Time-Shifted Maps for Industrial Data Analysis: Monitoring Production Processes and Predicting Undesirable Situations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Foundations
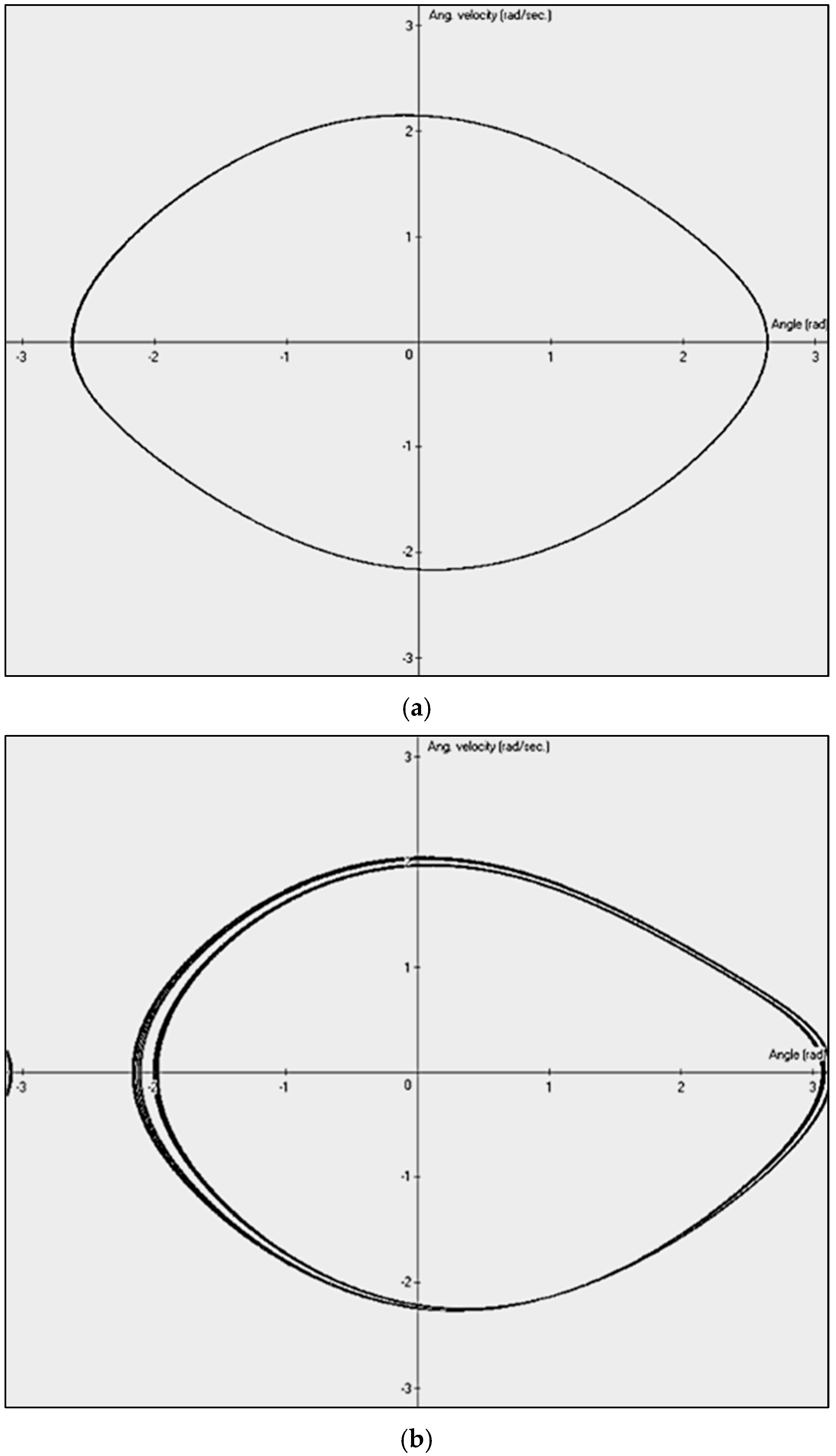
2.1. Deterministic Chaos as Example of Complex Behavior of Mechanical Systems
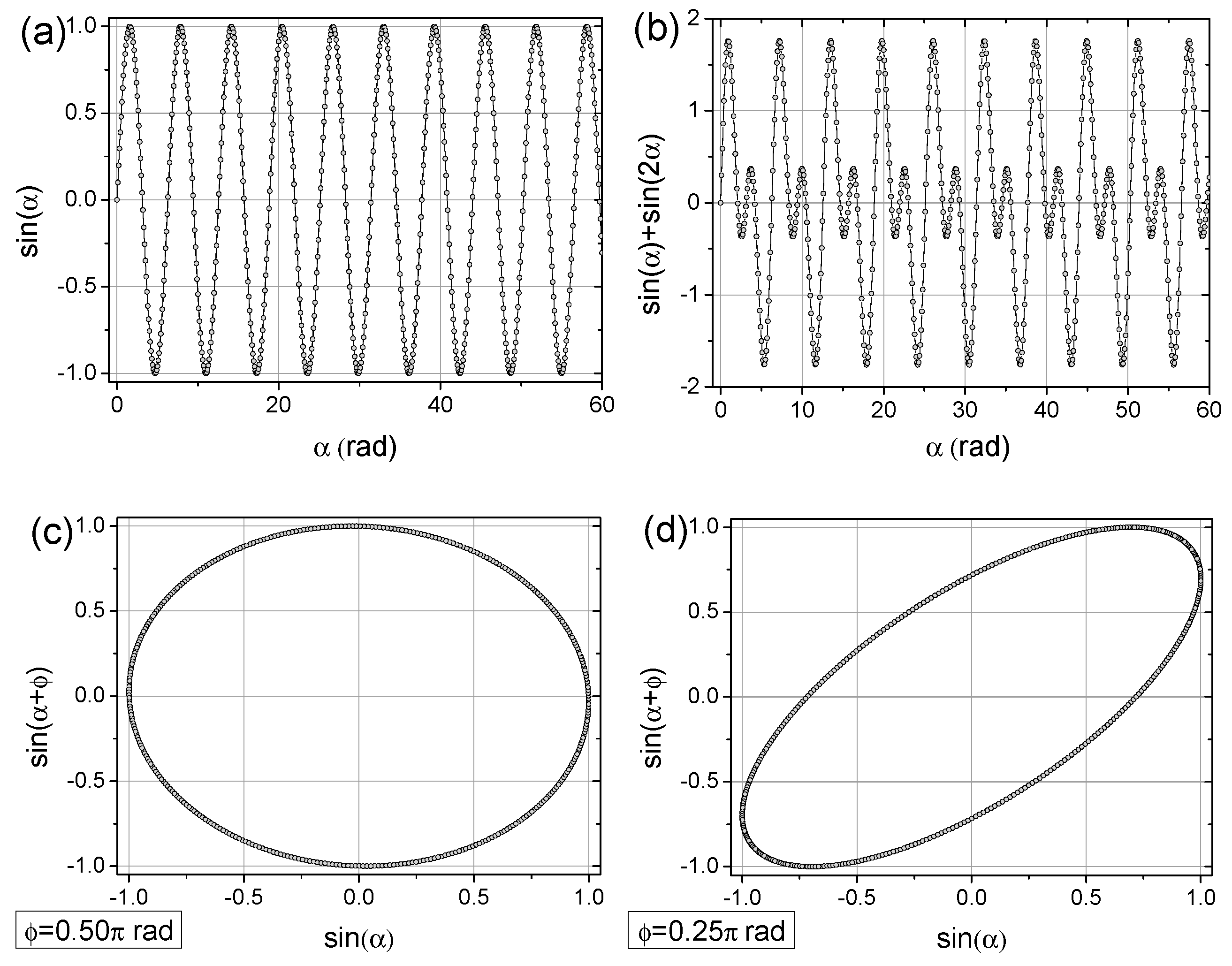
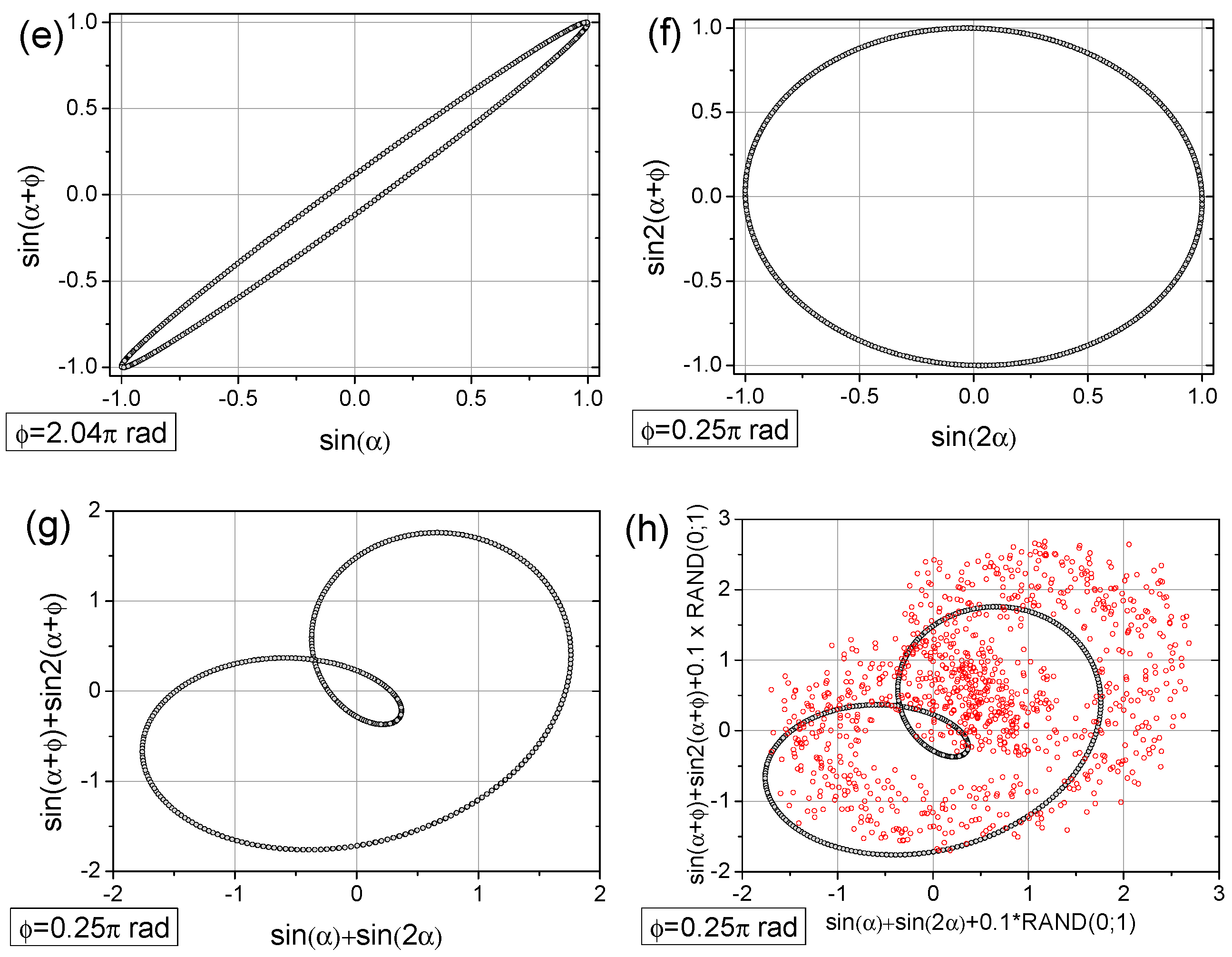
2.2. The Concept of Time-Shifted Mapping
3. Experiment and Analysis of Data
3.1. Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) Analysis of Signals
3.2. Continuous Wavelet Transform (CWT) Analysis of Signals
3.3. Experimental Data Analysis Using TSM Approach
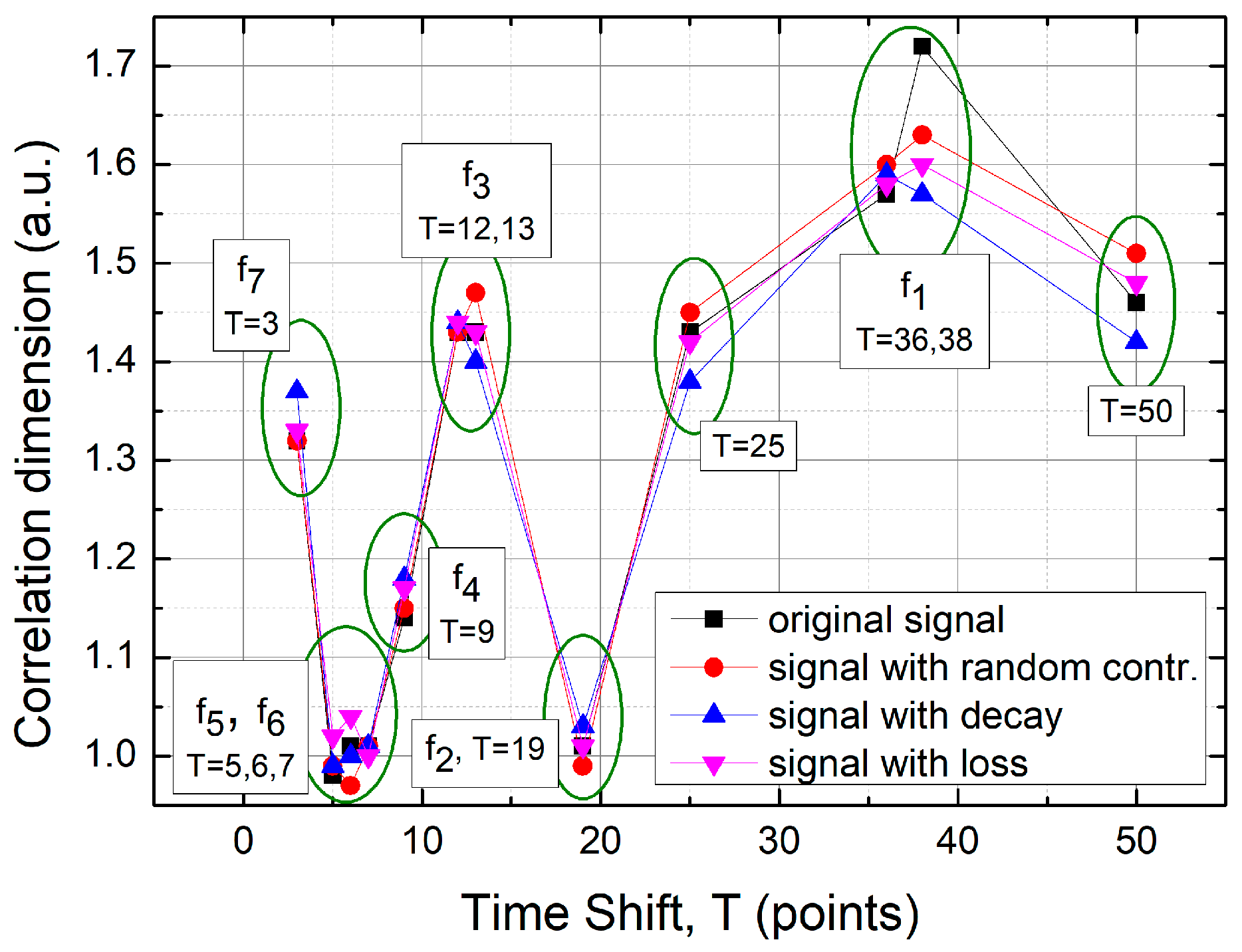
3.3.1. Classification of TSM Results Using the Correlation Dimension Approach
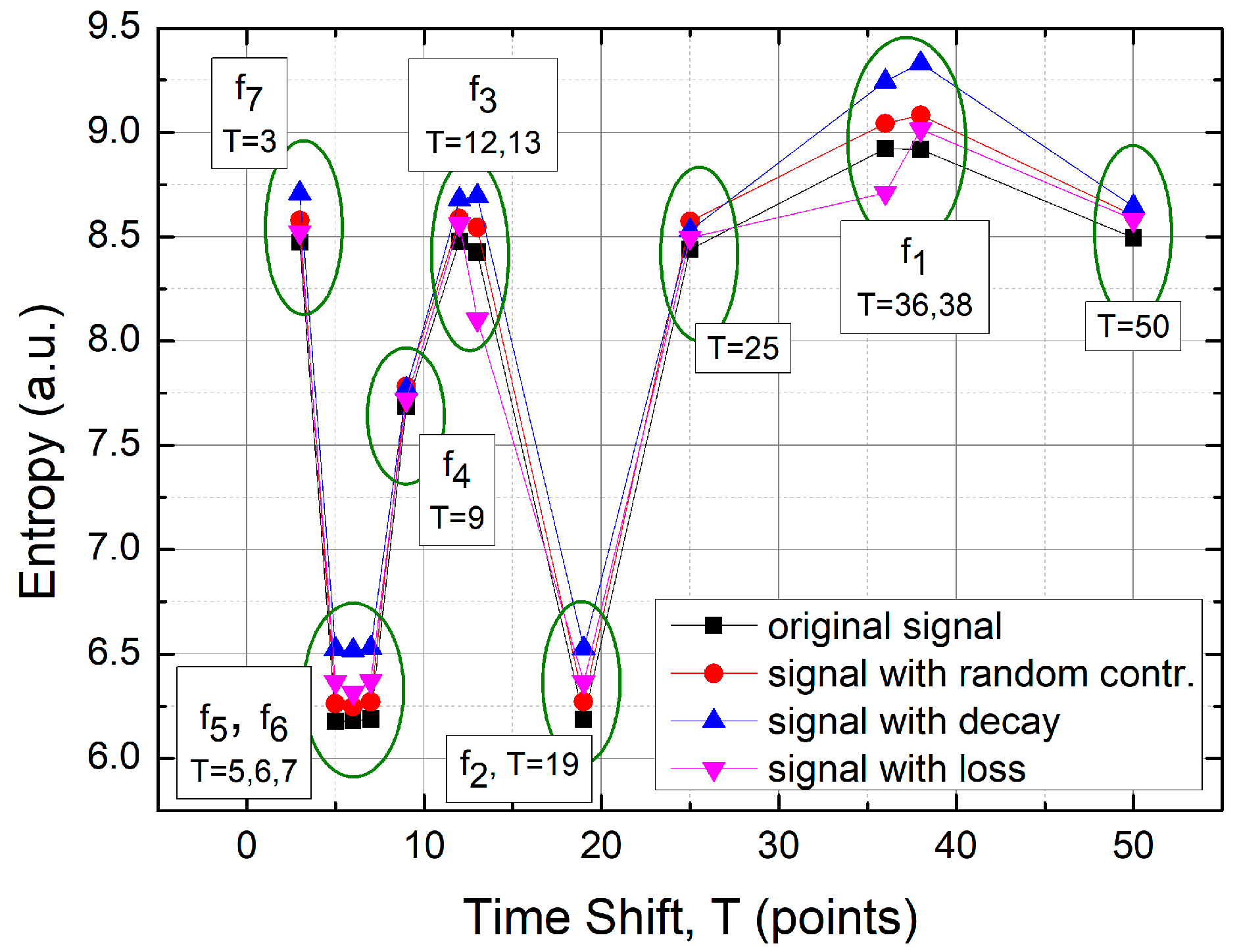
3.3.2. Classification of TSM Results Based on Metric Entropy Calculations
4. Discussion and Conclusions
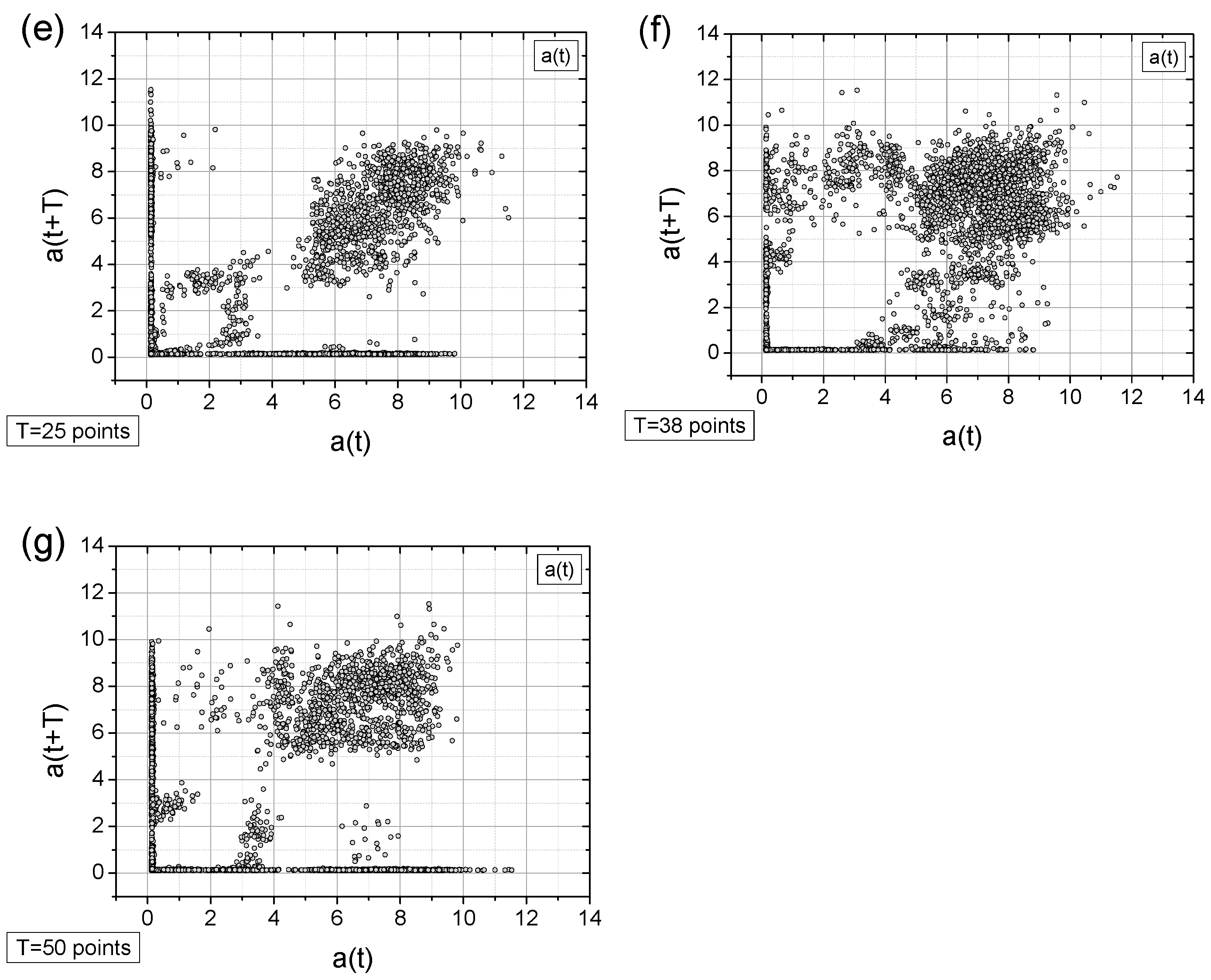
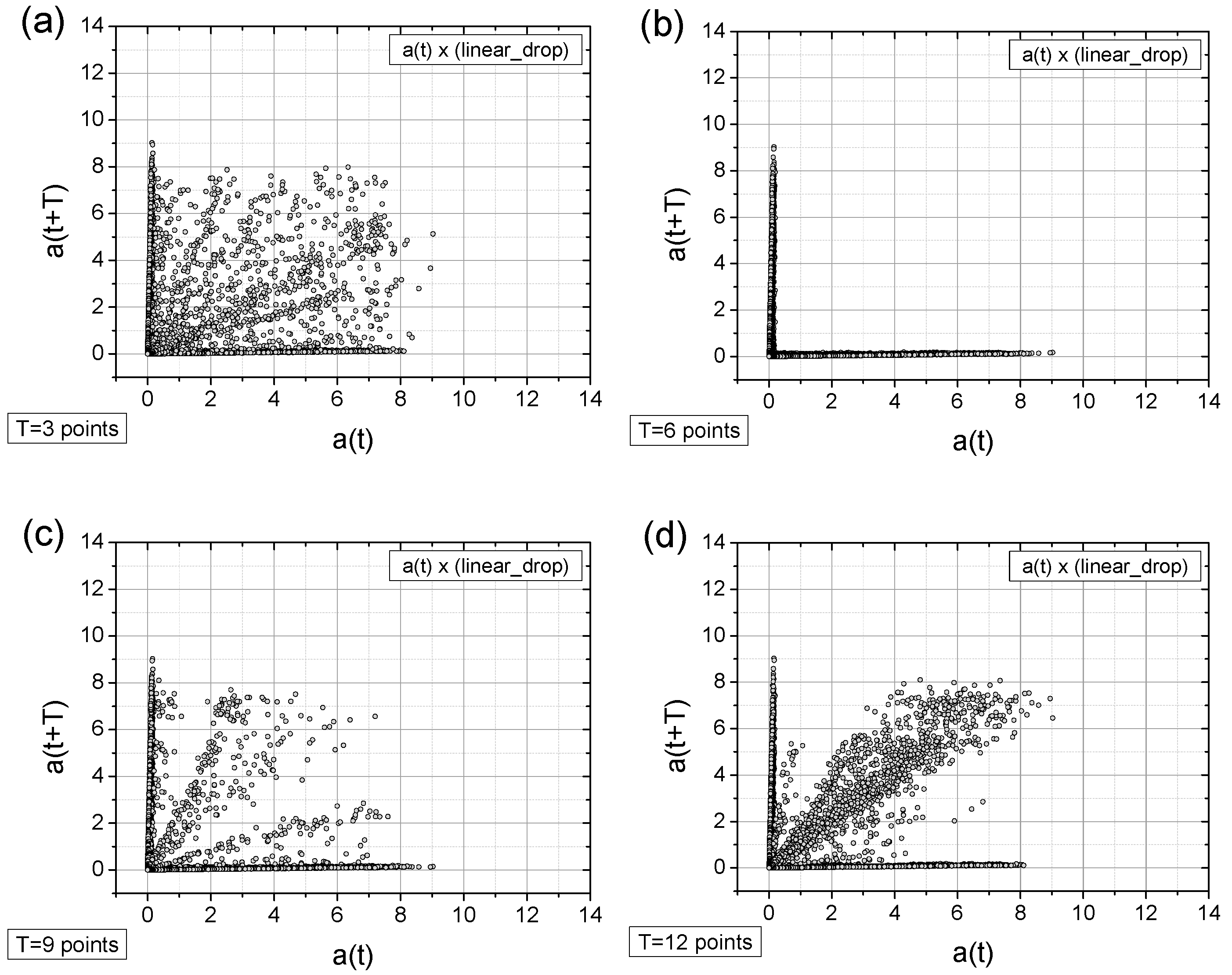
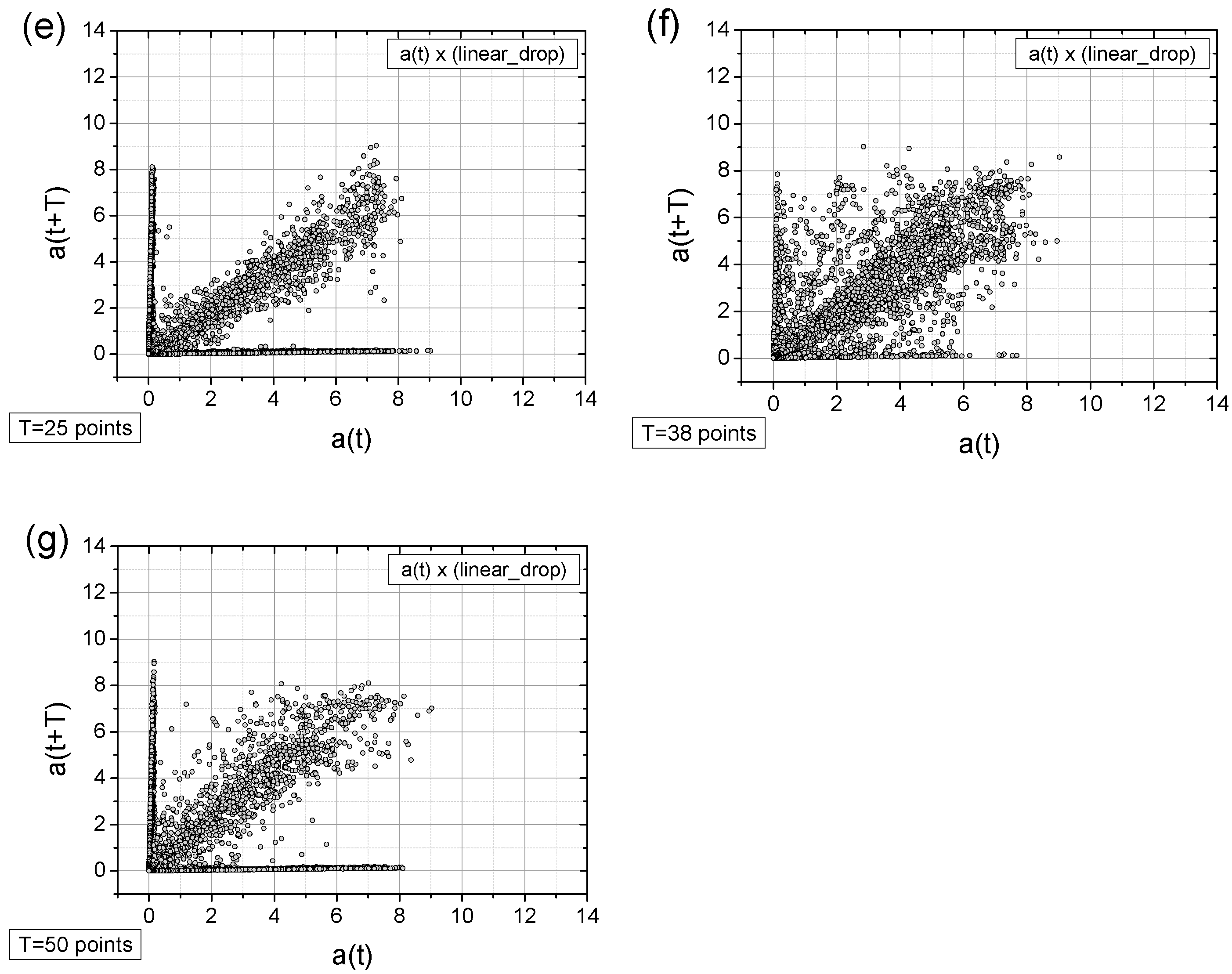
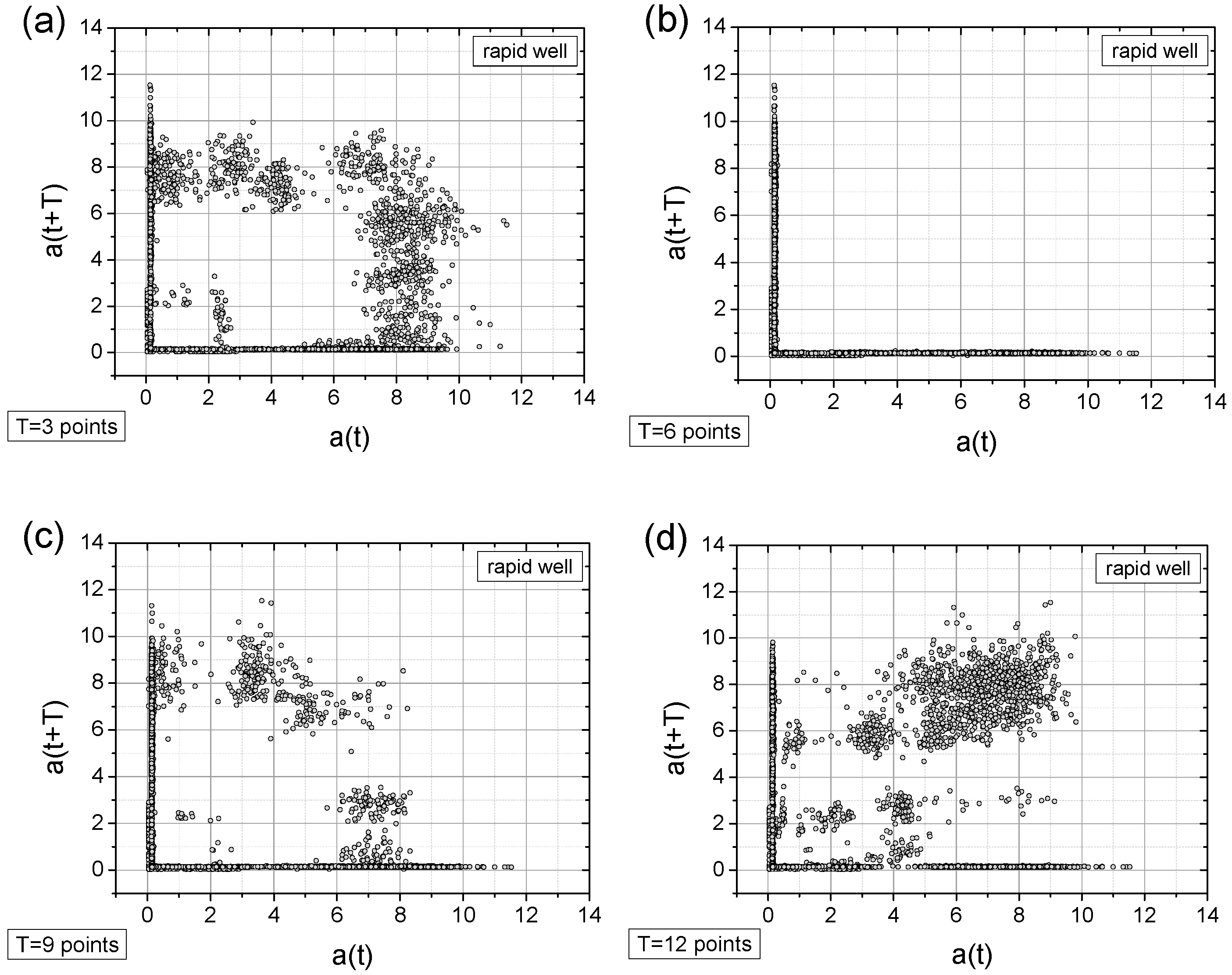
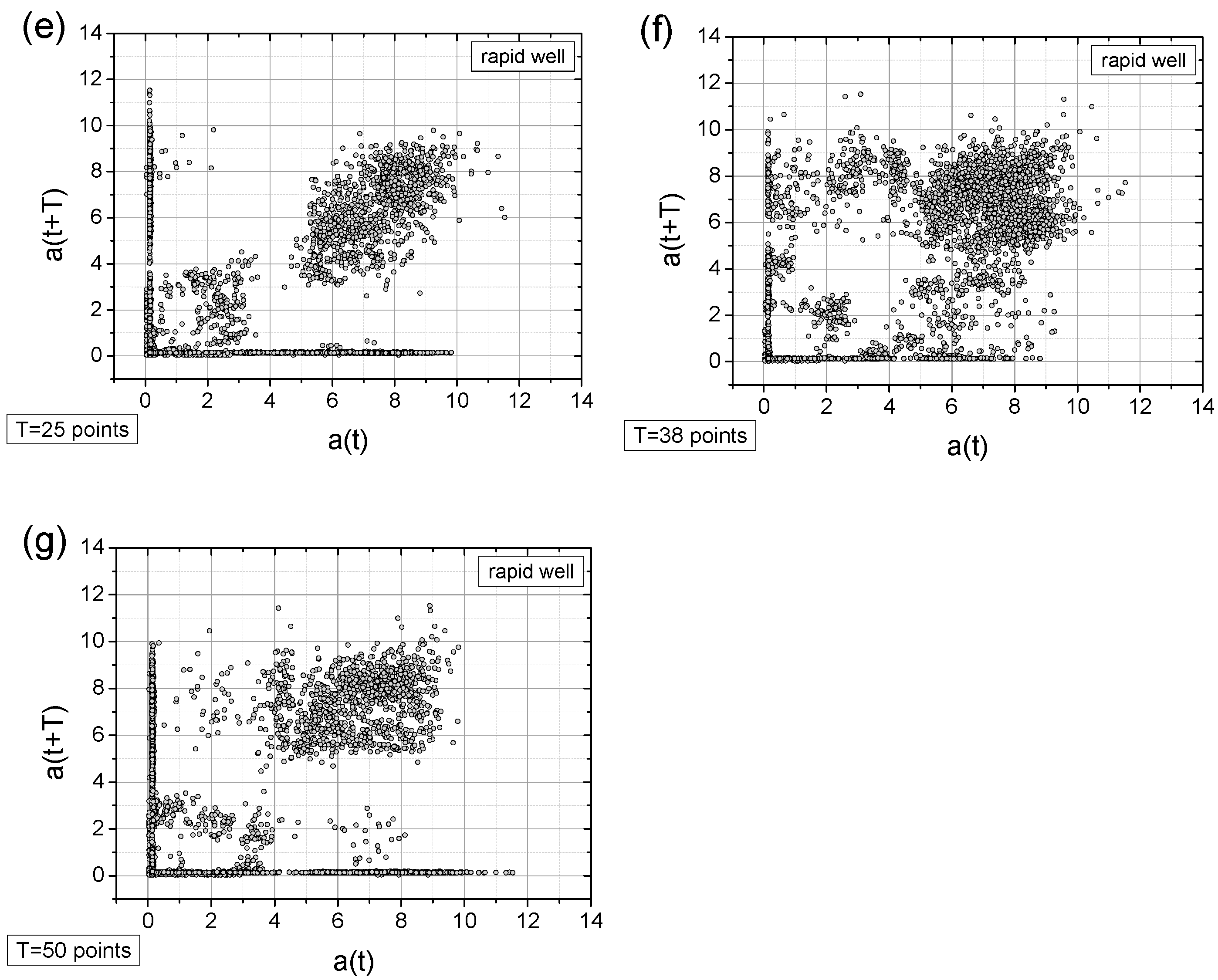
- In general, all charts, except those with a time shift of T = 6 points, proved to be effective for analyzing the registered signals.
- Adding a random factor to the signal disrupts its periodicity: On a map with a time shift of T = 9 points (cf. Figure 11a,c), the map completely changes its character.
- The linear decay of the signal results in the appearance of new collinear sets of points on the chart (e.g., Figure 12c).
- Along with the observed periodicities, areas of high randomness are clearly visible—cf. maps for T = 25 points, particularly for accelerations exceeding 5 g (depending on the signal type).
