Design and Structure of a Non-Coaxial Multi-Focal Composite Fresnel Acoustic Lens for Synergistic Ultrasound Stimulation of Multiple Brain Regions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
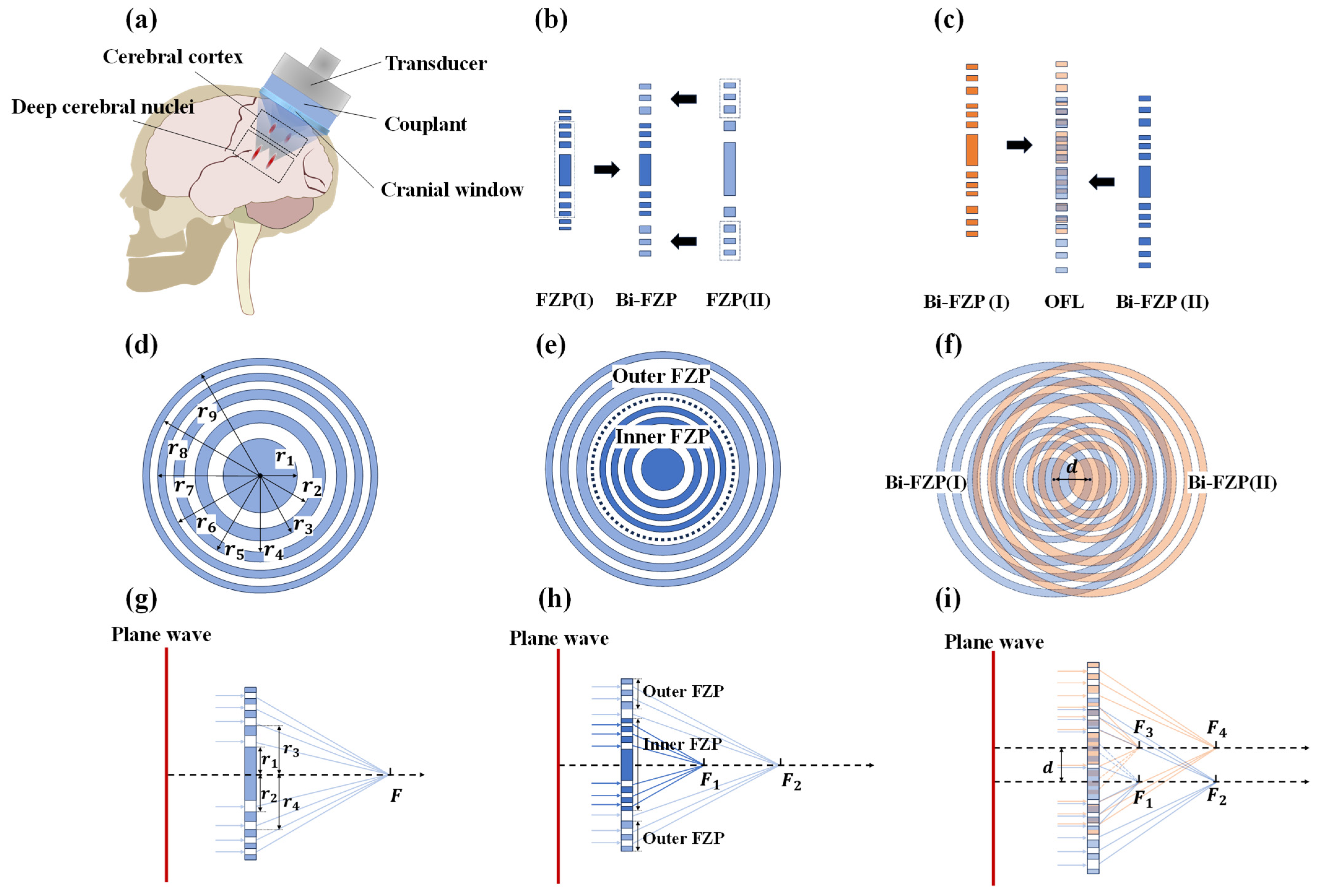
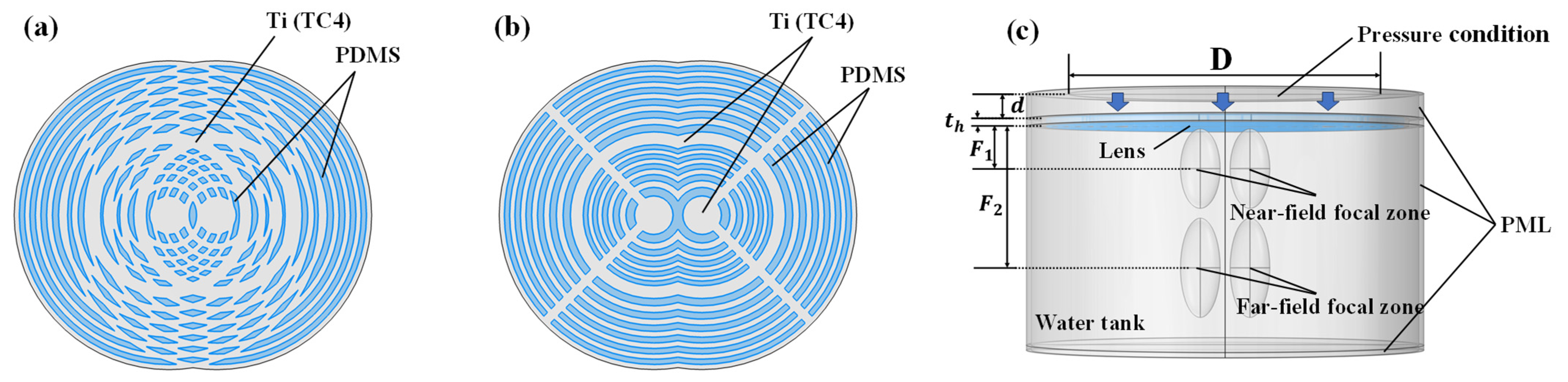
2.1. Design Methodology of Composite Fresnel Acoustic Lens
2.2. Numerical Method
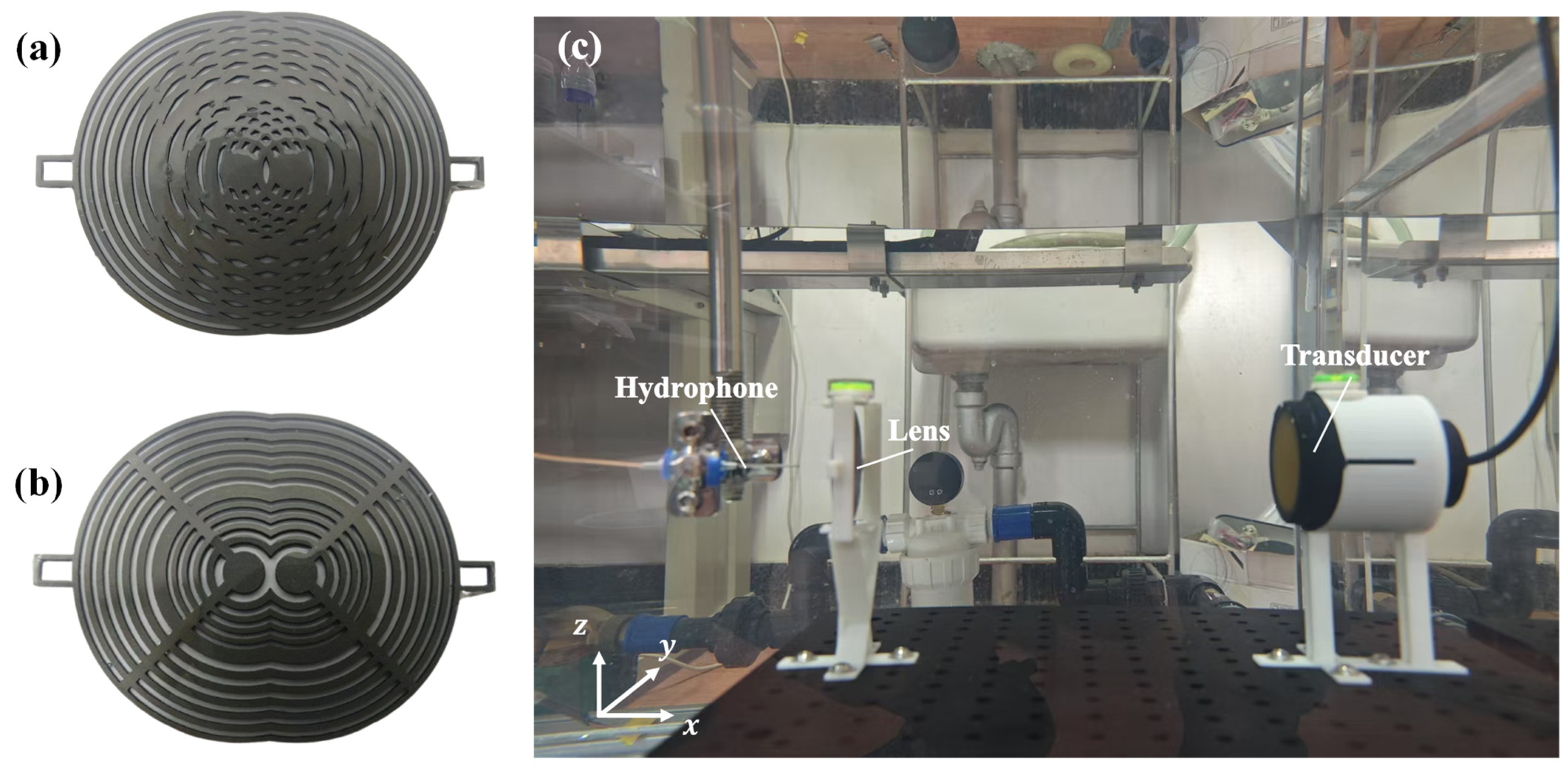
2.3. Experimental Setup
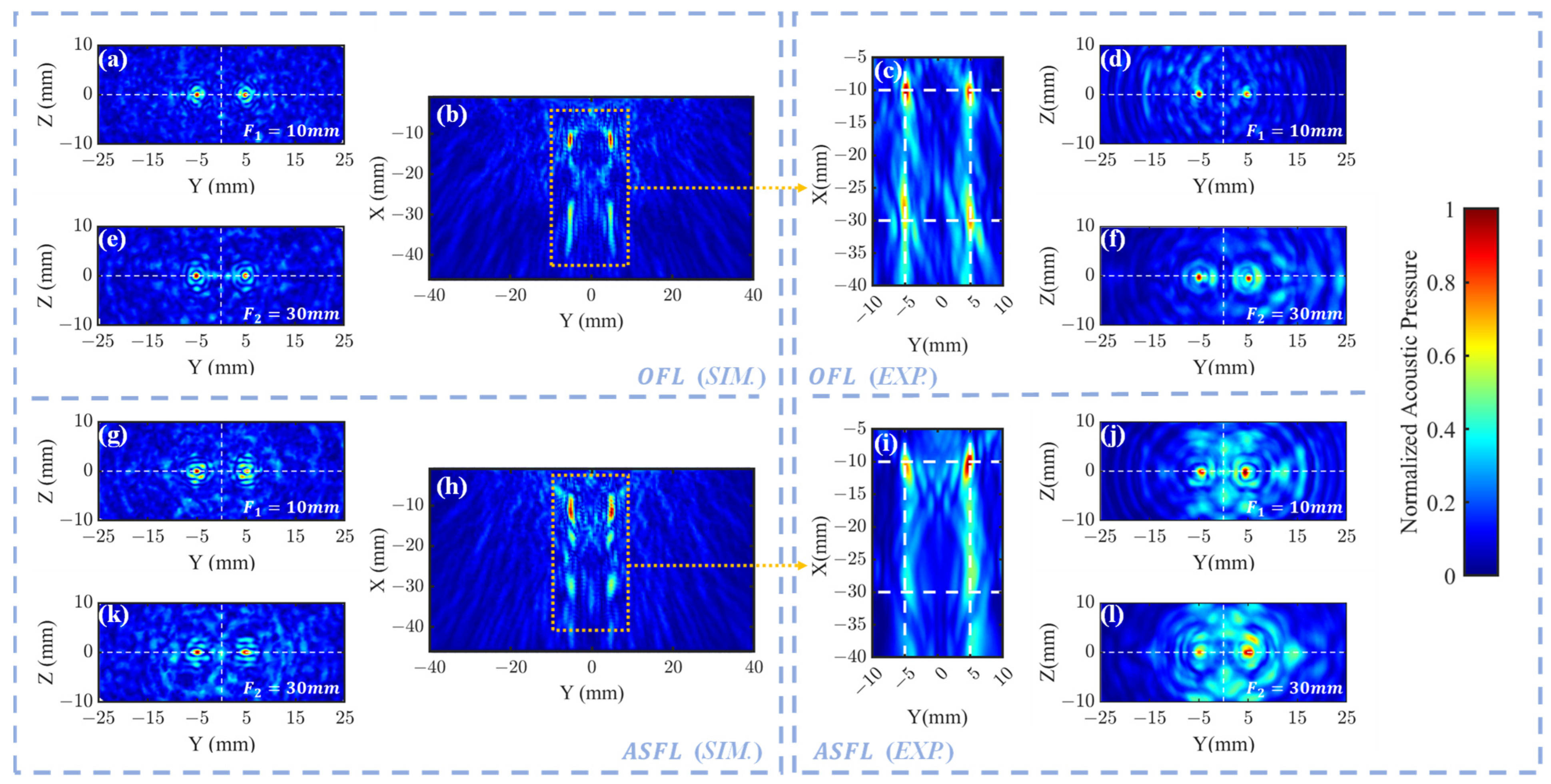
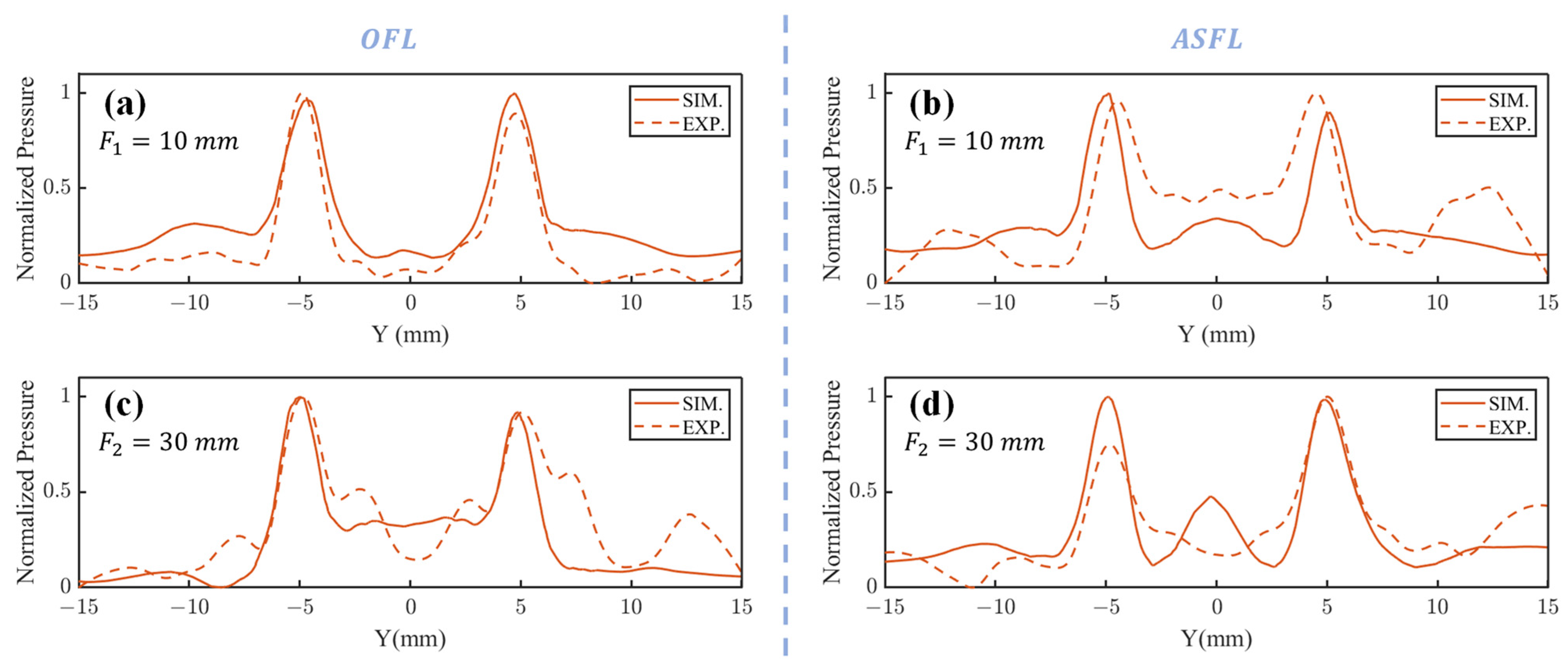
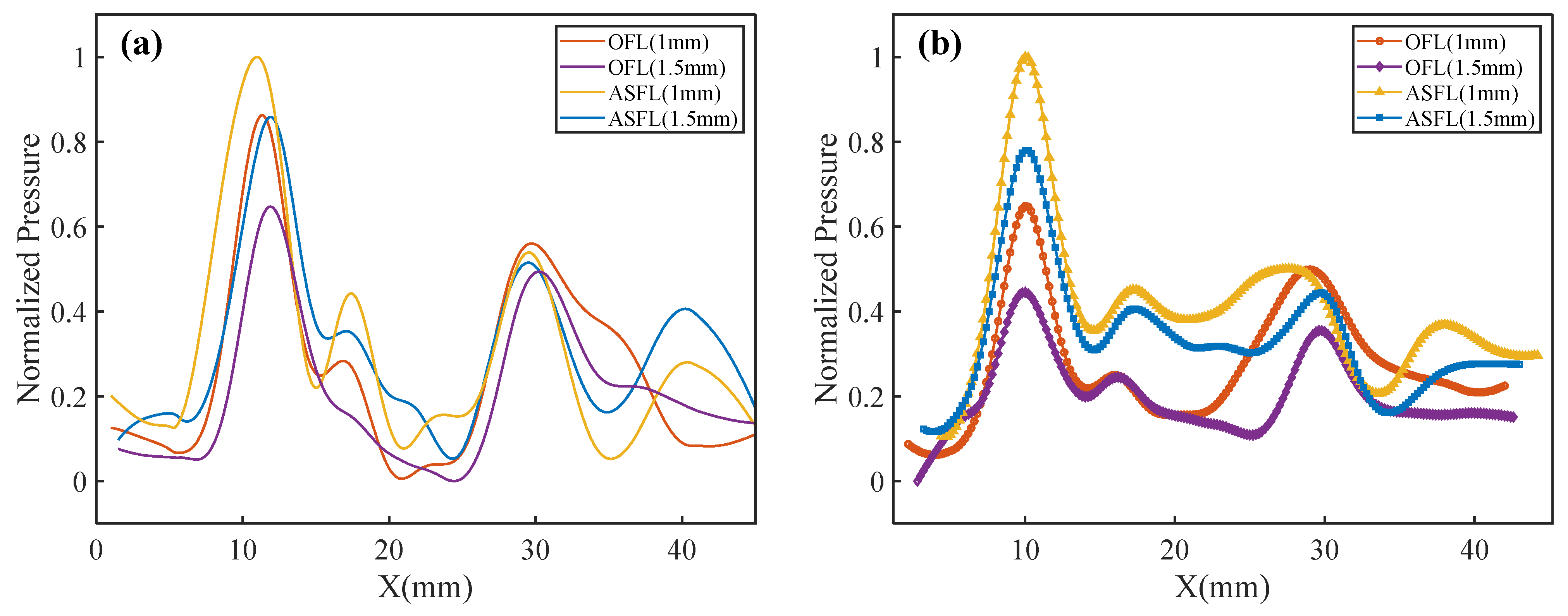
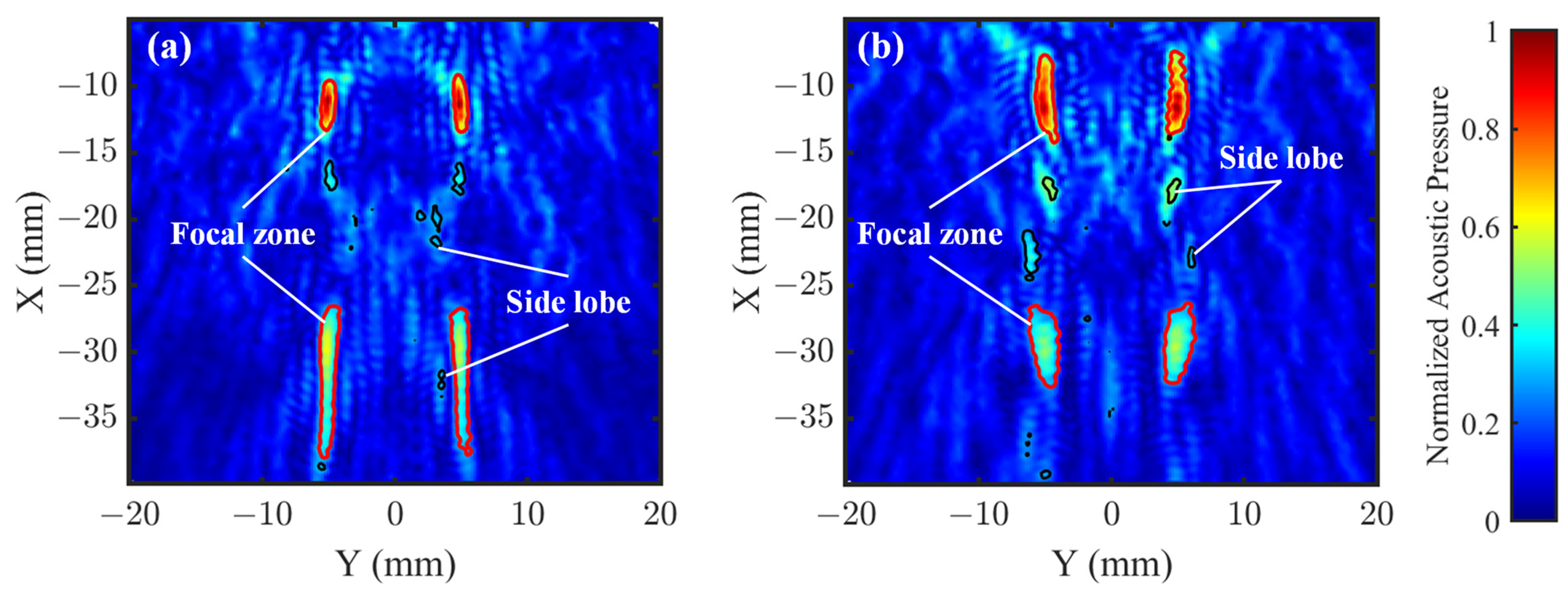
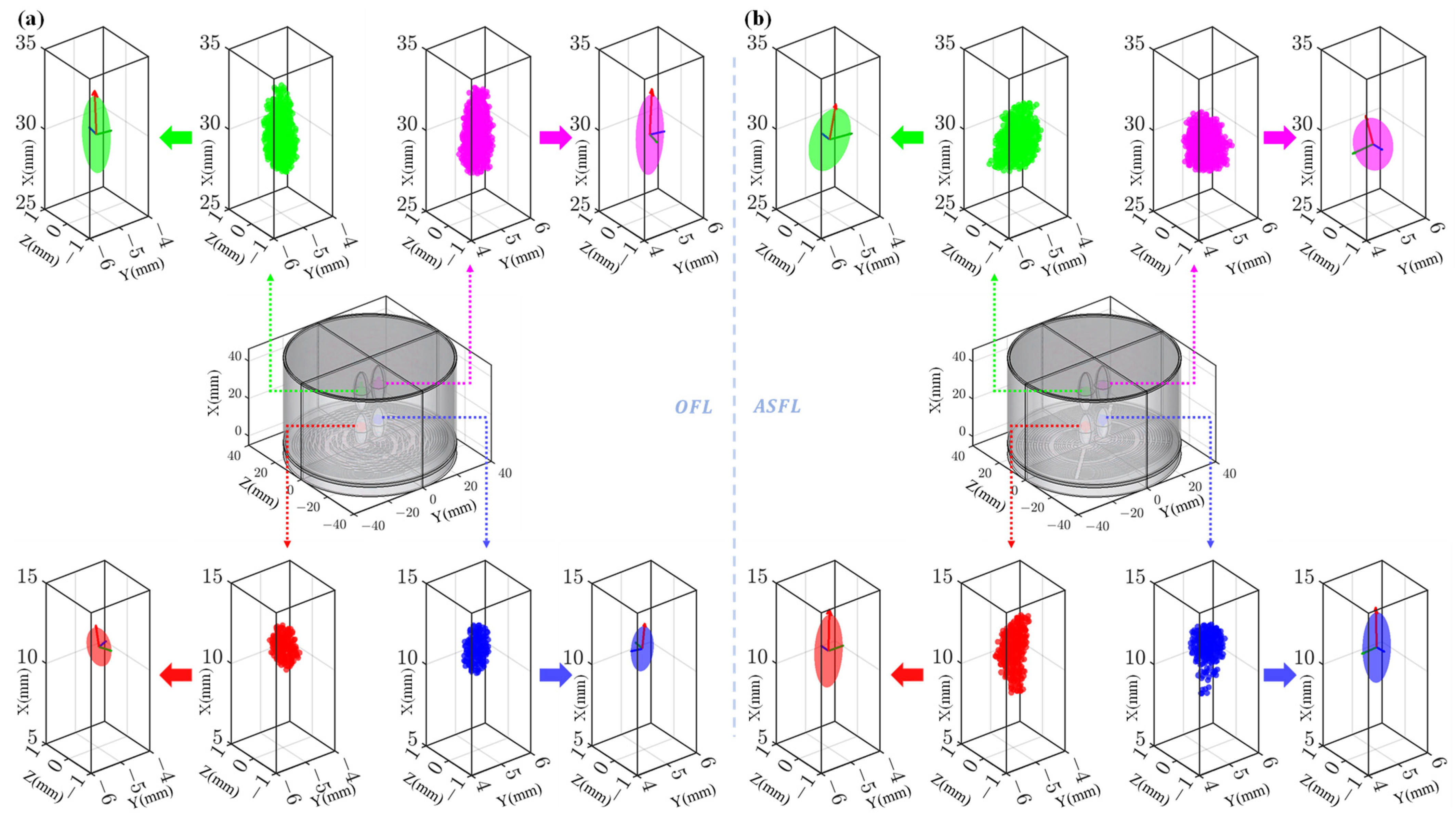
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TcFUS | Transcranial focused ultrasound |
| OFL | Overlapping Fresnel lens |
| ASFL | Alternating-segmented Fresnel lens |
| HIFU | High-intensity focused ultrasound |
| LIFU | Low-intensity focused ultrasound |
| USNM | Ultrasound neuromodulation |
| DBS | Deep brain stimulation |
| FHWB | Fresnel half-wave band |
| FZP | Fresnel zone plate |
| Bi-FZP | Bi-focal Fresnel zone plate |
| PDMS | Polydimethylsiloxane |
| PML | Perfectly matched layers |
References
- Izadifar, Z.; Izadifar, Z.; Chapman, D.; Babyn, P. An introduction to high intensity focused ultrasound: Systematic review on principles, devices, and clinical applications. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- di Biase, L.; Falato, E.; Di Lazzaro, V. Transcranial focused ultrasound (tFUS) and transcranial unfocused ultrasound (tUS) neuromodulation: From theoretical principles to stimulation practices. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patwardhan, A.; Wilkinson, T.; Meng, Y.; Alhashyan, I.; Black, S.E.; Lipsman, N.; Masellis, M. Safety, efficacy and clinical applications of focused ultrasound-mediated blood brain barrier opening in Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review. J. Prev. Alzheimers Dis. 2024, 11, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasielewska, J.M.; White, A.R. Focused ultrasound-mediated drug delivery in humans—A path towards translation in neurodegenerative diseases. Pharm. Res. 2022, 39, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darmani, G.; Bergmann, T.; Pauly, K.B.; Caskey, C.; de Lecea, L.; Fomenko, A.; Fouragnan, E.; Legon, W.; Murphy, K.; Nandi, T.; et al. Non-invasive transcranial ultrasound stimulation for neuromodulation. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2022, 135, 51–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.-Y.; Yang, G.; Liang, X.-S.; Ding, X.-S.; Xu, D.-E.; Li, Z.; Ma, Q.-H.; Chen, R.; Sun, Y.-Y. Transcranial low-intensity ultrasound stimulation for treating central nervous system disorders: A promising therapeutic application. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1117188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beisteiner, R.; Matt, E.; Fan, C.; Baldysiak, H.; Schönfeld, M.; Novak, T.P.; Amini, A.; Aslan, T.; Reinecke, R.; Lehrner, J.; et al. Transcranial pulse stimulation with ultrasound in Alzheimer’s disease—A new navigated focal brain therapy. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1902583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicodemus, N.E.; Becerra, S.; Kuhn, T.P.; Packham, H.R.; Duncan, J.; Mahdavi, K.; Iovine, J.; Kesari, S.; Pereles, S.; Whitney, M.; et al. Focused transcranial ultrasound for treatment of neurodegenerative dementia. Alzheimers Dement. 