A Vision-Based Procedure with Subpixel Resolution for Motion Estimation
Abstract
1. Introduction
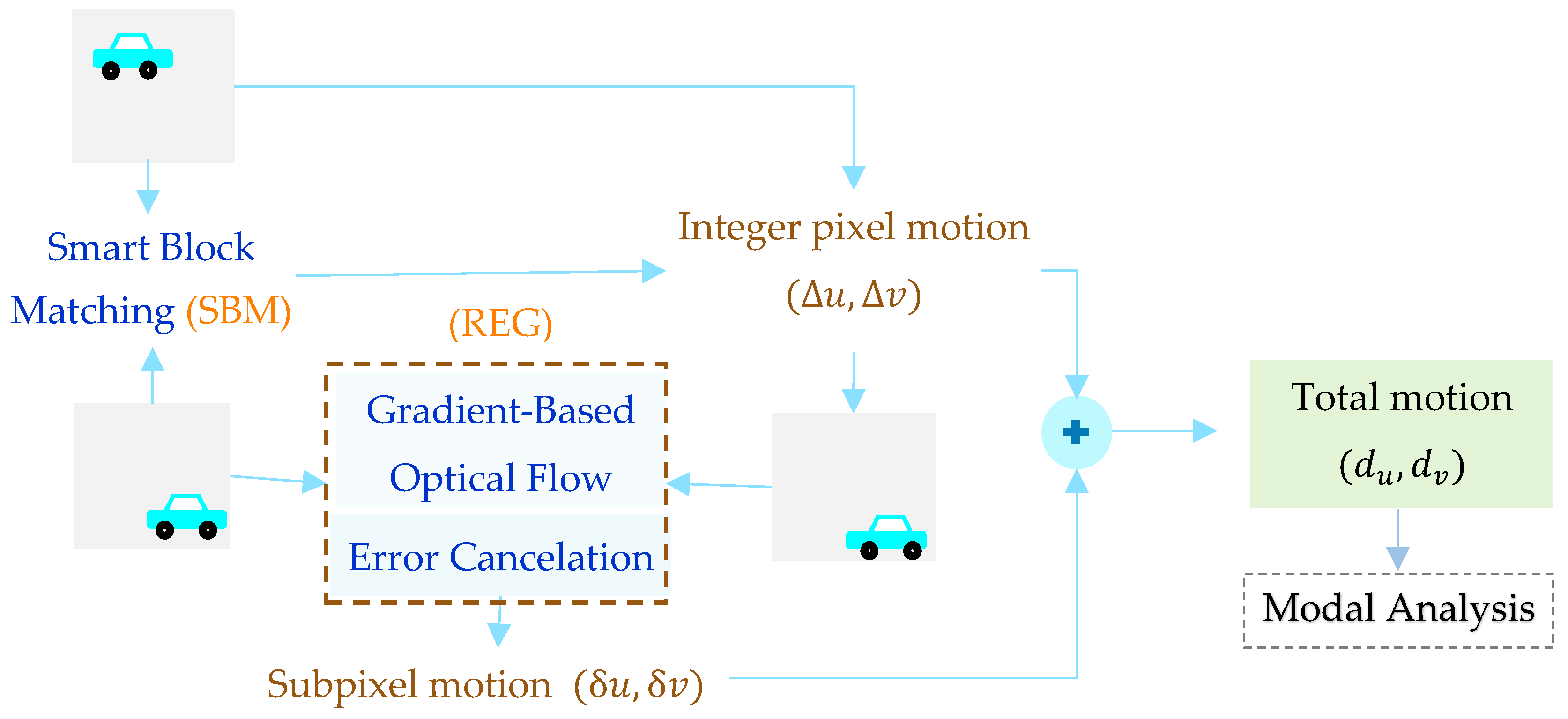
2. Smart BM and Reduced-Error Gradient Method
2.1. Enhanced Population-Based BM for Integer Pixel Motion Estimation
2.1.1. Block Matching
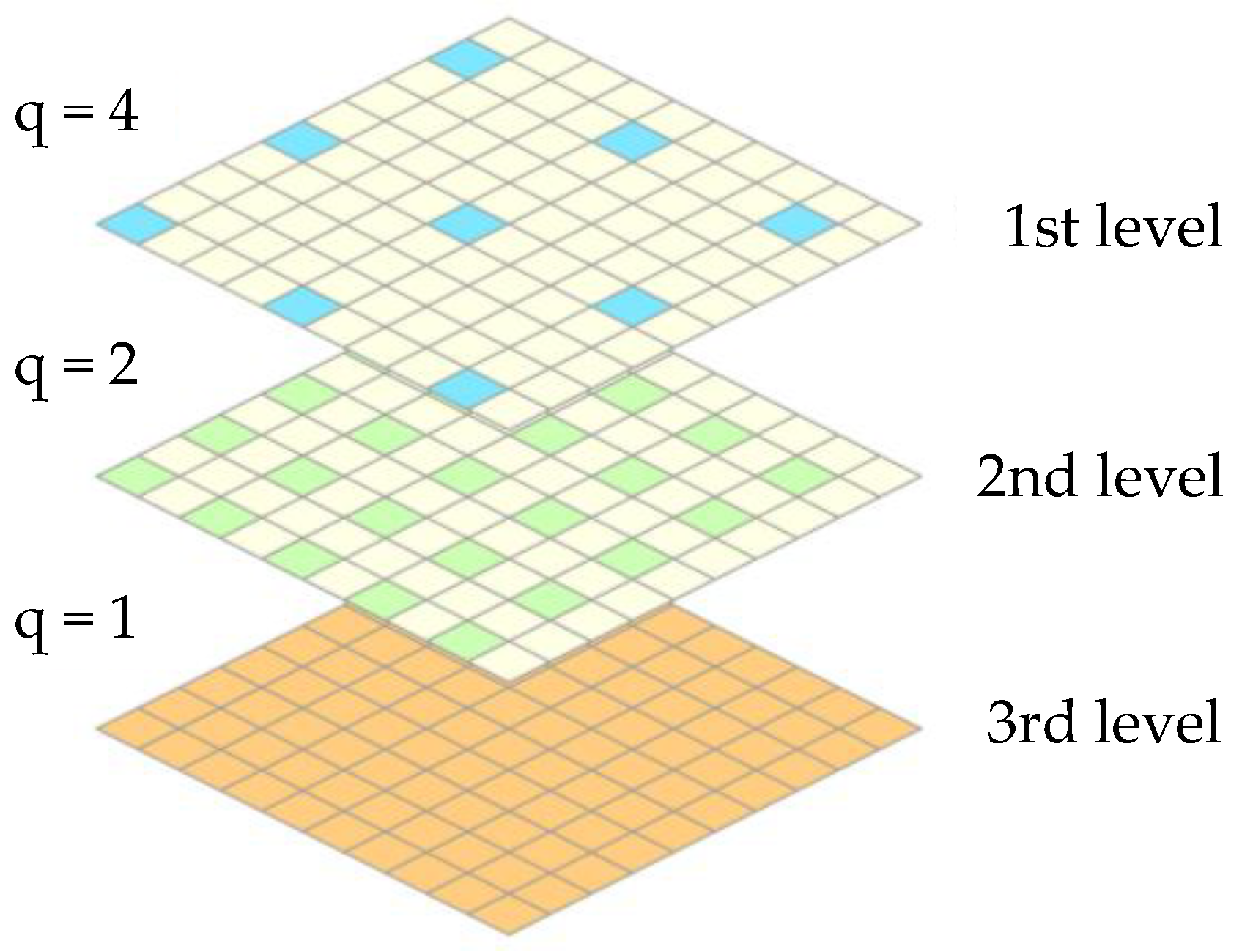
2.1.2. Particle Swarm Optimization
2.2. Enhanced Gradient-Based Solution with Error Cancelation for Subpixel Motion Estimation
3. Blind Modal Analysis with Complexity Pursuit
4. Experiments
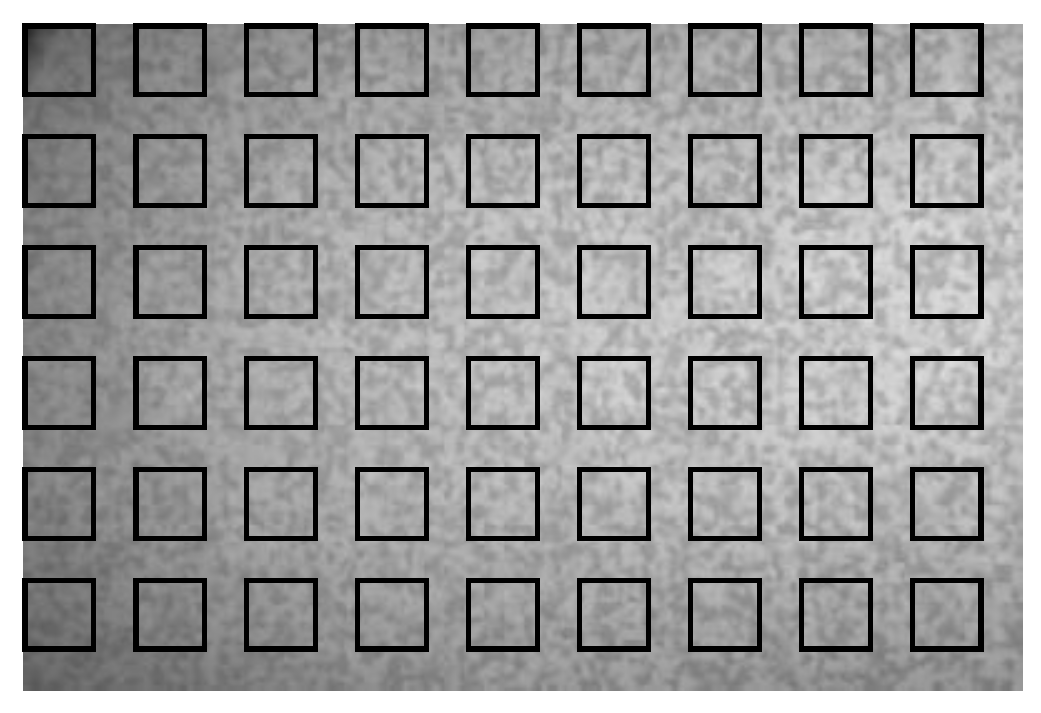
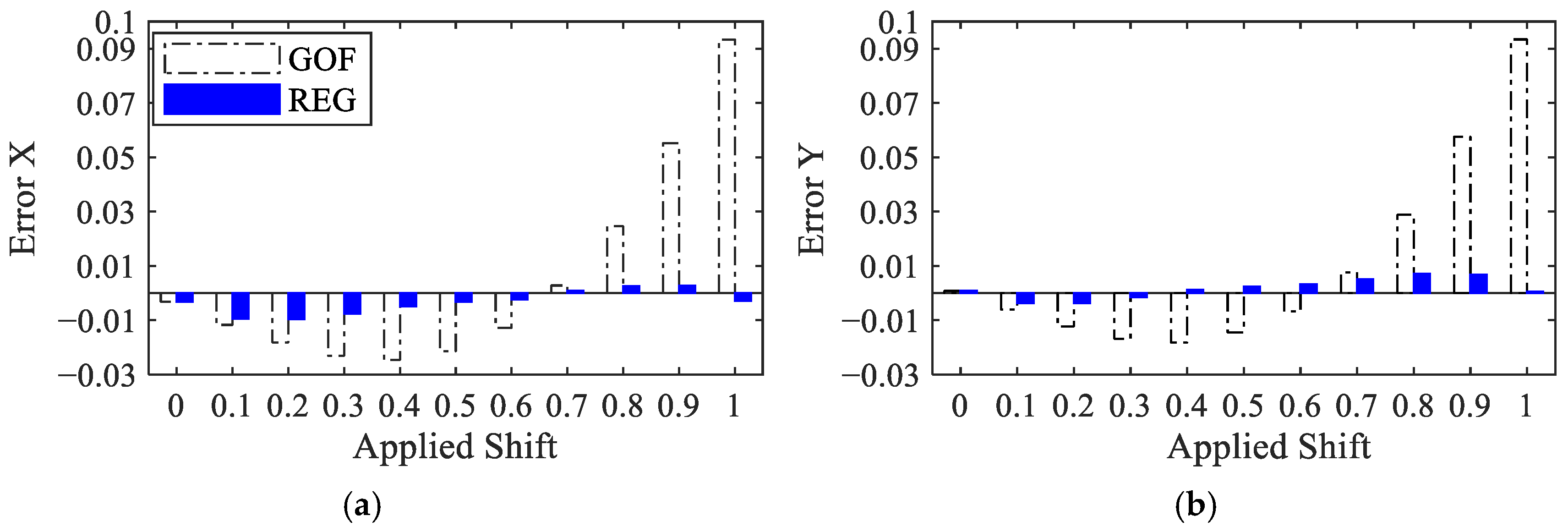
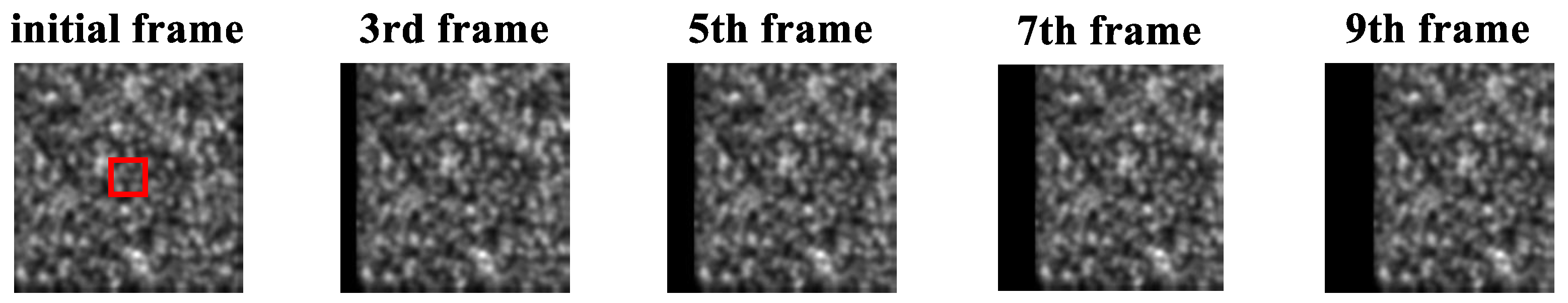
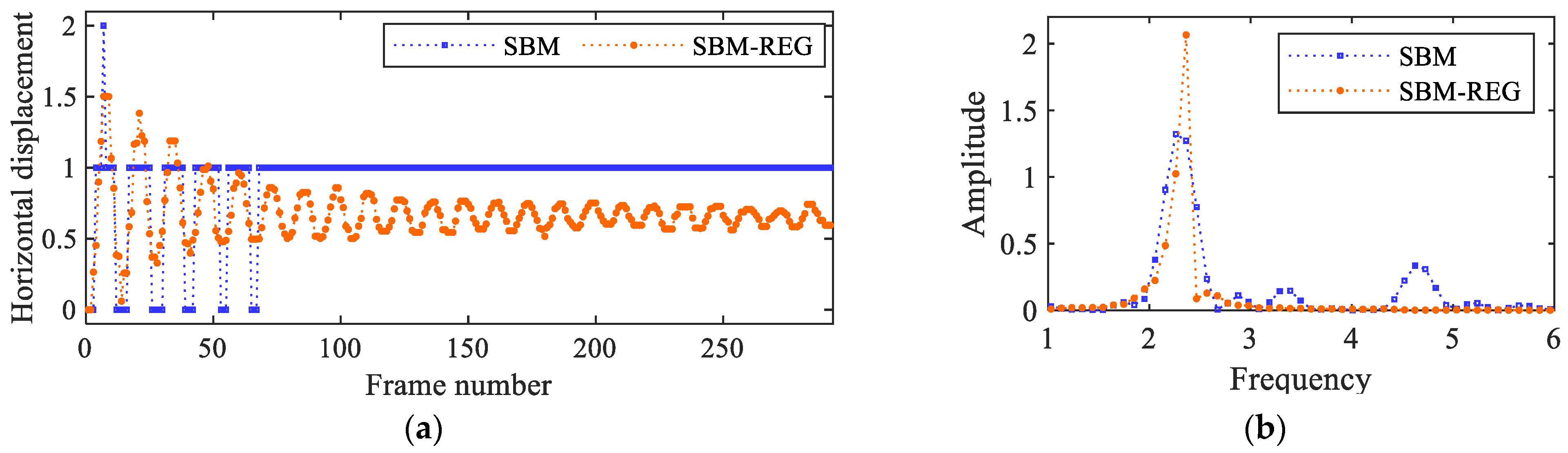
4.1. Synthetic Shifted Patterns
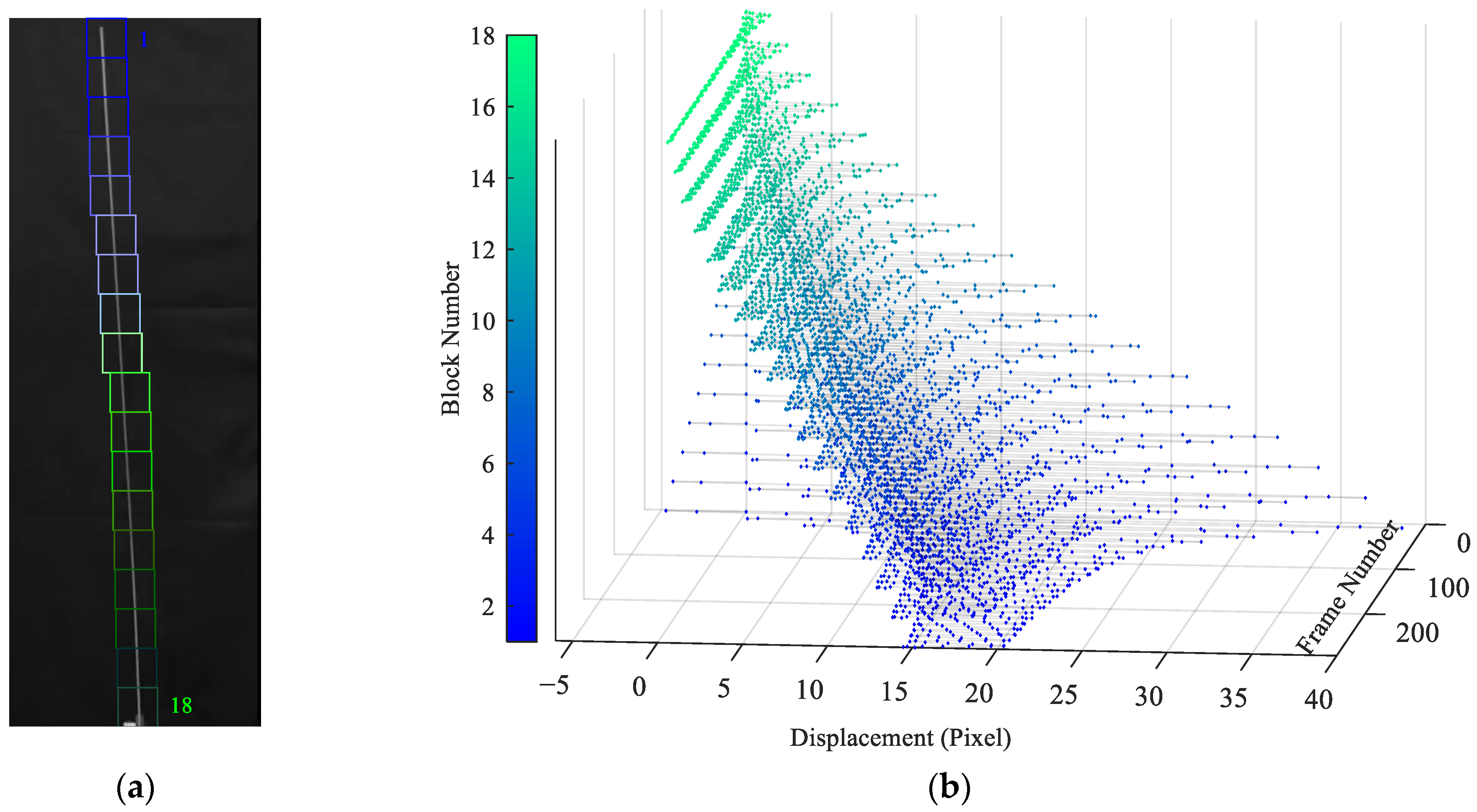
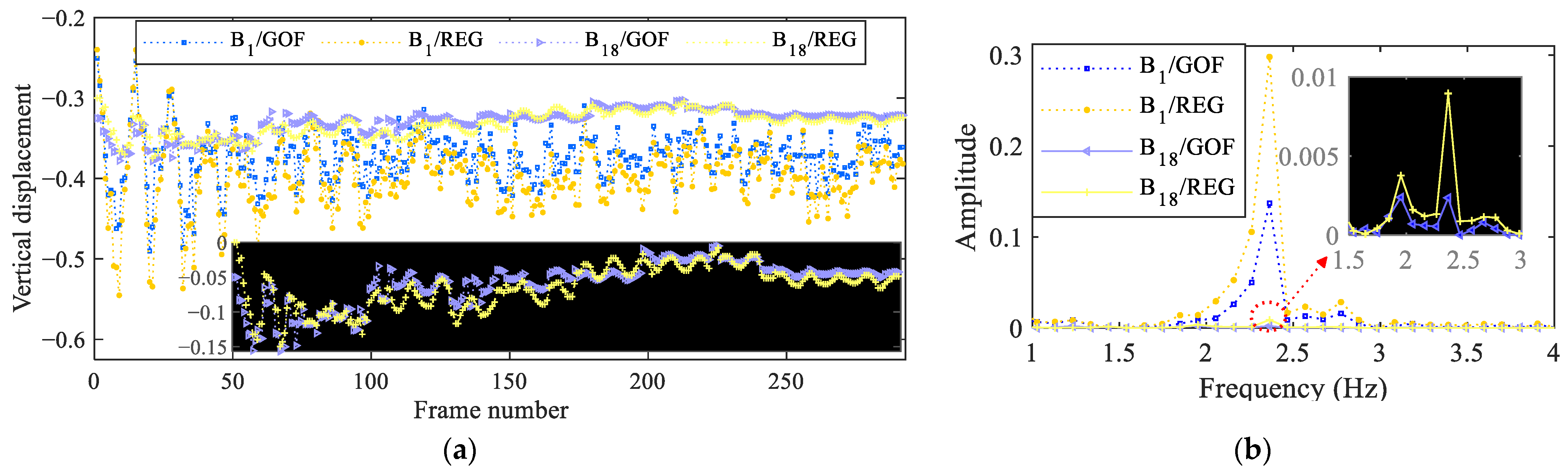
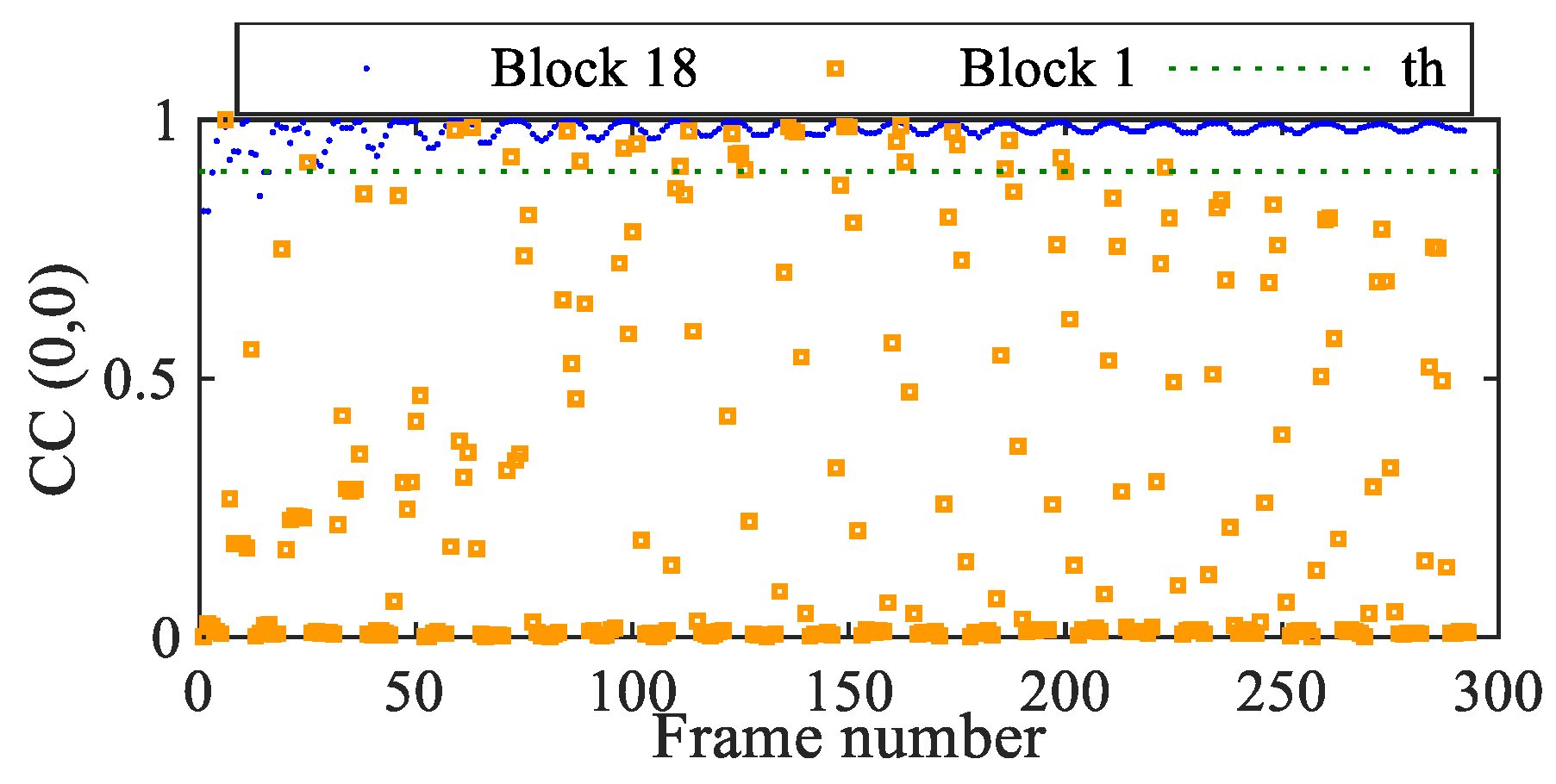
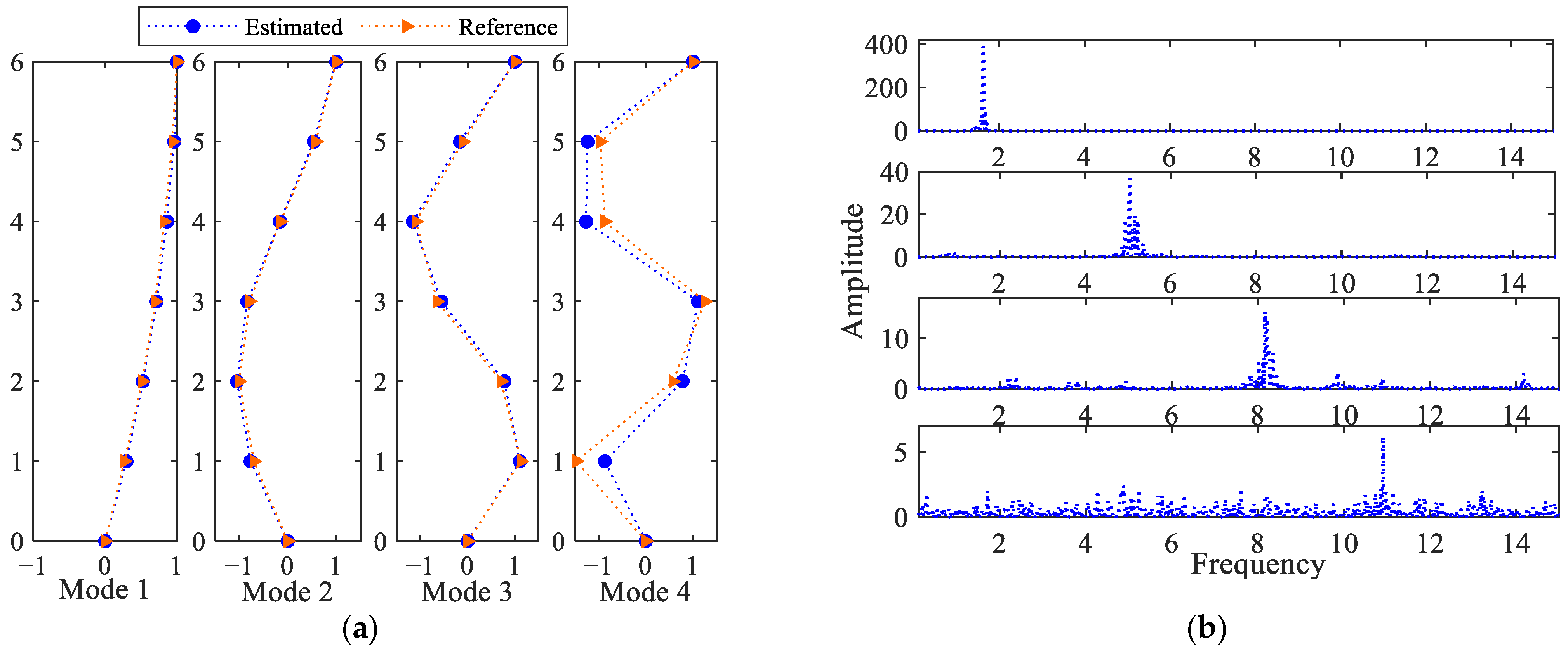
4.2. Cantilever Beam
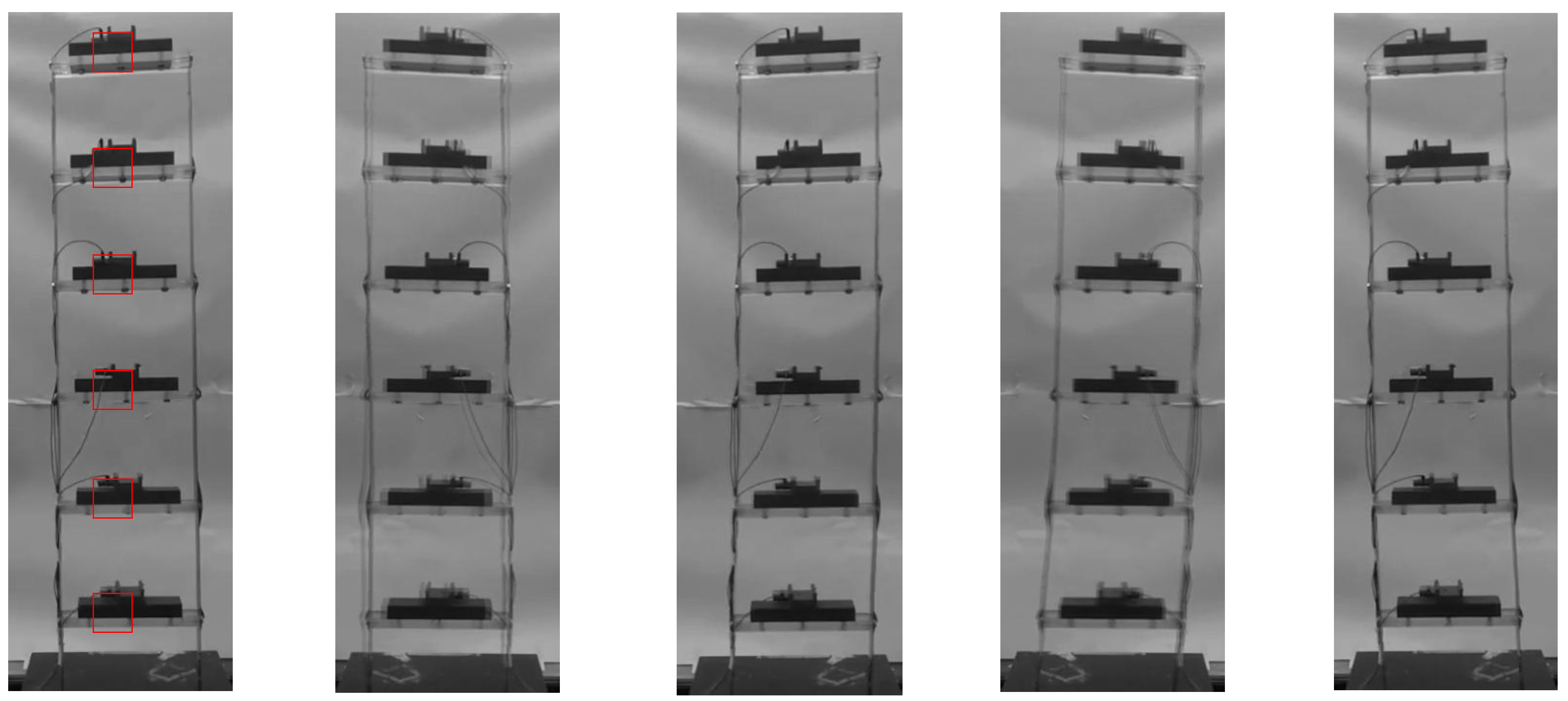
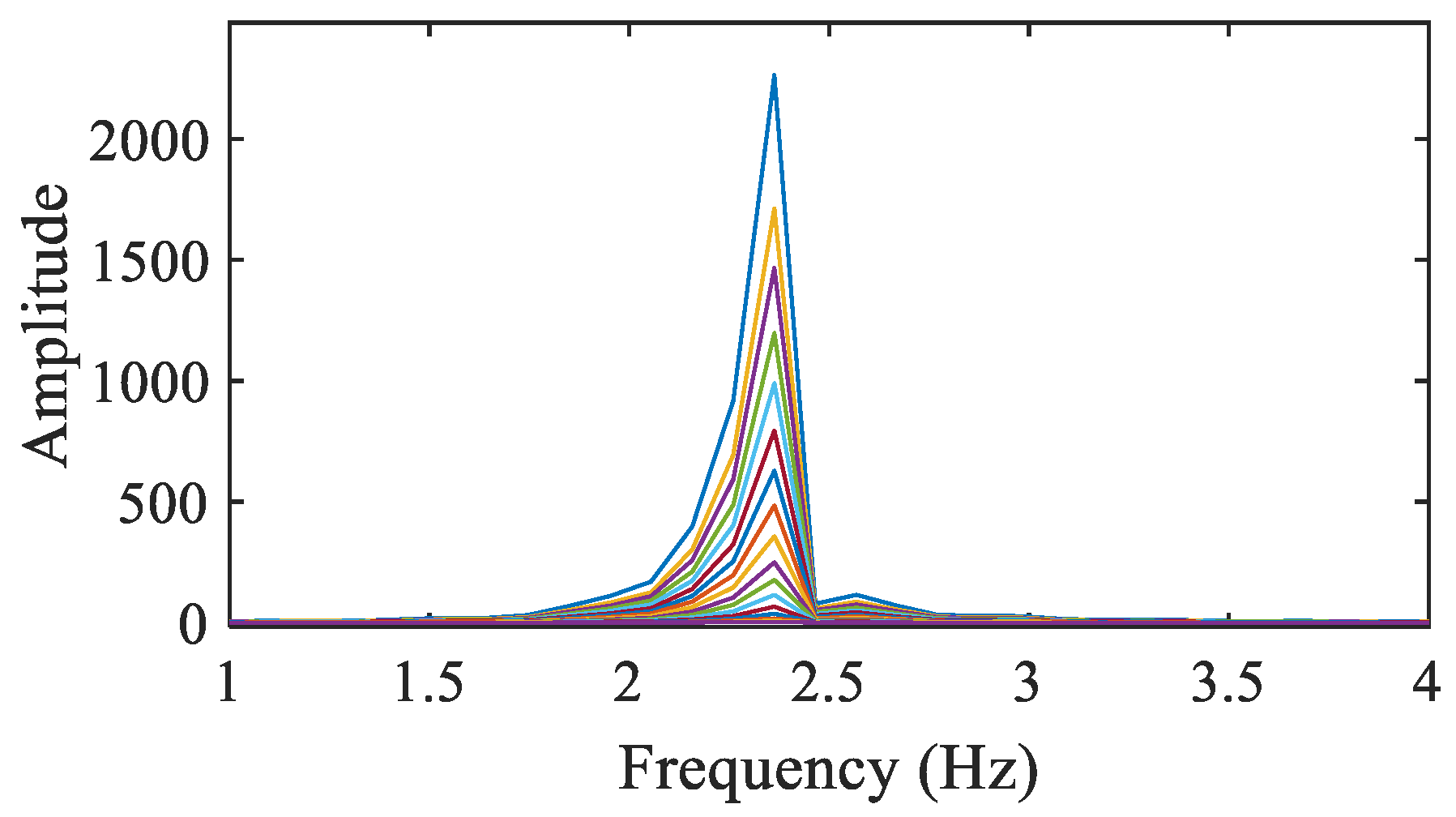
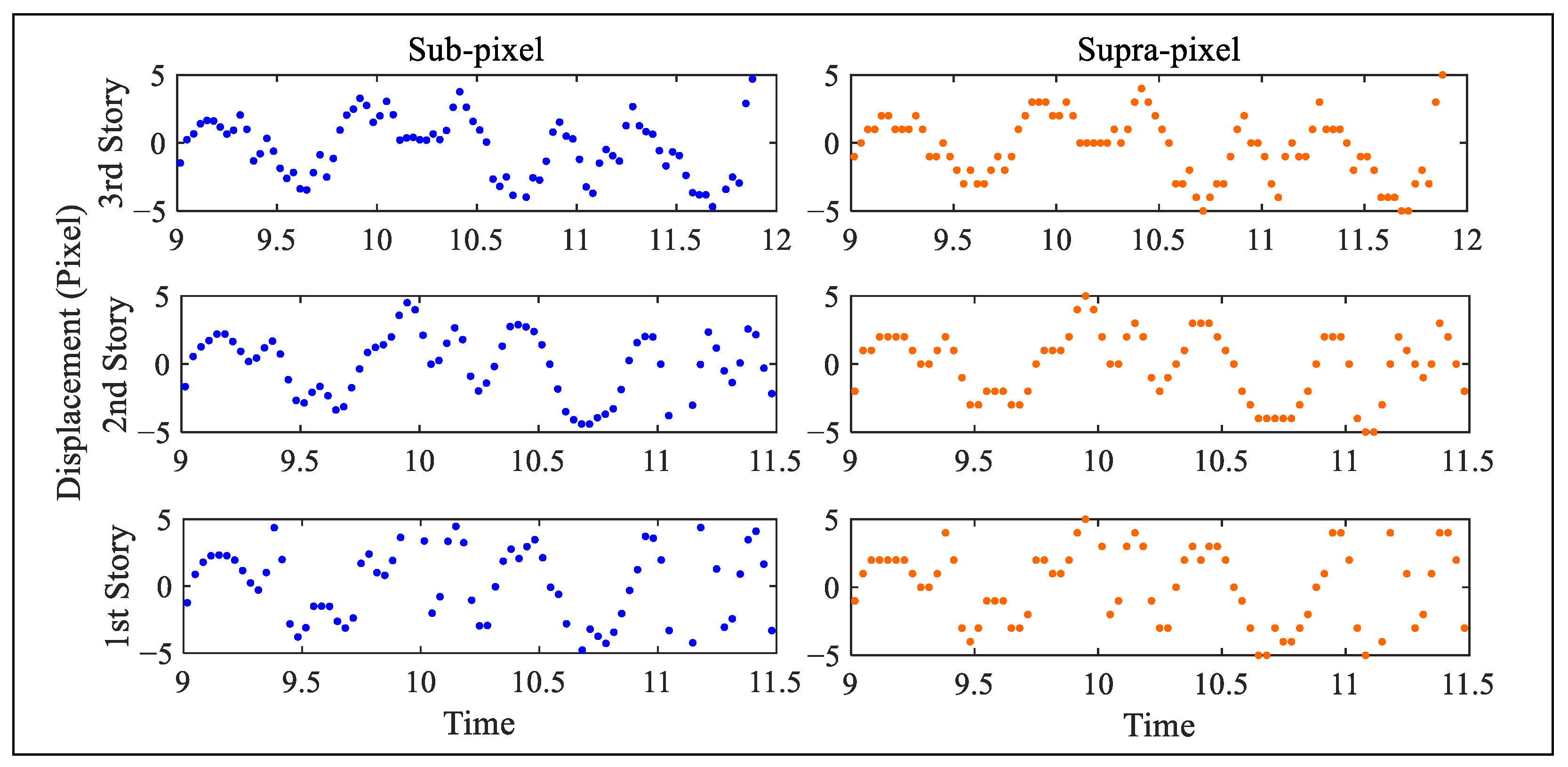
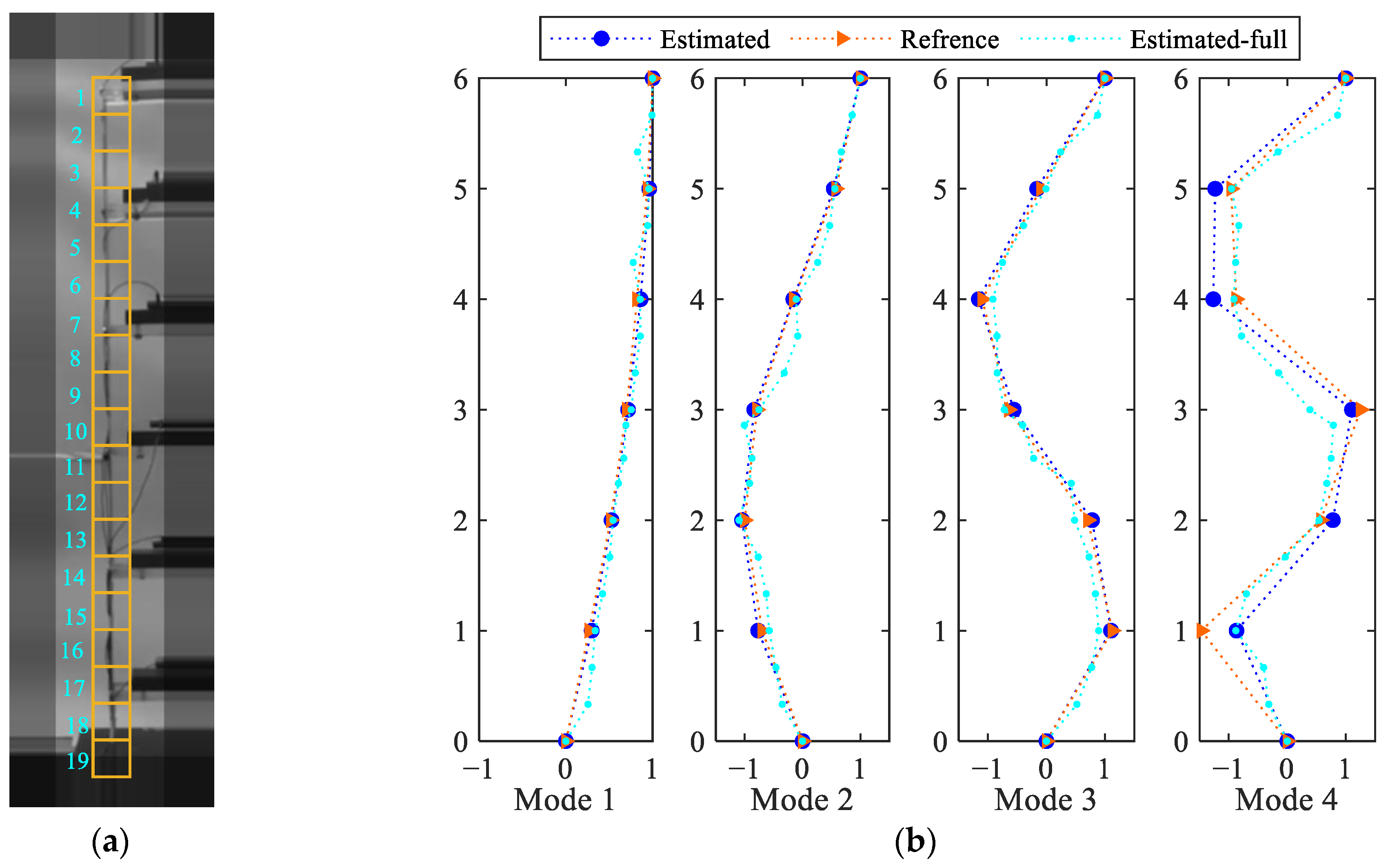
4.3. Six-Story Structure
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balageas, D.; Fritzen, C.-P.; Güemes, A. Structural Health Monitoring; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; Volume 90. [Google Scholar]
- Prabatama, N.A.; Nguyen, M.L.; Hornych, P.; Mariani, S.; Laheurte, J.M. Pavement Monitoring with a Wireless Sensor Network of MEMS Accelerometers. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Symposium on Measurements & Networking (M&N), Rome, Italy, 2–5 July 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Capellari, G.; Chatzi, E.; Mariani, S.; Azam, S.E. Optimal design of sensor networks for damage detection. Procedia Eng. 2017, 199, 1864–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabatama, N.A.; Nguyen, M.L.; Hornych, P.; Mariani, S.; Laheurte, J.-M. Zigbee-Based Wireless Sensor Network of MEMS Accelerometers for Pavement Monitoring. Sensors 2024, 24, 6487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzortzinis, G.; Ai, C.; Breña, S.F.; Gerasimidis, S. Using 3D laser scanning for estimating the capacity of corroded steel bridge girders: Experiments, computations and analytical solutions. Eng. Struct. 