- The choice of time shift (T) can be supported by the FFT method and effectively classified using the computed metric entropy.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ding, H.; Tian, J.; Yu, W.; Wilson, D.I.; Young, B.R.; Cui, X.; Xin, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, W. The Application of Artificial Intelligence and Big Data in the Food Industry. Foods 2023, 12, 4511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorger, M.; Ralph, B.J.; Hartl, K.; Woschank, M.; Stockinger, M. Big Data in the Metal Processing Value Chain: A Systematic Digitalization Approach under Special Consideration of Standardization and SMEs. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurnia Putri, R.; Athoillah, M. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Digital Transformation: Exploring the Role of AI and ML in Reshaping Businesses and Information Systems. In Advances in Digital Transformation—Rise of Ultra-Smart Fully Automated Cyberspace; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Iuhasz, G.; Forti, T.-F. Exploring machine learning methods for the identification of production cycles and anomaly detection. Internet Things 2025, 30, 101508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattera, G.; Mattera, R.; Vespoli, S.; Salatiello, E. Anomaly detection in manufacturing systems with temporal networks and unsupervised machine learning. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2025, 203, 11123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corli, S.; Moro, L.; Dragoni, D.; Dispenza, M.; Prati, E. Quantum machine learning algorithms for anomaly detection: A review. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2025, 166, 107632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raska, P.; Ulrych, Z.; Malaga, M. Data Reduction of Digital Twin Simulation Experiments Using Different Optimisation Methods. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Abassi, A.; Karimipour, H.; HaddadPajouh, H.; Dehghantanha, A.; Parizi, R.M. Industrial Big Data Analytics: Challenges and Opportunities. In Handbook of Big Data Privacy; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 37–61. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Shi, Y.; Duan, S.; Liu, J. Industrial Big Data Analytics: Challenges, Methodologies, and Applications. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.01016. [Google Scholar]
- Panza, M.A.; Pota, M.; Esposito, M. Anomaly Detection Methods for Industrial Applications: A Comparative Study. Electronics 2023, 12, 3971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunova, D.; Bakratsi, V.; Vrochidou, E.; Papakostas, G.A. Machine Learning for Anomaly Detection in Industrial Environments. Eng. Proc. 2024, 70, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Serradilla, O.; Zugasti, E.; Ramirez de Okariz, J.; Rodriguez, J.; Zurutuza, U. Adaptable and Explainable Predictive Maintenance: Semi-Supervised Deep Learning for Anomaly Detection and Diagnosis in Press Machine Data. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Dasgupta, A. Supervised and Unsupervised Machine Learning Algorithms for Forecasting the Fracture Location in Dissimilar Friction-Stir-Welded Joints. Forecasting 2022, 4, 787–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Wang, X. Industrial Image Anomaly Detection via Self-Supervised Learning with Feature Enhancement Assistance. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, S.; Gambetta, N. Technology-Driven Sustainability in Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises: A Systematic Literature Review. J. Small Bus. Strategy 2025, 35, 129–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupeika-Apoga, R.; Petrovska, K. Barriers to Sustainable Digital Transformation in Micro-, Small-, and Medium-Sized Enterprises. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Arancibia, J.; Hochstetter-Diez, J.; Bustamante-Mora, A.; Sepúlveda-Cuevas, S.; Albayay, I.; Arango-López, J. Navigating Digital Transformation and Technology Adoption: A Literature Review from Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises in Developing Countries. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodorakopoulos, L.; Theodoropoulou, A.; Stamatiou, Y. A State-of-the-Art Review in Big Data Management Engineering: Real-Life Case Studies, Challenges, and Future Research Directions. Eng 2024, 5, 1266–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andronie, M.; Lăzăroiu, G.; Iatagan, M.; Hurloiu, I.; Ștefănescu, R.; Dijmărescu, A.; Dijmărescu, I. Big Data Management Algorithms, Deep Learning-Based Object Detection Technologies, and Geospatial Simulation and Sensor Fusion Tools in the Internet of Robotic Things. ISPRS Int. J. Geoinf. 2023, 12, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andronie, M.; Lăzăroiu, G.; Karabolevski, O.L.; Ștefănescu, R.; Hurloiu, I.; Dijmărescu, A.; Dijmărescu, I. Remote Big Data Management Tools, Sensing and Computing Technologies, and Visual Perception and Environment Mapping Algorithms in the Internet of Robotic Things. Electronics 2022, 12, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Zhao, Q. Recent Advances in Robotics and Intelligent Robots Applications. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabala-Vargas, S.; Jaimes-Quintanilla, M.; Jimenez-Barrera, M.H. Big Data, Data Science, and Artificial Intelligence for Project Management in the Architecture, Engineering, and Construction Industry: A Systematic Review. Buildings 2023, 13, 2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licardo, J.T.; Domjan, M.; Orehovački, T. Intelligent