A Novel Lightweight Algorithm for Sonar Image Recognition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Proposed Work
3.1. MobileViT
3.2. Skip Connection
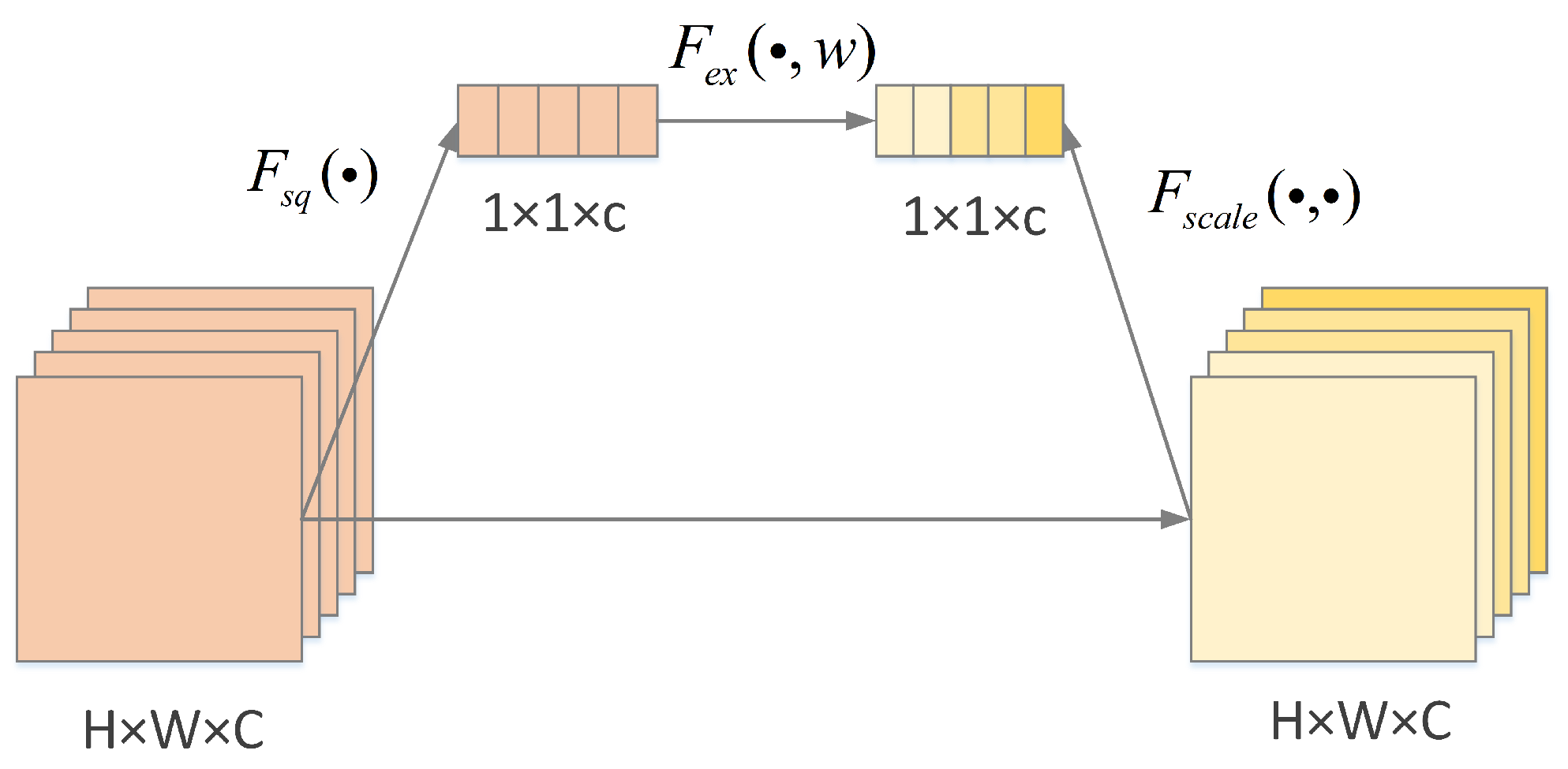
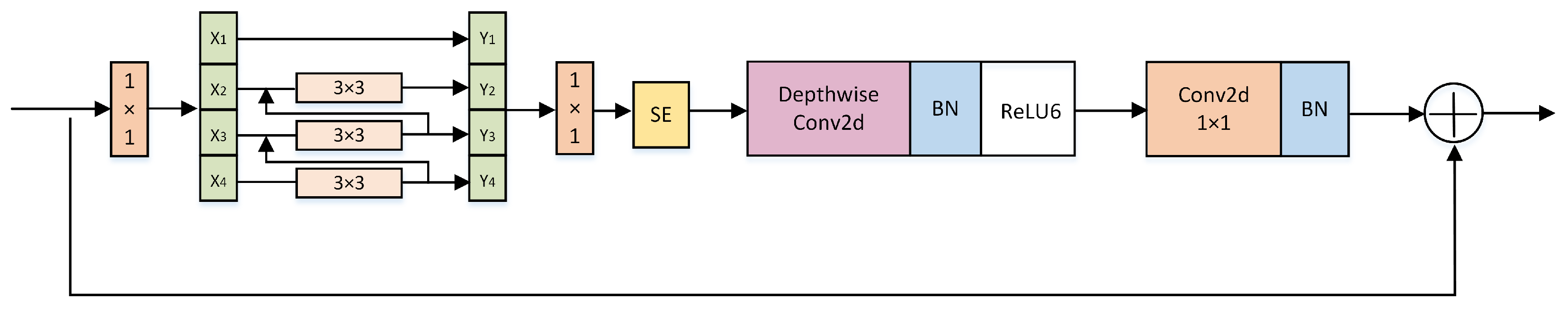
3.3. Multi-Scale Feature Fusion Module
3.4. Loss Function
4. Experimental Environment and Dataset
4.1. Experimental Environment
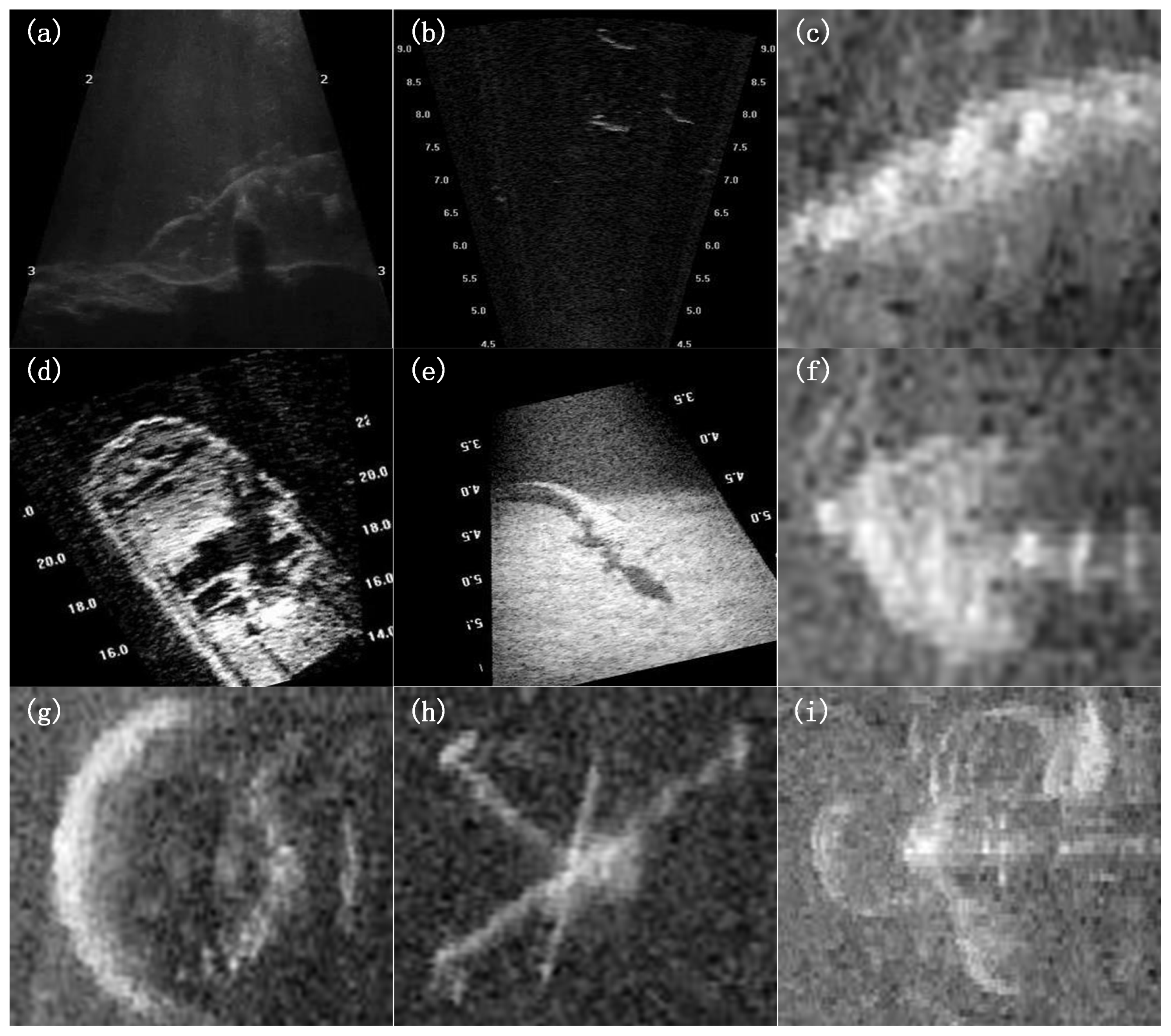
4.2. Experimental Dataset
5. Experimental Results and Analysis
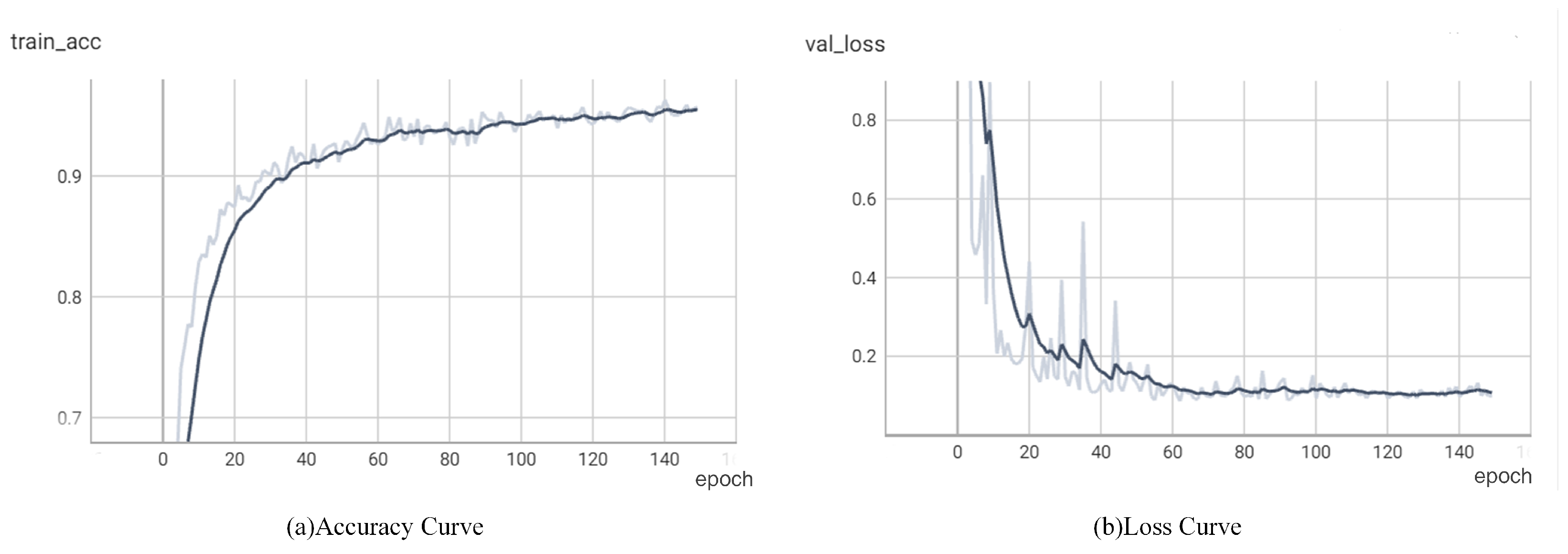
5.1. Ablation Experiment
5.2. Comparison Experiment
6. Discussion and Limitations
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, S.; Girshick, R.; Dollár, P.; Tu, Z.; He, K. Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1492–1500. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, S.; Wang, P.; Abbas, K. A survey on deep learning and its applications. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2021, 40, 100379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janiesch, C.; Zschech, P.; Heinrich, K. Machine learning and deep learning. Electron. Mark. 2021, 31, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Huang, W.; Guo, J.; Zeng, L. Sonar image target detection based on adaptive global feature enhancement network. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 22, 1509–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Sun, H.; Xin, Y.; He, Q.; Wang, X. SDNet: Image-based sonar detection network for multi-scale objects. IET Image Process. 