2022, 265, 114407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, J.P.; Loh, K.J. A summary review of wireless sensors and sensor networks for structural health monitoring. Shock Vib. Dig. 2006, 38, 91–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Feng, M.Q. Experimental validation of cost-effective vision-based structural health monitoring. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2017, 88, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Dorn, C. Affinity propagation clustering of full-field, high-spatial-dimensional measurements for robust output-only modal identification: A proof-of-concept study. J. Sound Vib. 2020, 483, 115473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dworakowski, Z.; Kohut, P.; Gallina, A.; Holak, K.; Uhl, T. Vision-based algorithms for damage detection and localization in structural health monitoring. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2016, 23, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, S.; Karami, K.; Nagarajaiah, S. Developing a semi-active adjustable stiffness device using integrated damage tracking and adaptive stiffness mechanism. Eng. Struct. 2021, 238, 112036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, A.; Tronci, E.M.; Feng, M.Q.; Leung, R.Y. A computer vision-based method for bridge model updating using displacement influence lines. Eng. Struct. 2022, 259, 114129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Sanchez, L.; Zhang, H.; Roeder, A.; Bowlan, J.; Crochet, J.; Farrar, C.; Mascareñas, D. Estimation of full-field, full-order experimental modal model of cable vibration from digital video measurements with physics-guided unsupervised machine learning and computer vision. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2019, 26, e2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmick, S.; Nagarajaiah, S.; Lai, Z. Measurement of full-field displacement time history of a vibrating continuous edge from video. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2020, 144, 106847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Feng, M.Q.; Wu, Z.Y. Robust vision sensor for multi-point displacement monitoring of bridges in the field. Eng. Struct. 2018, 163, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zeng, B.; Liou, M.L. A new three-step search algorithm for block motion estimation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 1994, 4, 438–442. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.; Ma, K.