2019, 5, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Chou, C.; Hsiao, F.; Chen, Y.; Lin, C.; Chen, C.; Peng, S.; Liu, H.; Yu, H. Pilot study of focused ultrasound for drug-resistant epilepsy. Epilepsia 2022, 63, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, J.M.; Spivak, N.M.; Becerra, S.A.; Kuhn, T.P.; Korb, A.S.; Kronemyer, D.; Khanlou, N.; Reyes, S.D.; Monti, M.M.; Schnakers, C.; et al. Safety of focused ultrasound neuromodulation in humans with temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain Stimul. 2021, 14, 1022–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, N.; Ding, M.Y.R.; Sarica, C.; Darmani, G.; Harmsen, I.E.; Grippe, T.; Chen, X.; Yang, A.; Nasrkhani, N.; Zeng, K.; et al. Accelerated transcranial ultrasound neuromodulation in Parkinson’s disease: A pilot study. Mov. Disord. 2023, 38, 2209–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clement, G.T.; Hynynen, K. Micro-receiver guided transcranial beam steering. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2002, 49, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, C.; Jones, R.M.; Yang, S.D.; Kan, W.M.; Leung, K.; Zhou, Y.; Lee, K.U.; Huang, Y.; Hynynen, K. Implementation of a skull-conformal phased array for transcranial focused ultrasound therapy. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 68, 3457–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batts, A.J.; Ji, R.; Kline-Schoder, A.R.; Noel, R.L.; Konofagou, E.E. Transcranial theranostic ultrasound for pre-planning and blood-brain barrier opening: A feasibility study using an imaging phased array in vitro and in vivo. