A Few-Shot Steel Surface Defect Generation Method Based on Diffusion Models
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- To address the issues of few-shot samples and long-tailed distribution in the field of steel surface defects, we proposed a novel method for generating steel surface defect samples capable of learning domain knowledge from limited data.
- (2)
- We introduced a defect mask-guided training approach into our network. By utilizing defect mask images in conjunction with the original images, our method enables the model to focus on the defect regions. Furthermore, through text-based class control and the collaborative control of text and masks, we achieved efficient learning of defect details and enabled controllable generation of defect classes.
- (3)
- We conducted extensive experiments on a real medium-thick steel plate dataset. The experimental results demonstrate that our method can generate higher-quality data compared to existing approaches. Moreover, the generated augmented data can effectively improve the performance of detection networks.
2. Related Work
2.1. Current Status of Few-Shot Industrial Sample Generation
2.2. Current Status of Text-to-Image Generation Research Based on Diffusion Models
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Preliminaries
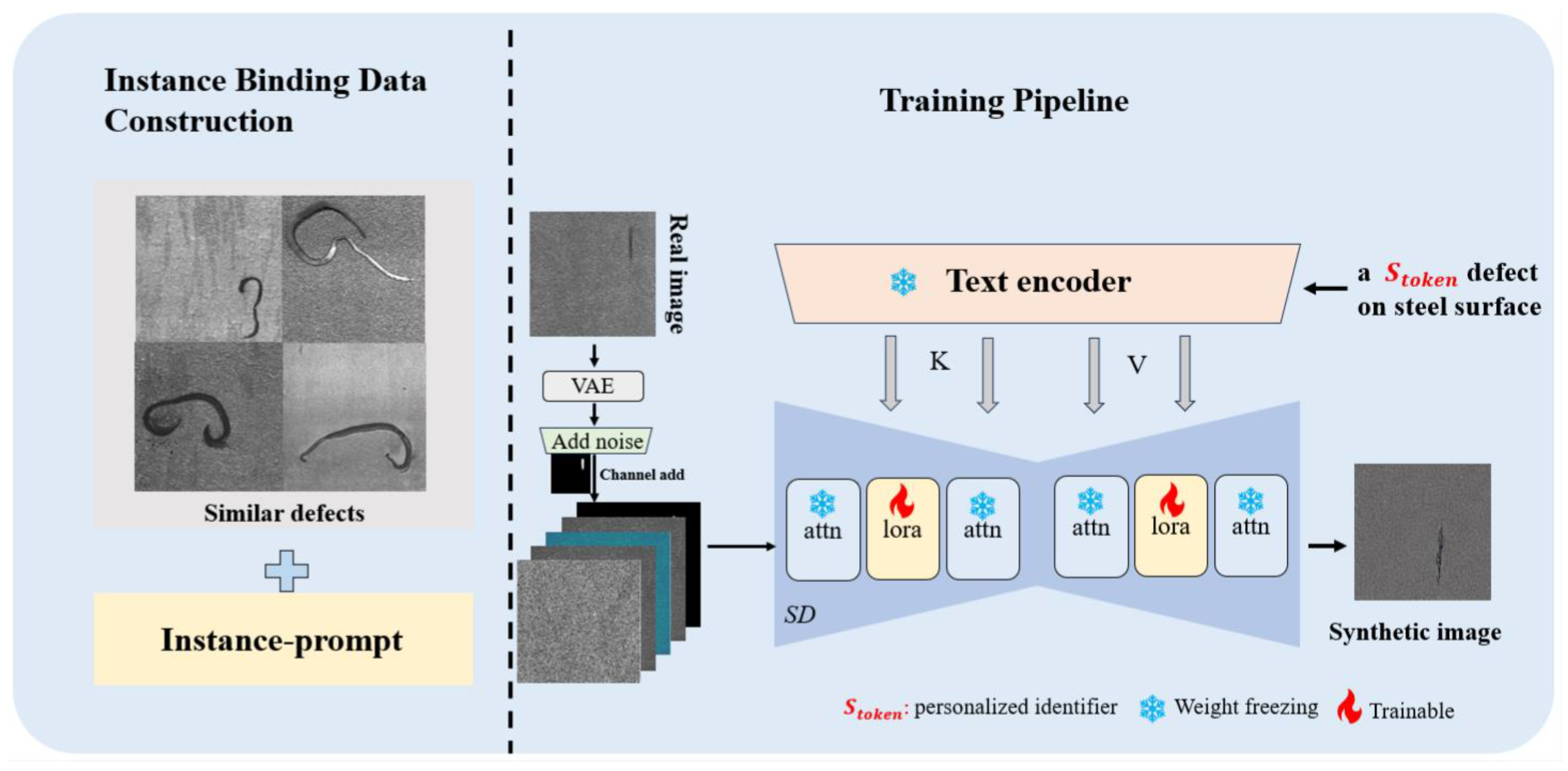
3.2. StableIDG
3.2.1. Parameter-Efficient Low-Rank Embedding Fine-Tuning Framework
3.2.2. Personalized Identifier Instance Binding
3.2.3. Defect Region Mask-Guided Approach
3.3. Quality Evaluation
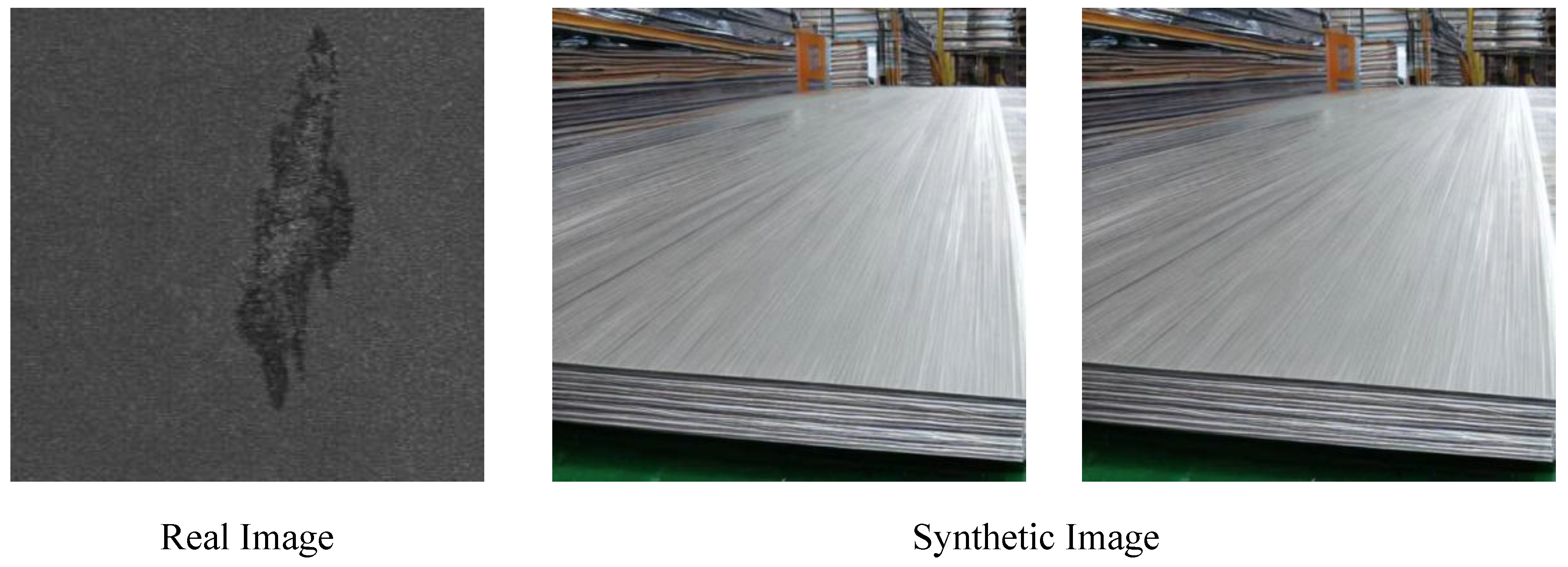
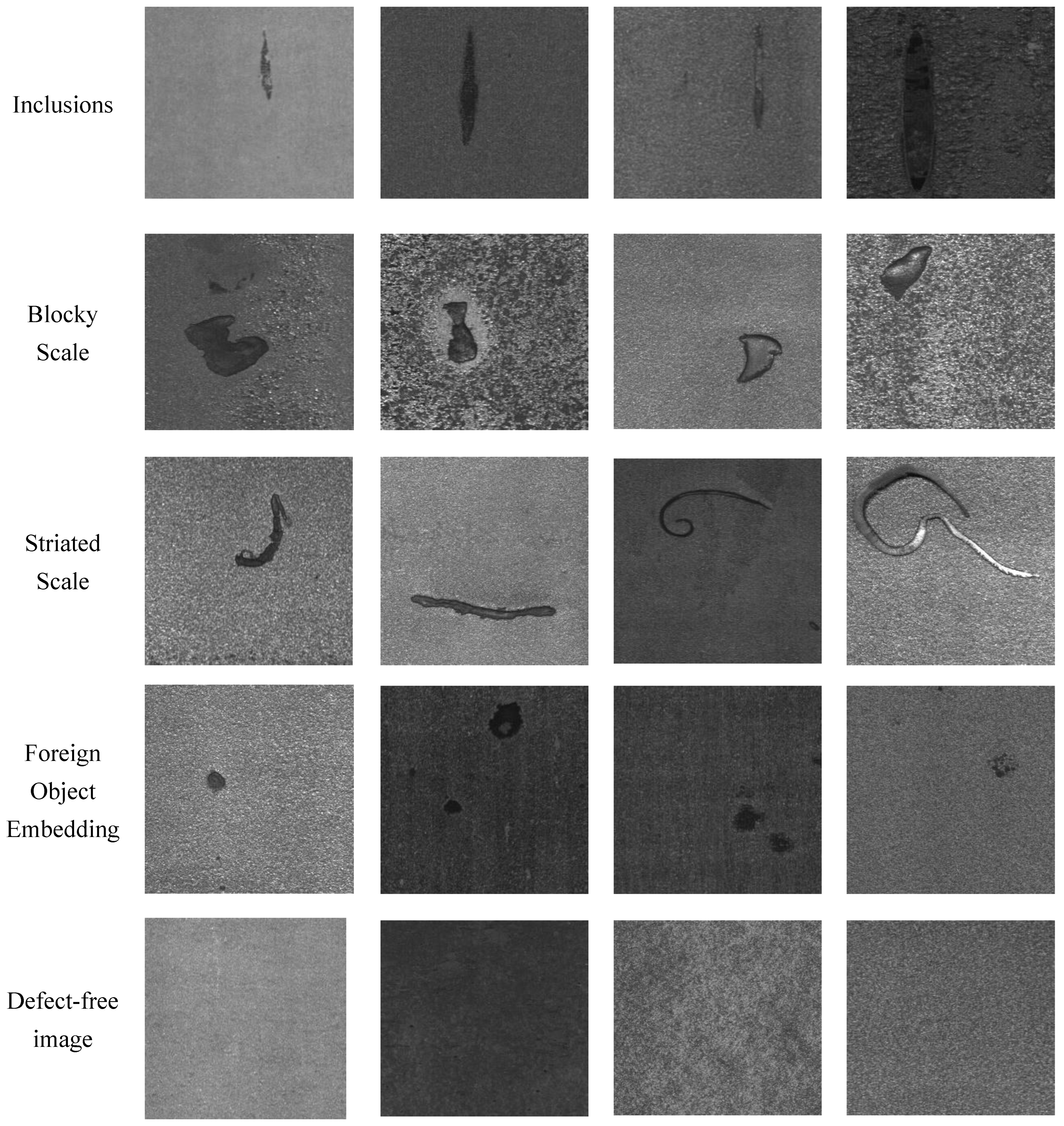
3.3.1. Datasets
3.3.2. Evaluation Metrics
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Experimental Setup
Implementation Details
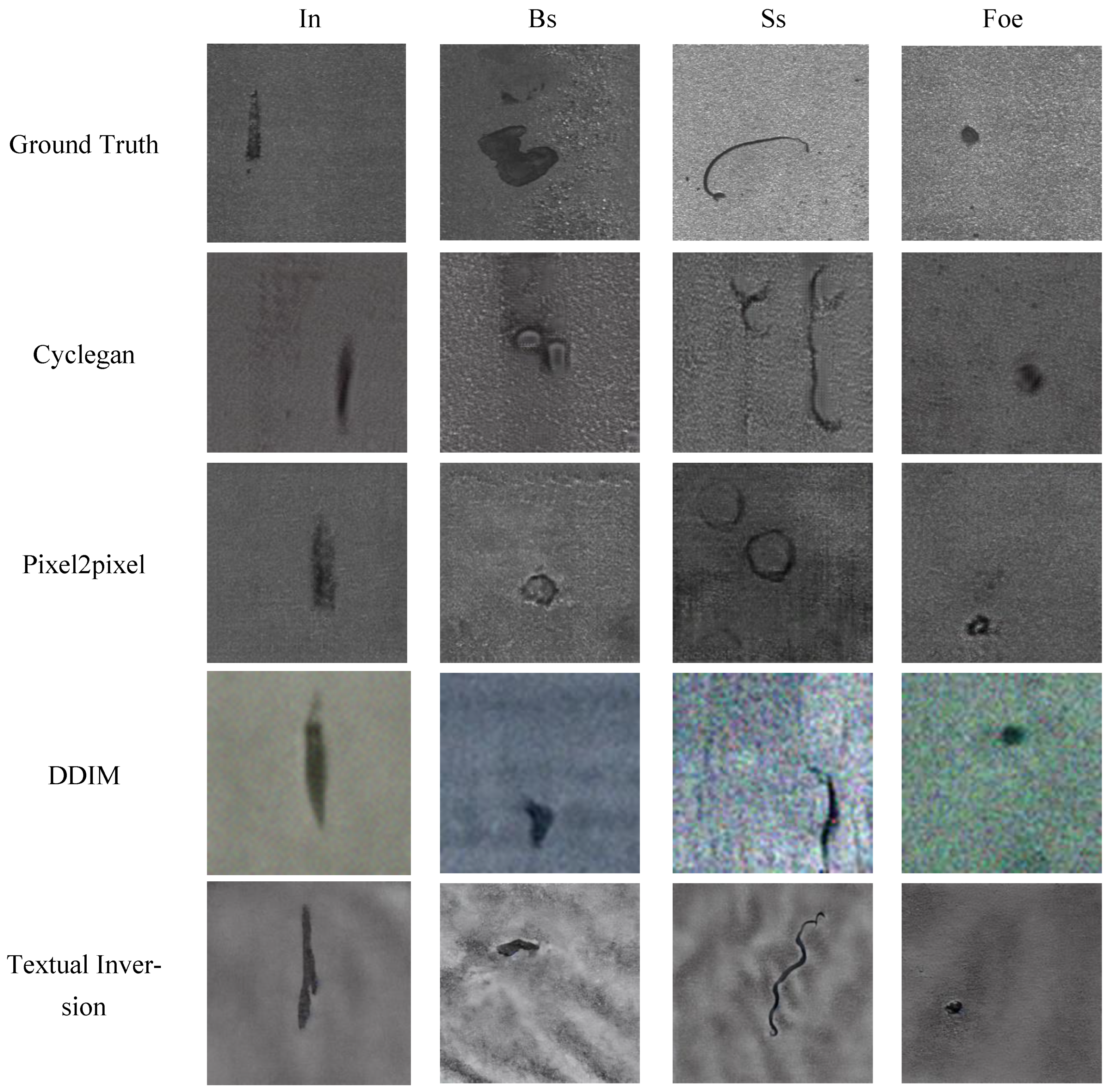
4.2. Comparison and Analysis of the Results
4.2.1. Results of the Generated Image Quality