-K. A new diamond search algorithm for fast block-matching motion estimation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2000, 9, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, B.; Mukherjee, R.; Chakrabarti, I. Efficient architecture of adaptive rood pattern search technique for fast motion estimation. Microprocess. Microsyst. 2015, 39, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Najdawi, N.; Al-Najdawi, M.N.; Tedmori, S. Employing a novel cross-diamond search in a modified hierarchical search motion estimation algorithm for video compression. Inf. Sci. 2014, 268, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, E.; Zaldívar, D.; Pérez-Cisneros, M.; Oliva, D. Block-matching algorithm based on differential evolution for motion estimation. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2013, 26, 488–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Bruck, H.A. Pointwise digital image correlation using genetic algorithms. Exp. Tech. 2005, 29, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandian, S.I.A.; Bala, G.J.; Anitha, J. A pattern based PSO approach for block matching in motion estimation. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2013, 26, 1811–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengar, S.S.; Mukhopadhyay, S. Motion segmentation-based surveillance video compression using adaptive particle swarm optimization. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 32, 11443–11457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, X.; Gan, J.; Li, H.; Ge, P. Displacement measurement system for inverters using computer micro-vision. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2016, 81, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Menq, C.-H. Visual Servo Control Achieving Nanometer Resolution in X-Y-Z. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2009, 25, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, L.; Shirinzadeh, B.; Bhagat, U.; Smith, J. A Vision-based measurement algorithm for micro/nano manipulation. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics, Wollongong, Australia, 9–12 July 2013; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 100–105. [Google Scholar]
- Anis, Y.H.; Mills, J.K.; Cleghorn, W.L. Visual-servoing of a six-degree-of-freedom robotic manipulator for automated microassembly task execution. J. Micro/Nanolithogr. MEMS MOEMS 2008, 7, 033017. [Google Scholar]