2023, 17, 1208–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerg, I.D.; Monga, V. Structural prior driven regularized deep learning for sonar image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, L.; Li, H.; Chen, B.C.; Lan, S.; Wu, Z.; Jiang, Y.G.; Lim, S.N. Adavit: Adaptive vision transformers for efficient image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 12309–12318. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Virtual, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Hu, H.; Lin, Y.; Yao, Z.; Xie, Z.; Wei, Y.; Ning, J.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, L.; et al. Swin transformer v2: Scaling up capacity and resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 12009–12019. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, S.; Rastegari, M. Mobilevit: Light-weight, general-purpose, and mobile-friendly vision transformer. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.02178. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Y.; Zheng, T.; Xue, C.; Zhou, L. MViT-PCD: A lightweight ViT-based network for Martian surface topographic change detection. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xie, G.; Deng, X.; Peng, J.; Qiu, H. DA-YOLOv7: A Deep Learning-Driven High-Performance Underwater Sonar Image Target Recognition Model. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, F.; Dang, L.; Ge, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Qiao, B.; Zuo, X. Dual-Path Residual “Shrinkage” Network for Side-Scan Sonar Image Classification. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 6962838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.; Huo, G.; Li, H. A multi-domain collaborative transfer learning method with multi-scale repeated attention mechanism for underwater side-scan sonar image classification. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhu, H.; Song, W.; Wang, J.; Yan, L.; Wang, K. Research on improved VGG-16 model based on transfer learning for acoustic image recognition of underwater search and rescue targets. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 18112–18128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; He, B.; Liu, P. Real-time object detection for AUVs using self-cascaded convolutional neural networks. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2019, 46, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, X.; Ma, Z.; Xue, J.H. Deep metric learning for few-shot image classification: A review of recent developments. Pattern Recognit. 2023, 138, 109381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, X.; Chen, M.; Sun, X. Deep learning and image recognition. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 6th International Conference on Electronic Information and Communication Technology (ICEICT), Qingdao, China, 21–24 July 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 557–562. [Google Scholar]
- Gulzar, Y. Fruit image classification model based on MobileNetV2 with deep transfer learning technique. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Lin, K.; Jain, A.K.; Zhou, J. Transfer learning in deep reinforcement learning: A survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 13344–13362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, H.; Huo, G.; Li, C.; Wei, Y. Multi-modal multi-stage underwater side-scan sonar target recognition based on synthetic images. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Bai, Z.; Zhang, X.; Ding, Q. MFSANet: Zero-shot side-scan sonar image recognition based on style transfer. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Shen, L.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J. Underwater forward-looking sonar images target detection via speckle reduction and scene prior. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.H.; Cheng, M.M.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, X.Y.; Yang, M.H.; Torr, P. Res2net: A new multi-scale backbone architecture. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 43, 652–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.; Lim, J.; Jeon, Y.; Choi, J.Y. Influence-balanced loss for imbalanced visual classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Virtual, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 735–744. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Tang, J.; Zhong, H.; Ning, M.; Liu, D.; Wu, K. Self-trained target detection of radar and sonar images using automatic deep learning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdenegro-Toro, M.; Preciado-Grijalva, A.; Wehbe, B. Pre-trained models for sonar images. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2021: San Diego—Porto, San Diego, CA, USA, 20–23 September 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Identity mappings in deep residual networks. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Proceedings, Part IV 14. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 630–645. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.; Sandler, M.; Chu, G.; Chen, L.C.; Chen, B.; Tan, M.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Pang, R.; Vasudevan, V.; et al. Searching for mobilenetv3. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 1314–1324. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Pleiss, G.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Convolutional networks with dense connectivity. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 44, 8704–8716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