Robotics—A Systematic Review of Emerging Technologies and Trends. Electronics 2024, 13, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skėrė, S.; Žvironienė, A.; Juzėnas, K.; Petraitienė, S. Decision Support Method for Dynamic Production Planning. Machines 2022, 10, 994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosin, F.; Forget, P.; Lamouri, S.; Pellerin, R. Enhancing the Decision-Making Process through Industry 4.0 Technologies. Sustainability 2022, 14, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaworski, M.; Borowski, P.F.; Kozioł, Ł. Supporting Decision-Making in the Technical Equipment Selection Process by the Method of Contradictory Evaluations. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-F.; Wang, S.-Y.; Tung, H.-H. A Comprehensive Decision-Making Approach for Strategic Product Module Planning in Mass Customization. Mathematics 2024, 12, 1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulewicz, R.; Siwiec, D.; Pacana, A. A New Model of Pro-Quality Decision Making in Terms of Products’ Improvement Considering Customer Requirements. Energies 2023, 16, 4378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajčovič, M.; Bastiuchenko, V.; Furmannová, B.; Botka, M.; Komačka, D. New Approach to the Analysis of Manufacturing Processes with the Support of Data Science. Processes 2024, 12, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Guo, R. An Unsupervised Method for Industrial Image Anomaly Detection with Vision Transformer-Based Autoencoder. Sensors 2024, 24, 2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Hong, S.H.; Kyzer, T.; Wang, Y. U-TFF: A U-Net-Based Anomaly Detection Framework for Robotic Manipulator Energy Consumption Auditing Using Fast Fourier Transform. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flegner, P.; Kačur, J.; Durdán, M.; Laciak, M.; Frančáková, R. Advanced Frequency Analysis of Signals with High-Frequency Resolution. Computation 2024, 12, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Low, M. FFT-Based Simultaneous Calculations of Very Long Signal Multi-Resolution Spectra for Ultra-Wideband Digital Radio Frequency Receiver and Other Digital Sensor Applications. Sensors 2024, 24, 1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
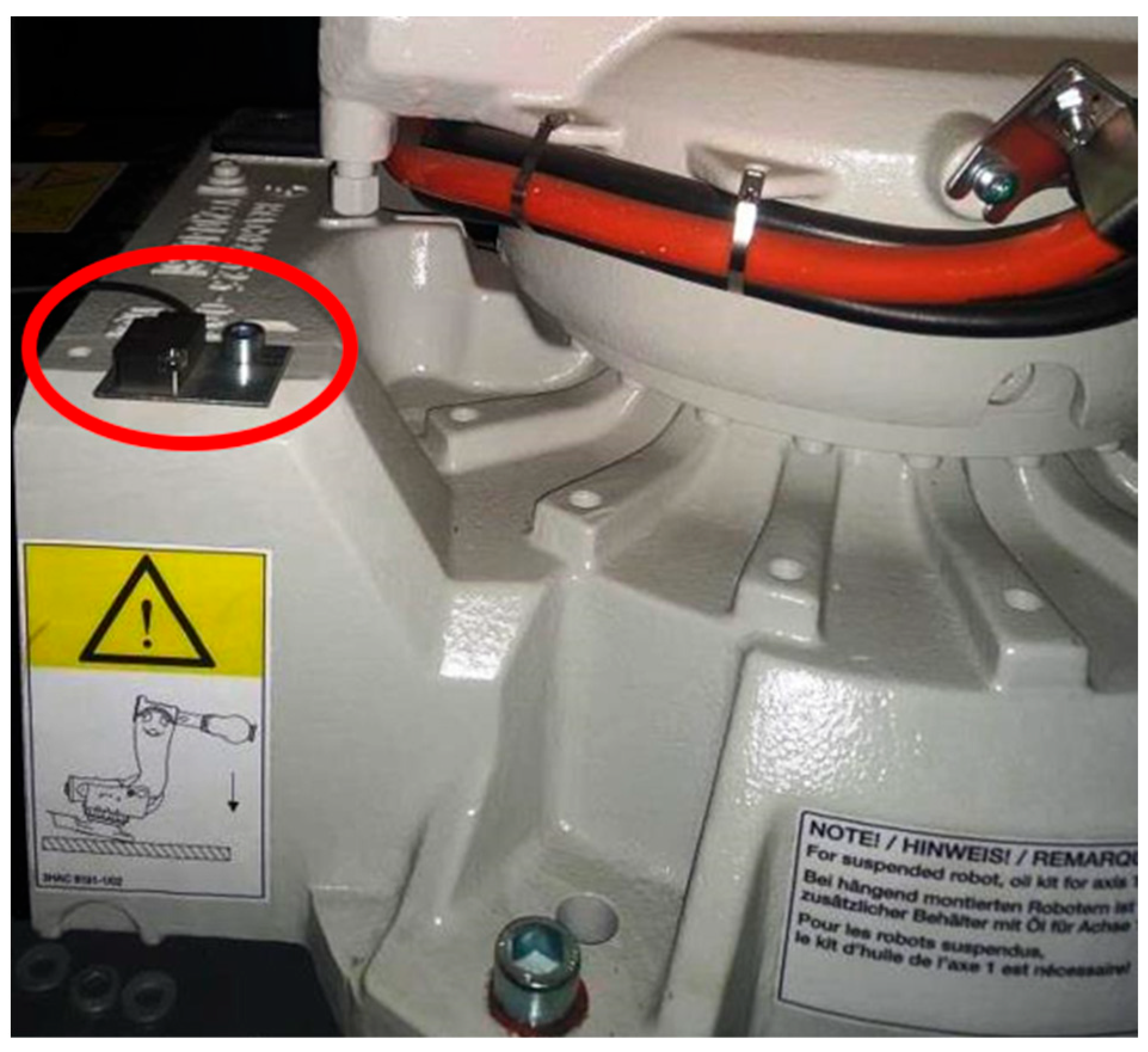
- Fedorova, D.; Tlach, V.; Kuric, I.; Dodok, T.; Zajačko, I.; Tucki, K. Technical Diagnostics of Industrial Robots Using Vibration Signals: Case Study on Detecting Base Unfastening. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadaoui, S.; Tabaa, M.; Monteiro, F.; Chehaitly, M.; Dandache, A. Discrete Wavelet Packet Transform-Based Industrial Digital Wireless Communication Systems. Information 2019, 10, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duda-Mróz, N.; Anufriiev, S.; Stefaniak, P. Application of Wavelet Filtering to Vibrational Signals from the Mining Screen for Spring Condition Monitoring. Minerals 2021, 11, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Luna, E.; Cuadros-Orta, D.E.; Candelo-Becerra, J.E.; Vasquez, J.C. The Development of a Novel Transient Signal Analysis: A Wavelet Transform Approach. Computation 2024, 12, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiao, Y.; Gadde, P.; Liu, C.-Y. Wavelet-Based Analysis of Motor Current Signals for Detecting Obstacles in Train Doors. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupea, I.; Lupea, M. Continuous Wavelet Transform and CNN for Fault Detection in a Helical Gearbox. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.C.B.d.; Lopes, B.D.M.; Blanquet, I.M.; Marques, C.A.F. Gaussian Distribution Model for Detecting Dangerous Operating Conditions in Industrial Fish Farming. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, A.; Baranowski, J. Gaussian Processes for Signal Processing and Representation in Control Engineering. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo, J.A.; Nieto, M.; Velez, J.F.; Velez, D. A New Machine Learning Forecasting Algorithm Based on Bivariate Copula Functions. Forecasting 2021, 3, 355–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C. Dynamics, Periodic Orbit Analysis, and Circuit Implementation of a New Chaotic System with Hidden Attractor. Fractal Fract. 2022, 6, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askar, S.S.; Al-Khedhairi, A. Further Discussions of the Complex Dynamics of a 2D Logistic Map: Basins of Attraction and Fractal Dimensions. Symmetry 2020, 12, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, G.L.; Gollub, J.P. Chaotic Dynamic: An Introduction; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- BCM0001 Sensor Specification. Available online: https://www.balluff.com/en-my/products/BCM0001 (accessed on 7 January 2025).
- KR 270 R3100 Ultra K-F ROBOT. Available online: https://my.kuka.com/s/product/kr-270-r3100-ultra-kf/01t58000002hninAAA?language=pl (accessed on 7 January 2025).












| Time Shift T (Points) | Original Signal | Signal with Random Contr. | Signal with Decay | Signal with Loss |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 1.32 | 1.32 | 1.37 | 1.33 |
| 5 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 1.02 |
| 6 | 1.01 | 0.97 | 1.00 | 1.04 |
| 7 | 1.01 | 1.01 | 1.01 | 1.00 |
| 9 | 1.14 | 1.15 | 1.18 | 1.17 |
| 12 | 1.43 | 1.43 | 1.44 | 1.44 |
| 13 | 1.43 | 1.47 | 1.40 | 1.43 |
| 19 | 1.01 | 0.99 | 1.03 | 1.01 |
| 25 | 1.43 | 1.45 | 1.38 | 1.42 |
| 36 | 1.57 | 1.60 | 1.59 | 1.58 |
| 38 | 1.72 | 1.63 | 1.57 | 1.60 |
| 50 | 1.46 | 1.51 | 1.42 | 1.48 |