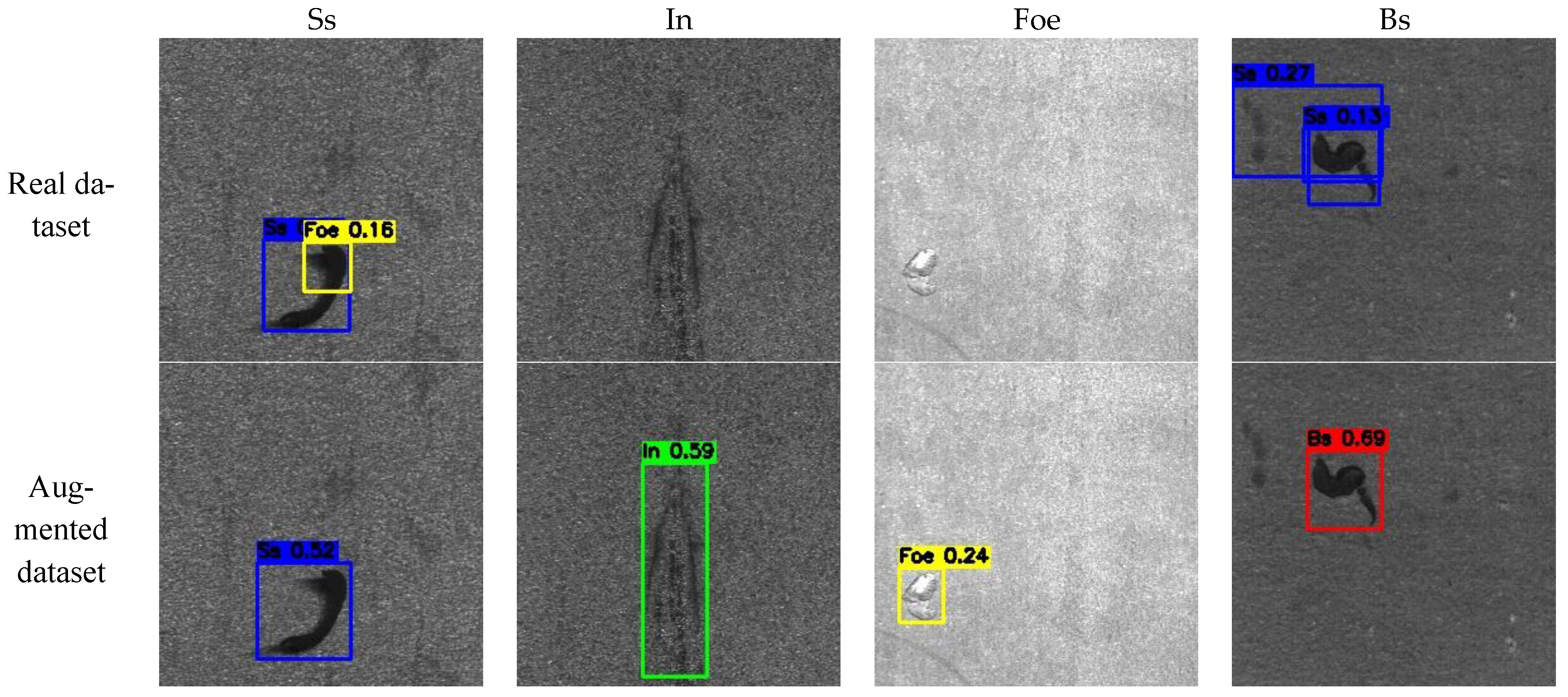
4.2.2. Defect Detection Results
4.3. Ablation Study
4.3.1. Impact of Modules
4.3.2. Impact of Training Step
4.3.3. Impact on Training Resources
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Ma, J.; Su, W.; Li, H. Real-Time Steel Surface Defect Detection with Improved Multi-Scale YOLO-v5. Processes 2023, 11, 1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholief, E.A.; Darwish, S.H.; Fors, M.N. Detection of steel surface defect based on machine learning using deep auto-encoder network. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Operations Management, Rabat, Morocco, 11–13 April 2017; pp. 218–229. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, S.I.; Dang, L.M.; Mehmood, I.; Im, S.; Choi, C.; Kang, J.; Park, Y.-S.; Moon, H. Underground sewer pipe condition assessment based on convolutional neural networks. Autom. Constr. 2019, 106, 102849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Fang, X.; Liu, L.; Yang, C.; Sun, Y. Automated Visual Defect Detection for Flat Steel Surface: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 626–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, J.; Feng, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, K.; Xiao, W. Imbalance fault diagnosis under long-tailed distribution: Challenges, solutions and prospects. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2022, 258, 110008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Xue, W.; Fu, W.-P.; Li, Z.-Q.; Fang, X. Defect Sample Image Generation Method Based on GANs in Diamond Tool Defect Detection. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, Q.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Huang, H.; Bao, G.; Zhang, D. Multiview Generative Adversarial Network and Its Application in Pearl Classification. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 66, 8244–8252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frid-Adar, M.; Klang, E.; Amitai, M.; Goldberger, J.; Greenspan, H. Synthetic data augmentation using GAN for improved liver lesion classification. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 15th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2018), Washington, DC, USA, 4–7 April 2018; pp. 289–293. [Google Scholar]
- Salimans, T.; Goodfellow, I.; Zaremba, W.; Cheung, W.; Radford, A.; Chen, X. Improved techniques for training gans. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 29 (NIPS 2016), Barcelona, Spain, 5–10 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Odena, A.; Dumoulin, V.; Olah, C. Deconvolution and Checkerboard Artifacts. Distill 2016, 1, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, R.; Lu, B.; Cheng, Y.; Li, X.; Huang, B. A steel surface defect inspection approach towards smart industrial monitoring. J. Intell. Manuf. 2020, 32, 1833–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avrahami, O.; Fried, O.; Lischinski, D. Blended latent diffusion. ACM Trans. Graph. 2023, 42, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertz, A.; Mokady, R.; Tenenbaum, J.; Aberman, K.; Pritch, Y.; Cohen-Or, D. Prompt-to-prompt image editing with cross attention control. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2208.01626. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, M.; Kweon, I.S.; Kim, J. Text-to-image diffusion models in generative ai: A survey. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.07909. [Google Scholar]
- Song, K.; Han, L.; Liu, B.; Metaxas, D.; Elgammal, A. Diffusion guided domain adaptation of image generators. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2212.04473. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, S.; Seth, G.; Paruthi, A.; Soni, U.; Kumar, G. Synthetic data augmentation for surface defect detection and classification using deep learning. J. Intell. Manuf. 