Boosting 3D Object Detection with Adversarial Adaptive Data Augmentation Strategy
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose an adversarial adaptive data augmentation strategy (AADA) to improve the robustness of 3D object detection. To the best of our knowledge, we present the first attempt to employ virtual adversarial training for adaptive augmentation.
- Extensive experiments show that our method significantly improves the performance of 3D object detection on the nuScenes-mini and Kitti datasets, demonstrating the effectiveness of our method.
2. Related Work
2.1. Lidar-Based 3D Perception
2.2. Camera-Based 3D Perception
2.3. Multi-Sensor Fusion
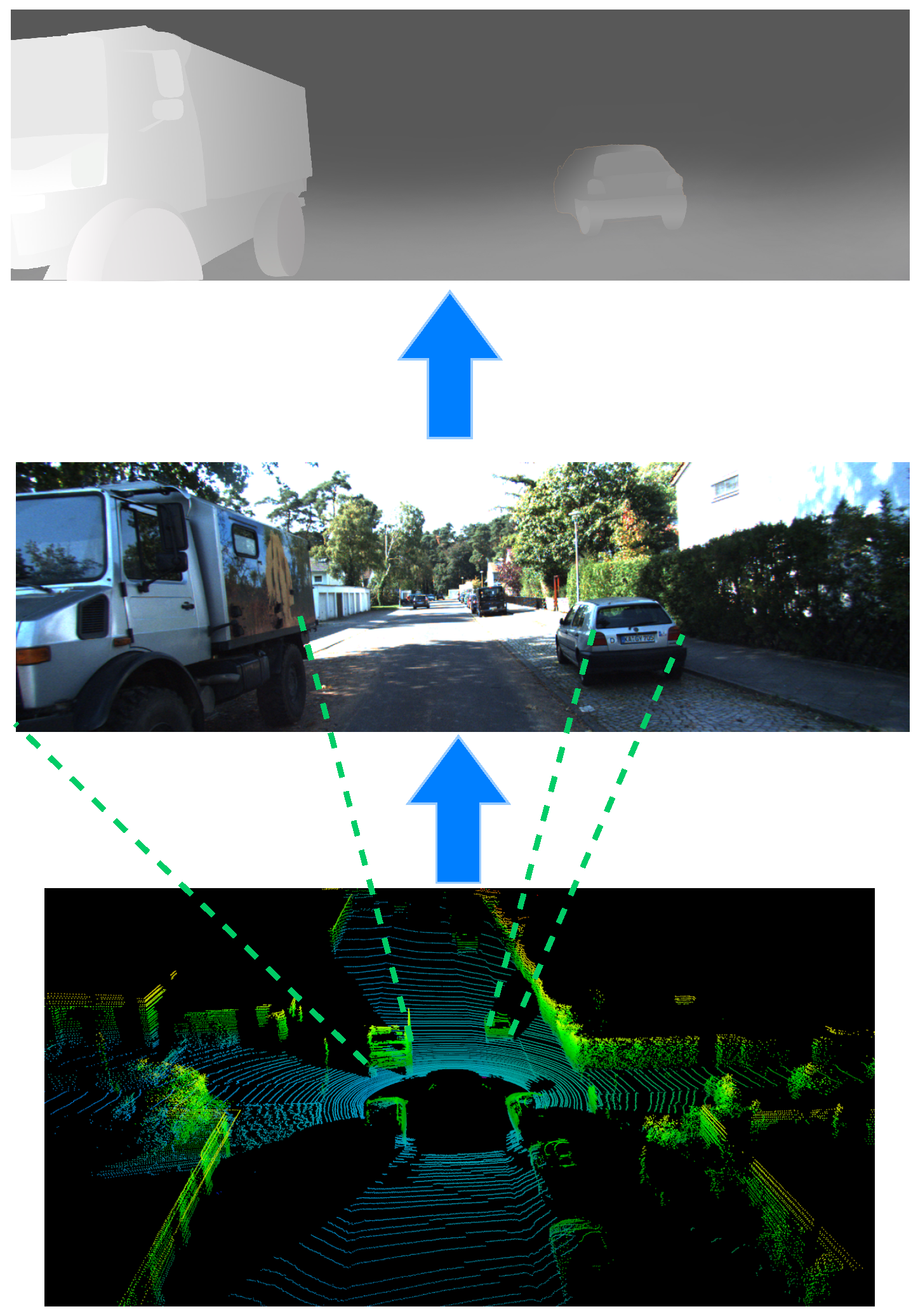
3. Methodology
3.1. Feature Extraction
3.1.1. Image Feature Encoding
3.1.2. Point Cloud Feature Encoding
3.2. BEV Feature Transformation
3.2.1. Image-to-BEV Transformation
3.2.2. Point Cloud-to-BEV Transformation