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 69, 1481–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanaro, H.; Pasquinelli, C.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, H.; Siebner, H.R.; Kuster, N.; Thielscher, A.; Neufeld, E. The impact of CT image parameters and skull heterogeneity modeling on the accuracy of transcranial focused ultrasound simulations. J. Neural Eng. 2021, 18, 046041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Yan, S.; Huang, J.; Zhang, B. Research on transcranial ultrasound focusing methods and acoustic field characteristics. Acta Acust. 2023, 48, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilham, S.J.; Kashani, Z.; Kiani, M. Design and optimization of ultrasound phased arrays for large-scale ultrasound neuro-modulation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2021, 15, 1454–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, M.I.; Sellappan, P.; Penilla, E.H.; Poblete-Naredo, I.; Vera, A.; Leija, L.; E Garay, J. Acoustically transparent alumina-based cranial implants enhance ultrasound transmission through a combined mechano-acoustic resonant effect. J. Phys. Mater. 2024, 7, 03LT02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzkin, J.C.; Kanungo, I.; D’Esposito, M.; Shirvalkar, P. Network targets for therapeutic brain stimulation: Towards personalized therapy for pain. Front. Pain Res. 2023, 4, 1156108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizarraga, K.J.; Jagid, J.R.; Luca, C.C. Comparative effects of unilateral and bilateral subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation on gait kinematics in Parkinson’s disease: A randomized, blinded study. J. Neurol. 