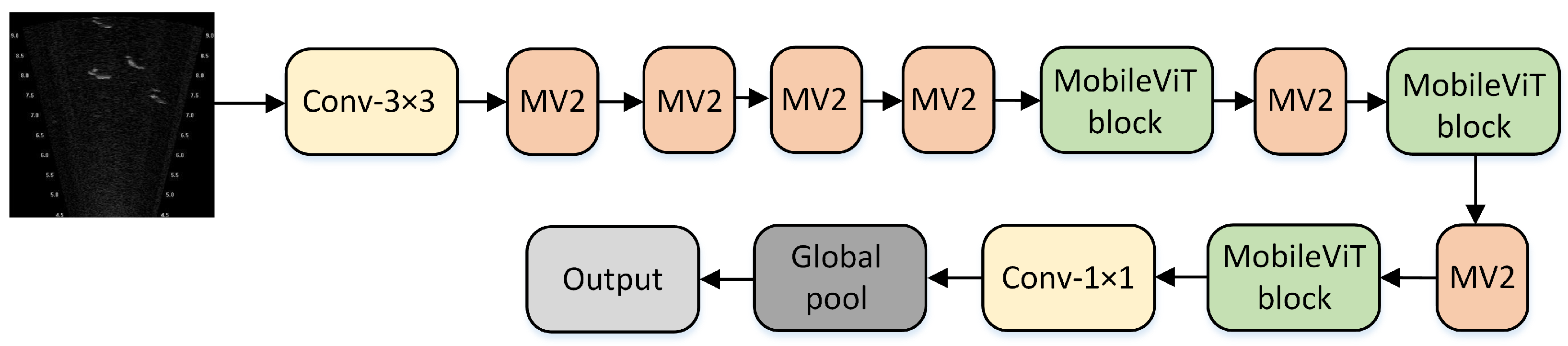

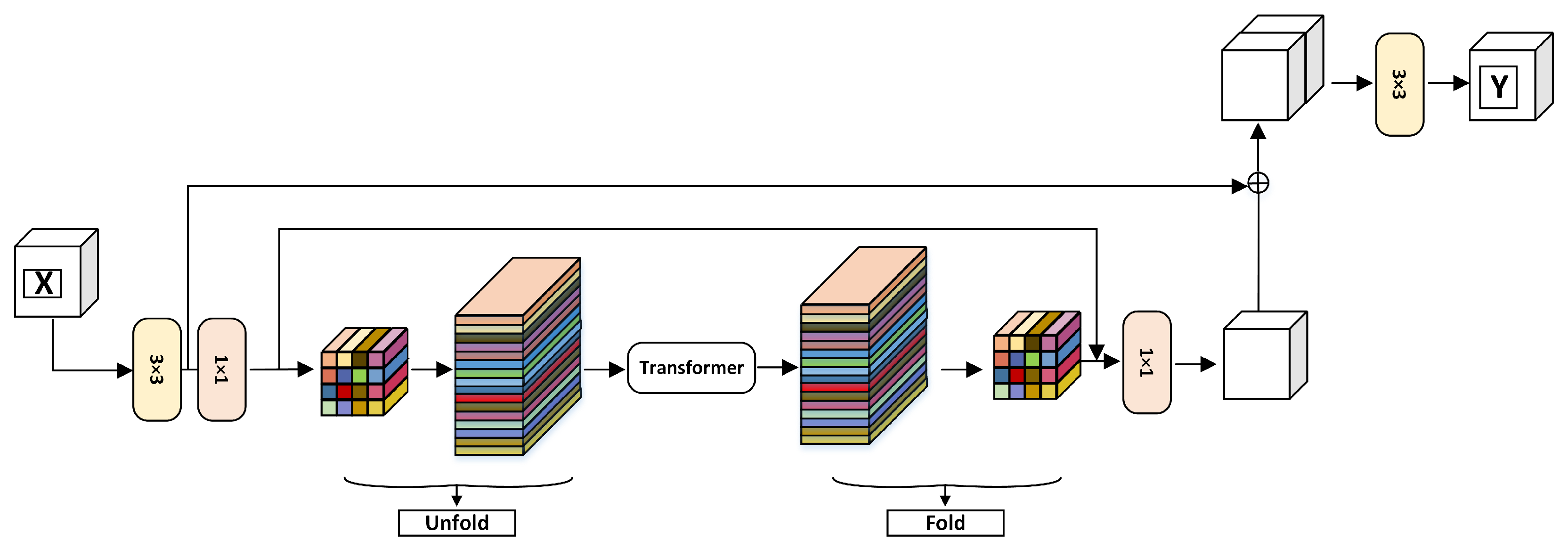

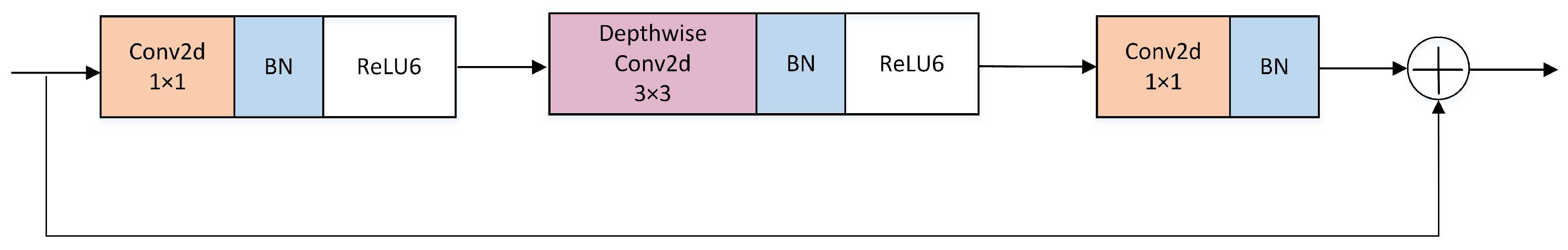

| Models of Different Sizes | Parameter Quantity (M) | Flops (G) |
|---|---|---|
| MobileViT-S | 4.94 | 1.46 |
| MobileViT-XS | 1.93 | 0.74 |
| MobileViT-XXS | 0.95 | 0.27 |
| Parameters | Setting |
|---|---|
| Batch size | 8 |
| Learning rate | 0.0002 |
| Optimizer | Adam |
| Epoch | 150 |
| Category | Total Size | Training Set Size | Validation Set Size | Test Set Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Person | 404 | 324 | 40 | 40 |
| Fish | 382 | 306 | 38 | 38 |
| Shipwreck | 831 | 665 | 83 | 83 |
| Alligator | 640 | 512 | 64 | 64 |
| Bottle | 449 | 361 | 44 | 44 |
| Can | 367 | 295 | 36 | 36 |
| Chain | 226 | 182 | 22 | 22 |
| Drink cartons | 349 | 281 | 34 | 34 |
| Hook | 133 | 107 | 13 | 13 |
| Propeller | 137 | 111 | 13 | 13 |
| Shampoo bottle | 99 | 81 | 9 | 9 |
| Standing bottles | 65 | 53 | 6 | 6 |
| Tire | 331 | 265 | 33 | 33 |
| Valve | 208 | 168 | 20 | 20 |
| Total | 4621 | 3711 | 455 | 455 |
| Hopper Connection | Res2Net | IB Loss | Average Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| − | − | − | 92.30% |
| ✓ | − | − | 93.15% |
| − | ✓ | − | 93.38% |
| − | − | ✓ | 93.23% |
| ✓ | ✓ | − | 94.65% |
| ✓ | − | ✓ | 94.63% |
| − | ✓ | ✓ | 94.45% |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 95.23% |