2020, 33, 1007–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.J.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial nets. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 27 (NIPS 2014), Montreal, QC, Canada, 8–13 December 2014; 27, pp. 2672–2680. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Metz, L.; Chintala, S. Unsupervised representation learning with deep convolutional generative adversarial networks. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.06434. [Google Scholar]
- Divakar, N.; Babu, R.V. Image Denoising via CNNs: An Adversarial Approach. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1076–1083. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.; Cha, M.; Kim, H.; Lee, J.K.; Kim, J. Learning to discover cross-domain relations with generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydney, Australia, 6–11 August 2017; 70, pp. 1857–1865. [Google Scholar]
- Karras, T.; Aila, T.; Laine, S.; Lehtinen, J. Progressive Growing of Gans for Improved Quality, Stability, and Variation. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1710.10196 (accessed on 3 May 2017).
- Mirza, M.; Osindero, S. Conditional generative adversarial nets. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1411.1784. [Google Scholar]
- Isola, P.; Zhu, J.-Y.; Zhou, T.; Efros, A.A. Image-to-Image Translation with Conditional Adversarial Networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1611.07004. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.-Y.; Park, T.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2223–2232. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, S.; Li, B.; Wang, X.; Lin, H. Defect Image Sample Generation with GAN for Improving Defect Recognition. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2020, 17, 1611–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Kang, W.