- Babu, D.V.; Subramanian, P.; Karthikeyan, C. Performance analysis of block matching algorithms for highly scalable video compression. In Proceedings of the 2006 International Symposium on Ad Hoc and Ubiquitous Computing, Mangalore, India, 20–23 December 2006; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 179–182. [Google Scholar]
- Khawase, S.T.; Kamble, S.D.; Thakur, N.V.; Patharkar, A.S. An Overview of Block Matching Algorithms for Motion Vector Estimation. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Research in Intelligent and Computing in Engineering, Gopeshwar, India, 24–26 March 2017; pp. 217–222. [Google Scholar]
- Kerfa, D.; Belbachir, M.F. Star diamond: An efficient algorithm for fast block matching motion estimation in H264/AVC video codec. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2016, 75, 3161–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commowick, O.; Wiest-Daesslé, N.; Prima, S. Block-matching strategies for rigid registration of multimodal medical images. In Proceedings of the 2012 9th IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Barcelona, Spain, 2–5 May 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 700–703. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Yin, Z.; Ma, X.; Yang, Z. SAR image despeckling based on block-matching and noise-referenced deep learning method. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Ma, D.; Ren, G.; Huang, Y. BM-IQE: An image quality evaluator with block-matching for both real-life scenes and remote sensing scenes. Sensors 2020, 20, 3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahbeh, A.M.; Caffrey, J.P.; Masri, S.F. A vision-based approach for the direct measurement of displacements in vibrating systems. Smart Mater. Struct. 2003, 12, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Feng, M.Q.; Ozer, E.; Fukuda, Y. A vision-based sensor for noncontact structural displacement measurement. Sensors 2015, 15, 16557–16575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mair, E.; Hager, G.D.; Burschka, D.; Suppa, M.; Hirzinger, G. Adaptive and generic corner detection based on the accelerated segment test. In Proceedings of the 11th European Conference on Computer Vision, Heraklion, Crete, Greece, 5–11 September 2010; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 183–196. [Google Scholar]