2016, 263, 1652–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; He, J.; Wu, C.; Wu, J.; Cheng, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, M.; Zeng, L.; Ji, X. Multi-target ultrasound neuromodulation in the treatment of freely moving depression mice. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS), Venice, Italy, 10–13 October 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Wu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, M.; Zeng, L.; Ji, X. Multitarget transcranial ultrasound therapy in small animals based on phase-only acoustic holographic lens. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2022, 69, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Huang, J.; Cai, F.; Xiao, Y.; Ma, T.; Zheng, H. Development of scalable 2D plane array for transcranial ultrasonic neuromodulation on non-human primates: An ex vivo study. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2020, 28, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xu, L.; Hao, Y.; Chen, H. Binary acoustic metasurfaces for dynamic focusing of transcranial ultrasound. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 984953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Shan, D.; Pu, C.; Guo, L.; Xu, H.; Peng, C. A systematic investigation of thermal effects of high-intensity focused ultrasound therapy for ultrasound neuromodulation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 4003512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kasoji, S.; Durham, P.G.; Dayton, P.A. Acoustic holograms for directing arbitrary cavitation patterns. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2021, 118, 051902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, W.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, Z. Simple broadband planar acoustic lenses design with a velocity gradient structure. Appl. Acoust. 2024, 217, 109832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-López, S.; Fuster, J.M.; Candelas, P.; Tarrazó-Serrano, D.; Castiñeira-Ibáñez, S.; Rubio, C. Bifocal ultrasound focusing using bi-Fresnel zone plate lenses. Sensors 2020, 20, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cafarelli, A.; Verbeni, A.; Poliziani, A.; Dario, P.; Menciassi, A.; Ricotti, L. Tuning acoustic and mechanical properties of materials for ultrasound phantoms and smart substrates for cell cultures. Acta Biomater. 2017, 49, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Liu, K.; Wu, G.; Huang, Y.; Luo, S.; Tai, Q. Influence of forging parameters on microstructure and ultrasonic velocity of TC4 titanium alloy forgings. Nondestruct. Test. 2017, 39, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, V.; Sammartino, F.; Rezai, A. A Review of the Current Therapies, Challenges, and Future Directions of Transcranial Focused Ultrasound Technology. JAMA Neurol. 2018, 75, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.F.; Su, W.S.; Wu, C.H.; Lan, T.H.; Yang, F.Y. Transcranial ultrasound stimulation improves long-term functional outcomes and protects against brain damage in traumatic brain injury. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 7079–7089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, K.; Zhou, X.; Liu, X.; Ma, R.; Wang, M.; Zhang, S.; Yin, T.; Liu, Z. The simulation and experimental validation of a novel noninvasive multi-target electrical stimulation method. