park, T.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2223–2232. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, S.; Rastegari, M.; Shapiro, L.; Hajishirzi, H. Espnetv2: A light-weight, power efficient, and general purpose convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 9190–9200. [Google Scholar]
- Maas, A.L.; Hannun, A.Y.; Ng, A.Y. Rectifier nonlinearities improve neural network acoustic models. In Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Machine Learning, Atlanta, GA, USA, 17–19 June 2013; p. 3. [Google Scholar]
- Rumelhart, D.E.; Hinton, G.E.; Williams, R.J. Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Nature 1986, 323, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diederik, K. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Mansour, Y.; Heckel, R. Zero-shot noise2noise: Efficient image denoising without any data. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 14018–14027. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.; Jeong, W.-K. ISCL: Interdependent self-cooperative learning for unpaired image denoising. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2021, 40, 3238–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Encoder and Decoder | U-Net | U-Net + EESP | |
|---|---|---|---|
| MSE | 10.45 | 7.54 | 6.98 |
| SSIM | 0.92 | 0.91 | 0.95 |
| C | 0.56 | 0.35 | 0.34 |
| SNR | 5.23 | 7.12 | 7.81 |
| 0 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 1 | 2 | 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSE | 7.83 | 7.81 | 7.42 | 7.22 | 7.12 | 6.98 | 9.89 | 12.56 |
| SSIM | 0.90 | 0.90 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.92 | 0.95 | 0.88 | 0.66 |
| C | 0.54 | 0.54 | 0.55 | 0.39 | 0.38 | 0.34 | 0.32 | 0.31 |
| SNR | 6.81 | 6.82 | 6.78 | 6.99 | 7.71 | 7.81 | 5.43 | 4.56 |
| 0 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 1 | 2 | 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSE | 7.73 | 7.31 | 7.31 | 7.12 | 6.89 | 6.98 | 7.12 | 8.54 |
| SSIM | 0.85 | 0.88 | 0.91 | 0.93 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.91 | 0.81 |
| C | 0.44 | 0.43 | 0.44 | 0.35 | 0.32 | 0.34 | 0.34 | 0.35 |
| SNR | 6.87 | 6.88 | 6.92 | 7.76 | 7.82 | 7.81 | 6.52 | 6.12 |
| KL Loss | Gradient Loss | MSE | SSIM | C | SNR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| √ | 6.92 | 0.88 | 0.41 | 7.13 | |
| √ | 6.95 | 0.86 | 0.44 | 7.05 | |
| 7.21 | 0.82 | 0.45 | 6.56 | ||
| √ | √ | 6.79 | 0.95 | 0.31 | 7.92 |
| Methods | Parameter | MSE | SSIM | C | SNR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original | Null | 9.55 | 0.78 | 0.53 | 5.54 |
| Median | W: 3 × 3; | 8.23 | 0.65 | 0.58 | 6.32 |
| W: 5 × 5; | 8.12 | 0.63 | 0.56 | 6.44 | |
| W: 7 × 7; | 7.78 | 0.62 | 0.54 | 6.54 | |
| Wiener | W: 3 × 3; | 8.89 | 0.72 | 0.48 | 6.78 |
| W: 5 × 5; | 8.45 | 0.71 | 0.47 | 6.98 | |
| W: 7 × 7; | 8.12 | 0.67 | 0.46 | 7.54 | |
| Wavelet | M: “db2”, DS: 3; | 9.56 | 0.83 | 0.47 | 6.82 |
| M: “db3”, DS: 3 | 9.12 | 0.81 | 0.48 | 7.06 | |
| BM3D | σ: 9; | 8.54 | 0.88 | 0.51 | 7.32 |
| σ: 16; | 8.82 | 0.85 | 0.49 | 7.41 | |
| σ: 25 | 8.23 | 0.81 | 0.47 | 7.59 | |
| ZS-N2N | Same Training Set | 7.34 | 0.92 | 0.38 | 7.51 |
| ISCL | Same Training Set | 7.12 | 0.91 | 0.35 | 6.98 |
| Ours | Same Training Set | 6.79 | 0.95 | 0.31 | 7.92 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, X.; Xie, F.; Yang, T.; Ming, M.; Chen, T. Physics-Informed Generative Adversarial Networks for Laser Speckle Noise Suppression. Sensors 2025, 25, 3842. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25133842
Guo X, Xie F, Yang T, Ming M, Chen T. Physics-Informed Generative Adversarial Networks for Laser Speckle Noise Suppression. Sensors. 2025; 25(13):3842. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25133842
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Xiangji, Fei Xie, Tingkai Yang, Ming Ming, and Tao Chen. 2025. "Physics-Informed Generative Adversarial Networks for Laser Speckle Noise Suppression" Sensors 25, no. 13: 3842. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25133842
APA StyleGuo, X., Xie, F., Yang, T., Ming, M., & Chen, T. (2025). Physics-Informed Generative Adversarial Networks for Laser Speckle Noise Suppression. Sensors, 25(13), 3842. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25133842