3.3. Convolutional BEV Fusion
3.4. Adversarial Adaptive Data Augmentation
| Algorithm 1: Adversarial Adaptive Augmentation Strategy |
Input: : Orignal image : Image feature extraction network : Against the size of the sample perturbation : The size of the antagonistic sample Output: : Local adversarial loss |
| 1 |
| 2 Create a tensor |
| 3 |
| 4 |
| 5 |
| 6 |
| 7 |
| 8 |
| 9 |
| 10 |
3.5. Loss Function
4. Experiments
4.1. Datasets
4.2. Implementation Details
4.3. Evaluation Results
4.3.1. Results on nuScenes-Mini Validation Set
4.3.2. Results on KITTI Validation Set
4.4. Ablation Study
4.4.1. Impact of
4.4.2. Impact of
4.4.3. Comparison with Other Data Augmentation Methods
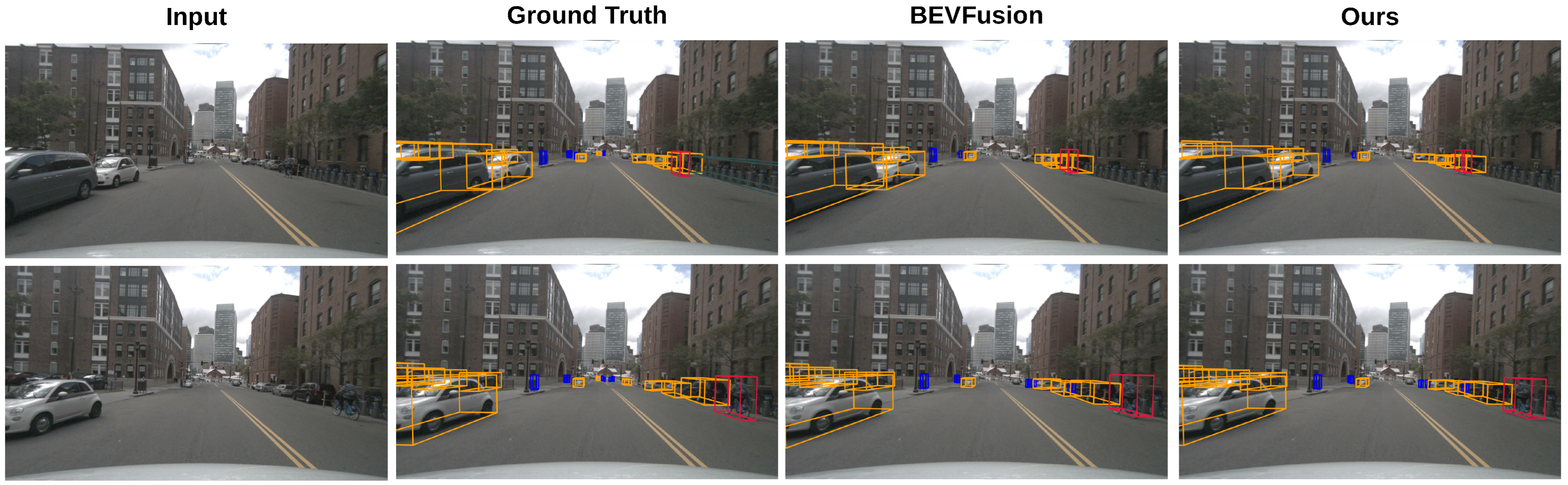
4.5. Visualization Results
5. Limitations and Future Research
5.1. Limitations
5.1.1. Poor Recognition of Small Objects
5.1.2. Limitations of Manual Hyperparameter Selection for AADA
5.2. Future Research Trends
- 1.