- Bay, H.; Ess, A.; Tuytelaars, T.; Van Gool, L. Speeded-up robust features (SURF). Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2008, 110, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedaldi, A.; Fulkerson, B. VLFeat: An open and portable library of computer vision algorithms. In Proceedings of the 18th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Firenze, Italy, 25–29 October 2010; pp. 1469–1472. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, H.; Elanwar, H.; Choi, H.; Golparvar-Fard, M.; Spencer, B.F., Jr. Target-free approach for vision-based structural system identification using consumer-grade cameras. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2016, 23, 1405–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, C.; Stephens, M. A combined corner and edge detector. In Proceedings of the Alvey Vision Conference, Manchester, UK, 31 August–2 September 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Lucas, B.D.; Kanade, T. An iterative image registration technique with an application to stereo vision. In Proceedings of the 7th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 August 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.W.; Cheung, J.H.; Park, J.B.; Na, S.O. Image-based back analysis for tension estimation of suspension bridge hanger cables. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2020, 27, e2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolognini, M.; Izzo, G.; Marchisotti, D.; Fagiano, L.; Limongelli, M.P.; Zappa, E. Vision-based modal analysis of built environment structures with multiple drones. Autom. Constr. 2022, 143, 104550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorini, A.; Cattaneo, N.; Bortolotto, S.; Massa, S.; Bocciolone, M.F.; Zappa, E. Metrological issues in 3D reconstruction of an archaeological site with aerial photogrammetry. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 22–25 May 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, D.; Feng, M.Q. Vision-based multipoint displacement measurement for structural health monitoring. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2016, 23, 876–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Feng, M.Q. Edge-enhanced matching for gradient-based computer vision displacement measurement. Comput. Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2018, 33, 1019–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Yu, L.; Zhang, Q. Review of single-camera stereo-digital image correlation techniques for full-field 3D shape and deformation measurement. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2018, 61, 2–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.; Wu, Z.; Christenson, R.; Lobo-Aguilar, S. Development of video analytics with template matching methods for using camera as sensor and application to highway bridge structural health monitoring. J. Civ. Struct. Health Monit. 2020, 10, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Scarangello, T.; Feng, M.Q.; Ye, Q. Cable tension force estimate using novel noncontact vision-based sensor. Measurement 2017, 99, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleet, D.J.; Jepson, A.D. Computation of component image velocity from local phase information. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 1990, 5, 77–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weldon, T.P.; Higgins, W.E.; Dunn, D.F. Efficient Gabor filter design for texture segmentation. Pattern Recognit. 1996, 29, 2005–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Dorn, C.; Mancini, T.; Talken, Z.; Kenyon, G.; Farrar, C.; Mascareñas, D. Blind identification of full-field vibration modes from video measurements with phase-based video motion magnification. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2017, 85, 567–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Dorn, C.; Mancini, T.; Talken, Z.; Theiler, J.; Kenyon, G.; Farrar, C.; Mascarenas, D. Reference-free detection of minute, non-visible, damage using full-field, high-resolution mode shapes output-only identified from digital videos of structures. Struct. Health Monit. 2018, 17, 514–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Jung, H.K.; Dorn, C.; Park, G.; Farrar, C.; Mascareñas, D. Estimation of full-field dynamic strains from digital video measurements of output-only beam structures by video motion processing and modal superposition. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2019, 26, e2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, L.; Liu, Y.; Sun, H. Extracting high-precision full-field displacement from videos via pixel matching and optical flow. J. Sound Vib. 2023, 565, 117904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merainani, B.; Xiong, B.; Baltazart, V.; Döhler, M.; Dumoulin, J.; Zhang, Q. Subspace-based