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Gao, J. Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) Based Data Augmentation for Palmprint Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2018 Digital Image Computing: Techniques and Applications (DICTA), Canberra, Australia, 10–13 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, S.; Li, B.; Wang, X.; Peng, Y. Region- and Strength-Controllable GAN for Defect Generation and Segmentation in Industrial Images. IEEE Trans. Ind. Informatics 2021, 18, 4531–4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rombach, R.; Blattmann, A.; Lorenz, D.; Esser, P.; Ommer, B. High-Resolution Image Synthesis with Latent Diffusion Models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 10674–10685. [Google Scholar]
- Gal, R.; Alaluf, Y.; Atzmon, Y.; Patashnik, O.; Bermano, A.H.; Chechik, G.; Cohen-Or, D. An image is worth one word: Personalizing text-to-image generation using textual inversion. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2208.01618. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, E.J.; Shen, Y.; Wallis, P.; Allen-Zhu, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Chen, W. LoRA: Low-rank adaptation of large language models. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.09685. [Google Scholar]
- Biderman, D.; Portes, J.; Ortiz, J.J.G.; Paul, M.; Greengard, P.; Jennings, C.; King, D.; Havens, S.; Chiley, V.; Frankle, J.; et al. Lora learns less and forgets less. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.09673. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Tam, D.; Muqeeth, M.; Mohta, J.; Huang, T.; Bansal, M.; Raffel, C.A. Few-shot parameter-efficient fine-tuning is better and cheaper than in-context learning. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2022, New Orleans, LA, USA, 28 November–9 December 2022; pp. 1950–1965. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz, N.; Li, Y.; Jampani, V.; Pritch, Y.; Rubinstein, M.; Aberman, K. DreamBooth: Fine Tuning Text-to-Image Diffusion Models for Subject-Driven Generation. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 22500–22510. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Rao, A.; Agrawala, M. Adding conditional control to text-to-image diffusion models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2–3 October 2023; pp. 3836–3847. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, T.; Zhang, J.; Yi, R.; Du, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C. AnomalyDiffusion: Few-Shot Anomaly Image Generation with Diffusion Model. In Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–27 February 2024; 38, pp. 8526–8534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Peng, J.; He, Q.; Hu, T.; Chen, H.; Wu, J.; Zhu, W.; Chi, M.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; et al. DualAnoDiff: Dual-Interrelated Diffusion Model for Few-Shot Anomaly Image Generation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.13509. [Google Scholar]
- Tai, Y.; Yang, K.; Peng, T.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, Z. Defect Image Sample Generation with Diffusion Prior for Steel Surface Defect Recognition. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2024, 22, 8239–8251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.; Jain, A.; Abbeel, P. Denoising diffusion probabilistic models. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2020, virtual, 6–12 December 2020; pp. 6840–6851. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Welling, M. Auto-encoding variational Bayes. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1312.6114. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Kim, J.W.; Hallacy, C.; Ramesh, A.; Goh, G.; Agarwal, S.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; Mishkin, P.; Clark, J.; et al. Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning 2021, virtual, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 8748–8763. [Google Scholar]