| Algorithm | Person | Fish | Shipwreck | Bottle | Alligator | Average Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 95.36% | 92.21% | 94.70% | 89.53% | 88.68% | 92.30% |
| ResNet50 | 95.20% | 90.01% | 90.34% | 85.78% | 88.73% | 91.75% |
| MobileNetV3 | 94.10% | 84.30% | 89.50% | 86.30% | 77.60% | 89.06% |
| DenseNet121 | 92.00% | 85.80% | 93.90% | 83.60% | 83.53% | 88.76% |
| ViT | 86.77% | 83.22% | 82.59% | 80.11% | 83.78% | 84.50% |
| Swin_Transformer | 95.80% | 94.00% | 93.40% | 90.50% | 94.60% | 95.10% |
| Ours | 96.80% | 93.33% | 95.10% | 91.32% | 93.55% | 95.23% |
| Model | Parameter Quantity (M) | Flops (G) |
|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 1.93 | 0.74 |
| ResNet50 | 25.06 | 3.03 |
| ViT | 85.50 | 16.50 |
| Swin_Transformer | 28.50 | 4.00 |
| Ours | 2.90 | 1.20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wan, G.; He, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Sun, H.; Fan, X.; Shi, P. A Novel Lightweight Algorithm for Sonar Image Recognition. Sensors 2025, 25, 3329. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113329
Wan G, He Q, Zhang Q, Wang H, Sun H, Fan X, Shi P. A Novel Lightweight Algorithm for Sonar Image Recognition. Sensors. 2025; 25(11):3329. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113329
Chicago/Turabian StyleWan, Gang, Qi He, Qianqian Zhang, Hanren Wang, Huanru Sun, Xinnan Fan, and Pengfei Shi. 2025. "A Novel Lightweight Algorithm for Sonar Image Recognition" Sensors 25, no. 11: 3329. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113329
APA StyleWan, G., He, Q., Zhang, Q., Wang, H., Sun, H., Fan, X., & Shi, P. (2025). A Novel Lightweight Algorithm for Sonar Image Recognition. Sensors, 25(11), 3329. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113329