| Time Shift T (Points) | Original Signal | Signal with Random Contr. | Signal with Decay | Signal with Loss |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 8.47 | 8.58 | 8.71 | 8.52 |
| 5 | 6.18 | 6.26 | 6.52 | 6.37 |
| 6 | 6.18 | 6.25 | 6.52 | 6.32 |
| 7 | 6.19 | 6.27 | 6.53 | 6.37 |
| 9 | 7.69 | 7.78 | 7.77 | 7.72 |
| 12 | 8.48 | 8.59 | 8.68 | 8.56 |
| 13 | 8.43 | 8.54 | 8.69 | 8.10 |
| 19 | 6.19 | 6.27 | 6.53 | 6.37 |
| 25 | 8.44 | 8.57 | 8.53 | 8.50 |
| 36 | 8.92 | 9.04 | 9.24 | 8.71 |
| 38 | 8.92 | 9.08 | 9.33 | 9.01 |
| 50 | 8.50 | 8.60 | 8.64 | 8.58 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Blachowicz, T.; Bysko, S.; Bysko, S.; Domanowska, A.; Wylezek, J.; Sokol, Z. Time-Shifted Maps for Industrial Data Analysis: Monitoring Production Processes and Predicting Undesirable Situations. Sensors 2025, 25, 3311. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113311
Blachowicz T, Bysko S, Bysko S, Domanowska A, Wylezek J, Sokol Z. Time-Shifted Maps for Industrial Data Analysis: Monitoring Production Processes and Predicting Undesirable Situations. Sensors. 2025; 25(11):3311. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113311
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlachowicz, Tomasz, Sara Bysko, Szymon Bysko, Alina Domanowska, Jacek Wylezek, and Zbigniew Sokol. 2025. "Time-Shifted Maps for Industrial Data Analysis: Monitoring Production Processes and Predicting Undesirable Situations" Sensors 25, no. 11: 3311. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113311
APA StyleBlachowicz, T., Bysko, S., Bysko, S., Domanowska, A., Wylezek, J., & Sokol, Z. (2025). Time-Shifted Maps for Industrial Data Analysis: Monitoring Production Processes and Predicting Undesirable Situations. Sensors, 25(11), 3311. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113311