- Jocher, G.; Qiu, J. Ultralytics yolo11. 2024. Available online: https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics (accessed on 10 May 2025).
- Song, J.; Meng, C.; Ermon, S. Denoising diffusion implicit models. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.02502. [Google Scholar]
- Rombach, R.; Blattmann, A.; Lorenz, D.; Esser, P.; Ommer, B. Stable-Diffusion-v1-5. Available online: https://huggingface.co/stable-diffusion-v1-5/stable-diffusion-v1-5 (accessed on 10 May 2025).




| Class | Cyclegan | Pixel2pixel | DDIM | Text_Inversion | Dreambooth | Our |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| In | 130.51 | 125.06 | 231.56 | 283.85 | 185.91 | 134.64 |
| Bs | 200.87 | 173.80 | 320.37 | 252.44 | 180.22 | 148.23 |
| Ss | 260.82 | 227.06 | 298.47 | 227.05 | 232.11 | 112.65 |
| Foe | 122.64 | 118.83 | 285.95 | 225.84 | 183.92 | 107.42 |
| Method | MMD | In | Bs | Ss | Foe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cyclegan | RBF | 0.0312 | 0.0647 | 0.0989 | 0.0321 |
| Linear | 36.018 | 75.945 | 118.390 | 36.943 | |
| Pixel2pixel | RBF | 0.0369 | 0.0513 | 0.0850 | 0.0407 |
| Linear | 42.132 | 58.493 | 99.219 | 45.667 | |
| DDIM | RBF | 0.0997 | 0.1556 | 0.1383 | 0.1502 |
| Linear | 116.394 | 182.767 | 163.221 | 175.379 | |
| Text_inversion | RBF | 0.1140 | 0.0761 | 0.0697 | 0.0853 |
| Linear | 137.174 | 92.951 | 84.363 | 101.779 | |
| Dreambooth | RBF | 0.0773 | 0.0536 | 0.0486 | 0.0853 |
| Linear | 89.324 | 62.603 | 60.102 | 98.173 | |
| our | RBF | 0.0288 | 0.0284 | 0.0202 | 0.0263 |
| Linear | 33.658 | 33.510 | 23.635 | 30.405 |
| In | Bs | Ss | Foe | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Real dataset | Recall↑ | 0.656 | 0.743 | 0.84 | 0.86 |