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 12416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Ianni, T.; Morrison, K.P.; Yu, B.; Murphy, K.R.; de Lecea, L.; Airan, R.D. High-throughput ultrasound neuromodulation in awake and freely behaving rats. Brain Stimul. 2023, 16, 1743–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Fresnel Zone Number () | (mm) | Fresnel Zone Number () | (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4.00 | 1 | 6.84 |
| 2 | 5.76 | 2 | 9.74 |
| 3 | 7.18 | 3 | 12.00 |
| 4 | 8.43 | 4 | 13.94 |
| 5 | 9.58 | 5 | 15.68 |
| 6 | 10.67 | 6 | 17.28 |
| 7 | 11.70 | 7 | 18.77 |
| 8 | 12.69 | 8 | 20.19 |
| 9 | 13.66 | 9 | 21.54 |
| 10 | 14.60 | 10 | 22.83 |
| 11 | 15.53 | 11 | 24.08 |
| 12 | 16.44 | 12 | 25.29 |
| 13 | 17.33 | 13 | 26.47 |
| 14 | 18.22 | 14 | 27.62 |
| 15 | 19.09 | 15 | 28.75 |
| 16 | 19.95 | 16 | 29.85 |
| 17 | 20.81 | 17 | 30.93 |
| 18 | 21.66 | 18 | 32.00 |
| Acoustic Material | Density (kg/m3) | Sound Velocity (m/s) |
|---|---|---|
| Water | 1000 | 1483 |
| PDMS [29] | 970 | 1080 |
| Titanium alloy (TC4) [30] | 4510 | 6100 |
| Parameter | OFL | ASFL | BAMs [24] | Ultrasound Phased Arrays [34] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of focal points | 4 | 4 | 1 or 2 | Single (enables multi-target stimulation) |
| Acoustic pressure FWHM | 2.27 mm laterally and 7.33 mm axially at 1 MHz | 2.20 mm laterally and 10.02 mm axially at 1 MHz | 3.3 mm laterally and 13.5 mm axially at 0.5 MHz | 1.69 mm laterally and 9.28 mm axially at 1 MHz |
| Manufacturing method | 3D print and spin coating | 3D print and spin coating | 3D print | Commercial array; Clip-on holder and baseplate were 3-D printed |
| Material | TC4 and PDMS | TC4 and PDMS | Polylactic Acid (PLA) | Anodized aluminum housing with epoxy coating |