modal identification and uncertainty quantification from video image flows. J. Sound Vib. 2024, 569, 117957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, C.Q.; Freeman, D.M. Statistics of subpixel registration algorithms based on spatiotemporal gradients or block matching. Opt. Eng. 1998, 37, 1290–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Eberhart, R. A modified particle swarm optimizer. In Proceedings of the 1998 IEEE International Conference on Evolutionary Computation Proceedings. IEEE World Congress on Computational Intelligence (Cat. No. 98TH8360), Anchorage, AK, USA, 4–9 May 1998; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1998; pp. 69–73. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Zou, L.; Deng, W. Fatigue life prediction for welding components based on hybrid intelligent technique. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 642, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, J.W. Analysis of bias in gradient-based optical-flow estimation. In Proceedings of the 1994 28th Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 31 October–2 November 1994; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1994; pp. 721–725. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Xie, R.; Li, M.; Cheng, W. A review on the application of blind source separation in vibration analysis of mechanical systems. Measurement 2024, 227, 114241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadhu, A.; Narasimhan, S.; Antoni, J. A review of output-only structural mode identification literature employing blind source separation methods. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2017, 94, 415–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Nagarajaiah, S. Blind modal identification of output-only structures in time-domain based on complexity pursuit. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2013, 42, 1885–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reu, P.L.; Toussaint, E.; Jones, E.; Bruck, H.A.; Iadicola, M.; Balcaen, R.; Turner, D.Z.; Siebert, T.; Lava, P.; Simonsen, M. DIC challenge: Developing images and guidelines for evaluating accuracy and resolution of 2D analyses. Exp. Mech. 2018, 58, 1067–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Pan, B. Smart DIC: User-independent, accurate and precise DIC measurement with self-adaptively selected optimal calculation parameters. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2025, 222, 111792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Pan, B. Camera calibration using synthetic random speckle pattern and digital image correlation. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2020, 126, 105919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siringoringo, D.M.; Wangchuk, S.; Fujino, Y. Noncontact operational modal analysis of light poles by vision-based motion-magnification method. Eng. Struct. 2021, 244, 112728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




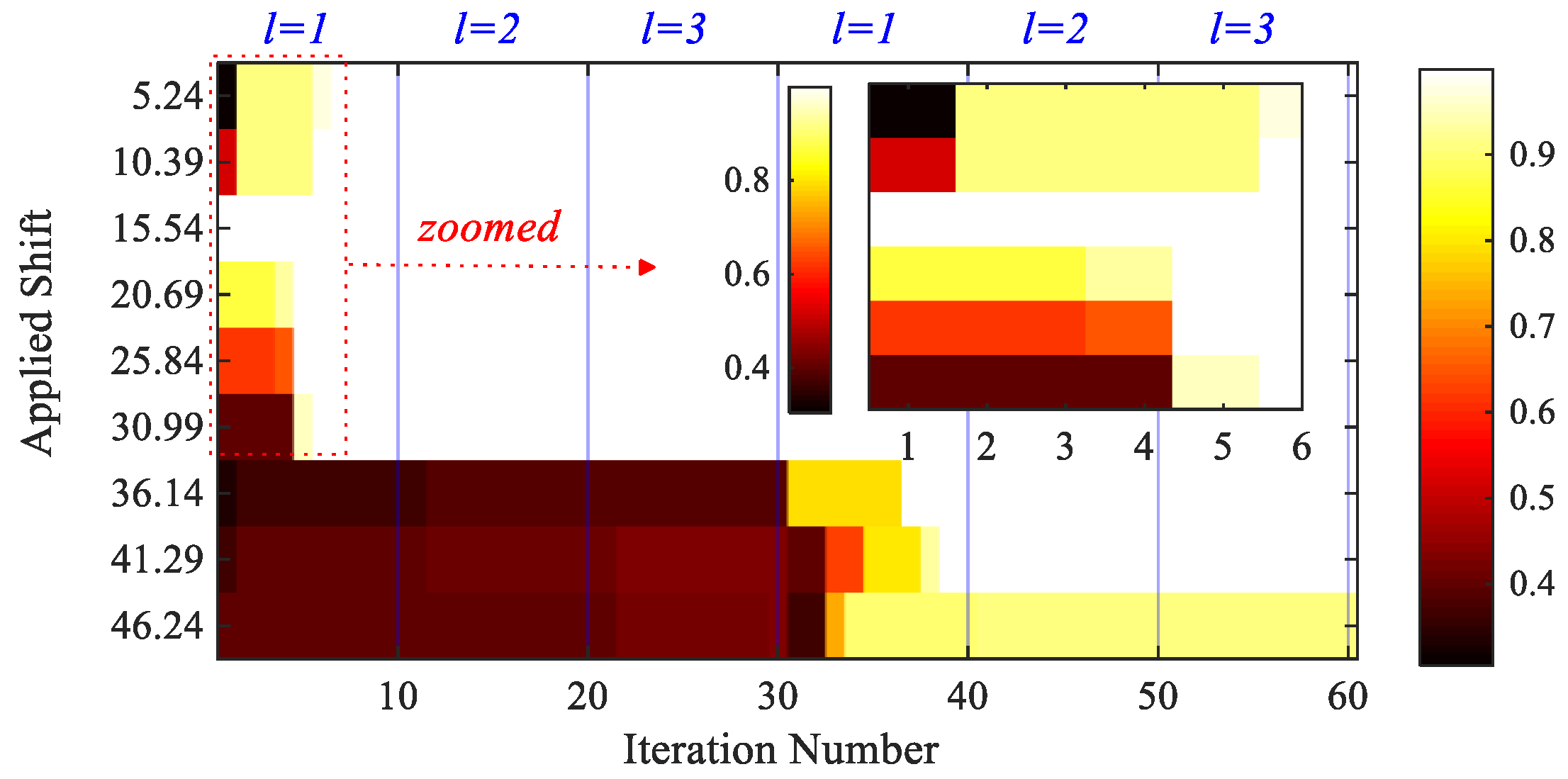





| Applied Shift | 5.24 | 10.39 | 15.54 | 20.69 | 25.84 | 30.99 | 36.14 | 41.29 | 46.44 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBM (coarse) EI % | 6 14.5 | 10 3.75 | 16 2.9 | 21 1.49 | 26 0.6 | 30 3.19 | 36 0.38 | 41 0.7 | 45 3.1 |
| SBM-GOF (fine) EI % | 5.1584 1.67 | 10.4525 0.6 | 15.4765 0.41 | 20.6465 0.21 | 25.8196 0.08 | 31.1679 0.57 | 36.1450 0.013 | 41.3357 0.1 | 46.9772 1.16 |
| SBM-REG (over fine) EI % | 5.2494 0.18 | 10.3964 0.006 | 15.5454 0.034 | 20.6853 0.022 | 25.8456 0.021 | 31 0.032 | 36.1450 0.013 | 41.3003 0.0249 | 46.8029 0.78 |
| FSF/SBM-REG calculation points | 5.83 | 13.35 | 85 | 22.02 | 27.03 | 25.86 | - | - | - |
| Mode 1 | Mode 2 | Mode 3 | Mode 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference | 1.657 | 5.038 | 8.138 | 10.833 |
| Estimated Estimated-Full | 1.644 1.631 | 5.045 5.045 | 8.167 8.208 | 10.91 10.64 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Azizi, S.; Karami, K.; Mariani, S. A Vision-Based Procedure with Subpixel Resolution for Motion Estimation. Sensors 2025, 25, 3101. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103101
Azizi S, Karami K, Mariani S. A Vision-Based Procedure with Subpixel Resolution for Motion Estimation. Sensors. 2025; 25(10):3101. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103101
Chicago/Turabian StyleAzizi, Samira, Kaveh Karami, and Stefano Mariani. 2025. "A Vision-Based Procedure with Subpixel Resolution for Motion Estimation" Sensors 25, no. 10: 3101. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103101
APA StyleAzizi, S., Karami, K., & Mariani, S. (2025). A Vision-Based Procedure with Subpixel Resolution for Motion Estimation. Sensors, 25(10), 3101. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103101