| mAP@50↑ | 0.526 | 0.658 | 0.704 | 0.77 | |
| Augmented dataset | Recall↑ | 0.908 | 0.881 | 0.88 | 0.986 |
| mAP@50↑ | 0.832 | 0.787 | 0.746 | 0.888 | |
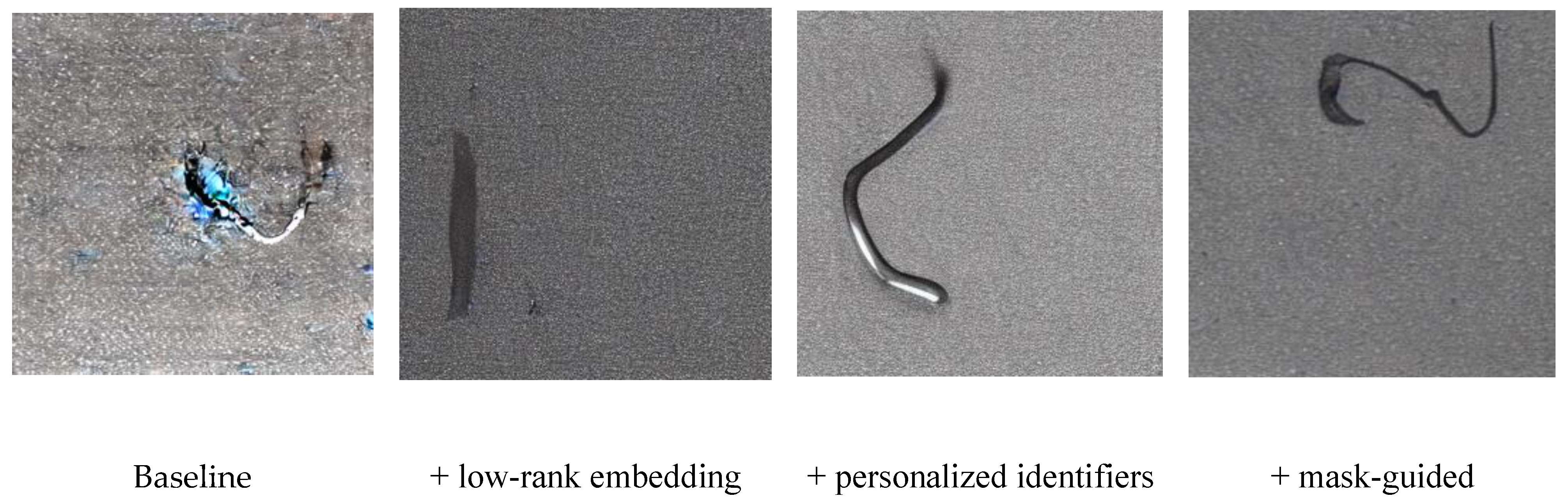
| Low-Rank Embedding | Personalized Identifiers | Mask-Guided | In | Bs | Ss | Foe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 157.719 | 182.3859 | 246.43 | 186.982 | |||
| ✔ | 150.3 | 204.720 | 149.56 | 149.145 | ||
| ✔ | ✔ | 158.083 | 175.684 | 130.58 | 138.161 | |
| ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | 134.64 | 148.23 | 112.65 | 107.42 |
| Class | 500 | 600 | 700 | 800 | 900 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| In | 144.8368 | 145.5329 | 134.64 | 207.2852 | 188.4764 |
| Bs | 214.6591 | 126.2226 | 148.23 | 192.3093 | 153.8693 |
| Ss | 157.0397 | 127.1116 | 112.65 | 148.1527 | 124.0734 |
| Foe | 152.0386 | 142.2851 | 107.42 | 151.0558 | 156.084 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; Pang, H.; Xu, K. A Few-Shot Steel Surface Defect Generation Method Based on Diffusion Models. Sensors 2025, 25, 3038. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103038
Li H, Liu Y, Liu C, Pang H, Xu K. A Few-Shot Steel Surface Defect Generation Method Based on Diffusion Models. Sensors. 2025; 25(10):3038. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103038
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Hongjie, Yang Liu, Chuni Liu, Hongxuan Pang, and Ke Xu. 2025. "A Few-Shot Steel Surface Defect Generation Method Based on Diffusion Models" Sensors 25, no. 10: 3038. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103038
APA StyleLi, H., Liu, Y., Liu, C., Pang, H., & Xu, K. (2025). A Few-Shot Steel Surface Defect Generation Method Based on Diffusion Models. Sensors, 25(10), 3038. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103038