- Enhancing small-object extraction capability: We will consider dynamically adjusting the size and position of local windows in the image feature extraction network based on image content, focusing on feature extraction in small-object regions. Meanwhile, we will design feature extraction modules tailored for small objects to increase the model’s sensitivity and extraction efficiency for small-object features.
- 2.
- Diverse environment evaluation: We will conduct comprehensive environmental adaptability assessments of the proposed method. The performance of the method will be tested under various environmental conditions, including night driving and adverse weather, to analyze its limitations and optimize the algorithm in a targeted manner.
- 3.
- Automated hyperparameter tuning: We will develop automated hyperparameter adjustment methods to efficiently explore the hyperparameter space and identify better parameter combinations, thereby improving the overall performance and stability of the algorithm.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, H.; Sima, C.; Dai, J.; Wang, W.; Lu, L.; Wang, H.; Zeng, J.; Li, Z.; Yang, J.; Deng, H.; et al. Delving Into the Devils of Bird’s-Eye-View Perception: A Review, Evaluation and Recipe. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. (TPAMI) 2023, 46, 2151–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Huang, G.; Zhu, Z.; Ye, Y.; Du, D. BEVDet: High-performance Multi-camera 3D Object Detection in Bird-Eye-View. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.11790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Tang, H.; Amini, A.; Yang, X.; Mao, H.; Rus, D.; Han, S. BEVFusion: Multi-Task Multi-Sensor Fusion with Unified Bird’s-Eye View Representation. arXiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.; Han, D.; Oh, S.; Chun, S.; Choe, J.; Yoo, Y. CutMix: Regularization Strategy to Train Strong Classifiers with Localizable Features. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Cisse, M.; Oh, S.; Dauphin, Y.N.; Lopez-Paz, D. mixup: Beyond Empirical Risk Minimization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 30 April–3 May 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Luo, W.; Urtasun, R. PIXOR: Real-time 3D Object Detection from Point Clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, B.; Engelcke, M.; Laurens, V.D.M. 3D Semantic Segmentation with Submanifold Sparse Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 9224–9232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Pu, S. RangeRCNN: Towards Fast and Accurate 3D Object Detection with Range Image Representation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2009.00206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Qi, X.; Jia, J. VoxelNeXt: Fully Sparse VoxelNet for 3D Object Detection and Tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 21674–21683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Pham, K.T.; Ye, M.; Shen, Z.; Chen, Q. Cross-Cluster Shifting for Efficient and Effective 3D Object Detection in Autonomous Driving. IEEE Int. Conf. Robot. Autom. 2024, 4273–4280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Chen, J.; Gao, G.; Li, J.; Liu, S.; Hu, X. SAFDNet: A Simple and Effective Network for Fully Sparse 3D Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Deng, J.; Li, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, J.; Zhang, Y. Neighbor-Vote: Improving Monocular 3D Object Detection through Neighbor Distance Voting. In Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Virtual, 20–24 October 2021; pp. 5239–5247. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Kundu, K.; Zhu, Y.; Ma, H.; Fidler, S.; Urtasun, R. 3D Object Proposals Using Stereo Imagery for Accurate Object Class Detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. (TPAMI) 2018, 40, 1259–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Chen, X.; Shen, S. Stereo R-CNN Based 3D Object Detection for Autonomous Driving. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 7636–7644. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Shi, S.; Wang, X.; Li, H. Learning LiDAR Geometry Aware Representations for Stereo-based 3D Detector. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 3133–3143. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, L.; Yan, P.; Xiong, S.; Xiang, X.; Tan, Y. MonoCD: Monocular 3D Object Detection with Complementary Depths. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 10248–10257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Wang, T.; Ye, X.; Liu, Z.; Gong, S.; Tan, X.; Ding, E.; Wang, J.; Bai, X. OPEN: Object-Wise Position Embedding for Multi-view 3D Object Detection. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 146–162. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.; Shi, S.; Wang, X.; Li, H. 3D Object Detection for Autonomous Driving: A Comprehensive Survey. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2022, 131, 1909–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, X.; Xu, H.; Chen, Z.; Yu, D.; Chang, J.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, F. Towards Domain Generalization for Multi-view 3D Object Detection in Bird-Eye-View. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 13333–13342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, E.; Yu, Z.; Zhou, D.; Philion, J.; Anandkumar, A.; Fidler, S.; Luo, P.; Alvarez, J.M. M2BEV: Multi-Camera Joint 3D Detection and Segmentation with Unified Birds-Eye View Representation. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2204.05088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Yang, B.; Chen, Y.; Hu, R.; Urtasun, R. Multi-Task Multi-Sensor Fusion for 3D Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2019; pp. 7337–7345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Sun, P.; Xu, Z.; Min, H.; Yu, H. Fusion of 3D LIDAR and Camera Data for Object Detection in Autonomous Vehicle Applications. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 4901–4913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; He, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Mao, Z. Multi-modality 3D object detection in autonomous driving: A review. Neurocomputing 2023, 553, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Mao, Y.; Li, B. SECOND: Sparsely Embedded Convolutional Detection. Sensors 2018, 18, 3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urtasun, R.; Lenz, P.; Geiger, A. Are we ready for autonomous driving? The KITTI vision benchmark suite. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; pp. 3354–3361. [Google Scholar]
- Caesar, H.; Bankiti, V.; Lang, A.H.; Vora, S.; Liong, V.E.; Xu, Q.; Krishnan, A.; Pan, Y.; Baldan, G.; Beijbom, O. nuScenes: A Multimodal Dataset for Autonomous Driving. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11618–11628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, A.H.; Vora, S.; Caesar, H.; Zhou, L.; Yang, J.; Beijbom, O. PointPillars: Fast Encoders for Object Detection from Point Clouds. arXiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhu, X.; Pang, J.; Lin, D. Probabilistic and Geometric Depth: Detecting Objects in Perspective. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning, London, UK, 8–11 November 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, T.; Zhou, X.; Krhenbühl, P. Center-based 3D Object Detection and Tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 11779–11788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Ye, Y.; Liang, Z.; Shan, Y.; Du, D. Detecting As Labeling: Rethinking LiDAR-camera Fusion in 3D Object Detection. arXiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Qi, X.; Li, Z.; Sun, J.; Jia, J. Unifying Voxel-based Representation with Transformer for 3D Object Detection. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 18442–18455. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Xu, C.; Rakotosaona, M.; Rim, P.; Tombari, F.; Keutzer, K.; Tomizuka, M.; Zhan, W. SparseFusion: Fusing Multi-Modal Sparse Representations for Multi-Sensor 3D Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Vishwanath, A.S.; Yin, Z.; Oncel, T. MVX-Net: Multimodal VoxelNet for 3D Object Detection. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 7276–7282. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Hu, H.; Lin, Y.; Yao, Z.; Xie, Z.; Wei, Y.; Ning, J.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, L.; et al. Swin Transformer V2: Scaling Up Capacity and Resolution. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Madry, A.; Makelov, A.; Schmidt, L.; Tsipras, D.; Vladu, A. Towards Deep Learning Models Resistant to Adversarial Attacks. arXiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Method | mAP | NDS | AP | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Car | Truck | Bus | Ped. | Motor | Bicycle | |||
| PointPillars | 29.6 | 40.8 | 83.5 | 31.2 | 75.1 | 77.5 | 7.0 | 21.4 |
| PGD | 30.7 | 32.3 | 52.0 | 44.2 | 52.8 | 45.3 | 35.1 | 19.3 |
| CenterPoint | 37.3 | 46.6 | 80.3 | 60.7 | 86.6 | 87.8 | 17.2 | - |
| DAL | 44.9 | 53.4 | 85.7 | 59.4 | 64.9 | 91.4 | 38.8 | 12.3 |
| UVTR | 42.9 | 50.0 | 86.7 | 63.5 | 94.7 | 85.4 | 41.1 | 4.0 |
| Sparsefusion | 49.3 | 47.0 | 85.4 | 72.5 | 72.9 | 91.8 | 54.0 | 34.4 |
| BEVFusion | 48.1 | 52.9 | 89.2 | 64.1 | 98.2 | 91.8 | 56.0 | 27.7 |
| Ours | 49.6 | 53.3 | 88.3 | 69.1 | 99.3 | 92.1 | 58.8 | 33.4 |
| Method | Training Time per Epoch(s) | GPU Memory (MIB) |
|---|---|---|
| BEVFusion | 216 | 17,847 |
| Ours | 263 | 20,410 |
| Method | mAP | Car | Pedestrain | Cyclist | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mod. | Easy | Mod. | Hard | Easy | Mod. | Hard | Easy | Mod. | Hard | |
| MvxNet-ResNet | 63.5 | 88.4 | 78.8 | 74.7 | 62.9 | 58.4 | 55.2 | 70.9 | 53.2 | 49.6 |
| MvxNet-SwinT | 64.1 | 88.2 | 78.2 | 75.5 | 64.1 | 58.5 | 54.1 | 71.9 | 55.6 | 52.7 |
| Ours | 64.9 | 89.5 | 78.3 | 75.7 | 64.7 | 58.0 | 53.6 | 75.3 | 58.2 | 54.4 |
| mAP | NDS | AP | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Car | Truck | Bus | Ped. | Motor | Bicycle | ||||
| 5.0 | 1.0 | 47.9 | 52.3 | 88.6 | 64.0 | 97.3 | 90.4 | 54.7 | 28.3 |
| 5.0 | 2.0 | 49.6 | 53.5 | 88.3 | 69.1 | 99.3 | 92.1 | 58.8 | 33.4 |
| 5.0 | 3.0 | 48.7 | 53.1 | 88.6 | 65.9 | 98.3 | 91.3 | 54.6 | 35.1 |
| mAP | NDS | AP | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Car | Truck | Bus | Ped. | Motor | Bicycle | ||||
| 3.0 | 2.0 | 48.8 | 52.2 | 88.4 | 63.4 | 99.2 | 91.5 | 47.7 | 39.2 |
| 4.0 | 2.0 | 48.8 | 52.6 | 88.1 | 66.6 | 98.3 | 91.4 | 48.6 | 36.2 |
| 5.0 | 2.0 | 49.6 | 53.5 | 88.3 | 69.1 | 99.3 | 92.1 | 58.8 | 33.4 |
| 6.0 | 2.0 | 48.1 | 52.9 | 88.3 | 67.0 | 99.3 | 91.0 | 50.4 | 34.8 |
| 7.0 | 2.0 | 48.8 | 53.0 | 88.4 | 65.0 | 97.9 | 91.2 | 54.7 | 35.4 |
| 8.0 | 2.0 | 48.6 | 53.2 | 88.3 | 67.0 | 97.9 | 91.2 | 57.9 | 30.2 |
| 9.0 | 2.0 | 49.1 | 53.7 | 88.6 | 69.0 | 99.3 | 91.0 | 56.5 | 29.1 |
| 10.0 | 2.0 | 49.3 | 52.9 | 88.2 | 67.8 | 99.4 | 91.8 | 51.8 | 36.1 |
| Method | mAP | NDS | AP | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Car | Truck | Bus | Ped. | Motor | Bicycle | |||
| Based on Gaussian noise | 49.0 | 53.2 | 88.8 | 66.9 | 99.7 | 91.6 | 57.5 | 36.3 |
| Based on view transformation | 48.1 | 52.9 | 89.2 | 64.1 | 98.2 | 91.8 | 56.0 | 27.7 |
| Based on PGD | 50.2 | 53.1 | 88.6 | 68.0 | 99.5 | 91.5 | 58.9 | 37.8 |
| Ours | 49.6 | 53.5 | 88.3 | 69.1 | 99.3 | 92.1 | 58.8 | 33.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Li, J.; Fu, J.; Chen, Q. Boosting 3D Object Detection with Adversarial Adaptive Data Augmentation Strategy. Sensors 2025, 25, 3493. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113493
Li S, Li J, Fu J, Chen Q. Boosting 3D Object Detection with Adversarial Adaptive Data Augmentation Strategy. Sensors. 2025; 25(11):3493. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113493
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shihao, Jingsong Li, Jianghua Fu, and Qiuyue Chen. 2025. "Boosting 3D Object Detection with Adversarial Adaptive Data Augmentation Strategy" Sensors 25, no. 11: 3493. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113493
APA StyleLi, S., Li, J., Fu, J., & Chen, Q. (2025). Boosting 3D Object Detection with Adversarial Adaptive Data Augmentation Strategy. Sensors, 25(11), 3493. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113493