| Need for patient-specific imaging | Not Compatible | Not Compatible | CT-based skull modeling | CT scans for acoustic simulations |
| Focal depth | 10 mm and 30 mm | 10 mm and 30 mm | 47.1 mm to 64.3 mm | 8 mm to 18 mm |
| Electronic complexity | Low (single driving channel) | Low (single driving channel) | Low (single driving channel) | High (64-channel independent drive) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, R.; Shi, F.; Tao, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, J.; Wu, X.; Xu, J. Design and Structure of a Non-Coaxial Multi-Focal Composite Fresnel Acoustic Lens for Synergistic Ultrasound Stimulation of Multiple Brain Regions. Sensors 2025, 25, 3299. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113299
Wu R, Shi F, Tao J, Zhao J, Zhang J, Wu X, Xu J. Design and Structure of a Non-Coaxial Multi-Focal Composite Fresnel Acoustic Lens for Synergistic Ultrasound Stimulation of Multiple Brain Regions. Sensors. 2025; 25(11):3299. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113299
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Ruiqi, Fangfang Shi, Juan Tao, Jiajia Zhao, Jinying Zhang, Xianmei Wu, and Jingjing Xu. 2025. "Design and Structure of a Non-Coaxial Multi-Focal Composite Fresnel Acoustic Lens for Synergistic Ultrasound Stimulation of Multiple Brain Regions" Sensors 25, no. 11: 3299. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113299
APA StyleWu, R., Shi, F., Tao, J., Zhao, J., Zhang, J., Wu, X., & Xu, J. (2025). Design and Structure of a Non-Coaxial Multi-Focal Composite Fresnel Acoustic Lens for Synergistic Ultrasound Stimulation of Multiple Brain Regions. Sensors, 25(11), 3299. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113299








